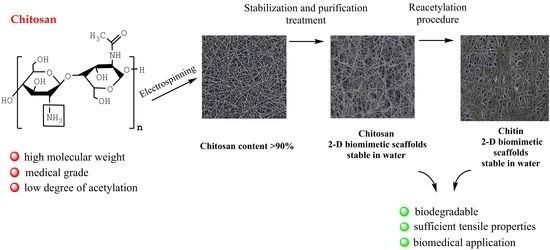
Conversion of Electrospun Chitosan into Chitin: A Robust Strategy to Tune the Properties of 2D Biomimetic Nanofiber Scaffolds
Abstract
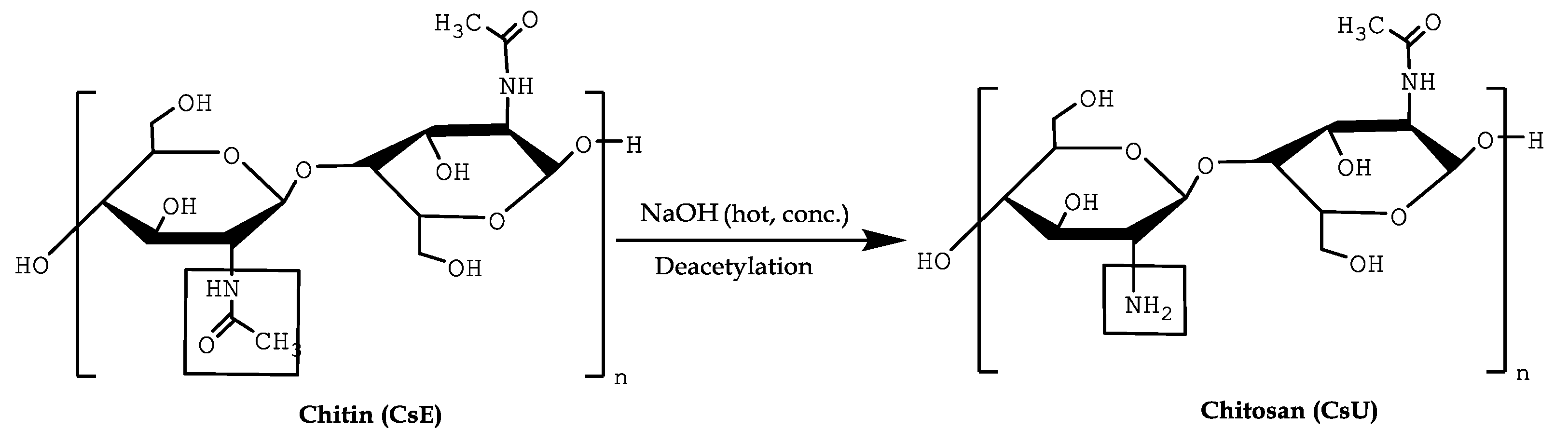
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
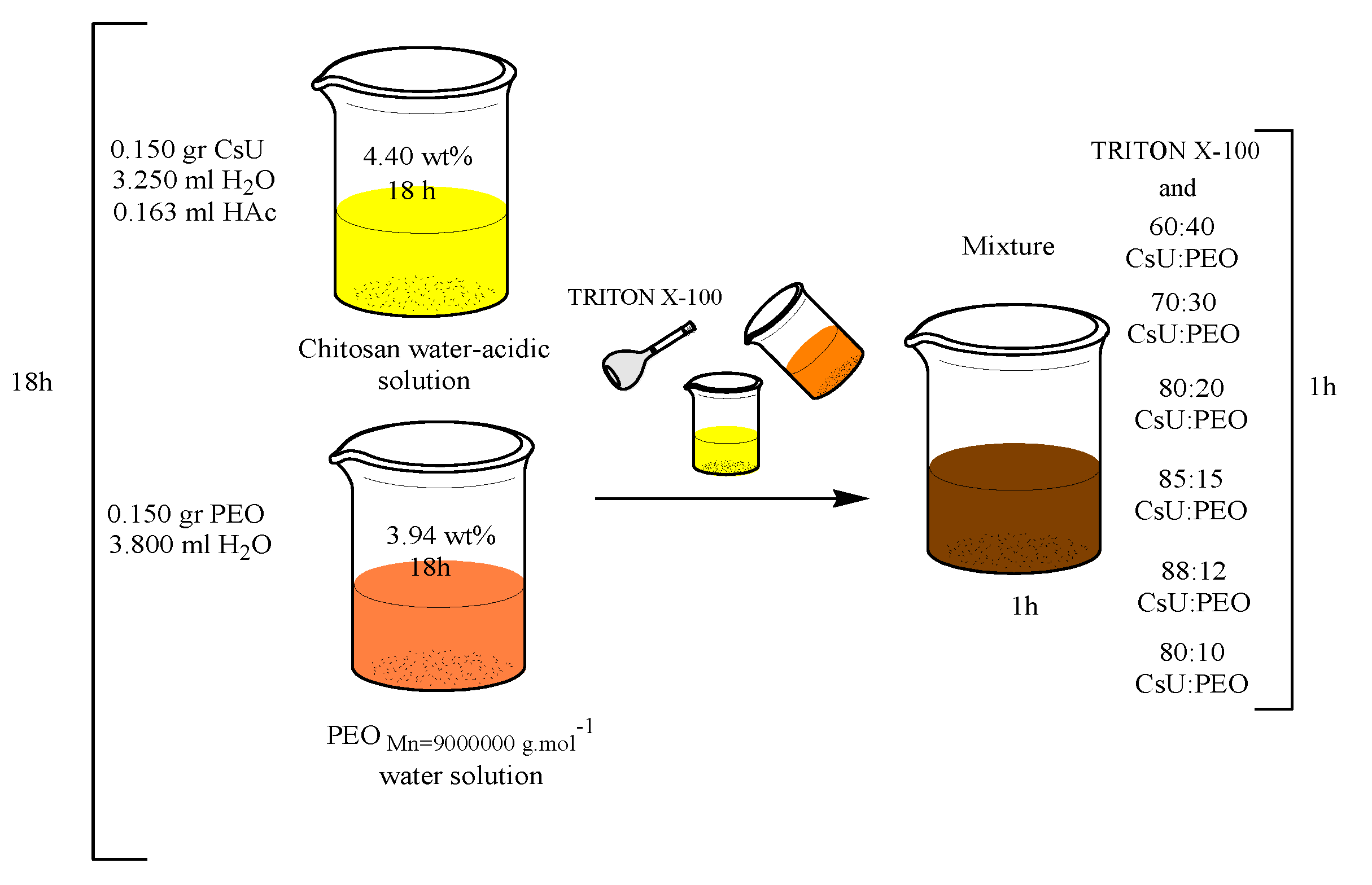
2.2. Mats Processing
2.2.1. Electrospinning Conditions
2.2.2. Stabilization of the Mats
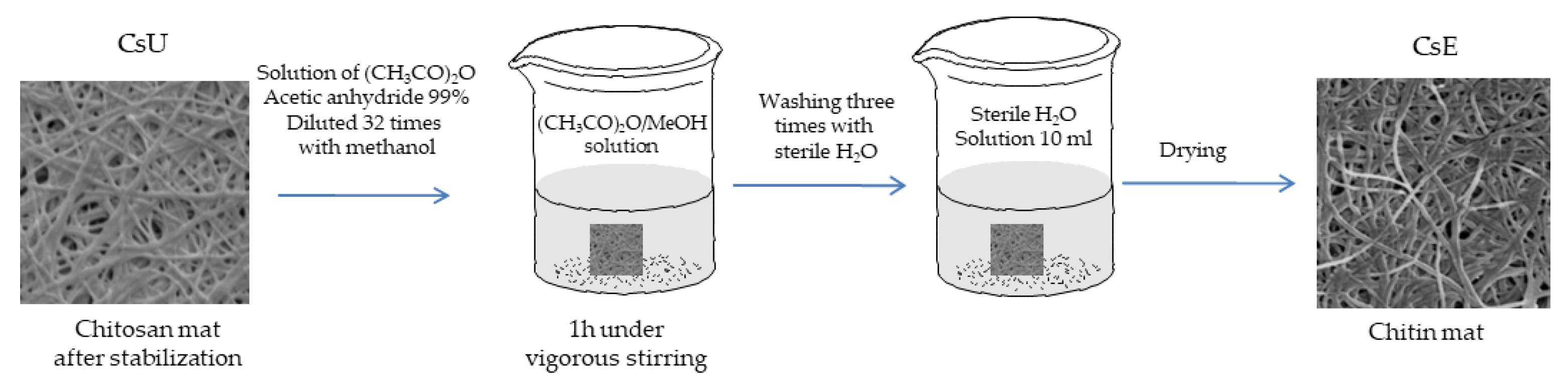
2.2.3. Reacetylation of the Mats
2.3. Characterization Methods
2.3.1. Rheology
2.3.2. Scanning and Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
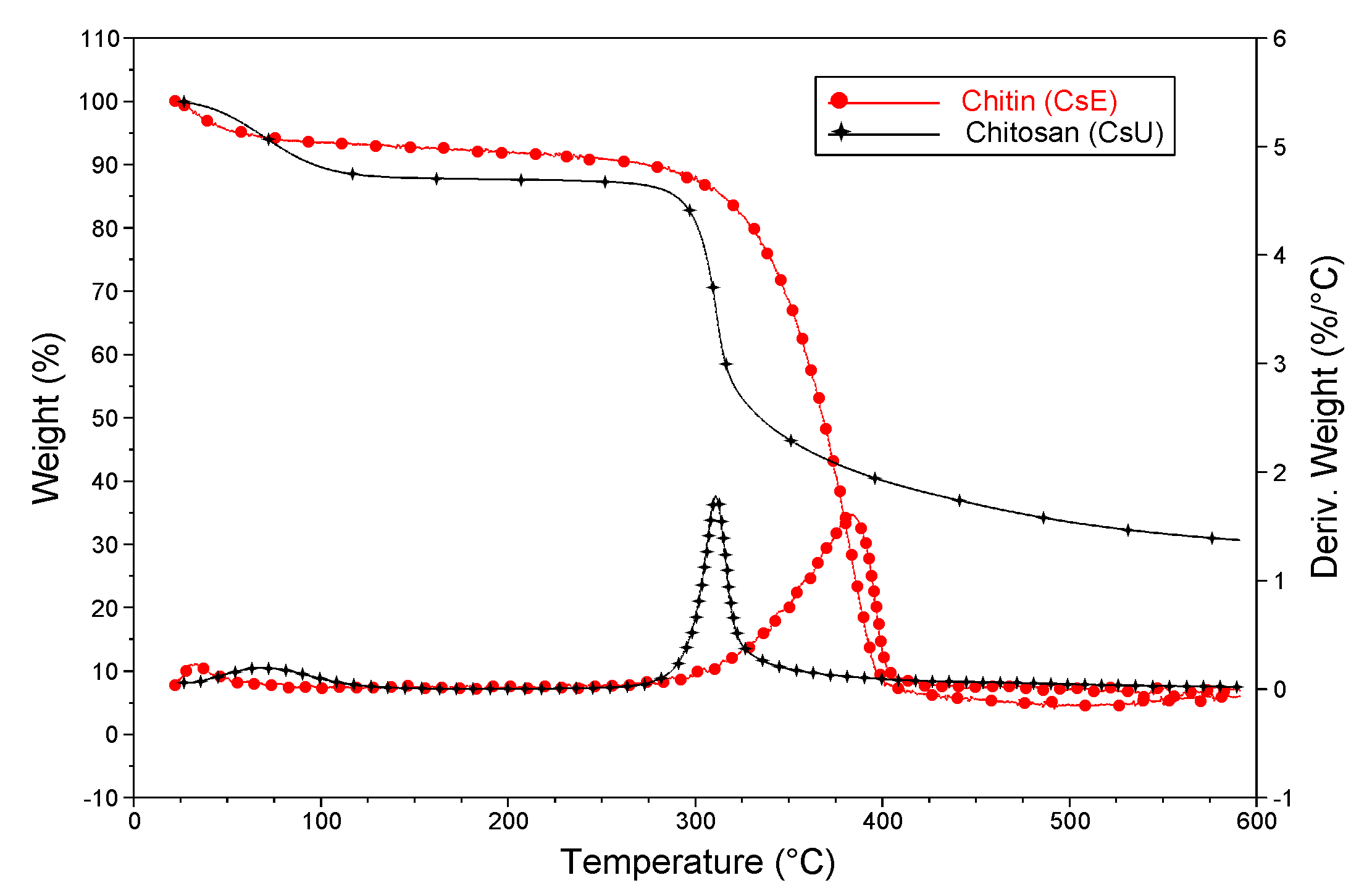
2.3.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.5. Enzymatic Biodegradation
2.3.6. Mechanical Properties—Tensile Strength on CsU Based Fiber Mats
3. Results and Discussion
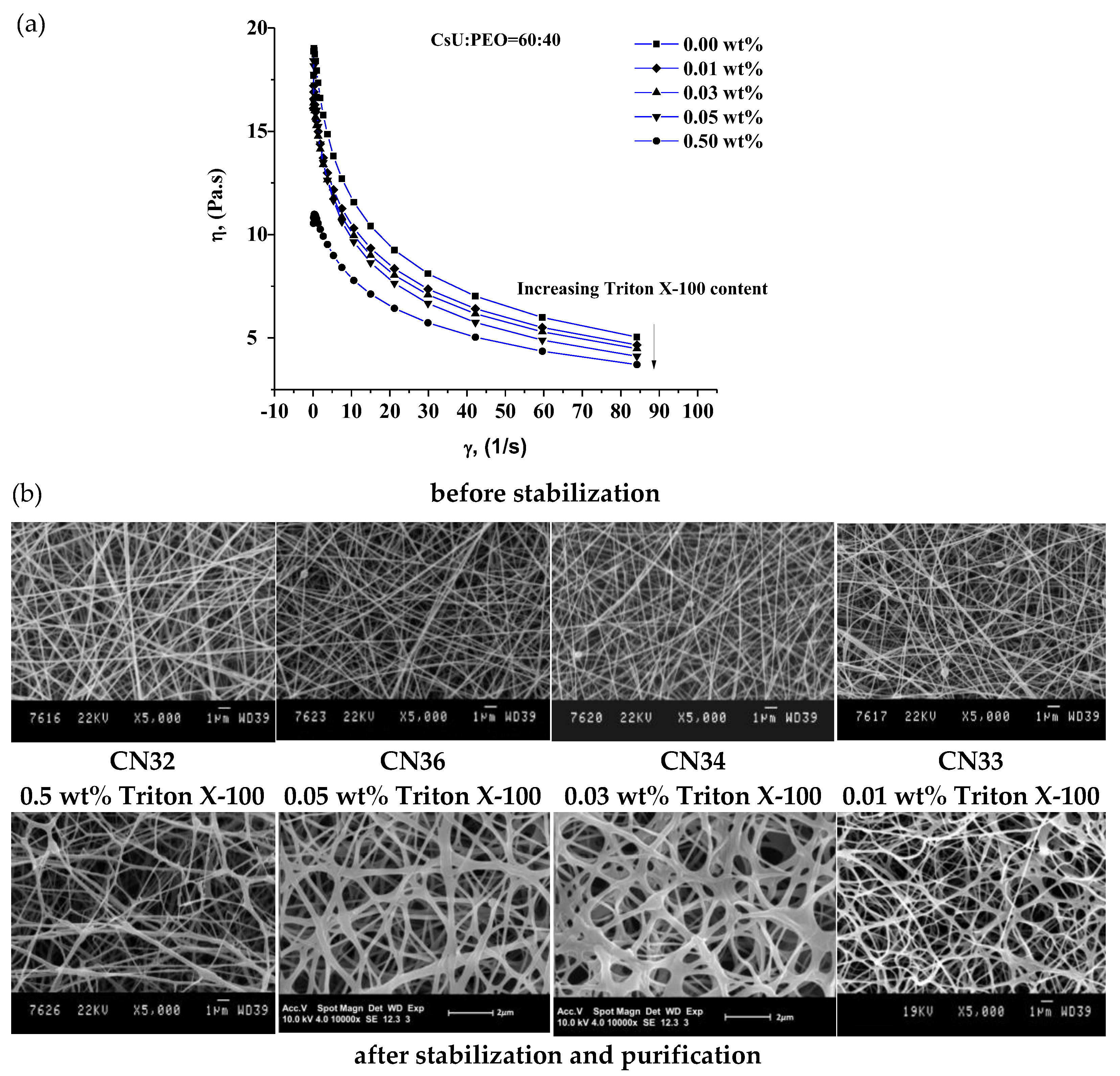
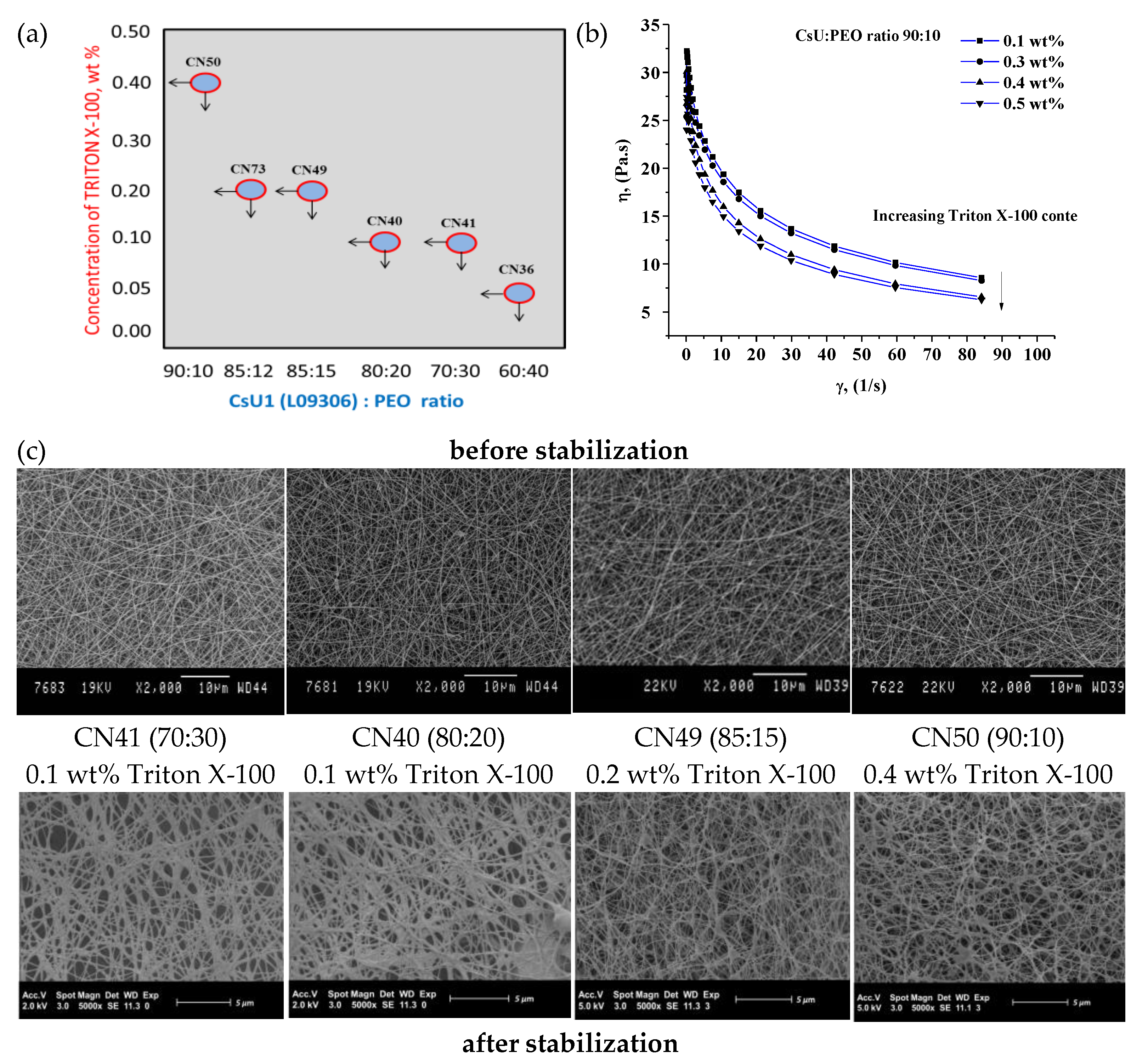
3.1. Electrospinning of Two-Component Water–Acidic Solutions Containing CsU and PEO
3.2. ESP of Three-Component Water–Acidic Solutions Containing CsU, PEO and Triton-X 100
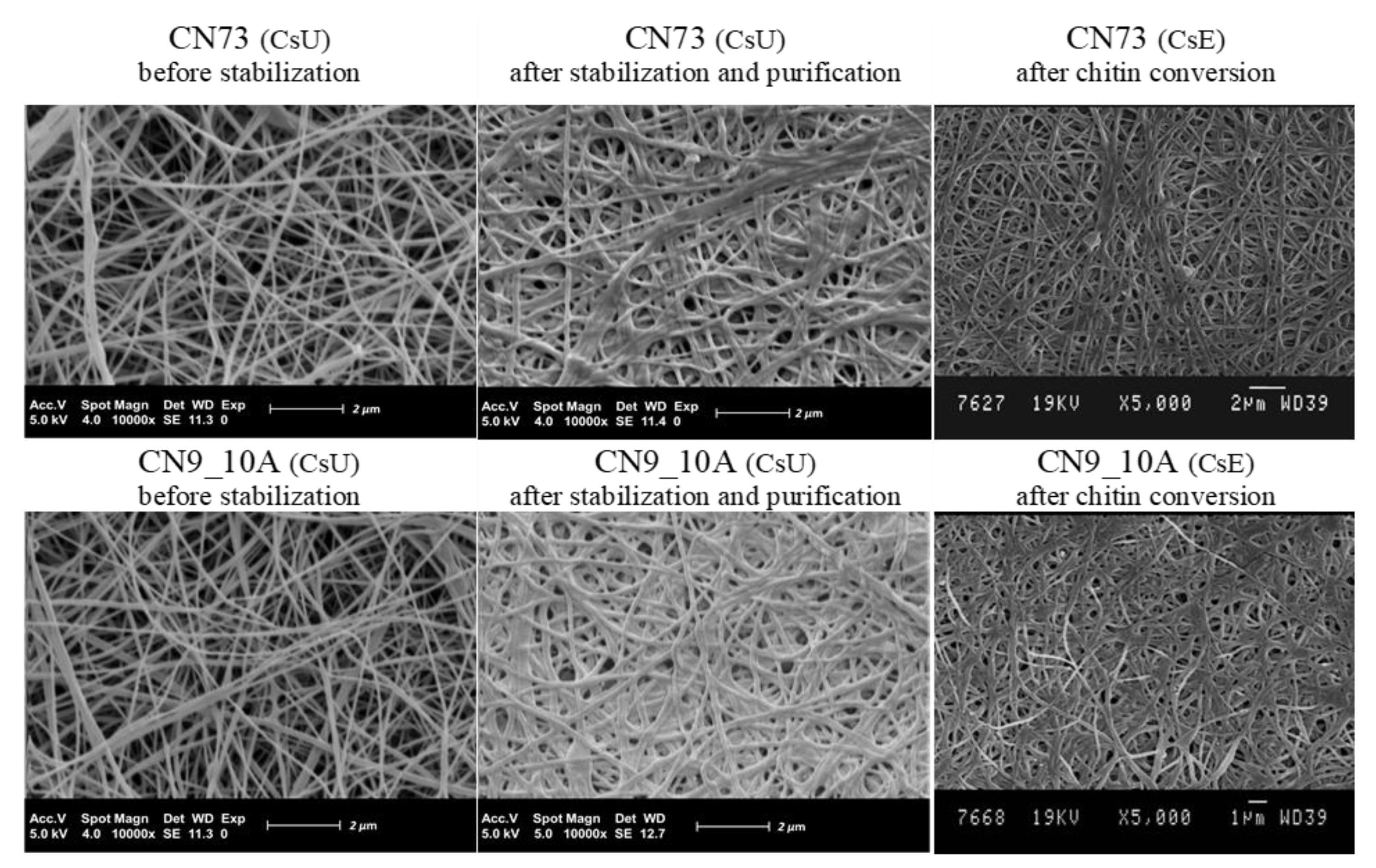
3.3. Reacetylation of the Electrospun Chitosan Mats into Chitin Nanofiber Mats
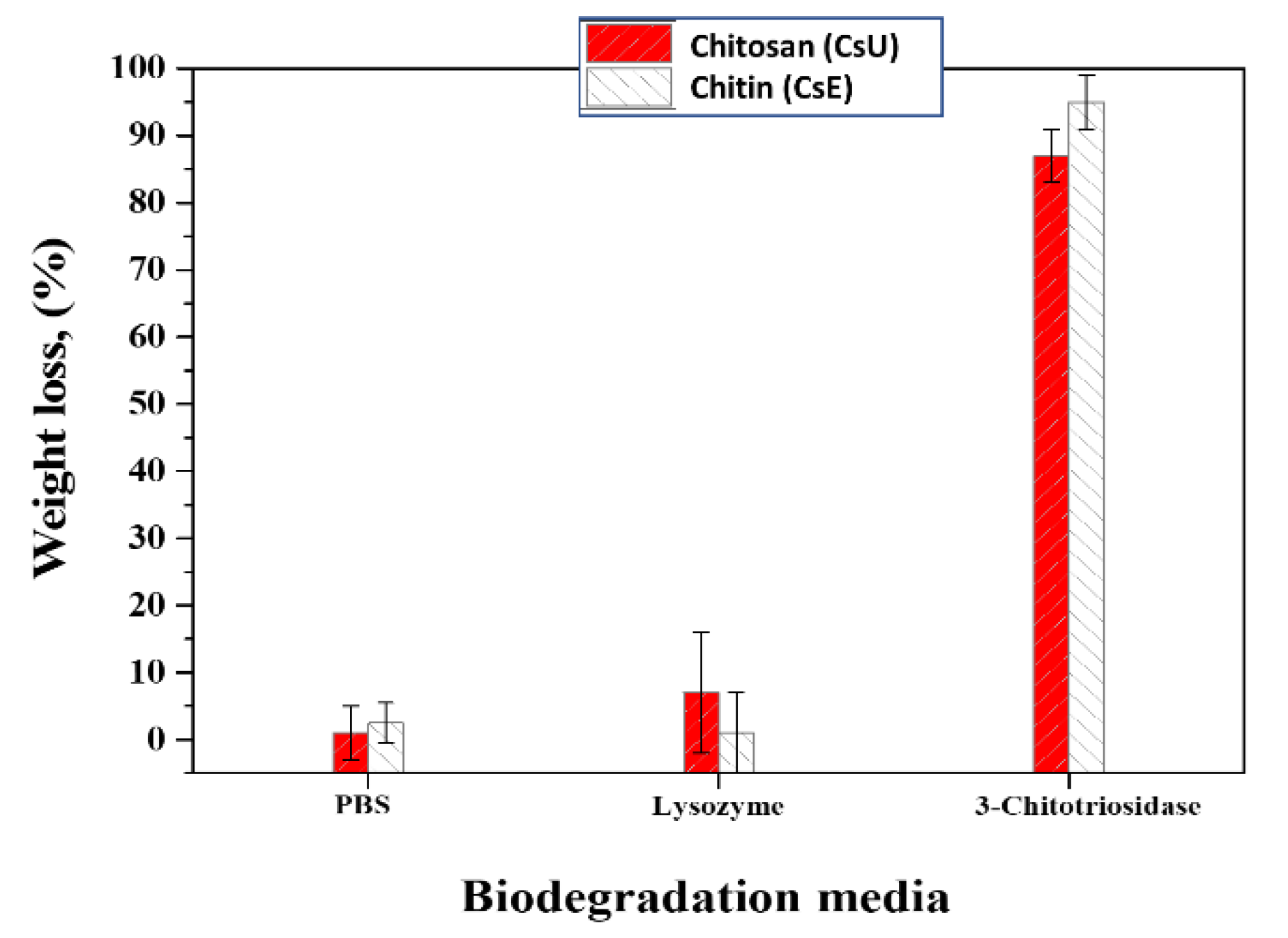
3.4. Biodegradation Properties of the Nanofiber Mats
3.5. Mechanical Properties Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croisier, F.; Jérôme, C. Chitosan-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Sharma, C.P. Electrospinning of chitin and chitosan nanofibers. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2009, 22, 179–201. [Google Scholar]
