Journal Description
Obesities
Obesities
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of obesity published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 13.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal Cluster of Food, Nutrition, and Health Science: Beverages, Dietetics, Foods, Nutraceuticals, Nutrients and Obesities.
Impact Factor:
1.3 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Stages of Change and Variation in Weight-Related Behaviors and Physical Activity: The Role of Motivation and Self-Efficacy in Adolescents
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 78; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040078 (registering DOI) - 30 Oct 2025
Abstract
The stages of change have been identified as a valuable framework for understanding the transition toward a healthy lifestyle. It is also important to recognize change through other psychosocial variables, such as motivation and self-efficacy. The objective of this study was to explore
[...] Read more.
The stages of change have been identified as a valuable framework for understanding the transition toward a healthy lifestyle. It is also important to recognize change through other psychosocial variables, such as motivation and self-efficacy. The objective of this study was to explore weight control over the course of an academic year (nine months) through three behaviors: the stage of change toward weight control (pre-contemplation, contemplation, preparation, action, maintenance), healthy and unhealthy eating behaviors for weight control, and the frequency of physical activity (PA). Furthermore, we wanted to ascertain whether the three distinct types of motivation (autonomous, controlled, and amotivation) and self-efficacy could account for fluctuations in weight control over time. The sample consisted of 303 adolescents (205 female and 98 male) between the ages of 15 and 23 (M = 17.26; SD = 1.65). Chi-square, t-test, and multiple linear stepwise regression analysis were employed. The results indicated that a higher proportion of adolescents were in the precontemplation and action stages at Time 2. Concurrently, an increase in the frequency of moderate-to-vigorous PA and an increase in healthy and unhealthy behaviors were observed during the school period. The present study posits that autonomous motivation, controlled motivation, and self-efficacy can explain healthy eating behaviors for weight control and the frequency of moderate-to-vigorous PA, while only controlled motivation explains unhealthy eating behaviors for weight control. The conclusion of the study points out that healthy behaviors can change over time due to individual regulation of motivation and increased self-perception of efficacy in one’s own abilities to perform a specific action to control weight.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Impact of a Vegetarian Diet upon Premature Aging, Metabolic Syndrome, and Health
by
Oana Codruta Bacean Miloicov, Georgiana Patricia Sitaru, Gabriel Cristian Vacaru, Ciprian Ioan Borca, Mihaela Cristina Simbrac, Roxana Folescu, Daniela Gurgus and Mirabela Anca Ursadan
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 77; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040077 - 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of an exclusively vegetarian diet, combined with physical activity and lifestyle interventions, on metabolic parameters in patients with metabolic syndrome, with a focus on preventing premature aging and improving overall health status. Materials and Methods:
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the impact of an exclusively vegetarian diet, combined with physical activity and lifestyle interventions, on metabolic parameters in patients with metabolic syndrome, with a focus on preventing premature aging and improving overall health status. Materials and Methods: A total of 150 participants (82 females, 68 males; aged 36–80 years, with a mean age of 61.45 years) diagnosed with metabolic syndrome were enrolled. Participants followed an exclusively vegetarian diet (≈2100 kcal/day; 65% carbohydrates, 23% lipids, 15% proteins, 52.4 g dietary fiber, and 0 mg cholesterol) along with a structured lifestyle program that included physical activity (2.5 h/day, intensity 2–6 METs), psychological counseling, smoking cessation support, weight and blood pressure management, hydrotherapy, massage, phytotherapy, and stress-reduction sessions. Baseline and post-intervention assessments were performed to measure total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides, glycemia, BMI, and blood pressure. Results: After 10 days of intervention, significant improvements were observed across all measured parameters: total cholesterol decreased by 41.21 mg/dL (−19.54%), triglycerides decreased by 72.86 mg/dL (−34.9%), LDL cholesterol decreased by 26.24 mg/dL (−19.71%), fasting glycemia decreased by 30.4 mg/dL (−21.61%), BMI decreased by 3%, systolic blood pressure decreased by 10.82 mmHg, and diastolic blood pressure decreased by 6.44 mmHg. Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that a structured lifestyle intervention, centered on a vegetarian diet and physical activity, has a significant beneficial effect on metabolic health. This approach improves cardiovascular risk factors, glycemic control, and body composition, and may play a preventive role against premature aging.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Prevalence and Correlates of Vitamin D Deficiency and Overweight/Obesity of School-Age Children in Colombia–Findings on the Double Burden of Malnutrition from Nationally-Representative Data
by
Edwin Guevara-Romero, Victor Florez-Garcia, Faith Ogungbe, Amy Harley and Alice Yan
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 76; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040076 - 24 Oct 2025
Abstract
The double burden of malnutrition (DBM)—the coexistence of overweight/obesity and micronutrient deficiency—is an emerging public health concern among school-aged children. Using data from 6063 participants in Colombia’s 2015 National Survey of Nutritional Status (ENSIN), this study estimated DBM prevalence and identified factors associated
[...] Read more.
