Overweight and Obesity Contribute to Inflammation and Reduction in Mean Corpuscular Volume and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin in Schoolchildren
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study’s Design and Ethical Aspects
2.2. Anthropometric Assessment
2.3. Hematimetric and Leukocyte Evaluation
2.4. Cytokine Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lobstein, T.; Brinsden, H. Atlas of Childhood Obesity; World Obesity Federation: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, A.C.; Perrin, E.M.; Skelton, J.A. Prevalence of obesity and severe obesity in US children, 1999–2014. Obesity 2016, 24, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trellakis, S.; Rydleuskaya, A.; Fischer, C.; Canbay, A.; Tagay, S.; Scherag, A.; Bruderek, K.; Schuler, P.J.; Brandau, S. Low adiponectin, high levels of apoptosis and increased peripheral blood neutrophil activity in healthy obese subjects. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.L. Cellular and molecular players in adipose tissue inflammation in the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 446–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, F.M.; Weschenfelder, J.; Sander, C.; Minkwitz, J.; Thormann, J.; Chittka, T.; Mergl, R.; Kirkby, K.C.; Faßhauer, M.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Inflammatory cytokines in general and central obesity and modulating effects of physical activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851. [Google Scholar]
- Assefa, S.; Mossie, A.; Hamza, L. Prevalence and severity of anemia among school children in Jimma Town, southwest Ethiopia. BMC Hematol. 2014, 14, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Woodman, R.C.; Bandinelli, S.; Lauretani, F.; Corsi, A.M.; Chaves, P.H.M.; Ershler, W.B.; Longo, D.L. Proinflammatory state circulating erythropoietin in persons with without anemia. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 1288.e11–1288.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Yuan, F.; Teng, J.; Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Lin, L.; Deng, H.; Ma, G.; Sun, C.; Li, Y. Weight loss, inflammatory markers, and improvements of iron status in overweight and child with obesityren. J. Pediatr. 2014, 164, 795–800.e2. [Google Scholar]
- Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Pusatcioglu, C.; Nemeth, E.; Braunschweig, C. Rethinking iron regulation and assessment in iron deficiency, anemia of chronic disease, and obesity: Introducing hepcidin. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Aeberli, I.; Hurrell, R.F.; Zimmermann, M.B. Overweight children have higher circulating hepcidin concentrations and lower iron status but have dietary iron intakes and bioavailability comparable with normal weight children. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Zeder, C.; Muthayya, S.; Winichagoon, P.; Chaouki, N.; Aeberli, I.; Hurrell, R.F. Adiposity in women and children from transition countries predicts decreased iron absorption, iron deficiency and a reduced response to iron fortification. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Domínguez, Á.; Visiedo-García, F.M.; Domínguez-Riscart, J.; González-Domínguez, R.; Mateos, R.M.; Lechuga-Sancho, A.M. Iron metabolism in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramastri, R.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lee, H.A.; Lin, L.Y.; Kurniawan, A.L.; Chao, J.C.F. Association between dietary pattern, lifestyle, anthropometric status, and anemia-related biomarkers among adults: A population-based study from 2001 to 2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panichsillaphakit, E.; Suteerojntrakool, O.; Pancharoen, C.; Nuchprayoon, I.; Chomtho, S. The Association between Hepcidin Iron Status in Children Adolescents with Obesity. J. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 2021, 9944035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Mao, D.; Li, W.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Piao, J.; Yang, L.; et al. Prevalence of anemia in Chinese children and adolescents and its associated factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamruzzaman, M. Is BMI associated with anemia and hemoglobin level of women and children in Bangladesh: A study with multiple statistical approaches. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde, Departamento de Atenção Básica. Orientações para a Coleta e Análise de Dados Antropométricos em Serviços de Saúde: Norma Técnica do Sistema de Vigilância Alimentar e Nutricional; Il.—(Série G. Estatística e Informação em Saúde); SISVAN/Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Atenção à Saúde, Departamento de Atenção Básica, Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2011; 76p, ISBN 978-85-334-1813-4.
