A Review of Passenger Counting in Public Transport Concepts with Solution Proposal Based on Image Processing and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Passenger Counting Technologies
2.1. Card Swiping and Ticketing Systems
2.2. RFID
2.3. Infrared Sensors
2.4. Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Tracking
2.5. LiDAR
2.6. CCTV with Image Processing
2.7. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches
2.8. Thermal Cameras
2.9. Ultrasonic Sensors
2.10. Weight Sensors and Sensor-Grid Mat
3. Literature Review
3.1. Manual Counting of Passengers
3.2. IR Sensors
3.3. CCTV Cameras
3.4. Wi-Fi Tracking
3.5. CCTV with Machine Learning
4. Methodology
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Precision Comparison
4.3. Computation and Real-Time Performance Comparison
5. Concepts, Techniques, and Challenges in Case of Using Cameras and Machine Learning
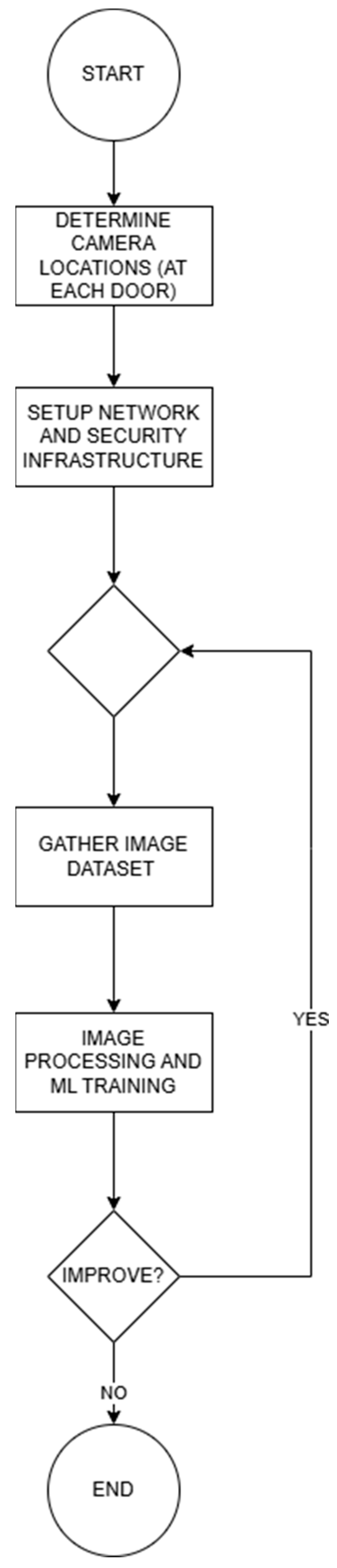
6. Solution Proposal
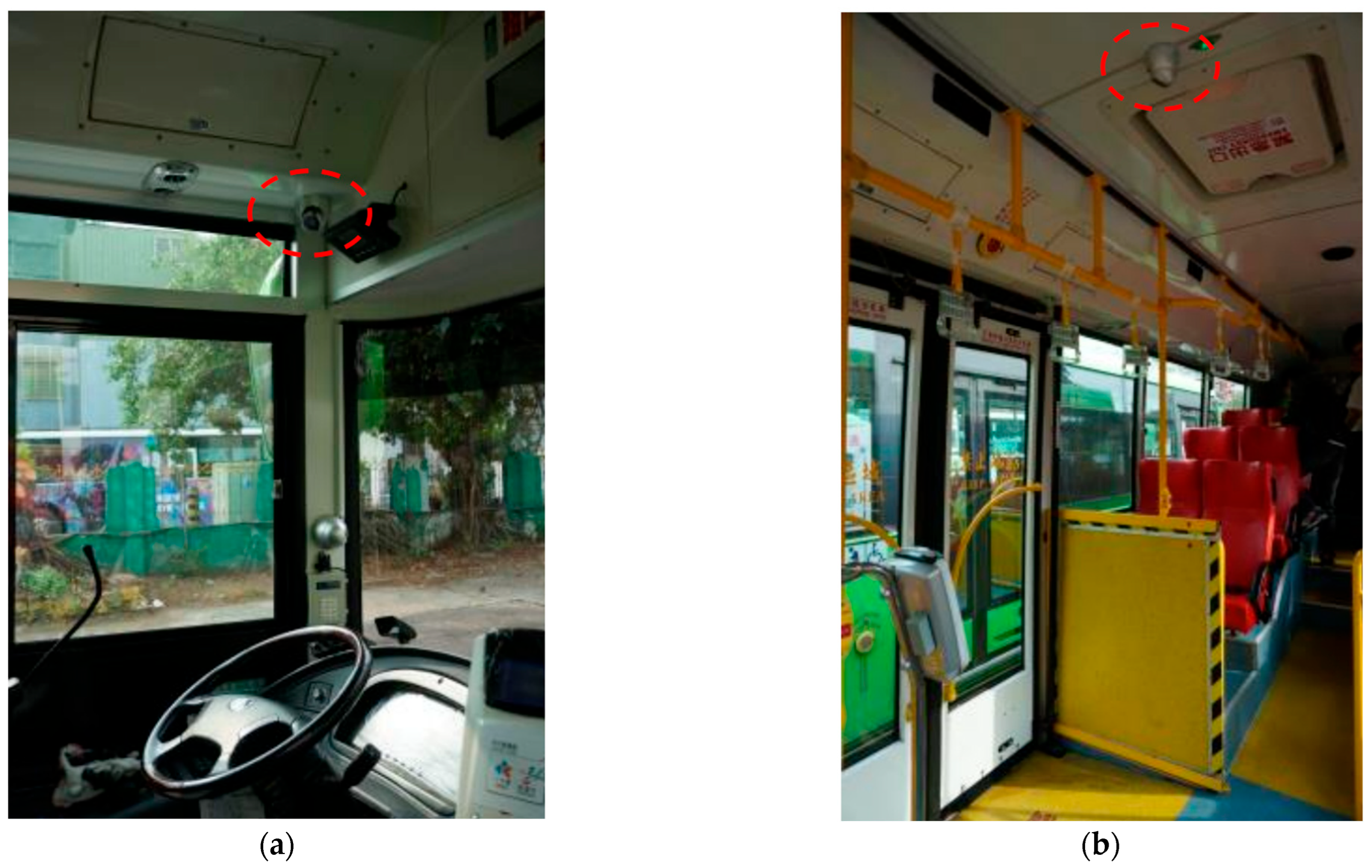
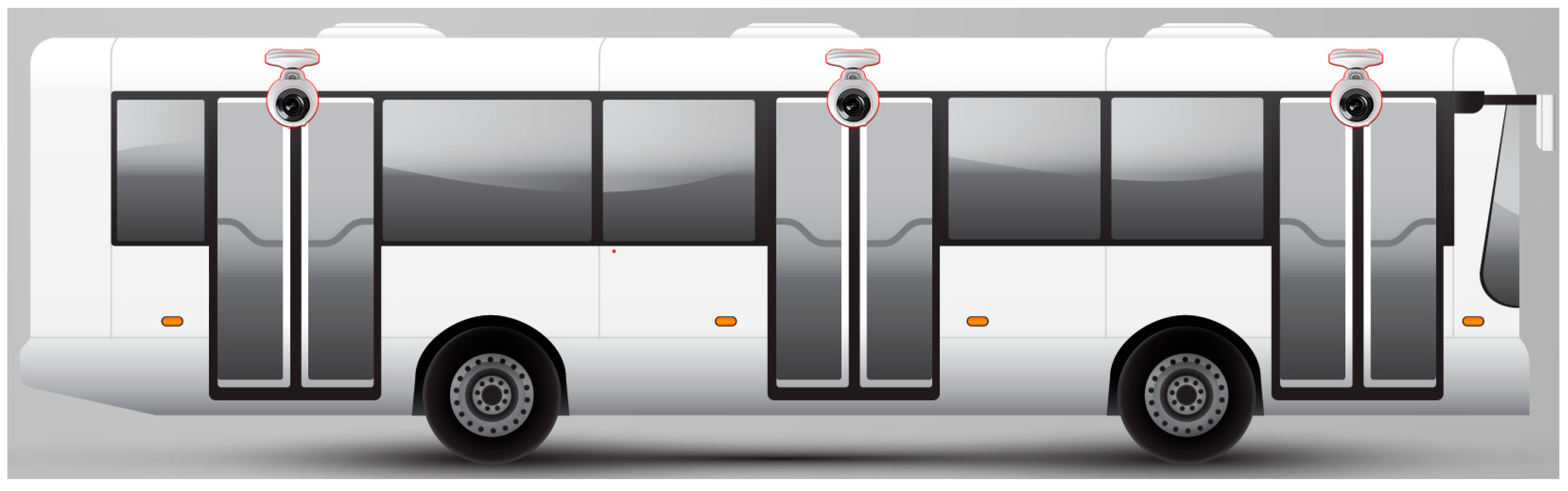
6.1. Camera Locations
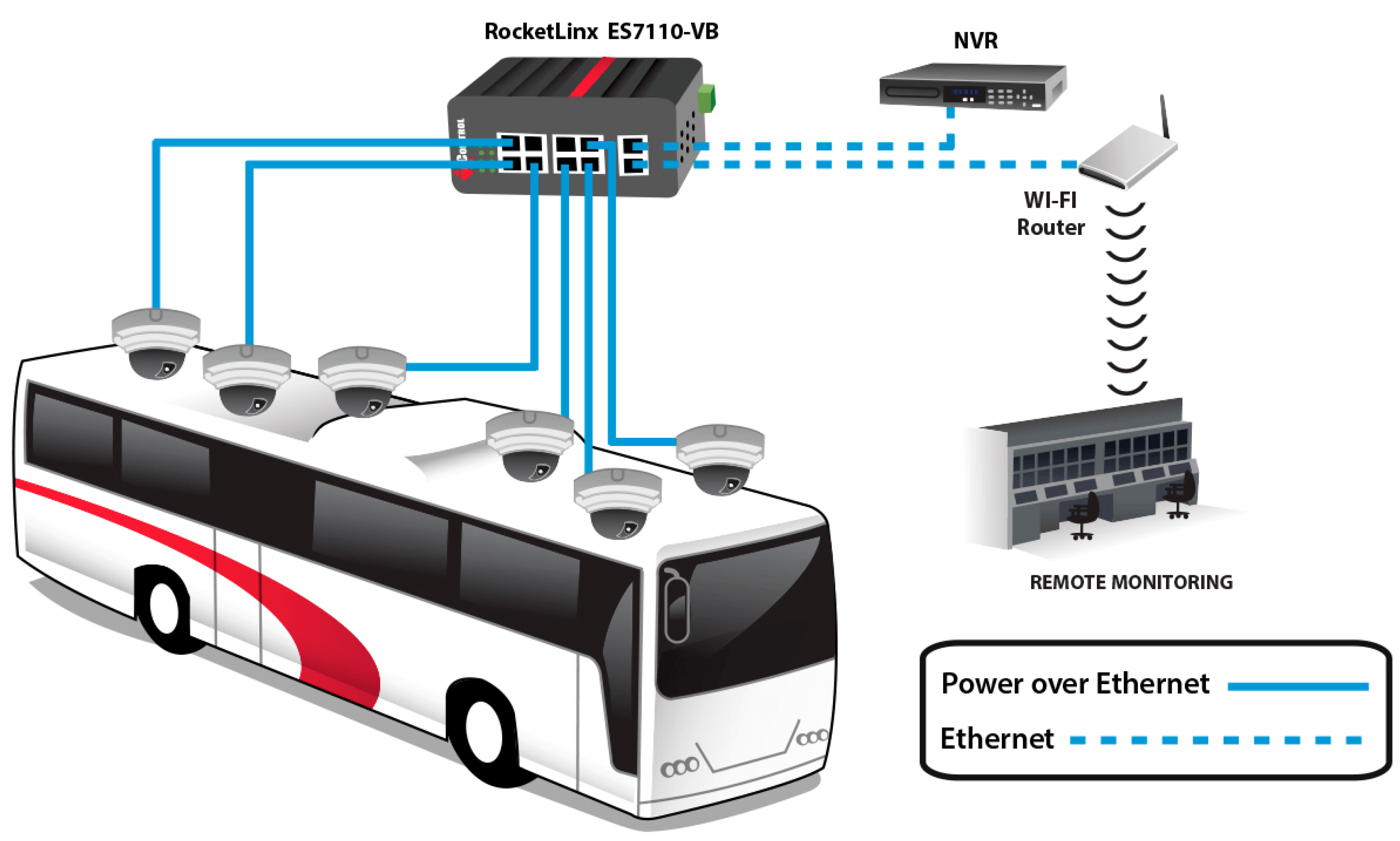
6.2. Public Transport Vehicle External and Internal Network Infrastructure
6.3. Gathering the Image Dataset
6.4. Image Processing and Machine Learning Model Training
7. GDPR Compliance and Passenger Counting Systems
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Public Transport Insights 2024: Analyzing Trends, Size, Share, Demands and Growth Opportunities to 2023. Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/public-transport-insights-2024-analyzing-trends-v4yne/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.-J.; Lim, Y. Use of Smart Card Data to Define Public Transit Use in Seoul, South Korea. Transp. Res. Rec. 2008, 2063, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, T.; Fujiyama, T. Investigating Paper Ticket Usage on London Underground’s Network. In Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Advanced Systems in Public Transport (CASPT), Brisbane, Australia, 23–25 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, P.; Bala, P.; Addy, D.; Giri, S.; Chaudhuri, A.R. RFID and Android based smart ticketing and destination announcement system. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Jaipur, India, 21–24 September 2016; pp. 2587–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lale, D.; Săvescu, C.; Gogoneață, S.; Nechifor, C.; Vasile, M.; Niculescu, F. Passengers Monitoring System with Infrared Sensors and Microcontroller. TURBO 2021, VIII, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, D.T.; Manfroi, D.; de Freitas, E.P. Improvement in the Detection of Passengers in Public Transport Systems by Using UHF RFID. Int. J. Wirel. Inf. Netw. 2020, 27, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, E.; Poigne, A. An Echo State Network based pedestrian counting system using wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Workshop on Intelligent Solutions in Embedded Systems, Regensburg, Germany, 10–11 July 2008; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrvoll, T.A.; Håkegård, J.E.; Matsui, T.; Septier, F. Counting public transport passenger using WiFi signatures of mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 16–19 October 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakos, V. Using Bluetooth to capture passenger trips on public transport buses. CoRR 2008. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220484433_Using_Bluetooth_to_capture_passenger_trips_on_public_transport_buses (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Seidel, R.; Jahn, N.; Seo, S.; Goerttler, T.; Obermayer, K. NAPC: A Neural Algorithm for Automated Passenger Counting in Public Transport on a Privacy-Friendly Dataset. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 3, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; Yousaf, M.H.; Murtaza, F.; Velastin, S. Passenger Detection and Counting for Public Transport System. NED Univ. J. Res. 2020, XVII, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-W.; Chen, Y.