The Endogenous Pain Modulatory System as a Healing Mechanism: A Proposal on How to Measure and Modulate It
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Definition of Healing
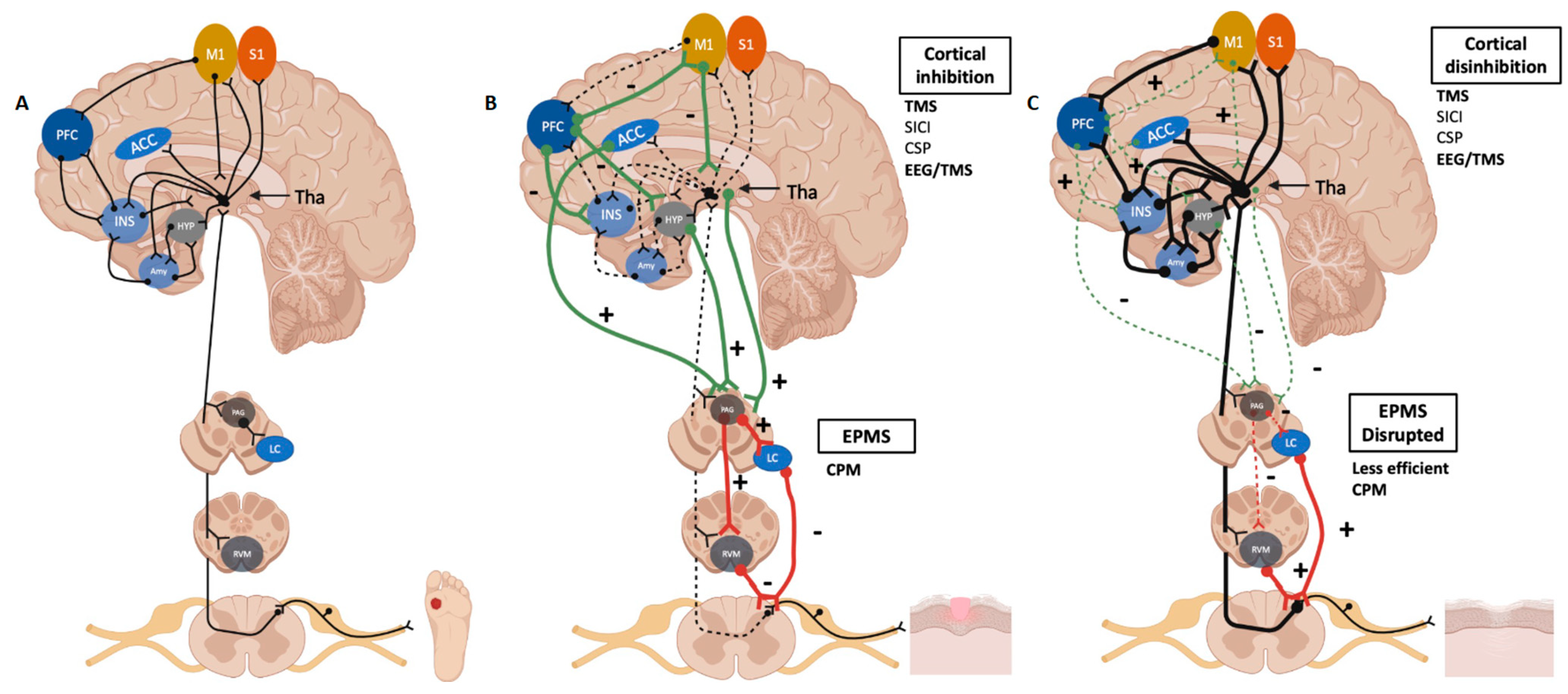
3. EPMS as a Key Component of the Healing Process
3.1. Measuring the EPMS: Conditioned Pain Modulation (CPM)
3.2. A Critical Modulator of the Endogenous Pain Inhibitory System: The Primary Motor Cortex
4. Factors That Disrupt the Balance of the Pain Healing Mechanisms
4.1. Sleep Quality
4.2. Medication Overuse and Opioids
4.3. Poor Mental Health
5. Factors That Improve the Balance of the Pain Healing Mechanisms
5.1. Exercise
5.2. Non-Invasive Neuromodulation
5.3. Mind–Body Techniques
5.4. Pharmacological Neuromodulation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Atkinson, C.; Bhalla, K.; Birbeck, G.; Burstein, R.; Chou, D.; Dellavalle, R.; Danaei, G.; Ezzati, M.; Fahimi, A.; et al. The state of US health, 1990–2010: Burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors. JAMA 2013, 310, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlhamer, J.; Lucas, J.; Zelaya, C.; Nahin, R.; Mackey, S.; DeBar, L.; Kerns, R.; Von Korff, M.; Porter, L.; Helmick, C. Prevalence of Chronic Pain and High-Impact Chronic Pain Among Adults—United States, 2016. Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steglitz, J.; Buscemi, J.; Ferguson, M.J. The future of pain research, education, and treatment: A summary of the IOM report “Relieving pain in America: A blueprint for transforming prevention, care, education, and research”. Transl. Behav. Med. 2012, 2, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, R.R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Sullivan, M.D.; Turk, D.C.; Wasan, A.D. The Role of Psychosocial Processes in the Development and Maintenance of Chronic Pain. J. Pain 2016, 17 (Suppl. 9), T70–T92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meints, S.M.; Edwards, R.R. Evaluating psychosocial contributions to chronic pain outcomes. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 87 Pt B, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoborec, S.; Ruseckaite, R.; Ayton, D.; Evans, S. Biopsychosocial factors associated with non-recovery after a minor transport-related injury: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.-J.; O’Connell, N.E.; Beckenkamp, P.R.; Alhassani, G.; Liston, M.B.; Schabrun, S.M. Altered Primary Motor Cortex Structure, Organization, and Function in Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pain 2018, 19, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, C.J.; Hodges, P.W.; Wrigley, T.V.; Bennell, K.L.; Farrell, M.J. Organisation of the motor cortex differs between people with and without knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te, M.; Baptista, A.F.; Chipchase, L.S.; Schabrun, S.M. Primary Motor Cortex Organization Is Altered in Persistent Patellofemoral Pain. Pain Med. 2017, 18, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chang, M.C. Chronic Pain: Structural and Functional Changes in Brain Structures and Associated Negative Affective States. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.D.; Aghaeepour, N.; Ahn, A.H.; Angst, M.S.; Borsook, D.; Brenton, A.; Burczynski, M.E.; Crean, C.; Edwards, R.; Gaudilliere, B. Discovery and validation of biomarkers to aid the development of safe and effective pain therapeutics: Challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moana-Filho, E.J.; Herrero Babiloni, A.; Theis-Mahon, N.R. Endogenous pain modulation in chronic orofacial pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2018, 159, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.T.; Deitos, A.; Triñanes Pego, Y.; Fregni, F.; Carrillo-de-la-Peña, M.T. Defective Endogenous Pain Modulation in Fibromyalgia: A Meta-Analysis of Temporal Summation and Conditioned Pain Modulation Paradigms. J. Pain 2018, 19, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.J.; Martin, P. Wound repair at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122 Pt 18, 3209–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.d.T.