- Mantzouranis, N.; Pilianidis, T.; Douda, H.; Tokmakidis, S. Comparison of international obesity taskforce cutoffs, centers for disease control and prevention growth charts, and body mass index Z-score values in the prevalence of childhood obesity: The Greek obesity and lifestyle study. Pediatrics 2008, 121, S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, M.; Sori´c, M.; Bovet, P.; Miranda, J.J.; Bhutta, Z.; Stevens, G.A.; Laxmaiah, A.; Kengne, A.P.; Bentham, J. The epidemiological burden of obesity in childhood: A worldwide epidemic requiring urgent action. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaben, A.L.; Scherer, P.E. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, A.; Moura Silva, H.; Moore, K.J.; Schmidt, A.M. Leukocyte heterogeneity in adipose tissue, including in obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1590–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe-Querol, E.; Rosales, C. Neutrophils Actively Contribute to Obesity-Associated Inflammation and Pathological Complications. Cells 2022, 11, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herishanu, Y.; Rogowski, O.; Polliack, A.; Marilus, R. Leukocytosis in obese individuals: Possible link in patients with unexplained persistent neutrophilia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2006, 76, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, A.B.; Lewis, J.B.; Arteta-Bulos, R. Chronic idiopathic neutrophilia: Experience and recommendations. South. Med. J. 2011, 104, 99–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Park, H.S. White blood cell count and abdominal fat distribution in female obese adolescents. Metabolism 2008, 57, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.B.; O’Brien, P.E. Obesity and the white blood cell count: Changes with sustained weight loss. Obes. Surg. 2006, 16, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshita, K.; Yamane, K.; Hanafusa, M.; Mori, H.; Mito, K.; Okubo, M.; Hara, H.; Kohno, N. Elevated White Blood Cell Count in Subjects with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Funtikova, A.N.; Fíto, M.; Schröder, H. Can metabolically healthy obesity be explained by diet, genetics, and inflammation? