Effect of High-Fat Diet and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v on the Gut Microbiome of Adolescent and Adult Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2. Microbiome Analysis and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Disclaimer
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chrissini, M.K.; Panagiotakos, D.B. Public health interventions tackling childhood obesity at European level: A literature review. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 30, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, A.C.; Ravanbakht, S.N.; Skelton, J.A.; Perrin, E.M.; Armstrong, S.C. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity in US Children, 1999–2016. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20173459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yli-Piipari, S.; El-Shahawy, O.; Tamura, K. Trends and key disparities of obesity among US adolescents: The NHANES from 2007 to 2020. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0290211. [Google Scholar]
- Hainsworth, K.R.; Simpson, P.M.; Raff, H.; Grayson, M.H.; Zhang, L.; Weisman, S.J. Circulating inflammatory biomarkers in adolescents: Evidence of interactions between chronic pain and obesity. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raff, H.; Phillips, J.M.; Simpson, P.M.; Weisman, S.J.; Hainsworth, K.R. Serum soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in adolescents: Interaction of chronic pain and obesity. Pain Rep. 2020, 5, e836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzi, A.; Briata, I.M.; Di Napoli, I.; Giugliano, S.; Di Sabatino, A.; Rescigno, M.; Cena, H. Prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics and postbiotics to adolescents in metabolic syndrome. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.G.; Guedes, D.P. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Evidence. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.R. Complications of obesity in children and adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33 (Suppl. 1), S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Martin, R.M.; Gunnell, D.; Galobardes, B.; Ebrahim, S.; Sandhu, J.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; McCarron, P.; Davey Smith, G. Association of body mass index measured in childhood, adolescence, and young adulthood with risk of ischemic heart disease and stroke: Findings from 3 historical cohort studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendor, C.D.; Bardugo, A.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Afek, A.; Twig, G. Cardiovascular morbidity, diabetes and cancer risk among children and adolescents with severe obesity. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simic, B.S. Childhood obesity as a risk factor in adulthood and its prevention. Prev. Med. 1983, 12, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, F.E. Health implications of childhood obesity. Ann. Intern. Med. 1985, 103, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, S.; Giles, H.; Jarvis, P.; New, K. The weight status of children in late childhood within south East Wales and predictions for their future health. J. Public Health 2022, 44, e557–e561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, A.; Simmonds, M.; Owen, C.G.; Woolacott, N. Childhood obesity as a predictor of morbidity in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Conte, C.; Cammarota, G.; Haley, A.P.; Styriak, I.; Gaspar, L.; Fusek, J.; Rodrigo, L.; Kruzliak, P. Probiotics in prevention and treatment of obesity: A critical view. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobyliak, N.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Boyko, N.; Tsyryuk, O.; Beregova, T.; Ostapchenko, L. Probiotics and nutraceuticals as a new frontier in obesity prevention and management. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 141, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez-Paez, A.; Gomez Del Pugar, E.M.; Lopez-Almela, I.; Moya-Perez, A.; Codoner-Franch, P.; Sanz, Y. Depletion of Blautia Species in the Microbiota of Obese Children Relates to Intestinal Inflammation and Metabolic Phenotype Worsening. mSystems 2020, 5, e00857-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislawski, M.A.; Dabelea, D.; Lange, L.A.; Wagner, B.D.; Lozupone, C.A. Gut microbiota phenotypes of obesity. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinart, M.; Dotsch, A.; Schlicht, K.; Laudes, M.; Bouwman, J.; Forslund, S.K.; Pischon, T.; Nimptsch, K. Gut Microbiome Composition in Obese and Non-Obese Persons: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cao, M.; Guo, M.; He, J.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, C. Gut Microbiota Characteristics of People with Obesity by Meta-Analysis of Existing Datasets. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, R.; Guo, M.; Zheng, H. Characteristics of gut microbiota in people with obesity. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, M.A.; Bird, A.R. The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health. Nutrients 2014, 7, 17–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; An, Y.; Hao, F.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Correlations of Fecal Metabonomic and Microbiomic Changes Induced by High-fat Diet in the Pre-Obesity State. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegal, K.M.; Troiano, R.P. Changes in the distribution of body mass index of adults and children in the US population. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, R.A.; Atkinson, S.N.; Burnett, C.M.L.; Grobe, J.L.; Kirby, J.R. The Gut Microbiome, Energy Homeostasis, and Implications for Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani-Perez, M.; Liebana-Garcia, R.; Flor-Duro, A.; Bonillo-Jimenez, D.; Bullich-Vilarrubias, C.; Olivares, M.; Sanz, Y. Obesity and the gut microbiota: Implications of neuroendocrine and immune signaling. FEBS J. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Savytska, M.; Kyriienko, D.; Zaychenko, G.; Ostapchenko, D.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Kobyliak, N. Probiotic co-supplementation with absorbent smectite for pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: A secondary-data analysis of a randomized double-blind controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1276642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumura, E.A.; Bersch-Ferreira, A.C.; Torreglosa, C.R.; da Silva, J.T.; Coqueiro, A.Y.; Kuntz, M.G.F.; Chrispim, P.P.; Weber, B.; Cavalcanti, A.B. Effects of oral supplementation with probiotics