Assessing Digestate at Different Stabilization Stages: Application of Thermal Analysis and FTIR Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Analytical Techniques
3. Results and Discussion
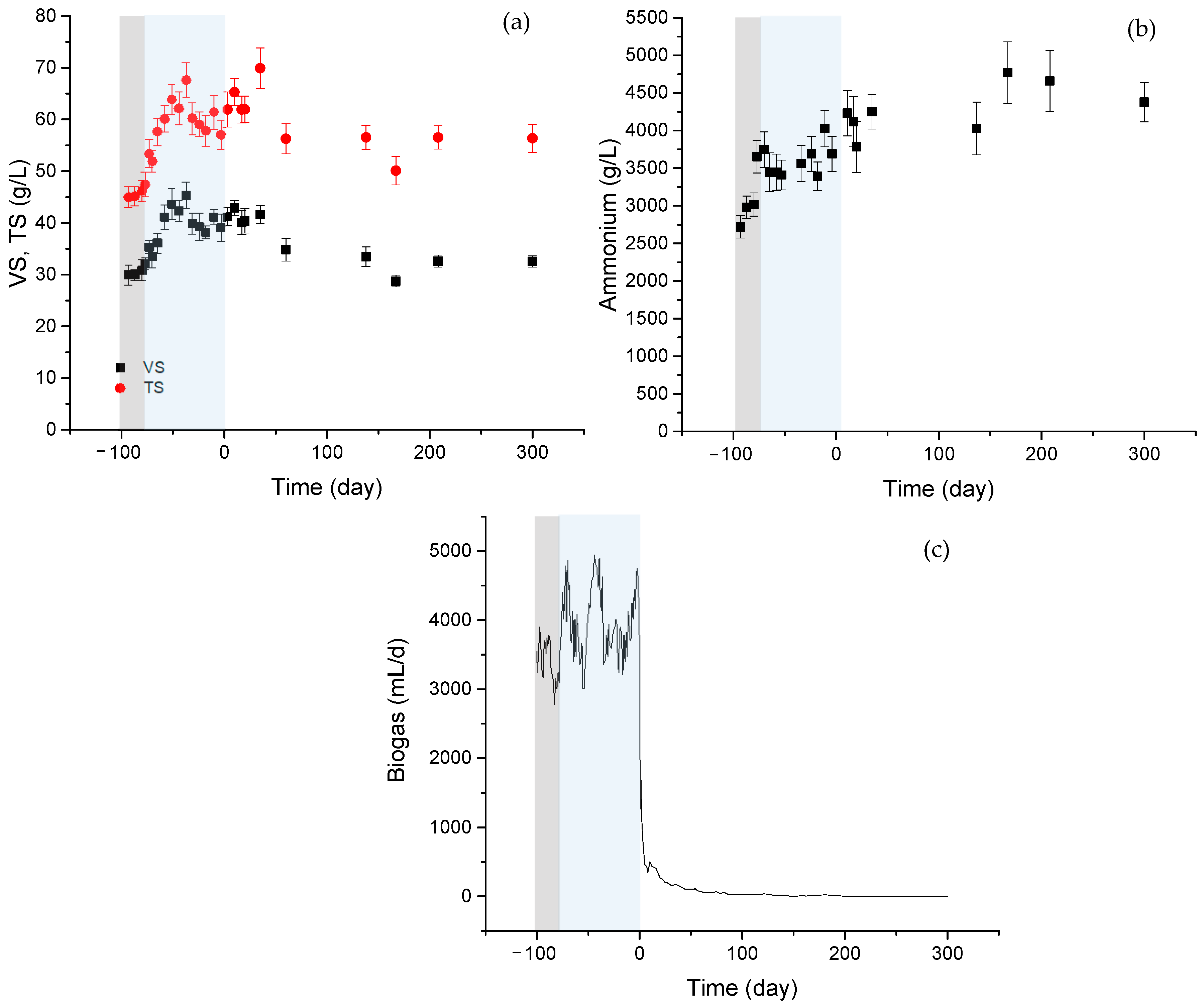
3.1. Digestion and Stabilization Period
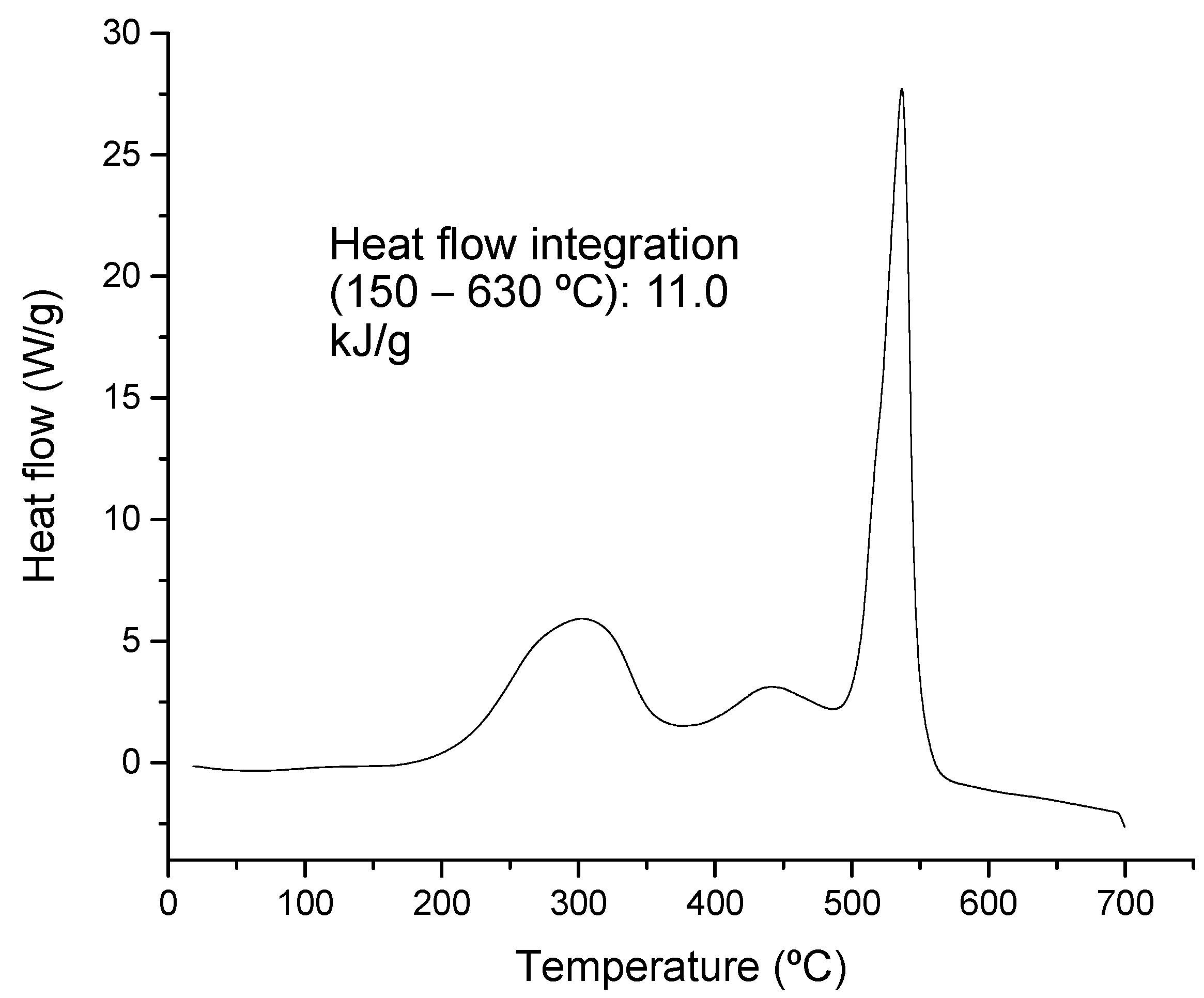
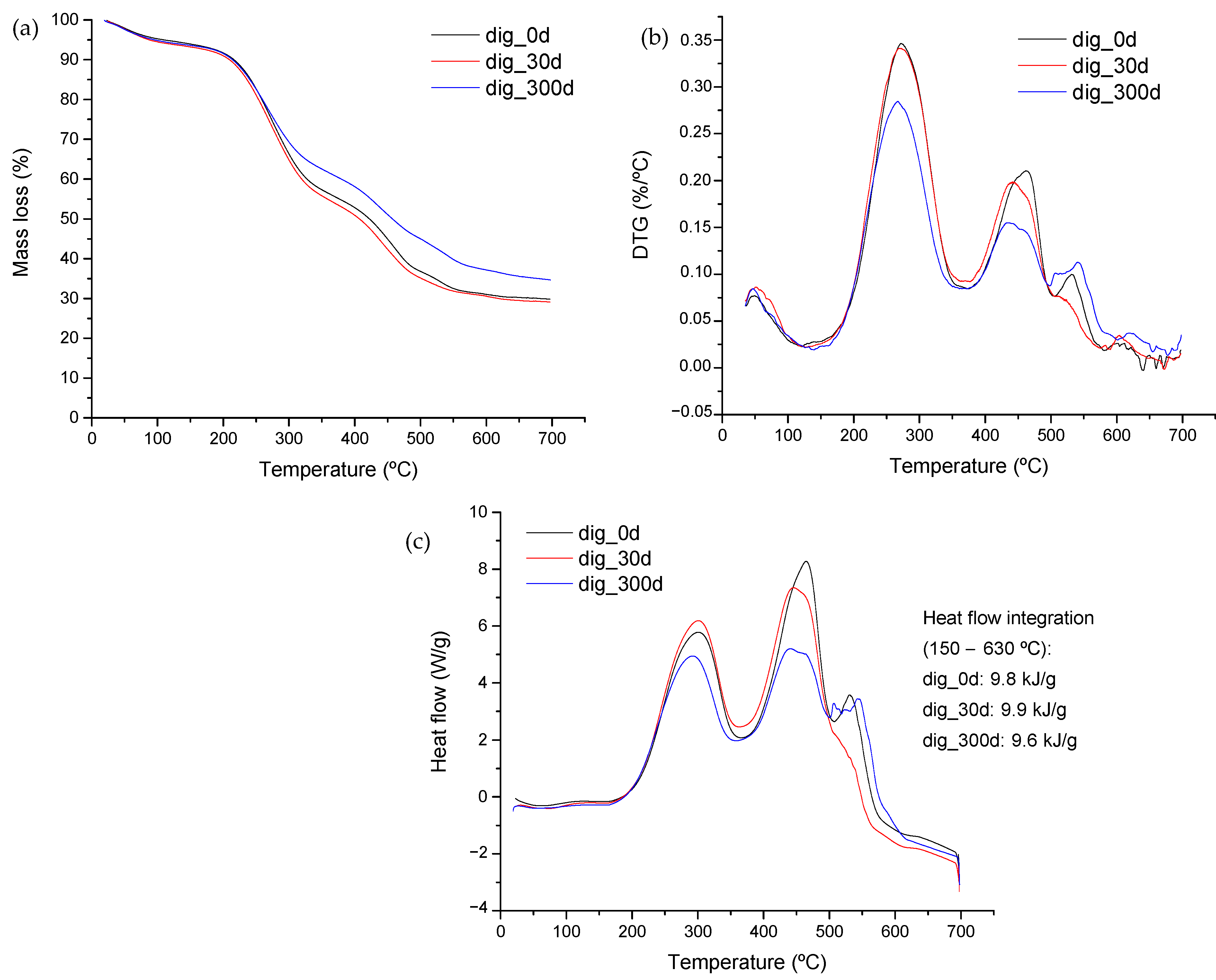
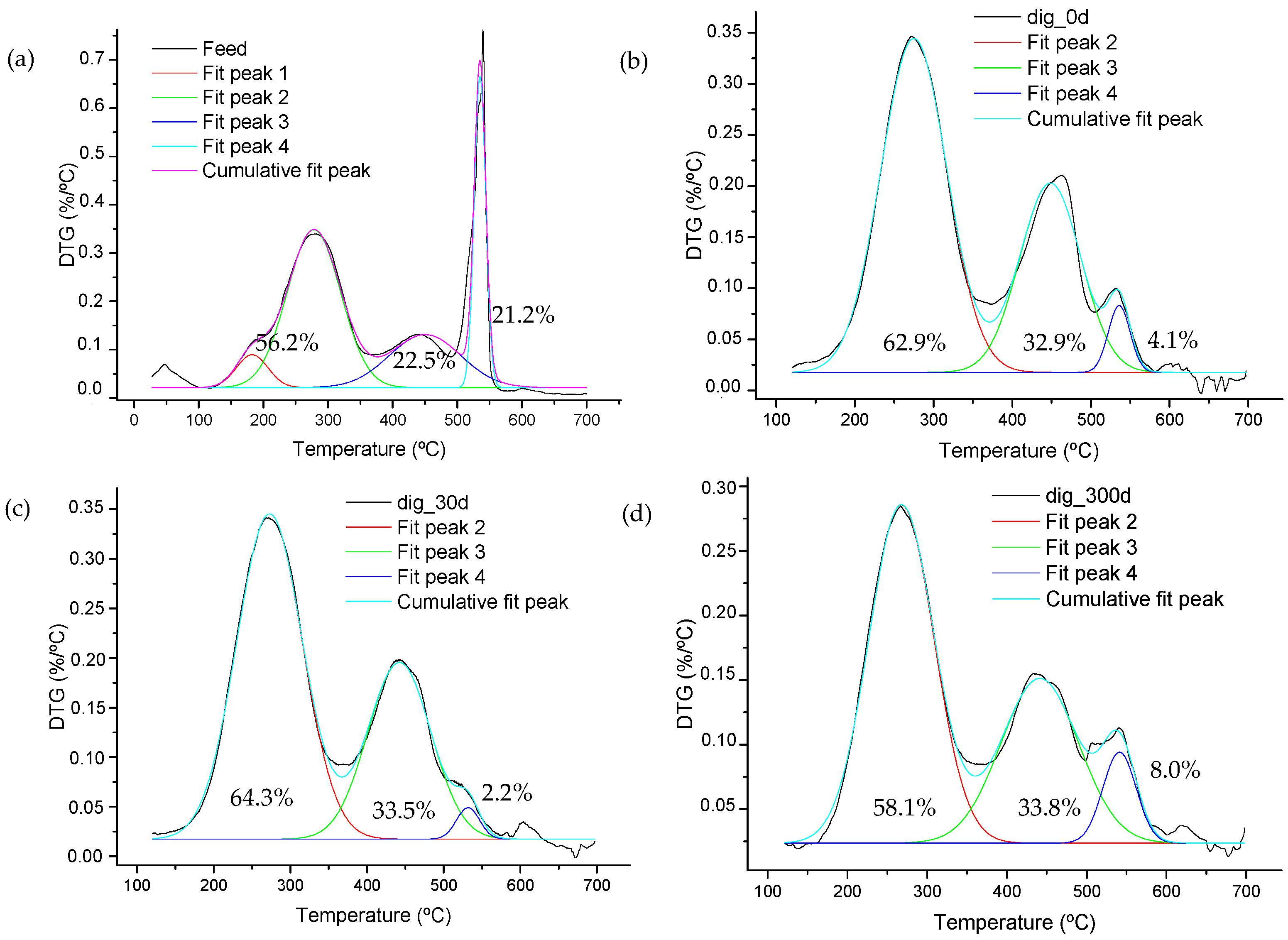
3.2. Thermal Analysis
3.3. Estimation of Activation Energy
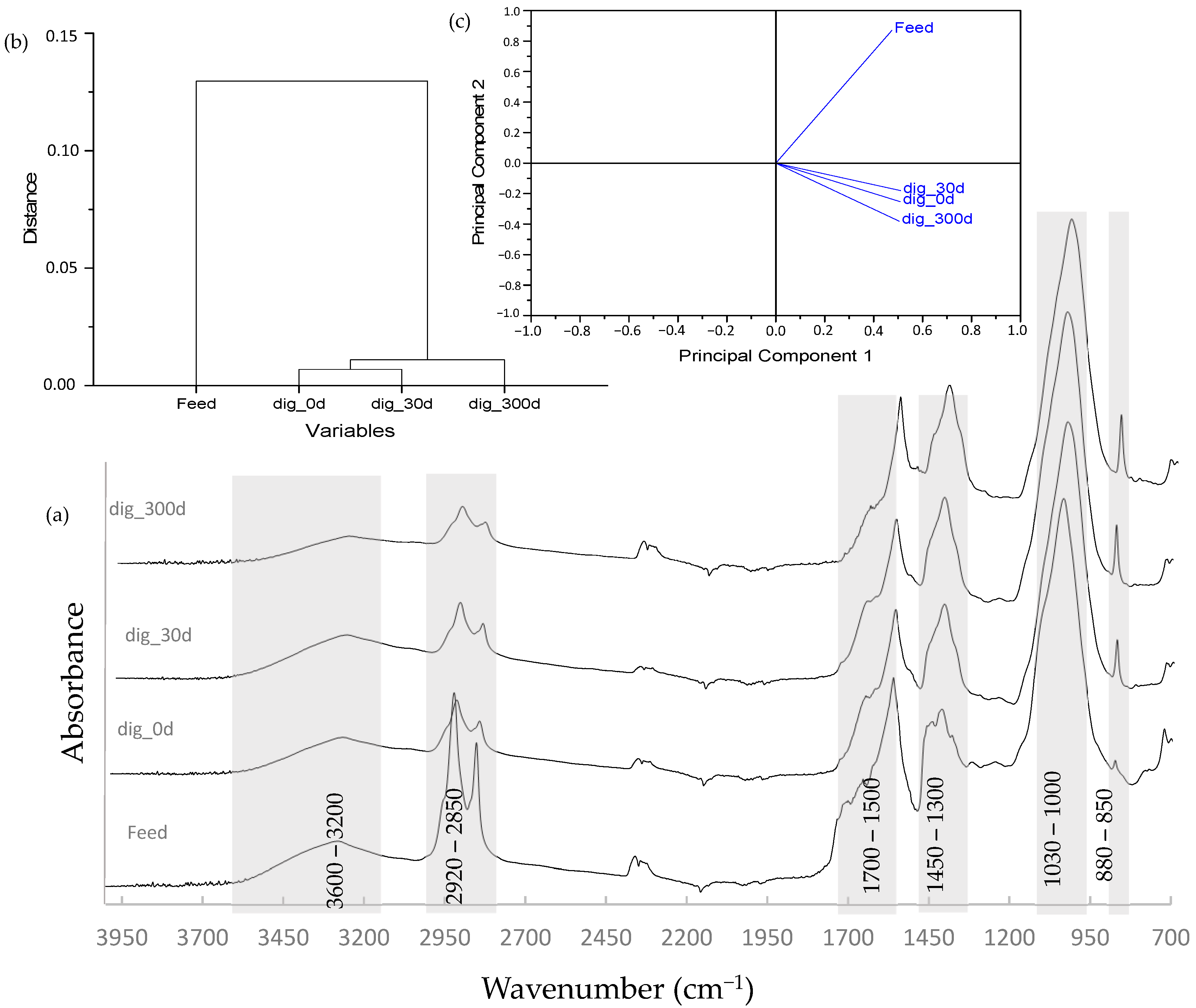
3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González, R.; García-Cascallana, J.; Gómez, X. Energetic valorization of biogas. A comparison between centralized and decentralized approach. Renew. Energy 2023, 215, 119013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crolla, A.; Kinsley, C.; Pattey, E. Land application of digestate. In The Biogas Handbook; Wellinger, A., Murphy, J., Baxter, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuccio, M.R.; Romeo, F.; Mallamaci, C.; Muscolo, A. Digestate application on two different soils: Agricultural benefit and risk. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 4341–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepetiene, A.; Kochiieru, M.; Jurgutis, L.; Mankeviciene, A.; Skersiene, A.; Belova, O. The Effect of Anaerobic Digestate on the Soil Organic Carbon and Humified Carbon Fractions in Different Land-Use Systems in Lithuania. Land 2022, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-López, A.M.; Delgado, A.; Anjos, O.; Horta, C. Digestate Not Only Affects Nutrient Availability but Also Soil Quality Indicators. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Environmental sustainability assessment of pig manure mono-and co-digestion and dynamic land application of the digestate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Domínguez, D.; Guilayn, F.; Patureau, D.; Jimenez, J. Characterising the stability of the organic matter during anaerobic digestion: A selective review on the major spectroscopic techniques. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. 2022, 21, 691–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Domínguez, D.; Patureau, D.; Jimenez, J. Impact of Substrate Biodegradability on the Identification of Endogenous Compounds During Anaerobic Digestion. Waste Biomass Valorization 2024, 15, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.; Sánchez, M.E.; Gómez, X. Enhancing Anaerobic Digestion: The Effect of Carbon Conductive Materials. C 2018, 4, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; Peña, D.C.