Numerical Modelling and Design of Aluminium Alloy Angles under Uniform Compression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Numerical Modelling
2.1. Angle Section Stub Columns
2.2. General Modelling Assumptions
2.3. Material Modelling
2.4. Initial Geometric Imperfections and Nonlinear Analysis
2.5. Validation of the FE Models
2.6. Parametric Study
3. Analysis and Discussion of the Results
3.1. Mechanical Behaviour and Failure Mode
3.2. Effect of Cross-Sectional Aspect Ratio
3.3. Effect of Cross-Sectional Slenderness
3.4. Effect of Material Properties
4. Design Recommendations
4.1. EN 1999-1-1
4.2. American Aluminium Design Manual
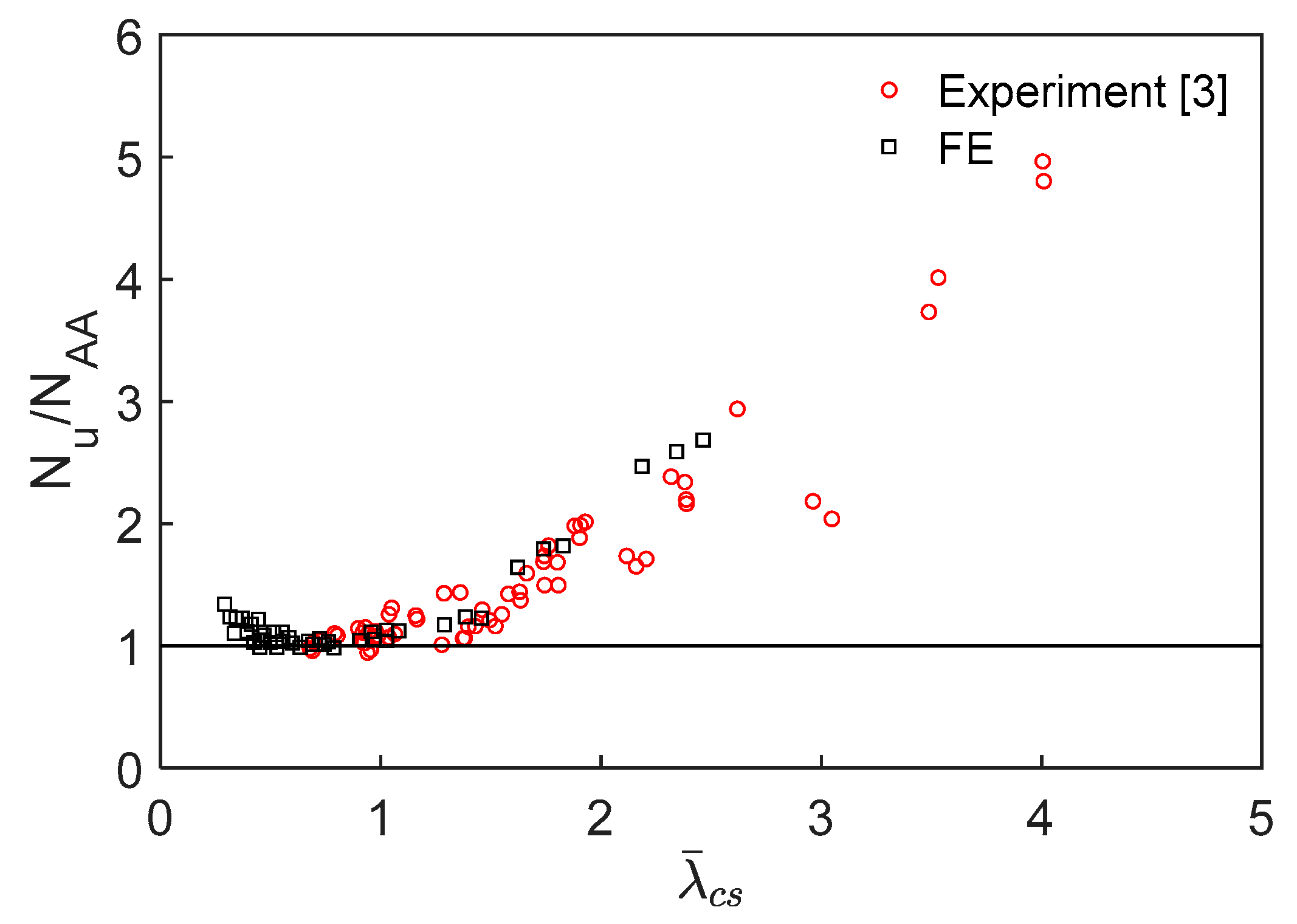
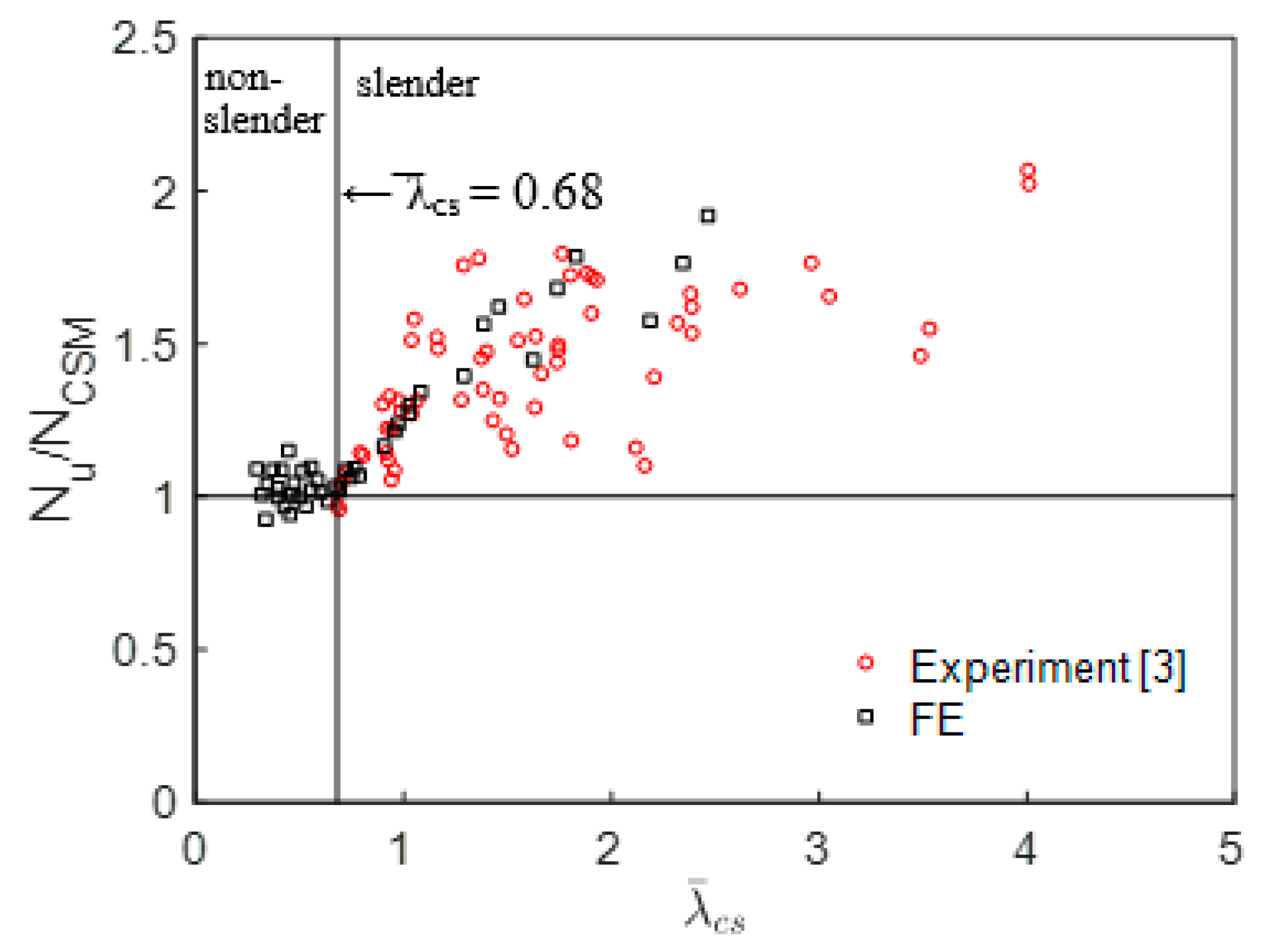
4.3. Continuous Strength Method
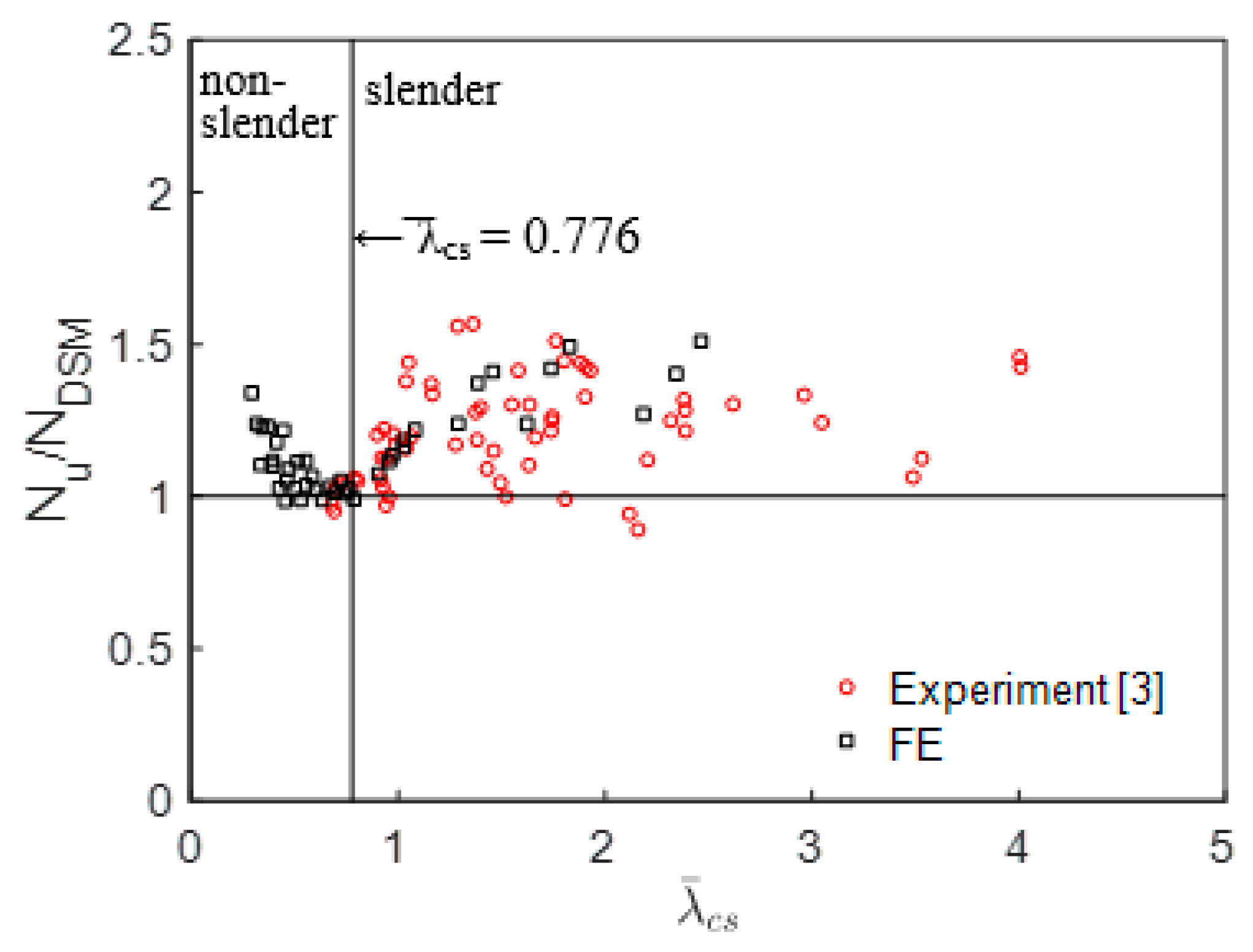
4.4. Direct Strength Method
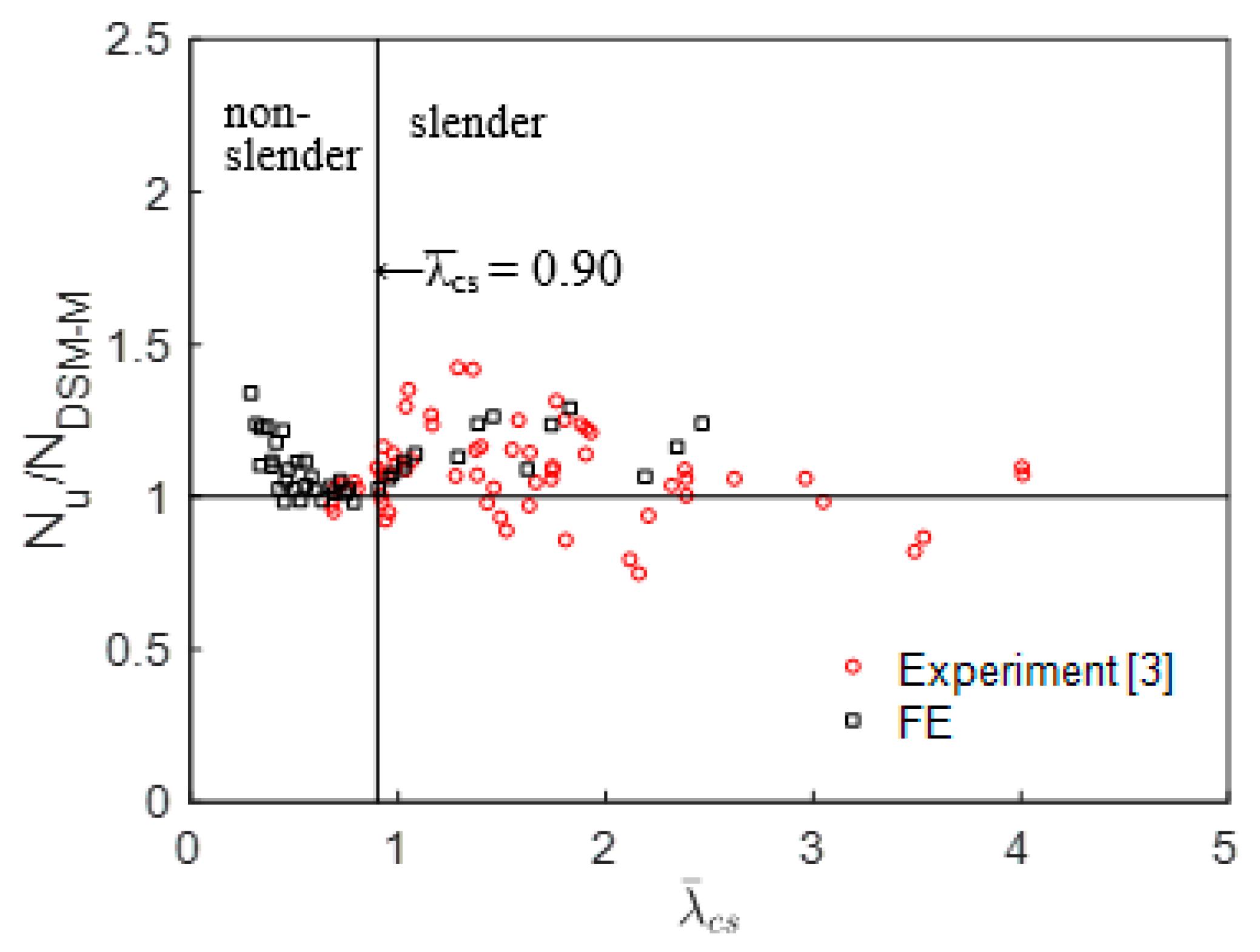
4.5. Proposal for Modified Direct Strength Method
4.6. Assessment of Design Strength Predictions
4.7. Reliability Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- All about Aluminium. Aluminium in Construction. Available online: https://www.aluminiumleader.com/application/construction/ (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Georgantzia, E.; Gkantou, M.; Kamaris, G.S. Aluminium alloys as structural material: A review of research. Eng. Struct. 2021, 227, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzolani, F.M.; Piluso, V.; Rizzano, G. Local Buckling of Aluminum Alloy Angles under Uniform Compression. J. Struct. Eng. 2011, 137, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Hu, X.G.; Han, J.K.; Xing, H.J. Experimental study and parametric analysis on the stability behavior of 7A04 high-strength aluminum alloy angle columns under axial compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2016, 108, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee for Standarization (EC9). Eurocode 9: Design of Aluminium Structures. Part 1-1: General Structural Rules—General Structural Rules and Rules for Buildings; BS EN 