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, J.K.; Gökhan, S.H. Metabolic messengers: Tumour necrosis factor. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasselin, J.; Magne, E.; Beau, C.; Ledaguenel, P.; Dexpert, S.; Aubert, A.; Layé, S.; Capuron, L. Adipose inflammation in obesity: Relationship with circulating levels of inflammatory markers and association with surgery-induced weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E53–E61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Hua, M. Adiponectin, TNF-α and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2016, 86, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, G.Y.; He, G.; Ali, S.R.; Holzer, R.G.; Österreicher, C.H.; Takahashi, H.; Karin, M. Dietary and genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell 2010, 140, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Umemura, A.; Taniguchi, K.; Font-Burgada, J.; Dhar, D.; Ogata, H.; Zhong, Z.; Valasek, M.A.; Seki, E.; Hidalgo, J.; et al. ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, V.Z.; Folco, E.J.; Sukhova, G.; Shimizu, K.; Gotsman, I.; Vernon, A.H.; Libby, P. Interferon-gama, uma citocina Th1, regula a inflamação da gordura: Um papel para a imunidade adaptativa na obesidade. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.B.; Sharma, S. Interleukin-10: A pleiotropic regulator in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2015, 73, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L.; Shin, S.; Yang, S.J. Iron Homeostasis and Energy Metabolism in Obesity. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2022, 11, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qiu, F.; Wu, L.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, N. The role of iron metabolism in chronic diseases related to obesity. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sal, E.; Yenicesu, I.; Celik, N.; Pasaoglu, H.; Celik, B.; Pasaoglu, O.T.; Kaya, Z.; Kocak, U.; Camurdan, O.; Bideci, A.; et al. Relationship between obesity and iron deficiency anemia: Is there a role of hepcidin? Hematology 2018, 23, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertinato, J.; Aroche, C.; Plouffe, L.J.; Lee, M.; Murtaza, Z.; Kenney, L.; Lavergne, C.; Aziz, A. Diet-induced obese rats have higher iron requirements are more vulnerable to iron deficiency. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 885–895.55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, S.; Catarino, C.; Santos-Silva, A. The role of adipocytes in the modulation of iron metabolism in obesity. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, B.J.; Hopkins, J.A.; Arceo, S.M.; Leitman, S.F. Evaluation of low red blood cell mean corpuscular volume in an apheresis donor population. Transfusion 2009, 49, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T. The role of hepcidin in iron metabolism. Acta Haematol. 2009, 122, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Becker, C.; Orozco, M.; Solomons, N.W.; Schümann, K. Iron metabolism in obesity: How interaction between homoeostatic mechanisms can interfere with their original purpose. Part I: Underlying homoeostatic mechanisms of energy storage and iron metabolisms and their interaction. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 30, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassebaum, N.J.; Jasrasaria, R.; Naghavi, M.; Wulf, S.K.; Johns, N.; Lozano, R.; Regan, M.; Weatherall, D.; Chou, D.P.; Eisele, T.P.; et al. A systematic analysis of global anemia burden from 1990 to 2010. Blood 2014, 123, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Cherayil, B.J. Iron and inflammation the gut reaction. Metallomics 2017, 9, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Ganz, T.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Schett, G. Anaemia in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccio, A.; Madeddu, C.; Gramignano, G.; Mulas, C.; Tanca, L.; Cherchi, M.C.; Floris, C.; Omoto, I.; Barracca, A.; Ganz, T. The role of inflammation, iron, and nutritional status in cancer-related anemia: Results of a large, prospective, observational study. Haematologica 2015, 100, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Leonard, M.B.; Herskovitz, R.; Baldassano, R.N.; Denburg, M.R. Changes in Hepcidin and hemoglobin after Anti-TNF-alpha therapy in children and adolescents with Crohn disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, G.