Strengthening Regenerated Cellulose Fibers Sourced from Recycled Cotton T-Shirt Using Glucaric Acid for Antiplasticization
Abstract
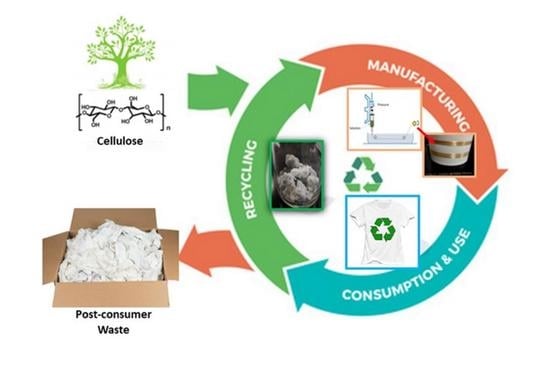
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Protocol for Fiber Spinning from Recycled T-Shirt
2.2.1. Activation of Cellulose Pulp
2.2.2. Dissolution Method
2.2.3. Fiber Spinning
2.3. Characterization of Activated Cellulose Pulp
2.3.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Analysis
2.4. Characterization of Drawn Fibers
2.4.1. Tensile Testing
2.4.2. Analysis of Fiber Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of Chemically Activated Pulp
3.2. Acid Neutralization on the Dissolution of Mercerized Pulp
3.3. Effect of GA on RC Wet Spinning
3.4. Effect of GA on Mechanical Properties
3.5. Understanding the Effect of GA Additives on Fiber Morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GA | Pure glucaric acid |
| GC | Unmercerized ground cotton cellulose pulp |
| GCS pulp | Strong acid treated cellulose pulp |
| GCW pulp | Weak acid treated cellulose pulp |
| GCS | Strong acid treated neat regenerated cellulose fibers |
| GA/GCS | Glucaric acid modified GCS regenerated cellulose fibers |
| GA/GCW | Glucaric acid modified GCW regenerated cellulose fibers |
References
- Worley, D. Preferred Fiber Reports. 2018. Available online: https://textileexchange.org/2018-preferred-fiber-reports/ (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Circular Economy Reports & Publications from the Ellen MacArthur Foundation”; EDT 2016. Available online: https://www.google.com/ (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Chakraborty, S.; Khatun, M.; Biswas, M.C. Influence of fiber surface morphology on the dyeing performance of polyester yarn. Researchgate 2020, 4, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- GLENZ 2007; Home: Plastics Europe. Available online: https://www.google.com/ (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Thomas, S.; Joseph, K.; Malhotra, S.K.; Goda, K.; Sreekala, M.S. Polymer Composites, Macro-and Microcomposites; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Domina, T.; Koch, K. Consumer reuse and recycling of post-consumer textile waste. J. Fash. Mark. Manag. Int. J. 1999, 3, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, C.C.; Davis, M.R.; Davison, B.; Eaton, L.M.; Efroymson, R.A.; Hilliard, M.R.; Kline, K.; Langholtz, M.H.; Myers, A.; Sokhansanj, S.; et al. 2016 Billion-Ton Report: Advancing Domestic Resources for a Thriving Bioeconomy, Volume 1: Economic Availability of Feedstocks; Office of Scientific and Technical Information (OSTI): Kerela, India, 2016; pp. 1–411. [Google Scholar]
- Rowell, R.M.; Stout, H.P. Jute and Kenaf. Handbook of Fiber Chemistry; International Fiber Science and Technology Series; CRC/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 409–456. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, H.-G.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Park, J. Effect of Low-Temperature Pyrolysis on the Properties of Jute Fiber-Reinforced Acetylated Softwood Kraft Lignin-Based Thermoplastic Polyurethane. Polymers 2018, 10, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fink, H.-P.; Weigel, P.; Purz, H.; Ganster, J. Structure formation of regenerated cellulose materials from NMMO-solutions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1473–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Tsianou, M.; Alexandridis, P. Assessment of solvents for cellulose dissolution. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.; Uniyal, V.; Naithani, S. Polymorphic transformation of cellulose I to cellulose II by alkali pretreatment and urea as an additive. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, P.; Blackburn, R.S.; El-Dessouky, H.M.; Taylor, J.; White, P. Effect of sodium hydroxide pre-treatment on the optical and structural properties of lyocell. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raus, V.; Šturcová, A.; Dybal, J.; Šlouf, M.; Vacková, T.; Šálek, P.; Kobera, L.; Vlček, P. Activation of cellulose by 1, 4-dioxane for dissolution in N, N-dimethylacetamide/LiCl. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1893–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Huang, W.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Pang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Structure and properties of regenerated cellulose fibers from different technology processes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikgor, H.; Remzi, F.; Becer, C. Lignocellulosic biomass: A sustainable platform for the production of bio-based chemicals and polymers. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 4497–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saberi, B.; Chockchaisawasdee, S.; Golding, J.B.; Scarlett, C.J.; Stathopoulos, C.E. Physical and mechanical properties of a new edible film made of pea starch and guar gum as affected by glycols, sugars and polyols. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, S.J. Antiplasticization and crystallinity in poly(vinyl chloride). Macromolecules 1989, 22, 3480–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggleman, R.A.; Douglas, J.F.; De Pablo, J.J. Antiplasticization and the elastic properties of glass-forming polymer liquids. Soft Matter 2009, 6, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukalin, E.B.; Douglas, J.F.; Freed, K.F. Plasticization and antiplasticization of polymer melts diluted by low molar mass species. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 132, 084504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.C.; Bush, B.; Ford, E. Glucaric acid additives for the antiplasticization of fibers wet spun from cellulose acetate/acetic acid/water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Ford, E. Antiplasticizing Behaviors of Glucarate and Lignin Bio-Based Derivatives on the Properties of Gel-Spun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Fibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1700523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fengel, D.; Strobel, C. FTIR spectroscopic studies on the heterogeneous transformation of cellulose I into cellulose II. Acta Polym. 1994, 45, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, M.A.; Mahmoud, O.M. FTIR spectroscopic study of the effect of microwave heating on the transformation of cellulose I into cellulose II during mercerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 107, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, W.J., Jr.; Caldwell, J.R. Antiplasticization. II. Characteristics of antiplasticizers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1967, 11, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, R.T. Instrumental Analysis of Cotton Cellulose and Modified Cotton Cellulose. 1972. Available online: https://www.bcin.ca/bcin/detail.app?id=135910 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Halonen, H.; Larsson, P.T.; Iversen, T. Mercerized cellulose biocomposites: A study of influence of mercerization on cellulose supramolecular structure, water retention value and tensile properties. Cellulose 2013, 20, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, S.; Nakano, T. Morphological changes induced in wood samples by aqueous NaOH treatment and their effects on the conversion of cellulose I to cellulose II. Holzforschung 2015, 69, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, A.-L.; Tétreault, J. Cellulose degradation in an acetic acid environment. Stud. Conserv. 2000, 45, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H. Lignocellulose Biorefinery Engineering: Principles and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Miller-Chou, B.A.; Koenig, J.L. A review of polymer dissolution. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 1223–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Rawat, P.; Louder, N.; Ford, E. Properties and Structural Anisotropy of Gel-Spun Lignin/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Fibers Due to Gel Aging. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Blackwell, C.; Ren, Q.; Ford, E. Effect of the Coagulation Bath on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Gel-Spun Lignin/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Fibers. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2949–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.-B.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Yang, J.-H.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, X.-T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.-W. Largely enhanced thermal conductivity of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/carbon nanotube composites achieved by adding graphene oxide. Carbon 2015, 90, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Characteristics of Flax/Linen Fiber. 2018. Available online: https://www.textileschool.com/2632/linen-fiber-from-flax-plants-and-the-linen-fabrics/ (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- McKenna, H.A.; Hearle, J.W.S.; O’Hear, N. Handbook of fibre rope technology. In Handbook of Fibre Rope Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 35–74. [Google Scholar]
- Properties of Cotton|Cotton Fiber Properties|Cotton Manufacturing. Available online: https://barnhardtcotton.net/technology/cotton-properties/ (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Tortora, P.G.; Collier, B.J. Understanding Textiles. 1997. Available online: https://www.bcin.ca/bcin/detail.app?id=179694 (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- Hospodarova, V.; Singovszka, E.; Stevulova, N. Characterization of Cellulosic Fibers by FTIR Spectroscopy for Their Further Implementation to Building Materials. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 9, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehydration of Alcohols. Available online: https://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/alcohols/dehydration.html (accessed on 11 October 2020).
