A Soft Robot Arm with Flexible Sensors for Master–Slave Operation †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Components and Structure of a Soft Robot Arm
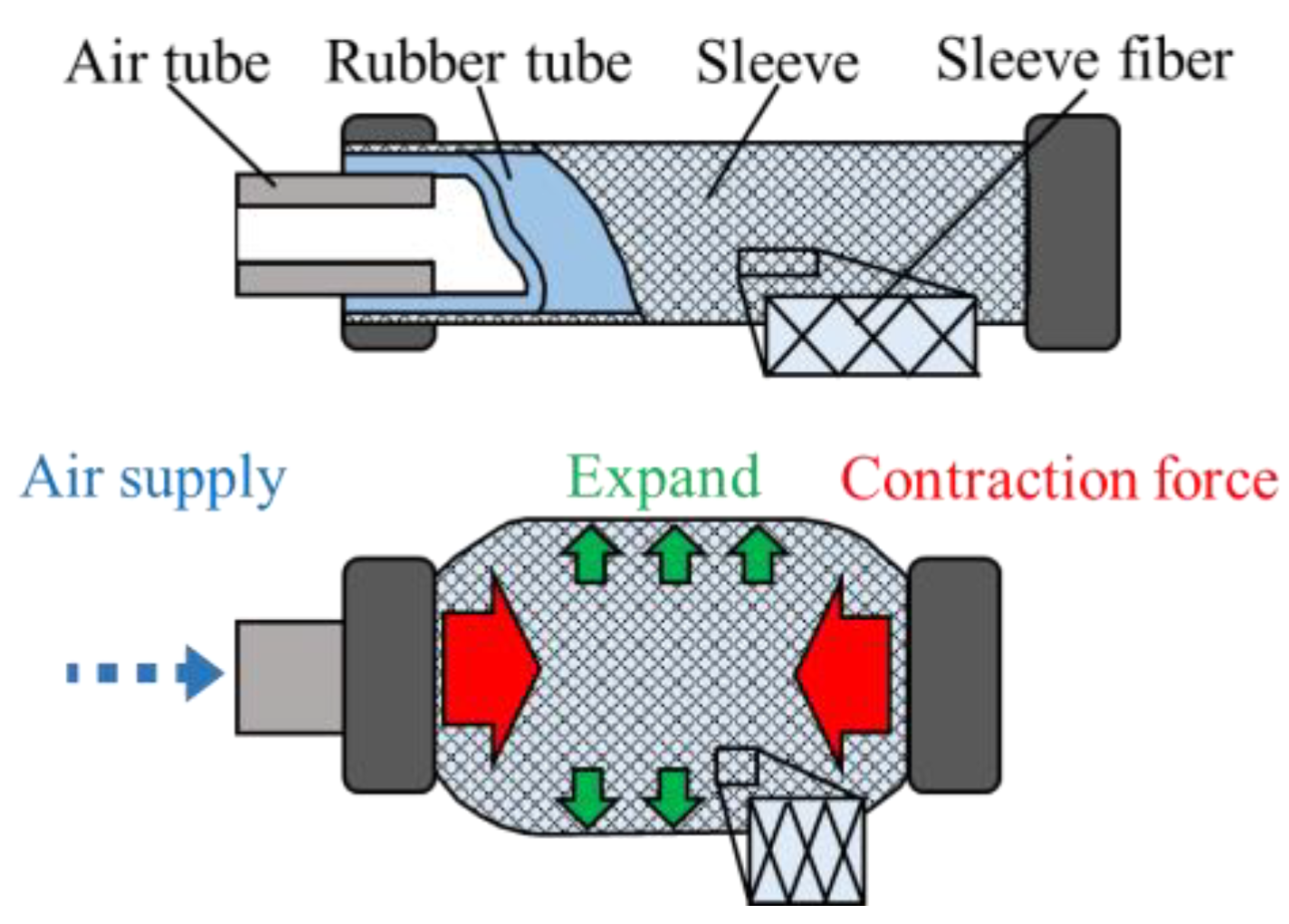
2.1.1. McKibben Artificial Muscle
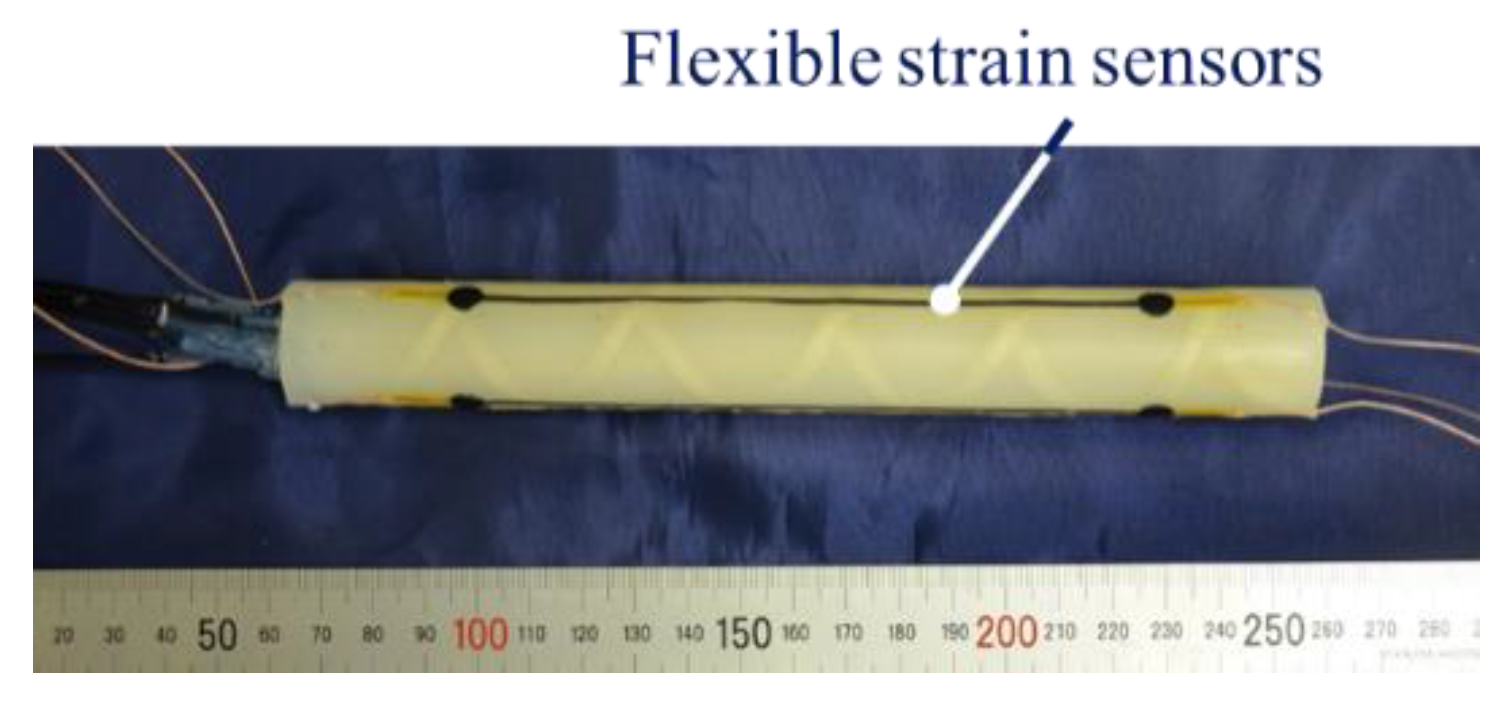
2.1.2. Flexible Strain Sensor
2.1.3. Structure of a Soft Robot Arm
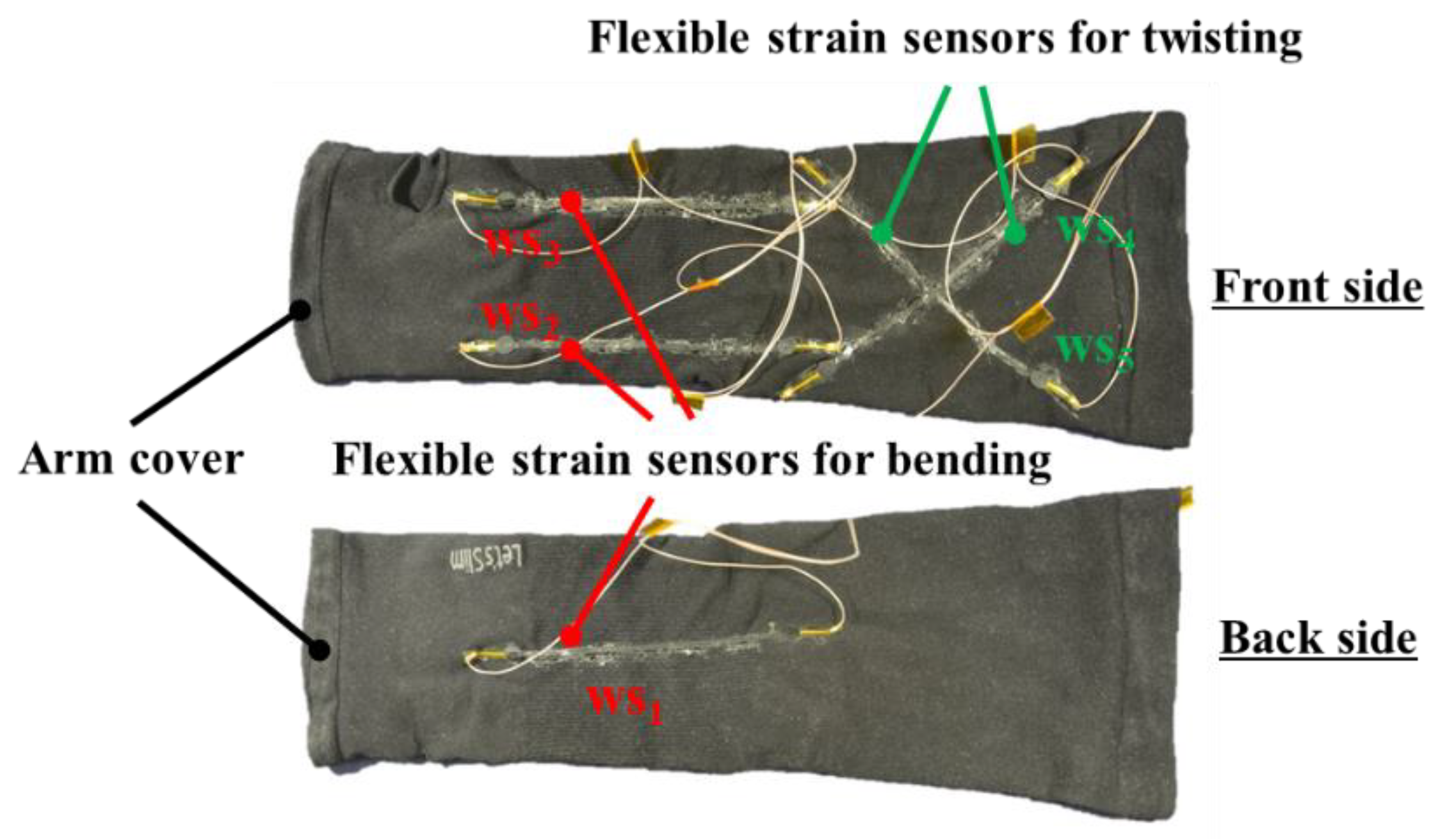
2.1.4. Mounting Flexible Strain Sensors on a Soft Robot Arm
2.2. Structure of a Wearable Interface
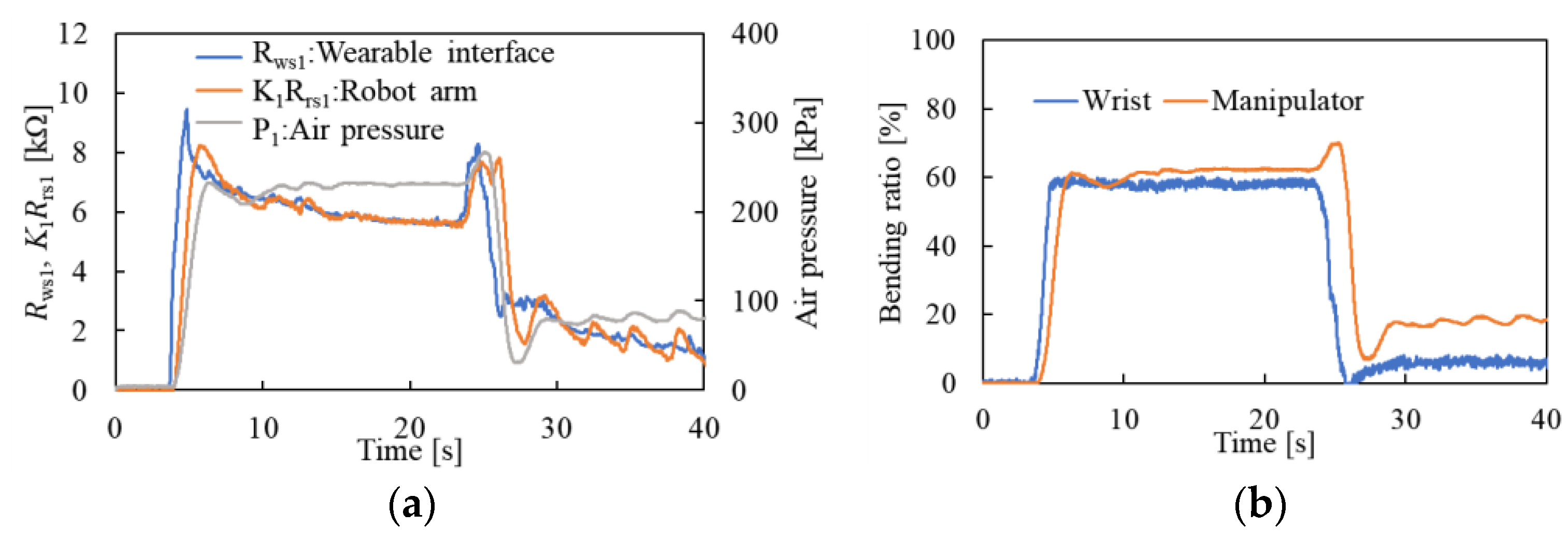
3. Experiments and Results
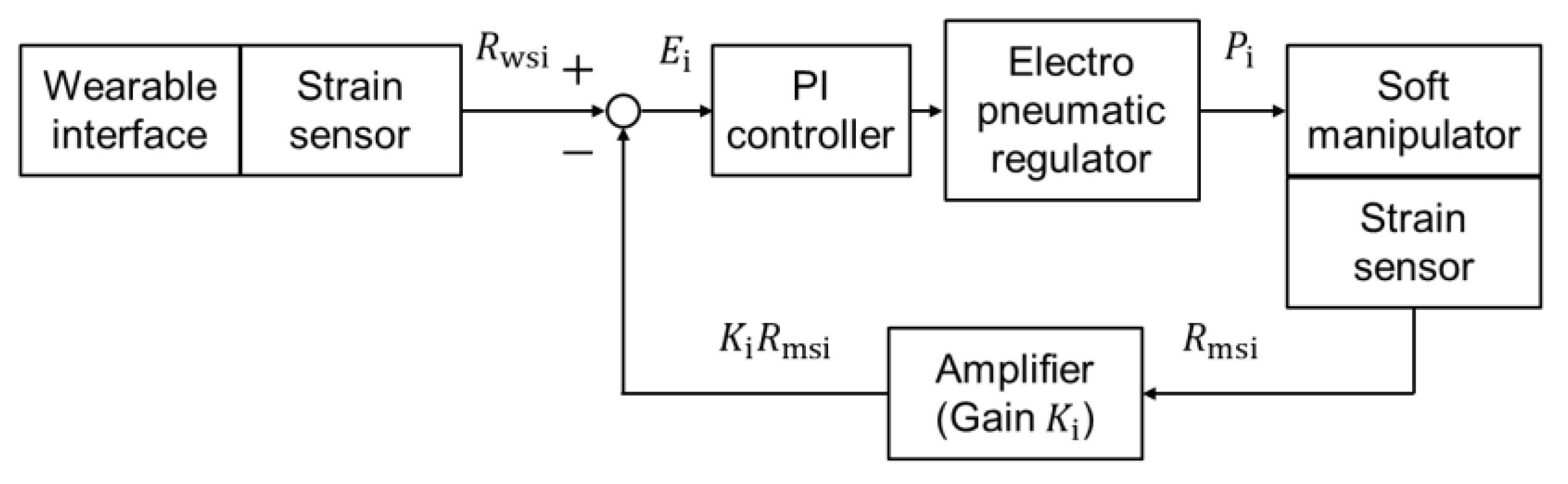
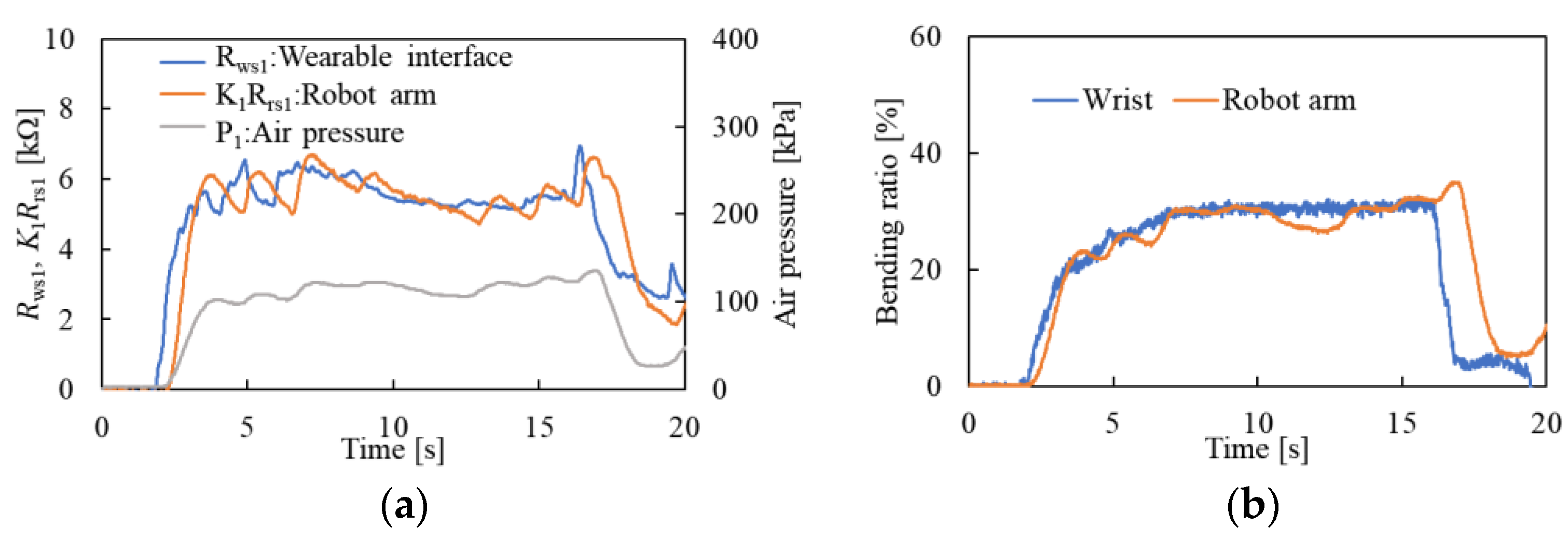
Feedback Control of Bending Motion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trivedi, D.; Dienno, D.; Rahn, C.D. Optimal, Model-Based Design of Soft Robotic Manipulators. ASME J. Mech. Des. 2008, 130, 