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of chronic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capocasale, R.J.; Makropoulos, D.A.; Achuthanandam, R.; Stowell, N.; Quinn, J.; Rafferty, P.A.; O’Brien, J.; Emmell, E.; Bugelski, P.J. Myelodysplasia and anemia of chronic disease in human tumor necrosis factor-alpha transgenic mice. Cytom. A 2008, 73, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murawska, N.; Fabisiak, A.; Fichna, J. Anemia of chronic disease and Iron defi ciency Anemia in inflammatory bowel diseases: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucendo, A.J.; Roncero, Ó.; Serrano-Duenas, M.T.; Hervías, D.; Alcázar, L.M.; Ruiz-Poncea, M.; Cristina Verdejo, C.; Laserna-Mendieta, E.; Lorentee, R.; Arias, A. Effects of anti–TNF-alpha therapy on hemoglobin levels and anemia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadaki, H.A.; Kritikos, H.D.; Valatas, V.; Boumpas, D.T.; Eliopoulos, G.D. Anemia of chronic disease in rheuma toid arthritis is associated with increased apoptosis of bone marrow erythroid cells: Improvement following anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha antibody ther apy. Blood 2002, 100, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, M.K.; Rahman, M.U.; Han, C.; Han, J.; Giles, J.O.; Bingham, C.O.; Bathon, J. Treatment with infliximab plus methotrex ate improves anemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis independent of improvement in other clinical outcome measures-a pooled analysis from three large, multicenter, double-blind, randomized clinical trials. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 39, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, D.E.; Kay, J.; Wasko, M.C.; Keystone, E.; Kavanaugh, A.; Deodhar, A.; Murphy, F.T.; Magnus, J.H.; Hsia, E.C.; Hsu, B. The effect of golimumab on haemoglobin levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameters | Study Group (n = 15) Mean ± SD (Median) | Control Group (n = 24) Mean ± SD (Median) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 10.13 ± 2.59 (10.00) | 9.25 ± 2.42 (9.00) | 0.2869 |
| Weight (kg) | 47.24 ± 18.40 (41.30) | 30.54 ± 10.41(27.80) | * 0.0009 |
| Height (cm) | 140.60 ± 13.48 (136.00) | 133.40 ± 12.45 (132.80) | 0.1084 |
