Effects of Ethanol Feeding in Early-Stage NAFLD Mice Induced by Western Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Liver Samples
2.2. Human Liver Histology
2.3. Animal Experimentation
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. Hepatic Triglyceride Content
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Histological Staining Methodology and Quantification
2.8. Measurement of Serum Metabolites and Enzymes
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. WD and Ethanol Feeding Led to Increase of Body and Liver Weight
3.2. WD and Ethanol Feeding Led to An. Increase of Serum ALT, But No Change in Triglycerides
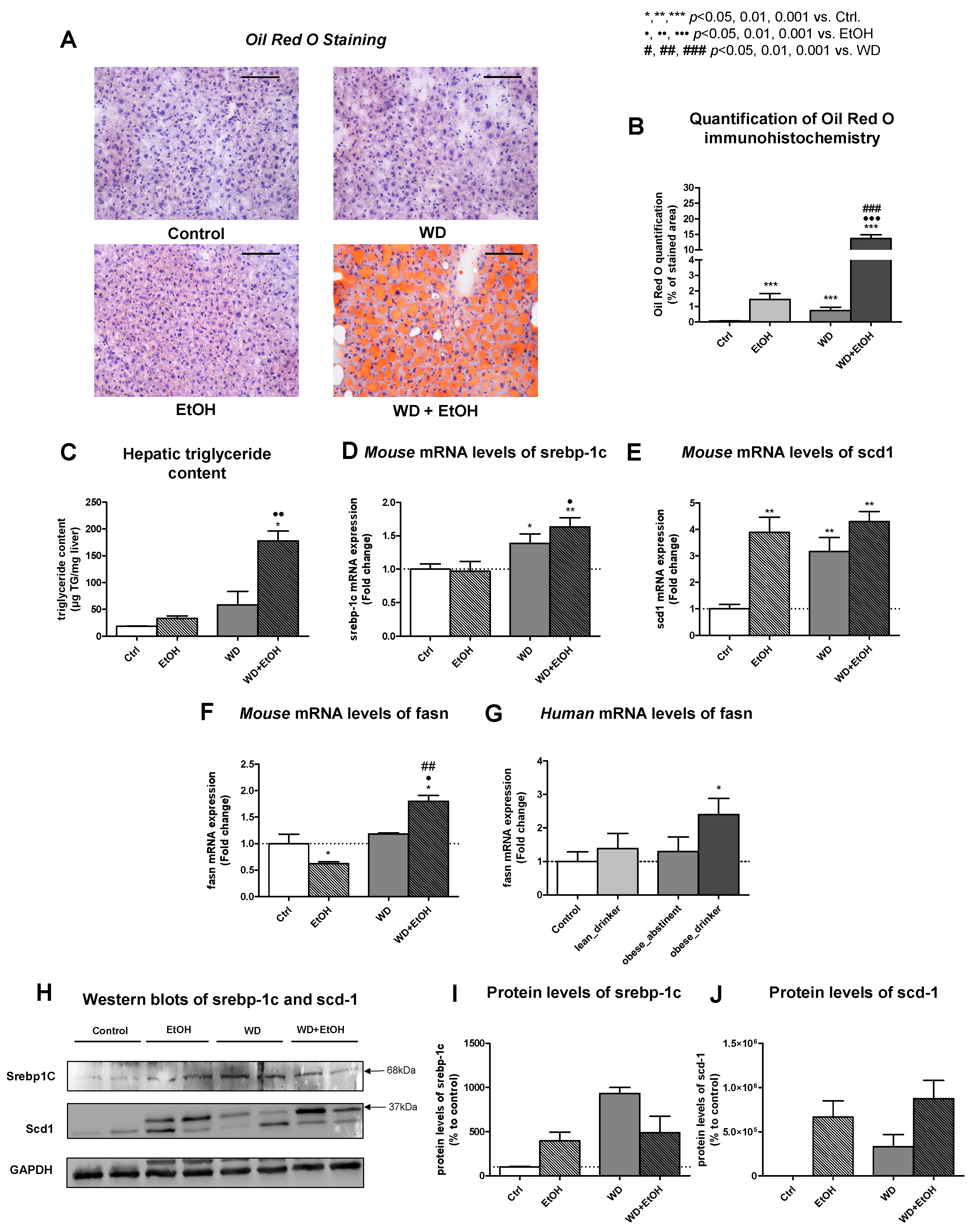
3.3. WD and Ethanol Feeding Led to Significant Liver Steatosis Comparable to Humans
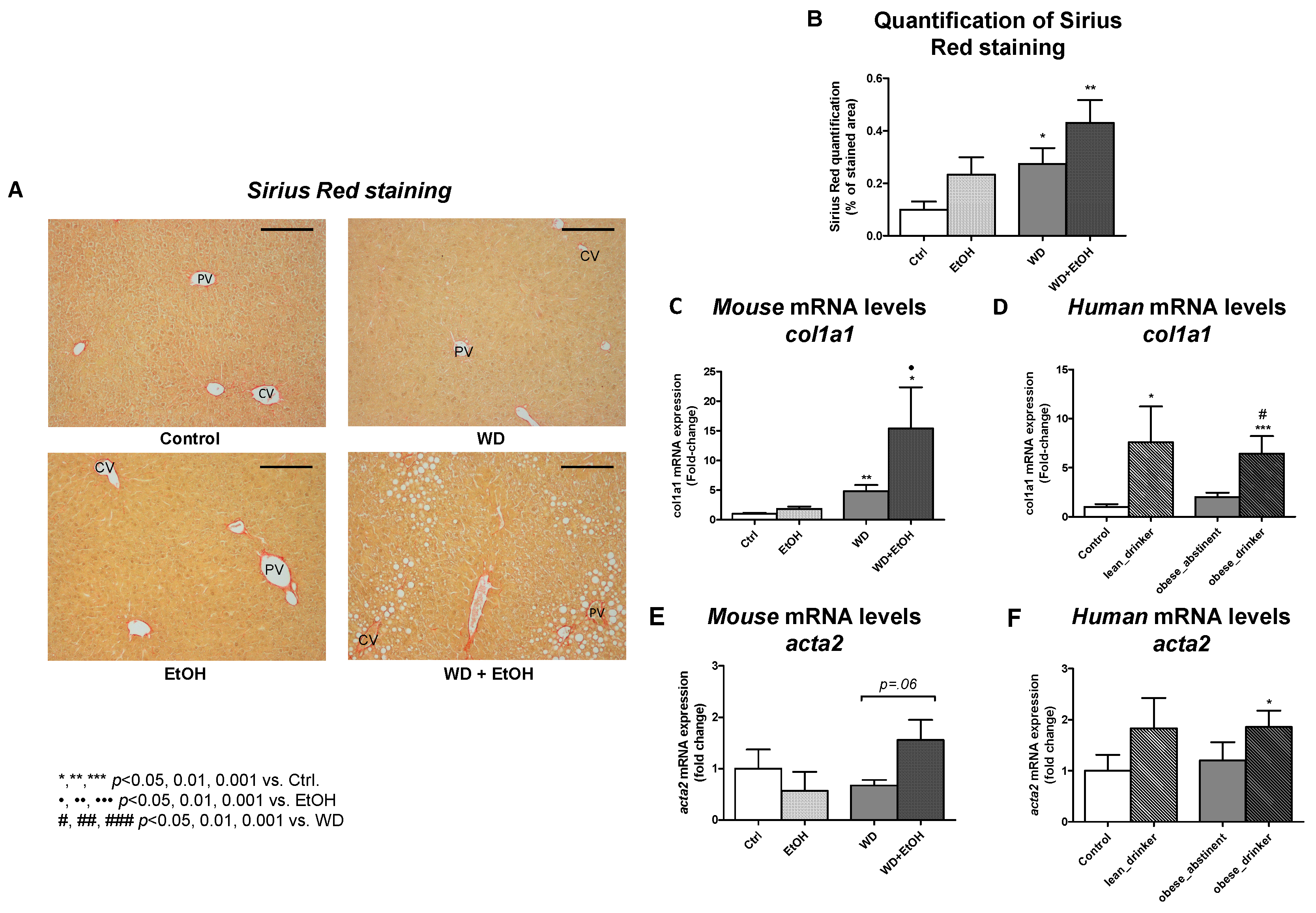
3.4. WD and Ethanol Feeding Promoted Fibrosis Similar to Human Disease
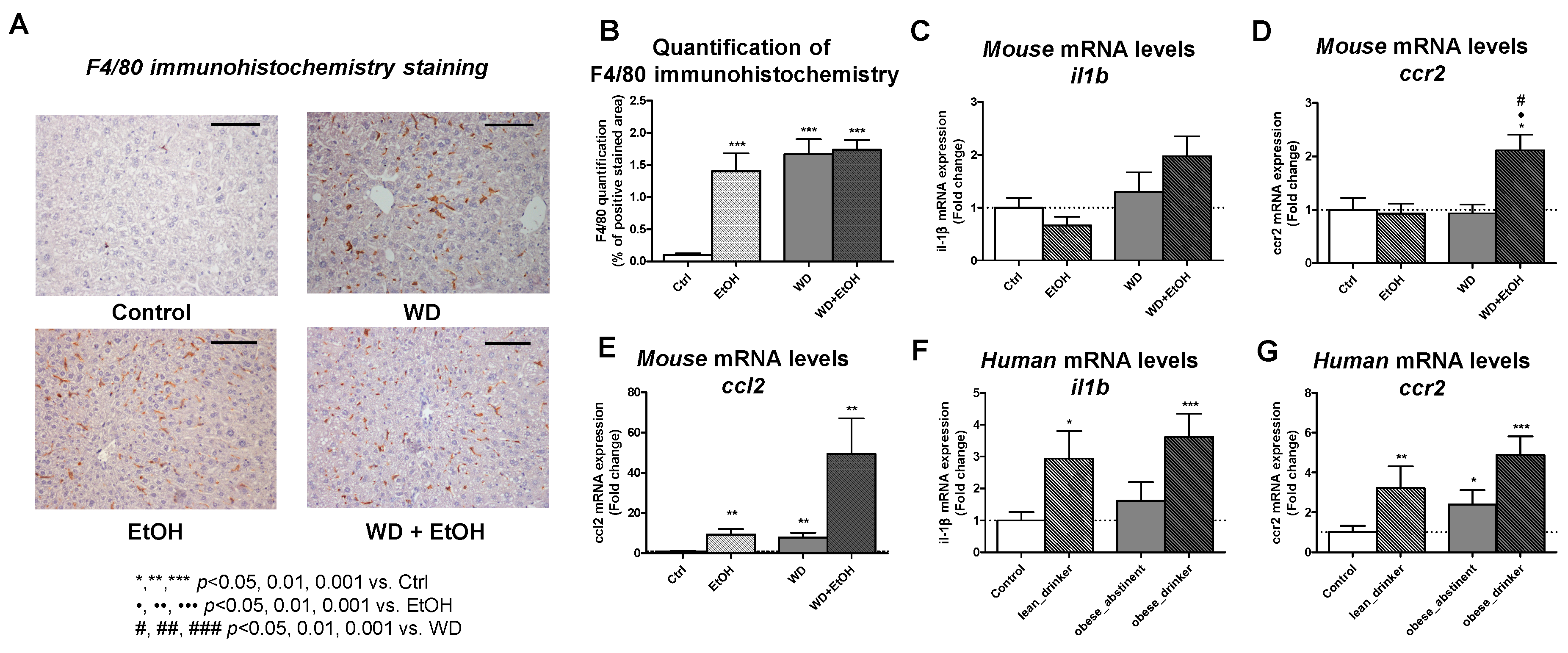
3.5. WD and Ethanol Feeding Increased Liver Inflammation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blachier, M.; Leleu, H.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Valla, D.-C.; Roudot-Thoraval, F. The Burden of Liver Disease in Europe: A Review of Available Epidemiological Data. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Y.; Golabi, P.; Mishra, A.; Rafiq, N.; Henry, L. Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Diseases in the USA in the Past Three Decades. Gut 2020, 69, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD Development and Therapeutic Strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Allen, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Fibrosis Progression in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver vs. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Paired-Biopsy Studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 643–654e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- WHO|Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health. 