The double burden of malnutrition (DBM)—the coexistence of overweight/obesity and micronutrient deficiency—is an emerging public health concern among school-aged children. Using data from 6063 participants in Colombia’s 2015 National Survey of Nutritional Status (ENSIN), this study estimated DBM prevalence and identified factors associated with its occurrence among children aged 5–12 years. DBM was defined as concurrent overweight/obesity (BMI-for-age z-score > 1) and vitamin D deficiency, applying thresholds of <30, <37.5, and <50 nmol/L. The prevalence of DBM ranged from 0.7% to 6.9%. Firth’s penalized logistic regression models were conducted separately for (1) overweight/obese combined, (2) overweight-only, and (3) obesity-only groups. For DBM1, insufficient physical activity was linked to higher odds across all three models. For DBM2, smaller household size and higher maternal education were associated with greater odds in the combined model. Living in large urban areas was related to lower odds compared with major metropolitan areas, a pattern also observed in the overweight-only model. For DBM3, children from the second wealth quartile (Q2) showed higher odds than those from the poorest (Q1), with a similar pattern in the overweight-only analysis. Stricter DBM definitions tended to capture behavioral and household characteristics, whereas broader thresholds reflected structural and contextual conditions. Despite its relatively low prevalence, DBM remains a relevant public health issue among Colombian schoolchildren.
Full article
Open AccessCommunication
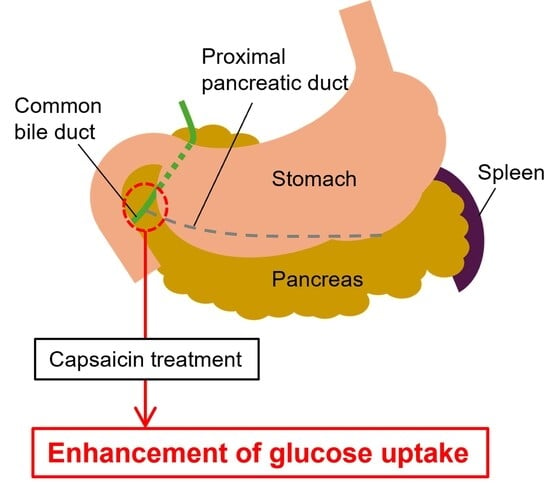
Blockade of the Proximal Pancreatic C Fiber Enhances Insulin Sensitivity in Rats
by
Masataka Kusunoki, Daisuke Sato, Fumiya Hisano, Kazuhiko Tsutsumi and Tetsuro Miyata
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 75; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040075 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Numerous reports have been published on the putative mechanisms of development of insulin resistance in diabetes mellitus. However, no unified view has been established yet, especially in regard to involvement of the nervous system in the regulation of insulin sensitivity. In this study,
[...] Read more.
Numerous reports have been published on the putative mechanisms of development of insulin resistance in diabetes mellitus. However, no unified view has been established yet, especially in regard to involvement of the nervous system in the regulation of insulin sensitivity. In this study, we investigated the involvement of the autonomic nervous system in cellular glucose uptake by blocking Group C nerve fibers (C fibers) in the rat pancreas with capsaicin. When the junction of the proximal pancreatic duct and common bile duct was treated with capsaicin, glucose uptake was enhanced, probably due to increased insulin sensitivity. This suggests that capsaicin may partially block the vagal nerve fibers innervating the pancreas, resulting in enhanced insulin sensitivity. In other words, our finding suggests that pancreatic autonomic nerves may be involved in the regulation of insulin sensitivity and that partial blockade of these nerves may improve insulin sensitivity.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of L-Fucose in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
by
Tomoya Nakamura, Tomohiko Nakao, Kazuyuki Ohara, Yuri Kominami, Miho Ito, Kazuki Mochizuki, Teruki Aizawa, Yusuke Akahori, Tomoya Ueno and Hideki Ushio
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 74; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040074 (registering DOI) - 11 Oct 2025
Abstract
L-fucose is a monosaccharide derived from brown algae and has potential applications as a functional food ingredient. Previous studies have reported that L-fucose reduces lipid accumulation in murine adipose tissue. Adipose tissue not only regulates energy metabolism but also functions as an endocrine
[...] Read more.
