Fabrication of Metal/Carbon Nanotube Composites by Electrochemical Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fabrication of Metal/CNT Composites Using Composite Plating by Electrodeposition or Electro Less Deposition
2.1. Composite Plating
2.2. Preparation of Plating Bath for Metal/CNT Composite Plating
2.3. Unique Feature of Composite Plating Using CNTs as Inert Particles
2.4. Fabrication of Metal/CNT Composites Using Composite Plating by Electrodeposition
2.4.1. Ni/CNT and Ni Alloy/CNT Composites
2.4.2. Cu/CNT Composites
2.4.3. Zn/CNT and Zn Alloy/CNT Composites
2.4.4. Cr/CNT Composites
2.4.5. Co/CNT and Co Alloy/CNT Composites
2.4.6. Au/CNT and Ag/CNT Composites
2.4.7. Al/CNT Composites
2.4.8. Other Metal/CNT Composites
2.5. Fabrication of Metal/CNT Composites Using Composite Plating by Electroless Deposition
2.5.1. Ni-P Alloy/CNT Composites
2.5.2. Cu/CNT Composites
2.5.3. Other Metal/Composites
3. Metal-Coated CNTs by Electroless Deposition
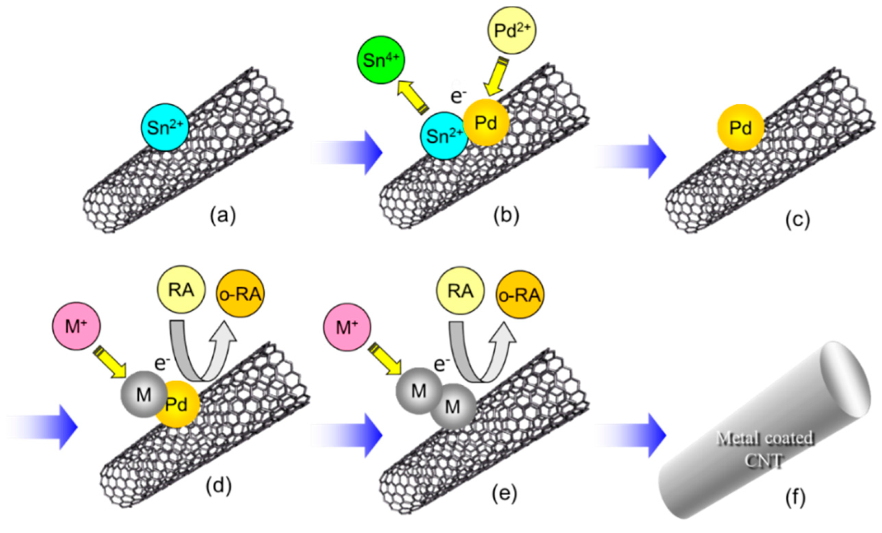
3.1. Fabrication Process
3.2. Metal-Coated CNTs
3.2.1. Ni- or Ni Alloy-Coated CNTs
3.2.2. Other Metal-Coated CNTs
4. Metal/CNT Composites by Electrodeposition Using CNT Templates (Sheet, Yarn)
4.1. Metal/CNT Composite Using CNT Sheet (Paper, Film)
4.2. Metal/CNT Composite Using CNT Yarn (Fiber)
5. Future Challenges
5.1. Metal/CNT Composites by Composite Plating
5.2. Metal-Coated CNTs by Electroless Deposition
5.3. Metal/CNT Composites Using CNT Template
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oberlin, A.; Endo, M.; Koyama, T. Filamentous growth of carbon through benzene decomposition. J. Cryst. Growth 1976, 32, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, S.R.; Lahiri, D.; Agarwal, A. Carbon nanotube reinforced metal matrix composites—A review. Int. Mater. Rev. 2010, 55, 41–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, C.G.; Prince, J.D. The codeposition of copper and graphite. Trans. Am. Electrochem. Soc. 1928, 54, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmi, N. Kinetics of the Deposition of Inert Particles from Electrolytic Baths. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1972, 119, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelens, C.; Celis, J.P.; Roos, J.R. Electrochemical aspect of the codeposition of gold and copper with inert particles. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1983, 13, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis, J.P.; Roos, J.R.; Buelens, C. A mathematical model for the electrolytic codeposition of particles with a metallic matrix. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1987, 134, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransaer, J.; Celis, J.P.; Roos, J.R. Analysis of the electrolytic codeposition of non-brownian particles with metals. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1992, 139, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.J.; Hawang, C.S. Mechanism of codeposition of silicon carbide with electrolytic cobalt. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1993, 140, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovestad, A.; Janssen, L.J.J. Electrochemical deposition of inert particles in a metallic matrix. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1995, 25, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigolo, B.; Penicaud, A.; Coulon, C.; Sauder, C.; Pailler, R.; Journet, C.; Bernier, P.; Paulin, P. Macroscopic fibers and ribbons of oriented carbon nanotubes. Science 2000, 290, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M.J.; Bachilo, S.M.; Huffman, C.B.; Moore, V.C.; Strano, M.S.; Haroz, E.H.; Rialon, K.L.; Boul, P.J.; Noon, W.H.; Kittrell, C.; et al. Band gap fluoresence from individual single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 2002, 297, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, C.; Balavoine, F.; Schultz, P.; Ebbesen, T.W.; Mioskowski, C. Supramolecular self-assembly of lipid derivatives on car bon nanotubes. Science 2003, 300, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.F.; Rojas, E.; Bergey, D.M.; Johnson, A.T.; Yodh, A.G. High weight fraction surfactant solubilization of single-wall carbon nanotubes in water. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, V.C.; Strano, M.S.; Haroz, E.H.; Hauge, R.H.; Smally, R.E. Individually suspended single-walled carbon nanotubes in various surfactants. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gao, L.; Sun, J. Production of aqueous colloidal dispersions of carbon nanotubes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 260, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurekli, K.; Mitchell, C.A.; Krishnamoorti, R. Small-angle neutron scattering from surfactant-assisted aqueous dispersions of carbon nanotubes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9902–9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, T.; Hagen, A.; Talalaev, V.; Arnold, K.; Hennrich, F.; Kappes, M.; Rosenthal, S.; McBride, J.; Ulbricht, H.; Flahaut, E. Spectroscopy of single—And double-wall carbon nanotubes environments. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J.; Glerup, M.; Paillet, M.; Bernier, P.; Holzinger, M. Production of pure nanotube fibers using a modified wet-spinning method. Carbon 2005, 43, 2397–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Resasco, D.E. Dispersion of single-walled carbon nanotubes of narrow diameter distribution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 14454–14460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossiord, N.; van der Schoot, P.; Meuldijk, J.; Koning, C.E. Determination of the surface coverage of exfoliated carbon nanotubes by surfactant molecules in aqueous solution. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3646–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Nicolosi, V.; Rickard, D.; Bergin, S.D.; Aherne, D.; Coleman, J.N. Quantitative evaluation of surfactant-stabilized single-walled carbon nanotubes: Dispersion quality and its correlation with zeta potential. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 10692–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, A.J.; Lenehan, C.E.; Quinton, J.S. Optimizing surfactant concentrations for dispersion of single-walled carbon nanotubes in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 9805–9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.H.; Wang, Q.; Collins, F. Dispersion of carbon nanotubes with SDS surfactants: A study from a binding energy perspective. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisci, J.N.; Tahhan, M.; Wallace, G.G.; Badaire, S.; Vaugien, T.; Maugey, M.; Poulin, P. Properties of carbon nanotube fibers spun from DNA-stabilized dispersions. Adv. Func. Mat. 2004, 14, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Luculescu, C.R.; Uchida, K.; Ishii, T.; Yajima, H. Dispersion behavior and spectroscopic properties of single-walled carbon nanotubes in chitosan acidic aqueous solutions. Chem. Lett. 2005, 34, 1516–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Cui, J.; Potschke, P.; Voit, B. Dispersion of pristine single-walled carbon nanotubes using pyrene-capped polystyrene and its application for preparation of polystyrene matrix composites. Carbon 2010, 48, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, B.; Simonet, B.M.; Cardenas, S.; Valcarcel, M. Separation of carbon nanotubes in aqueous medium by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromagr. A 2006, 1128, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esumi, K.; Ishigami, M.; Nakajima, A.; Sawada, K.; Honda, H. Chemical treatment of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 1995, 33, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Dai, L.; Gao, M.; Huang, S.; Mau, A. Plasma activation of carbon nanotubes for chemical modification. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Gao, L. Modified carbon nanotubes: An effective way to selective attachment of gold nanoparticles. Carbon 2003, 41, 2923–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, M.K.; Shi, Y.L.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.L. Preparation and properties of Ni/P/single-walled carbon nanotubes composite coatings by means of electroless plating. Thin Solid Films 2004, 466, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Osaki, T.; Hirota, M.; Uejima, M. Fabrication of copper/single-walled carbon nanotube composite film with homogeneously dispersed nanotubes by electroless deposition. Mater. Today Commun. 2016, 7, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Endo, M.; Norio, K. Ni-deposited multi-walled carbon nanotubes by electrodepositon. Carbon 2004, 42, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Endo, M. Carbon nanofiber-copper composite powder prepared by electrodeposition. Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Peng, J.C.; Li, X.Q.; Deng, F.M.; Wang, J.X.; Li, W.Z. Tribological behavior of carbon nanotubes-reinforced nickel matrix composite coatings. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Cheng, F.Q.; Li, S.L.; Zhou, L.P.; Li, D.Y. Electrodeposited nickel composites containing carbon nanotubes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 155, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Chen, C.S.; Xiao, H.N.; Cheng, F.Q.; Zhang, G.; Yi, G.J. Corrosion behavior of carbon nanotube-Ni composite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 191, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Endo, M.; Sato, T.; Koide, A. Fabrication of nickel-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films with excellent thermal conductivity by an electrodeposition technique. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2006, 9, C131–C133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Saito, T.; Endo, M. Low-internal-stress nickel multiwalled carbon nanotube composite electrodeposited from a sulfmate bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, D530–D533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Fujimori, A.; Murai, M.; Endo, M. Excellent solid lubrication of electrodeposited nickel-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3545–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Arai, S.; Endo, M. Preparation of nickel-carbon nanofiber composites by a pulse-reverse electrodeposition process. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, J. The effects of pulse-reverse parameter on the properties of Ni-carbon nanotube composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 9491–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, J. The effects of electrodeposition current density on properties of Ni-CNTs composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3246–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zuo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, J. Effects of surfactants on electrodeposition of nickel-carbon nanotubes composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 3385–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, P.Q.; Xu, W.C.; Huang, Q.Y. Mechanical properties and microstructure of nanocrystalline nickel-carbon nanotube composites produced by electrodeposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 483, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.S.; Byun, J.Y.; Oh, T.S. Electrodeposition and mechanical properties of Ni-carbon nanotube composite coatings. J. Phys. Chem. Solid 2008, 69, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickrell, P.L.; Sinnott, S.B.; Hahn, D.W.; Raravikar, N.R.; Schadler, L.S.; Ajayan, P.M.; Sawyer, W.G. Friction anisotropy of oriented carbon nanotube surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 18, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, K.; Street, K.W., Jr.; Wal, R.L.V.; Andrews, R.; Sayir, A. Solid lubrication by multiwalled carbon nanotubes in air and in vacuum. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 19, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martis, P.M.; Dilimon, V.S.; Delhalle, J.; Mekhalif, Z. Electro-generated nickel/carbon nanotube composites in ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5407–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.G.; Sun, J.; Gui, Z.X.; Song, K.J.; Luo, L.M.; Wu, Y.C. Super-low friction nickel based carbon nanotube composite coating electro-deposited from eutectic solvents. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2017, 74, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Oh, T.S. Electrodeposition behavior and characteristics of Ni-carbon nanotube composite coatings. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, s68–s72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J. Morphological and compositional engineering of Ni/carbon nanotube composite film via a novel cyclic voltammetric route. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Konno, T. Improvement in tool life of electroplated diamond tools by Ni-based carbon nanotube composite coatings. Precis. Eng. 2014, 38, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Preparation and characterization of polydopamine-modified Ni/carbon nanotubes friction composite coating. Coatings 2019, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, R.S.; Chukwuike, V.I.; Bhakyaraj, K.; Mohan, S.; Barik, R.C. Electrochemical and hydrodynamic flow characterization of corrosion protection of nickel/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 507, 145073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotheender, K.S.; Gupta, A.; Srivastava, C. Grain boundary engineering in Ni-carbon nanotube composite coatings and its effect on the corrosion behavior of the coatings. Materialia 2020, 9, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, M.K.; Li, H.L. Preparation of electroplated Ni-P-ultrafine diamond, Ni-P-carbon nanotubes composite coatings and their corrosion properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5809–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Sun, C.F.; Gao, P.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.M. Electrodeposition and characterization of Ni-Co-carbon manotubes composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 4870–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Arai, S.; Endo, M. Electrodeposition of Ni-P alloy-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, D50–D53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Kumari, N.; Srivastava, C. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of NiCo-carbon nanotube composite coatings. J. Alloy. Comp. 2019, 801, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Endo, M. Carbon nanofiber-copper composites fabricated by electrodeposition. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2004, 7, C25–C26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Endo, M. Various carbon nanofiber-copper composite films prepared by electrodeposition. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Saito, T.; Endo, M. Metal-fixed multiwalled carbon nanotube patterned emitters using photolithography and electrodeposition technique. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2008, 11, D72–D74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Arai, S.; Saito, T.; Endo, M. Cu-MWCNT composite films fabricated by electrodeposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, D147–D153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Suwa, Y.; Endo, M. Cu/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films fabricated by pulse-reverse electrodeposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, D49–D53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; McGuire, G.E.; Shenderova, O.A.; Ke, H.; Burkett, S.L. Fabrication of copper/carbon nanotube composite thin films by periodic pulse reverse electroplating using nanodiamond as a dispersing agent. Thin Solid Film. 2016, 615, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, Q. Carbon nanotubes reinforced copper composite with uniform CNT distribution and high yield of fabrication. Micro Nano Lett. 2017, 12, 722–725. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, X.; Yang, C.; Zhou, L. Improving strength and high electrical conductivity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes/copper composites fabricated by electrodeposition and powder metallurgy. J. Alloy. Comp. 2018, 735, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, X.; Yang, C.; Zhou, L. An electrodeposition approach to obtaining carbon nanotubes embedded copper powders for the synthesis of copper matrix composites. J. Alloy. Comp. 2018, 735, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Zhang, A.; Wu, H. Enhanced wear performance of Cu-carbon nanotubes composite coatings prepared by jet electrodeposition. Materials 2019, 12, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Ogasawara, T.; Ohnuki, T.; Arai, S. Multi-layered copper foil reinforced by co-deposition of single-walled carbon nanotube based on electroplating technique. Mater. Lett. 2020, 261, 126993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.D.; Ren, Y.; He, C.S.; Deng, J.N.; Nan, J.; Chen, J.G.; Zuo, L. Single-walled carbon nanotube-reinforced copper composite coatings prepared by electrodeposition under ultrasonic field. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, G.; Sun, Y.; Jenny Sun, J.; Chen, Q. Mechnical properties of carbon nanotube-copper nanocomposites. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 035013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heer, W.A.; Chatelain, A.; Ugarte, D. A carbon nanotube field-emission electron source. Science 1995, 270, 1179–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.X.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, F.; Ji, J. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes as second phase on the copper electrochemical reduction behavior for fabricating their nanostructured composite films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 651, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Kato, A. Mechanism for codeposition of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with copper from acid copper sulfate bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, D380–D385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Fukuoka, R. A carbon nanotube-reinforced noble tin anode structure for lithium-ion batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2016, 46, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Ohnuki, T.; Ogasawara, T.; Banno, T.; Arai, S. Electrodeposited Cu/MWCNT composite film: A potential current collector of silicon-based negative-electrodes for Li-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2019, 38, 21939–21945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tao, J.; Yi, J.; Li, C.; Bao, R.; Liu, Y.; You, X.; Tan, S. Balancing the strength and ductility of carbon nanotubes reinforced copper matrix composites with microlaminated structure and interdiffusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Tao, J.; Bu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pu, Z.; Yi, J. Achieving high ductility in layered carbon nanotube/copper composite prepared by composite electrodeposition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 108, 107992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H. Electrodeposition and properties of composites consisting of carbon nanotubes and copper. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 5511–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.M.; Esquenazi, G.L.; Gowenlock, C.E.; Jones, D.R.; Li, J.; Brinson, B.; Barron, A.R. Electrodeposition of Cu-SWCNT composites. C 2019, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xue, J.; Zuo, T.; Gao, Z.; Xiao, L.; Han, L.; Li, S.; Yang, Y. Copper/functionalized-carbon nanotubes composite films with ultrahigh electrical conductivity prepared by pulse reverse electrodeposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 14184–14191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.; Srivastava, C. Corrosion between growth texture, crystallite size, lattice strain and corrosion behavior of copper-carbon nanotube composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, B.M.; Venkatesha, T.V.; Naik, Y.A.; Prashantha, K. Corrosion studies of carbon nanotube-Zn composite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 5836–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseluikin, V.N.; Strilets, A.A.; Yakovlev, A.V. Electrochemical deposition of zinc-based composite coatings modified with carbon nanotubes form alkaline electrolyte. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2020, 56, 1186–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseluikin, V.N.; Koreshkova, A.A. Electrodeposition of zinc-nickel-carbon nanotubes composite coatings in a reversing mode. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2016, 52, 1040–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyotheender, K.S.; Srivastava, C. Correlating the five-parameter grain boundary character distribution and corrosion behavior of zinc-carbon nanotube composite coatings. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2021, 52A, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhen, Z.; Lin, Y. Mechanical properties of hard Cr-MWNT composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 3610–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Awasthi, S.; Ramkumar, J.; Balani, K. Protective trivalent Cr-based electrochemical coatings for gun barrels. J. Alloy. Comp. 2018, 769, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.; Katiyar, P.K.; Ramkumar, J.; Balani, K. Synergistic role of carbon nanotube and yttria stabilized zirconia reinforcement on wear and corrosion resistance of Cr-based nano-composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel, H.; Shipway, P.H.; Harris, S.J. Sliding wear behavior of electrodeposited cobalt-tungsten and cobalt-tungsten-iron alloys. Wear 2003, 255, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Liu, C.; Guo, J.; Huang, P. Characterization of nanocrystalline Co and Co/MWCNT coatings produced by different electrodeposition techniques. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 217, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Miyagawa, K. Frictional and wear properties of cobalt/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films formed by electrodeposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 235, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Miyagawa, K. Field emission properties of cobalt/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films fabricated by electrodeposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 280, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pereira, N.M.; Brincoveanu, O.; Pantazi, A.G.; Pereira, C.M.; Araujo, J.P.; Silva, A.F.; Enachescu, M.; Anicai, L. Electrodeposition of Co and Co composites with carbon nanotubes using choline chloride-based ion liquids. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 324, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Miyagawa, K. Fabrication of Co-W alloy/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films by electrodeposition for improved frictional properties. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, M39–M43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, E.E.; Natarajan, S. Effect of carbon nanotubes on corrosion and tribological properties of pulse-electrodeposited Co-W composite coatings. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugishige, M.; Wongwiriyapan, W.; Wang, F.; Park, K.C.; Takeuchi, K.; Arai, S.; Endo, M. Gold-carbon nanotube composite plating film deposited using non-cyanide bath. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 48, 070217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishige, M.; Sekino, M.; Fujisawa, K.; Morimoto, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Arai, S.; Kawai, A. Electric contact characteristic under low load of silver-carbon nanotube composite plating film corroded using H2S gas. Appl. Phys. Express. 2010, 3, 065801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Kikuhara, T.; Shimizu, M.; Horita, M. Electrodeposition of Ag/CNT composite films from iodide plating baths. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 122515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Kikuhara, T.; Shimizu, M.; Horita, M. Superior electrical contact characteristics of Ag/CNT composite films formed in a cyanide-free plating bath and tested against corrosion by H2S gas. Mater. Lett. 2021, 303, 130504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandao, A.T.S.C.; Rosoiu, S.; Costa, R.; Lazar, O.A.; Silva, A.F.; Anicai, L.; Pereira, C.M.; Enachescu, M. Characterization and electrochemical studies of MWCNTs decorated with Ag nanoparticles through pulse reversed current electrodeposition using a deep eutectic solvent for energy storage applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsushiro, T.; Koura, N.; Nakano, S.; Ui, K.; Takeuchi, K. Electrodeposition of aluminum-carbon nanotube composite from room-temperature molten salt electrolyte. Electrochemistry 2006, 74, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Kitada, A.; Chen, T.; Fukami, K.; Shimizu, M.; Arai, S.; Yao, Z.; Murase, K. Dispersion of multiwalled carbon nanotubes into a diglyme solution, electrodeposition of aluminum-based composite, and improvement of hardness. J. Alloy. Comp. 2020, 816, 152585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Jie, X.; Lu, G. Corrosion resistance of Pb-Sn composite coatings reinforced by carbon nanotubes. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2010, 7, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandao, A.T.S.C.; Anicai, L.; Lazar, O.A.; Rosoiu, S.; Pantazi, A.; Costa, R.; Enachescu, M.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Electrodeposition of Sn and Sn composites with carbon materials using choline chloride-based ionic liquids. Coatings 2019, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Tu, J.P.; Gan, H.Y.; Xu, Z.D.; Wang, Q.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhang, X.B. Electroless preparation and tribological properties of Ni-P-carbon nanotube composite coatings under lubricated condition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 160, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Tu, J.P.; Xu, Z.D.; Chen, W.L.; Zhang, X.B.; Cheng, D.H. Tribological properties of Ni-P-multi-walled carbon nanotubes electroless composite coating. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.X.; Tu, J.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Gan, H.Y.; Xu, Z.D.; Zhang, X.B. Tribological application of carbon nanotubes in a metal-based composite coatings and composites. Carbon 2003, 41, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, H.; Shi, Y.L.; Li, M.K.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.L. The fabrication and corrosion behavior of electroless Ni-P-carbon nanotube composite coatings. Mater. Res. Bull. 2005, 40, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Chen, C.S.; Xiao, H.N.; Liu, H.B.; Zhou, L.P.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, G. Dry friction and wear characteristics of nickel/carbon nanotube electroless composite deposits. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.F.; Ge, H.L. Preparation and tribological properties of the carbon nanotube-Ni-P composite coating. Tribol. Int. 2006, 39, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chan, Y.C.; Yang, D.; Wu, B.Y. The shearing behavior and microstructure of Sn-4Ag-0.5Cu solder joints on a Ni-P-carbon nanotubes composite coating. J. Alloy. Comp. 2009, 468, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.L.; Fujishige, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Arai, S.; Morimoto, S.; Endo, M. Inter-collisional cutting of multi-walled carbon nanotubes by high-speed agitation. J. Phys. Chem. Solid 2008, 69, 2481–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Sato, T.; Endo, M. Fabrication of various electrolessb Ni-P alloy/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films and their frictional properties. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, D570–D576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firoozbakht, M.; Monirvaghefi, S.M.; Niroumand, B. Electroless composite coating of Ni-P-carbon nanotubes on magnesium powder. J. Alloy. Comp. 2011, 509S, S496–S502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ren, C.; He, Y. Ni-P-multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite coatings prepared by mechanical attrition (MA)-assisted electroless plating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 2774–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishahi, M.; Monirvaghefi, S.M.; Saatchi, A.; Hosseini, S.M. The effect of carbon nanotubes on the corrosion and tribological behavior of electroless Ni-P-CNT composite coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2439–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.Q.; Li, X.B.; Xiong, Y.J.; Zhan, J. Preparation and tribological performances of Ni-P-multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite coatings. T. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2012, 22, 2719–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes de Oliveira, M.C.; Correa, O.V.; Pereira da Silva, R.M.; Batista de Lima, N.; Dias de Oliveira, J.T.; Antonio de Oliveira, L.; Antunes, R.A. Structural characterization, global and local electrochemical activity of electroless Ni-P-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite coatings on pipeline steel. Metals 2021, 11, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Kanazawa, T. Electroless deposition of Cu/multiwalled carbon nanotube composite films with improved frictional properties. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2014, 3, P201–P206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, V.; Anderson, P.; Hall, J.; Robinson, F.; Bohm, S. Electroless Co-P-carbon nanotube composite coating to enhance magnetic properties of grain-oriented electrical steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 407, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Fan, S.; Han, W.; Sun, C.; Liang, W. Coating of carbon nanotube with nickel by electroless plating method. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 36, L501–L503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.M.; Andy Hor, T.S.; Xu, G.Q.; Tung, C.H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.L.S. Electroless plating of metals onto carbon nanotubes activated by a single-step activation method. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 2115–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.Z.; Zhang, X.B.; Xiong, W.Q.; Liu, F.; Huang, W.Z.; Sun, Y.L.; Tu, J.P.; Chen, X.W. Continuous Ni-layer on multiwall carbon nanotubes by an electroless plating method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2002, 155, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Endo, M.; Hashizume, S.; Shimojima, Y. Nickel-coated carbon nanofibers prepared by electroless deposition. Electochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Arai, S.; Endo, M. The preparation of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with a Ni-P coating by an electroless deposition process. Carbon 2005, 43, 1716–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Endo, M. Pure-nickel-coated multiwalled carbon nanotubes prepared by electroless deposition. Electochem. Solis State Lett. 2010, 13, D94–D96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Imoto, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Endo, M. Fabrication of Ni-B alloy coated vapor-grown carbon nanofibers by electroless deposition. Carbon 2011, 49, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jin, H.; Hao, Y.; Chen, T.; Dai, J.; Wang, Q. The microstructure of Ni layer on single-walled carbon nanotubes prepared by an electroless coating process. J. Nanomater. 2010, 2011, 348958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannatham, M.; Sankaran, S.; Haridoss, P. Electroless nickel plating of arc discharged synthesized carbon nanotubes for metal matrix composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 324, 475–481. [Google Scholar]
- Ergul, E.; Kurt, H.I.; Oduncuohlu, M.; Yilmas, N.F. Electroless nickel-phosphorous and cobalt-phosphorous coatings on multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 115604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakagawa, J.; Yamamoto, T.; Endo, M. Fabrication of metal coated carbon nanotubes by electroless deposition for improved wettability with molten aluminum. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 212, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mani, M.K.; Viola, G.; Reece, M.J.; Hall, J.P.; Evans, S.L. Improvement of interfacial bonding in carbon nanotube reinforced Fe-50Co composites by Ni-P coating: Effect on magnetic and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2014, 188, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gupta, M.C. Novel carbon nanotube-polystyrene form composites for electromagnetic interference shielding. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Huang, Y.; Du, F.; He, X.; Lin, X.; Gao, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Eklund, C.P. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding of single-walled carbon nanotube epoxy composites. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.L.; Li, X.; Shen, Z.M. Microwave absorbing property and complex permittivity and permeability of epoxy composites containing Ni-coated and Ag filled carbon nanotubes. Comp. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2902–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.Y.; Han, J.H.; Lee, S.B.; Yi, J.W. Microwave absorbing hybrid composites containing Ni-Fe coated carbon nanofibers prepared by electroless plating. Compos. Part A 2011, 42, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, R.; Yu, D. High-electromagnetic-shielding cotton fabric prepared using multiwalled carbon nanotubes/nickel-phosphorous electroless plating. Appl. Orgnometal. Chem. 2020, 34, e5434. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Xia, J.; Peng, J.; Li, W.; Xie, S. Carbon-nanotube metal-matrix composites prepared by electroless plating. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Arai, S.; Endo, M. Metallization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with copper by an electroless deposition process. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoush, W.M.; Lim, B.K.; Mo, C.B.; Nam, D.H.; Hong, S.H. Electrical and mechanical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced copper nanocomposites fabricated by electroless deposition process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 513, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yuan, H. Electroless plating of carbon nanotubes with silver. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 3241–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.; Amal, M.K.E. Development of an AlCl3-urea ionic liquid for the electroless deposition of aluminum on carbon nanotubes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5756–5761. [Google Scholar]
- Rinzler, A.G.; Liu, J.; Dai, H.; Nikolaev, P.; Huffman, C.B.; Rodriguez-Macias, F.J.; Boul, P.J.; Lu, A.H.; Heymnn, D.; Colbert, D.T.; et al. Large-scale purification of single-wall carbon nanotubes: Process, product, and characterization. Appl. Phys. A 1998, 67, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahr, J.L.; Yang, J.; Kosynkin, D.V.; Bronikowski, M.J.; Smally, R.E.; Tour, J.M. Functionalization of carbon nanotubes by electrochemical reduction of aryl diazonium salts: A bucky paper electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6536–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.J.; Hou, H.; Li, Q.; Graham, M.J.; Greiner, A.; Reneker, D.H.; Harris, F.W.; Cheng, S.Z.D. Assembly of well-aligned multiwalled carbon nanotubes in confined polyacrylonitrile environments; electrospun composite nanofiber sheets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15754–15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Liu, K.; Wu, J.S.; Liu, L.; Cheng, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Fan, S.; Jiang, K. Flexible, stretchable, transparent conducting films made from superaligned carbon nanotubes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Li, Q.; Fan, S. Spinning continuous carbon nanotube yarns. Nature 2002, 419, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, F.; Gogotsi, Y.; Ali, A.; Naguib, N.; Ye, H.; Yang, G.; Li, C.; Willis, P. Electrospinning of continuous carbon nanotube-filled nanofiber yarns. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Atkinson, K.R.; Baughman, R.H. Multifunctional carbon nanotube yarns by downsizing an ancient technology. Science 2004, 306, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Kinloch, I.A.; Windle, A.H. Direct spinning of carbon nanotube fibers from chemical vapor deposition synthesis. Science 2004, 304, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, M.; Kim, Y.A.; Hayashi, T.; Nishimura, K.; Matsusita, T.; Miyashita, K.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Vapor-grown carbon fibers (VGCFs): Basic properties and their battery application. Carbon 2001, 39, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.J.; Zhu, L.; Xue, W.D.; Li, W.Z. Fabrication of superaligned carbon nanotubes reinforced copper matrix laminar composite by electrodeposition. Trans. Nonferrous. Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2994–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, J.; Xiong, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, W. Enhanced strength and excellent transport properties of a superaligned carbon nanotubes reinforced copper matrix laminar composite. Compos. Part A 2016, 88, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.C.; Xiong, L.Q.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.Z. Preparation of super-aligned carbon nanotube-reinforced nickel-matrix laminar composites with excellent mechanical properties. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2019, 26, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, J.; Xiong, L.; Hou, Z.; Zhu, L.; Li, W. Nickel-coated super-aligned carbon nanotube reinforced copper composite for improved strength and conductivity. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.M.; Chen, X.F.; Hong, P.; Yi, J.H. Microstructure and electrical conductivity of laminated Cu/CNT/Cu composites prepared by electrodeposition. J. Alloy. Compos. 2017, 717, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Kirihata, K.; Shimizu, M.; Ueda, M.; Katada, A.; Uejima, M. Fabrication of copper/single-walled carbon nanotube composites by electrodeposition using free-standing nanotube film. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, D922–D929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshman, K.; Randeniya, K.; Bendavid, A.; Martin, P.J.; Tran, C.D. Composite yarns of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with metallic electrical conductivity. Small 2010, 6, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Yong, Z.; Li, Q. Continuous electrodeposition for lightweight, highly conducting and strong carbon nanotube-copper composite fibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4215–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Cai, Z.; Qiu, L.; Li, H.; Ren, J.; Lin, H.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X.; Peng, H. Synthesis of aligned carbon nanotube composite fibers with high performances by electrochemical deposition. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2211–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannula, P.M.; Peltonen, A.; Aromaa, J.; Janas, D.; Lundstrom, M.; Wilson, B.P.; Koziol, K.; Forsen, O. Carbon nanotube-copper composites by electrodeposition on carbon nanotube fibers. Carbon 2016, 107, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Kane, C.L.; Dekker, C. High-field electrical transport in single-wall carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 27, 2941–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.Q.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M. Reliability and current carrying capacity of carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 1172–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.G.; Hersam, M.; Arnold, M.; Martel, R.; Avouris, P. Current saturation and electrical breakdown in multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 3128–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, C.; Yamada Kobayashi, K.; Sekiguchi, A.; Futaba, D.N.; Yumura, M.; Hata, K. One hundred fold increase in current carrying capacity in a carbon nanotube-copper composite. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, R.; Yamada, T.; Hata, K.; Sekiguchi, A. Electrical performance of lightweight CNT-Cu composite wires impacted by surface and internal Cu spatial distribution. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, R.; Yamada, T.; Hata, K.; Sekiguchi, A. The influence of Cu electrodeposition parameters on fabricating structurally uniform CNT-Cu composite wires. Mater. Today Commun. 2017, 13, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, R.; Yamada, T.; Hata, K.; Sekiguchi, A. The importance of carbon nanotube wire density, structural uniformity, and purity for fabricating homogeneous carbon nanotube-copper wire composites by copper electrodeposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 04FP08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, C.; Yasuda, Y.; Takeya, S.; Ata, S.; Nishizawa, A.; Futaba, D.N.; Yamada, T.; Hata, K. Carbon nanotube-copper exhibiting metal-like thermal conductivity and silicon-like thermal expansion for efficient cooling electronics. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2669–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, C.; Sekiguchi, A.; Yasuda, Y.; Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K. Nano-scall, planar and multi-tiered current pathways from a carbon nanotube-copper composite with high conductivity, ampacity and stability. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3888–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sundaram, R.; Sekiguchi, A.; Hata, K.; Fukuda, D.N. Through-solicon-via interposers with Cu-level electrical conductivity and Si-level thermal expansion based on carbon nanotube-Cu composites for microelectronics packaging applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, H.; Park, M.; Park, M.; Park, J.; Han, J.; Lee, A.; Bae, S.; Kim, T.W.; Ha, J.S.; Kim, S.M.; et al. Metal nanofibrils embedded in long free-standing nanotube fiber with a high critical current density. NPA Asia Mater. 2018, 10, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Murakami, I.; Shimizu, M.; Oshigane, A. Fabrication of CNT/Cu composite yarn via single-step electrodeposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 102509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Lee, D.M.; Park, M.; Park, S.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, H.S.; Hong, B.H.; et al. Performance enhancement of graphene assisted CNT/Cu composites for lightweight electrical cables. Carbon 2021, 179, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Metal | CNT | Treatment of CNT | Base Plating Bath | Surfactant | Remarks | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Dull Watts bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Corrosion behavior | 2020 | [57] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Dull Watts bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Corrosion protection | 2020 | [56] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Wrapped by polydopamine | Dull Watts bath | Non | Wear and corrosion resistance | 2019 | [55] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Ionic liquid (choline chloride/carbamide) | Non | Non-aqueous solvent | 2017 | [51] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Sulfamate bath | Cationic surfactant, compound name is unknown | Improvement in tool life | 2014 | [54] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | NiSO4+NaCl | Polyvinylpyrrolidone | Cyclic voltametric route | 2011 | [53] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Ball milling | Bright Watts bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate and Hydroxypropylcellulose | Corrosion behavior | 2011 | [52] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Choline chloride/urea | Non | Non-aqueous solvent | 2010 | [50] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Bright Watts bath | Polyacrylic acid | Solid lubrication | 2008 | [41] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Ball milling | Watts type bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate, Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Effects of surfactants | 2008 | [45] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Dull Watts bath | Non | Effects of current density | 2008 | [44] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Ball milling | Bright Watts bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate and Hydroxypropylcellulose | Mechanical properties | 2008 | [47] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Bright Watts bath | Non | Mechanical properties | 2008 | [46] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Bright Sulfamate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Low internal stress | 2007 | [40] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Dull Watts bath | Non | Pulse-reverse parameter | 2007 | [43] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Bright Watts bath | Polyacrylic acid | Thermal conductivity | 2006 | [39] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Dull Watts bath | Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chrolide) | Pulse-reverse electrodeposition | 2005 | [42] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Dull Watts bath | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Corrosion behavior | 2005 | [38] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Non | Dull Watts bath | Polyacrylic acid | Ni deposition on incorporated CNT | 2004 | [34] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Ball milling | Dull Watts bath | Non | CNT content | 2002 | [37] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Ball milling | Dull Watts bath | Non | Tribological property | 2001 | [36] |