2018. Available online: http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/global_alcohol_report/gsr_2018/en/ (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A New Definition for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An International Expert Consensus Statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brol, M.J.; Rösch, F.; Schierwagen, R.; Magdaleno, F.; Uschner, F.E.; Manekeller, S.; Queck, A.; Schwarzkopf, K.; Odenthal, M.; Drebber, U.; et al. Combination of CCl4 with Alcoholic and Metabolic Injuries Mimics Human Liver Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G182–G194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, M.; Detlefsen, S.; Møller, L.S.; Madsen, B.S.; Hansen, J.F.; Fialla, A.D.; Trebicka, J.; Krag, A. Transient and 2-Dimensional Shear-Wave Elastography Provide Comparable Assessment of Alcoholic Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, M.; Madsen, B.S.; Hansen, J.F.; Detlefsen, S.; Antonsen, S.; Krag, A. Accuracy of the Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test vs. FibroTest, Elastography, and Indirect Markers in Detection of Advanced Fibrosis in Patients With Alcoholic Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and Validation of a Histological Scoring System for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing Real-Time PCR Data by the Comparative C(T) Method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicka, J.; Racz, I.; Siegmund, S.V.; Cara, E.; Granzow, M.; Schierwagen, R.; Klein, S.; Wojtalla, A.; Hennenberg, M.; Huss, S.; et al. Role of Cannabinoid Receptors in Alcoholic Hepatic Injury: Steatosis and Fibrogenesis Are Increased in CB2 Receptor-Deficient Mice and Decreased in CB1 Receptor Knockouts. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierwagen, R.; Maybüchen, L.; Zimmer, S.; Hittatiya, K.; Bäck, C.; Klein, S.; Uschner, F.E.; Reul, W.; Boor, P.; Nickenig, G.; et al. Seven Weeks of Western Diet in Apolipoprotein-E-Deficient Mice Induce Metabolic Syndrome and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis with Liver Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasband, W.S. ImageJ, V.1.51j8; U.S. National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1997.
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J. International Consensus Panel MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israelsen, M.; Juel, H.B.; Detlefsen, S.; Madsen, B.S.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Larsen, T.R.; Kjærgaard, M.; Jo Fernandes Jensen, M.; Stender, S.; Hansen, T.; et al. Metabolic and Genetic Risk Factors Are the Strongest Predictors of Severity of Alcohol-Related Liver Fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Making Progress in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) as We Are Transitioning from the Era of NAFLD to Dys-Metabolism Associated Fatty Liver Disease (DAFLD). Metabolism 2020, 111, 154318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahli, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Alcohol and Obesity: A Dangerous Association for Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34 (Suppl. 1), 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Åberg, F.; Helenius-Hietala, J.; Puukka, P.; Färkkilä, M.; Jula, A. Interaction between Alcohol Consumption and Metabolic Syndrome in Predicting Severe Liver Disease in the General Population. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stockwell, T.; Zhao, J.; Sherk, A.; Rehm, J.; Shield, K.; Naimi, T. Underestimation of Alcohol Consumption in Cohort Studies and Implications for Alcohol’s Contribution to the Global Burden of Disease. Addiction 2018, 113, 2245–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-M.; Kong, C.