L-fucose is a monosaccharide derived from brown algae and has potential applications as a functional food ingredient. Previous studies have reported that L-fucose reduces lipid accumulation in murine adipose tissue. Adipose tissue not only regulates energy metabolism but also functions as an endocrine organ involved in inflammation through the production and secretion of various adipokines. L-fucose is expected to exert anti-inflammatory effects and modulate adipokine secretion in adipocytes. In the present study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of L-fucose in adipocytes. L-fucose significantly suppressed the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators and reduced the production of reactive oxygen species induced by inflammatory stimulation with a combination of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), tumor necrosis factor-⍺ (TNF-⍺), and interferon-γ (IFN-γ). These effects are likely mediated through the inhibition of key signaling pathways, including mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathways. Additionally, we found that L-fucose promoted the multimerization and secretion of high molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin, even under inflammatory conditions. Our results suggest that although L-fucose downregulates adiponectin expression, it contributes to the formation and/or stabilization of HMW adiponectin, which is functionally more relevant in anti-inflammatory and metabolic regulation. L-fucose thus holds promise as a functional food ingredient for mitigating inflammation in adipocytes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue How to Prevent Obesity and Inflammatory Disease 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Appetite Assessment Using the Arabic CNAQ Following a Telenutrition Weight-Loss Intervention with Health Coaching and Telemonitoring: A Cross-Sectional Analysis
by
Sarah N. Alsharif, Noura M. S. Eid, Noor A. Hakim, Najlaa M. M. Jawad and Soaad F. Alsulami
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 73; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040073 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Obesity is closely associated with appetite dysregulation, influenced by behavioral, hormonal, and neurological factors. The Council on Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ) is a validated tool, translated into Arabic, but its application in weight-loss interventions remains underexplored. This secondary cross-sectional analysis evaluated whether the
[...] Read more.
Obesity is closely associated with appetite dysregulation, influenced by behavioral, hormonal, and neurological factors. The Council on Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ) is a validated tool, translated into Arabic, but its application in weight-loss interventions remains underexplored. This secondary cross-sectional analysis evaluated whether the Arabic CNAQ can differentiate appetite levels after a 6-month telenutrition weight-loss intervention supported by telemonitoring and health coaching, and whether appetite is associated with weight-loss outcomes. A total of 36 participants were assessed: the intervention group (n = 21), who completed the program, and the control group (n = 15), who received no continuous support. Appetite was measured using the CNAQ after 6 months. Independent-samples t-tests and Mann–Whitney U tests were applied to compare appetite scores, while Chi-square tests were used for appetite categories. Results showed mean CNAQ scores of 27.87 (SD = 2.64) for the control group and 26.86 (SD = 4.46) for the intervention group (p = 0.402). Most participants reported moderate appetite (93.3% control; 76.2% intervention), with no significant between-group differences (p = 0.367). Although differences were not statistically significant, the findings demonstrate the feasibility of using the Arabic CNAQ in telehealth weight management. Larger studies with repeated measures are needed to confirm its utility in clinical and dietetic practice.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Impacts of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor-Agonist (GLP-1 RA) Treatment for Metabolic Disturbances and Weight Gain in Patients on Clozapine/Olanzapine: A Systematic Review
by
Karan Varshney, Shivani Panda, Hilary Fernando, Sergiu Sava and Taimur Khan
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 72; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040072 - 9 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Clozapine and olanzapine are important medications in the management of psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia. However, metabolic disturbances and weight gain are common side effects of these drugs. We aimed to evaluate the effects of GLP-1 RAs treatment for metabolic disturbances and weight
[...] Read more.
Clozapine and olanzapine are important medications in the management of psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia. However, metabolic disturbances and weight gain are common side effects of these drugs. We aimed to evaluate the effects of GLP-1 RAs treatment for metabolic disturbances and weight gain in patients on clozapine/olanzapine. For this systematic review, searches were conducted in eight different databases. After screening, outcome data was synthesized regarding weight gain and biochemical and clinical indicators of metabolic disturbance, as well as for adverse events/side effects, and any other benefits of GLP-1 RA treatment. A total of 14 studies were included in this medical systematic review, of which four were unique randomized control trials (RCTs), with study contexts including Australia and Denmark. GLP-1 RAs that were utilized include semaglutide, exenatide, and liraglutide. It was consistently demonstrated across studies that, when followed-up, those on GLP-1 RAs had achieved statistically lower levels of weight gain compared to those receiving placebo. A similar effect was seen on fasting glucose levels and glycated haemoglobin levels. Effects on other metabolic parameters were inconsistent. There were minimal gastrointestinal, psychological, cardiac, and other side effects noted across studies. GLP-1 RAs may offer utility in addressing the metabolic side effects of olanzapine/clozapine, but further research is needed. There remains a need to better understand impacts and potential side effects in larger and more diverse populations, as well as a need to better evaluate the long-term outcomes for patients.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Body Mapping as Risk Factors for Non-Communicable Diseases in Ghana: Evidence from Ghana’s 2023 Nationwide Steps Survey
by
Pascal Kingsley Mwin, Benjamin Demah Nuertey, Joana Ansong, Edmond Banafo Nartey, Leveana Gyimah, Philip Teg-Nefaah Tabong, Emmanuel Parbie Abbeyquaye, Priscilla Foriwaa Eshun, Yaw Ampem Amoako, Terence Totah, Frank John Lule, Sybil Sory Opoku Asiedu and Abraham Hodgson
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 71; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040071 - 3 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are the leading global cause of death, causing over 43 million deaths in 2021, including 18 million premature deaths, disproportionately affecting low- and middle-income countries. NCDs also incur significant economic losses, estimated at USD 7 trillion from 2011 to 2025,
[...] Read more.
Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are the leading global cause of death, causing over 43 million deaths in 2021, including 18 million premature deaths, disproportionately affecting low- and middle-income countries. NCDs also incur significant economic losses, estimated at USD 7 trillion from 2011 to 2025, despite low prevention costs. This study evaluated body mapping indicators: body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio—for predicting NCD risk, including hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases, using data from a nationally representative survey in Ghana. The study sampled 5775 participants via multistage stratified sampling, ensuring proportional representation by region, urban/rural residency, age, and gender. Ethical approval and informed consent were obtained. Anthropometric and biochemical data, including height, weight, waist and hip circumferences, blood pressure, fasting glucose, and lipid profiles, were collected using standardized protocols. Data analysis was conducted with STATA 17.0, accounting for complex survey design. Significant sex-based differences were observed: men were taller and lighter, while women had higher BMI and waist/hip circumferences. NCD prevalence increased with age, peaking at 60–69 years, and was higher in females. Lower education and marital status (widowed, divorced, separated) correlated with higher NCD prevalence. Obesity and high waist circumference strongly predicted NCD risk, but individual anthropometric measures lacked screening accuracy. Integrated screening and tailored interventions are recommended for improved NCD detection and management in resource-limited settings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Magnitude of Dyslipidemia and Factors Associated with Elevated LDL-C Among Black South Africans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Hospital
by
Mashudu Nemukula, Siphesihle Mkhwanazi, Tumelo Jessica Mapheto, Arun Kumar Malaisamy, Neel Sarovar Bhavesh, Olebogeng Harold Majane and Sechene Stanley Gololo
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 70; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040070 - 27 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a major global public health challenge with a significant impact on human life. The current study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the magnitude of dyslipidemia and the factors associated with elevated LDL-C levels among
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a major global public health challenge with a significant impact on human life. The current study aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the magnitude of dyslipidemia and the factors associated with elevated LDL-C levels among Black South Africans with T2DM. Methods: This was a cross-sectional study conducted in a tertiary hospital. Blood samples for glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and lipid profile were collected from the study participants and analyzed using Siemens Atellica™ analyzer. The data was entered into Microsoft excel and analyzed using SPSS version 24. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression was employed to identify variables significantly associated with the outcomes, with a p-value ≤ 0.05 and a 95% confidence interval. Results: A total of 194 study participants with T2DM were recruited in the study. The overall prevalence of dyslipidemia was 90.72%. Of those with dyslipidemia, 40.9% had an isolated dyslipidemia, 39.7% had a combined dyslipidemia and 19.3% had atherogenic dyslipidemia. Significant factors associated with elevated levels of LDL-C included age, non-adherence to treatment (NAT) and duration. However, after multivariate analysis, NAT was found to be an independent associated factor with elevated levels of LDL-C (AOR: 4.596; 95% CI: 0.177–2.874; p = 0.027). Conclusions: Our study found that dyslipidemia is highly prevalent among Black South African patients with T2DM at a tertiary hospital, despite the use of lipid-lowering therapy. NAT was significantly associated with elevated levels of LDL-C. However, it is important to note that the study employed a cross-sectional design, conducted at a single hospital, which may impair the generalizability of the findings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Relationship of Education Level, Lifestyle, and Personality to BMI and Obesity Differs Between Men and Women
by
Keisuke Kokubun, Kiyotaka Nemoto and Yoshinori Yamakawa
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 69; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040069 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Obesity has become a major global health concern, but few studies have examined the determinants of body mass index (BMI, kg/m2) and overweight/obesity (BMI ≥ 25) specifically in women. This study investigated the roles of education, lifestyle, and personality using data
[...] Read more.
Obesity has become a major global health concern, but few studies have examined the determinants of body mass index (BMI, kg/m2) and overweight/obesity (BMI ≥ 25) specifically in women. This study investigated the roles of education, lifestyle, and personality using data from a questionnaire survey of 4276 Japanese adults (2215 women and 2061 men) aged 30–79 years. Multiple regression and logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify factors associated with BMI (continuous) and obesity (BMI ≥ 25) in women. The multiple regression results indicated that educational attainment, rest, diet, and conscientiousness were negatively associated with BMI, whereas extraversion and openness were positively associated with BMI. Logistic regression further showed that higher education, regular exercise, sufficient rest, and conscientiousness were associated with non-obesity (BMI < 25), while openness was associated with obesity (BMI ≥ 25). To our knowledge, this is the first study to identify determinants of BMI and obesity in women with a simultaneous focus on education, lifestyle, and personality traits.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Combined Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials
by
Luiza Teixeira, Diogo Monteiro, Rui Matos, Raúl Antunes and Miguel Jacinto
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 68; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040068 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a global public health challenge, characterized by the coexistence of cardiometabolic risk factors such as abdominal obesity, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, and insulin resistance. Non-pharmacological strategies, including the Mediterranean diet (MD) and physical activity (PA), have been widely studied for their
[...] Read more.
