Abstract
The ongoing coronavirus and its variants are alarming the world inadequately. Extreme reciprocal pneumonia is the primary element of serious COVID-19, and sufficient ventilator help is vital for patient endurance. Supplemental oxygen is the first fundamental stage for the cure of serious COVID-19 patients with hypoxemia. In this regard, oxygen concentrators can be used for patients of COVID-19 to supply oxygen. This paper primarily focuses on designing a portable medical device oxygen concentrator using the technology pressure swing adsorption (PSA), which takes air from the atmosphere, adsorbs nitrogen, and supplies oxygen. A detailed study with the simulation has been done to benchmark the outcome of LiX, LiLSX, and 5A zeolite as adsorbents. Results show LiX is the most suitable with better nitrogen to oxygen selectivity ratio with a flow rate of 5LPM.
1. Introduction
There is a huge interest in a versatile oxygen supply for individual use by individuals requiring oxygen treatment. Medical conditions in humans, for example, diseases, such as COPD, significantly reduce the lung’s capacity to oxygenate the blood, making the supply of heavily oxygenated air to the lungs that are employing external mechanisms very crucial [1]. In the study [2], 80% or more of the concentration of oxygen can be achieved and maintained with flowrate ranges from 2 to 5 L per min.
In past, the O2 concentrator utilizing the PSA technique holds a significant share in clinical application, since it is low cost and environment friendly [3]. Work in [2] developed a PSA-based oxygen concentrator to facilitate oxygen production in remote areas. On the other hand, PSA units have a crucial importance in industrial activities as well [3].
It contains four stages of cycle pressurization, adsorption, blow down, purge. Each stage requires specific pressure to complete the stage and proceed to the next stage of the cycle, as the incompletion of any stage will affect oxygen production and its purity level. Zeolites tend to adsorb twice as much N2 as O2 due to the interlinkage of cations of Zeolite molecules and the quadrupole moment of N2 [4].
This paper is arranged as follows: Section 2 talks about the four stages of the pressure swing adsorption (PSA) cycle, along with the comparative study of zeolites and the schematic design of 3/2 pressure pneumatic valves. Section 3 provides comparative graphical results of all three adsorbents. Section 4 provides the conclusion and future direction of research.
2. Proposed Method and Literature Review
2.1. Literature Review of Effects of Different Zeolites on PSA
Zeolites are a group of crystalline materials that are made of evenly sized pores and a tunnel system. It is an efficient adsorbent for many non-volatile (organic) compounds since it can withstand higher temperatures and regenerate completely after adsorption [5]. From the study of 4 zeolites-based PSA systems, we found the following