| Ni-Co | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Dull Watts bath + Co salt | Non | Corrosion behavior | 2019 | [61] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Non | Dull Watts bath + citric acid + P compound | Polyacrylic acid | Tribological properties | 2010 | [60] |
| Ni-Co | MWCNT | Non | Dull Watts bath + Co salt | Compound name is unknown | Mechanical and tribological properties | 2006 | [59] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Non | Ni salts + citric acid + P compounds | Compound name is unknown | Corrosion properties | 2004 | [58] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Citric bath | Non | Corrosion behavior | 2021 | [85] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Non | Pulse reverse, electrical conductivity | 2020 | [84] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment? | Sulfate bath | Non-ionic surfactants, Compound name is unknown | Mechanical properties, Microlaminated structure | 2020 | [81] |
| Cu | SWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Stearyltrimethylammonium chloride | Mechanical properties | 2020 | [72] |
| Cu | SWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Non | Microstructure | 2019 | [83] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Jet electrodeposition, Tribological properties | 2019 | [71] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Current collector for LIB anode | 2019 | [79] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Stearyltrimethylammonium bromide | Electrical conductivity, Corrosion resistance | 2018 | [82] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Non-ionic surfactants, Compound name is unknown | Mechanical properties, Laminated structure | 2018 | [80] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Non | Cu/CNT powder + powder metallurgy | 2018 | [70] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Non | Cu/CNT powder + powder metallurgy | 2018 | [69] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Non | Cu/CNT powder + powder metallurgy | 2017 | [68] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Commercially available | Nano diamond | Periodic pulse reverse electrodeposition | 2016 | [67] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Current collector for LIB anode | 2016 | [78] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Co-deposition mechanism of CNT | 2013 | [77] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Non | Electrochemical reduction behavior | 2011 | [76] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Pulse-reverse | 2011 | [66] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Surface morphology, Hardness, Internal stress | 2010 | [65] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Patterned field emitter | 2008 | [64] |
| Cu | SWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Commercial products | Mechanical properties | 2008 | [74] |
| Cu | SWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Cetyltrimethylammonium chloride | Mechanical properties | 2008 | [73] |
| Cu | Cup-stacked CNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Various CNTs | 2005 | [63] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Microstructure | 2004 | [62] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Cu/MWCNT composite powder | 2003 | [35] |
| Zn | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Corrosion resistance | 2021 | [89] |
| Zn | MWCNT | Non | Zincate bath | Unknown | Pulse electrodeposition, Corrosion resistance | 2020 | [87] |
| Zn | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | Sulfate bath | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Corrosion resistance | 2007 | [86] |
| Zn-Ni | MWCNT | Non | Chloride bath | Non | Pulse reverse, Tribological and Corrosion properties | 2016 | [88] |
| Cr | MWCNT | Non | Trivalent Cr bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Tribological properties, Corrosion resistance | 2020 | [92] |
| Cr | MWCNT | Non | Trivalent Cr bath | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Tribological properties | 2018 | [91] |
| Cr | MWCNT | Non | Trivalent Cr bath | Non | Mechanical properties | 2009 | [90] |
| Co | MWCNT | Non | Choline chloride/urea | Non | Non-aqueous solvent | 2017 | [97] |
| Co | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Field emission properties | 2013 | [96] |
| Co | MWCNT | Non | Sulfate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Tribological properties | 2013 | [95] |
| Co | MWCNT | Acid-treatment | Sulfate bath + citrate | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Tribological properties, Corrosion properties | 2013 | [94] |
| Co-W | MWCNT | Non | Co salt + Tungstate + Citrate | Polyacrylic acid | Tribological properties Corrosion properties | 2015 | [99] |
| Co-W | MWCNT | Non | Co salt + Tungstate + Citrate | Polyacrylic acid | Tribological properties | 2013 | [98] |
| Au | MWCNT | Non | Sulfite bath | Stearyltrimethylammonium chloride | Electrical conductivity, Tribological properties | 2009 | [100] |
| Ag | MWCNT | Non | Choline chloride + glycerol | Poly (N-vinyl pyrrolidone) | Pulse reverse electrodeposition | 2021 | [104] |
| Ag | MWCNT | Non | Iodide bath | Non | Electrical contact resistance against H2S gas | 2021 | [103] |
| Ag | MWCNT | Non | Iodide bath | Non | Hardness, Electrical and Tribological properties | 2020 | [102] |
| Ag | MWCNT | Non | Cyanide bath | Unknown | Electrical contact resistance against H2S gas | 2010 | [101] |
| Al | MWCNT | Acid treatment | Diethylene glycol dimethyl ether | Non | Hardness | 2020 | [106] |
| Al | MWCNT | Non | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride | Non | Hardness | 2006 | [105] |
| Sn | MWCNT | Non | Choline chloride + ethylene glycole | Non | Nucleation study | 2019 | [108] |
| Pb-Sn | MWCNT | Acid treatment | Fluoroborate bath | Polyacrylic acid | Corrosion resistance | 2010 | [107] |
| Metal | CNT | Pre-Treatment of CNT | Reducing Agent | Surfactant | Remarks | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Non | NaH2PO2 | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Tribological properties, Corrosion resistance | 2021 | [122] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Ball milling | NaH2PO2 | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Tribological properties | 2012 | [121] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Ball milling, Chemical treatment | NaH2PO2 | Commercial product | Tribological properties, Corrosion resistance | 2012 | [120] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Chemical treatment Ball milling | NaH2PO2 | Sodium lauryl sulfate | Mechanical attrition, Tribological properties | 2012 | [119] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | HNO3 | Commercial product | Commercial product | Substrate: Mg powder | 2011 | [118] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Non | NaH2PO2 | Stearyltrimethylammonium chloride | Substrate: ABS resin Tribological properties | 2011 | [117] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Non | NaH2PO2 | Stearyltrimethylammonium chloride | Various P content, Tribological properties | 2010 | [116] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | NaH2PO2 | Unknown | Effects on solder joint | 2009 | [115] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | NaH2PO2 | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Tribological properties | 2009 | [114] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Chemical treatment | NaH2PO2 | unknown | Tribological properties | 2006 | [113] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Ball milling | NaH2PO2 | Compound name is unknown | Hardness, Corrosion resistance | 2005 | [112] |