1999-1-1:2007, CEN:2007. BSI; European Committee for Standarization (EC9): Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- The Aluminum Association (AA). Aluminum Design Manual; The Aluminum Association (AA): Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbit, Karlsson, Sorensen. ABAQUS: Theory Manual. Providence, RI (USA); Dassault Systemes Corporation: Vélizy-Villacoublay, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, O.; Gardner, L. The continuous strength method for the design of mono-symmetric and asymmetric stainless steel cross-sections in bending. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 150, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North American Specification for the Design of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members; American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI): Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Ziemian, R.D. Guide to Stability Design Criteria for Metal Structures, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Orihara, S.; Nishiyama, I.; Kuwamura, H. Stress-strain relations of cruciform section stub-columns. AIJ J. Struct. Eng. 1989, 35B, 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hopperstad, O.S.; Langseth, M.; Hanssen, L. Ultimate compressive strength of plate elements in aluminium: Correlation of finite element analyses and tests. Thin Walled Struct. 1997, 29, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopperstad, O.S.; Langseth, M.; Tryland, T. Ultimate strength of aluminium alloy outstands in compression: Experiments and simplified analysis. Thin Walled Struct. 1999, 34, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galambos, T.V. Guide to Stability Design Criteria for Metal Structures, 5th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Georgantzia, E.; Gkantou, M.; Kamaris, G.S.; Kansara, K.; Hashim, K. Aluminium alloy cross-sections under uniaxial bending and compression: A numerical study. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1058, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgantzia, E.; Gkantou, M. Flexural buckling of concrete-filled aluminium alloy CHS columns: Numerical modelling and design. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Trends and Recent Advances in Civil Engineering, Uttar Pradesh, Noida, India, 20–21 August 2020; pp. 697–707. [Google Scholar]
- Gkantou, M. Numerical study of aluminium alloy square hollow section columns. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Trends and Recent Advances in Civil Engineering, Uttar Pradesh, Noida, India, 20–21 August 2020; pp. 709–717. [Google Scholar]
- Gkantou, M.; Bock, M.; Theofanous, M. Design of stainless steel cross-sections with outstand elements under stress gradients. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 179, 106491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Afshan, S.; Gkantou, M.; Theofanous, M.; Baniotopoulos, C.; Gardner, L. Flexural behaviour of hot-finished high strength steel square and rectangular hollow sections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 121, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkantou, M.; Antoniou, N.; Theofanous, M.; Baniotopoulos, C. Compressive behaviour of high-strength steel cross-sections. Struct. Build. 2017, 170, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.; Ellobody, E. Buckling Analysis of Cold-Formed Steel Lipped Angle Columns. J. Struct. Eng. 2005, 131, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellobody, E.; Young, B. Behavior of Cold-Formed Steel Plain Angle Columns. J. Struct. Eng. 2005, 131, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, K.; Zhao, O. Experimental and numerical studies of fixed-ended cold-formed stainless steel equal-leg angle section columns. Eng. Struct. 2019, 184, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, K.; Zhao, O. Press-braked S690 high strength steel equal-leg angle and plain channel section stub columns: Testing, numerical simulation and design. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, X.; Wang, Z.; Gardner, L. Full-Range Stress—Strain Curves for Aluminum Alloys. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Chang, Y. Experimental investigation on local buckling behaviors of stiffened closed-section thin-walled aluminum alloy columns under compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2015, 94, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, O.A.; Feng, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, X. Structures Stability of 6082-T6 aluminium alloy columns with H-section and rectangular hollow sections. Thin Walled Struct. 2015, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ramberg, W.; Osgood, W.R. Description of Stress-Strain Curves by Three Parameters; Volume Technical; National Advisory Committe for Aeronautics: Washington, DC, USA, 1943. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, H.N.; Clark, J.W.; Brungraber, R.J. Design of welded aluminum structures. J. Struct. Div. ASCE 1960, 86, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhao, O.; Young, B. Testing and numerical modelling of S960 ultra-high strength steel angle and channel section stub columns. Eng. Struct. 2020, 204, 109902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgantzia, E.; Bin Ali, S.; Gkantou, M.; Kamaris, G.S.; Kansara, K.; Atherton, W. Flexural buckling performance of concrete-filled aluminium alloy tubular columns. Eng. Struct. 2021, 242, 112546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Li, Z.Q.; Su, M.N.; Young, B. Behaviour of aluminium alloy plain and lipped channel columns. Thin Walled Struct. 2019, 135, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Yuan, H.X.; Chang, T.; Du, X.X.; Yu, M. Compressive buckling strength of extruded aluminium alloy I-section columns with fixed-pinned end conditions. Thin Walled Struct. 2017, 119, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzolani, F.M. Aluminum Alloy Structures, 2nd ed.; E& FN Spon: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, R.; Liu, J. Numerical investigation and design of perforated aluminium alloy SHS and RHS columns. Eng. Struct. 