Valorization of Agave angustifolia Bagasse Biomass from the Bacanora Industry in Sonora, Mexico as a Biochar Material: Preparation, Characterization, and Potential Application in Ibuprofen Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
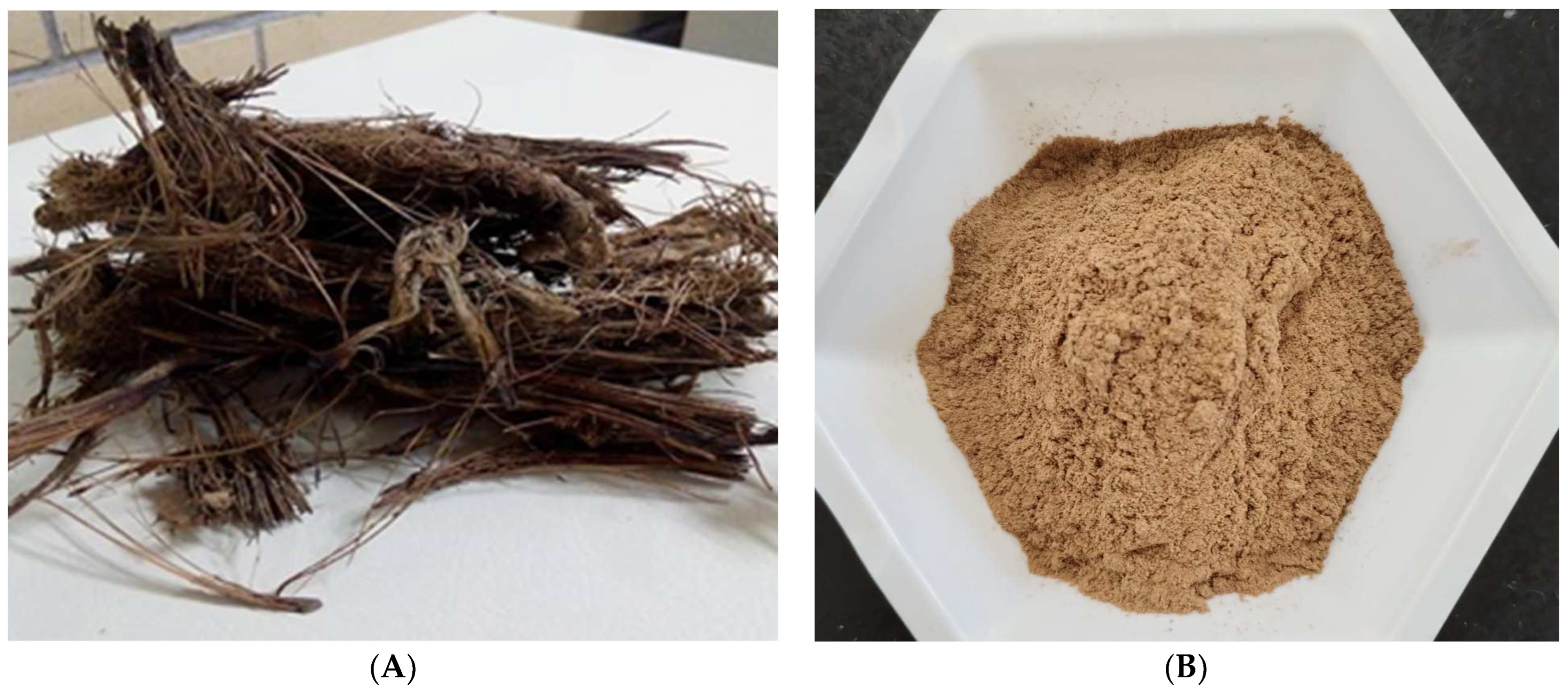
2.2. Biomass Acquisition and Conditioning
2.3. Proximal Analysis of Biomass
2.4. Bioadsorbent Preparation
2.5. Characterization of Agave angustifolia Bagasse and Bioadsorbents
2.5.1. Bioadsorbent Yield
2.5.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.5.3. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.6. Thermal Analysis
2.6.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.6.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7. Preliminary Adsorption Tests
2.7.1. Preparation of Mother Solution
2.7.2. Adsorption Experiments
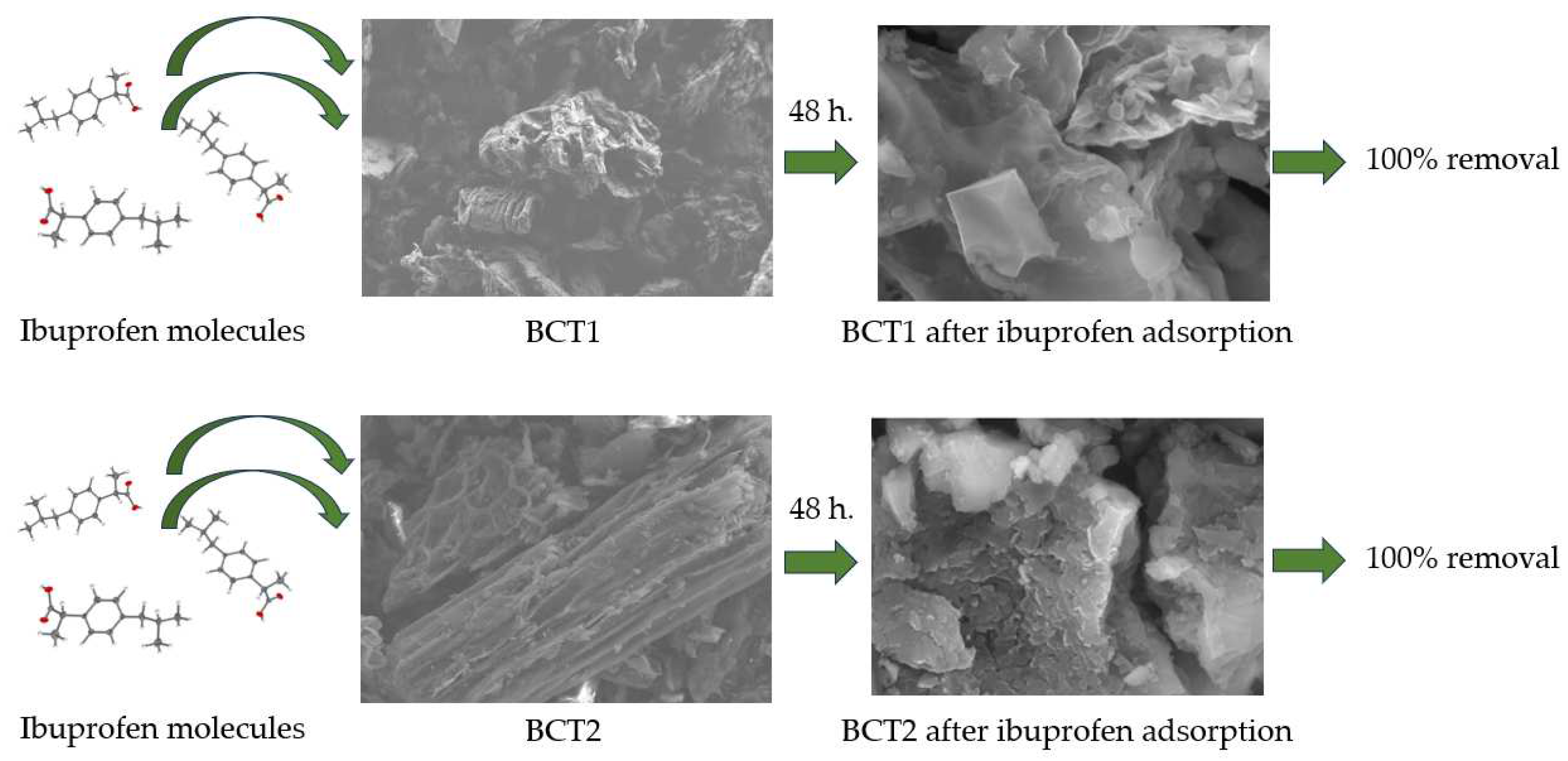
2.7.3. Demonstration of Bioadsorbent Functionality
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
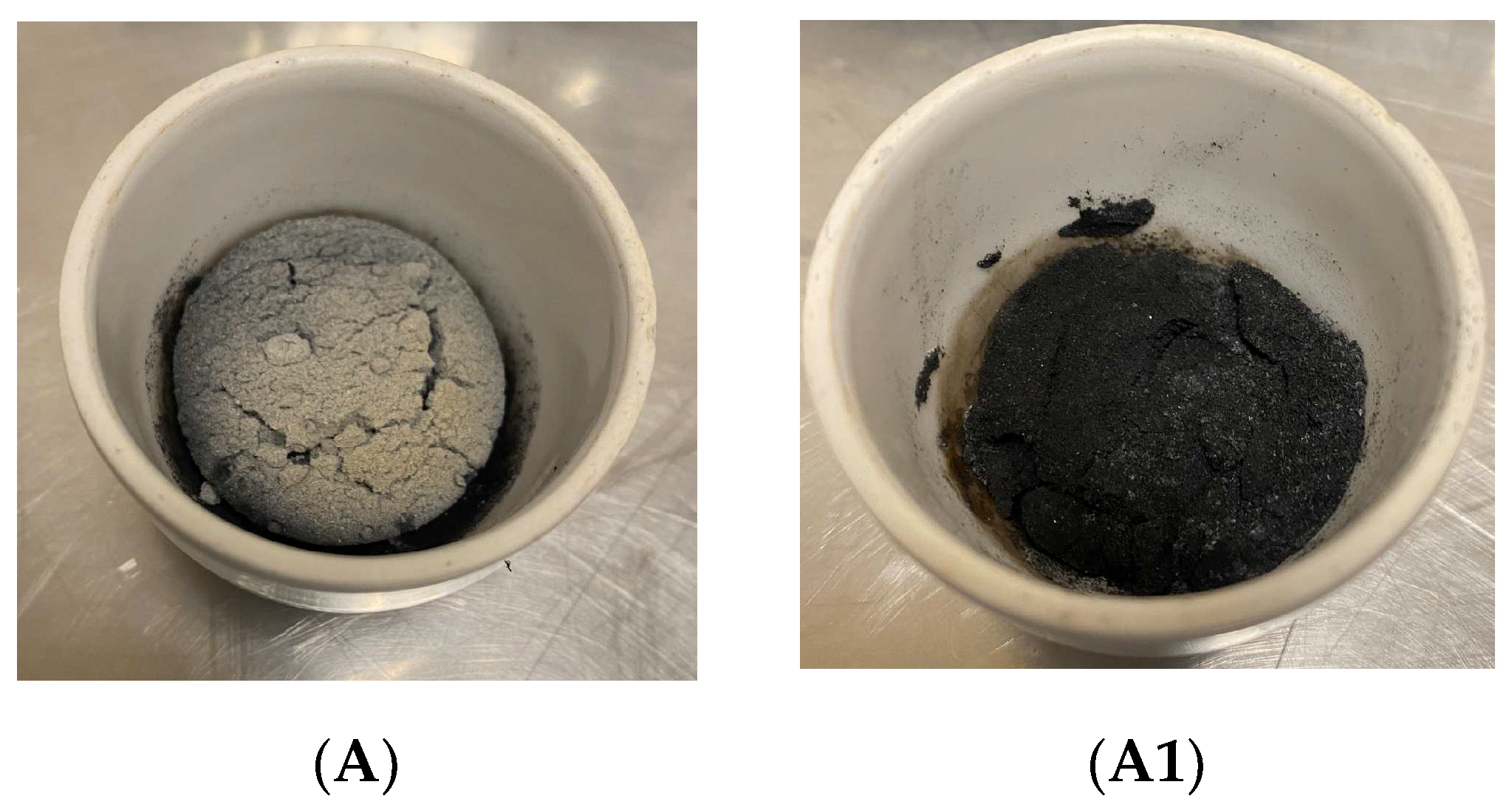
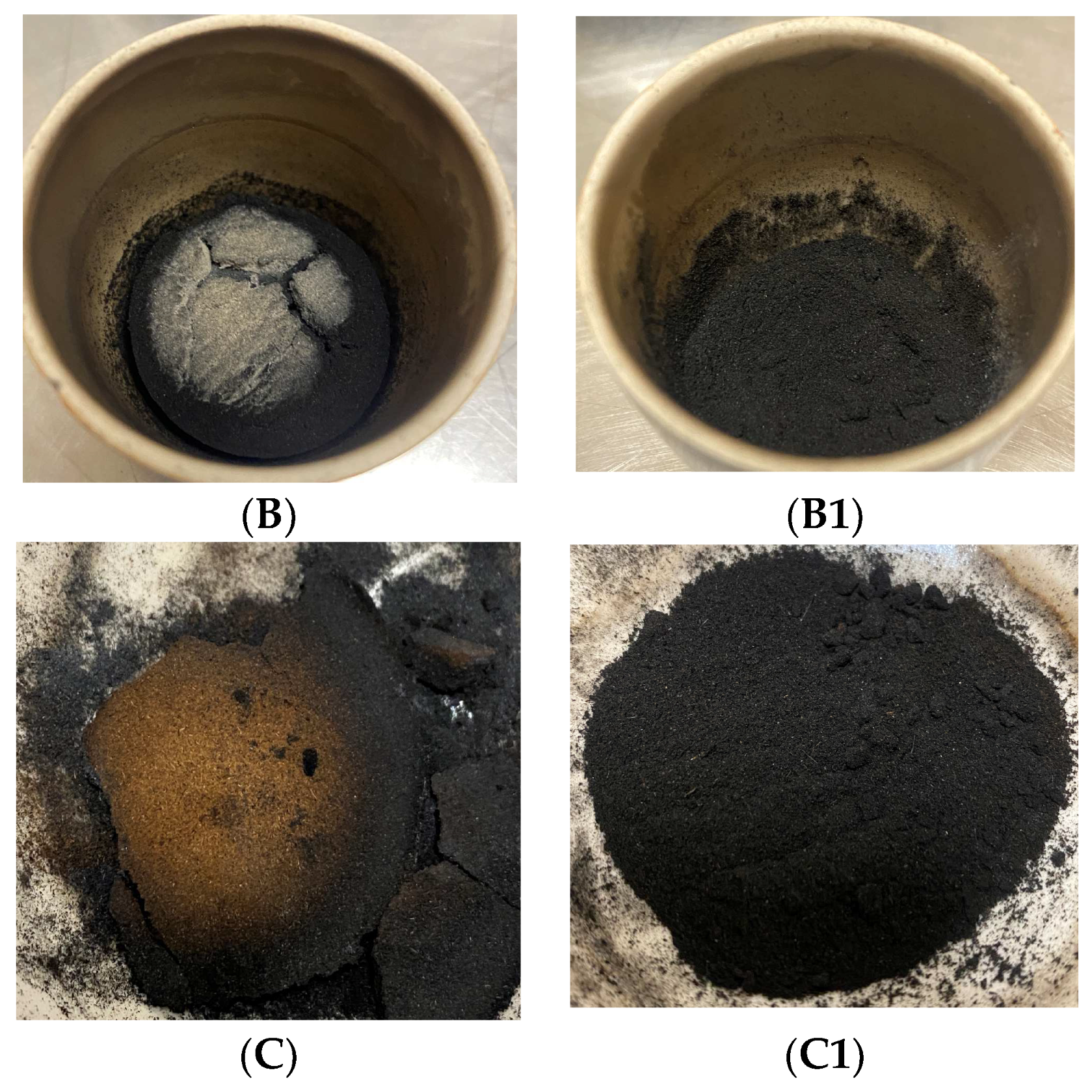
3.1. Bioadsorbent Preparation
3.2. Proximate Analysis of Biomass
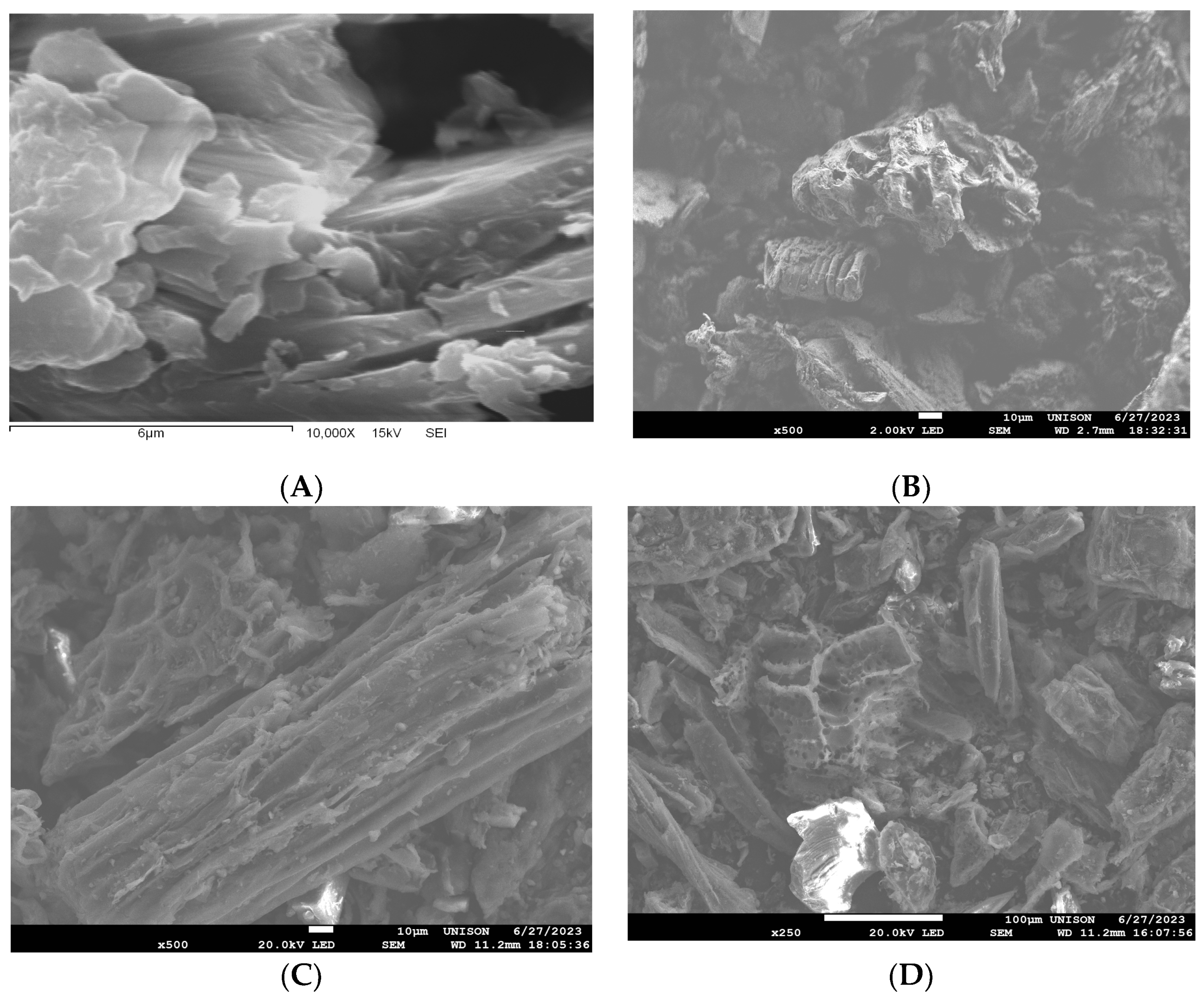
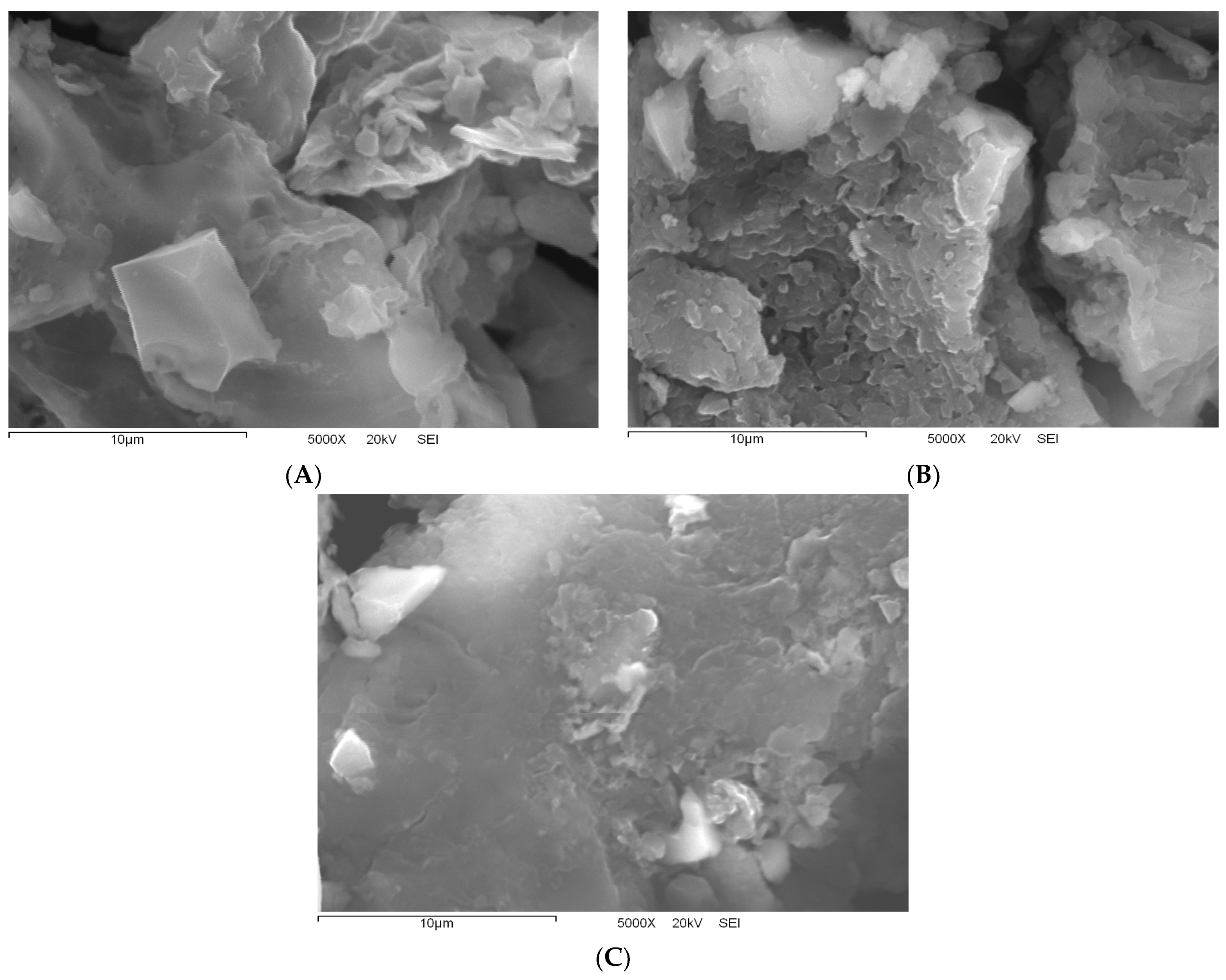
3.3. Morphological Characterization (SEM) of Biomass and Bioadsorbents
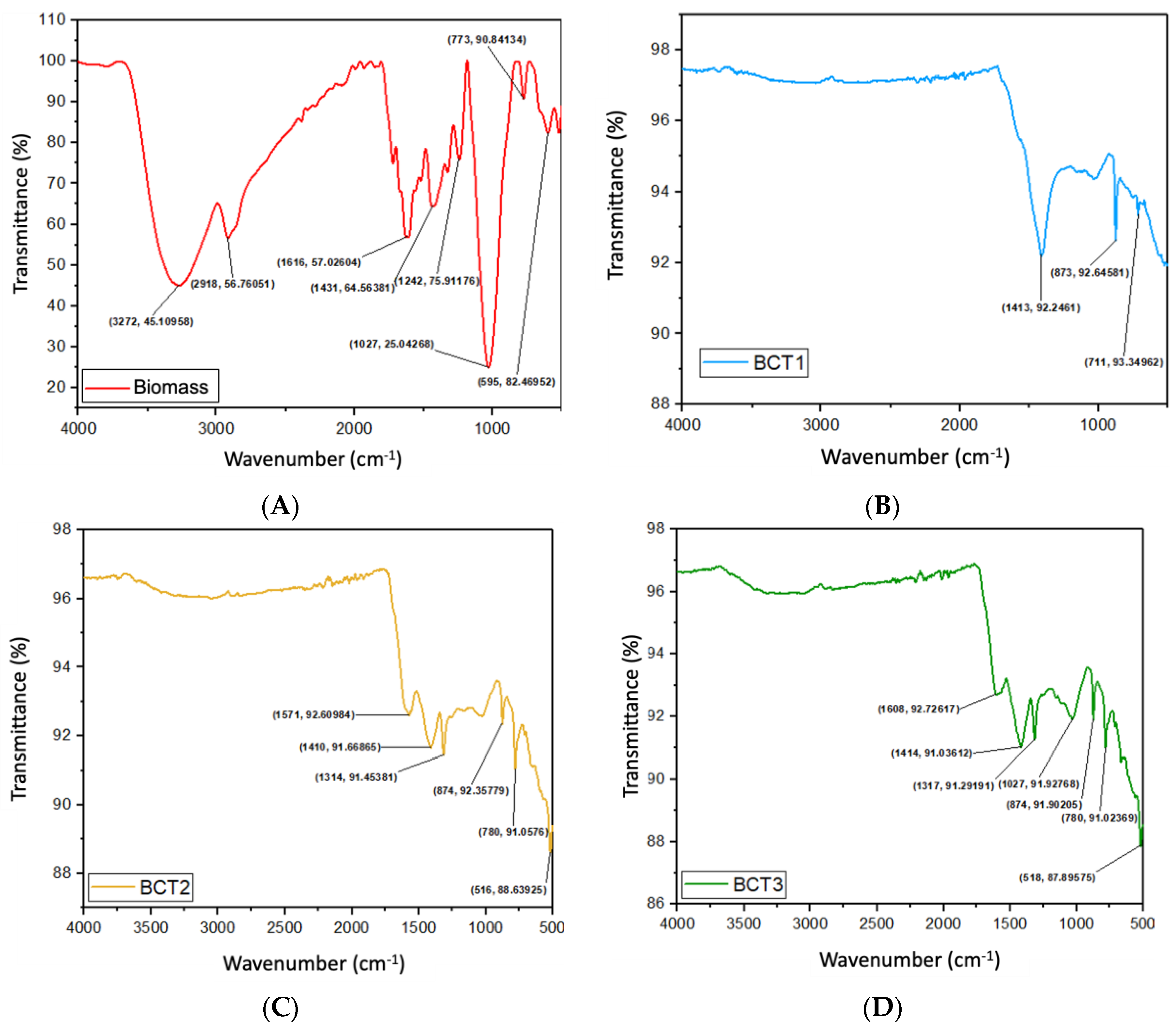
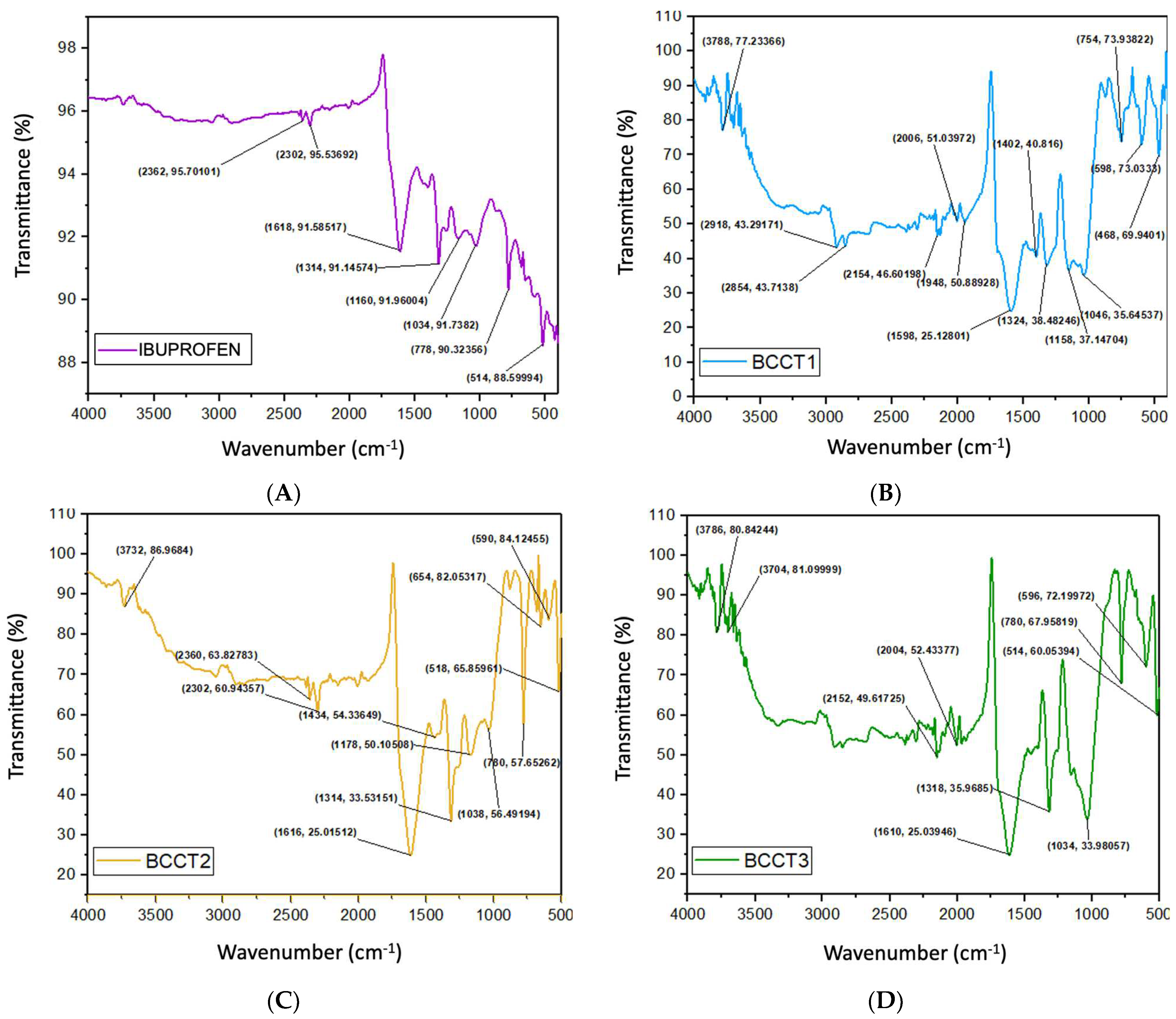
3.4. Biomass and Bioadsorbents Structural Characterization (FTIR)
3.5. Thermal Analysis
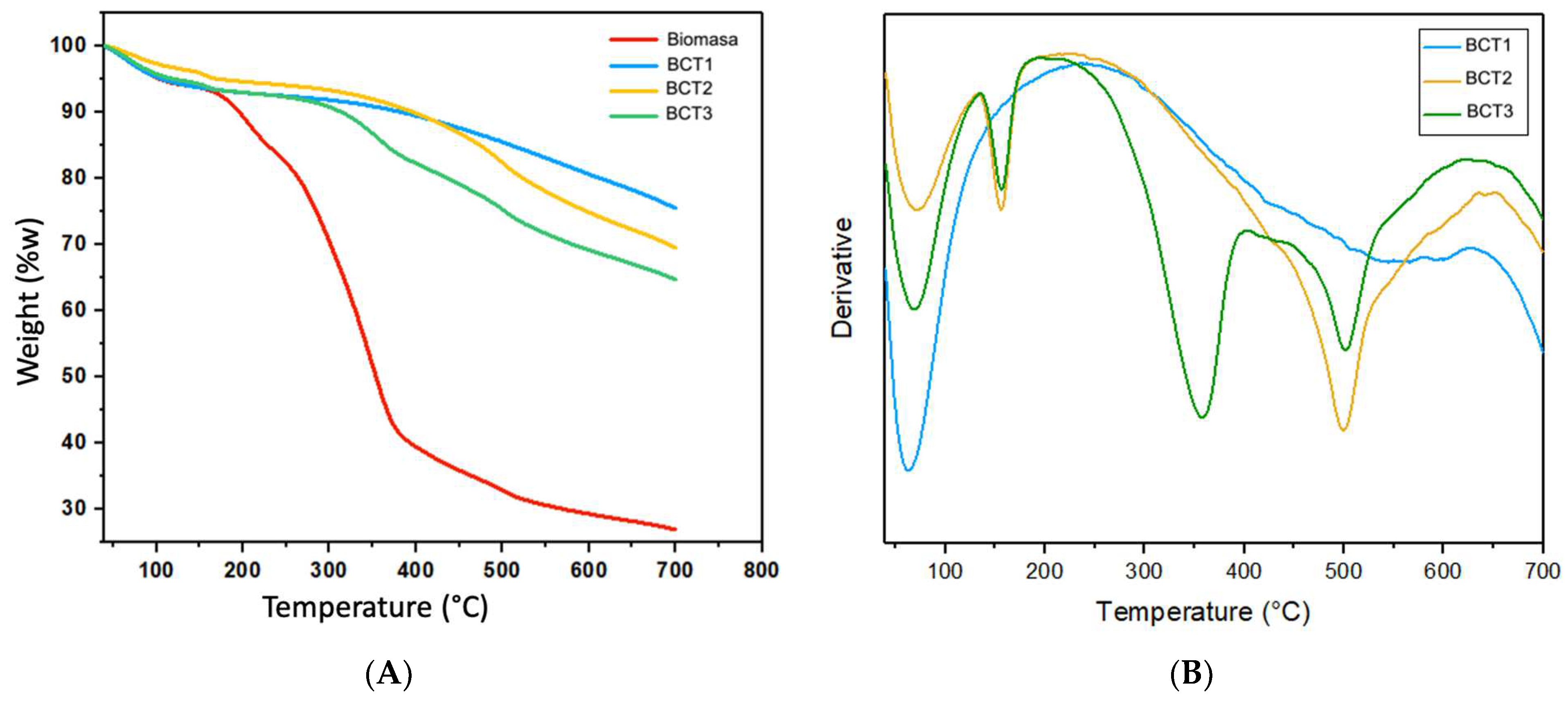
3.5.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of Biomass and Bioadsorbents
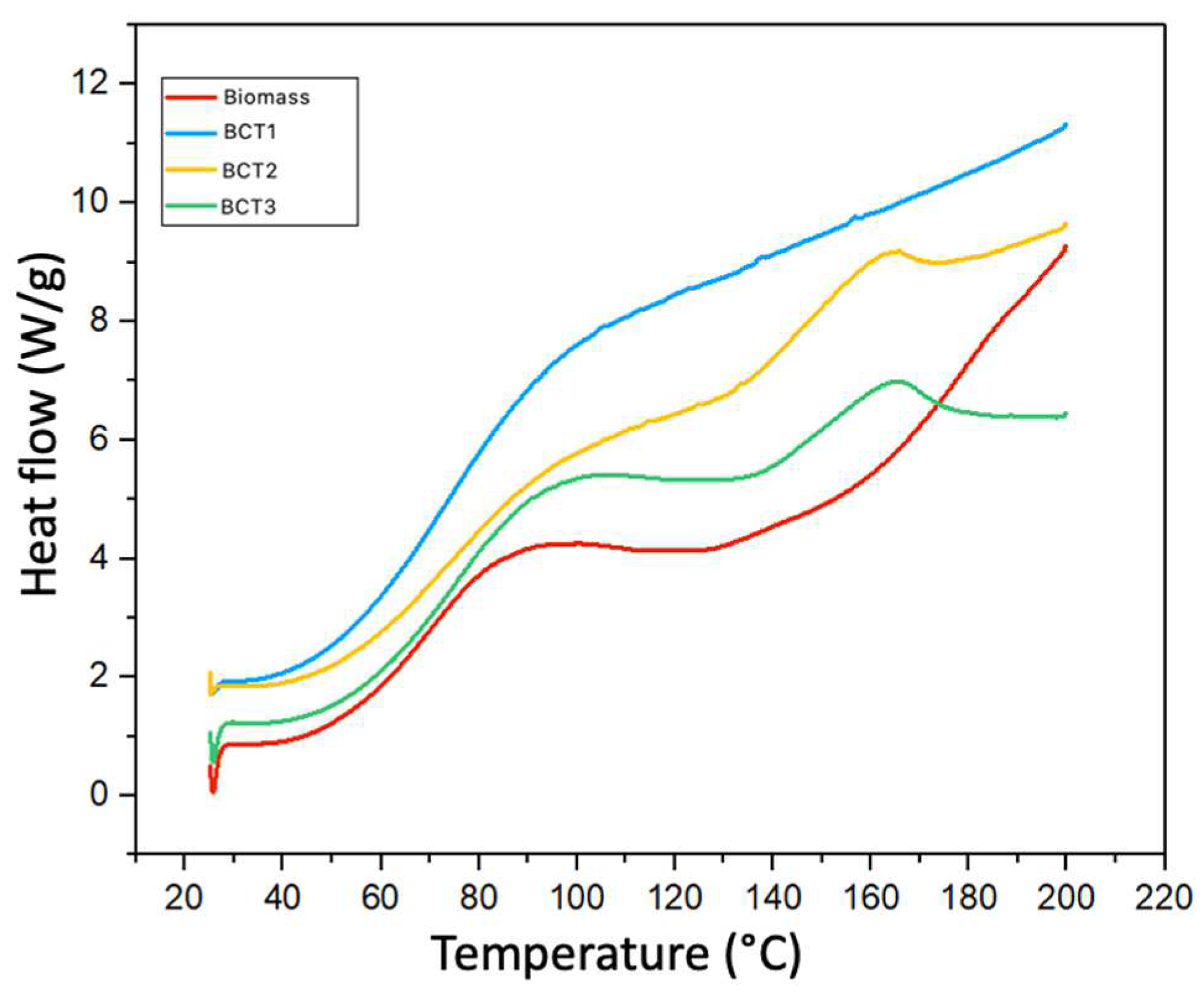
3.5.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.6. Preliminary Adsorption Tests
4. Discussion
4.1. Bioadsorbent Structure
4.2. Demonstration of the Functionality of Bioadsorbents
4.3. Contribution of the Study to Sustainability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nwokediegwu, Z.Q.S.; Daraojimba, O.H.; Oliha, J.S.; Obaigbena, A.; Dada, M.A.; Majemite, M.T. Review of emerging contaminants in water: USA and African perspectives. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 2024, 11, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, L.A.P.; Ly, L.T.M.; Do, H.T.; Chinh, P.M. Occurrence and risks of emerging pollutants in water bodies. In Advanced Functional Materials and Methods for Photodegradation of Toxic Pollutants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munzhelele, E.P.; Mudzielwana, R.; Ayinde, W.B.; Gitari, W.M. Pharmaceutical Contaminants in Wastewater and Receiving Water Bodies of South Africa: A Review of Sources, Pathways, Occurrence, Effects, and Geographical Distribution. Water 2024, 16, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiha, O.; Hadoudi, N.; Zaki, N.; Salhi, A.; Amhamdi, H.; Akichouh, E.H.; Mourabit, F.; Ahari, M. Comprehensive review on the adsorption of pharmaceutical products from wastewater by clay materials. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, M.; Gandhi, K.; Kumar, M.S. Emerging environmental contaminants: A global perspective on policies and regulations. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, P.; Anctil, A. End-of-life solar photovoltaic waste management: A comparison as per European Union and United States regulatory approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. Adv. 2024, 21, 200212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainsford, K.D. Ibuprofen: Pharmacology, efficacy and safety. Inflammopharmacology 2009, 17, 275–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, H.-R.; Poiger, T.; Müller, M.D. Occurrence and Environmental Behavior of the Chiral Pharmaceutical Drug Ibuprofen in Surface Waters and in Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2529–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchlewicz, A.; Guzik, U.; Wojcieszyńska, D. Over-the-Counter Monocyclic Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Environment—Sources, Risks, Biodegradation. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz-González, A.-B. Ibuprofen as an emerging pollutant on non-target aquatic invertebrates: Effects on Chironomus riparius. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 81, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M.; Binelli, A.; Provini, A. Chronic effects induced by ibuprofen on the freshwater bivalve Dreissena polymorpha. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 1586–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.; Kumar, D. Ibuprofen as an emerging organic contaminant in environment, distribution and remediation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan-Roblero, J.; Cruz-Maya, J.A. Ibuprofen: Toxicology and Biodegradation of an Emerging Contaminant. Molecules 2023, 28, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey Chowdhury, S.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Bhunia, P. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Microconstituents Removal in Aquatic Environments. In Microconstituents in the Environment: Occurrence, Fate, Removal and Management; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 367–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Sumpradit, T.; Salama, E.-S.; Li, X.; Qu, J. Simultaneous degradation of NSAIDs in aqueous and sludge stages by an electron-Fenton system derived from sediment microbial fuel cell based on a novel Fe@Mn biochar GDC. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Vera, L.; Gómez, Y. Técnicas aplicadas a la remoción de fármacos, usados en el tratamiento del COVID-19: Una revisión. Polo Del Conoc. 2021, 6, 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R. Green and Sustainable Imprinting Technology for Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water via Selective Adsorption. Sustainability 2023, 16, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Taweel, R.M.; Mohamed, N.; Alrefaey, K.A.; Husien, S.; Abdel-Aziz, A.; Salim, A.I.; Mostafa, N.G.; Said, L.A.; Fahim, I.S.; Radwan, A.G. A review of coagulation explaining its definition, mechanism, coagulant types, and optimization models; RSM, and ANN. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 6, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Dhiman, P.; Mola, G.T.; Shan, A.; Si, C. Microplastic pollutants in water: A comprehensive review on their remediation by adsorption using various adsorbents. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Fang, W.; Tan, Y.; He, Z.; Liao, H. Research status, trends, and mechanisms of biochar adsorption for wastewater treatment: A scientometric review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ai, Y.; Jin, J.; Hayat, T.; Alsaedi, A.; Zhuang, L.; Wang, X. Efficient elimination of organic and inorganic pollutants by biochar and biochar-based materials. Biochar 2020, 2, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.-H.; Kwon, E.E.; Rajendran, S.; Zhang, Y. Multistage utilization of soybean straw-derived P-doped biochar for aquatic pollutant removal and biofuel usage. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska, D.; Olchowski, R.; Nowicka, A.; Zborowska, M.; Marszalkiewicz, K.; Shams, M.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Anastopoulos, I.; Barczak, M. Activated biochars derived from wood biomass liquefaction residues for effective removal of hazardous hexavalent chromium from aquatic environments. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 1247–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Asim, M.; Khan, T.A. Low cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 113, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homem, V.; Santos, L. Degradation and removal methods of antibiotics from aqueous matrices—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2304–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherpa, S.W.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Kapoor, A.; Jacob, M.M.; Sivaraman, P. Facile removal of sulfamethoxazole antibiotic from contaminated water using bagasse-derived pyrolytic biocarbon: Parametric assessment, mechanistic insights and scale-up analysis. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 60, 105110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavero, V.O.; Weber, A.; Schröder, W.; Curticapean, D. Spectral analysis of bacanora (agave-derived liquor) by using FT-Raman spectroscopy. In Optical Sensing and Detection IV; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9899, pp. 