091402-1–091402-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Follador, M.; Dario, P. Soft Robot Arm Inspired by the Octopus. Adv. Robot. 2012, 26, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramses, V.M.; Jamie, L.B.; Carina, R.F.; Lihua, J.; Robert, F.S.; Rui, M.D.N.; Zhigang, S.; George, M.W. Robotic Tentacles with Three-Dimensional Mobility Based on Flexible Elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2012, 25, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Xu, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Design and Implementation of a Soft Robotic Arm Driven by SMA Coils. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 6108–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Pfeifer, R. A cable-driven soft robot surgical system for cardiothoracic endoscopic surgery: Preclinical tests in animals. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 31, 3152–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, Y.; Manti, M.; Falotico, E.; Cianchetti, M.; Laschi, C. Multiobjective Optimization for Stiffness and Position Control in a Soft Robot Arm Module. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, H.F. The Characteristics of the McKibben Artificial Muscle. In The Application of External Power in Prosthetics and Orthotics; National Academy of Science-National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 1961; pp. 94–115. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, T.; Wakimoto, S.; Suzumori, K.; Mori, K. Proposal of Flexible robotic arm with thin McKibben actuators mimicking octopus arm structure. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aliff, M.; Dohta, S.; Akagi, T.; Li, H. Development of a simple-structured pneumatic robot arm and its control using low-cost embedded controller. Procedia Eng. 2012, 41, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, S.; Wakimoto, S.; Kanda, T.; Hagihara, H. A Soft Master-Slave Robot Mimicking Octopus Arm Structure Using Thin Artificial Muscles and Wire Encoders. Actuators 2019, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frazelle, C.G.; Kapadia, A.; Walker, I. Developing a Kinematically Similar Master Device for Extensible Continuum Robot Manipulators. ASME J. Mech. Des. 2018, 10, 025005-1–025005-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.; Son, D.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.B.; Song, J.; Choi, S.; Lee, D.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.; Hyeon, T.; et al. Transparent and Stretchable Interactive Human Machine Interface Based on Patterned