The Dutch HbA1c Lifestyle Study (DAF-Study): Seasonal Variation of HbA1c in the Dutch Diabetes Population—Associations with Macronutrient Intake and Physical Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. National HbA1c Data
2.2. HbA1c Analysis
2.3. National Food Consumption Data
2.4. National Sports Participation Data
2.5. COVID-19
2.6. Data Transformation
2.7. HbA1c Prediction by PA and TEI
2.8. Statistical Analysis and Calculations
3. Results
3.1. HbA1c Results over Time and Seasonal Variation
3.2. Macronutrient Intake (MNI) and Seasonal Variation
3.3. Physical Activity (PA) and Seasonal Variation
3.4. HbA1c Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PA | Physical activity |
| MNI | Macronutrient intake |
| NGSP | National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program |
| IFCC | International Federation for Clinical Chemistry |
| EQA | External Quality Assessment |
| TEI | Total Energy Intake |
| TCI | Total Carbohydrate Intake |
| TFI | Total Fat Intake |
| TPI | Total Protein Intake |
| SPI | Sports Participation Index |
| ADA | American Diabetes Association |
| EASD | European Association for the Study of Diabetes |
References
- Magliano, D.J.; Boyko, E.J.; IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th Edition Scientific Committee. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; IDF Diabetes Atlas; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group; Nathan, D.M.; Genuth, S.; Lachin, J.; Cleary, P.; Crofford, O.; Davis, M.; Rand, L.; Siebert, C. The Effect of Intensive Treatment of Diabetes on the Development and Progression of Long-Term Complications in Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study. IV. Characteristics of Newly Presenting Type 2 Diabetic Patients: Male Preponderance and Obesity at Different Ages. Multi-Center Study. Diabet. Med. 1988, 5, 154–159. [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; ElSayed, N.A.; McCoy, R.G.; Aleppo, G.; Balapattabi, K.; Beverly, E.A.; Briggs Early, K.; Bruemmer, D.; Ebekozien, O.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; et al. 1. Improving Care and Promoting Health in Populations: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48 (Suppl. 1), S14–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of Hyperglycaemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanas, R.; John, G.; International HbA(1c) Consensus Committee. 2010 Consensus Statement on the Worldwide Standardization of the Hemoglobin A1c Measurement. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1362–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee Report on the Role of the A1C Assay in the Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrie, C.D.; Sharpe, T.C.; Price, D.A.; Surtees, R.A. Seasonal Variation of Glycosylated Haemoglobin. Arch. Dis. Child. 1987, 62, 959–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplund, J. Seasonal Variation of HbA1c in Adult Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, G.A.; Edwards, O.M. Seasonal Variation in Glycated Haemoglobin in Diabetics. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2001, 38 Pt 1, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Suzuki, H.; Baba, T.; Nakamura, K.; Watanabe, T. Seasonal Variation of Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Park, S.; Yi, W.; Yu, K.-S.; Kim, T.H.; Oh, T.J.; Choi, J.; Cho, Y.M. Seasonal Variation in Hemoglobin A1c in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.T.R.e.P.; Lira, D.; Bacelar, C.; Oliveira, J.C.; de Carvalho, A.C. Seasonal Variation of Haemoglobin A1c in a Portuguese Adult Population. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 59, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-L.; Brimacombe, M.; Xie, M.; Rajan, M.; Wang, H.; Kolassa, J.; Crystal, S.; Chen, T.-C.; Pogach, L.; Safford, M. Seasonal Patterns in Monthly Hemoglobin A1c Values. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 161, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, T.; Saw, S.; Sikaris, K.; Wiley, C.L.; Cembrowski, G.C.; Lyon, A.W.; Khajuria, A.; Tran, D. Seasonal Variation in Hemoglobin A1c: Is It the Same in Both Hemispheres? J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2009, 3, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, A.; Friger, M.; Biderman, A. Seasonal Variations in HbA1c among Type 2 Diabetes Patients on a Semi-Arid Climate between the Years 2005–2015. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilbronn, L.K.; Noakes, M.; Clifton, P.M. Effect of Energy Restriction, Weight Loss, and Diet Composition on Plasma Lipids and Glucose in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonekamp, N.E.; van Damme, I.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Winkels, R.M.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Morris, P.B.; Koopal, C. Effect of Dietary Patterns on Cardiovascular Risk Factors in People with Type 2 Diabetes. A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 195, 110207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garonzi, C.; Forsander, G.; Maffeis, C. Impact of Fat Intake on Blood Glucose Control and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, C.E.M.; Evans, M.; O’Connell, S.M.; McElduff, P.; Lopez, P.E.; Jones, T.W.; Davis, E.A.; King, B.R. Both Dietary Protein and Fat Increase Postprandial Glucose Excursions in Children with Type 1 Diabetes, and the Effect Is Additive. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3897–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.; Nishida, Y.; Hara, M.; Shimanoe, C.; Koga, K.; Iwasaka, C.; Higaki, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Nakashima, R.; Ikezaki, H.; et al. Effect of the Interaction between Physical Activity and Estimated Macronutrient Intake on HbA1c: Population-Based Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Studies. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2022, 10, e002479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraeten, S.; Griffith-Lendering, M.; Pin, R. De Nationale Gezondheidsenquête Curaçao 2017; Volksgezondheid Instituut Curaçao: Willemstad, Curaçao, 2018; pp. 1–174. [Google Scholar]
- Weykamp, C.; John, G.; Gillery, P.; English, E.; Ji, L.; Lenters-Westra, E.; Little, R.R.; Roglic, G.; Sacks, D.B.; Takei, I.; et al. Investigation of 2 Models to Set and Evaluate Quality Targets for Hb A1c: Biological Variation and Sigma-Metrics. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderman-Nawijn, E.; Brants, H.; Dinnissen, C.; Ocké, M.; van Rossum, C. Energy and Nutrient Intake in the Netherlands. Results of the Dutch National Food Consumption Survey 2019–2021; Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu RIVM: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOC*NSF Landelijke Sportdeelname Index-NOCNSF. Available online: https://nocnsf.nl:/sportdeelnameindex (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- van Duin, M.; Luesink, M. Evaluatie COVID-19 Crisis in Curaçao; Nederlands Instituut Publieke Veiligheid (NIPV): Arnhem, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 1–28. Available online: https://nipv.nl/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/20230802-NIPV-Evaluatie-COVID-19-crisis-in-Curacao.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Coronavirus Tijdlijn. Available online: https://www.rijksoverheid.nl/onderwerpen/coronavirus-tijdlijn (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- National Institute for Public Health and the Enviroment, RIVM, Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport. Beweegrichtlijnen|Sport en Bewegen in Cijfers. Available online: https://www.sportenbewegenincijfers.nl/kernindicatoren/beweegrichtlijnen (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Duijvestijn, M.; Schurink, T.; van den Berg, S. Sport-En Beweeggedrag in 2020; RIVM-2021-0117; RIVM Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, R.J.; Aoyagi, Y. Seasonal Variations in Physical Activity and Implications for Human Health. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 251–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Council of the Netherlands. Dietary Reference Intakes: Energy, Proteins, Fats, and Digestible Carbohydrates; Gezondheidsraad: Den Haag, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerie van Volksgezondheid, Welzijn en Sport. Dietary Reference Values for Energy-Advisory Report-The Health Council of the Netherlands. Available online: https://www.healthcouncil.nl/documents/advisory-reports/2022/08/16/dietary-reference-values-for-energy (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Belsare, P.; Bartolome, A.; Stanger, C.; Prioleau, T. Understanding Temporal Changes and Seasonal Variations in Glycemic Trends Using Wearable Data. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetes mellitus|Volksgezondheid en Zorg. Available online: https://www.vzinfo.nl/diabetes-mellitus (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Bonsembiante, L.; Targher, G.; Maffeis, C. Type 2 Diabetes and Dietary Carbohydrate Intake of Adolescents and Young Adults: What Is the Impact of Different Choices? Nutrients 2021, 13, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, C. Explaining Seasonal Patterns of Food Consumption. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2021, 24, 100332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.R.; Sudati, I.P.; Konzen, V.D.M.; de Campos, A.C.; Wibelinger, L.M.; Correa, C.; Miguel, F.M.; Silva, R.N.; Borghi-Silva, A. COVID-19 and the Impact on the Physical Activity Level of Elderly People: A Systematic Review. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 159, 111675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, K.; Kienberger, K.; Niessner, C. Changes in Physical Activity Patterns Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M.; Smith, K.; Stroud, R. The Dietary Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Health Econ. 2022, 84, 102641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; Schaap, L.A.; Wijnhoven, H.A.H. Self-Reported Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Nutrition and Physical Activity Behaviour in Dutch Older Adults Living Independently. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebl, A.; Mata, M.; Eschwège, E. Evaluation of Risk Factors for Development of Complications in Type II Diabetes in Europe. Diabetologia 2002, 45 (Suppl. 