trends in their parameters such as cycle type, cycle duration, operating pressure, purity, and flow rate as shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Literature study on Zeolite for Medical Oxygen Concentrators.
2.2. Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) Technology and Cycle Description
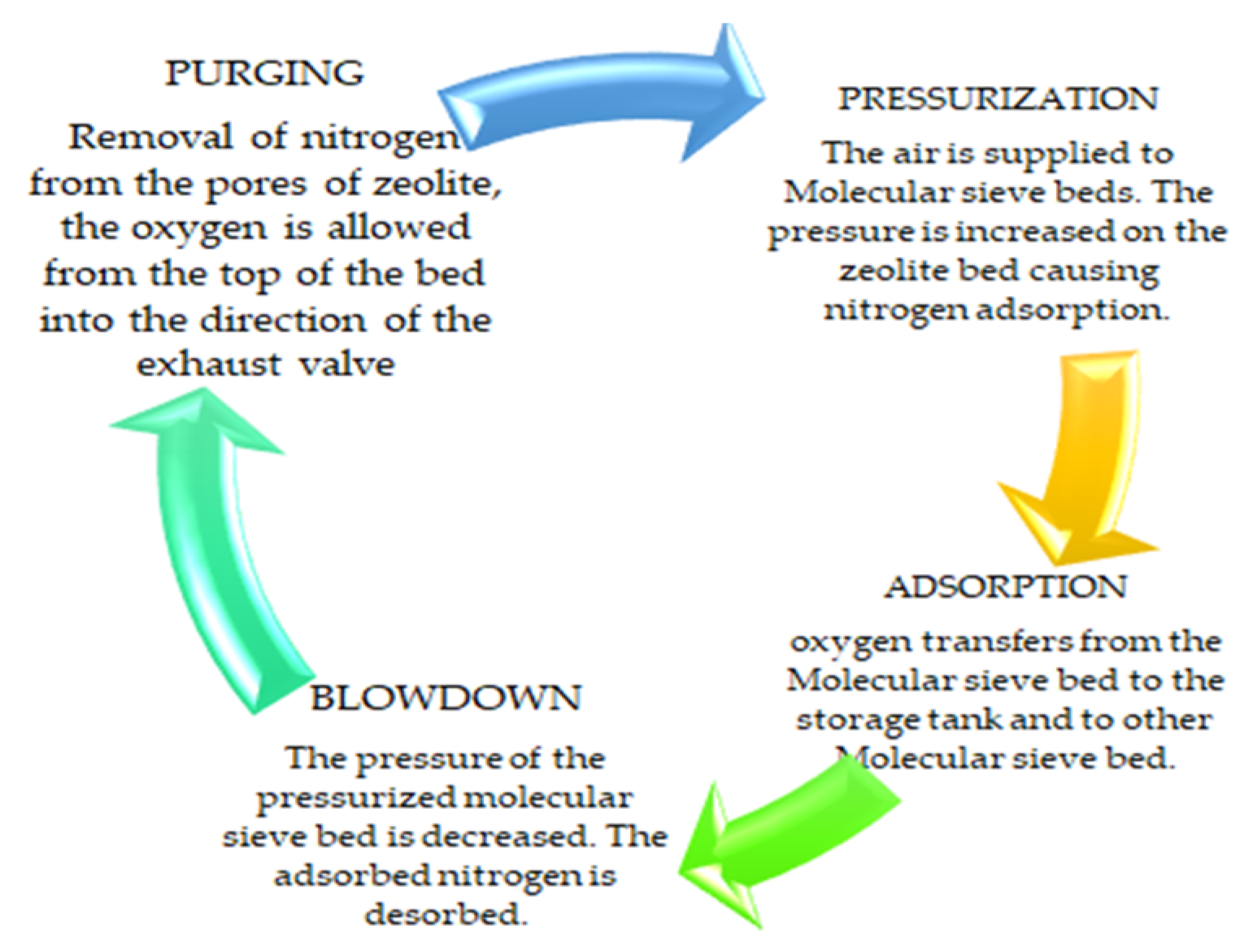
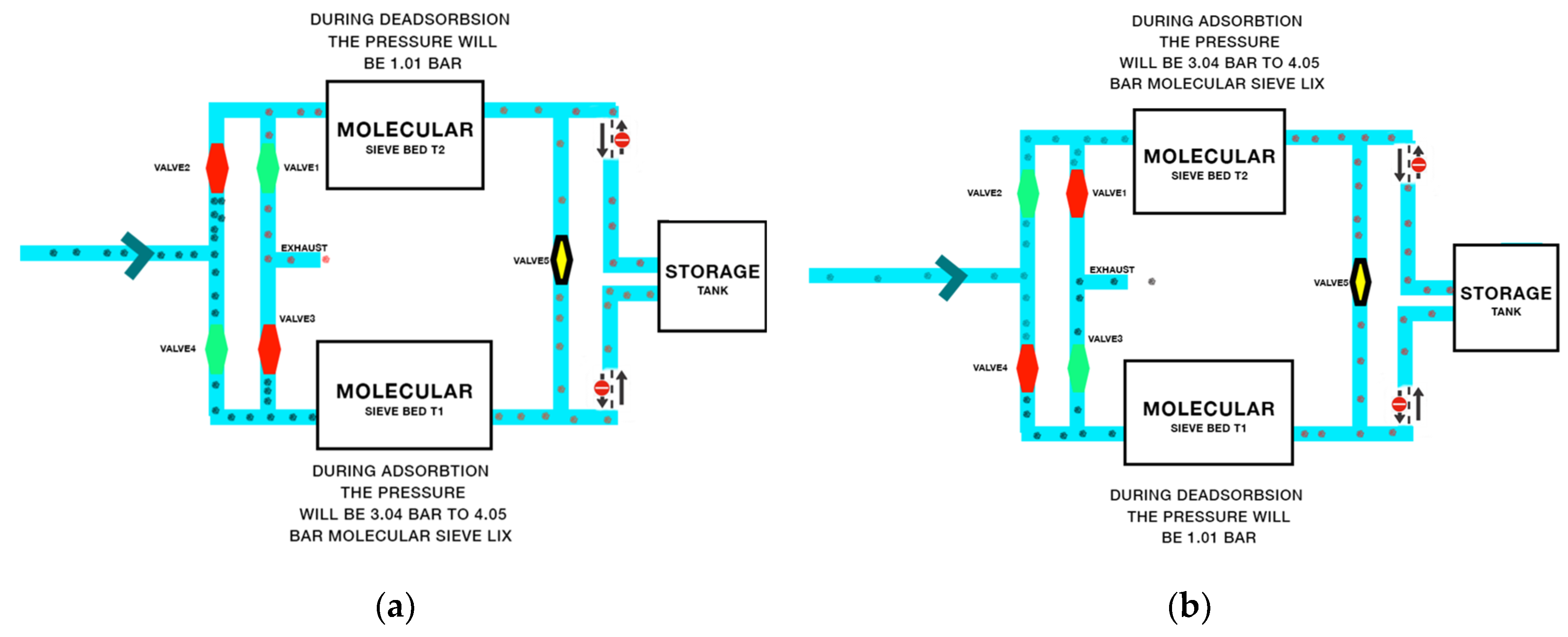
PSA technology is used to separate the mixture of gas species under pressure, according to their molecular structure and the properties and affinity of the adsorbent. This process works around an ambient range of temperatures [10]. Compared to other methods, PSA is more effective due to controlled temperature [11]. It requires four stages of pressurization, adsorption, blowdown, and purging, as shown in Figure 1. Each stage requires specific pressure to complete the stage, as the incompletion of any stage will affect oxygen production and its purity level. The further procedure of the design by controlling 3/2-way valves is shown in Figure 2.
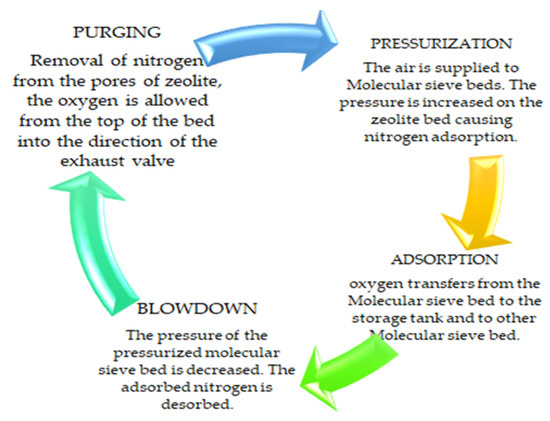
Figure 1.
Four stages of the pressure swing adsorption cycle (PSA).
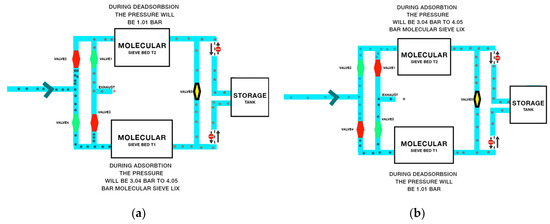
Figure 2.
Control of PSA cycle using 3/2-way valves (a) Pressurization and adsorption in molecular sieve bed T1 and desorption and purging in molecular sieve bed T2. (b) Pressurization and adsorption of molecular sieve bed T2 and desorption and purging of molecular sieve bed T1.