-W.; Perng, J.-W. Estimation of the Number of Passengers in a Bus Using Deep Learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchár, P.; Pirník, R.; Tichý, T.; Rástočný, K.; Skuba, M.; Tettamanti, T. Noninvasive Passenger Detection Comparison Using Thermal Imager and IP Cameras. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutjarittham, T.; Gharakheili, H.H.; Kanhere, S.S.; Sivaraman, V. Estimating Passenger Queue for Bus Resource Optimization Using LoRaWAN-Enabled Ultrasonic Sensors. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 16, 6265–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, A.J.; Kittelson, D.B.; Northrop, W.F. Novel Vehicle Mass-Based Automated Passenger Counter for Transit Applications. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2563, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, R.; Nadai, L.; Horvath, G. Concept validation of an automatic passenger counting system for trams. In Proceedings of the 2009 5th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics, Timisoara, Romania, 28–29 May 2009; pp. 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, B.F.; Frølich, L.; Nielsen, O.A.; Filges, D. Estimating passenger numbers in trains using existing weighing capabilities. Transp. A Transp. Sci. 2013, 10, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Gu, J.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Z. Research on Counting Method of Bus Passenger Flow Based on Kinematics of Human Body and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2008 Second International Symposium on Intelligent Information Technology Application, Shanghai, China, 20–22 December 2008; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, I.; McCarthy, C.; Jayaraman, P.P.; Ghaderi, H.; Dia, H.; Li, R.; Simmons, M.; Mehmood, U.; Tan, A.M.; Weizman, Y.; et al. A Methodology for Empirically Evaluating Passenger Counting Technologies in Public Transport. In Proceedings of the 41st Australasian Transport Research Forum, Canberra, Australia, 30 September–2 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grgurević, I.; Juršić, K.; Rajič, V. Review of Automatic Passenger Counting Systems in Public Urban Transport. In 5th EAI International Conference on Management of Manufacturing Systems; Knapčíková, L., Peraković, D., Behúnová, A., Periša, M., Eds.; EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chato, P.; Chipantasi, D.J.M.; Velasco, N.; Rea, S.; Hallo, V.; Constante, P. Image processing and artificial neural network for counting people inside public transport. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Third Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM), Cuenca, Ecuador, 15–19 October 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenCV Library. Available online: https://opencv.org/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, D.; Li, Y. Clustering method for counting passengers getting in a bus with single camera. Opt. Eng. 2010, 49, 037203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Beaugendre, A.; Goto, S. A KLT-based approach for occlusion handling in human tracking. In Proceedings of the 2012 Picture Coding Symposium, Krakow, Poland, 7–9 May 2012; pp. 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoudour, L.; Yahiaoui, T.; Meurie, C. Real-time passenger counting in buses using dense stereovision. J. Electron. Imaging 2010, 19, 031202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, M.; Pinna, F.; Pintor, L.; Pilloni, V.; Barabino, B. iABACUS: A Wi-Fi-Based Automatic Bus Passenger Counting System. Energies 2020, 13, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, B.-K.; Kim, Y.-S.; Suryanto; Jung, J.-Y.; Ko, S.-J. Robust people counting system based on sensor fusion. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2012, 58, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, F.-W.; Liang, H.-W.; Yang, W.-M. Automatic Passenger Counting System for Bus Based on RGB-D Video. In Proceedings of the 2nd Annual International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Information Science, Xi’an China, 2–4 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, A.; Gharib, N.; Jaafar, H. Automatic Passenger Counting System Using Image Processing Based on Skin Colour Detection Approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computational Approach in Smart Systems Design and Applications (ICASSDA), Kuching, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oransirikul, T.; Nishide, R.; Piumarta, I.; Takada, H. Measuring Bus Passenger Load by Monitoring Wi-Fi Transmissions from Mobile Devices. Procedia Technol. 2014, 18, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalikova, J.; Krcal, J. People counting by means of Wi-Fi. In Proceedings of the 2017 Smart City Symposium Prague (SCSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 25–26 May 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, U.; Moser, I.; Jayaraman, P.P.; Banerjee, A. Occupancy Estimation using WiFi: A Case Study for Counting Passengers on Busses. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Limerick, Ireland, 15–18 April 2019; pp. 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.; Schneider, D.; De Souza, J.; Shen, W. Mobile Device Detection Through WiFi Probe Request Analysis. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 98579–98588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, T.; Schwefel, H.-P.; Mikkelsen, L.; Burggraf, A. Comparison of WLAN Probe and Light Sensor-Based Estimators of Bus Occupancy Using Live Deployment Data. Sensors 2022, 22, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velastin, S.A.; Fernández, R.; Espinosa, J.E.; Bay, A. Detecting, Tracking and Counting People Getting On/Off a Metropolitan Train Using a Standard Video Camera. Sensors 2020, 20, 6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedestrian Accessibility and Movement Environment Laboratory. Available online: https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1414/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- PAMELA UANDES Dataset. Available online: http://velastin.dynu.com/PAMELA-UANDES/whole_data.html (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Hsu, Y.-W.; Wang, T.-Y.; Perng, J.-W. Passenger flow counting in buses based on deep learning using surveillance video. Optik 2020, 202, 163675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liciotti, D.; Cenci, A.; Frontoni, E.; Mancini, A.; Zingaretti, P. An Intelligent RGB-D Video System for Bus Passenger Counting. In Intelligent Autonomous Systems 14 IAS 2016, Proceedings of the IAS 2016, Shanghai, China, 3–7 July 2016; Chen, W., Hosoda, K., Menegatti, E., Shimizu, M., Wang, H., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, E.U.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Fan, J.; Abid, F. A fast hybrid computer vision technique for real-time embedded bus passenger flow calculation through camera. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 1007–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisner, D.A.; Schnyer, D.M. Chapter 6—Support vector machine. In Machine Learning; Mechelli, A., Vieira, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 101–121. ISBN 9780128157398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.; Su, H.; Wang, C.; Stevanovic, A.; Wang, W. An automatic traffic density estimation using Single Shot Detection (SSD) and MobileNet-SSD. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2019, 110, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YOLOv8. Available online: https://yolov8.com/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Ultralytics YOLOv8 Github Repository. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/docs/en/models/yolov8.md (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Yoshida, T.; Kihsore, N.A.; Thapaswi, A.; Venkatesh, P.; Ponderti, R.K. Smart metro: Real-time passenger counting and compartment occupancy optimization using IoT and Deep Learning. Int. Res. J. Mod. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2024, 6, 3684–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Pronello, C.; Garzón Ruiz, X.R. Evaluating the Performance of Video-Based Automated Passenger Counting Systems in Real-World Conditions: A Comparative Study. Sensors 2023, 23, 7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, W.D.M.; Anillo, C.B.; Jaramillo-Ramirez, D.; Carrillo, H. Passenger Counting in Mass Public Transport Systems using Computer Vision and Deep Learning. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2023, 21, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sohn, M.K.; Lee, S.H. Development of a Real-Time Automatic Passenger Counting System using Head Detection Based on Deep Learning. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 18, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labit-Bonis, C.; Thomas, J.; Lerasle, F. Visual and automatic bus passenger counting based on a deep tracking-by-detection system. HAL Open Sci. 2021. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-03363502 (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Bishop, C.M.; Bishop, H. Convolutional Networks. In Deep Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, K.; Bhuvan, S.; Palangappa, M.B. Social Distance Identification Using Optimized Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 8–10 April 2021; pp. 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.F.; Lim, H.-Y.; Kang, D.-S. Object Detection Based on VGG with ResNet Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC), Auckland, New Zealand, 22–25 January 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisong, E. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). In Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, A. Long Short-Term Memory. In Supervised Sequence Labelling with Recurrent Neural Networks; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Georgiou, T.; Lew, M.S. A review of semantic segmentation using deep neural networks. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2018, 7, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Zeng, Z.; Lian, C.; Tang, H. Pixel-wise regression using U-Net and its application on pansharpening. Neurocomputing 2018, 312, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, G. DeepLab-Based Spatial Feature Extraction for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, K.; Pawar, S.; Dhulekar, P. Moving object tracking using optical flow and motion vector estimation. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (ICRITO) (Trends and Future Directions), Noida, India, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, B.; Bouwmans, T.; Silva, A.J.R. Background subtraction in real applications: Challenges, current models and future directions. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2020, 35, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Sanz, S.; Rojo-Álvarez, J.L.; Martínez-Ramón, M.; Camps-Valls, G. Support vector machines in engineering: An overview. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2014, 4, 234–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.; Rousseau, A.-J.; Geubbelmans, M.; Burzykowski, T.; Valkenborg, D. Decision trees and random forests. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 164, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liu, H.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, H. A novel method for people and vehicle classification based on Hough line feature. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 26–28 March 2011; pp. 