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Rebello-Sanchez, I.; Castelo-Branco, L.; de Melo, P.S.; Parente, J.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Firigato, I.; Pessotto, A.V.; Imamura, M.; et al. Association of Mu opioid receptor (A118G) and BDNF (G196A) polymorphisms with rehabilitation-induced cortical inhibition and analgesic response in chronic osteoarthritis pain. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2023, 23, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xian, C.J.; Zhong, J.H.; Zhou, X.F. Upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the sensory pathway by selective motor nerve injury in adult rats. Neurotox Res. 2006, 9, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siniscalco, D.; Giordano, C.; Rossi, F.; Maione, S.; de Novellis, V. Role of neurotrophins in neuropathic pain. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2011, 9, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakkar, B.; Acevedo, E.O. BDNF as a biomarker for neuropathic pain: Consideration of mechanisms of action and associated measurement challenges. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivoli, E.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Salvicchi, A.; Bartolini, A.; Koverech, A.; Nicolai, R.; Benatti, P.; Ghelardini, C. Acetyl-L-carnitine increases artemin level and prevents neurotrophic factor alterations during neuropathy. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Gerwing, T.D.; Stucky, C.L.; McComb, G.W.; Verge, V.M. Neurotrophin-3 significantly reduces sodium channel expression linked to neuropathic pain states. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 213, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garraway, S.M.; Huie, J.R. Spinal Plasticity and Behavior: BDNF-Induced Neuromodulation in Uninjured and Injured Spinal Cord. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 9857201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Deng, G.; Huang, H. The activation of BDNF reduced inflammation in a spinal cord injury model by TrkB/p38 MAPK signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.N.; Carr, D.B.; Cohen, M.; Finnerup, N.B.; Flor, H.; Gibson, S.; Keefe, F.; Mogil, J.S.; Ringkamp, M.; Sluka, K.A. The revised IASP definition of pain: Concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain 2020, 161, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, G.L.; Vlaeyen, J.W.S. Beyond nociception: The imprecision hypothesis of chronic pain. Pain 2015, 156, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauw, D.J.; Essex, M.N.; Pitman, V.; Jones, K.D. Reframing chronic pain as a disease, not a symptom: Rationale and implications for pain management. Postgrad. Med. 2019, 131, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, T.; Magerl, W.; Treede, R.D. Perceptual correlate of nociceptive long-term potentiation (LTP) in humans shares the time course of early-LTP. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 96, 3551–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Beltrá, P.; Ruiz-Del-Portal, I.; Ortega, F.J.; Valdesuso, R.; Delicado-Miralles, M.; Velasco, E. Sensorimotor effects of plasticity-inducing percutaneous peripheral nerve stimulation protocols: A blinded, randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Pain 2022, 26, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisien, M.; Lima, L.V.; Dagostino, C.; El-Hachem, N.; Drury, G.L.; Grant, A.V.; Huising, J.; Verma, V.; Meloto, C.B.; Silva, J.R. Acute inflammatory response via neutrophil activation protects against the development of chronic pain. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabj9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronoff, G.M. What Do We Know About the Pathophysiology of Chronic Pain? Implications for Treatment Considerations. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 100, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, M.E.; Pinto, C.B.; Velez, F.G.S.; Duarte, D.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Lopes, F.; Fregni, F. Motor cortex reorganization in limb amputation: A systematic review of TMS motor mapping studies. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Pinto, C.B.; Saleh Velez, F.G.; Duarte, D.; Gunduz, M.E.; Simis, M.; Lepesteur Gianlorenco, A.C.; Barouh, J.L.; Crandell, D.; Guidetti, M.; et al. Structural and functional motor cortex asymmetry in unilateral lower limb amputation with phantom limb pain. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teles, A.R.; Ocay, D.D.; Bin Shebreen, A.; Tice, A.; Saran, N.; Ouellet, J.A.; Ferland, C.E. Evidence of impaired pain modulation in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis and chronic back pain. Spine J. 2019, 19, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnitsky, D. Role of endogenous pain modulation in chronic pain mechanisms and treatment. Pain 2015, 156, S24–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.; Pidal-Miranda, M.; Samartin-Veiga, N.; Carrillo-de-la-Peña, M.T. Conditioned pain modulation as a biomarker of chronic pain: A systematic review of its concurrent validity. Pain 2019, 160, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri-Heir, C.; Khan, J.; Benoliel, R.; Feng, C.; Yarnitsky, D.; Kuo, F.; Hirschberg, C.; Hartwell, G.; Huang, C.Y.; Heir, G.; et al. Altered pain modulation in patients with persistent postendodontic pain. Pain 2015, 156, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, S.; Wodehouse, T. Conditioned pain modulation-A comprehensive review. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2021, 51, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, I.G.; Dixon, E.A.; Johnson, K.; Kong, J.-T. Dynamic Quantitative Sensory Testing to Characterize Central Pain Processing. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 54452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürsteler, C.; Salazar, Y.; Rodriguez, U.; Pelfort, X.; Verdié, L.P. Conditioned pain modulation predicts persistent pain after knee replacement surgery. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnitsky, D.; Granot, M.; Granovsky, Y. Pain modulation profile and pain therapy: Between pro- and antinociception. Pain 2014, 155, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damien, J.; Colloca, L.; Bellei-Rodriguez, C.-É.; Marchand, S. Chapter Eleven—Pain Modulation: From Conditioned Pain Modulation to Placebo and Nocebo Effects in Experimental and Clinical Pain. In International Review of Neurobiology; Colloca, L., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 139, pp. 255–296. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C.P.N. The Phenomenon of Pain. Pain Res. Manag. 2014, 19, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Granovsky, Y. Conditioned pain modulation: A predictor for development and treatment of neuropathic pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aranda-Villalobos, P.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Navarro-Espigares, J.L.; Hernández-Torres, E.; Villalobos, M.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Arroyo-Morales, M. Normalization of widespread pressure pain hypersensitivity after total hip replacement in patients with hip osteoarthritis is associated with clinical and functional improvements. Arthritis Rheum 2013, 65, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graven-Nielsen, T.; Wodehouse, T.; Langford, R.M.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Kidd, B.L. Normalization of widespread hyperesthesia and facilitated spatial summation of deep-tissue pain in knee osteoarthritis patients after knee replacement. Arthritis Rheum 2012, 64, 2907–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarnitsky, D.; Granot, M.; Nahman-Averbuch, H.; Khamaisi, M.; Granovsky, Y. Conditioned pain modulation predicts duloxetine efficacy in painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 2012, 153, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosen, K.; Vase, L.; Pilegaard, H.K.; Pfeiffer-Jensen, M.; Drewes, A.M. Conditioned pain modulation and situational pain catastrophizing as preoperative predictors of pain following chest wall surgery: A prospective observational cohort study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.N.; Rice, D.A.; McNair, P.J. Conditioned pain modulation in populations with chronic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Pain 2012, 13, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghi, M.; Pearce, S.L.; Nordstrom, M.A. Differential modulation of intracortical inhibition in human motor cortex during selective activation of an intrinsic hand muscle. J. Physiol. 