Graphene Heterostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 25, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, H.; Wakimoto, S.; Kanda, T.; Furukawa, S. Operation of a pneumatic soft manipulator using a wearable interface with flexible strain sensors. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019. [Google Scholar]





| Robot arm | Overall length [mm] | 190 |
| Outer diameter [mm] | 22 | |
| Artificial muscles in the axial direction | Length [mm] | 180 |
| Outer diameter [mm] | 5.5 | |
| Artificial muscles in the clockwise and counterclockwise directions | Length [mm] | 350 |
| Outer diameter [mm] | 2.5 | |
| Number of rolls [times] | 5 | |
| Rubber material | Hardness | 30 (durometer OO) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamamoto, Y.; Wakimoto, S.; Kanda, T.; Yamaguchi, D. A Soft Robot Arm with Flexible Sensors for Master–Slave Operation. Eng. Proc. 2021, 10, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-8-11311
Yamamoto Y, Wakimoto S, Kanda T, Yamaguchi D. A Soft Robot Arm with Flexible Sensors for Master–Slave Operation. Engineering Proceedings. 2021; 10(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-8-11311
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamamoto, Yoshie, Shuichi Wakimoto, Takefumi Kanda, and Daisuke Yamaguchi. 2021. "A Soft Robot Arm with Flexible Sensors for Master–Slave Operation" Engineering Proceedings 10, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-8-11311
APA StyleYamamoto, Y., Wakimoto, S., Kanda, T., & Yamaguchi, D. (2021). A Soft Robot Arm with Flexible Sensors for Master–Slave Operation. Engineering Proceedings, 10(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-8-11311






