Hand-Eye Calibration via Linear and Nonlinear Regressions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The proposed method has more stability and explainability than the neural network-based method because the regression equations are obtained;
- The proposed approach needs reduced effort because the number of hyperparameters, which must be adjusted by a user, is smaller;
- Compared to the approach based on the neural network, the proposed method can achieve better calibration performance.
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Method
| Algorithm 1 Flow of the proposed method. |
|
3.1. Preparation
3.2. Linear Regression
3.3. Nonlinear Regression Based on B-Splines
3.3.1. Optimization of Control Point Locations with ABC
| Algorithm 2 Optimization by artificial bee colony (ABC). |
|
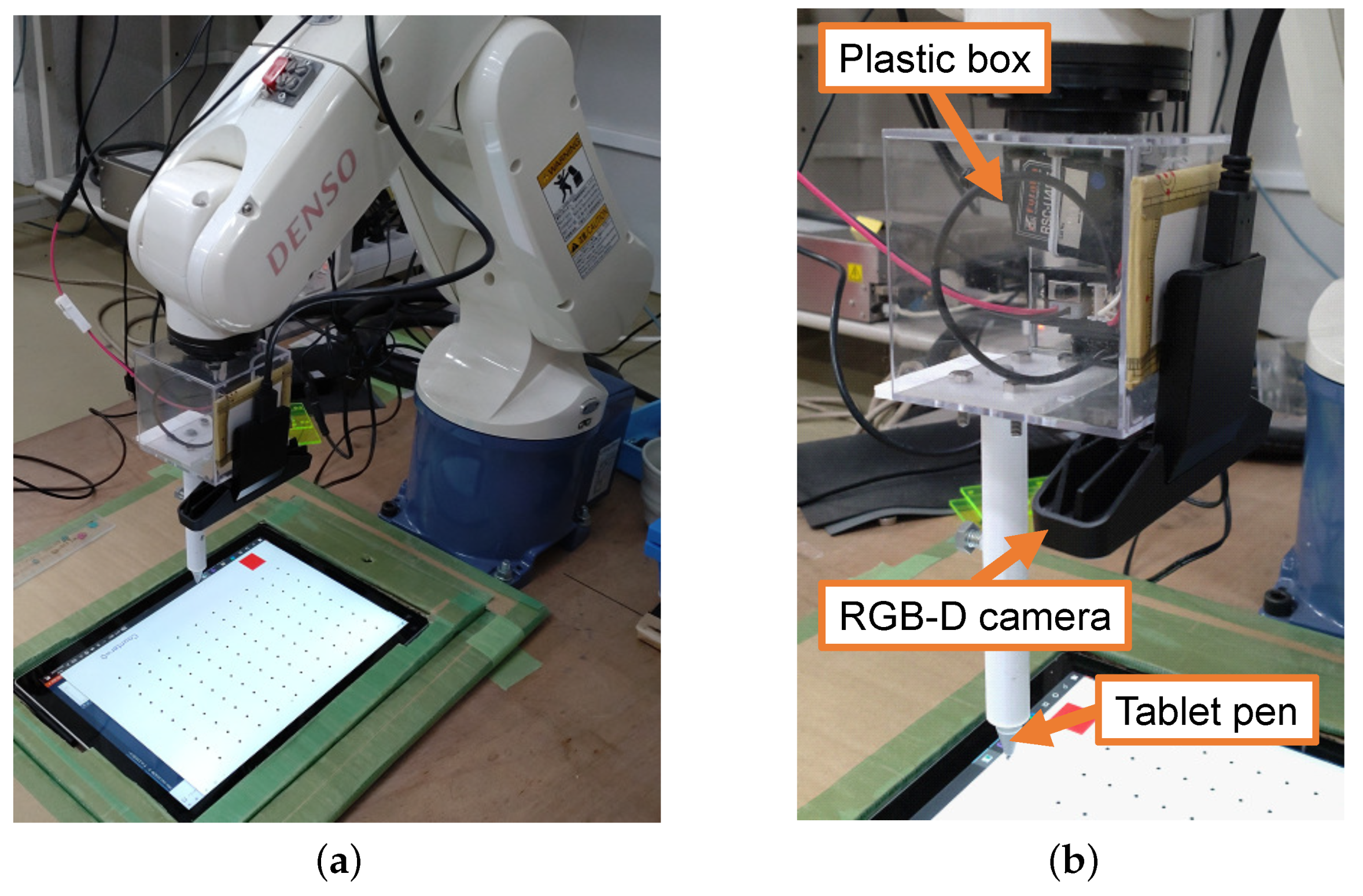
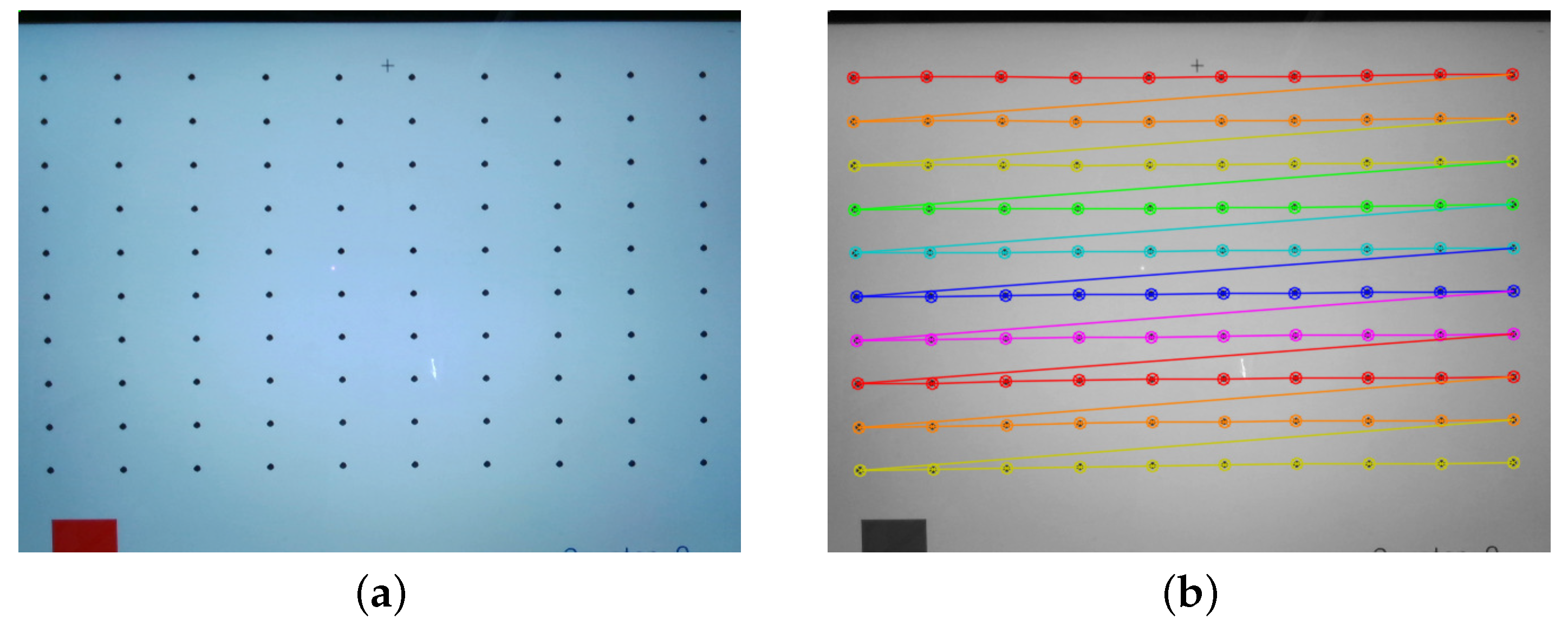
4. Experiment
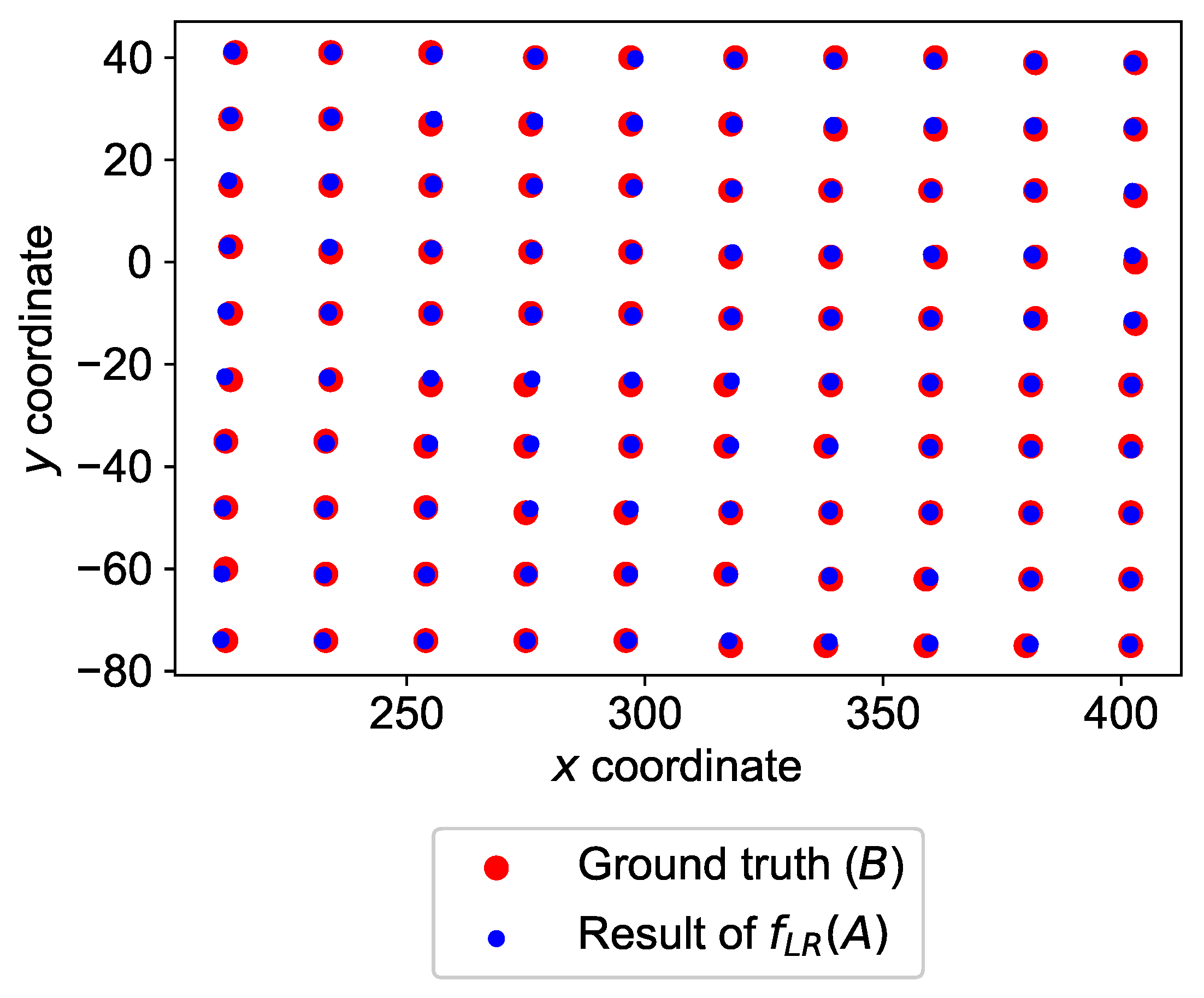
4.1. Results and Discussion
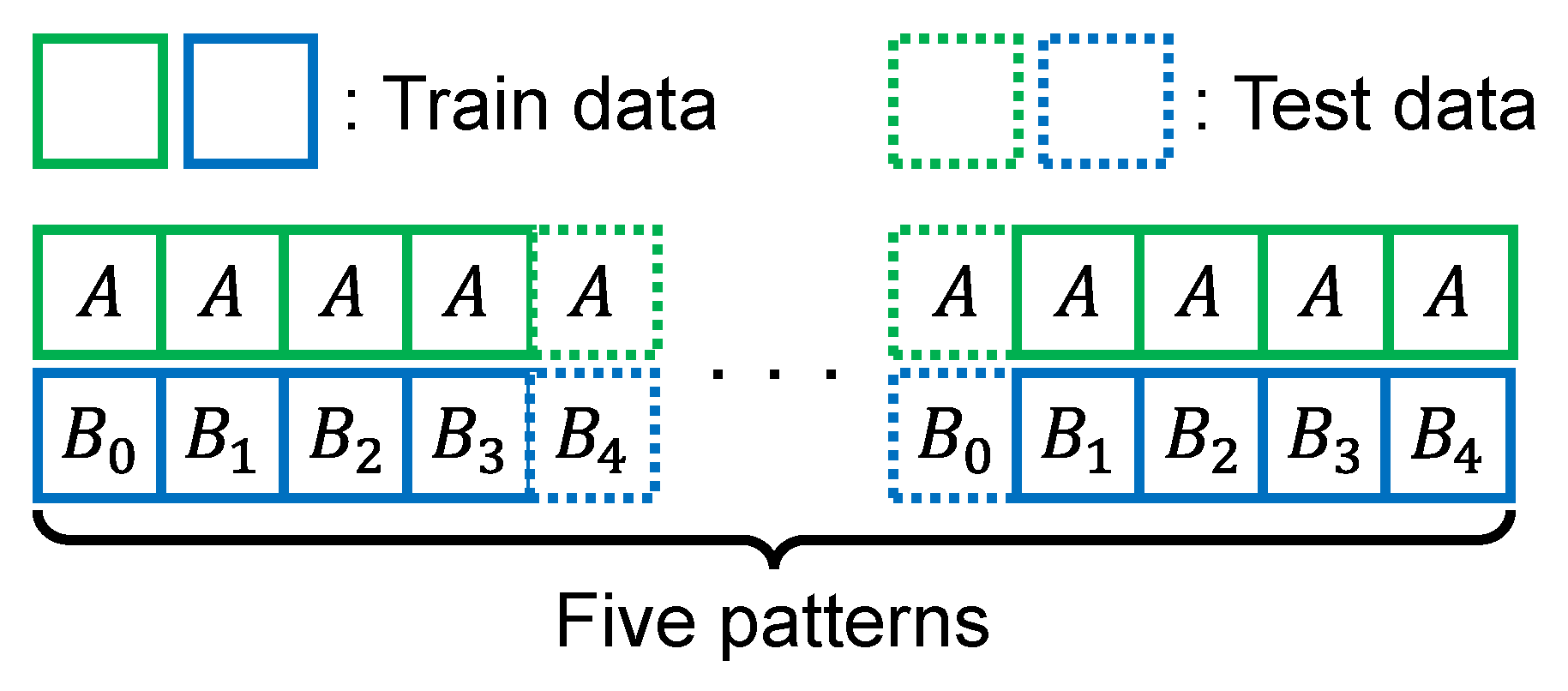
4.1.1. Five-Fold Cross Validation (CV)
4.1.2. Evaluation Using Robot
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sato, J. Hand-Eye Calibration Using a Tablet Computer. Math. Comput. Appl. 2023, 28, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enebuse, I.; Foo, M.; Ibrahim, B.S.K.K.; Ahmed, H.; Supmak, F.; Eyobu, O.S. A Comparative Review of Hand-Eye Calibration Techniques for Vision Guided Robots. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 113143–113155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Luo, X.; Luo, Q.; Qiao, L.; Li, M. An Overview of Hand-Eye Calibration. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 22, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, Y.C.; Ahmad, S. Calibration of wrist-mounted robotic sensors by solving homogeneous transform equations of the form AX = XB. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motai, Y.; Kosaka, A. Hand-Eye Calibration Applied to Viewpoint Selection for Robotic Vision. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3731–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Roth, Z.; Sudhakar, R. Simultaneous robot/world and tool/flange calibration by solving homogeneous transformation equations of the form AX = YB. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1994, 10, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Lenz, R.K. A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3D robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C. Extrinsic calibration of a vision sensor mounted on a robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1992, 8, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, F.C.; Martin, B.J. Robot sensor calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean group. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1994, 10, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.D. A self-calibration technique for active vision systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1996, 12, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Daniilidis, K. Hand-Eye Calibration Using Dual Quaternions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1999, 18, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horaud, R.; Dornaika, F. Hand-Eye Calibration. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1995, 14, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreff, N.; Horaud, R.; Espiau, B. Robot Hand-Eye Calibration using Structure from Motion. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. Hand-eye calibration using convex optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 2947–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Heller, J.; Havlena, M.; Pajdla, T. Globally Optimal Hand-Eye Calibration Using Branch-and-Bound. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, J.; Zeng, L. Hand-Eye Calibration Algorithm Based on an Optimized Neural Network. Actuators 2021, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, G. A Novel Point Set Registration-Based Hand-Eye Calibration Method for Robot-Assisted Surgery. Sensors 2022, 22, 8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Schwertfeger, S. Simultaneous Hand-Eye Calibration and Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 1470–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, A.; Hui Liu, Y.; Kim, S.; Deguet, A.; Reiter, A.; Kazanzides, P.; Taylor, R.H. Vision-Based Calibration of Dual RCM-Based Robot Arms in Human-Robot Collaborative Minimally Invasive Surgery. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Liang, P.; Luo, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C. Research of Online Hand-Eye Calibration Method Based on ChArUco Board. Sensors 2022, 119, 3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Ding, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, X. Hand-eye calibration method with a three-dimensional-vision sensor considering the rotation parameters of the robot pose. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, Q.T.; Chang, W.Y.; Chen, L.W. Dynamic Workpiece Modeling with Robotic Pick-Place Based on Stereo Vision Scanning Using Fast Point-Feature Histogram Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Gao, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W. Research on the Hand-Eye Calibration Method of Variable Height and Analysis of Experimental Results Based on Rigid Transformation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, A.; Häenstam-Nielsen, L.; Caccamo, S. Optimal least-squares solution to the hand-eye calibration problem. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’2020), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13595–13603. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Gong, L.; Liu, C. Efficient TCP Calibration Method for Vision Guided Robots Based on Inherent Constraints of Target Object. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 8902–8911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, M.; Cheng, Q.; Liang, G.; Fan, F. A novel hand-eye calibration method of picking robot based on TOF camera. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1099033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, M.; Mathur, P.; Navab, N.; Salcudean, S.E. Marker-less real-time intra-operative camera and hand-eye calibration procedure for surgical augmented reality. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valassakis, E.; Drezckowski, K.; Johns, E. Learning Eye-in-Hand Camera Calibration from a Single Image. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL’2021), Virtual, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lembono, T.S.; Suárez-Ruiz, F.; Pham, Q.C. SCALAR: Simultaneous Calibration of 2D Laser and Robot Kinematic Parameters Using Planarity and Distance Constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS’2018), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 5570–5575. [Google Scholar]
- Denso Robot User Manuals. Available online: http://eidtech.dyndns-at-work.com/support/RC8_Manual/005929.html (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Furukawa, H.; Sato, J.; Yamada, T.; Ito, K.; Ito, S. Grasping Position Detection Using Template Matching and Differential Evolution for Bulk Bolts. In Proceedings of the 45th Annual Conference of the Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 5482–5487. [Google Scholar]
- Projection in Intel RealSense SDK 2.0. Available online: https://dev.intelrealsense.com/docs/projection-in-intel-realsense-sdk-20 (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- OpenCV. Available online: https://opencv.org/ (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Nakane, T.; Xie, H.; Zhang, C. Image Deformation Estimation via Multiobjective Optimization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53307–53323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Wolberg, G.; Shin, S.Y. Scattered Data Interpolation with Multilevel B-Splines. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 1997, 3, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Yamada, T.; Ito, K.; Akashi, T. Artificial Bee Colony for Affine and Perspective Template Matching. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 17, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Yamada, T.; Ito, K.; Akashi, T. Performance Comparison of Population-Based Meta-Heuristic Algorithms in Affine Template Matching. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2021, 16, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]