1), S23–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, A.; Wagner, R.; Heni, M.; Kantartzis, K.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Lehmann, R.; Peter, A.; Dannecker, C.; Fritsche, L.; et al. Different Effects of Lifestyle Intervention in High- and Low-Risk Prediabetes: Results of the Randomized Controlled Prediabetes Lifestyle Intervention Study (PLIS). Diabetes 2021, 70, 2785–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagastume, D.; Siero, I.; Mertens, E.; Cottam, J.; Colizzi, C.; Peñalvo, J.L. The Effectiveness of Lifestyle Interventions on Type 2 Diabetes and Gestational Diabetes Incidence and Cardiometabolic Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Evidence from Low- and Middle-Income Countries. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 53, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A.B.; Lu, D.; Qin, F.; Hedlin, H.; Johannsen, N.M.; Chung, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Haddad, F.; Lamendola, C.; Basina, M.; et al. Effectiveness of a Community-Based Structured Physical Activity Program for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2247858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilafranca-Cartagena, M.; Bonet-Augè, A.; Colillas-Malet, E.; Puiggrós-Binefa, A.; Tort-Nasarre, G. Physical Activity Interventions in People with Diabetes: A Systematic Review of The Qualitative Evidence. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yom-Tov, E.; Feraru, G.; Kozdoba, M.; Mannor, S.; Tennenholtz, M.; Hochberg, I. Encouraging Physical Activity in Patients with Diabetes: Intervention Using a Reinforcement Learning System. J. Med. Internet Res. 2017, 19, e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirk, H.; Blake, H.; Tennyson, R.; Randell, T.L.; Glazebrook, C. Physical Activity Interventions in Children and Young People with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Forbes, A.; Ghazaleh, H.A.; He, Q.; Huang, J.; Asaad, M.; Cheng, L.; Duaso, M. Interventions and Behaviour Change Techniques for Improving Physical Activity Level in Working-Age People (18–60 years) with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2024, 160, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

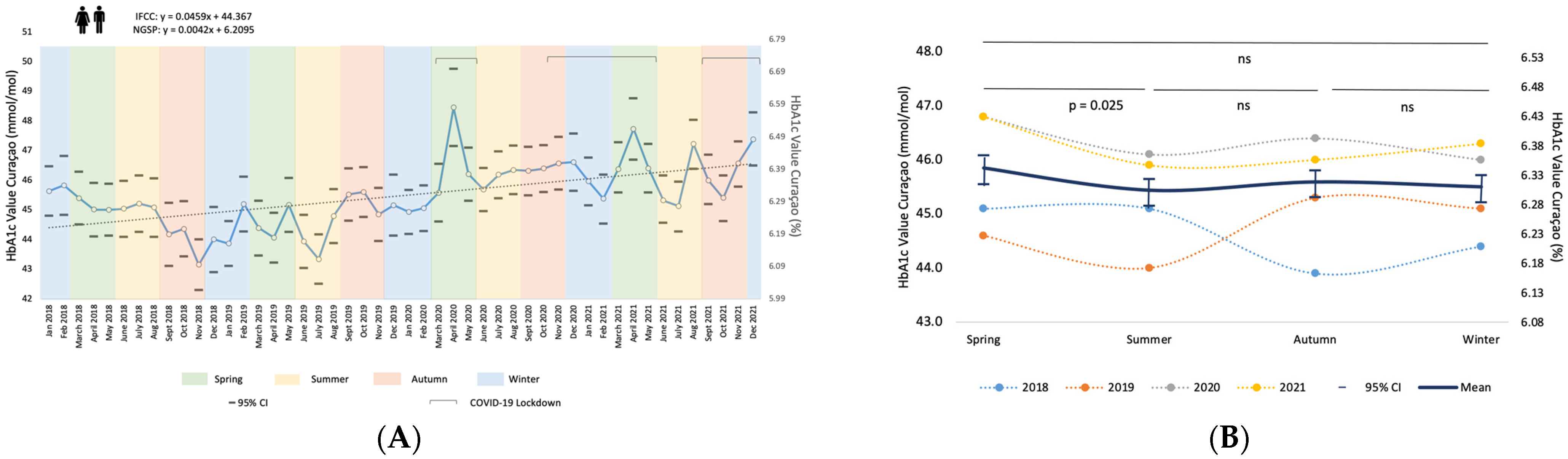

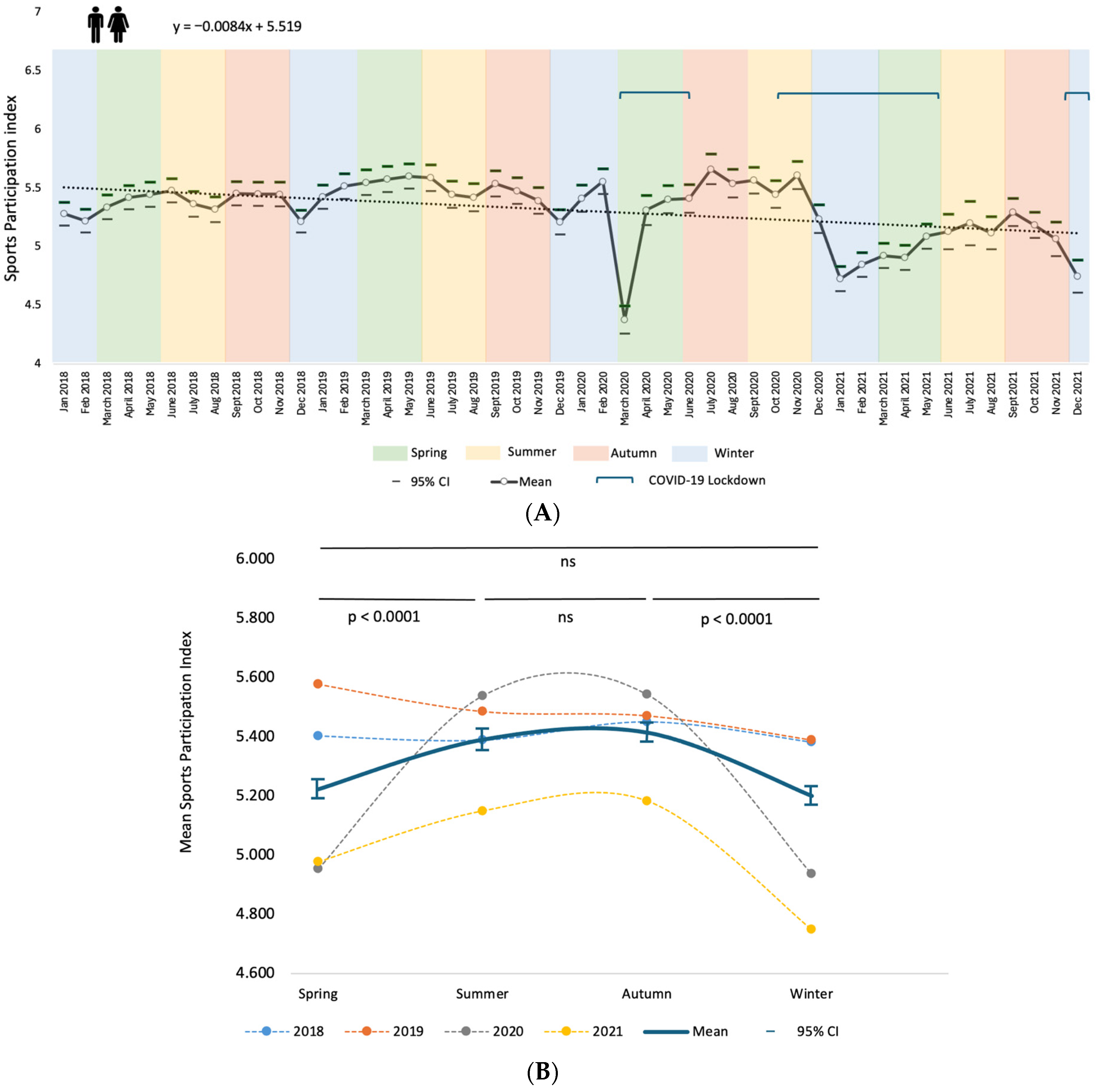
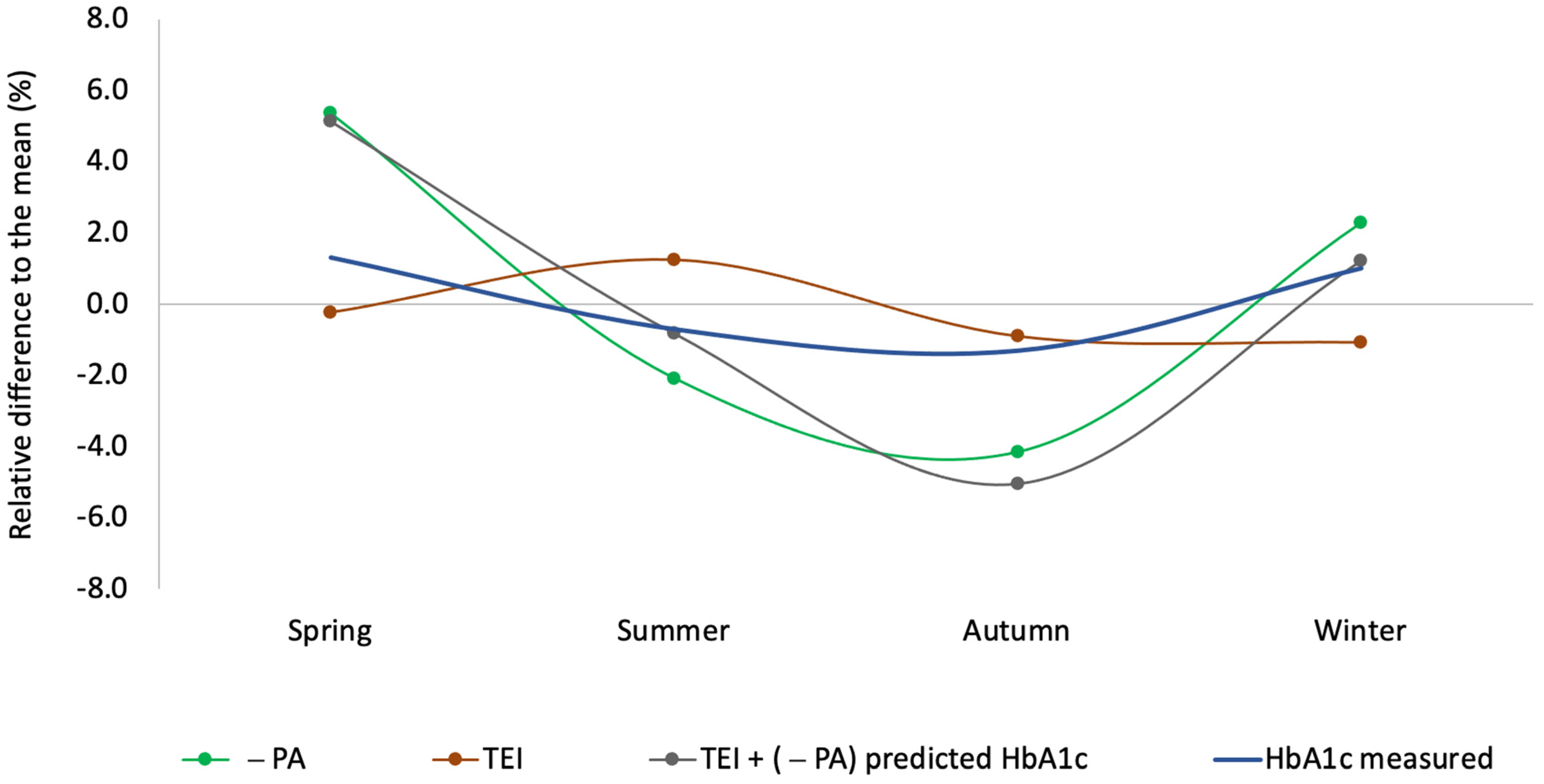
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Annual Mean/ Total N | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | XHbA1c | 52.9 (6.99) * | ||||
| N | 227,117 | |||||