-Y.; Zhang, S.-L.; Han, B.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Wang, L.-S. Alcohol and HBV Synergistically Promote Hepatic Steatosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, S.; Begriche, K.; Catheline, D.; Trak-Smayra, V.; Tiaho, F.; Coulouarn, C.; Pinon, G.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Rioux, V.; Fromenty, B. Moderate Chronic Ethanol Consumption Exerts Beneficial Effects on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver in Mice Fed A High-Fat Diet: Possible Role of Higher Formation of Triglycerides Enriched in Monounsaturated Fatty Acids. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, M.T.; Ntambi, J.M. Role of Stearoyl-Coenzyme A Desaturase in Regulating Lipid Metabolism. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2008, 19, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gopal, T.; Kumar, N.; Perriotte-Olson, C.; Casey, C.A.; Donohue, T.M.; Harris, E.N.; Talmon, G.; Kabanov, A.V.; Saraswathi, V. Nanoformulated SOD1 Ameliorates the Combined NASH and Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease Partly via Regulating CYP2E1 Expression in Adipose Tissue and Liver. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G428–G438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, H.K.; Bataller, R.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Gao, B.; Gual, A.; Lackner, C.; Mathurin, P.; Mueller, S.; Szabo, G.; Tsukamoto, H. Alcoholic Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.S.; Jones, D.P.; Decarli, L.M. Effects of Prolonged Ethanol Intake: Production of Fatty Liver Despite Adequate Diets. J. Clin. Investig. 1965, 44, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.