Influence of Processing Parameters on Laser-Assisted Reactive Sintering of a Mixture of Ni and Ti Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
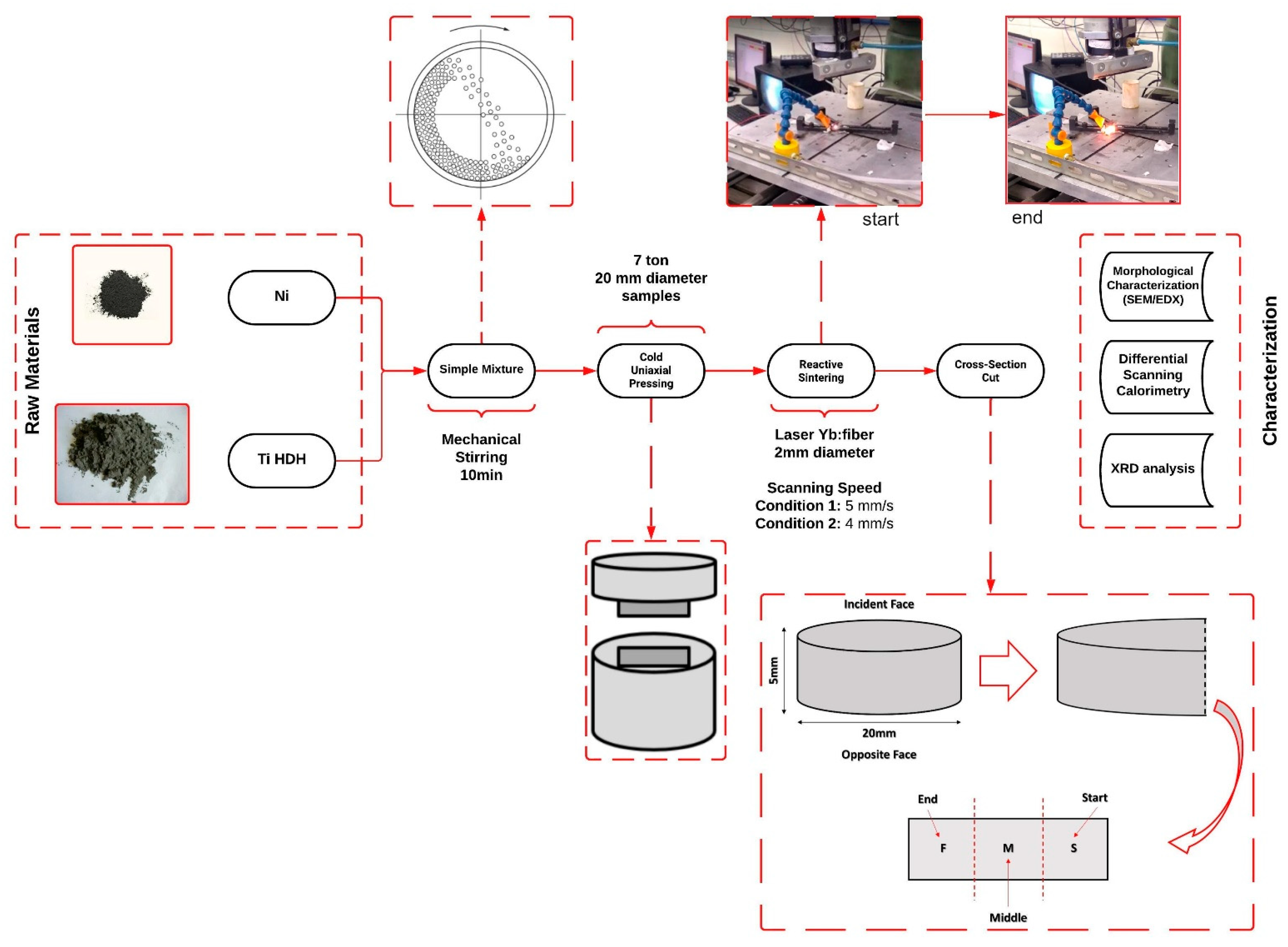
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Processing and Characterization of Ni-Ti Samples
3. Results and Discussion
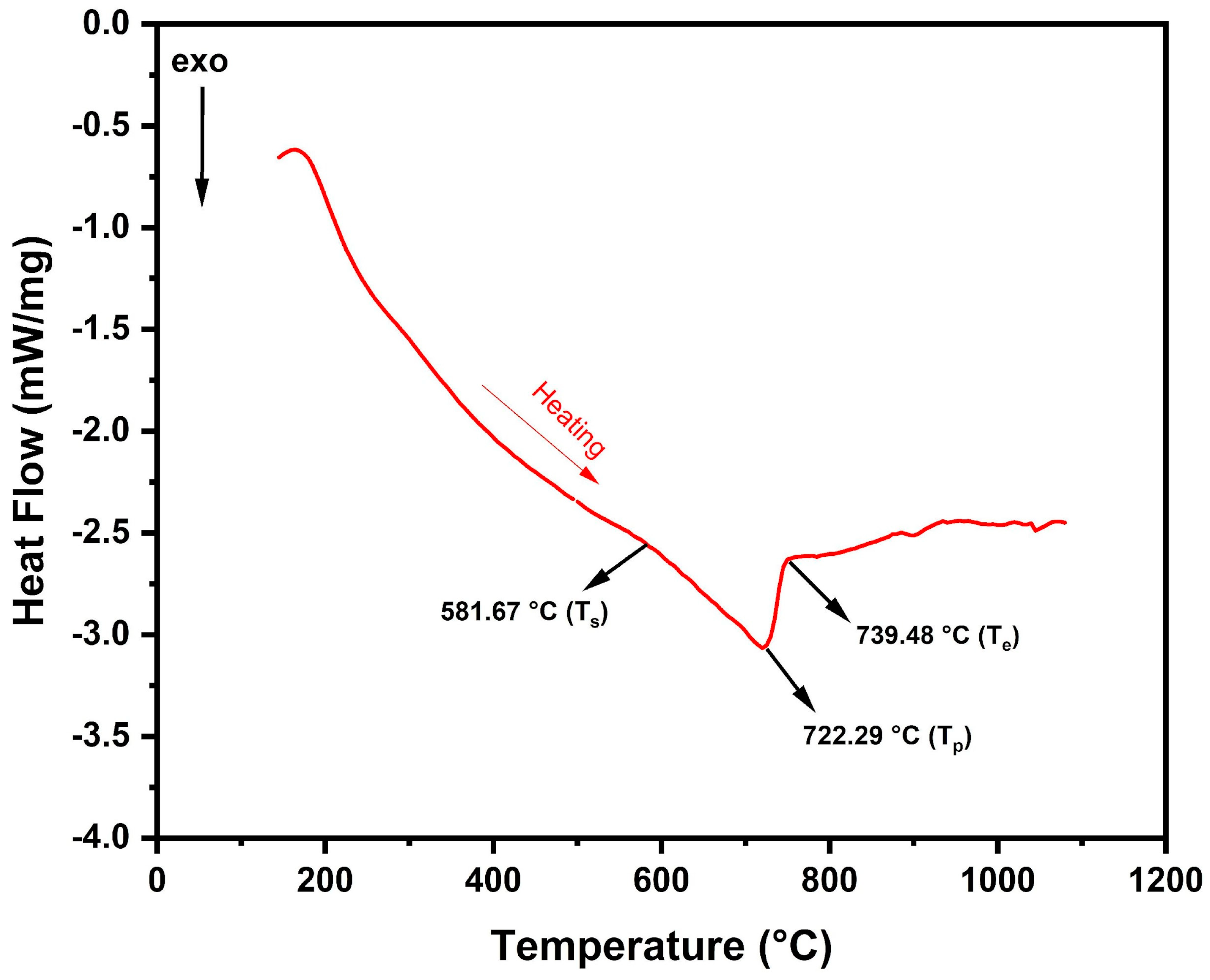
3.1. Powder Characterization
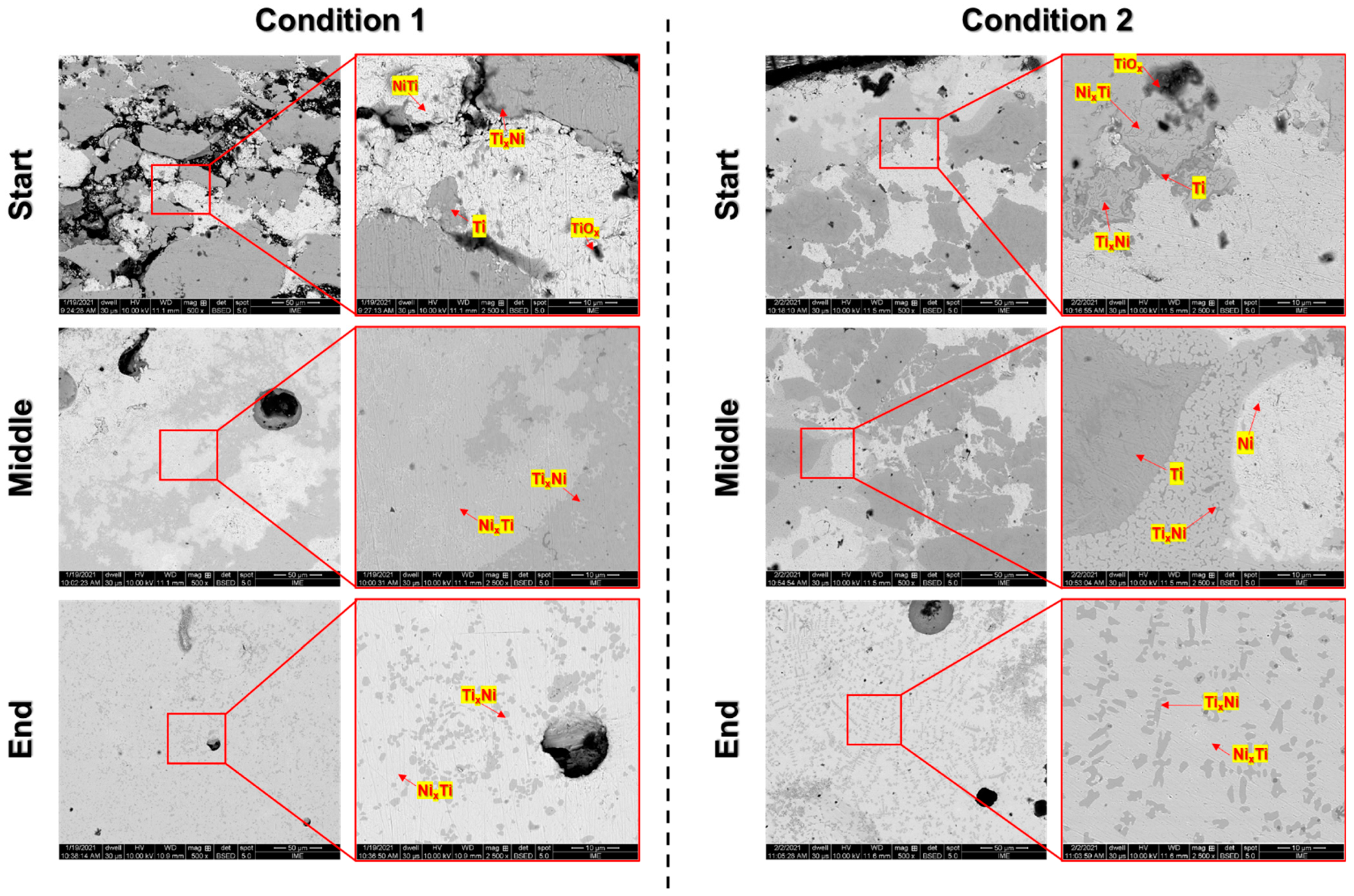
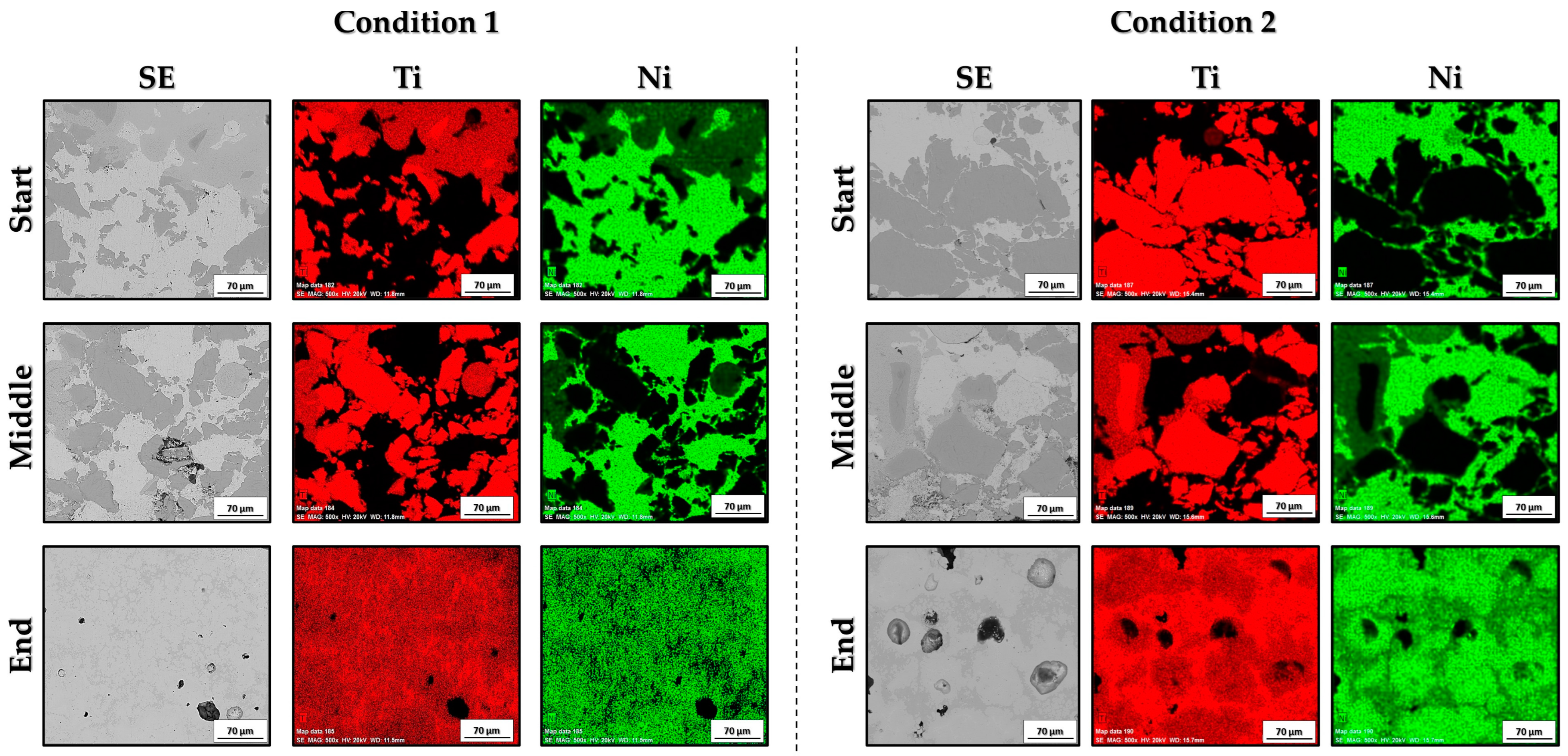
3.2. Microstructural and Morphological Characterization of Sintered Bodies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | Additive Manufacturing |
| BSE | Backscattering Electrons |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| EDX | Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometry |
| HDH | Hydride-Dehydrogenation Process |
| IEAv | Instituto de Estudos Avançados |
| IPT | Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas do Estado de São Paulo |
| Ni | Nickel |
| PM | Powder Metallurgy |
| RS | Reactive Sintering |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SHS | Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis |
| SM | Simple Mixture |
| SMA | Shape Memory Alloys |
| Ti | Titanium |
| VAR | Vacuum Arc Remelting |
| VIM | Vacuum Induction Melting |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
References
- Safaei, K.; Andani, N.T.; Nematollahi, M.; Benafan, O.; Poorganji, B.; Elahinia, M. The Build Orientation Dependency of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy Processed by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2022, 8, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaparova, E.; Heller, L.; Tyc, O.; Sittner, P. Thermally induced reorientation and plastic deformation of B19’ monoclinic martensite in nanocrystalline NiTi wires. Acta Mater. 