- Majeti, N.V.; Kumar, R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, M.; Nesakumari, M.; Rajarathinam, K.; Ranjit Singh, A.J.A. Production and characterization of mushroom chitosan under solid-state fermentation conditions. Adv. Biol. Res. 2010, 4, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Madihally, S.V.; Howard, M.W.T. Porous chitosan scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 1999, 20, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, D.R.; Forsythe, J.S.; Shen, W.; Finkelstein, D.I.; Horne, M.K. Review paper: A review of the cellular response on electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2009, 24, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 641–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoni, H.; Ravandi, S.A.H.; Valizadeh, M. Electrospinning of chitosan nanofibers: Processing optimization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Minato, K.-I.; Kumagai, G.; Hayashi, S.; Yamamoto, H. Chitosan Nanofiber. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3291–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, K.; Kit, K.; Li, J.; Zivanovic, S. Morphological and surface properties of electrospun chitosan nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Su, B.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Chitosan Nanofibers from an easily electrospinnable UHMWPEO-Doped chitosan solution system. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Park, S.-Y. Preparation of the electrospun chitosan nanofibers and their applications to the adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) ions from an aqueous solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 328, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, T.J.; Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatova, M.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Novel antibacterial fibers of quaternized chitosan and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) prepared by electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Novel chitin and chitosan nanofibers in biomedical applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, R.; Menon, D.; Manzoor, K.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H. Biomedical applications of chitin and chitosan based nanomaterials -A short review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogias, I.A.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Williams, A.C. Exploring the factors affecting the solubility of chitosan in water. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, B.; Neves, J. Chitosan-Based Systems for Bbiopharmaceuticals: Delivery, Targeting and Polymer Therapeutics, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagstrom, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.S.; Park, W.H.; Daewoo, I.; Hudson, S.M. Effect of the degree of deacetylation on the thermal decomposition of chitin and chitosan nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 291–295. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, R.; Ragelle, H.; des Rieux, A.; Duhem, N.; Jérôme, C.; Preat, V. Chitosan and chitosan derivatives in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2011, 244, 19–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sathiyaseelan, A.; Shajahan, A.; Kalaichelvan, P.T.; Kaviyarasan, V. Fungal chitosan based nanocomposites sponges—An alternative medicine for wound dressing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathiyaseelan, A.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Application of tetracycline hydrochloride loaded-fungal chitosan and Aloe vera extract based composite sponges for wound dressing. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 14, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, P.K.; Rinki, K.; Dutta, J. Chitosan: A Promising Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. In Chitosan for Biomaterials II; Jayakumar, R., Prabaharan, M., Muzzarelli, R., Eds.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 244, pp. 45–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ziani, K.; Henrist, C.; Jerome, C.; Aqil, A.; Maté, J.I.; Cloots, R. Effect of nonionic surfactant and acidity on chitosan nanofibers with different molecular weights. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 470–476. [Google Scholar]
- Kriegel, C.; Kit, K.M.; McClemens, D.J.; Weiss, J. Electrospinning of chitosan-poly(ethylene oxide) blend nanofibers in the presence of micellar surfactant solutions. Polymer 2009, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepić, I.; Filipović-Grčić, J.; Jalšenjak, I. Interactions in a nonionic surfactant and chitosan mixtures. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 327, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsanoh, P.; Supaphol, P. Stability improvement of electrospun chitosan nanofibrous membranes in neutral or weak basic aqueous solutions. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2710–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, Y.K.; Kim, K.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Development of a nanostructured DNA delivery scaffold via electrospinning of PLGA and PLA–PEG block copolymers. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, M.G. Chitin and chitosan in fungi. In Biopolymers, Online ed.; Steinbüchel, A., Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; Part 6; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Corazzari, I.; Nistico, R.; Turci, F.; Faga, M.G.; Franzoso, F.; Tabasso, S.; Magnacca, G. Advanced physico-chemical characterization of chitosan by means of TGA coupled on-line with FTIR and GCMS: Thermal degradation and water adsorption capacity. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 112, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, C.; Thompson, Z.; Bhattarai, N. 15—Electrospun chitosan fibers. In Electrospun Nanofibers; Afshari, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 371–398. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.; Nwe, N.; Furuike, T.; Tokura, S.; Tamura, H. Methods of N-acetylated chitosan scaffolds and it’s in vitro biodegradation by lysozyme. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2012, 5, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzelanny, C.; Pöppelmann, B.; Pappelbaum, K.; Moerschbacher, B.M.; Schneider, S.W. Human macrophage activation triggered by chitotriosidase-mediated chitin and chitosan degradation. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8556–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, bio distribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croisier, F.; Atanasova, G.; Poumay, Y.; Jérôme, C. Polysaccharide-Coated PCL nanofibers for wound dressing applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchemtchoua, V.T.; Atanasova, G.; Aqil, A.; Filee, P.; Garbacki, N.; Vanhooteghem, O.; Deroanne, C.; Noel, A.; Jerome, C.; Nusgens, B.; et al. Development of a Chitosan Nanofibrillar Scaffold for Skin Repair and Regeneration. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3194–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Chitosan Code | Molecular Weight (Mv) (g/mol) | Degree of Acetylation (mol %) | Apparent Viscosity (1% sol. in 1% HAc) (mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CsU1 (L09306) | 174,000 | 32.3 | 115 |
| CsU2 (L10204) | 205,000 | 34.0 | 125 |
| Mat Samples Code * | Type of CsU Used | Initial CsU:PEO Ratio | Final Solution Conc. (wt%) | Triton X-100 Conc. (wt%) | ΔV (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN14 | CsU1 (L09306) | 60:40 | 4.22 | - | 27.0 |
| CN36 | 60:40 | 4.22 | 0.05 | 28.0 | |