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Wastes: Reviewing Current Status and Approaches for Enhancing Biogas Production. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadaleta, G.; De Gisi, S.; Notarnicola, M. Feasibility Analysis on the Adoption of De-centralized Anaerobic Co-Digestion for the Treatment of Municipal Organic Waste with Energy Recovery in Urban Districts of Metropolitan Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellacuriaga, M.; González, R.; Gómez, X. Is Decentralized Anaerobic Digestion a Solution? Analyzing Biogas Production and Residential Energy Demand. Eng 2022, 3, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, R.; García-Cascallana, J.; Gutiérrez-Bravo, J.; Gómez, X. Decentralized Bio-gas Production in Urban Areas: Studying the Feasibility of Using High-Efficiency Engines. Eng 2023, 4, 2204–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, G.M.; Andersen, D.S.; Martens, B.J.; Raman, D.R. Cost Assessment of Centralizing Swine Manure and Corn Stover Co-Digestion Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, O.; de la Rosa, J.M.; González-Pérez, J.A.; Knicker, H.; Pezzolla, D.; Gigliotti, G.; Provenzano, M.R. Molecular characterization of digestates from solid-state anaerobic digestion of pig slurry and straw using analytical pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2018, 134, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, X.; Blanco, D.; Lobato, A.; Calleja, A.; Martínez-Núñez, F.; Martin-Villacorta, J. Digestion of cattle manure under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions: Characterization of organic matter applying thermal analysis and 1 H NMR. Biodegradation 2011, 22, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monlau, F.; Sambusiti, C.; Ficara, E.; Aboulkas, A.; Barakat, A.; Carrère, H. New opportunities for agricultural digestate valorization: Current situation and perspectives. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2600–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arias, J.; Gil, M.V.; Fernández, R.Á.; Martínez, E.J.; Fernández, C.; Papaharalabos, G.; Gómez, X. Integrating anaerobic digestion and pyrolysis for treating digestates derived from sewage sludge and fat wastes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32603–32614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubonova, L.; Janakova, I.; Malikova, P.; Drabinova, S.; Dej, M.; Smelik, R.; Skalny, P.; Heviankova, S. Evaluation of Waste Blends with Sewage Sludge as a Potential Material Input for Pyrolysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untoria, S.; Rouboa, A.; Monteiro, E. Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production from Gasification of Sewage Sludge: Catalonia Case. Energies 2024, 17, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, R. Cost-effective production of Bacillus thuringiensis biopesticides by solid-state fermentation using wastewater sludge: Effects of heavy metals. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4820–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Bueis, R.; Mulas, R.; Gómez, X.; González-Andrés, F. Innovative liquid formulation of digestates for producing a biofertilizer based on Bacillus siamensis: Field testing on sweet pepper. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2017, 180, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Frison, N.; Pavan, P.; Cavinato, C.; Gottardo, M.; Fatone, F.; Eusebi, A.L.; Majone, M.; Zeppilli, M.; Valentino, F.; et al. Food wastes and sewage sludge as feedstock for an urban biorefinery producing biofuels and added-value bioproducts. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chang, J.S.; Lee, D.J. Anaerobic digestate valorization beyond agricultural application: Current status and prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 373, 128742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamolinara, B.; Pérez-Martínez, A.; Guardado-Yordi, E.; Fiallos, C.G.; Diéguez-Santana, K.; Ruiz-Mercado, G.J. Anaerobic digestate management, environmental impacts, and techno-economic challenges. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizia, P.; Neofytou, N.; Zorpas, A.A. The concept of circular economy strategy in food waste management for the optimization of energy production through anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14766–14773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellacuriaga, M.; García-Cascallana, J.; Gómez, X. Biogas Production from Organic Wastes: Integrating Concepts of Circular Economy. Fuels 2021, 2, 144–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, S. Post-treatment of food waste digestate towards land application: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 303, 127033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radetic, B. Solar Sludge Drying. In Handbook of Water and Used Water Purification; Lahnsteiner, J., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathioudakis, V.L.; Kapagiannidis, A.G.; Athanasoulia, E.; Diamantis, V.I.; Melidis, P.; Aivasidis, A. Extended dewatering of sewage sludge in solar drying plants. Desalination 2009, 248, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An-nori, A.; Ezzariai, A.; El Mejahed, K.; El Fels, L.; El Gharous, M.; Hafidi, M. Solar drying as an eco-friendly Technology for sewage sludge stabilization: Assessment of micropollutant behavior, pathogen removal, and agronomic value. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 814590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, J.; Martínez, E.J.; Rosas, J.G.; Blanco, D.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic codigestion of poultry manure and sewage sludge under solid-phase configuration. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2014, 33, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobato, A.; Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Morán, A. Improvement of biogas production by co-digestion of swine manure and residual glycerine. Biofuels 2010, 1, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, J.; Martinez, E.J.; Rosas, J.G.; Fernández, R.A.; López, R.; Gomez, X. Co-Digestion of swine manure and crude glycerine: Increasing glycerine ratio results in preferential degradation of labile compounds. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environmental Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- González, R.; Smith, R.; Blanco, D.; Fierro, J.; Gómez, X. Application of thermal analysis for evaluating the effect of glycerine addition on the digestion of swine manure. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 135, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, X.; Bernal, M.P.; Zárate, P.P.; Álvarez-Robles, M.J.; González, R.; Clemente, R. Thermal evaluation of plant biomass from the phytostabilisation of soils contaminated by potentially toxic elements. Chemosphere 2023, 342, 140116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodampola, R.; Amarasingha, S.; Attygalle, D.; Weragoda, S. Improved method to extract kinetic parameters from thermograms. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 23, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas, C.B.; Meredith, W.; Snape, C.E.; Gómez, X.; González, J.F.; Martinez, E.J. Effect of char addition on anaerobic digestion of animal by-products: Evaluating biogas production and process performance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24387–24399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Siurana, A.; Marcilla, A.; Beltrán, M.; Berenguer, D.; Martínez-Castellanos, I.; Catalá, L.; Menargues, S. TGA/FTIR study of the MCM-41-catalytic pyrolysis of tobacco and tobacco–glycerol mixtures. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 587, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Mata, J.; Lahoz-Ramos, C.; Bustamante, M.A.