2023, 242, 118477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Jangra, K.K.; Raj, T. Fabrication of NiTi alloy: A review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2015, 232, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, J.; Vahdat-Pajouh, N.; Schäfer, E. New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys—A review. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1088–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnina, N.; Palani, I.; Belyaev, S.; Prabu, S.M.; Liulchak, P.; Karaseva, U.; Manikandan, M.; Jayachandran, S.; Bryukhanova, V.; Sahu, A.; et al. Structure, martensitic transformations and mechanical behaviour of NiTi shape memory alloy produced by wire arc additive manufacturing. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 851, 156851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Peng, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wen, Y. Effect of Second Phase Precipitation On Martensitic Transformation and Hardness in Highly Ni-Rich NiTi Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 739, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Michalcová, A.; Marek, I.; Mudrová, M.; Saksl, K.; Bednarčík, J.; Zikmund, P.; Vojtěch, D. On the formation of intermetallics in Fe–Al system—An in situ XRD study. Intermetallics 2013, 32, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahinia, M.H.; Hashemi, M.; Tabesh, M.; Bhaduri, S.B. Manufacturing and processing of NiTi implants: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 911–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, J.; Mannschatz, A.; Teuber, R.; Müller, B.; Al Noaimy, O.; Riecker, S.; Thielsch, J.; Matthey, B.; WEIßGÄRBER, T. Fused Filament Fabrication of NiTi Components and Hybridization with Laser Powder Bed Fusion for Filigree Structures. Materials 2021, 14, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bram, M.; Ahmad-Khanlou, A.; Heckmann, A.; Fuchs, B.; Buchkremer, H.; Stöver, D. Powder metallurgical fabrication processes for NiTi shape memory alloy parts. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 337, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, S.; Hashemi, S.M.; Asgarinia, F.; Nematollahi, M.; Elahinia, M. Effective parameters on the final properties of NiTi-based alloys manufactured by powder metallurgy methods: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, C.; Giuliani, P.; Terrosu, A.; Gennari, S.; Maglia, F. Porous Ni–Ti ignition and combustion synthesis. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Veronesi, P.; Leonelli, C. Use of combustion synthesis/self-propagating high- temperature synthesis (SHS) for the joining of similar/dissimilar materials. In Woodhead Publishing Reviews: Mechanical Engineering Series, Joining Processes for Dissimilar and Advanced Materials; Pawan Rakesh, J., Paulo, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022; pp. 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.N. 2-Kinetics and mechanisms of densification. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Metals and Surface Engineering, Sintering of Advanced Materials; Fang, Z.Z., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2010; pp. 33–64. ISBN 9781845695620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosewicz, S. Discrete Element Modeling of Powder Metallurgy Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut of Fundamental Technological Research, Polish Academy of Sciences, Warszawa, Poland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Novák, P.; Pokorný, P.; Vojtěch, V.; Knaislová, A.; Školáková, A.; Čapek, J.; Karlík, M.; Kopeček, J. Formation of Ni–Ti intermetallics during reactive sintering at 500–650 °C. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 155, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Mejzlíková, L.; Michalcová, A.; Čapek, J.; Beran, P.; Vojtěch, D. Effect of SHS conditions on microstructure of NiTi shape memory alloy. Intermetallics 2013, 42, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Kadlecová, B.; Salvetr, P.; Knaislová, A.; Školáková, A.; Karlík, M.; Kopeček, J. Effect of Reaction Atmosphere and Heating Rate During Reactive Sintering of Ni–Ti Intermetallics. Procedia Eng. 2017, 184, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Mohammadi, K.; Movahhedy, M.R.; Karimi, F.; Sadrnezhaad, S.K.; Chernyshikhin, S.V.; Shishkovsky, I.V. SLM Additive Manufacturing of NiTi Porous Implants: A Review of Constitutive Models, Finite Element Simulations, Manufacturing, Heat Treatment, Mechanical, and Biomedical Studies. Met. Mater. Int. 2023, 29, 2458–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junio, R.F.P.; da Silveira, P.H.P.M.; Neuba, L.d.M.; Monteiro, S.N.; Nascimento, L.F.C. Development and Applications of 3D Printing-Processed Auxetic Structures for High-Velocity Impact Protection: A Review. Eng 2023, 4, 903–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namlu, R.H.; Lotfi, B.; Kılıç, S.E.; Yılmaz, O.D.; Akar, S. Combined Use of Ultrasonic-Assisted Drilling and Minimum Quantity Lubrication for Drilling of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy. Mach. Sci. Technol. 2023, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, M.S.; Bordbar-Khiabani, A.; Walsh, F.C.; Mozafari, M.; Khalil-Allafi, J. Surface Modified NiTi Smart Biomaterials: Surface Engineering and Biological Compatibility. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 25, 100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Vojtěch, V.; Pecenová, Z.; Průša, F.; Pokorný, P.; Deduytsche, D.; Detavernier, C.; Bernatiková, A.; Salvetr, P.; Knaislová, A.; et al. Formation of Ni-Ti intermetallics during reactive sintering at 800–900 °C. Mater. Teh. 2017, 51, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina, H.; Surreddi, K.B.; Iyengar, S. Phase evolution during the reactive sintering of ternary Al–Ni–Ti powder compacts. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 661, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Yao, S.; Song, X.; Qi, Q. Effect of Ni on the formation mechanism of TiC/Ni composites fabricated by reactive sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 100, 105611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, J.; Nobre, R.d.M.; Nunes, E.R.; Bayerlein, D.; Falcão, R.; Sallica-Leva, E.; Neto, J.B.F.; Oliveira, H.R.; Chastinet, V.L.; Landgraf, F.J. Laser powder bed fusion parameters to produce high-density Ti–53%Nb alloy using irregularly shaped powder from hydride-dehydride (HDH) process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Asherloo, M.; Jiang, R.; Delpazir, M.H.; Sivakumar, N.; Paliwal, M.; Capone, J.; Gould, B.; Rollett, A.; Mostafaei, A. Study of printability and porosity formation in laser powder bed fusion built hydride-dehydride (HDH) Ti-6Al-4V. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 47, 102323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liss, K.-D.; Cao, P. An In Situ Study of Sintering Behavior and Phase Transformation Kinetics in NiTi Using Neutron Diffraction. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 5887–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, M.; Corbin, S.; Gorbet, R. Investigation of the mechanisms of reactive sintering and combustion synthesis of NiTi using differential scanning calorimetry and microstructural analysis. Acta Mater. 