The Role of Cytochrome P450 3A4-Mediated Metabolism in Sorafenib and Lapatinib Hepatotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals
2.3. Hepatocyte Isolation
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Cell Viability
2.6. Cytochrome P450 Activity
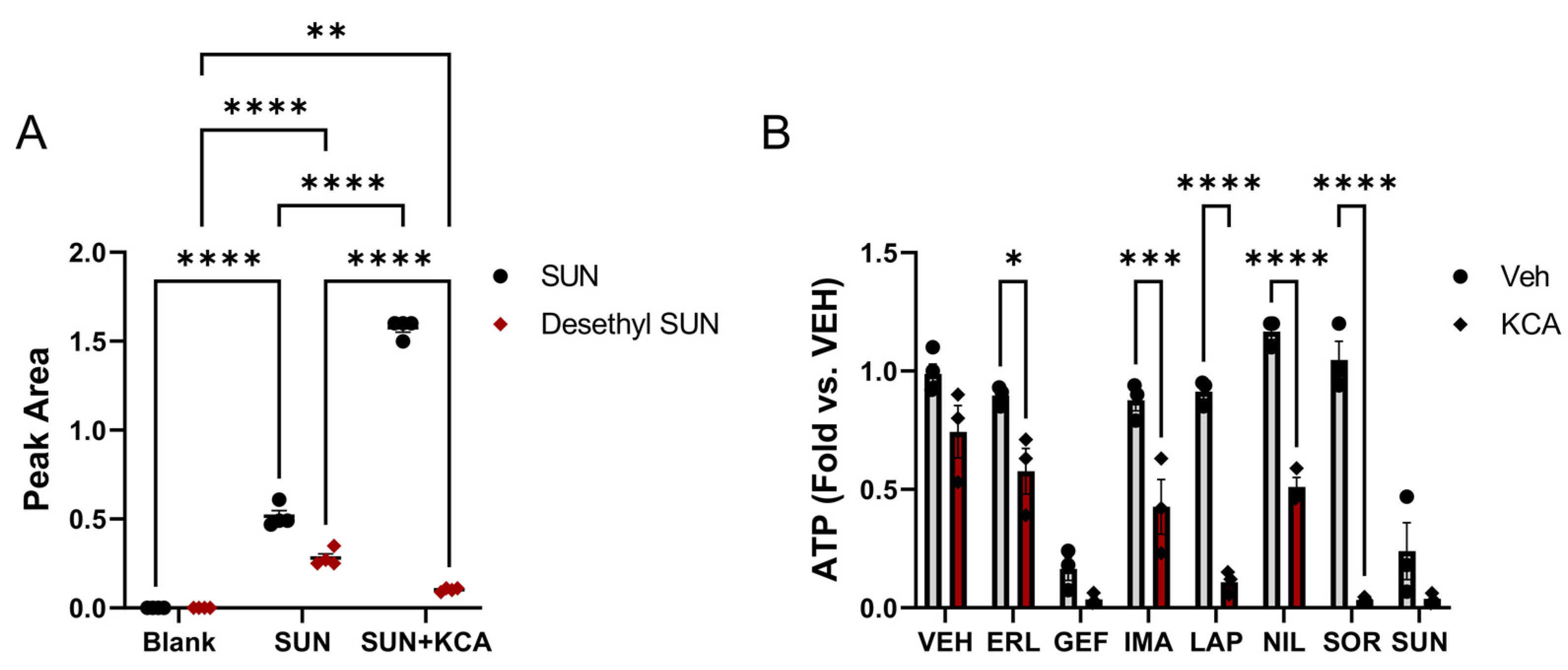
2.7. Sunitinib Metabolism Study
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
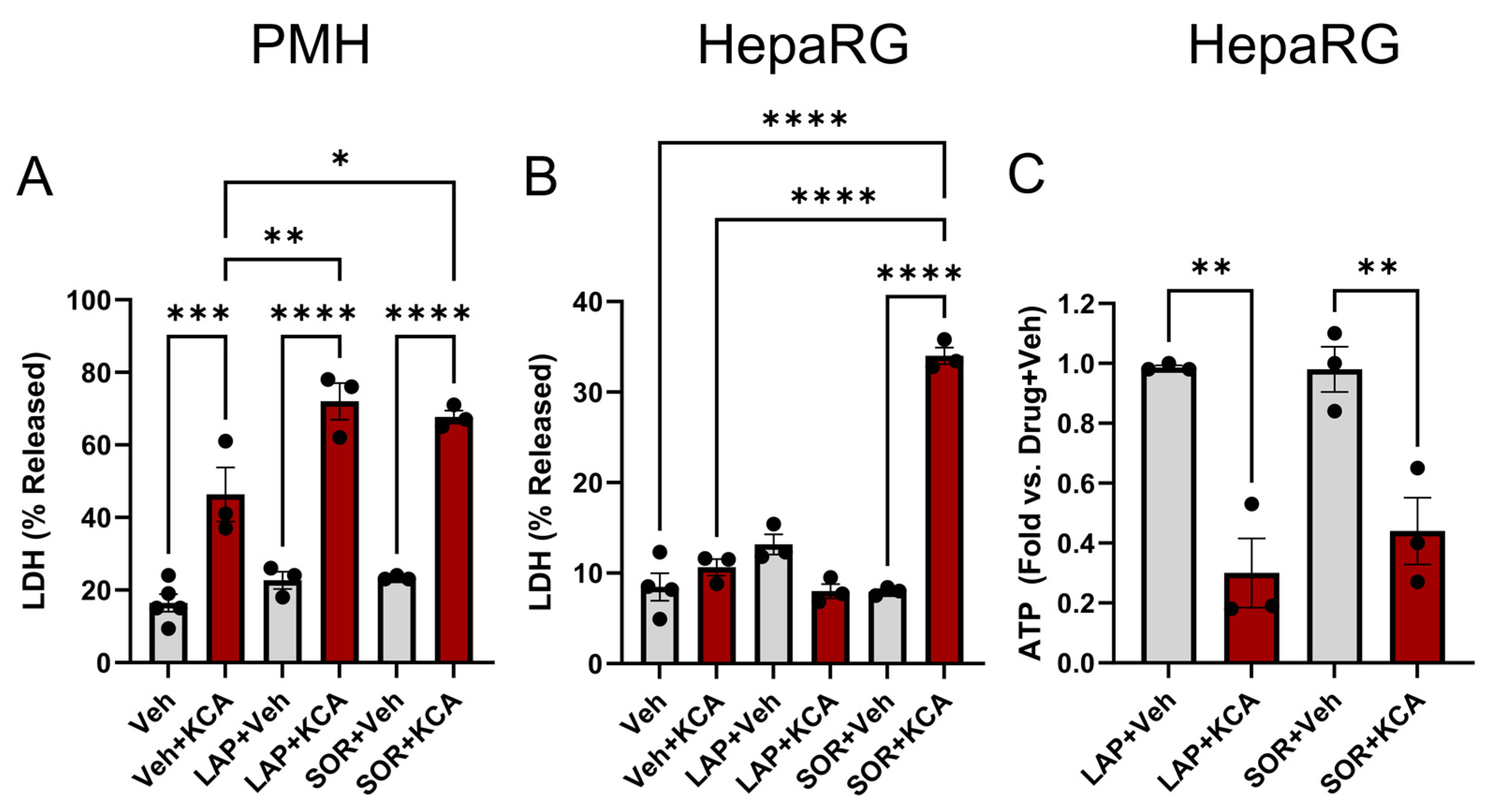
3.1. Inhibition of TKI Metabolism Increased Toxicity in Primary Mouse Hepatocytes
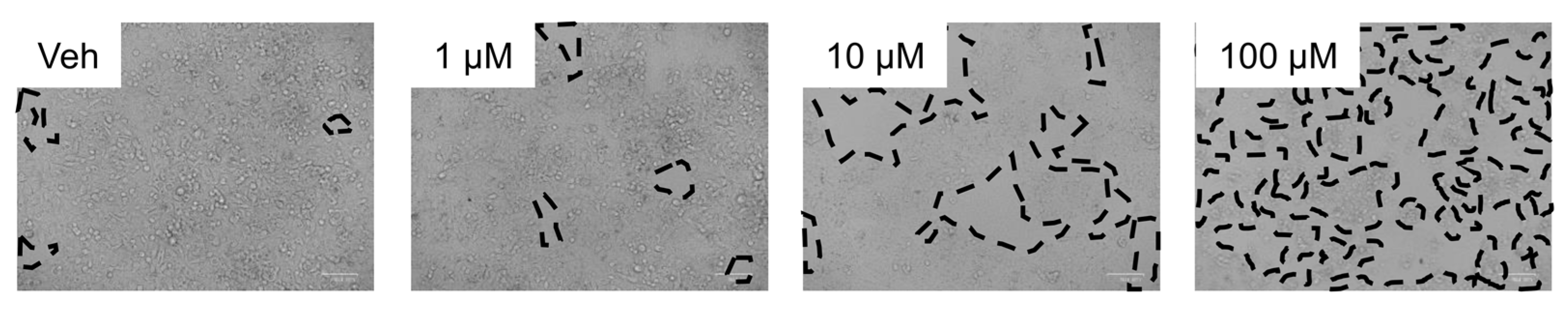
3.2. Inhibition of Metabolism Increased Toxicity of Sorafenib in Human HepaRG Cells
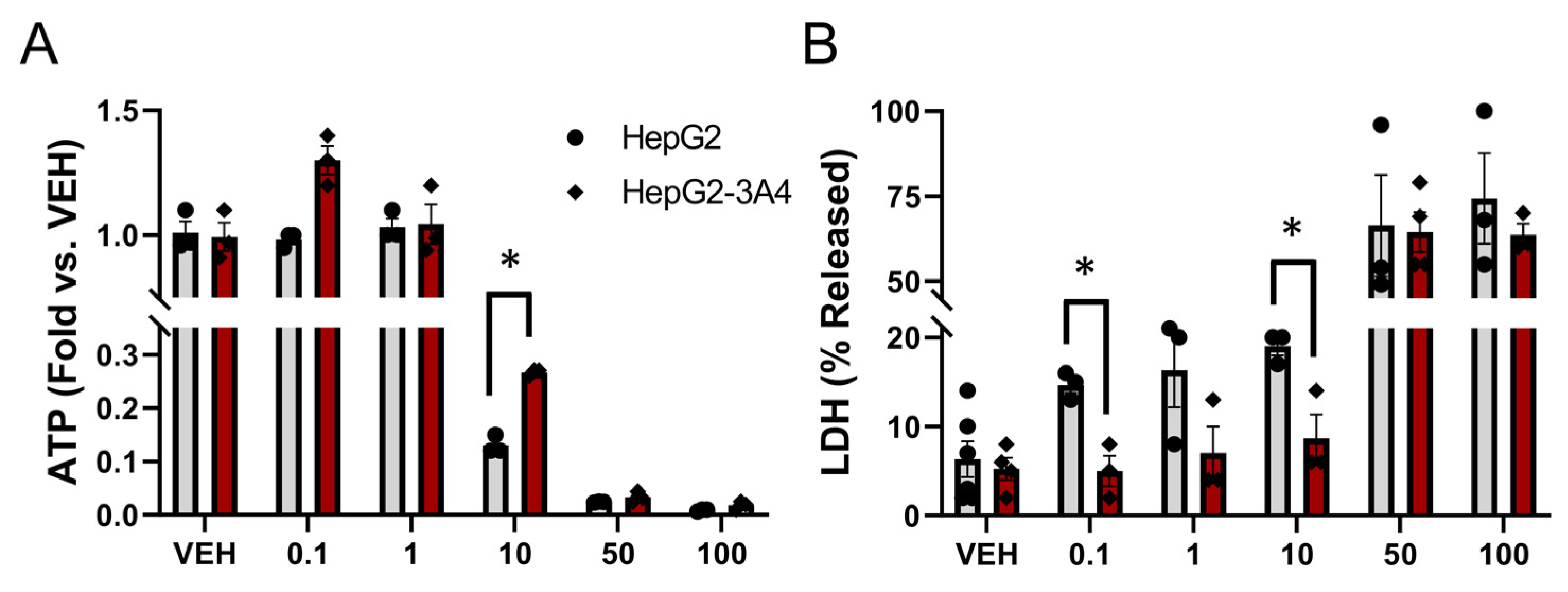
3.3. Expression of CYP3A4 Activity Decreased Sorafenib Toxicity in HepG2 Cells
4. Discussion
4.1. CYP3A Enzymes Detoxify Sorafenib, Lopatinib, and Some Other TKIs
4.2. Competing Toxicity Mechanisms and Detoxification Pathways May Be Common for TKIs
4.3. The Confounding Role of the Immune System in TKI Toxicity
4.4. Limitations of Our Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, P.; Nielsen, T.E.; Clausen, M.H. Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors: An Analysis of FDA-Approved Drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhullar, K.S.; Lagarón, N.O.; McGowan, E.M.; Parmar, I.; Jha, A.; Hubbard, B.P.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Kinase-Targeted Cancer Therapies: Progress, Challenges and Future Directions. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, R.R.; Morganroth, J.; Shah, D.R. Hepatotoxicity of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Clinical and Regulatory Perspectives. Drug Saf. 2013, 36, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, Z.E.; Li, B.; Li, F. Recent Advances in Metabolism and Toxicity of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 237, 108256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.D. Mechanisms of the Formation and Disposition of Reactive Metabolites That Can Cause Acute Liver Injury. Drug Metab. Rev. 1995, 27, 147–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebler, D.C.; Guengerich, F.P. Elucidating Mechanisms of Drug-Induced Toxicity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.; Lucena, M.I.; Andrade, R.J. Genetic Risk Factors in the Development of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paech, F.; Bouitbir, J.; Krähenbühl, S. Hepatocellular Toxicity Associated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Mitochondrial Damage and Inhibition of Glycolysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mingard, C.; Paech, F.; Bouitbir, J.; Krähenbühl, S. Mechanisms of Toxicity Associated with Six Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Human Hepatocyte Cell Lines. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paludetto, M.N.; Puisset, F.; Chatelut, E.; Arellano, C. Identifying the Reactive Metabolites of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in a Comprehensive Approach: Implications for Drug-Drug Interactions and Hepatotoxicity. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2105–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, S.R.; Li, C.Y.; Jiang, L.L.; Wei, P.; He, M.F. Mechanism of Hepatotoxicity of First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Gefitinib and Afatinib. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 343, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, Y.L.; Ho, H.K.; Chan, A. Formation of Reactive Metabolites and Management of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Literature Review. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2015, 11, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya, G.M.; Durandis, R.; Bourgeois, D.S.; Perkins, J.A.; Abouda, A.A.; Wines, K.J.; Mohamud, M.; Starks, S.A.; Daniels, R.N.; Jackson, K.D. Cytochromes P450 1A2 and 3A4 Catalyze the Metabolic Activation of Sunitinib. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martignoni, M.; Groothuis, G.; De Kanter, R. Comparison of Mouse and Rat Cytochrome P450-Mediated Metabolism in Liver and Intestine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burke, A.S.; MacMillan-Crow, L.A.; Hinson, J.A. Reactive Nitrogen Species in Acetaminophen-Induced Mitochondrial Damage and Toxicity in Mouse Hepatocytes. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2010, 23, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshitomi, S.; Ikemoto, K.; Takahashi, J.; Miki, H.; Namba, M.; Asahi, S. Establishment of the transformants expressing human cytochrome P450 subtypes in HepG2, and their applications on drug metabolism and toxicology. Toxicol. In Vitro 2001, 15, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, M.R.; Yan, H.M.; Ramachandran, A.; Murray, G.J.; Rollins, D.E.; Jaeschke, H. HepaRG Cells: A Human Model to Study Mechanisms of Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 2011, 53, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajt, M.L.; Knight, T.R.; Lemasters, J.J.; Jaeschke, H. Acetaminophen-Induced Oxidant Stress and Cell Injury in Cultured Mouse Hepatocytes: Protection by N-Acetyl Cycteine. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 80, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khojasteh, S.S.; Prabhu, S.; Kenny, J.R.; Halladay, J.S.; Lu, A.Y. Chemical inhibitors for cytochrome P450 isoforms in human liver microsomes: A re-evaluation of the P450 isoform selectivity. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, J.H.; Knott, K.; Miller, G.P. CYP2E1 hydroxylation of aniline involves negative cooperativity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauret, N.; Gauthier, A.; Nicoll-Griffith, D.A. Effect of common organic solvents on in vitro cytochrome P450-mediated metabolic activities in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1998, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Busby, W.F., Jr.; Ackermann, J.M.; Crespi, C.L. Effect of methanol, ethanol, dimethyl sulfoxide, and acetonitrile on in vitro activities of cDNA-expressed human cytochromes P-450. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1999, 27, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Han, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wan, L.; Huo, Y.; Guo, C. Effect of regular organic solvents on cytochrome P450-mediated metabolic activities in rat liver microsomes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1922–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Liao, M.; Wang, X.; Du, H.; Chen, J.; Yao, M.; Li, Q. Determination of sunitinib and its active metabolite, N-desethyl sunitinib in mouse plasma and tissues by UPLC-MS/MS: Assay development and application to pharmacokinetic and tissue distribution studies. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurice, M.; Pichard, L.; Daujat, M.; Fabre, I.; Joyeux, H.; Domergue, J.; Maurel, P. Effects of Imidazole Derivatives on Cytochromes P450 from Human Hepatocytes in Primary Culture. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Available online: Livertox.nih.gov (accessed on 9 May 2023).
- Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Yang, X.; White, M.; Greenhaw, J.; Harris, T.; Wu, Q.; Bryant, M.; Papoian, T.; Mattes, W.; et al. Cytotoxicity of 34 FDA Approved Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors in Primary Rat and Human Hepatocytes. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 291, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aninat, C.; Piton, A.; Glaise, D.; Le Charpentier, T.; Langouët, S.; Morel, F.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Guillouzo, A. Expression of Cytochromes P450, Conjugating Enzymes and Nuclear Receptors in Human Hepatoma HepaRG Cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillouzo, A.; Corlu, A.; Aninat, C.; Glaise, D.; Morel, F.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C. The Human Hepatoma HepaRG Cells: A Highly Differentiated Model for Studies of Liver Metabolism and Toxicity of Xenobiotics. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 168, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.N.; Li, Y.; Nakamoto, K.; Subileau, E.A.; Steen, D.; Zhong, X.B. A Comparison of Whole Genome Gene Expression Profiles of HepaRG Cells and HepG2 Cells to Primary Human Hepatocytes and Human Liver Tissues. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukami, T.; Iida, A.; Konishi, K.; Nakajima, M. Human Arylacetamide Deacetylase Hydrolyzes Ketoconazole to Trigger Hepatocellular Toxicity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 116, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegler, P.; Joerin, L.; Krähenbühl, S.; Bouitbir, J. Hepatocellular Toxicity of Imidazole and Triazole Antimycotic Agents. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 157, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Knox, B.; Gong, B.; Chen, S.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.; Tong, W.; Ning, B. Identification of Translational MicroRNA Biomarker Candidates for Ketoconazole-Induced Liver Injury Using next-Generation Sequencing. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 179, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosedale, M.; Watkins, P.B. Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Advances in Mechanistic Understanding That Will Inform Risk Management. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 101, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Hootegem, A.; Verslype, C.; Van Steenbergen, W. Sorafenib-Induced Liver Failure: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Hepatol. 