or synbiotics in overweight and obese adults: A systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized trials. Nutr. Rev. 2019, 77, 430–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechelotte, P.; Breton, J.; Trotin-Picolo, C.; Grube, B.; Erlenbeck, C.; Bothe, G.; Fetissov, S.O.; Lambert, G. The Probiotic Strain H. alvei HA4597® Improves Weight Loss in Overweight Subjects under Moderate Hypocaloric Diet: A Proof-of-Concept, Multicenter Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savytska, M.; Kozyk, M.; Strubchevska, K.; Yosypenko, K.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Kobyliak, N.; Boccuto, L.; Pellicano, R.; Fagoonee, S.; Scarpellini, E.; et al. Association between intestinal microflora and obesity. Minerva Gastroenterol. 2024, 70, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raff, H.; Hainsworth, K.R.; Woyach, V.L.; Weihrauch, D.; Wang, X.; Dean, C. Probiotic and high-fat diet: Effects on pain assessment, body composition, and cytokines in male and female adolescent and adult rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2024, 327, R123–R132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, A.; Dib, A.L.; Lakhdara, N.; Kadja, L.; Espigares, E.; Moreno, E.; Bouaziz, O.; Gagaoua, M. Study of Probiotic Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 and Lactobacillus plantarum 299v Strains on Biochemical and Morphometric Parameters of Rabbits after Obesity Induction. Biology 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, E.A.; Teixeira, C.; Montelius, C.; Jeppsson, B.; Larsson, N. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v (LP299V®): Three decades of research. Benef. Microbes 2021, 12, 441–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofeld, B.C.; Puppala, V.K.; Tyagi, S.; Ahn, K.W.; Anger, A.; Jia, S.; Salzman, N.H.; Hessner, M.J.; Widlansky, M.E. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v probiotic supplementation in men with stable coronary artery disease suppresses systemic inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Bozadjieva-Kramer, N.; Shao, Y.; Lyons-Abbott, S.; Rupp, A.C.; Sandoval, D.A.; Seeley, R.J. The gut peptide Reg3g links the small intestine microbiome to the regulation of energy balance, glucose levels, and gut function. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1765–1778.e1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, C.; Tiffay, A.; Breemeersch, C.E.; Dreux, V.; Bole-Feysot, C.; Guerin, C.; Breton, J.; Maximin, E.; Monnoye, M.; Dechelotte, P.; et al. Sex-dependent effects of a high fat diet on metabolic disorders, intestinal barrier function and gut microbiota in mouse. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Derrien, M.; Rocher, E.; van-Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.; Strissel, K.; Zhao, L.; Obin, M.; et al. Modulation of gut microbiota during probiotic-mediated attenuation of metabolic syndrome in high fat diet-fed mice. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thriene, K.; Michels, K.B. Human Gut Microbiota Plasticity throughout the Life Course. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fak, F.; Ahrne, S.; Linderoth, A.; Molin, G.; Jeppsson, B.; Westrom, B. Age-related effects of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus plantarum 299v on gastrointestinal function in suckling rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fak, F.; Ahrne, S.; Molin, G.; Jeppsson, B.; Westrom, B. Maternal consumption of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v affects gastrointestinal growth and function in the suckling rat. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jacobs, J.P.; Lagishetty, V.; Yuan, P.Q.; Wu, S.V.; Million, M.; Reeve, J.R., Jr.; Pisegna, J.R.; Tache, Y. High-protein diet improves sensitivity to cholecystokinin and shifts the cecal microbiome without altering brain inflammation in diet-induced obesity in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 313, R473–R486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingbeil, E.; de La Serre, C.B. Microbiota modulation by eating patterns and diet composition: Impact on food intake. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R1254–R1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xie, W.; Chen, S.; Strong, J.A.; Print, M.S.; Wang, J.I.; Shareef, A.F.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Zhang, J.M. High-fat diet increases pain behaviors in rats with or without obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xie, W.; Strong, J.A.; Berta, T.; Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.M. High-fat diet exacerbates postoperative pain and inflammation in a sex-dependent manner. Pain 2018, 159, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. BMJ Open Sci. 2020, 4, e100115. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, P. The Laboratory Rat: Relating Its Age With Human’s. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M. Adolescence as a vulnerable period to alter rodent behavior. Cell Tissue Res. 2013, 354, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P.G.; Alvarez, P.; Levine, J.D. A role for gut microbiota in early-life stress-induced widespread muscle pain in the adult rat. Mol. Pain 2021, 17, 17448069211022952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommineni, S.; Bretl, D.J.; Lam, V.; Chakraborty, R.; Hayward, M.; Simpson, P.; Cao, Y.; Bousounis, P.; Kristich, C.J.; Salzman, N.H. Bacteriocin production augments niche competition by enterococci in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. Nature 2015, 526, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D. Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Gonzalez, A.; Smarr, L.; McDonald, D.; Morton, J.T.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Knight, R. Bringing the Dynamic Microbiome to Life with Animations. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez-Baeza, Y.; Pirrung, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Knight, R. EMPeror: A tool for visualizing high-throughput microbial community data. Gigascience 2013, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Weingart, G.; Tickle, T.L.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with GraPhlAn. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, W.; Meng, L.; Huang, H. Oscillospira—A candidate for the next-generation probiotics. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1987783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benard, M.V.; de Goffau, M.C.; Blonk, J.; Hugenholtz, F.; van Buuren, J.; Paramsothy, S.; Kaakoush, N.O.; D’Haens, G.; Borody, T.J.; Kamm, M.A.