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, V. La industria del bacanora: Historia y tradición de resistencia en la sierra sonorense. Reg. Soc. 2007, 19, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, C. Propiedades Mecánicas a Tensión de las Fibras del Bagazo del Agave Angustifolia Haw, Residuo Proveniente de la Producción Artesanal del Mezcal. Master’s Thesis, Instituto Politécnico Nacional, Mexico City, Mexico, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, E.; Alcaraz, J.; Valdivia, A.; Rosas, A.; Hernández, M.; Vivaldo, E.; Martínez, A. Bagazo de Agave: De Desecho Agroindustrial a Materia Prima en las Biorrefinerías. Universidad Autónoma de México. 2021. Available online: http://ciencia.unam.mx/leer/1112/bagazo-de-agave-de-desecho-agroindustrial-a-materia-prima-en-las-biorrefinerias- (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- Hidalgo-Reyes, M.; Caballero-Caballero, M.; Hernández-Gómez, L.H.; Urriolagoitia-Calderón, G. Chemical and morphological characterization of Agave angustifolia bagasse fibers. Bot. Sci. 2015, 93, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ortega, L.A.; Valdez-Baro, O.; Bernal-Millán, M.J.; Rivera-Salas, M.M.; Heredia, J.B. Agave Byproducts: As Sources of Phytochemicals with Functional Activities and Their Management for Industrial Applications. In Food Byproducts Management and Their Utilization; Apple Academic Press: Palm Bay, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 385–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómora-Hernández, J.C.; Tecante, A.; del Carmen Carreño-De-León, M.; Flores-Álamo, N.; Ventura-Cruz, S. Preparation of porous microcrystalline cellulose from mezcal industry agave bagasse by low reagent loading sequential chemical treatment. Cellulose 2023, 30, 2067–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Cortés, A.; Arancibia-Bulnes, C.A.; Villafán-Vidales, H.I.; Lobato-Peralta, D.R.; Martínez-Casillas, D.C.; Cuentas-Gallegos, A.K. Solar pyrolysis of agave and tomato pruning wastes: Insights of the effect of pyrolysis operation parameters on the physicochemical properties of biochar. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2126, 180001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato-Peralta, D.R.; Ayala-Cortes, A.; Longoria, A.; Pacheco-Catalan, D.E.; Okoye, P.U.; Villafan-Vidales, H.I.; Arancibia-Bulnes, C.A.; Cuentas-Gallegos, A.K. Activated carbons obtained by environmentally friendly activation using solar energy for their use in neutral electrolyte supercapacitors. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-García, M.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; Barrera-Rodríguez, A.; Aguilar, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Reynoso-Marín, F.J.; Ceja, I.; Dórame-Miranda, R.; Rodríguez-Félix, F. Nanofibers of cellulose bagasse from Agave tequilana Weber var. azul by electrospinning: Preparation and characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMA Oficial Mexicana. NOM-116-SSA1-1994, Determinación de Humedad en Alimentos por Tratamiento Térmico. Método por Arena o Gasa; Pub. L. No. 116; Diario Oficial de la Federación: Mexico City, Mexico, 1994.
- Proyecto de Norma Mexicana PROY-NMX-F-607-NORMEX-2020. Determinación de Cenizas en Alimentos-Método de Prueba; Diario Oficial de la Federación: Mexico City, Mexico, 2020.