2.3. Operation of Solenoid Valve
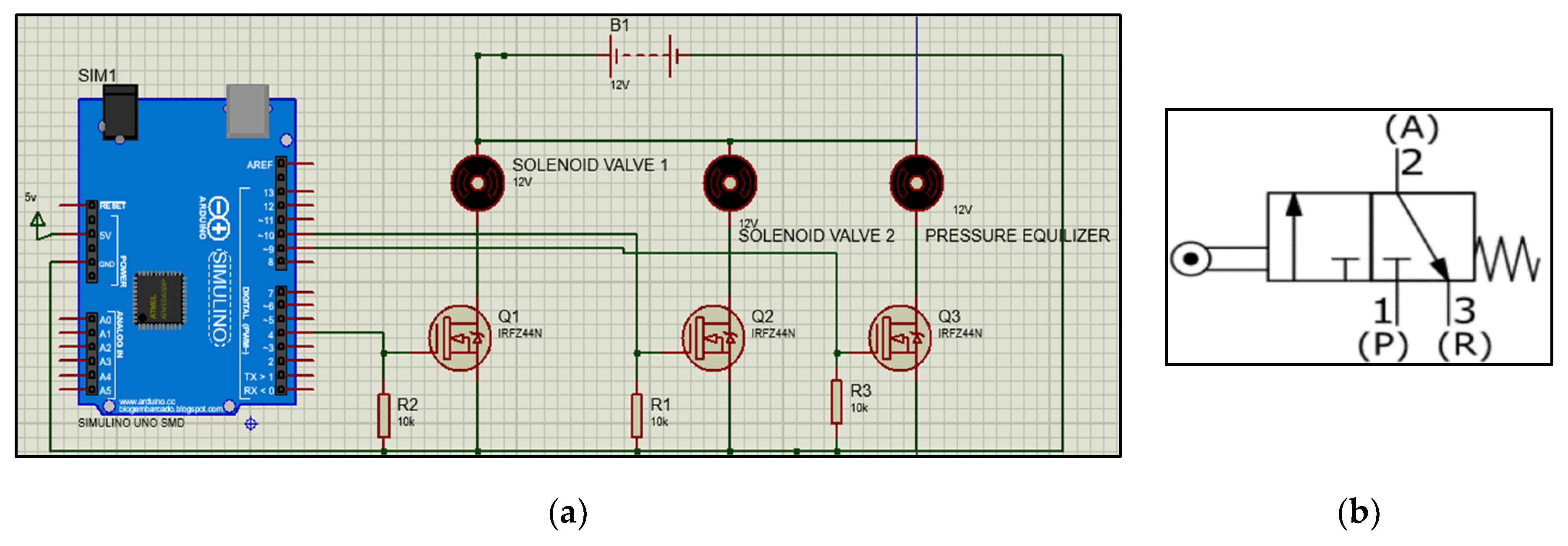
A solenoid valve is a valve that utilizes electromagnetic power to work [12]. A 3/2-way NC solenoid valve has been used. It has three ports and two states that can be driven electrically and also manually. It has 3 ports, inlet (P), outlet (A), and exhaust (R). When the supply is not connected then outlet port (A) is connected with exhaust port (R) that is normally closed condition, and when the supply of 10.8–13.2 VDC is provided, it changes its state from normally closed to open condition, hence air moves from inlet (P) port to outlet (A) port [13].
A simple circuit for controlling two 3/2-way valves and pressure equalizer for four cycles of PSA, i.e., pressurization, adsorption, purging, and de-adsorption is made using Arduino UNO microcontroller and IRFZ44N N-channel MOSFET. IRFZ44N is N-channel type MOSFET as shown in Figure 3. It processes high-speed switching capabilities with a very low on-state resistor, which makes it ideal to use in applications where high-speed switching is the essential requirement.
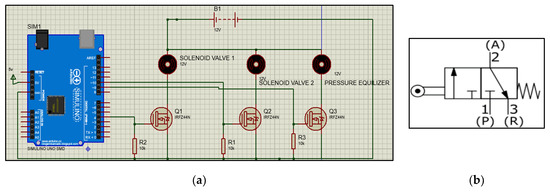
Figure 3.
This is a Schematic of 3/2 NC solenoid valves (a) showing switching of valves along with pressure equalizer (b) Working of normally closed 3/2-way valve circuit.