2011, 2011, 941395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, K.D.; Durandis, R.; Vergne, M.J. Role of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes in the Metabolic Activation of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kenny, J.R.; Mukadam, S.; Zhang, C.; Tay, S.; Collins, C.; Galetin, A.; Khojasteh, S.C. Drug-Drug Interaction Potential of Marketed Oncology Drugs: In Vitro Assessment of Time-Dependent Cytochrome P450 Inhibition, Reactive Metabolite Formation and Drug-Drug Interaction Prediction. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 1960–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.C.; Oh, J.W.; New, L.S.; Wahlin, M.D.; Nelson, S.D.; Ho, H.K.; Chan, E.C.Y. Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 3A4 by Lapatinib. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, C.; Zhou, J.; Guo, Z.; Diao, X.; Gao, Z.; Zhong, D.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X. Metabolism and Bioactivation of Famitinib, a Novel Inhibitor of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase, in Cancer Patients. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1687–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Towles, J.K.; Clark, R.N.; Wahlin, M.D.; Uttamsingh, V.; Rettie, A.E.; Jackson, K.D. Cytochrome P450 3A4 and CYP3A5-Catalyzed Bioactivation of Lapatinib. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1584–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghassabian, S.; Rawling, T.; Zhou, F.; Doddareddy, M.R.; Tattam, B.N.; Hibbs, D.E.; Edwards, R.J.; Cui, P.H.; Murray, M. Role of Human CYP3A4 in the Biotransformation of Sorafenib to Its Major Oxidized Metabolites. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, T.B.; Rawling, T.; Murray, M. Cytochrome P450-Mediated Biotransformation of Sorafenib and Its N-Oxide Metabolite: Implications for Cell Viability and Human Toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sernoskie, S.C.; Jee, A.; Uetrecht, J.P. The Emerging Role of the Innate Immune Response in Idiosyncratic Drug Reactionss. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 861–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourrié, M.; Meunier, V.; Berger, Y.; Fabre, G. Cytochrome P450 isoform inhibitors as a tool for the investigation of metabolic reactions catalyzed by human liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 277, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eagling, V.A.; Tjia, J.F.; Back, D.J. Differential selectivity of cytochrome P450 inhibitors against probe substrates in human and rat liver microsomes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 45, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klaeger, S.; Gohlke, B.; Perrin, J.; Gupta, V.; Heinzlmeir, S.; Helm, D.; Qiao, H.; Bergamini, G.; Handa, H.; Savitski, M.M.; et al. Chemical Proteomics Reveals Ferrochelatase as a Common Off-Target of Kinase Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiff, M.A.; Crosby, S.; Blue, M.; Schleiff, B.M.; Boysen, G.; Miller, G.P. CYP2C9 and 3A4 Play Opposing Roles in Bioactivation and Detoxification of Diphenylamine NSAIDs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 194, 114824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleiff, M.A.; Payakachat, S.; Schleiff, B.M.; Swamidass, S.J.; Boysen, G.; Miller, G.P. Impacts of Diphenylamine NSAID Halogenation on Bioactivation Risks. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, C.; Sundqvist, L.; Ho, H.; Niskanen, J.; Honkakoski, P.; Brouwer, K.L.R. Novel Bile Acid-Dependent Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity Associated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2022, 380, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Drug | Concentration (µM) a |
|---|---|
| Erolotinib (ERL) | 17.2 |
| Gefitinib (GEF) | 27 |
| Imatinib (IMA) | 20 |
| Lapatinib (LAP) | 10.45 |
| Nilotinib (NIL) | 21.35 |
| Sorafenib (SOR) | 8.6 |
| Sunitinib (SUN) | 12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McGill, M.R.; Kaufmann, Y.; LoBianco, F.V.; Schleiff, M.A.; Aykin-Burns, N.; Miller, G.P. The Role of Cytochrome P450 3A4-Mediated Metabolism in Sorafenib and Lapatinib Hepatotoxicity. Livers 2023, 3, 310-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020022
McGill MR, Kaufmann Y, LoBianco FV, Schleiff MA, Aykin-Burns N, Miller GP. The Role of Cytochrome P450 3A4-Mediated Metabolism in Sorafenib and Lapatinib Hepatotoxicity. Livers. 2023; 3(2):310-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcGill, Mitchell R., Yihong Kaufmann, Francesca V. LoBianco, Mary A. Schleiff, Nukhet Aykin-Burns, and Grover P. Miller. 2023. "The Role of Cytochrome P450 3A4-Mediated Metabolism in Sorafenib and Lapatinib Hepatotoxicity" Livers 3, no. 2: 310-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020022
APA StyleMcGill, M. R., Kaufmann, Y., LoBianco, F. V., Schleiff, M. A., Aykin-Burns, N., & Miller, G. P. (2023). The Role of Cytochrome P450 3A4-Mediated Metabolism in Sorafenib and Lapatinib Hepatotoxicity. Livers, 3(2), 310-321. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020022