2007, 56, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.V.; de Lima, Y.P.; Sallet, E.H.; Gonçalves, D.A.C.; Le Sénèchal, N.V.; Melo, E.A.O.; Teixeira, R.; Rodrigues, P.F.; Neto, P.I.; da Silva, J.V.L.; et al. Production of Cylindrical Specimens Based on the Ni-Ti System by Selective Laser Melting from Elementary Powders. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 5477–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qi, Q.; Ma, M.; Han, R.; Shang, Q.; Yao, S. The formation mechanism of TiC/Ni composites fabricated by pressureless reactive sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 97, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F. Ceramic-matrix composites via in-situ reaction sintering. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual Conference on Composites and Advanced Ceramic Materials; Part 2 of 2; John Wiley & Sons: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2009; p. 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yang, X.; Hu, F.; Deng, S.; Cui, Z. Processing of porous TiNi shape memory alloy from elemental powders by Ar-sintering. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 2369–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ni | Ti | Fe | O |
| 55.2 | 44.3 | 0.102 | 0.290 |
| Al | C | S | N |
| 0.0148 | 0.091 | 0.015 | 0.0066 |
| Magnification/Voltage | Ti (wt.%) | Ni (wt.%) | Ti (at.%) | Ni (at.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50×/30 keV | 37.76 | 62.24 | 42.65 | 57.35 |
| 500×/30 keV | 35.58 | 64.42 | 40.37 | 59.63 |
| 50×/20 keV | 31.70 | 68.30 | 36.26 | 63.74 |
| 500×/20 keV | 25.71 | 74.29 | 29.79 | 70.21 |
| Condition 1 (5 mm/s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regions | Ti (wt.%) | Ni (wt.%) | Ti (at.%) | Ni (at.%) |
| Start | 54.47 | 45.53 | 59.45 | 40.55 |
| Middle | 50.77 | 49.23 | 55.84 | 44.16 |
| End | 50.74 | 49.26 | 55.80 | 44.20 |
| Condition 2 (4 mm/s) | ||||
| Ti (wt.%) | Ni (wt.%) | Ti (at.%) | Ni (at.%) | |