| XHbA1c | 52.3 (6.94) | 51.6 (6.87) | 51.5 (6.73) | 52.9 (6.99) ** | 52.0 (6.91) | |
| N | 348,010 | 326,414 | 368,228 | 347,245 | ||
| 2019 | XHbA1c | 52.7 (6.97) | 52.3 (6.94) | 51.6 (6.87) | 52.7 (6.97) | 52.3 (6.94) |
| N | 376,682 | 338,322 | 386,652 | 368,016 | ||
| 2020 | XHbA1c | 53.2 (7.02) | 51.8 (6.89) | 52.2 (6.93) | 53.7 (7.06) | 52.5 (6.95) |
| N | 213,464 | 358,450 | 371,330 | 352,560 | ||
| 2021 | XHbA1c | 53.3 (7.03) | 52.5 (6.95) | 52.2 (6.93) | 53.2 (7.02) *** | 52.9 (6.99) |
| N | 374,936 | 363,433 | 396,230 | 118,631 | ||
| Ntotal | 1,313,092 | 1,386,619 | 1,522,640 | 1,413,569 | 5,635,920 | |
| Xtotal HbA1c | 52.9 (6.99) | 52.1 (6.92) | 51.9 (6.90) | 53.1 (7.01) | 52.4 (6.95) | |
| 95% CI | +/− 0.03 (0.003) | +/− 0.02 (0.002) | +/− 0.02 (0.002) | +/− 0.02 (0.002) | +/− 0.01 (0.001) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kemna, E.; Bilo, H.; Deckers, M.; Slim, C.; Loot, A.; Henricks, L.M.; Brinkman, J.; Ouweland, J.v.d.; Kurstjens, S.; Bosma, M.; et al. The Dutch HbA1c Lifestyle Study (DAF-Study): Seasonal Variation of HbA1c in the Dutch Diabetes Population—Associations with Macronutrient Intake and Physical Activity. Diabetology 2025, 6, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110135
Kemna E, Bilo H, Deckers M, Slim C, Loot A, Henricks LM, Brinkman J, Ouweland Jvd, Kurstjens S, Bosma M, et al. The Dutch HbA1c Lifestyle Study (DAF-Study): Seasonal Variation of HbA1c in the Dutch Diabetes Population—Associations with Macronutrient Intake and Physical Activity. Diabetology. 2025; 6(11):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110135
Chicago/Turabian StyleKemna, Erwin, Henk Bilo, Martine Deckers, Christiaan Slim, Annemarieke Loot, Linda M. Henricks, Jacoline Brinkman, Jody van den Ouweland, Steef Kurstjens, Madeleen Bosma, and et al. 2025. "The Dutch HbA1c Lifestyle Study (DAF-Study): Seasonal Variation of HbA1c in the Dutch Diabetes Population—Associations with Macronutrient Intake and Physical Activity" Diabetology 6, no. 11: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110135
APA StyleKemna, E., Bilo, H., Deckers, M., Slim, C., Loot, A., Henricks, L. M., Brinkman, J., Ouweland, J. v. d., Kurstjens, S., Bosma, M., Vlodrop, I. v., Verschuure, P., Kooren, J., Coolen, S., Mohrmann, K., Schuijt, M., Krabbe, J., Wever, R., Oostendorp, M., ... Weykamp, C. (2025). The Dutch HbA1c Lifestyle Study (DAF-Study): Seasonal Variation of HbA1c in the Dutch Diabetes Population—Associations with Macronutrient Intake and Physical Activity. Diabetology, 6(11), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6110135