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavachari, C.; Aparna, V.; Chithira, S.; Balasubramanian, V. A Comparative Study of Vision Based Human Detection Techniques in People Counting Applications. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 58, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mutlag, W.K.; Ali, S.K.; Aydam, Z.M.; Taher, B.H. Feature Extraction Methods: A Review. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1591, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.D.; Jiang, X.H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J. Color image segmentation: Advances and prospects. Pattern Recognit. 2001, 34, 2259–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, N.S.T.; Papakostas, G.A. On Machine-Learning Morphological Image Operators. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernov, V.; Alander, J.; Bochko, V. Integer-based accurate conversion between RGB and HSV color spaces. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2015, 46, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Qiu, J. Ultralytics YOLO11. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- COCO Dataset Limited (PersonOnly). Available online: https://universe.roboflow.com/shreks-swamp/coco-dataset-limited--person-only (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Osorio, F.G.; Xinran, M.; Liu, Y.; Lusina, P.; Cretu, E. Sensor network using Power-over-Ethernet. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference and Workshop on Computing and Communication (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 15–17 October 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transportation and Bus Surveillance: Mobile Security, 10 July 2018. Available online: https://iebmedia.com/applications/transportation/transportation-and-bus-surveillance-mobile-security/ (accessed on 13 October 2024).
- Bus Surveillance with Axiomtek’s tBOX810-838-FL. Available online: https://www.axiomtek.com/ArticlePageView.aspx?ItemId=1909&t=27 (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Pons, M.; Valenzuela, E.; Rodríguez, B.; Nolazco-Flores, J.A.; Del-Valle-Soto, C. Utilization of 5G Technologies in IoT Applications: Current Limitations by Interference and Network Optimization Difficulties—A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Mark Liao, H.Y. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Label Studio Documentation. Available online: https://labelstud.io/guide/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Hossen, M.A.; Naim, A.G.; Abas, P.E. Deep Learning for Skeleton-Based Human Activity Segmentation: An Autoencoder Approach. Technologies 2024, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A Survey of Convolutional Neural Networks: Analysis, Applications, and Prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, K.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Wang, D.D. A survey of transfer learning. J. Big Data 2016, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Data Protection Regulation—GDPR. Available online: https://gdpr-info.eu/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016 on the Protection of Natural Persons with Regard to the Processing of Personal Data and on the Free Movement of Such Data, and Repealing Directive 95/46/EC (General Data Protection Regulation) (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2016/679/oj (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Voigt, P.; Bussche, A. The EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): A Practical Guide; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahya, M.; Kechagia, S.; Collen, A.; Nijdam, N.A. The Interface of Privacy and Data Security in Automated City Shuttles: The GDPR Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines on Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) (wp248rev.01). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/newsroom/article29/items/611236/en (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- EU AI Act: First Regulation on Artificial Intelligence. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20230601STO93804/eu-ai-act-first-regulation-on-artificial-intelligence (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- Olivo, A.; Maternini, G.; Barabino, B. Empirical Study on the Accuracy and Precision of Automatic Passenger Counting in European Bus Services. Open Transp. J. 2019, 13, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-H.; Leung, J.M.; Yan, Y. Public transport for smart cities: Recent innovations and future challenges. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2023, 306, 1001–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukic Vujadinovic, V.; Damnjanovic, A.; Cakic, A.; Petkovic, D.R.; Prelevic, M.; Pantovic, V.; Stojanovic, M.; Vidojevic, D.; Vranjes, D.; Bodolo, I. AI-Driven Approach for Enhancing Sustainability in Urban Public Transportation. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, C.; Ghaderi, H.; Martí, F.; Jayaraman, P.; Dia, H. Video-based automatic people counting for public transport: On-bus versus off-bus deployment. Comput. Ind. 2025, 164, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Banos, O.; Lee, S.; Kang, B.H.; Kim, E.-S.; Le-Tien, T. NIC: A Robust Background Extraction Algorithm for Foreground Detection in Dynamic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 27, 1478–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchár, P.; Pirník, R.; Janota, A.; Malobický, B.; Kubík, J.; Šišmišová, D. Passenger Occupancy Estimation in Vehicles: A Review of Current Methods and Research Challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, T.; Anirudh, G.; Tembhurne, J.V. Object detection using YOLO: Challenges, architectural successors, datasets and applications. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 9243–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Heureux, A.; Grolinger, K.; Elyamany, H.F.; Capretz, M.A.M. Machine Learning With Big Data: Challenges and Approaches. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 7776–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, G.; Xue, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, L. A survey on dataset quality in machine learning. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2023, 162, 107268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tercan, H.; Guajardo, A.; Meisen, T. Industrial Transfer Learning: Boosting Machine Learning in Production. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Helsinki, Finland, 22–25 July 2019; pp. 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczyk, M.; Kempski, A.; Socha, M.; Cogiel, M.; Foszner, P.; Staniszewski, M. Passenger Location Estimation in Public Transport: Evaluating Methods and Camera Placement Impact. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 17878–17887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, B.; Xiao, T.; Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. CrowdHuman: A benchmark for detecting human in a crowd. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00123. [Google Scholar]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv11: An Overview of the Key Architectural Enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronello, C.; Baratti, L.; Anbarasan, D. Benchmarking the Functional, Technical, and Business Characteristics of Automated Passenger Counting Products. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 302–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, N.; Jeengar, K.; Agarwal, A.; Kaur Chahal, R.J. Boarding Alighting Counting in Different Transit Vehicles under Crowded Conditions. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), Bangalore, India, 12–14 July 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Hua, M.; Pu, Z. A two-stage method for bus passenger load prediction using automatic passenger counting data. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 15, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, N.; Siebert, M. Engineering the Neural Automatic Passenger Counter. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 114, 105148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaeipour, N.; Stanciu, V.-D.; van Steen, M.; Wang, M. Understanding the protection of privacy when counting subway travelers through anonymization. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2024, 110, 102091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ref. nr. | PT Vehicle Type | Used Technology | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Card Swiping | IR | Weight | RFID | Wi-Fi | Bluetooth | Cameras | LiDAR | ML | TC | US | ||
| [2] | Bus and Metro | X | ||||||||||
| [3] | Metro | X | ||||||||||
| [4] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [5] | - | X | ||||||||||
| [6] | Bus, Subway trains | X | ||||||||||
| [7] | - | X | ||||||||||
| [8] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [9] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [10] | Train | X | X | |||||||||
| [11] | Train, Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [12] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [13] | Car | X | X | X | ||||||||
| [14] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [15] | Bus | X | X | X | ||||||||
| [16] | Tram | X | ||||||||||
| [17] | Train | X | X | X | ||||||||
| [18] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [19] | Bus | X | X | X | ||||||||
| [21] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [23] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [24] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [25] | - | X | ||||||||||
| [26] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [27] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [28] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [29] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [30] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [8] | - | X | ||||||||||
| [31] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [32] | - | X | ||||||||||
| [33] | - | X | ||||||||||
| [34] | Bus | X | X | X | ||||||||
| [26] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [35] | X | X | ||||||||||
| [36] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [37] | Bus | X | ||||||||||
| [38] | - | X | X | |||||||||
| [39] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [47] | Metro | X | X | |||||||||
| [48] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [49] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [50] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| [51] | Bus | X | X | |||||||||
| Technology | Typical Precision Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Card swiping data [2] | 70–90% | It achieves the best results when passengers enter the vehicle. In most cases it is not used when passengers leave the vehicle and in cases where passengers use cards. |
| Infrared Sensors [15,16] | 80–95% | The best precision is achieved by placing the sensors in positions near the vehicle doors where it is possible to best detect the movement of passengers. It achieves the best results in situations where several passengers overlap, but inadequate results in large crowds. |
| Weight Sensors [19] | 80–90% | It achieves the best results when calculating the total weight of passengers, but it achieves inadequate results when individual passengers enter and exit. It is based on the average weight of passengers, which sometimes varies and is not always reliable. |
| RFID Technology [9] | 82–98% | It achieves high precision if all passengers use RFID devices. Accuracy is worse in the case when device signals overlap, or passengers use RFID devices. |