- Pană, A.-M.; Rusnac, L.-M.; Bandur, G.; Silion, M.; Deleanu, C.; Balan, M. Novel D-glucose and D-mannose based oligomers: Synthesis and characterization. e-Polymers 2011, 11, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johar, N.; Ahmad, I.; Dufresne, A. Extraction, preparation and characterization of cellulose fibres and nanocrystals from rice husk. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2012, 37, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’sullivan, A.C. The structure slowly unravels. Cellulose 1997, 4, 173–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.D. Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 2013, 21, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.N.J.; Mendon, S.K.; Thames, S.F.; Rawlins, J.W. X-ray diffraction of cotton treated with neutralized vegetable oil-based macromolecular crosslinkers. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Process Conditions | Glucaric Acid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Additive Conc. | 0.0% GCS | 10% GA/GCS | 10% GA/GCW | |
| As spun Draw Ratio (DR) | 1.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | |
| Stage 1 Drawing | Oil Temp. °C | 65 | 110 | 110 |
| DR | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | |
| Stage 2 Drawing | Oil Temp. °C | 100 | 120 | 120 |
| DR | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.6 | |
| Total DR | 2.6 | 6.5 | 6.4 | |
| Linear Density (dtex) | 8.4 | 7.2 | 6.6 | |
| Effective Diameter(µm) | 27 | 25 | 24 | |
| Sample | Dry Condition | Wet Condition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Modulus (cN/dtex) | Tenacity (cN/dtex) | Strain at Break (%) | Toughness J/g | Specific Modulus (cN/dtex) | Tenacity (cN/dtex) | |
| GCS | 114 ± 3.20 | 1.77 ± 0.10 | 6.5 ± 1.0 | 1.50 ± 0.50 | 70 ± 2.80 | 0.62 ± 0.09 |
| GA/GCS | 664 ± 2.32 | 9.70 ± 0.11 | 13 ± 2.0 | 6.20 ± 2.16 | 194 ± 1.96 | 4.40 ± 0.13 |
| GA/GCW | 81 ± 3.30 | 2.70 ± 0.14 | 10 ± 2.0 | 1.20 ± 0.50 | 26 ± 2.62 | 1.77 ± 0.09 |
| Cotton * | 53 | 1.87–3.77 | - | - | - | 2.92–5.66 |
| Flax * | 177 | 4.85–5.75 | - | - | - | 5.82–6.89 |
| Rayon * | 34 | 1.77 | - | - | - | 0.70 |
| Lyocell * | - | 4.3–5.9 | - | - | - | 2.70 |
| Sample | Specific Modulus (cN/dtex) | Tenacity (cN/dtex) |
|---|---|---|
| GCS | 96 ± 4.16 | 0.009 ± 0.001 |
| GA/GCS | 596 ± 6.33 | 0.09 ± 0.02 |
| GA/GCW | 145 ± 4.51 | 0.02 ± 0.005 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biswas, M.C.; Dwyer, R.; Jimenez, J.; Su, H.-C.; Ford, E. Strengthening Regenerated Cellulose Fibers Sourced from Recycled Cotton T-Shirt Using Glucaric Acid for Antiplasticization. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 138-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2010010
Biswas MC, Dwyer R, Jimenez J, Su H-C, Ford E. Strengthening Regenerated Cellulose Fibers Sourced from Recycled Cotton T-Shirt Using Glucaric Acid for Antiplasticization. Polysaccharides. 2021; 2(1):138-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiswas, Manik Chandra, Ryan Dwyer, Javier Jimenez, Hsun-Cheng Su, and Ericka Ford. 2021. "Strengthening Regenerated Cellulose Fibers Sourced from Recycled Cotton T-Shirt Using Glucaric Acid for Antiplasticization" Polysaccharides 2, no. 1: 138-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2010010
APA StyleBiswas, M. C., Dwyer, R., Jimenez, J., Su, H.-C., & Ford, E. (2021). Strengthening Regenerated Cellulose Fibers Sourced from Recycled Cotton T-Shirt Using Glucaric Acid for Antiplasticization. Polysaccharides, 2(1), 138-153. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2010010