2019, 199, 109591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Compressive testing and numerical modelling of concrete- filled double skin CHS with austenitic stainless steel outer tubes. Thin Walled Struct. 2019, 141, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Li, Z.Q.; Su, M.N.; Young, B. Numerical study and design of aluminium alloy channel section columns with welds. Thin Walled Struct. 2019, 139, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.N.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Flexural response of aluminium alloy SHS and RHS with internal stiffeners. Eng. Struct. 2016, 121, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.; Theofanous, M. Discrete and continuous treatment of local buckling in stainless steel elements. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2008, 64, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, S.; Gardner, L. The continuous strength method for structural stainless steel design. Thin Walled Struct. 2013, 68, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, O.; Afshan, S.; Gardner, L. Structural response and continuous strength method design of slender stainless steel cross-sections. Eng. Struct. 2017, 140, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, M.N.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. The continuous strength method for the design of aluminium alloy structural elements. Eng. Struct. 2016, 122, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.N.; Young, B.; Gardner, L. Testing and design of aluminum alloy cross sections in compression. J. Struct Eng. 2014, 140, 04014047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seif, M.; Schafer, B.W. Local buckling of structural steel shapes. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2010, 66, 1232–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Schafer, B.W. Buckling analysis of cold-formed steel members with general boundary conditions using CUFSM: Conventional and constrained finite strip methods. In Proceedings of the 20th International Specialty Conference on Cold-Formed Steel Structures, St. Louis, MI, USA, 3 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schafer, B.W.; Peköz, T. Direct strength prediction of cold-formed steel members using numerical elastic buckling solutions. In Proceedings of the International Specialty Conference on Cold-Formed Steel Structures, St. Louis, MI, USA, 15–16 October 1998; pp. 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Schafer, B.W. Review: The Direct Strength Method of cold-formed steel member design. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2008, 64, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


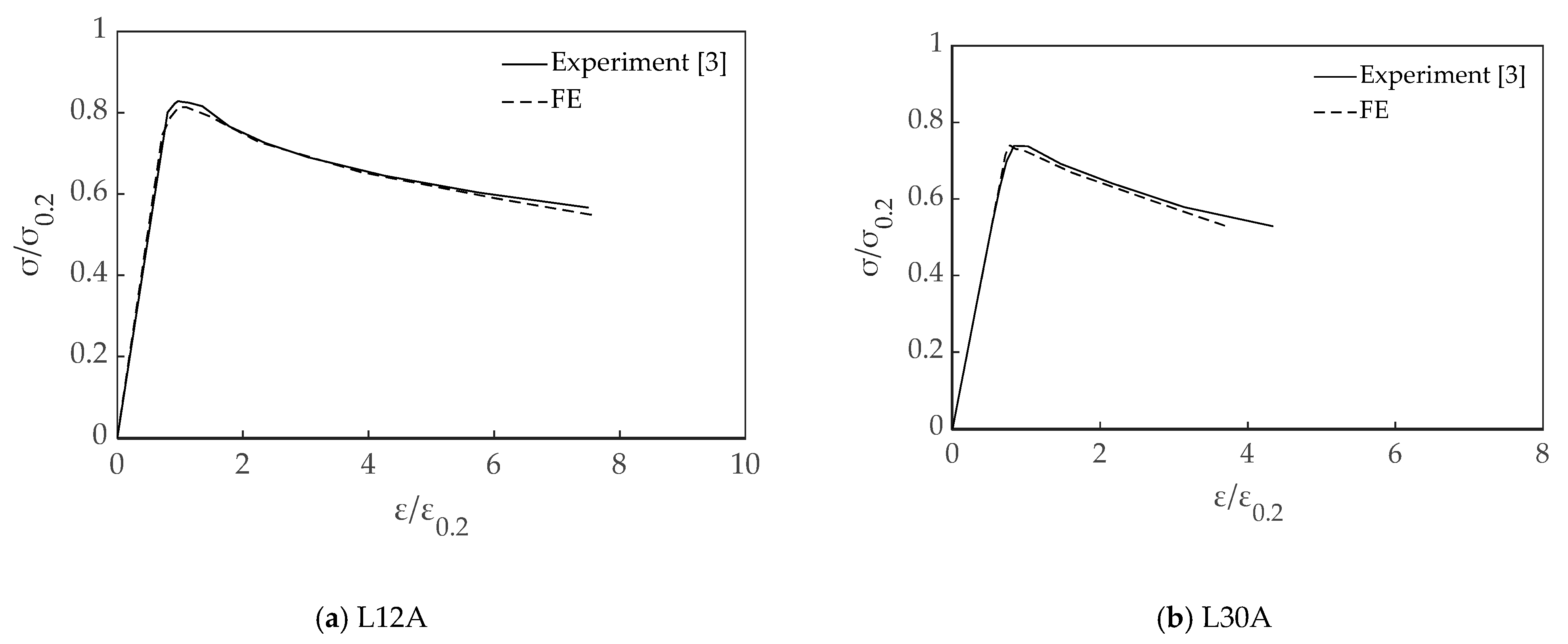
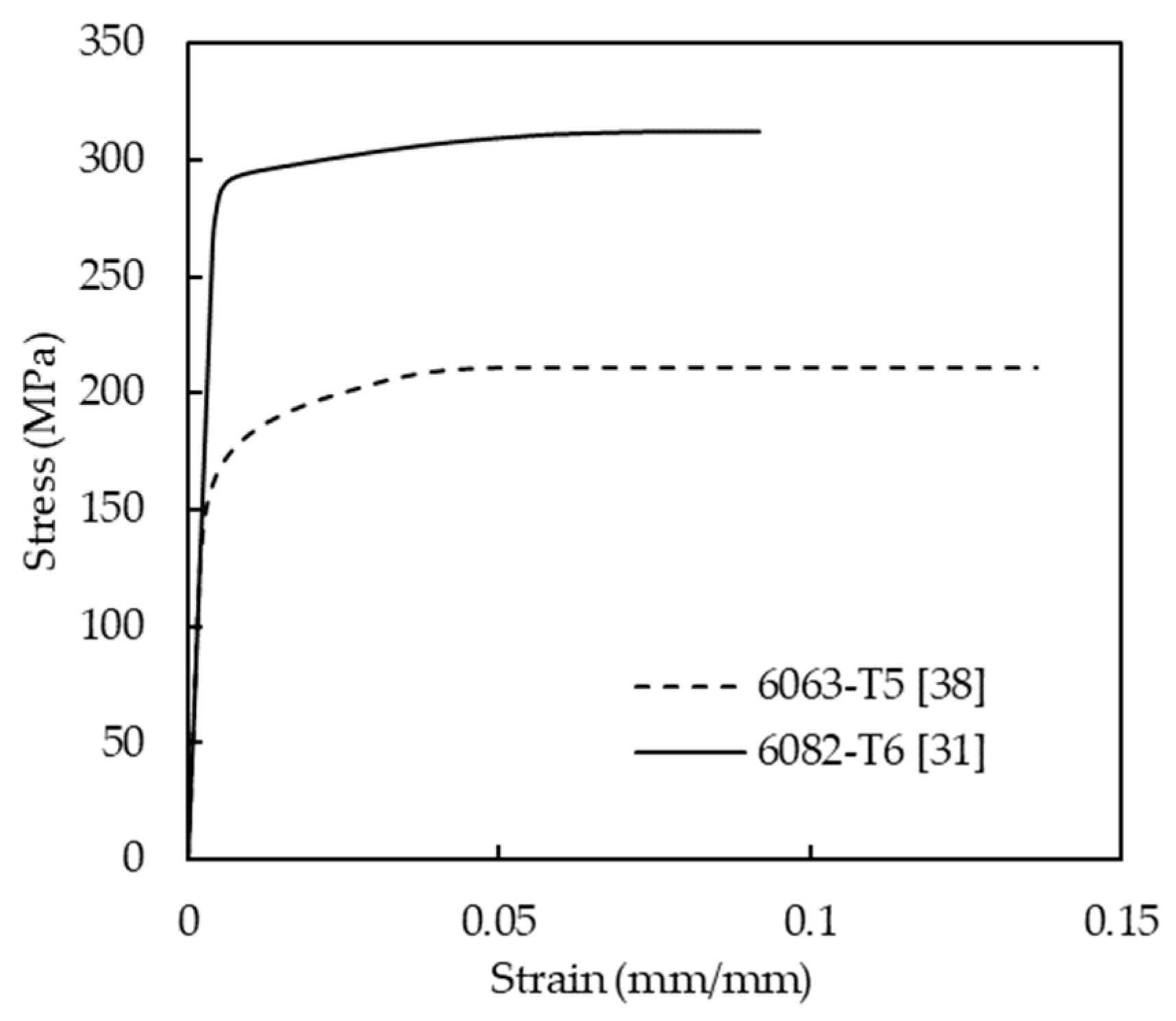


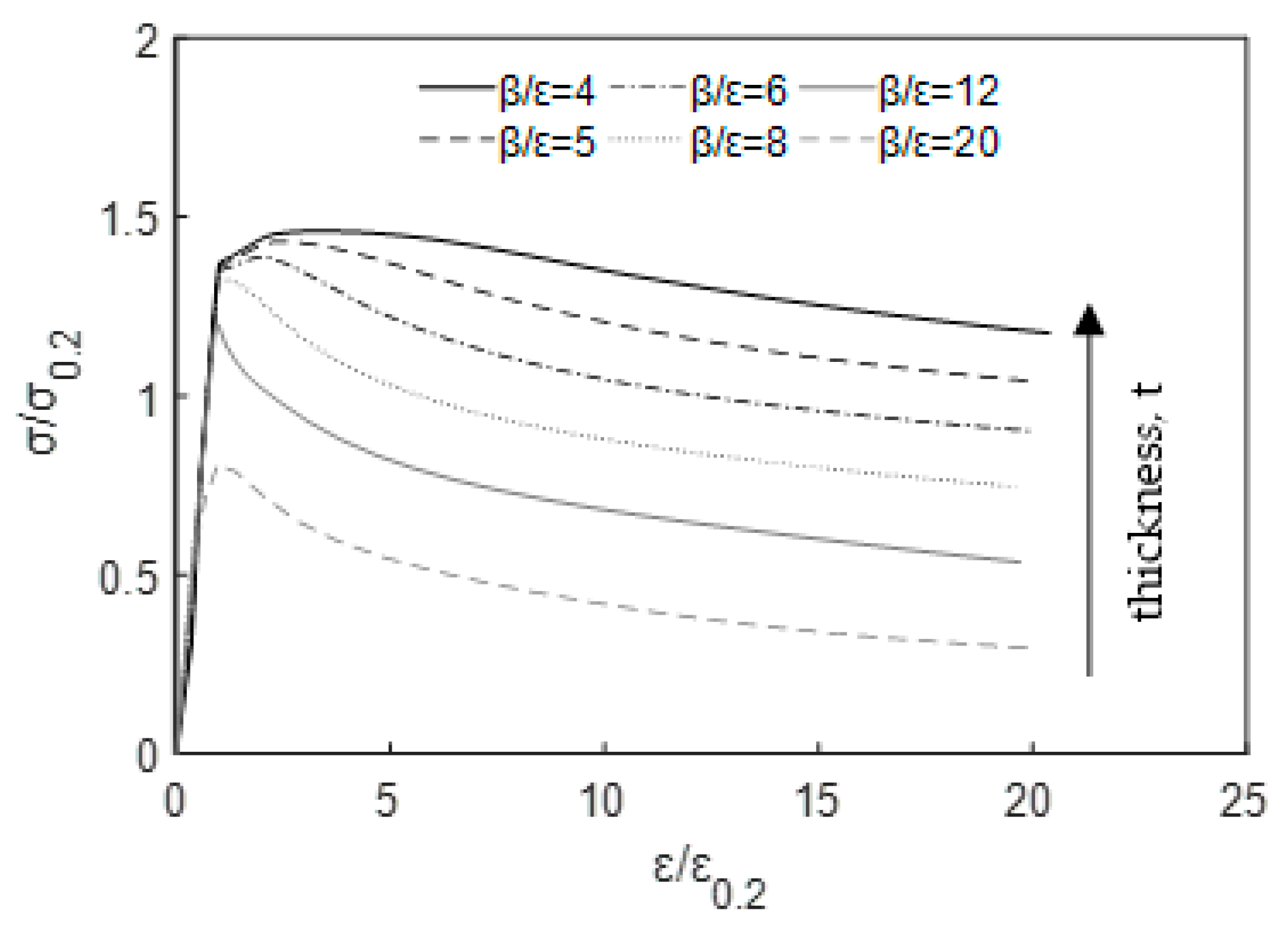
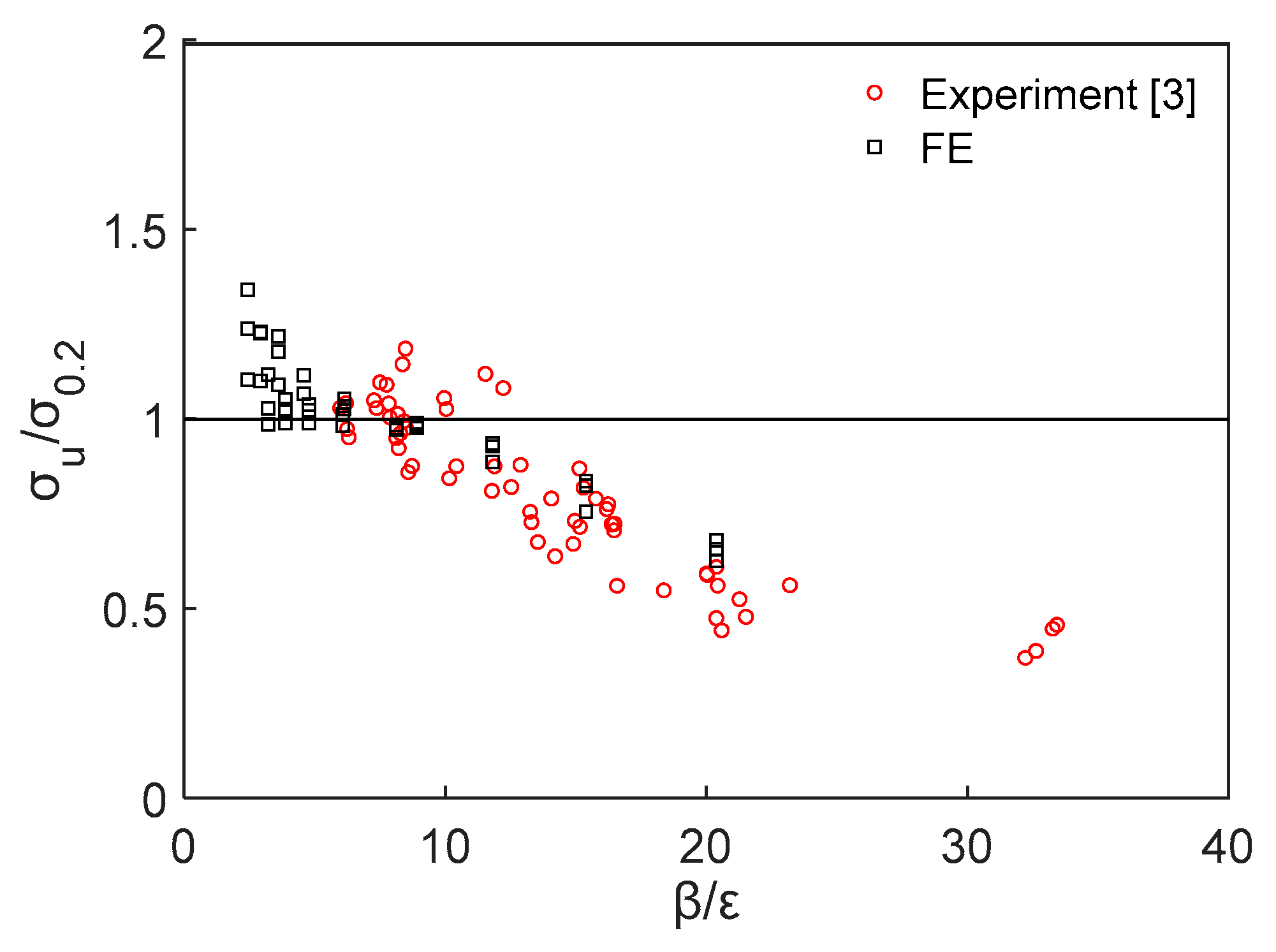


| Specimen | α (mm) | b (mm) | tα (mm) | tb (mm) | L (mm) | E (MPa) | σ0.1 (MPa) | σ0.2 (MPa) | σt (MPa) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L4A | 43.55 | 22.25 | 3.10 | 3.00 | 141.00 | 64,863 | 217.20 | 222.50 | 244.80 | 28.90 |
| L5A | 43.05 | 32.80 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 130.00 | 70,211 | 169.90 | 175.70 | 202.90 | 20.60 |
| L6A | 42.45 | 42.25 | 4.30 | 4.15 | 152.95 | 64,090 | 198.10 | 202.06 | 225.20 | 30.60 |
| L8A | 45.30 | 43.75 | 2.95 | 2.95 | 134.40 | 64,863 | 217.20 | 222.50 | 244.80 | 28.90 |
| L9A | 39.25 | 17.25 | 3.95 | 3.85 | 119.50 | 69,329 | 184.00 | 188.90 | 212.40 | 26.80 |
| L10A | 32.95 | 22.55 | 4.00 | 3.85 | 105.25 | 70,211 | 169.90 | 175.70 | 202.90 | 20.60 |
| L11A | 37.00 | 36.95 | 4.00 | 3.90 | 120.00 | 69,329 | 184.00 | 188.90 | 212.40 | 26.80 |
| L13A | 60.25 | 33.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 178.20 | 70,211 | 169.90 | 175.70 | 202.90 | 20.60 |
| L14A | 38.85 | 37.80 | 1.90 | 1.95 | 108.20 | 65,125 | 182.10 | 186.70 | 203.90 | 27.50 |
| L15A | 38.90 | 26.10 | 1.90 | 2.00 | 120.65 | 65,125 | 182.10 | 186.70 | 203.90 | 27.50 |