| BMI/age percentile | 94.90 ± 4.10 (95.16) | 45.77 ± 26.94 (48.84) | * <0.0001 |
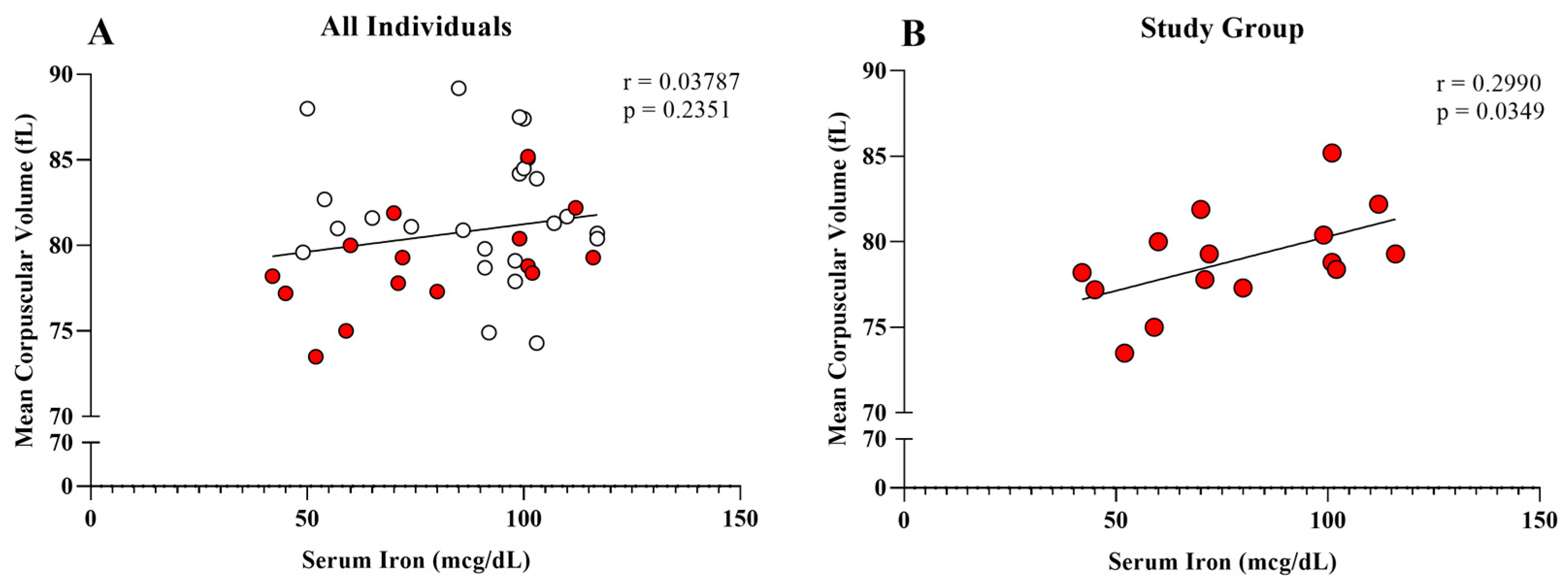
| Iron (mcg/dL) | 78.80 ± 24.73 (72.00) | 89.42 ± 20.52 (98.00) | 0.1548 |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 51.55 ± 27.46 (49.00) | 55.74 ± 30.38 (50.60) | 0.6670 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.77 ± 1.03 (12.80) | 13.01 ± 0.91 (13.10) | 0.4540 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 38.97 ± 2.82 (12.80) | 39.4 ± 2.67 (39.55) | 0.6354 |
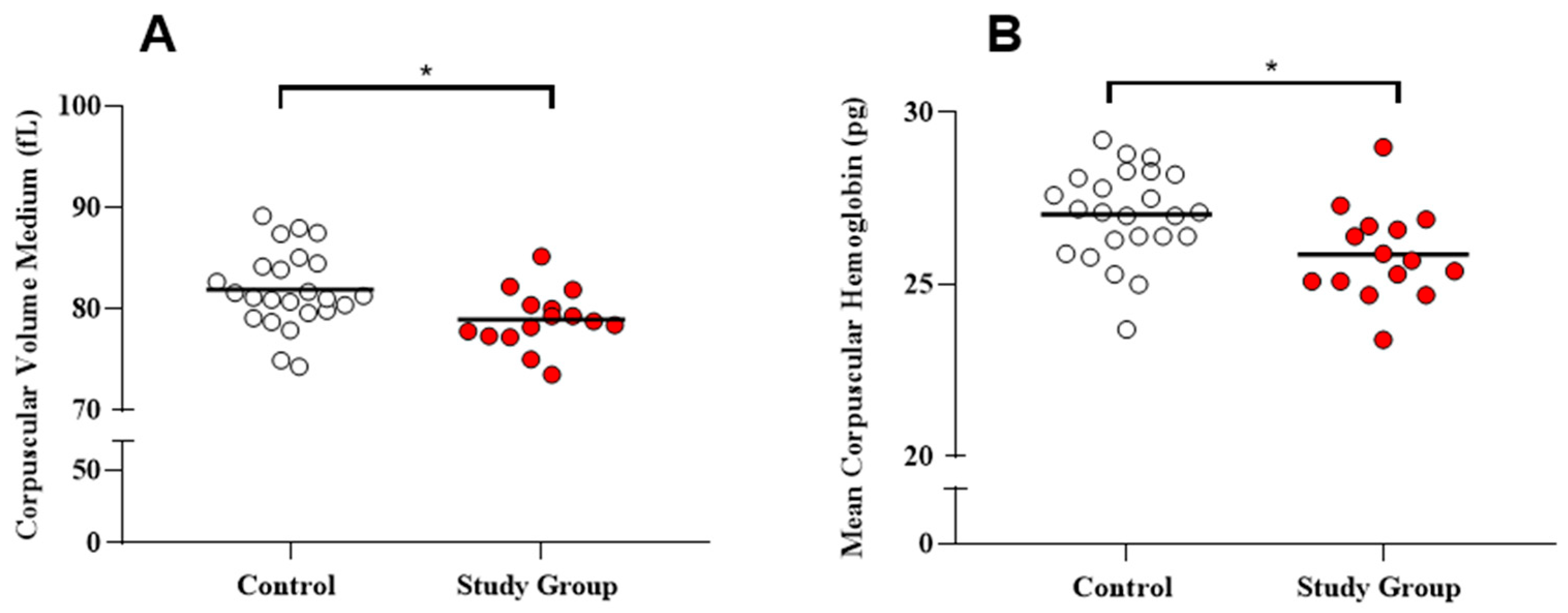
| Mean Corpuscular Volume (fL) | 78.97 ± 2.87 (78.80) | 81.90 ± 3.82 (81.20) | * 0.0099 |
| Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (Pg) | 25.88 ± 1.34 (25.70) | 27.05 ± 1.32 (27.10) | * 0.0125 |
| Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (%) | 32.78 ± 0.66 (32.70) | 33.29 ± 1.30 (33.30) | 0.1671 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width (%) | 12.69 ± 1.34 (12.60) | 12.61 ± 1.70 (11.85) | 0.8766 |
| Total leukocytes (cells/mm3) | 6513.00 ± 1599.00 (6600.00) | 5642.00 ± 1130.00 (5650.00) | 0.0784 |
| Eosinophils (cells/mm3) | 445.20 ± 281.30 (405.00) | 333.80 ± 231.00 (313.80) | 0.1862 |
| Neutrophils (cells/mm3) | 3064.00 ± 1341.00 (3004.00) | 2552.00 ± 726.80 (2371.00) | 0.1896 |
| Lymphocytes (cells/mm3) | 2662.00 ± 678.90 (2406.00) | 2428.00 ± 629.20 (2423.00) | 0.2905 |
| Monocytes (cells/mm3) | 338.20 ± 114.10 (308.00) | 304.30 ± 104.30 (283.10) | 0.3469 |
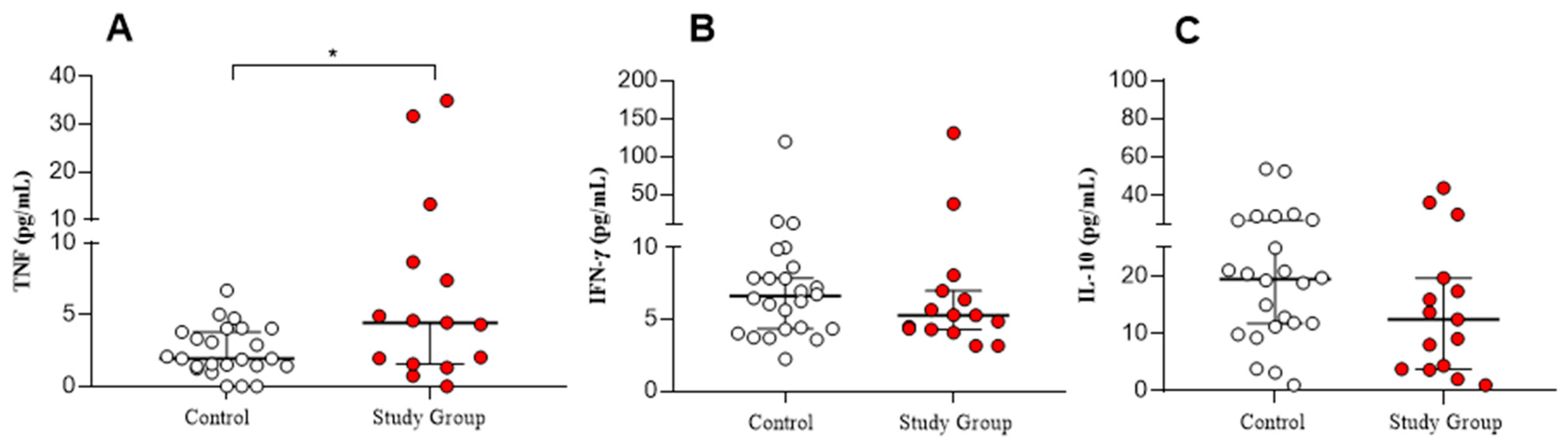
| TNF (Pg/mL) | 8.13 ± 10.82 (4.44) | 2.47 ± 1.73 (1.95) | ** 0.0429 |
| IFN-Ƴ (Pg/mL) | 15.63 ± 33.01 (5.29) | 11.39 ± 23.23 (6.62) | 0.3950 |
| IL-10 (Pg/mL) | 14.75 ± 12.98 (12.46) | 20.16 ± 13.22 (19.48) | 0.1402 |
| Parameters | Percentile | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| r Coefficient | 95% Confidence Interval (CI) | p-Value | |
| Mean Corpuscular Volume (fL) | 0.1464 | −0.0803 to 0.0087 | 0.0162 |
| Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (Pg) | 0.1460 | −0.0307 to −0.0033 | 0.0164 |
| Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (%) | 0.0006 | −0.0124 to 0.0107 | 0.8839 |
| Red Cell Distribution Width (%) | 0.0107 | −0.0209 to 0.0109 | 0.5300 |
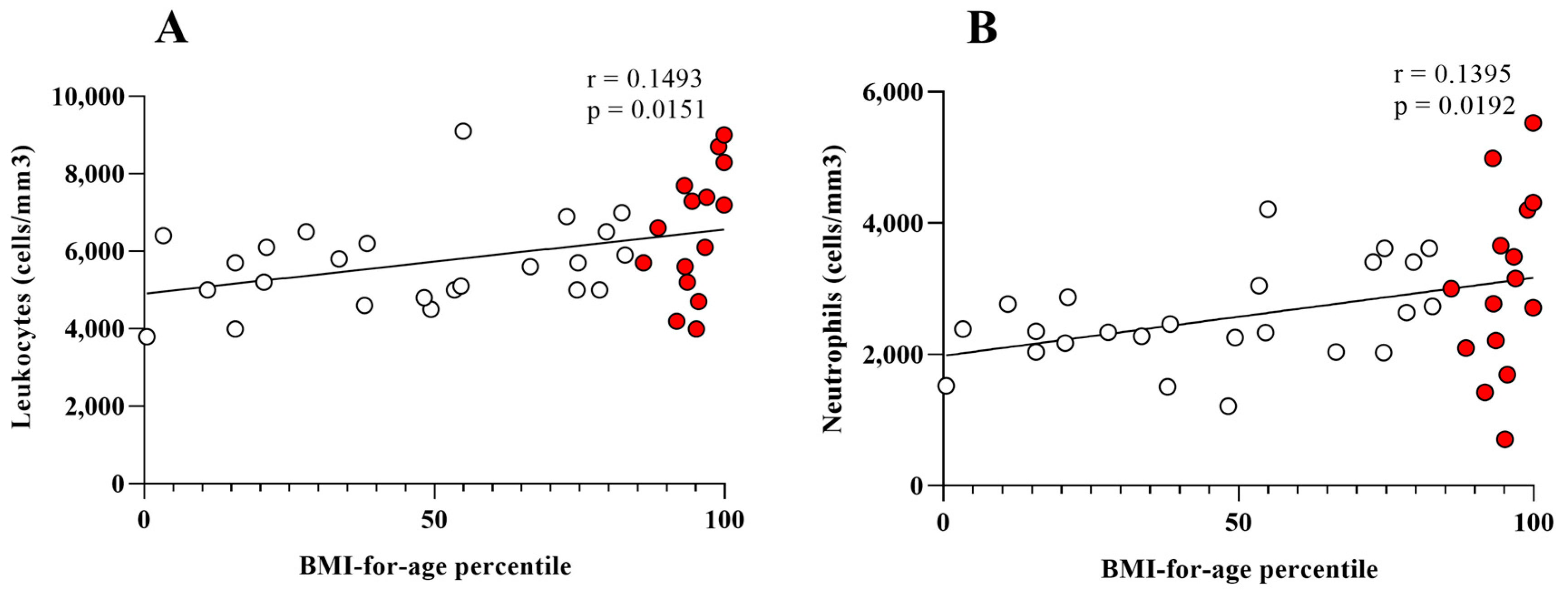