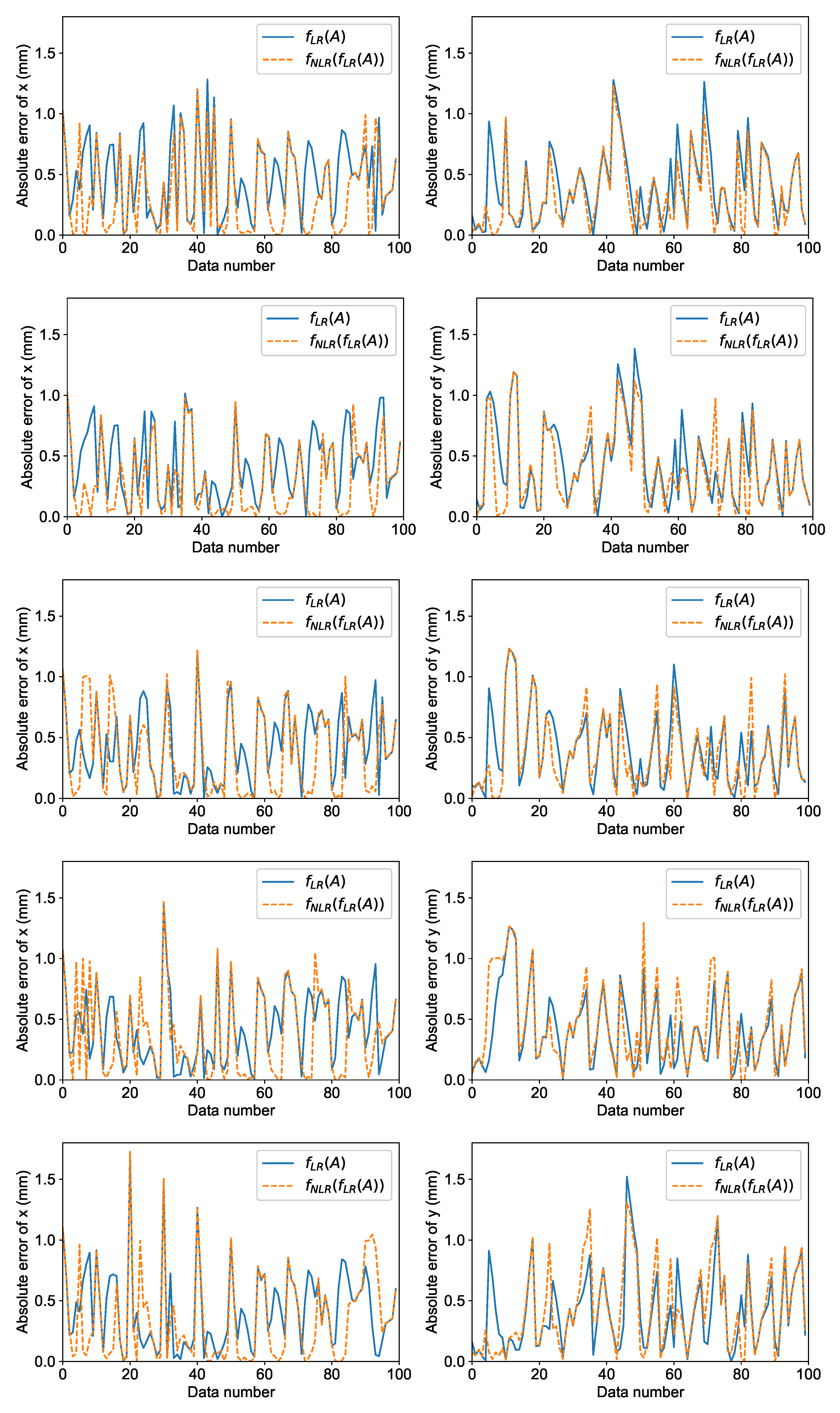
| Mean Distance Error (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV | (Model 1) | (Model 2) | (Model 3) | ||
| 1 | 0.53 | 0.69 | 1.08 | 0.80 | 0.86 |
| 2 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 4.64 |
| 3 | 0.61 | 0.66 | 1.44 | 0.88 | 5.08 |
| 4 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 1.65 | 1.61 | 2.84 |
| 5 | 0.64 | 0.68 | 2.15 | 1.98 | 5.67 |
| Ave. | 0.60 | 0.68 | 1.40 | 1.21 | 3.82 |
| SD | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 1.76 |
| CV | Partial Regression Coefficients | Constants |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 |
| Mean Touching Error | ||
|---|---|---|
| Method | px | mm |
| 2.63 | 0.50 | |
| 4.12 | 0.78 | |
| (Model 2) | 5.79 | 1.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sato, J. Hand-Eye Calibration via Linear and Nonlinear Regressions. Automation 2023, 4, 151-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020010
Sato J. Hand-Eye Calibration via Linear and Nonlinear Regressions. Automation. 2023; 4(2):151-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Junya. 2023. "Hand-Eye Calibration via Linear and Nonlinear Regressions" Automation 4, no. 2: 151-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020010
APA StyleSato, J. (2023). Hand-Eye Calibration via Linear and Nonlinear Regressions. Automation, 4(2), 151-163. https://doi.org/10.3390/automation4020010