| L16A | 41.45 | 30.00 | 3.00 | 3.20 | 139.60 | 70,873 | 209.80 | 217.40 | 242.50 | 19.50 |
| L17A | 93.75 | 19.00 | 4.00 | 4.00 | 265.20 | 68,796 | 212.40 | 224.60 | 255.50 | 13.50 |
| L18B | 53.10 | 40.10 | 2.45 | 2.45 | 146.10 | 62,761 | 229.40 | 234.60 | 258.90 | 31.30 |
| L20A | 42.90 | 23.50 | 4.30 | 4.10 | 146.60 | 64,090 | 198.10 | 202.06 | 225.20 | 30.60 |
| L21A | 47.70 | 34.10 | 5.85 | 5.85 | 143.00 | 65,321 | 286.00 | 293.50 | 323.70 | 26.90 |
| L24A | 77.50 | 72.85 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 239.00 | 65,125 | 182.10 | 186.70 | 203.90 | 27.50 |
| L25B | 52.20 | 39.50 | 1.90 | 1.85 | 167.80 | 65,125 | 182.10 | 186.70 | 203.90 | 27.50 |
| L26A | 77.00 | 38.35 | 2.00 | 1.90 | 219.35 | 65,125 | 182.10 | 186.70 | 203.90 | 27.50 |
| L30A | 79.70 | 70.65 | 4.00 | 4.10 | 242.00 | 71,733 | 189.20 | 194.20 | 220.30 | 26.80 |
| L32A | 59.55 | 47.10 | 5.85 | 5.75 | 175.75 | 65,321 | 286.00 | 293.50 | 323.70 | 26.90 |
| Specimen | Nu,Exp (kN) | Nu,FE (kN) | Νu,Exp/Nu,FE |
|---|---|---|---|
| L4A | 34.94 | 35.49 | 0.98 |
| L5A | 51.15 | 50.20 | 1.02 |
| L6A | 65.25 | 67.28 | 0.97 |
| L8A | 38.17 | 37.53 | 1.02 |
| L9A | 38.92 | 37.85 | 1.03 |
| L10A | 37.05 | 36.03 | 1.03 |
| L11A | 54.79 | 54.68 | 1.00 |
| L13A | 50.83 | 49.88 | 1.02 |
| L14A | 15.04 | 15.45 | 0.97 |
| L15A | 16.58 | 17.05 | 0.97 |
| L16A | 51.54 | 50.10 | 1.03 |
| L17A | 51.23 | 54.88 | 0.93 |
| L18B | 30.73 | 33.63 | 0.91 |
| L20A | 50.79 | 51.69 | 0.98 |
| L21A | 142.18 | 138.26 | 1.03 |
| L24A | 21.48 | 21.29 | 1.01 |
| L25B | 17.66 | 18.13 | 0.97 |
| L26A | 18.43 | 19.04 | 0.97 |
| L30A | 81.21 | 83.04 | 0.98 |
| L32A | 176.18 | 168.69 | 1.04 |
| mean | 0.99 | ||
| COV | 0.03 |
| Total FE Analyses: 42 | |
|---|---|
| 2 aluminium alloys | 6063-T5 6082-T6 |
| 3 aspect ratios α/b (α × b) | 1.0 (120 × 120), L = 360 mm 1.5 (120 × 80), L = 360 mm 2.0 (120 × 60), L = 360 mm |
| 7 thicknesses ta = tb (mm) | 6, 10, 14, 18, 22, 26, 30 |
| Resulting slenderness | |
| β/ε: 2.43–20.39 | |
| : 0.29–2.46 |