- U.S. Department of Energy. Standard Test Method for Volatile Matter in the Analysis of Particulate Wood Fuels; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019.
- Martínez, A.; Bohórquez, L. Evaluación de la Eficiencia de Biochar Producido a Partir de Pirólisis Lenta de Bagazo de Caña Como Medio Filtrante Para Retención de Fenoles en Matriz Acuosa [Monography]; Universidad de La Salle: Bogotá, Colombia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.T.; Nugranad, N. Comparison of products from the pyrolysis and catalytic pyrolysis of rice husks. Energy 2000, 25, 493–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Abad, S.; Alvarez-Vera, M.; Salas, C.; Vázquez, J. Biochar of residual biomass from eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus) by two pyrolysis methods. Manglar 2020, 17, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Jung, S.-C.; Ryu, C.; Jeon, J.-K.; Shin, M.-C.; Park, Y.-K. Production and utilization of biochar: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, P.; Robles, C.; Castañeda, E. Generación y caracterización básica de bagazos de la agroindustria del mezcal en Oaxaca. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agrícolas 2020, 11, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimbaya, C.; Rosas, N.; Endara, D.; Guerrero, V. Obtención de Carbón Activado a partir de Residuos Lignocelulósicos de Canelo, Laurel y Eucalipto. Rev. Politécnica 2016, 36, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez, A.; Bolaños, E.; Pliego, Y. Optimización de la Producción de Carbón Activado a Partir de Bambú. Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2010, 9, 359–366. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, M.; Rigal, L. Caracterización y valorización del bagazo de Agave tequilana Weber de la industria del tequila. Rev. Chapingo 1997, 3, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeh, Y.; Olatunji, G.A.; Mamza, P.A. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Kinetic Studies of Ketene-Acetylated Wood/Cellulose High-Density Polyethylene Blends. Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2012, 2012, 456491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.; Quicker, P. Properties of biochar. Fuel 2018, 217, 240–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Minami, E.; Asmadi, M.; Kawamoto, H. Effect of delignification on thermal degradation reactivities of hemicellulose and cellulose in wood cell walls. J. Wood Sci. 2021, 67, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janu, R.; Mrlik, V.; Ribitsch, D.; Hofman, J.; Sedláček, P.; Bielská, L.; Soja, G. Biochar surface functional groups as affected by biomass feedstock, biochar composition and pyrolysis temperature. Carbon Resour. Convers. 