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a global public health challenge, characterized by the coexistence of cardiometabolic risk factors such as abdominal obesity, dyslipidaemia, hypertension, and insulin resistance. Non-pharmacological strategies, including the Mediterranean diet (MD) and physical activity (PA), have been widely studied for their potential to prevent and manage MetS. This systematic review aimed to synthesize the evidence on the combined effect of MD and PA on MetS components in adults, based on randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Twenty-two RCTs published between 2018 and 2024 were included, involving 11,478 participants. The interventions ranged from 8 weeks to 3 years and combined adapted or hypocaloric MDs with moderate-to-high-intensity PA, typically including walking, aerobic exercise, or high-intensity interval training (HIIT), performed 3 to 7 times per week. The combined interventions resulted in reductions in body weight (−2.5 to −7.2 kg), body mass index (−0.7 to −2.2 kg/m2), waist circumference (−5.1 to −7.8 cm), and blood pressure (up to −9.0 mmHg systolic and −6.7 mmHg diastolic). Improvements in HDL cholesterol, triglyceride levels, and insulin sensitivity were also observed. These findings suggest that integrated interventions based on the Mediterranean lifestyle are effective in reducing MetS components and may support future public health strategies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Supplementation Effects of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. Flower Aqueous Extract on Body Composition and Metabolism in Eutrophic and Obese Rats
by
João Fernando Bernardo da Costa, Alana Louzada Millions Monteiro, Bruna Almeida Nascimento, Clarice Maia Vinagre de Oliveira, Karen Pereira Coutinho, Anderson Junger Teodoro, Barbara Elisabeth Teixeira-Costa and Mariana Sarto Figueiredo
Obesities 2025, 5(4), 67; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040067 - 25 Sep 2025
Abstract
Obesity is a chronic, multifactorial disease characterized by excess body fat and is a major risk factor for various metabolic disorders. Bioactive compounds from the diet have been recognized for their role in preventing chronic non-communicable diseases and as adjuvants in managing endocrine–metabolic
[...] Read more.
Obesity is a chronic, multifactorial disease characterized by excess body fat and is a major risk factor for various metabolic disorders. Bioactive compounds from the diet have been recognized for their role in preventing chronic non-communicable diseases and as adjuvants in managing endocrine–metabolic dysfunctions. Hibiscus sabdariffa L. (HSL) is rich in bioactive compounds with antioxidant, antihypertensive, and antihyperlipidemic properties. This study evaluated the effects of HSL flower extract supplementation on body composition, lipid profile, and biochemical parameters in both eutrophic and high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Thirty-two Wistar rats were assigned to four groups: control, control plus HSL extract, high-fat diet, and high-fat diet plus HSL extract. The extract was administered orally at 150 mg kg−1 for thirty days. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry revealed that HSL supplementation significantly attenuated fat mass gain (from 98 g to 75 g) and adiposity indices (10.23 to 8.86) in obese rats without altering total body mass. Moreover, the HSL extract improved lipid profiles by reducing LDL cholesterol from 23 to 13 mg dL−1 and exhibited potential hepatoprotective effects linked with decreased ALT (40 to 26.7 U L−1) and total bilirubin (0.12 to 0.07 mg dL−1) levels. Although glucose metabolism parameters had no significant differences, a trend toward improved insulin sensitivity was observed. These results suggest that the aqueous HSL extract may exert cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, and anti-obesity effects, supporting its potential as a complementary therapeutic agent in obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Impact of Food Compounds on Obesity Mechanisms)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cross-European Patterns of Obesity: Where Does Croatia Stand?—Descriptive Analysis of Waves 2015–2022 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Including Adults Aged Over 50
by
Manuela Maltarić, Mirela Kolak, Branko Kolarić, Darija Vranešić Bender and Jasenka Gajdoš Kljusurić
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 66; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030066 - 18 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This paper investigates the prevalence of obesity and its links to health and dietary habits in middle-aged and older populations in Europe (50+), with a particular focus on Croatia. In Croatia, only 33.9% of adults have a normal BMI, while almost two-thirds (64.8%)
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates the prevalence of obesity and its links to health and dietary habits in middle-aged and older populations in Europe (50+), with a particular focus on Croatia. In Croatia, only 33.9% of adults have a normal BMI, while almost two-thirds (64.8%) are classified as overweight or obese, placing Croatia among the EU countries with the highest prevalence of overweight. Obesity significantly increases the risk of serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes. Therefore, we used data from the SHARE (Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe), for the last four waves (wave 6–wave 9). The nutritional status was investigated (using the body mass index, BMI) as well as its relationship with cardiovascular disease and dietary habits. Different BMI categorizations were used (i) for the population under and (ii) over 65 years of age, and the results show that a significant proportion of the middle-aged and older European population is overweight or obese. When it comes to dietary habits, statistically significant differences in meat, fish, or chicken consumption were noted (p < 0.001): the Croatian population, especially men, consumes them significantly more often on a daily basis compared to the EU average. Similar patterns of dairy, legumes/eggs, and fruit/vegetable consumption were observed between the EU and Croatia, although there are some statistically significant differences in daily dairy consumption among the older population and in consumption of legumes/eggs and fruit/vegetables 3–6 times a week among the older population. The prevalence of CVD generally increases with increasing BMI in both regions and age groups. However, Croatia has a statistically significantly lower prevalence of high cholesterol compared to the EU in both age groups. Also, the trend of diabetes is more pronounced in the middle-aged population in Croatia compared to the EU. These results indicate specific differences in dietary habits and the association of BMI with certain CVDs in Croatia compared to the European Union average.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Associations Between Occupational Stress, Disordered Eating, and Obesity Among Police Officers in North Carolina
by
Ya-Ke Wu and Hanxin Liu
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 65; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030065 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
Obesity is a major public health concern among police officers, yet the links between occupational stress, disordered eating, and obesity remain unclear. This cross-sectional study examined 496 North Carolina officers to (1) assess severity of occupational stress (posttraumatic stress disorder [PTSD] symptoms, anti-police
[...] Read more.