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Moral, R.; Santos, A.; Sáez, J.A.; Bernal, M.P. Thermal and spectroscopic analysis of organic matter degradation and humification during composting of pig slurry in different scenarios. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17357–17369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Sanchez, M.E.; Gómez, X.; Morán, A. Thermogravimetric analysis of biowastes during combustion. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Wei, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Deng, L. Thermal Decomposition Characteristics and Kinetic Analysis of Chicken Manure in Various Atmospheres. Agriculture 2022, 12, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Chong, C.T.; Mong, G.R.; Ng, J.-H.; Chong, W.W.F. Determination of Pyrolysis and Kinetics Characteristics of Chicken Manure Using Thermogravimetric Analysis Coupled with Particle Swarm Optimization. Energies 2023, 16, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.R.; Crespi, M.S.; Crnkovic, P.C.; Ribeiro, C.A. Pyrolysis, combustion and oxy-combustion studies of sugarcane industry wastes and its blends. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 121, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Ramzan, N.; Khan, R.U.; Durrani, A.K. Analysis of mixed cattle manure: Kinetics and thermodynamic comparison of pyrolysis and combustion processes. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 26, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, E.J.; González, R.; Ellacuriaga, M.; Gómez, X. Valorization of Fourth-Range Wastes: Evaluating Pyrolytic Behavior of Fresh and Digested Wastes. Fermentation 2022, 8, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; He, S.; Cheng, Z.; Guan, Y.; Yan, B.; Ma, W.; Leung, D.Y. Comparison of kinetic analysis methods in thermal decomposition of cattle manure by themogravimetric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; He, T.; Cao, H.; Yuan, Q. Cattle manure pyrolysis process: Kinetic and thermodynamic analysis with isoconversional methods. Renew. Energy 2017, 107, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharara, M.; Sadaka, S. Thermogravimetric analysis of swine manure solids obtained from farrowing, and growing-finishing farms. J. Sustain. Bioenergy Syst. 2014, 4, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Palacios, C.; Echegaray, M.; Mazza, G.; Rodriguez, R. Pyrolysis and combustion of regional agro-industrial wastes: Thermal behavior and kinetic parameters comparison. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2018, 190, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, R.; Cai, J. Kinetics and reaction chemistry of pyrolysis and combustion of tobacco waste. Fuel 2015, 156, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lopez, M.; Pedrosa-Castro, G.J.; Valverde, J.L.; Sanchez-Silva, L. Kinetic analysis of manure pyrolysis and combustion processes. Waste Manag. 2016, 58, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, M.; Lobato, A.; Cuetos, M.J.; Sánchez, M.E.; Gómez, X. Digestion of cattle manure: Thermogravimetric kinetic analysis for the evaluation of organic matter conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 3404–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, T.; Gil, M.V.; Gómez, X.; González-Andrés, F.; Morán, A. Characterization of different compost extracts using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and thermal analysis. Biodegradation 2008, 19, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Effect of microbiological inoculants DN-1 on lignocellulose degradation during co-composting of cattle manure with rice straw monitored by FTIR and SEM. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2016, 35, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokač Cvetnić, T.; Krog, K.; Benković, M.; Jurina, T.; Valinger, D.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Jurinjak Tušek, A. Application of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Monitoring and/or Control of Composting Processes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Morán, A.; Otero, M.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of poultry blood with OFMSW: FTIR and TG–DTG study of process stabilization. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Abalde, Á.; Gómez, X.; Blanco, D.; Cuetos, M.J.; Fernández, B.; Flotats, X. Study of thermal pre-treatment on anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste by TGA-MS and FTIR spectroscopy. Waste Manag. Res. 2013, 31, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Domínguez, D.; Patureau, D.; Houot, S.; Sertillanges, N.; Zennaro, B.; Jimenez, J. Prediction of organic matter accessibility and complexity in anaerobic digestates. Waste Manag. 2021, 136, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Provenzano, M.R.; Malerba, A.D.; Pezzolla, D.; Gigliotti, G. Chemical and spectroscopic characterization of organic matter during the anaerobic digestion and successive composting of pig slurry. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Cuetos, M.J.; Martínez, E.J.; Gómez, X. Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of cheese whey: Coupling H2 and CH4 production. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 81, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Fang, X.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Carmo, A.M.; Hundal, L.S.; Thompson, M.L. Molecular-scale heterogeneity of humic acid in particle-size fractions of two Iowa soils. Geoderma 2007, 140, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, S.; Jouraiphy, A.; Meddich, A.; El Gharous, M.; Winterton, P.; Hafidi, M. Structural study of humic acids during composting of activated sludge-green waste: Elemental analysis, FTIR and 13C NMR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuetos, M.J.; Gómez, X.; Otero, M.; Morán, A. Anaerobic digestion of solid slaughterhouse waste: Study of biological stabilization by Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetry combined with mass spectrometry. Biodegradation 2010, 21, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Gao, H.J.; Mao, J.; Chu, W.; Thompson, M.L. Biochemical stabilization of soil organic matter in straw-amended, anaerobic and aerobic soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, E.J.; Fierro, J.; Sánchez, M.E.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of FOG and sewage sludge: Study of the process by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 75, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafidi, M.; Amir, S.; Revel, J.C. Structural characterization of olive mill waster-water after aerobic digestion using elemental analysis, FTIR and 13C NMR. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2615–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, E.; Parravicini, V. Effect of sewage sludge treatment and additional aerobic post-stabilization revealed by infrared spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, E.J.; Gil, M.V.; Fernandez, C.; Rosas, J.G.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic codigestion of sludge: Addition of butcher’s fat waste as a cosubstrate for increasing biogas production. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Gaëtan, J.; Giura, P.; Azaïs, T.; Benzerara, K. Detection of biogenic amorphous calcium carbonate (ACC) formed by bacteria using FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 278, 121262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter 1 | Inoculum | Swine Manure | Glycerin |
|---|---|---|---|
| TS (g/L) | 22.6 ± 0.3 | 46.2 ± 0.6 | 990.8 ± 5.3 |
| VS (g/L) | 14.0 ± 0.4 | 32.1 ± 0.7 | 961.4 ± 5.7 |