| CN64_65 | 85:15 | 4.32 | 0.20 | 30.0 | |
| CN73 | 88:12 | 4.33 | 0.20 | 34.0 | |
| CN50 | 90:10 | 4.34 | 0.40 | 31.0 | |
| CN7_8A | CsU2 (L10204) | 60:40 | 4.22 | 0.05 | 20.0 |
| CN5_6A | 85:15 | 4.32 | 0.10 | 28.0 | |
| CN9_10A | 88:12 | 4.33 | 0.20 | 30.4 |
| Mat Samples Code | Initial CsU:PEO Ratio * | Triton X-100 (wt%) | Voltage (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN32 | 60:40 | 0.5 | 22 |
| CN36 | 0.05 ** | 25 | |
| CN34 | 0.03 | 26 | |
| CN33 | 0.01 | 25 | |
| CN41 | 70:30 | 0.1 ** | 25 |
| CN48 | 80:20 | 0.05 | 27 |
| CN40 | 0.1 ** | 27 | |
| CN47 | 85:15 | 0.3 | 27 |
| CN49 | 0.2 ** | 28 | |
| CN46 | 0.1 | 27 | |
| CN73 | 88:12 | 0.2 ** | 35 |
| CN43 | 90:10 | 0.1 | 35 |
| CN44 | 0.3 | 32 | |
| CN50 | 0.4 ** | 31 | |
| CN45 | 0.5 | 27 |
| Sample Code | Type of CsU Used | Initial CsU:PEO Ratio | Young’s Modulus * (MPa) | Tensile Stress at Break * (MPa) | Tensile Strain at Break * (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Stabilization and Purification (bs) CsU | |||||
| CN36 bs | CsU1 (L09306) | 60:40 | 155± 22 | 6.99 ± 0.13 | 8.55 ± 1.63 |
| CN64_65 bs | 85:15 | 79 ± 22 | 2.12 ± 0.23 | 2.99 ± 0.83 | |
| CN7_8A bs | CsU2 (L10204) | 60:40 | 114 ± 18 | 11.27 ± 2.81 | 20.81 ± 7.8 |
| CN5_6A bs | 85:15 | 147 ± 19 | 10.98 ± 1.47 | 14.70 ± 1.51 | |
| CN9_10A bs | 88:12 | 147 ± 21 | 9.49 ± 0.97 | 12.32 ± 1.79 | |
| After Stabilization and Purification (as) CsU | |||||
| CN36 as | CsU1 (L09306) | 60:40 | 181 ± 25 | 7.54 ± 0.97 | 10.44 ± 4.85 |
| CN64_65 as | 85:15 | 125 ± 19 | 3.36 ± 0.53 | 3.67 ± 1.36 | |