Obesity is a major public health concern among police officers, yet the links between occupational stress, disordered eating, and obesity remain unclear. This cross-sectional study examined 496 North Carolina officers to (1) assess severity of occupational stress (posttraumatic stress disorder [PTSD] symptoms, anti-police sentiment, fear of victimization), disordered eating (binge eating and loss-of-control eating), and obesity by county type, region, and sex; (2) evaluate associations between occupational stress and disordered eating; and (3) explore relationships between disordered eating and weight-related measures. Officers completed online surveys, and trained staff measured body mass index (BMI), waist and hip circumferences, and waist-to-hip ratio. Nearly 60 percent of officers were classified as obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2), and over 20 percent reported moderate to severe binge eating. Rural officers reported higher PTSD symptoms, binge eating, and loss-of-control eating than those in urban or suburban areas. Coastal Plain and Piedmont officers had higher BMI and larger waist and hip circumferences than those in the Mountain region. Higher occupational stress was linked to more severe disordered eating, which was associated with greater BMI and adiposity, although the effect sizes were modest. Findings support targeted interventions addressing occupational stress and disordered eating to prevent obesity and enhance officer well-being.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Obesity–Housing Nexus: An Integrative Conceptualization of the Impact of Housing and Built Environment on Obesity
by
Kritika Rana and Ritesh Chimoriya
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 64; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030064 - 20 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Obesity has emerged as one of the most significant public health challenges of the 21st century, with its prevalence increasing at an alarming rate globally. While individual factors such as diet and physical inactivity are well-known contributors, the built environment, particularly housing, plays
[...] Read more.
Obesity has emerged as one of the most significant public health challenges of the 21st century, with its prevalence increasing at an alarming rate globally. While individual factors such as diet and physical inactivity are well-known contributors, the built environment, particularly housing, plays a critical yet understudied role in shaping obesity-related behaviors. This study examines the multilayered relationship between housing and obesity, focusing on built and neighborhood environment, affordability, and the social environment. Poor housing quality, such as overcrowding and inadequate ventilation, can potentially lead to chronic stress and sedentary behaviors, while housing design influences physical activity through characteristics such as design features and outdoor spaces. Housing location affects access to amenities such as parks and healthy food options, with disparities in access contributing to obesity in low-income areas. Similarly, neighborhood walkability, influenced by infrastructure and land use, encourages active transportation and recreation. Housing affordability also impacts dietary choices and access to recreational facilities, particularly for low-income families. Moreover, the social environment within housing communities can foster or hinder healthy behaviors through social networks and community engagement. This study emphasizes the need for health-conscious urban planning and policies that address these housing-related factors to combat obesity and promote healthier lifestyles. By integrating these Obesity–Housing Nexus, policymakers can create environments that support physical activity, healthy eating, as well as overall health and well-being.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
“Super-Responders” to Liraglutide Monotherapy and the Growing Evidence of Efficacy of GLP-1 Analogues in Obesity Management: A Longitudinal Prospective Cohort Study
by
Ellina Lytvyak, Eduardo Grunvald, Devika Shreekumar, Peter Rye, Olexandr Troshyn, Sarah Cawsey, Aldo J. Montano-Loza, Arya M. Sharma and Renuca Modi
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 63; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030063 - 20 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aims: Individual weight loss results achieved with Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) vary significantly. Our aim was to describe the characteristics of patients with obesity who achieved ≥ 20% total weight loss (TWL) on liraglutide and appraise those findings through the prism
[...] Read more.