2003, 550 Pt 3, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcangio, M. GABA(B) receptors and pain. Neuropharmacology 2018, 136 Pt A, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fregni, F.; El-Hagrassy, M.M.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Carvalho, S.; Leite, J.; Simis, M.; Brunelin, J.; Nakamura-Palacios, E.M.; Marangolo, P.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; et al. Evidence-Based Guidelines and Secondary Meta-Analysis for the Use of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation in Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 24, 256–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoni-Luza, S.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Mejia-Pando, P.F.; Luna-Cuadros, M.A.; Barouh, J.L.; Gnoatto-Medeiros, M.; Candido-Santos, L.; Barra, A.; Caumo, W.; et al. Noninvasive motor cortex stimulation effects on quantitative sensory testing in healthy and chronic pain subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2020, 161, 1955–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, T.J.; Keaser, M.L.; Khan, S.A.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Seminowicz, D.A.; Greenspan, J.D. Non-invasive Motor Cortex Neuromodulation Reduces Secondary Hyperalgesia and Enhances Activation of the Descending Pain Modulatory Network. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Gangadharan, V.; Liu, S.; Körber, C.; Tan, L.L.; Li, H.; Oswald, M.J.; Kang, J.; Martin-Cortecero, J.; Männich, D. Layer-specific pain relief pathways originating from primary motor cortex. Science 2022, 378, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zortea, M.; Ramalho, L.; Alves, R.L.; Alves, C.F.d.S.; Braulio, G.; Torres, I.L.d.S.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation to Improve the Dysfunction of Descending Pain Modulatory System Related to Opioids in Chronic Non-cancer Pain: An Integrative Review of Neurobiology and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S.; Katayama, Y.; Maejima, S.; Hirayama, T.; Fujii, M.; Tsubokawa, T. Thalamic neuronal hyperactivity following transection of the spinothalamic tract in the cat: Involvement ofN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. Brain Res. 1993, 612, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, F.A.; Kwan, H.C.; Dostrovsky, J.O.; Tasker, R.R. Characteristics of the bursting pattern of action potentials that occurs in the thalamus of patients with central pain. Brain Res. 1989, 496, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragert, P.; Vandermeeren, Y.; Camus, M.; Cohen, L.G. Improvement of spatial tactile acuity by transcranial direct current stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, T.D.; Garg, R.R.; Chen, R. Interactions between two different inhibitory systems in the human motor cortex. J. Physiol. 2001, 530 Pt 2, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Drouot, X.; Ménard-Lefaucheur, I.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J.P. Motor cortex rTMS restores defective intracortical inhibition in chronic neuropathic pain. Neurology 2006, 67, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Lima, D.; Pimenta, D.; Slawka, E.; Navarro-Flores, A.; Parente, J.; Rebello-Sanchez, I.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Gonzalez-Mego, P.; Castelo-Branco, L. Motor cortex inhibition as a fibromyalgia biomarker: A meta-analysis of transcranial magnetic stimulation studies. Brain Netw. Modul. 2022, 1, 88–101. [Google Scholar]