| Total leukocytes (cells/mm3) | 0.1493 | 3.398 to 29.76 | 0.0151 |
| Eosinophils (cells/mm3) | 0.0023 | −2.250 to 3.010 | 0.7714 |
| Neutrophils (cells/mm3) | 0.1395 | 2.054 to 21.73 | 0.0192 |
| Lymphocytes (cells/mm3) | 0.0395 | −2.580 to 10.63 | 0.2246 |
| Monocytes (cells/mm3) | 0.0558 | −0.2935 to 1.882 | 0.1475 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, B.L.; Cozer, A.W.D.; Vasconcelos Souza, F.C.; Santiago, L.D.; Lima, M.R.; Leite, P.M.; Silveira, A.M.S.; Enes, B.N.; Ottoni, M.H.F.; Gama, R.S.; et al. Overweight and Obesity Contribute to Inflammation and Reduction in Mean Corpuscular Volume and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin in Schoolchildren. Obesities 2024, 4, 524-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities4040041
Fernandes BL, Cozer AWD, Vasconcelos Souza FC, Santiago LD, Lima MR, Leite PM, Silveira AMS, Enes BN, Ottoni MHF, Gama RS, et al. Overweight and Obesity Contribute to Inflammation and Reduction in Mean Corpuscular Volume and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin in Schoolchildren. Obesities. 2024; 4(4):524-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities4040041
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Bárbara Leles, Alexandre Wallace Dias Cozer, Filipe Caldeira Vasconcelos Souza, Luana Dias Santiago, Marlucy Rodrigues Lima, Pauline Martins Leite, Alda Maria Soares Silveira, Barbara Nery Enes, Marcelo Henrique Fernandes Ottoni, Rafael Silva Gama, and et al. 2024. "Overweight and Obesity Contribute to Inflammation and Reduction in Mean Corpuscular Volume and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin in Schoolchildren" Obesities 4, no. 4: 524-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities4040041
APA StyleFernandes, B. L., Cozer, A. W. D., Vasconcelos Souza, F. C., Santiago, L. D., Lima, M. R., Leite, P. M., Silveira, A. M. S., Enes, B. N., Ottoni, M. H. F., Gama, R. S., & Gomides, T. A. R. (2024). Overweight and Obesity Contribute to Inflammation and Reduction in Mean Corpuscular Volume and Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin in Schoolchildren. Obesities, 4(4), 524-534. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities4040041