3. Results and Discussion
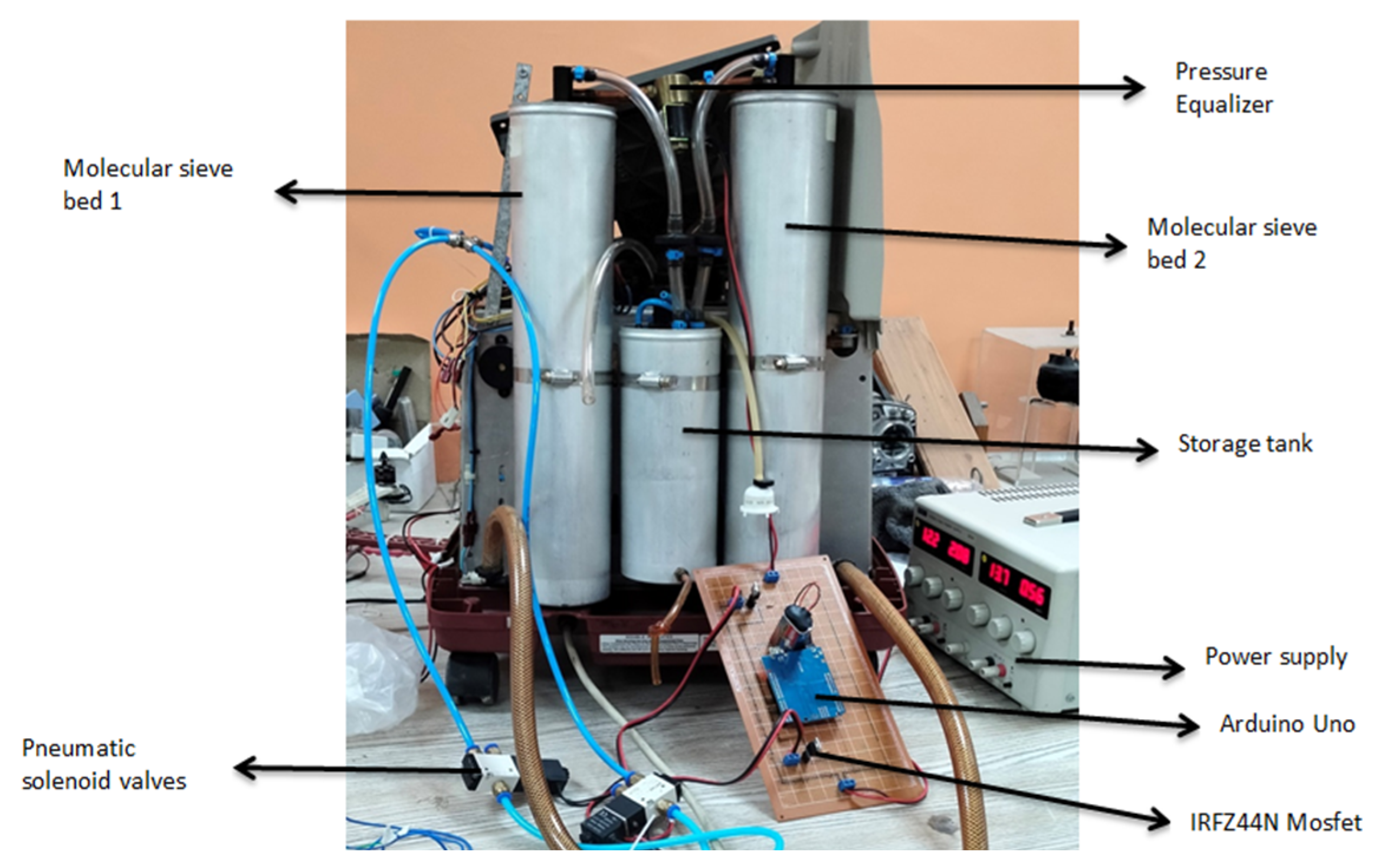
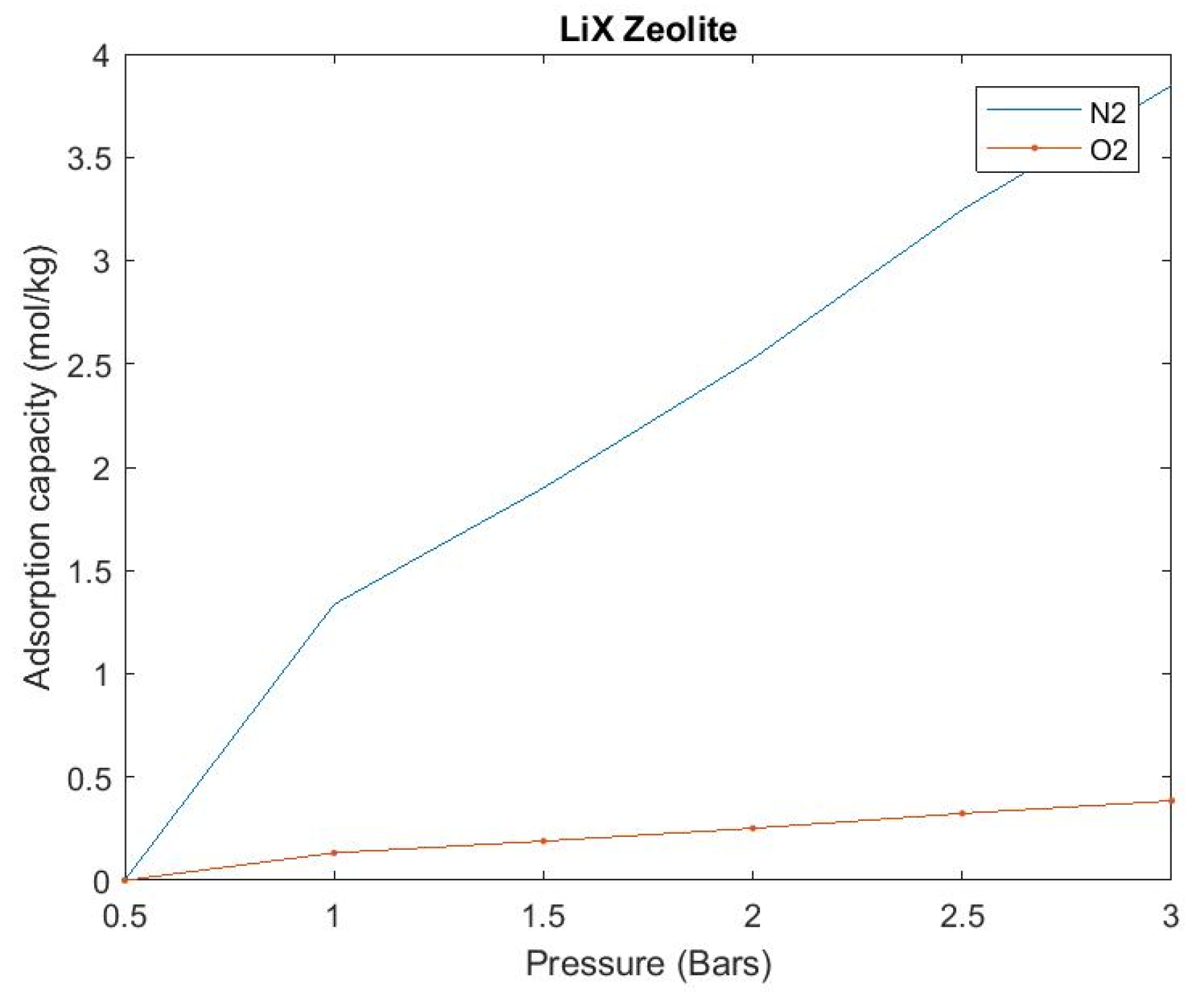
In order to check the validity of our zeolite which is LiX we performed the following experiment using the setup shown in Figure 4. We took 2.4 Kg of LiX zeolite and sealed the containers with proper airtight caps along with a filter and cotton inside the container. Then we pressurized the sieve bed through the compressor and set down the variable pressure inside the cylinder through a pressure regulator, from the oxygen sensor placed at the outlet of the sieve bed. We received a percentage of oxygen at different levels of pressure. We also kept a weighting machine beneath the sieve bed to measure the mass of the sieve bed at different pressure. The detailed experimental data and results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 5.
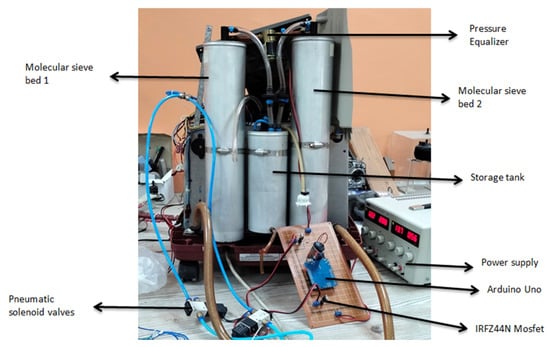
Figure 4.
Prototype of the oxygen concentrator.

Table 2.