Aims: Individual weight loss results achieved with Glucagon-like Peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) vary significantly. Our aim was to describe the characteristics of patients with obesity who achieved ≥ 20% total weight loss (TWL) on liraglutide and appraise those findings through the prism of an evolving spectrum of GLP-1RA. Methods: This longitudinal prospective cohort study included 21 patients (90.5% females, age 50 (IQR 17) years, class II/III obesity (Body Mass Index ≥ 35 kg/m2) followed at the Edmonton Adult Bariatric Clinic for 65.1 (IQR 15.5) weeks. All patients received treatment with liraglutide 3.0 mg subcutaneously daily along with involvement in an integrated lifestyle modification program. Results: Liraglutide was well-tolerated, with its benefits experienced by >90% of patients. The vast majority were consistently tracking calories (95.2%, n = 20) and protein intake (90.5%, n = 19), achieving a calorie deficit of 651 (IQR 323) kcal/day, and had their mental health conditions and psychological issues successfully managed. At 16, 26, and 52 weeks, TWL was 14.3% (IQR 3.7), 18.7% (IQR 8.8), and 25.9% (IQR 9.6), respectively (p < 0.001). Over 20% TWL was achieved by 72.2% of patients by week 52. Conclusions: A select number of patients with obesity will attain weight loss that rivals bariatric surgery using liraglutide monotherapy. Despite liraglutide being less effective compared to newer agents on the market, some individuals will respond strongly and should be considered when other therapies are inaccessible. Given the societal burden and numerous challenges faced by people with obesity, GLP-1RA should be pursued in clinical practice to assist in achieving weight loss goals while being convenient and safe.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in University Students: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Sónia Mateus, Ana Miguel Amaral, Patrícia Coelho and Francisco Rodrigues
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 62; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030062 - 18 Aug 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Subclinical atherosclerosis is increasingly recognized in younger populations, often progressing silently until the onset of overt cardiovascular events. Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is a validated, non-invasive biomarker of early vascular alterations. Although the Mediterranean diet (MD) is well established as cardioprotective, its
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Subclinical atherosclerosis is increasingly recognized in younger populations, often progressing silently until the onset of overt cardiovascular events. Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) is a validated, non-invasive biomarker of early vascular alterations. Although the Mediterranean diet (MD) is well established as cardioprotective, its relationship with CIMT in young adults remains insufficiently studied. Objective: To assess sex-specific adherence to the Mediterranean diet and its association with carotid intima-media thickness in a cohort of university students. Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed involving 60 university students (50% male, aged 17–25 years), selected through stratified probabilistic sampling. Data were collected on sociodemographic characteristics, vascular risk factors, MD adherence via the PREDIMED questionnaire, and CIMT measured using a high-resolution carotid Doppler ultrasound. Statistical analyses included chi-square tests and descriptive statistics, with significance set at ρ ≤ 0.05. Results: A notable 95% of participants showed low adherence to the Mediterranean diet. Significant sex differences in dietary patterns were identified: males consumed more red meat (ρ = 0.023), while females reported higher fish intake (ρ = 0.037). Despite behavioral risk factors, all CIMT values remained within normal ranges (≤0.9 mm). No significant association was found between MD adherence and CIMT (ρ = 0.554). Conclusion: This exploratory study reveals a high prevalence of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors, including poor dietary adherence, among young adults, despite the absence of detectable vascular structural changes. Although no significant association was found, the findings reflect the dietary and behavioral profiles of a young, low-risk population.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Phase Angle Is Related with Visceral Obesity in Young Adults
by
Izabela Mandryk, Joanna Bonior and Magdalena Koszarska
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 61; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030061 - 15 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Obesity is a global problem, increasing interest in adipose tissue (AT) biology. One of the techniques for analyzing visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and phase angle (PhA) is bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). PhA is considered an indicator of cell integrity and health and can
[...] Read more.
Obesity is a global problem, increasing interest in adipose tissue (AT) biology. One of the techniques for analyzing visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and phase angle (PhA) is bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). PhA is considered an indicator of cell integrity and health and can be a prognostic marker in diseases and clinical conditions. The aim of the study was to assess the nutritional status and level of visceral fat area (VFA) to investigate the association between phase angle (PhA) and content of visceral adipose tissue in young adults. Our cohort consisted of 292 young adults (18–25), both sexes. Body composition was performed by the inBody 770 analyzer. We confirmed the relationship between PhA and gender (female vs. male: 5.3 vs. 6.5; p < 0.001) and BMI (female vs. male: 22.56 kg/m2 vs. 23.78 kg/m2; p = 0.013). A total of 20.2% of examined students had a VFA of more than 100 cm2 (Visceral Obesity, VO). We demonstrated a dependence between VFA and PhA value (PhA = 5.4 (VFA > 100 cm2) vs. PhA = 5.7 (VFA < 100 cm2), p = 0.003). Students with VO and normal BMI had a significantly lower PhA than those with VO and BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (p = 0.021). PhA may be a useful indicator for assessing nutritional status and physiological differences related to gender, BMI, and visceral obesity in young adults.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Associations Between Self-Perceived Psychosocial Stress and Markers of Adiposity in Ga Mashie, Urban Ghana: Evidence from a Cross-Sectional Population-Based Survey
by
Emeline Rougeaux, Samuel Amon, Leonard Baatiema, Sandra Boatemaa Kushitor, Mawuli Komla Kushitor, Sedzro Kojo Mensah, Rolando Leiva-Granados, Akanksha A. Marphatia, Jonathan C. K. Wells, Carlos Salvador Grijalva-Eternod, Irene Akwo Kretchy and Edward Fottrell
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 60; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030060 - 9 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Prior research from Ghana suggests psychosocial stress is associated with lower body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC), both markers of adiposity, contrasting with meta-analyses showing positive associations in other settings. This study aimed to explore how stress was associated with markers
[...] Read more.