| Start | 59.17 | 40.83 | 63.98 | 36.02 |
| Middle | 53.38 | 46.62 | 58.39 | 41.61 |
| End | 49.84 | 50.16 | 54.92 | 45.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Sénéchal, N.V.; da Silveira, P.H.P.M.; Rodrigues, P.F.; Gonçalves, D.A.C.; Dyer, S.A.S.; Teixeira, R.d.S.; de Siqueira, R.H.M.; de Lima, M.S.F.; Bayerlein, D.L.; Paula, A.d.S. Influence of Processing Parameters on Laser-Assisted Reactive Sintering of a Mixture of Ni and Ti Powders. Eng 2024, 5, 1451-1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030077
Le Sénéchal NV, da Silveira PHPM, Rodrigues PF, Gonçalves DAC, Dyer SAS, Teixeira RdS, de Siqueira RHM, de Lima MSF, Bayerlein DL, Paula AdS. Influence of Processing Parameters on Laser-Assisted Reactive Sintering of a Mixture of Ni and Ti Powders. Eng. 2024; 5(3):1451-1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030077
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Sénéchal, Naiara Vieira, Pedro Henrique Poubel Mendonça da Silveira, Patrícia Freitas Rodrigues, Danilo Abílio Corrêa Gonçalves, Silvelene Alessandra Silva Dyer, Rodolfo da Silva Teixeira, Rafael Humberto Mota de Siqueira, Milton Sergio Fernandes de Lima, Daniel Leal Bayerlein, and Andersan dos Santos Paula. 2024. "Influence of Processing Parameters on Laser-Assisted Reactive Sintering of a Mixture of Ni and Ti Powders" Eng 5, no. 3: 1451-1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030077
APA StyleLe Sénéchal, N. V., da Silveira, P. H. P. M., Rodrigues, P. F., Gonçalves, D. A. C., Dyer, S. A. S., Teixeira, R. d. S., de Siqueira, R. H. M., de Lima, M. S. F., Bayerlein, D. L., & Paula, A. d. S. (2024). Influence of Processing Parameters on Laser-Assisted Reactive Sintering of a Mixture of Ni and Ti Powders. Eng, 5(3), 1451-1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030077