Experimental results of LiX zeolite from the Proposed System.
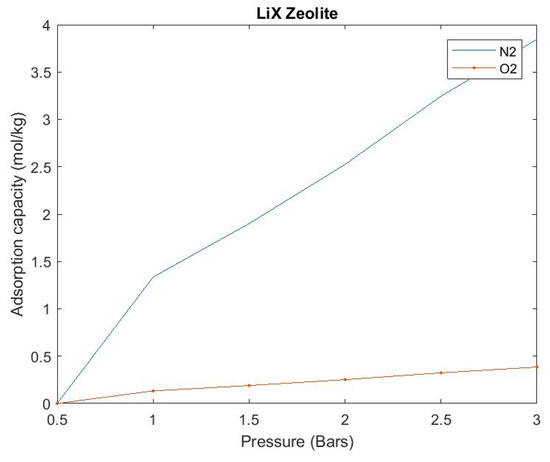
Figure 5.
Experimental results of equilibrium adsorption capacity of LiX zeolite.
4. Conclusions
This paper discusses the four-stage pressure swing adsorption cycle to extract a high level of filtered oxygen from the atmosphere. The presented schematic design of the 3/2 pressure numeric valve allows the pressure to swing between the two beds of adsorbent zeolite. The paper also presented a comparison of the zeolite Li-X, zeolite Lil-SX, and zeolite 5A and Oxysiv 5,7 & Sylobead MS s 624 and concluded zeolite Li-X to be the most effective adsorbent. The future direction of the research will be focused on (1) the implementation of an auto-flow mechanism in the hardware that will check the blood oxygen level of the patients to set oxygen concentrator parameters. (2) More experimentation will be done, similar to work reported in [14], on a wider range of pressure for LiX zeolite to further enhance the validity of our design.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.U.; Methodology, A.S.; software, M.I. and E.K.; validation, A.S. and M.S.; investigation, A.S. and A.H.A.; writing—original draft preparation, M.I.; writing—review and editing, A.H.A. and H.K.; supervision, R.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan under grant titled “Establishment of National Centre of Robotic and Automation (DF-1009-31)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to acknowledge Ayaz Shirazi of the Haptic, Human Robotics, and condition Monitoring Lab for his insights.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rao, V.R.; Farooq, S.; Krantz, W.B. Design of a Two-Step Pulsed Pressure-Swing Adsorption-Based Oxygen Concentrator. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, A.; Litch, M.D. Oxygen concentrators for the delivery of.supplemental oxygen in remote high-altitude areas. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2000, 11, 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, V. Linde AG; Spring Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, H. Oxygen and Nitrogen Separation from Air Using Zeolite Type 5A. Al-Qadisiyah J. Eng. Sci. 2015, 8, 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- ZEOTECH. Available online: https://www.zeotech.se/ (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Kopaygorodsky, E.; Guliants, V.; Krantz, W. Predictive dynamic model of single-stage ultra-rapid pressure swing adsorption. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Portugal, A.; Magalhaes, F.; Mendes, A. Simulation and optimization of small oxygen pressure swing adsorption units. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 8328–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.R.; Kothare, M.V.; Sircar, S. Novel design and performance of a medical oxygen concentrator using a rapid pressure swing adsorption concept. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, S.W.; Kothare, M.V.; Sircar, S. Rapid pressure swing adsorption for reduction of bed size factor of a medical oxygen concentrator. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 8703–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokroo, E.J.; Farsani, D.J.; Meymandi, H.K.; Yadollahi, N. Comparative study of zeolite 5A and zeolite 13X in air separation by pressure swing adsorption. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZEOCHEM. Available online: https://www.zeochem.com/news/psa-vs-tsa-whats-the-difference (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- NORGEN. Available online: https://www.norgren.com/my/en/expertise/industrial-automation/what-is-a-pneumatic-solenoid-valve (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- TAMESON. Available online: https://tameson.com/32-way-pneumatic-valve.html#:~:text=A%203%2F2%2Dway%20valve,electrically%20via%20a%20solenoid%20valve.&text=A%20valve%20is%20used%20to,working%20stroke%20can%20be%20realized (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Rege, S.U.; Yang, R.T. Limits for air separation by adsorption with LiX zeolite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1997, 36, 5358–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).