| Ni-P | SWCNT | Heat treatment | NaH2PO2 | Compound name is unknown | Tribological properties | 2004 | [32] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Ball milling | NaH2PO2 | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Tribological properties | 2003 | [111] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Ball milling | NaH2PO2 | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Tribological properties | 2003 | [110] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Ball milling | NaH2PO2 | Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide | Tribological properties | 2002 | [109] |
| Cu | SWCNT | Non | CHOCOOH | Sodium lauryl sulfate Hydroxypropylcellulose | Mechanical disintegration, | 2016 | [33] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Non | CHOCOOH | Sodium lauryl sulfate Hydroxypropylcellulose | Various CNTs Tribological properties | 2014 | [123] |
| Co-P | MWCNT | Non | NaH2PO2 | Non | Magnetic properties | 2016 | [124] |
| Metal | CNT | Pre-Treatment of CNT | Reducing Agent | Surfactant | Remarks | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Non | Microstructure, Co-coated CNTs | 2020 | [134] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Introduction of -COOH on CNT + Pd2+ | NaH2PO2 | Non | EMI properties, Cotton fabric substrate | 2020 | [141] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Non | Arc discharge synthesized CNTs | 2015 | [133] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+/Pd2+ commercial product | NaH2PO2 | Non | Fe-50Co composites, magnetic properties | 2014 | [136] |
| Au/Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Polyacrylic acid (Pre-treatment) | Improved wettability with molten Al | 2012 | [135] |
| Fe-B/Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2, KBH4 | Non | Microwave absorbing properties | 2011 | [140] |
| Ni-P | SWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Non | Microstructure of Ni-layer | 2011 | [132] |
| Ni-B | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | (CH3)2NH·BH3 | Polyacrylic acid (Pre-treatment) | Graphitized MWCNTs Heat treatment | 2011 | [131] |
| Ni | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | N2H4 | Polyacrylic acid (Pre-treatment) | Graphitized MWCNTs Magnetic properties | 2010 | [130] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | K2Cr2O7+H2SO4 Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Non | Microwave absorbing properties, Ni-N alloy | 2008 | [139] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | HNO3 Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Diallyl-dimethylammonium chloride | Graphitized MWCNTs | 2005 | [129] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Polyacrylic acid (Pre-treatment) | Graphitized MWCNTs | 2004 | [128] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Non | Continuous Ni-layer | 2002 | [127] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Mixed Pd2+/Sn2+ | NaH2PO2 | Non | Pd-coated CNTs | 1999 | [126] |
| Ni-P | MWCNT | Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Non | Magnetic property | 1997 | [125] |
| Al | MWCNT | Sn2+/Pd2+ commercial product | LiAlH4 | Non | Non-aqueous bath: AlCl3-urea | 2020 | [146] |
| Ag | MWCNT | H2SO4 + HNO3 Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | HCHO | Non | Interfacial adhesion of composites | 2004 | [145] |
| Cu | MWCNT | Sulphoric acid + HNO3 Sn2+sensitization + Cu2+activation | HCHO | Non | Electrical and mechanical properties | 2009 | [144] |
| Cu | MWCNT | HNO3 Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation HNO3 | CHOCOOH | Diallyl-dimethylammonium chloride | Graphitized MWCNTs | 2004 | [143] |
| Co-P | MWCNT | K2Cr2O7+H2SO4 Sn2+sensitization + Pd2+activation | NaH2PO2 | Non | Heat-treatment | 2000 | [142] |
| CNT Template | Feature of CNT Template | Metal | Plating Bath | Remarks | Year | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNT film | Super-aligned | Cu, Ni | Acid sulfuric bath + glucose Dull Watts Bath | Improved mechanical and electrical properties | 2019 | [159] |
| MWCNT film | Super-aligned | Ni | Dull Watts Bath | Improved mechanical properties | 2019 | [158] |
| SWCNT paper (Bucky paper) | Orientation: in-plane direction | Cu | Acid sulfate bath + polyethylene glycol + Cl− + bis(3-sulfopropyl) disulfide + Janus green B | One-step electrodeposition by a combination of additives | 2017 | [161] |
| MWCNT paper | Super-aligned | Cu | Acid sulfuric bath + glucose + polyethylene glycol + Cl− Alkaline bath (EDTA, Citrate) | Electrical conductivity | 2017 | [160] |
| MWCNT film | Super-aligned | Cu | Acid sulfuric bath + glucose | Improved mechanical properties | 2016 | [157] |
| MWCNT film | Super-aligned | Cu | Acid sulfuric bath + glucose | Improved mechanical properties | 2015 | [156] |
| SWCNT yarn | Straight | Cu | Acid sulfate bath | Graphen growth on the surface of electrodeposited Cu | 2021 | [178] |
| MWCNT yarn | Twisted | Cu | Acid sulfate bath + polyethylene glycol + Cl− + bis(3-sulfopropyl) disulfide + Janus green B | One-step electrodeposition by a combination of additives | 2020 | [177] |
| CNT yarn | Straight | Cu | Acid sulfate bath | Superior current carrying capacity | 2018 | [176] |
| MWCNT yarn | Twisted | Cu | (CH3COO)2 + CH3CN Acid sulfuric bath | Effect of CNT yarn density | 2018 | [172] |
| MWCNT yarn | Twisted | Cu | Cu (CH3COO)2 + CH3CN Acid sulfuric bath | Two-step electrodeposition Uniform composite wire | 2017 | [171] |
| MWCNT yarn | Twisted | Cu | (CH3COO)2 + CH3CN Acid sulfuric bath | Two-step electrodeposition Electrical properties, Solderability, | 2017 | [170] |
| MWCNT yarn | Straight | Cu | Acid sulfuric bath | Electrodeposition of Cu interior of CNT yarn | 2016 | [165] |
| MWCNT yarn | Twisted | Ag, Pt | KNO3+AgNO3 H2SO4 + H2Pt6Cl6 | Improved tensile strength and electrical conductivity | 2013 | [164] |
| MWCNT yarn | Twisted | Cu | Acid sulfuric bath + octyl phenyl poly (ethylene gylcol) ether | Continuous process: fiber spinning, anodization, electrodeposition | 2011 | [163] |
| MWCNT yarn | Twisted | Au, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Ni | Metal salt solution | Self-fueled electrodeposition Improved electrical conductivity | 2010 | [162] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arai, S. Fabrication of Metal/Carbon Nanotube Composites by Electrochemical Deposition. Electrochem 2021, 2, 563-589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem2040036
Arai S. Fabrication of Metal/Carbon Nanotube Composites by Electrochemical Deposition. Electrochem. 2021; 2(4):563-589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem2040036
Chicago/Turabian StyleArai, Susumu. 2021. "Fabrication of Metal/Carbon Nanotube Composites by Electrochemical Deposition" Electrochem 2, no. 4: 563-589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem2040036
APA StyleArai, S. (2021). Fabrication of Metal/Carbon Nanotube Composites by Electrochemical Deposition. Electrochem, 2(4), 563-589. https://doi.org/10.3390/electrochem2040036