Prior research from Ghana suggests psychosocial stress is associated with lower body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC), both markers of adiposity, contrasting with meta-analyses showing positive associations in other settings. This study aimed to explore how stress was associated with markers of adiposity in urban Ghanaian adults. Data included 854 adults from the Contextual Awareness, Response and Evaluation Diabetes in Ghana survey carried out in November–December 2022 in Ga Mashie, a deprived area of the capital Accra. Associations between self-perceived stress (Perceived Stress Scale 10, categorized into low and average–high stress) and BMI or WC-for-height ratio (WHR) were assessed using linear regression. Results were adjusted for survey design and confounders and stratified by sex. Greater stress was associated with higher BMI and WHR in females (adjusted coeff. [95% CI]: BMI: 2.3 [0.5, 4.0], WHR: 0.03 [0.00, 0.06]). No associations were found in males. These findings highlight the need to understand the complex interactions between gender, stress, and increasing burdens of obesity and other associated non-communicable diseases in urban African settings, with a view to designing context-specific interventions to reduce risk.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Resetting Time: The Role of Exercise Timing in Circadian Reprogramming for Metabolic Health
by
Stuart J. Hesketh
Obesities 2025, 5(3), 59; https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030059 - 7 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Circadian rhythms are intrinsic 24 h cycles that regulate metabolic processes across multiple tissues, with skeletal muscle emerging as a central node in this temporal network. Muscle clocks govern gene expression, fuel utilisation, mitochondrial function, and insulin sensitivity, thereby maintaining systemic energy homeostasis.
[...] Read more.
Circadian rhythms are intrinsic 24 h cycles that regulate metabolic processes across multiple tissues, with skeletal muscle emerging as a central node in this temporal network. Muscle clocks govern gene expression, fuel utilisation, mitochondrial function, and insulin sensitivity, thereby maintaining systemic energy homeostasis. However, circadian misalignment, whether due to behavioural disruption, nutrient excess, or metabolic disease, impairs these rhythms and contributes to insulin resistance, and the development of obesity, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Notably, the muscle clock remains responsive to non-photic cues, particularly exercise, which can reset and amplify circadian rhythms even in metabolically impaired states. This work synthesises multi-level evidence from rodent models, human trials, and in vitro studies to elucidate the role of skeletal muscle clocks in circadian metabolic health. It explores how exercise entrains the muscle clock via molecular pathways involving AMPK, SIRT1, and PGC-1α, and highlights the time-of-day dependency of these effects. Emerging data demonstrate that optimally timed exercise enhances glucose uptake, mitochondrial biogenesis, and circadian gene expression more effectively than time-agnostic training, especially in individuals with metabolic dysfunction. Finally, findings are integrated from multi-omic approaches that have uncovered dynamic, time-dependent molecular signatures that underpin circadian regulation and its disruption in obesity. These technologies are uncovering biomarkers and signalling nodes that may inform personalised, temporally targeted interventions. By combining mechanistic insights with translational implications, this review positions skeletal muscle clocks as both regulators and therapeutic targets in metabolic disease. It offers a conceptual framework for chrono-exercise strategies and highlights the promise of multi-omics in developing precision chrono-medicine approaches aimed at restoring circadian alignment and improving metabolic health outcomes.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Behavioral Sciences, Children, Healthcare, IJERPH, JFMK, Obesities
The Effect of Physical Activity on the Population's Health
Topic Editors: Stefania Paduano, Federica ValerianiDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
Geriatrics, IJMS, Life, Sports, Neurology International, Obesities
Exercise and Human Aging: Physiological and Psychological Functions
Topic Editors: Samuel Da Silva Aguiar, Ismael Perez-SuarezDeadline: 20 September 2026
Topic in
Nutrients, Metabolites, Healthcare, Children, Obesities, Life
Non-Communicable Diseases Silent Killer: Metabolic and Obesity Risks of Sedentary Behaviors
Topic Editors: Kotsedi Daniel Monyeki, Machoene Derrick SekgalaDeadline: 30 September 2026
Topic in
Dietetics, Nutrients, Obesities, Diseases, IJMS, Metabolites
Dietary Habits in Liver Health and Disease: Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Topic Editors: Evelyn Nunes Goulart Da Silva Pereira, Rosane Harter Griep, Anissa DaliryDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Obesities
The Impact of Food Compounds on Obesity Mechanisms
Guest Editor: Nobuyuki TakahashiDeadline: 30 November 2025
Special Issue in
Obesities
How to Prevent Obesity and Inflammatory Disease 2025
Guest Editor: Sara BaldassanoDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Obesities
Obesity in the 21st Century: Public Health Perspectives and Population Solutions
Guest Editors: Ritesh Chimoriya, Kritika RanaDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Obesities
Novel Technology-Based Exercise for Childhood Obesity Prevention
Guest Editors: Alessandra Amato, Sara BaldassanoDeadline: 31 May 2026