-J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, H.; Altamirano, J.; Chang, B.; Bertola, A.; Odena, G.; Lu, J.; Tanaka, N.; Matsusue, K.; et al. Fat-Specific Protein 27/CIDEC Promotes Development of Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice and Humans. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1030–1041.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, B.; Xu, M.-J.; Zhou, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Feng, D.; Bertola, A.; Wang, H.; Kunos, G.; et al. Short- or Long-Term High-Fat Diet Feeding plus Acute Ethanol Binge Synergistically Induce Acute Liver Injury in Mice: An Important Role for CXCL1. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1070–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, M.-J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J.X.; Varga, Z.V.; Feng, D.; Pacher, P.; Kunos, G.; Torok, N.J.; et al. Neutrophil-Hepatic Stellate Cell Interactions Promote Fibrosis in Experimental Steatohepatitis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khanova, E.; Wu, R.; Wang, W.; Yan, R.; Chen, Y.; French, S.W.; Llorente, C.; Pan, S.Q.; Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Pyroptosis by Caspase11/4-Gasdermin-D Pathway in Alcoholic Hepatitis in Mice and Patients. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1737–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leclercq, I.A.; Farrell, G.C.; Schriemer, R.; Robertson, G.R. Leptin Is Essential for the Hepatic Fibrogenic Response to Chronic Liver Injury. J. Hepatol. 2002, 37, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Soejima, Y.; Fukusato, T. Animal Models of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppan, D.; Surabattula, R.; Wang, X.Y. Determinants of Fibrosis Progression and Regression in NASH. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402.