| Wi-Fi Technology [8,24] | 75–94% | It provides a rough estimate of the number of passengers, as it is assumed that passengers will have devices that connect to the Wi-Fi network and only have one device. Inadequate results are also achieved due to signal interference. |
| Bluetooth technology [7] | 73–77% | Like Wi-Fi technology, accuracy depends on the number of Bluetooth devices and the number of devices per user. |
| CCTV Cameras (without ML) [22,27] | 75–97% | Accuracy depends on manual counting or motion detection, which can result in low accuracy in case of overlapping passengers or objects, and problems such as insufficient image quality. |
| CCTV Cameras (with ML) [11,26,32] | 92–99% | In the case of using CCTV cameras and machine learning, a significant improvement in accuracy is achieved. The biggest challenges are based on the lighting of the image, the camera angle or large crowds of vehicles. |
| LiDAR sensors [8] | 95–96% | A very high level of accuracy is achieved in counting and tracking passengers, even in large crowds or in different lighting conditions inside the vehicle. |
| Thermo Cameras [12] | 70–98% | It is based on the detection of the heat of the passenger’s body and achieves the best results when visibility is reduced, but most challenges exist when there are large crowds in vehicles, during which the bodies of the passengers overlap. |
| Ultrasonic Sensors [13] | 88–89% | It achieves good results in detecting the entry and exit of passengers and has the most challenges in crowded and noisy environments. |
| Technology | Computational Complexity | Real-Time Performance | Hardware Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Card swiping data [2] | Low | High | Low (simple card reader and server) |
| Infrared sensors [5] | Low-Medium | High | Moderate (infrared sensors and microcontroller) |
| Weight sensors [15,17,18,19,40] | Low | Medium | Moderate (weight sensor array) |
| RFID technology [3,9] | Low-Medium | Medium-High | Moderate (RFID readers and tags) |
| Wi-Fi technology [8,24,30,31] | Medium | Medium | Moderate (Wi-Fi receivers and data processing units) |
| Bluetooth Technology [7] | Medium | Medium | Moderate (Bluetooth receivers and processors) |
| CCTV cameras (without ML) [20,22,35] | Low | Medium | High (basic CCTV camera and server) |
| CCTV cameras (with ML) [11,26,40,46] | High | Medium | High (GPU-enabled server or edge AI hardware) |
| LiDAR sensors [8] | High | High | High (LiDAR sensor and GPU or high-end processor) |
| Thermo cameras [12] | High | Medium-High | High (thermal camera and GPU or real-time analysis) |
| Ultrasonic sensors [13] | Low | High | Low-Moderate (ultrasonic sensor array) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radovan, A.; Mršić, L.; Đambić, G.; Mihaljević, B. A Review of Passenger Counting in Public Transport Concepts with Solution Proposal Based on Image Processing and Machine Learning. Eng 2024, 5, 3284-3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040172
Radovan A, Mršić L, Đambić G, Mihaljević B. A Review of Passenger Counting in Public Transport Concepts with Solution Proposal Based on Image Processing and Machine Learning. Eng. 2024; 5(4):3284-3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040172
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadovan, Aleksander, Leo Mršić, Goran Đambić, and Branko Mihaljević. 2024. "A Review of Passenger Counting in Public Transport Concepts with Solution Proposal Based on Image Processing and Machine Learning" Eng 5, no. 4: 3284-3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040172
APA StyleRadovan, A., Mršić, L., Đambić, G., & Mihaljević, B. (2024). A Review of Passenger Counting in Public Transport Concepts with Solution Proposal Based on Image Processing and Machine Learning. Eng, 5(4), 3284-3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5040172