| CN7_8A as | CsU2 (L10204) | 60:40 | 191 ± 34 | 10.70 ± 2.01 | 16.75 ± 4.37 |
| CN5_6A as | 85:15 | 276 ± 31 | 10.70 ± 0.87 | 10.87 ± 1.18 | |
| CN9_10A as | 88:12 | 224 ± 22 | 9.14 ± 0.22 | 9.97 ± 1.08 | |
| After Reacetylation(ar) CsE | |||||
| CN9_10Aar | CsU2 (L10204) | 88:12 | 216 ± 23 | 7.56 ± 0.35 | 8.44 ± 0.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toncheva-Moncheva, N.; Aqil, A.; Galleni, M.; Jérôme, C. Conversion of Electrospun Chitosan into Chitin: A Robust Strategy to Tune the Properties of 2D Biomimetic Nanofiber Scaffolds. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 271-286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2020019
Toncheva-Moncheva N, Aqil A, Galleni M, Jérôme C. Conversion of Electrospun Chitosan into Chitin: A Robust Strategy to Tune the Properties of 2D Biomimetic Nanofiber Scaffolds. Polysaccharides. 2021; 2(2):271-286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleToncheva-Moncheva, Natalia, Abdelhafid Aqil, Moreno Galleni, and Christine Jérôme. 2021. "Conversion of Electrospun Chitosan into Chitin: A Robust Strategy to Tune the Properties of 2D Biomimetic Nanofiber Scaffolds" Polysaccharides 2, no. 2: 271-286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2020019
APA StyleToncheva-Moncheva, N., Aqil, A., Galleni, M., & Jérôme, C. (2021). Conversion of Electrospun Chitosan into Chitin: A Robust Strategy to Tune the Properties of 2D Biomimetic Nanofiber Scaffolds. Polysaccharides, 2(2), 271-286. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides2020019