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Outcome and Gut Microbiota Composition in Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, N.; Chen, J.; Wu, A.; Nepovimova, E.; Valis, M.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Bacillus velezensis A2 Inhibited the Cecal Inflammation Induced by Zearalenone by Regulating Intestinal Flora and Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 806115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmeyer, S.; Lee, K.; Jayaraman, A.; Alaniz, R.C. Microbiota metabolite regulation of host immune homeostasis: A mechanistic missing link. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2015, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicks, L.M.T. How important are fatty acids in human health and can they be used in treating diseases? Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2420765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobionda, S.; Sittipo, P.; Kwon, H.Y.; Lee, Y.K. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Intestinal Inflammation with Respect to Diet and Extrinsic Stressors. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricaboni, D.; Mailhe, M.; Cadoret, F.; Vitton, V.; Fournier, P.E.; Raoult, D. ’Colidextribacter massiliensis’ gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from human right colon. N. Microbes N. Infect. 2017, 17, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Yin, J.; Liuqi, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, B.; Wang, S. Fucoidan Ameliorated Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14864–14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardzikova, S.; Gajewska, M.; Galka, N.; Stefanek, M.; Balaz, A.; Garaiova, M.; Holic, R.; Swiderek, W.; Soltys, K. Can longer lifespan be associated with gut microbiota involvement in lipid metabolism? FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2024, 100, fiae135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, P.A.; Simcox, J.; Raff, H.; Wade, G.; Von Bank, H.; Weisman, S.; Hainsworth, K. Lipid signatures of chronic pain in female adolescents with and without obesity. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maesschalck, C.; Van Immerseel, F.; Eeckhaut, V.; De Baere, S.; Cnockaert, M.; Croubels, S.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Vandamme, P. Faecalicoccus acidiformans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the chicken caecum, and reclassification of Streptococcus pleomorphus (Barnes et al. 1977), Eubacterium biforme (Eggerth 1935) and Eubacterium cylindroides (Cato et al. 1974) as Faecalicoccus pleomorphus comb. nov., Holdemanella biformis gen. nov., comb. nov. and Faecalitalea cylindroides gen. nov., comb. nov., respectively, within the family Erysipelotrichaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 3877–3884. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.; Rios-Covian, D.; Huillet, E.; Auger, S.; Khazaal, S.; Bermudez-Humaran, L.G.; Sokol, H.; Chatel, J.M.; Langella, P. Faecalibacterium: A bacterial genus with promising human health applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Duan, Y.; Dai, H.; An, Y.; Cheng, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; et al. Investigation of gut microbiome changes in type 1 diabetic mellitus rats based on high-throughput sequencing. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, M.D.; Westwater, C.; Novince, C.M. Adolescence and the Microbiome: Implications for Healthy Growth and Maturation. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Wang, S.; Solberg Woods, L.C.; Seshie, O.; Chung, S.T.; Shively, C.A.; Register, T.C.; Craft, S.; McClain, D.A.; Yadav, H. Comparative Microbiome Signatures and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Mouse, Rat, Non-human Primate, and Human Feces. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalesi, S.; Bellissimo, N.; Vandelanotte, C.; Williams, S.; Stanley, D.; Irwin, C. A review of probiotic supplementation in healthy adults: Helpful or hype? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 73, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainsworth, K.R.; Davies, W.H.; Khan, K.A.; Weisman, S.J. Co-occurring chronic pain and obesity in children and adolescents: The impact on health-related quality of life. Clin. J. Pain 2009, 25, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainsworth, K.R.; Miller, L.A.; Stolzman, S.C.; Fidlin, B.M.; Davies, W.H.; Weisman, S.J.; Skelton, J.A. Pain as a Comorbidity of Pediatric Obesity. Infant. Child. Adolesc. Nutr. 2012, 4, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, A.M.; Jastrowski Mano, K.E.; Weisman, S.J.; Hainsworth, K.R. Obesity impedes functional improvement in youth with chronic pain: An initial investigation. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
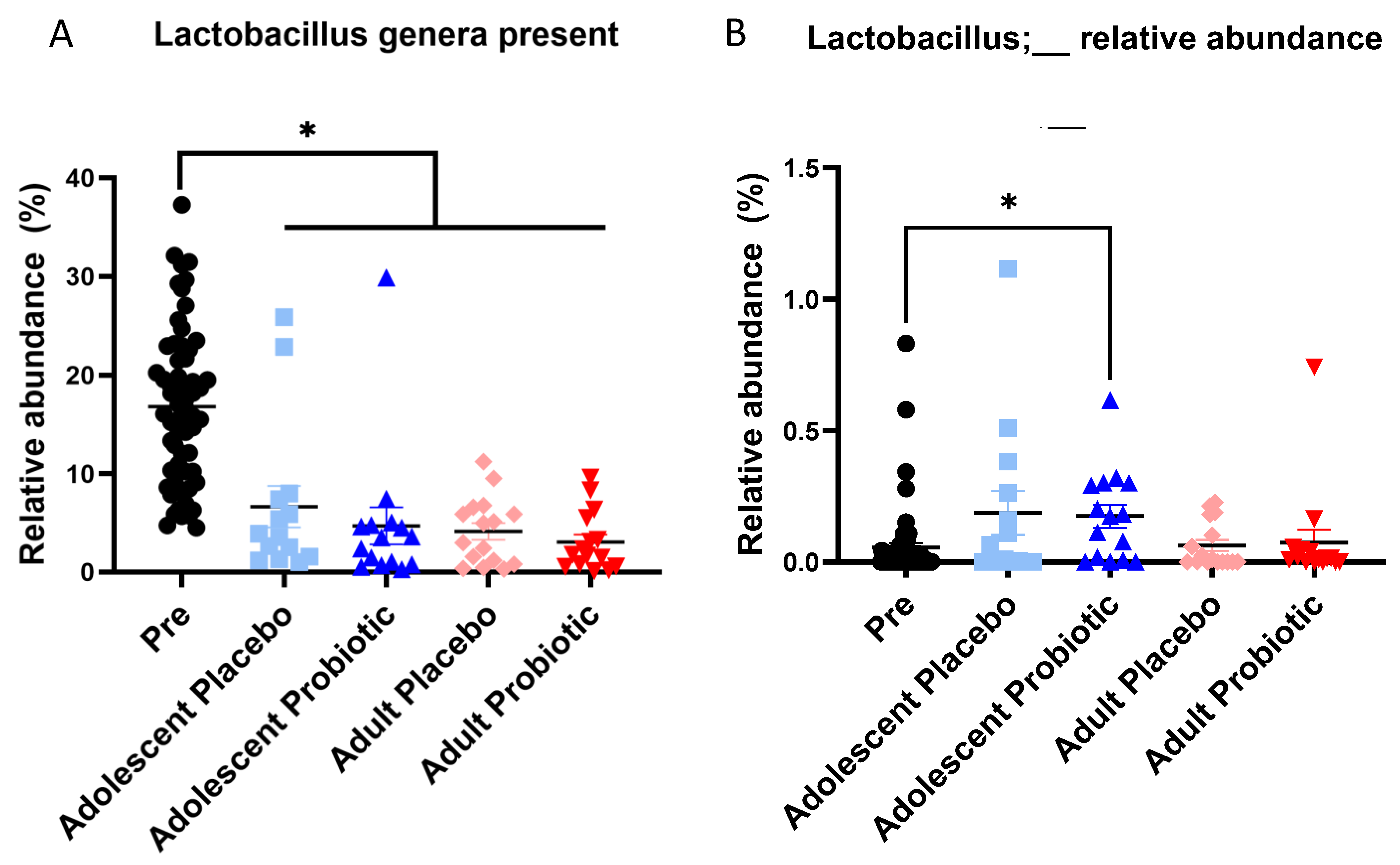

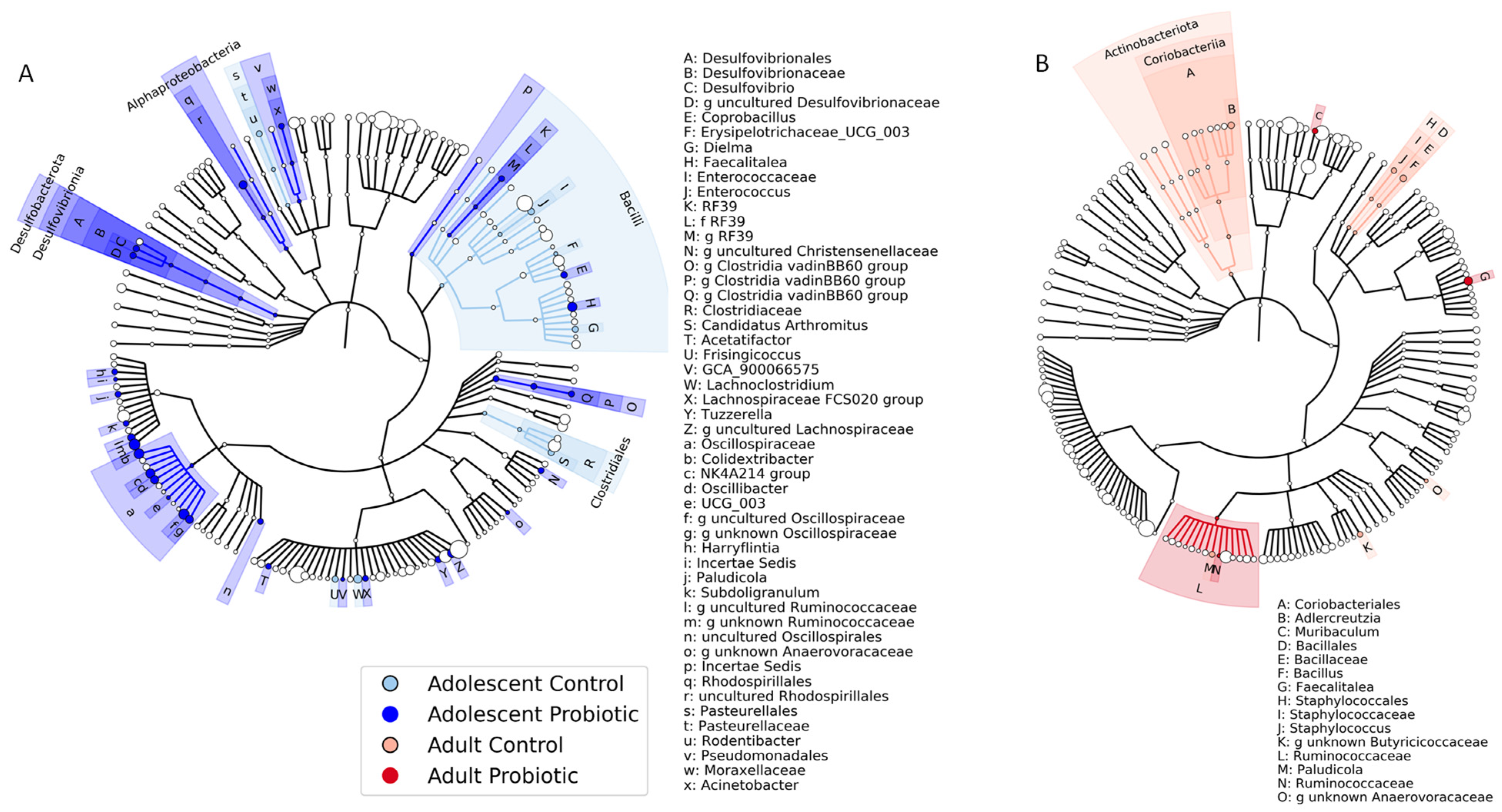


| Standard-Fat Diet | High-Fat Diet (HFD) | Probiotic Lp299v | Placebo | Duration of Diet +/− Probiotic from Weaning (Weeks) | n | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adolescent | + | − | − | + | 6 | 6 |
| − | + | − | + | 6 | 8 | |
| + | − | + | − | 6 | 8 | |
| − | + | + | − | 6 | 7 | |
| Adult | + | − | − | + | 11 | 8 |
| − | + | − | + | 11 | 8 | |
| + | − | + | − | 11 | 7 | |
| − | + | + | − | 11 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atkinson, S.N.; Dean, C.; Woyach, V.L.; Hainsworth, K.R.; Raff, H. Effect of High-Fat Diet and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v on the Gut Microbiome of Adolescent and Adult Rats. Obesities 2025, 5, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5010017
Atkinson SN, Dean C, Woyach VL, Hainsworth KR, Raff H. Effect of High-Fat Diet and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v on the Gut Microbiome of Adolescent and Adult Rats. Obesities. 2025; 5(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtkinson, Samantha N., Caron Dean, Victoria L. Woyach, Keri R. Hainsworth, and Hershel Raff. 2025. "Effect of High-Fat Diet and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v on the Gut Microbiome of Adolescent and Adult Rats" Obesities 5, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5010017
APA StyleAtkinson, S. N., Dean, C., Woyach, V. L., Hainsworth, K. R., & Raff, H. (2025). Effect of High-Fat Diet and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 299v on the Gut Microbiome of Adolescent and Adult Rats. Obesities, 5(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5010017