- Xiao, G.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, X.; Yan, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, G. Comparison of Laboratory Tests, Ultrasound, or Magnetic Resonance Elastography to Detect Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denayer, T.; Stöhr, T.; Van Roy, M. Animal Models in Translational Medicine: Validation and Prediction. New Horiz. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurrell, T.; Kastrinou-Lampou, V.; Fardellas, A.; Hendriks, D.F.G.; Nordling, Å.; Johansson, I.; Baze, A.; Parmentier, C.; Richert, L.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Human Liver Spheroids as A Model to Study Aetiology and Treatment of Hepatic Fibrosis. Cells 2020, 9, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, S.; Li, M.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, M.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; Qian, L.; Zhai, L.; Li, J.; et al. Proteome-Wide Analysis of USP14 Substrates Revealed Its Role in Hepatosteatosis via Stabilization of FASN. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rein-Fischboeck, L.; Haberl, E.M.; Pohl, R.; Feder, S.; Liebisch, G.; Krautbauer, S.; Buechler, C. Variations in Hepatic Lipid Species of Age-Matched Male Mice Fed A Methionine-Choline-Deficient Diet and Housed in Different Animal Facilities. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fouad, Y.; Waked, I.; Bollipo, S.; Gomaa, A.; Ajlouni, A.; Attia, D. What’s in A Name? Renaming “NAFLD’’ to “MAFLD”. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balmer, M.L.; Dufour, J.-F. Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis—From NAFLD to MAFLD. Ther. Umsch. 2011, 68, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.; Dhaliwal, A.J.S.; Lopez, R.; Noureddin, M.; Alkhouri, N. Trends of Awareness of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Alcoholic Liver Disease and Both Fatty Liver Diseases (BAFLD) Using National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: 836. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, S465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Ctrl (n = 30) | LD (n = 11) | OA (n = 18) | OD (n = 21) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data at liver biopsy | |||||
| Body mass index, kg/m2, mean ± SD | 23.07 ± 2.03 | 21.53 ± 3.34 | 29.48 ± 4.17 | 30.67 ± 3.22 | 0.000 * |
| HbA1c, mM, mean ± SD | 36.4 ± 5.5 | 32.4 ± 6.5 | 36.1 ± 7.4 | 34.7 ± 7.5 | 0.178 |
| Histological score, mean ± SD | |||||
| Kleiner Fibrosis Stage | 1.47 ± 1.45 | 2.00 ± 1.34 | 2.22 ± 1.52 | 2.23 ± 1.07 | 0.129 |
| NAS Steatosis Grade | 0.27 ± 0.058 | 1.45 ± 1.04 | 0.22 ± 0.55 | 1.41 ± 0.91 | 0.000 * |
| NAS Inflammation Grade | 1.00 ± 1.11 | 2.27 ± 1.74 | 1.50 ± 1.39 | 2.73 ± 1.49 | 0.001 * |
| Characteristic | Ctrl (n = 5) | EtOH (n = 5) | WD (n = 5) | WD/EtOH (n = 5) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data at sacrifice | |||||
| Body weight, g, mean ± SD | 27.3 ± 1.2 | 26.6 ± 1.2 | 29.1 ± 1.00 | 26.8 ± 1.84 | 0.050 * |
| Liver weight, g, mean ± SD | 1.41 ± 0.13 | 1.40 ± 0.08 | 1.37 ± 0.11 | 1.65 ± 0.28 | 0.097 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brol, M.J.; Georgiou, S.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Ortiz, C.; Klein, S.; Schierwagen, R.; Uschner, F.E.; Eberle, L.; Detlefsen, S.; Pantazopoulou, V.I.; et al. Effects of Ethanol Feeding in Early-Stage NAFLD Mice Induced by Western Diet. Livers 2021, 1, 27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1010003
Brol MJ, Georgiou S, Rasmussen DN, Ortiz C, Klein S, Schierwagen R, Uschner FE, Eberle L, Detlefsen S, Pantazopoulou VI, et al. Effects of Ethanol Feeding in Early-Stage NAFLD Mice Induced by Western Diet. Livers. 2021; 1(1):27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrol, Maximilian Joseph, Stella Georgiou, Ditlev Nytoft Rasmussen, Cristina Ortiz, Sabine Klein, Robert Schierwagen, Frank Erhard Uschner, Larissa Eberle, Sönke Detlefsen, Vasiliki I. Pantazopoulou, and et al. 2021. "Effects of Ethanol Feeding in Early-Stage NAFLD Mice Induced by Western Diet" Livers 1, no. 1: 27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1010003
APA StyleBrol, M. J., Georgiou, S., Rasmussen, D. N., Ortiz, C., Klein, S., Schierwagen, R., Uschner, F. E., Eberle, L., Detlefsen, S., Pantazopoulou, V. I., Thiele, M., Filippa, V., Torres, S., Anastasiadou, E., Krag, A., & Trebicka, J. (2021). Effects of Ethanol Feeding in Early-Stage NAFLD Mice Induced by Western Diet. Livers, 1(1), 27-39. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers1010003