| COD (g/L) | 30.5 ± 1.3 | 58.7 ± 1.9 | - |
| pH | 7.6 ± 0.2 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 10.0 ± 0.2 |
| Sample | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 | Peak 4 | Global 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pmax (°C) | Ea (kJ/mol) | Pmax (°C) | Ea (kJ/mol) | Pmax (°C) | Ea (kJ/mol) | Pmax (°C) | Ea (kJ/mol) | Ea (kJ/mol) | |
| feed 1 | 183 | 63.0 | 278 | 54.0 | 450 | 69.5 | 535 | 955 | 249.5 |
| dig_0d | - | - | 275 | 52.3 | 448 | 99.5 | 536 | 356.8 | 80.4 |
| dig_30d | - | - | 273 | 50.8 | 442 | 92.0 | 532 | 322.7 | 70.6 |
| dig_300d | - | - | 267 | 52.5 | 441 | 76.9 | 541 | 241.0 | 75.9 |
| Spectrum Signal (cm−1) | Main Components | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 3600–3200 | OH groups in phenol, carbohydrate, and carboxylic acid NH- of amines and amides | [63] |
| 2920 and 2850 | CH3- and -CH2- stretching in aliphatic structure | [64] |
| 1720 | C=O functional group of carboxylic acids | [58,65] |
| 1650–1620 | Amides groups and carboxylates (C=O stretching) | [66,67] |
| 1550–1520 | H-N and C-N in amides II Lignin-type structures (-CH2-vibrations) | [7] |
| 1440–1410 | CH bending in aliphatic structures O–H deformation C=O stretching of phenols and anti-symmetric COO-stretching | [68] |
| 1240 | C-N vibration (amide III), phospholipids (PO2) asymmetric stretching | [69,70] |
| 1030 | Polysaccharides (C-O stretching) | [7] |
| 870 | Carbonate ions | [71] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Rojo, S.; Carrillo-Peña, D.; González, R.G.; Gómez, X. Assessing Digestate at Different Stabilization Stages: Application of Thermal Analysis and FTIR Spectroscopy. Eng 2024, 5, 1499-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030080
González-Rojo S, Carrillo-Peña D, González RG, Gómez X. Assessing Digestate at Different Stabilization Stages: Application of Thermal Analysis and FTIR Spectroscopy. Eng. 2024; 5(3):1499-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030080
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Rojo, Silvia, Daniela Carrillo-Peña, Rubén González González, and Xiomar Gómez. 2024. "Assessing Digestate at Different Stabilization Stages: Application of Thermal Analysis and FTIR Spectroscopy" Eng 5, no. 3: 1499-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030080
APA StyleGonzález-Rojo, S., Carrillo-Peña, D., González, R. G., & Gómez, X. (2024). Assessing Digestate at Different Stabilization Stages: Application of Thermal Analysis and FTIR Spectroscopy. Eng, 5(3), 1499-1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5030080