| E (MPa) | σ0.2 (MPa) | σt (MPa) | n | εu (mm/mm) | εf (mm/mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6063-T5 | 69,000 | 164 | 211 | 10.0 | 7.28 | 13.65 |
| 6082-T6 | 66,805 | 290 | 312 | 55.4 | 7.30 | 9.19 |
| Nu/Npred | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Experiments [3] | No FE | Mean | COV | |
| Stocky cross-sections | ||||
| EC9 [5] (Classes 1–3) | 0 | 21 | 1.11 | 0.09 |
| AA [6] (b/t < S2) | 28 | 33 | 1.10 | 0.10 |
| CSM [8] ≤ 0.68) | 1 | 22 | 1.03 | 0.05 |
| DSM [9] ≤ 0.776) | 4 | 26 | 1.08 | 0.09 |
| ≤ 0.90) | 4 | 27 | 1.08 | 0.09 |
| Slender cross-sections | ||||
| EC9 [5] (Class 4) | 61 | 21 | 1.22 | 0.12 |
| AA [6] (b/t ≥ S2) | 33 | 9 | 2.03 | 0.44 |
| CSM [8] > 0.68) | 60 | 20 | 1.42 | 0.18 |
| DSM [9] > 0.776) | 57 | 16 | 1.24 | 0.13 |
| > 0.90) | 57 | 15 | 1.09 | 0.11 |
| All cross-sections | ||||
| EC9 [5] (All) | 61 | 42 | 1.20 | 0.12 |
| AA [6] (All) | 61 | 42 | 1.48 | 0.50 |
| CSM [8] (All) | 61 | 42 | 1.33 | 0.21 |
| DSM [9] (All) | 61 | 42 | 1.19 | 0.13 |
| modified DSM (All) | 61 | 42 | 1.09 | 0.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgantzia, E.; Gkantou, M.; Kamaris, G.S. Numerical Modelling and Design of Aluminium Alloy Angles under Uniform Compression. CivilEng 2021, 2, 632-651. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng2030035
Georgantzia E, Gkantou M, Kamaris GS. Numerical Modelling and Design of Aluminium Alloy Angles under Uniform Compression. CivilEng. 2021; 2(3):632-651. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng2030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgantzia, Evangelia, Michaela Gkantou, and George S. Kamaris. 2021. "Numerical Modelling and Design of Aluminium Alloy Angles under Uniform Compression" CivilEng 2, no. 3: 632-651. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng2030035
APA StyleGeorgantzia, E., Gkantou, M., & Kamaris, G. S. (2021). Numerical Modelling and Design of Aluminium Alloy Angles under Uniform Compression. CivilEng, 2(3), 632-651. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng2030035