- Simis, M.; Imamura, M.; Sampaio de Melo, P.; Marduy, A.; Battistella, L.; Fregni, F. Deficit of Inhibition as a Marker of Neuroplasticity (DEFINE Study) in Rehabilitation: A Longitudinal Cohort Study Protocol. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 695406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, M.; Imamura, M.; de Melo, P.S.; Marduy, A.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Teixeira, P.E.P.; Battistella, L.; Fregni, F. Increased motor cortex inhibition as a marker of compensation to chronic pain in knee osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, M.; Imamura, M.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Marduy, A.; de Melo, P.S.; Mendes, A.J.; Teixeira, P.E.P.; Battistella, L.; Fregni, F. EEG theta and beta bands as brain oscillations for different knee osteoarthritis phenotypes according to disease severity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simis, M.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Uygur-Kucukseymen, E.; Castelo-Branco, L.; Battistella, L.R.; Fregni, F. Specific Electroencephalographic Signatures for Pain and Descending Pain Inhibitory System in Spinal Cord Injury. Pain Med. 2022, 23, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artner, J.; Cakir, B.; Spiekermann, J.A.; Kurz, S.; Leucht, F.; Reichel, H.; Lattig, F. Prevalence of sleep deprivation in patients with chronic neck and back pain: A retrospective evaluation of 1016 patients. J. Pain Res. 2013, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, J.A.; Urrestarazu, E.; Iriarte, J. Sleep loss as risk factor for neurologic disorders: A review. Sleep Med. 2013, 14, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borbély, S.; Világi, I.; Haraszti, Z.; Szalontai, Ö.; Hajnik, T.; Tóth, A.; Détári, L. Sleep deprivation decreases neuronal excitability and responsiveness in rats both in vivo and ex vivo. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 137, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, P.; Langguth, B.; Popp, R.; Raster, R.; Busch, V.; Frank, E.; Hajak, G.; Landgrebe, M. Reduced intra-cortical inhibition after sleep deprivation: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 493, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civardi, C.; Boccagni, C.; Vicentini, R.; Bolamperti, L.; Tarletti, R.; Varrasi, C.; Monaco, F.; Cantello, R. Cortical excitability and sleep deprivation: A transcranial magnetic stimulation study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 71, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staffe, A.T.; Bech, M.W.; Clemmensen, S.L.K.; Nielsen, H.T.; Larsen, D.B.; Petersen, K.K. Total sleep deprivation increases pain sensitivity, impairs conditioned pain modulation and facilitates temporal summation of pain in healthy participants. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, G.; Schoenen, J. Cortical excitability in chronic migraine. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2012, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jia, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Ma, L.; Yu, S. Volumetric abnormalities of thalamic subnuclei in medication-overuse headache. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brush, D.E. Complications of Long-Term Opioid Therapy for Management of Chronic Pain: The Paradox of Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-H.; Liu, K.; Tan, P.-H.; Chia, Y.-Y. Effects of postoperative background PCA morphine infusion on pain management and related side effects in patients undergoing abdominal hysterectomy. J. Clin. Anesth. 2011, 23, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, C.; Armstrong-Brown, A.; Burstal, R. Perioperative intravenous ketamine infusion for the prevention of persistent post-amputation pain: A randomized, controlled trial. Anaesth Intensive Care 2004, 32, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salengros, J.-C.; Huybrechts, I.; Ducart, A.; Faraoni, D.; Marsala, C.; Barvais, L.; Cappello, M.; Engelman, E. Different Anesthetic Techniques Associated with Different Incidences of Chronic Post-thoracotomy Pain: Low-Dose Remifentanil Plus Presurgical Epidural Analgesia is Preferable to High-Dose Remifentanil with Postsurgical Epidural Analgesia. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2010, 24, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahman-Averbuch, H.; Nir, R.R.; Sprecher, E.; Yarnitsky, D. Psychological Factors and Conditioned Pain Modulation: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Pain 2016, 32, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. The Link between Depression and Chronic Pain: Neural Mechanisms in the Brain. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 9724371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinrichs-Rocker, A.; Schulz, K.; Järvinen, I.; Lefering, R.; Simanski, C.; Neugebauer, E.A. Psychosocial predictors and correlates for chronic post-surgical pain (CPSP)—A systematic review. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.N.; Rice, D.A.; McNair, P.J.; Kluger, M. Predictors of persistent pain after total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth 2015, 114, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, N.A.; Pocovi, N.C.; Dylke, E.S.; Graham, P.L.; De Groef, A. Psychological Factors Are Associated with Pain at All Time Frames After Breast Cancer Surgery: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses. Pain Med. 2021, 22, 915–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Wang, J.; Qiu, S.; Chen, P.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y. Common and distinct patterns of intrinsic brain activity alterations in major depression and bipolar disorder: Voxel-based meta-analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliz, D.; Hayley, S. Major depressive disorder and alterations in insular cortical activity: A review of current functional magnetic imaging research. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.P.; Di Pietro, F.; Alshelh, Z.; Peck, C.C.; Murray, G.M.; Vickers, E.R.; Henderson, L.A. Brainstem Pain-Control Circuitry Connectivity in Chronic Neuropathic Pain. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Carolyna Gianlorenco, A.; Machado, R.; Queiroga, M.; Zeng, H.; Shaikh, E.; Yang, Y.; Nogueira, B.; Castelo-Branco, L.; Fregni, F. Exercise-induced pain threshold modulation in healthy subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Princ. Pract. Clin. Res. 2020, 6, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, D.; Nijs, J.; Kosek, E.; Wideman, T.; Hasenbring, M.I.; Koltyn, K.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; Polli, A. Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia in Pain-Free and Chronic Pain Populations: State of the Art and Future Directions. J. Pain 2019, 20, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluka, K.A.; Frey-Law, L.; Hoeger Bement, M. Exercise-induced pain and analgesia? Underlying mechanisms and clinical translation. Pain 2018, 159 (Suppl. 1), S91–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Thibaut, A.; Costa, B.; Ferreira, I.; Caumo, W.; Fregni, F. Methods and strategies of tDCS for the treatment of pain: Current status and future directions. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunduz, M.E.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Bonin Pinto, C.; Duarte, D.; Vélez, F.G.S.; Gianlorenco, A.C.L.; Teixeira, P.E.P.; Giannoni-Luza, S.; Crandell, D.; Battistella, L.R.; et al. Effects of Combined and Alone Transcranial Motor Cortex Stimulation and Mirror Therapy in Phantom Limb Pain: A Randomized Factorial Trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2021, 35, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Meng, X.; Fregni, F. Neuromodulation Techniques in Phantom Limb Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 2310–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Fregni, F. Non-invasive neuromodulation effects on painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, N.E.; Marston, L.; Spencer, S.; DeSouza, L.H.; Wand, B.M. Non-invasive brain stimulation techniques for chronic pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 4, CD008208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.; Slawka, E.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Castelo-Branco, L.; Fregni, F. The pros and cons of tDCS as a therapeutic tool in the rehabilitation of chronic pain. Princ. Pract. Clin. Res. 2022, 8, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Castelo-Branco, L.; Giannoni-Luza, S.; Balbuena-Pareja, A.; Luna-Cuadros, M.A.; Vasconcelos Felippe, L.; Uygur-Kucukseymen, E.; Gonzalez-Mego, P.; Gunduz, M.E.; et al. Barriers and facilitators for clinical trial participation of underrepresented and non-underrepresented fibromyalgia patients: A cross-sectional internet survey. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelo-Branco, L.; Uygur Kucukseymen, E.; Duarte, D.; El-Hagrassy, M.M.; Bonin Pinto, C.; Gunduz, M.E.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Yang, Y.; Gonzalez-Mego, P.; et al. Optimised transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for fibromyalgia—Targeting the endogenous pain control system: A randomised, double-blind, factorial clinical trial protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e032710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; de Melo, P.S.; Marduy, A.; Gonzalez-Mego, P.; Castelo-Branco, L.; Mendes, A.J.; Vasquez-Avila, K.; Teixeira, P.E.P.; Gianlorenco, A.C.L.; et al. Home-based transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and motor imagery for phantom limb pain using statistical learning to predict treatment response: An open-label study protocol. Princ. Pract. Clin. Res. 2021, 7, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carandina, A.; Bellocchi, C.; Della Torre, A.; Beretta, L.; Tobaldini, E.; Montano, N. Transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation ameliorates chronic pain in patients with systemic sclerosis: Results from a pilot interventional trial. Brain Stimul. Basic Transl. Clin. Res. Neuromodul. 2021, 14, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; Day, M.A.; Miró, J. Neuromodulatory treatments for chronic pain: Efficacy and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.P. The neurophysiology of pain perception and hypnotic analgesia: Implications for clinical practice. Am. J. Clin. Hypn. 2008, 51, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, H.L. Pain modulation: Expectation, opioid analgesia and virtual pain. Prog. Brain Res. 2000, 122, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.D.; Robinson, J.P. Antidepressant and anticonvulsant medication for chronic pain. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 17, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.S. Anticonvulsants in neuropathic pain: Rationale and clinical evidence. Eur. J. Pain 2002, 6 (Suppl. A), 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodehouse, T.; Poply, K.; Ramaswamy, S.; Snidvongs, S.; Bourke, J.; Tahir, H.; Ullrich, K.; Mehta, V. A pilot study investigating whether quantitative sensory testing alters after treatment in patients with fibromyalgia. Br. J. Pain 2018, 12, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Melo, P.S.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Marduy, A.; Vasquez-Avila, K.; Simis, M.; Imamura, M.; Cardenas-Rojas, A.; Navarro-Flores, A.; Batistella, L.; Fregni, F. The Endogenous Pain Modulatory System as a Healing Mechanism: A Proposal on How to Measure and Modulate It. NeuroSci 2024, 5, 230-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030018
de Melo PS, Pacheco-Barrios K, Marduy A, Vasquez-Avila K, Simis M, Imamura M, Cardenas-Rojas A, Navarro-Flores A, Batistella L, Fregni F. The Endogenous Pain Modulatory System as a Healing Mechanism: A Proposal on How to Measure and Modulate It. NeuroSci. 2024; 5(3):230-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030018
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Melo, Paulo S., Kevin Pacheco-Barrios, Anna Marduy, Karen Vasquez-Avila, Marcel Simis, Marta Imamura, Alejandra Cardenas-Rojas, Alba Navarro-Flores, Linamara Batistella, and Felipe Fregni. 2024. "The Endogenous Pain Modulatory System as a Healing Mechanism: A Proposal on How to Measure and Modulate It" NeuroSci 5, no. 3: 230-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030018
APA Stylede Melo, P. S., Pacheco-Barrios, K., Marduy, A., Vasquez-Avila, K., Simis, M., Imamura, M., Cardenas-Rojas, A., Navarro-Flores, A., Batistella, L., & Fregni, F. (2024). The Endogenous Pain Modulatory System as a Healing Mechanism: A Proposal on How to Measure and Modulate It. NeuroSci, 5(3), 230-243. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5030018