2021, 4, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, D.; Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, R. Effect of temperature on structure evolution in char from hydrothermal degradation of lignin. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 106, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, E.; Alrawashdeh, K.A.B.; Masek, O.; Skreiberg, Ø.; Corona, A.; Zampilli, M.; Wang, L.; Samaras, P.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, H.; et al. Production and use of biochar from lignin and lignin-rich residues (such as digestate and olive stones) for wastewater treatment. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 158, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Miao, Y.; Mai, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. A lignin-biochar with high oxygen-containing groups for adsorbing lead ion prepared by simultaneous oxidization and carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, M.; Sahu, J.; Ganesan, P. Effect of process parameters on production of biochar from biomass waste through pyrolysis: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.E.; Varanda, L.D.; de Carvalho, N.R.; Sette, C., Jr.; de Padua, F.A.; De Conti, A.C.; Yamaji, F.M. Biochar produced from poultry litter waste. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e351101119704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cuesta, J.; Montoya, U.; Betancourt, S.; Álvarez, C. Effect of processing temperature on the mechanical properties of binderless fiberboards. Prospect 2011, 9, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Rasapoor, M.; Young, B.; Asadov, A.; Brar, R.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zhuang, W.-Q.; Baroutian, S. Effects of biochar and activated carbon on biogas generation: A thermogravimetric and chemical analysis approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 203, 112221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nemr, M.A.; Abdelmonem, N.M.; Ismail, I.M.A.; Ragab, S.; El Nemr, A. Ozone and Ammonium Hydroxide Modification of Biochar Prepared from Pisum sativum Peels Improves the Adsorption of Copper (II) from an Aqueous Medium. Environ. Process. 2020, 7, 973–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dios Naranjo, C.; Alamilla, L.; Gutiérrez, G.; Terres, E.; Solorza, J.; Romero, S.; Yee-Madeira, H.; Flores, A.; Mora, R. Isolation and characterization of cellulose obtained from Agave salmiana fibers using two acid-alkali extraction methods. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agrícolas 2016, 7, 31–43. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardino, C.A.R.; Mahler, C.F.; Veloso, M.C.C.; Romeiro, G.A. Preparation of Biochar from Sugarcane By-product Filter Mud by Slow Pyrolysis and Its Use Like Adsorbent. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2017, 8, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, L.; Schnoor, J.L. Insight into Multiple and Multilevel Structures of Biochars and Their Potential Environmental Applications: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5027–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Shang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, C. Preparation of Chladophora-Based Biochar and Its Adsorption Properties for Antibiotics. ChemistrySelect 2024, 9, e202303598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nama, M.; Satasiya, G.; Sahoo, T.P.; Moradeeya, P.G.; Sadukha, S.; Singhal, K.; Saravaia, H.T.; Dineshkumar, R.; Kumar, M.A. Thermo-chemical behaviour of Dunaliella salina biomass and valorising their biochar for naphthalene removal from aqueous rural environment. Chemosphere 2024, 353, 141639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Bobde, K.; Aikat, K.; Halder, G. Biosorptive uptake of ibuprofen by steam activated biochar derived from mung bean husk: Equilibrium, kinetics, thermodynamics, modeling and eco-toxicological studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Devi, M.S.; Karmakar, B.; Halder, G. Linear and non-linear analysis of Ibuprofen riddance efficacy by Terminalia catappa active biochar: Equilibrium, kinetics, safe disposal, reusability and cost estimation. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 942–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P.; Show, S.; Banerjee, S.; Halder, G. Mechanistic insight into sorptive elimination of ibuprofen employing bi-directional activated biochar from sugarcane bagasse: Performance evaluation and cost estimation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5287–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, D.; Ye, A.; Hou, T. Research progress on biochar-based material adsorption and removal of ibuprofen. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1327000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekene, R.B.N.; Ntep, T.M.M.; Fetzer, M.N.A.; Strothmann, T.; Nsami, J.N.; Janiak, C. The efficient removal of ibuprofen, caffeine, and bisphenol A using engineered egusi seed shells biochar: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 100095–100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Ayati, A.; Farghali, M.; Krivoshapkin, P.; Tanhaei, B.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Krivoshapkina, E.; Taheri, P.; Tracey, C.; Al-Fatesh, A.; et al. Advanced adsorbents for ibuprofen removal from aquatic environments: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 373–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Fronstistis, Z.; Zorpas, A.A.; Pashalidis, I.; Triantafyllidis, K. Βiomass-derived adsorbents: Universal database development for their synthesis and remediation efficiency as a necessary step to move from laboratory- to pilot-scale applications. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 47, 100902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gworek, B.; Kijeńska, M.; Wrzosek, J.; Graniewska, M. Pharmaceuticals in the Soil and Plant Environment: A Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; UNEP. Global Assessment of Soil Pollution—Summary for Policy Makers; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- De Oliveira Souza, H.; dos Santos Costa, R.; Quadra, G.R.; dos Santos Fernandez, M.A. Pharmaceutical pollution and sustainable development goals: Going the right way? Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Proximate Analysis | Mass Percentage |
|---|---|
| Moisture | 1.94 ± 0.154% |
| Ash | 9.00 ± 0.100% |
| Volatile matter | 84.82 ± 1.297% |
| Fixed carbon | 4.24 ± 0.982% |
| Protein | 4.02 ± 0.107% |
| Ethereal extract | 0.70 ± 0.097% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-Velducea, H.A.; Moreno-Vásquez, M.d.J.; Guzmán, H.; Esquer, J.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Graciano-Verdugo, A.Z.; Santos-Sauceda, I.; Quintero-Reyes, I.E.; Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Vásquez-López, C.; et al. Valorization of Agave angustifolia Bagasse Biomass from the Bacanora Industry in Sonora, Mexico as a Biochar Material: Preparation, Characterization, and Potential Application in Ibuprofen Removal. Sustain. Chem. 2024, 5, 196-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem5030013
Ruiz-Velducea HA, Moreno-Vásquez MdJ, Guzmán H, Esquer J, Rodríguez-Félix F, Graciano-Verdugo AZ, Santos-Sauceda I, Quintero-Reyes IE, Barreras-Urbina CG, Vásquez-López C, et al. Valorization of Agave angustifolia Bagasse Biomass from the Bacanora Industry in Sonora, Mexico as a Biochar Material: Preparation, Characterization, and Potential Application in Ibuprofen Removal. Sustainable Chemistry. 2024; 5(3):196-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem5030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-Velducea, Hylse Aurora, María de Jesús Moreno-Vásquez, Héctor Guzmán, Javier Esquer, Francisco Rodríguez-Félix, Abril Zoraida Graciano-Verdugo, Irela Santos-Sauceda, Idania Emedith Quintero-Reyes, Carlos Gregorio Barreras-Urbina, Claudia Vásquez-López, and et al. 2024. "Valorization of Agave angustifolia Bagasse Biomass from the Bacanora Industry in Sonora, Mexico as a Biochar Material: Preparation, Characterization, and Potential Application in Ibuprofen Removal" Sustainable Chemistry 5, no. 3: 196-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem5030013
APA StyleRuiz-Velducea, H. A., Moreno-Vásquez, M. d. J., Guzmán, H., Esquer, J., Rodríguez-Félix, F., Graciano-Verdugo, A. Z., Santos-Sauceda, I., Quintero-Reyes, I. E., Barreras-Urbina, C. G., Vásquez-López, C., Burruel-Ibarra, S. E., Ozuna-Valencia, K. H., & Tapia-Hernández, J. A. (2024). Valorization of Agave angustifolia Bagasse Biomass from the Bacanora Industry in Sonora, Mexico as a Biochar Material: Preparation, Characterization, and Potential Application in Ibuprofen Removal. Sustainable Chemistry, 5(3), 196-214. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem5030013












