Understanding the Behavior of Gas Sensors Using Explainable AI †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Results
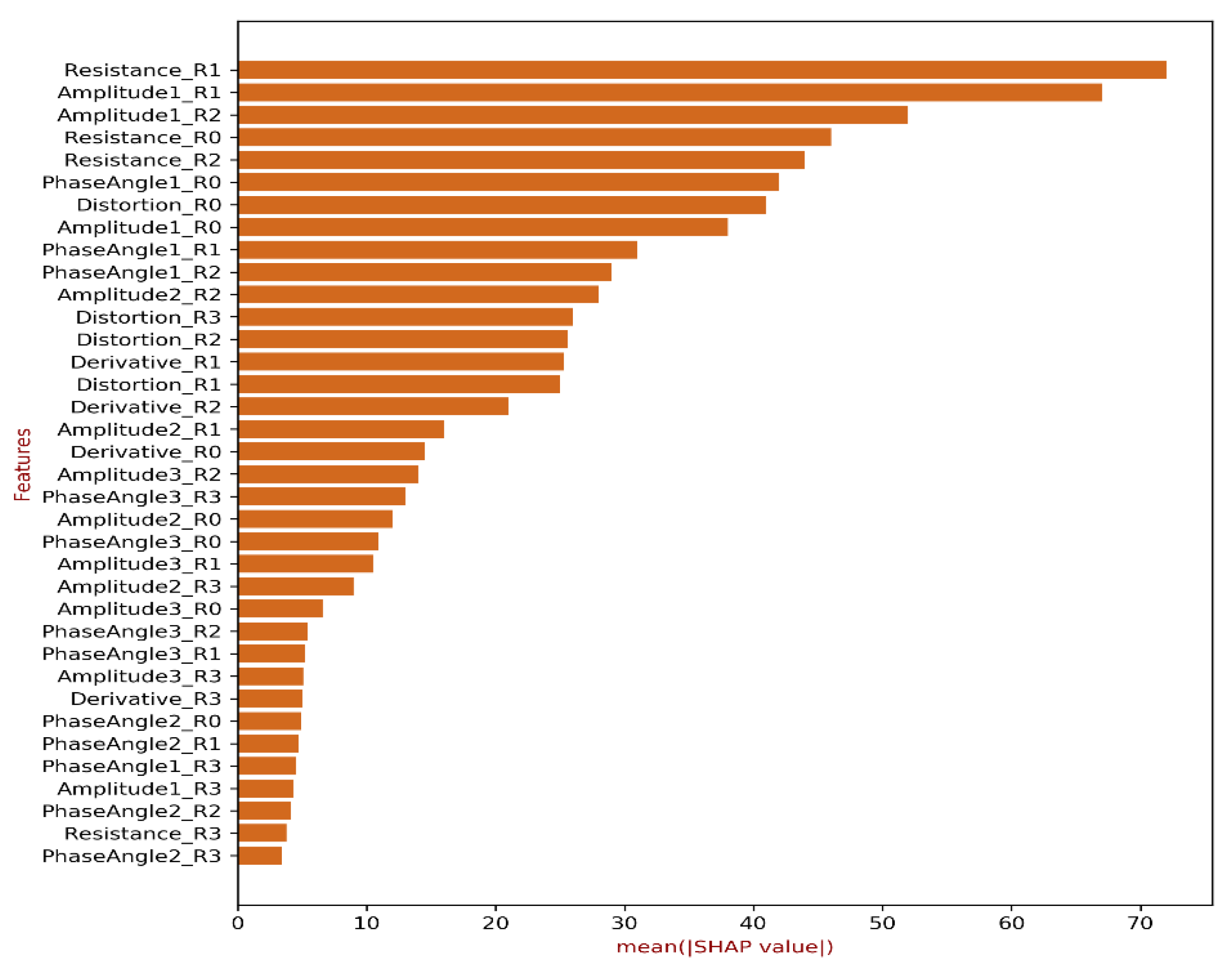
2.1. SHAP Method
2.2. Results for SHAP Analysis
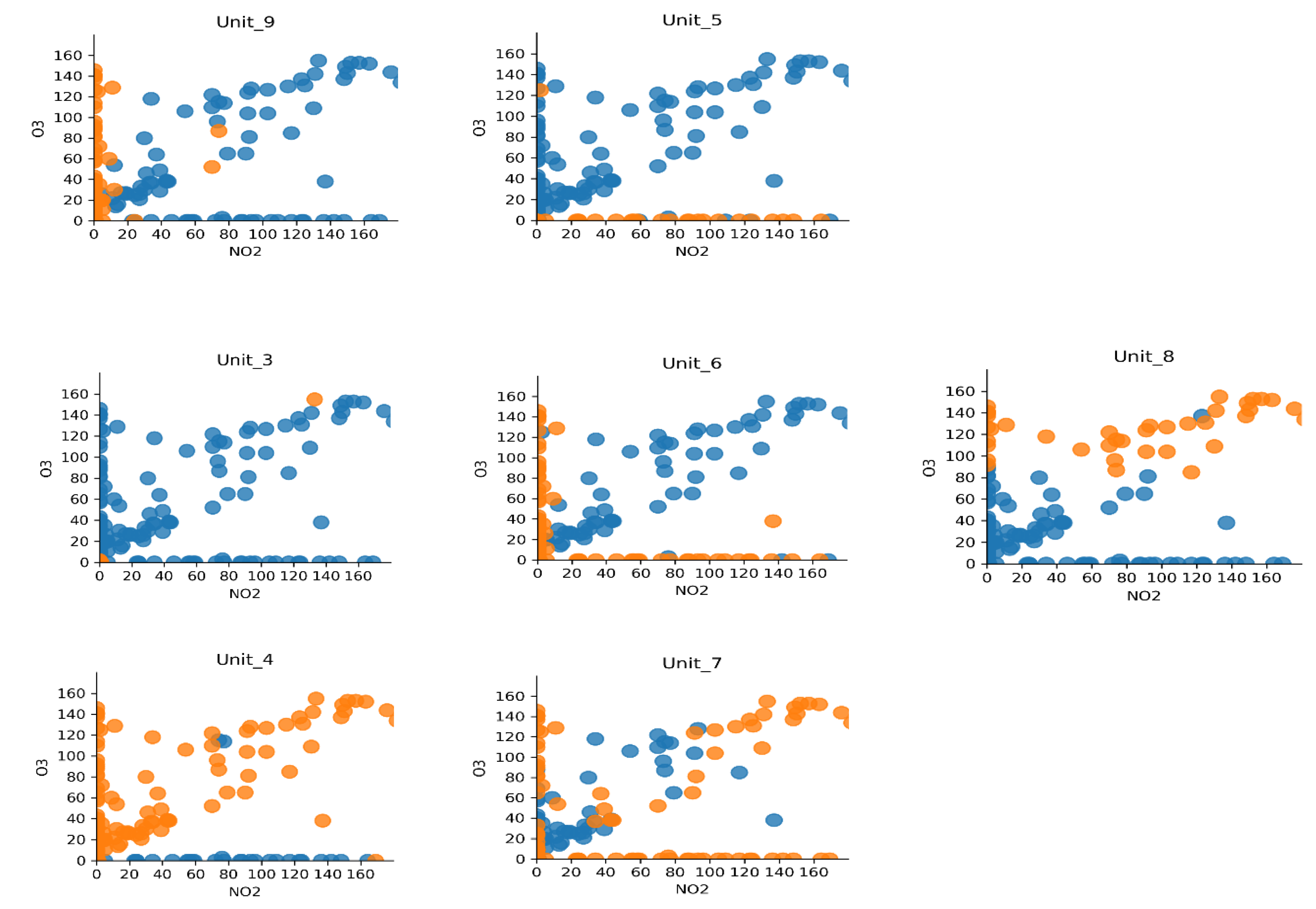
2.3. Network Dissection
2.4. Results for Network Dissection
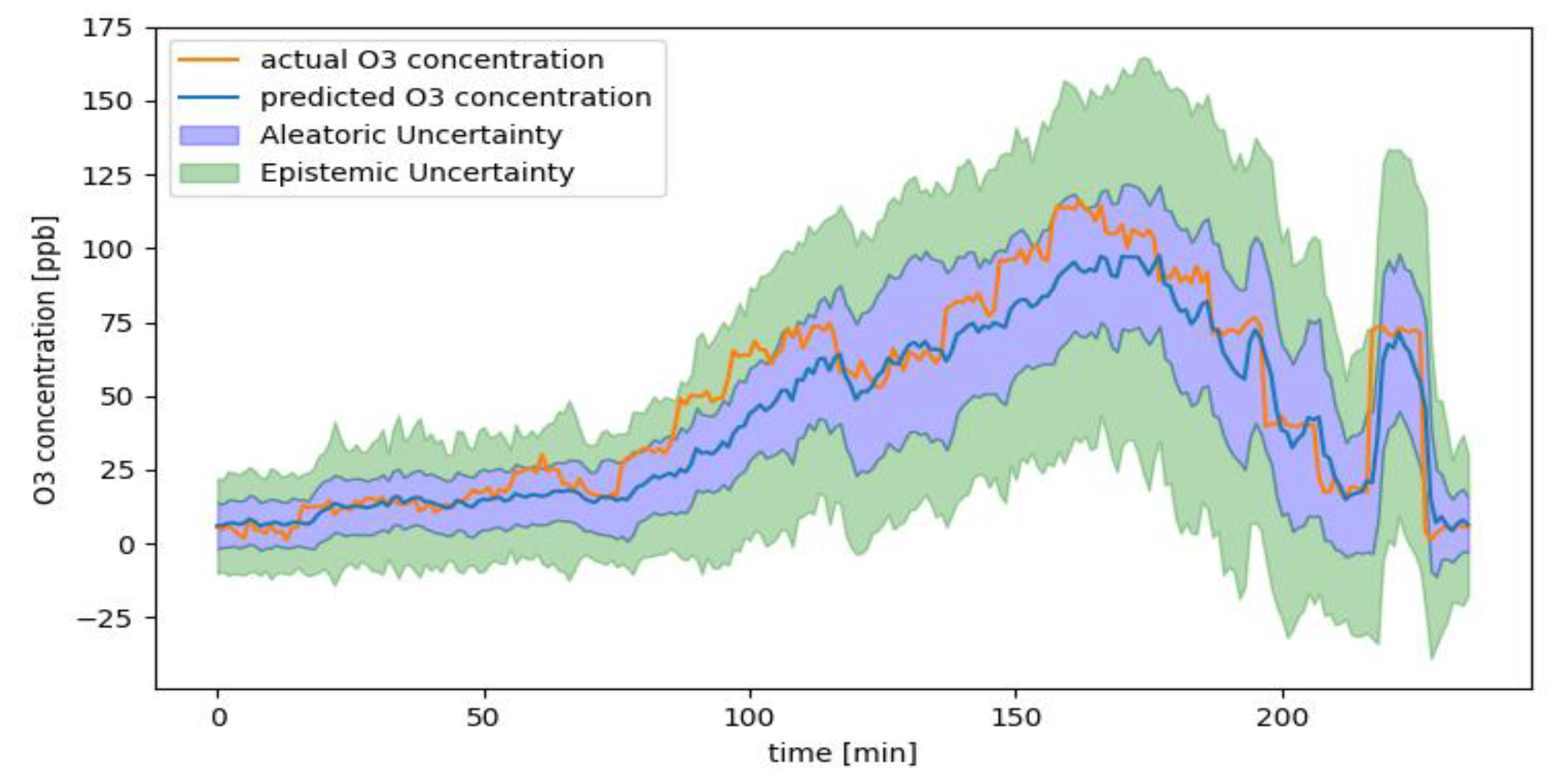
2.5. Bayesian Deep Learning
2.6. Results for Bayesian Deep Learning
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zöpfl, A.; Lemberger, M.M.; König, M.; Ruhl, G.; Matysik, F.M.; Hirsch, T. Reduced graphene oxide and graphene composite materials for improved gas sensing at low temperature. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 173, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayasaka, T.; Lin, A.; Copa, V.C.; Lopez, L.P.; Loberternos, R.A.; Ballesteros, L.I.; Kubota, Y.; Liu, Y.; Salvador, A.A.; Lin, L. An electronic nose using a single graphene FET and machine learning for water, methanol, and ethanol. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Bahdanau, D.; Bengio, Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. In Proceedings of the SSST-8, Eighth Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation, Doha, Qatar, 25 October 2014; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch, W.J.; Singh, C.; Kumbier, K.; Abbasi-Asl, R.; Yu, B. Definitions, methods, and applications in interpretable machine learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22071–22080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi-Velez, F.; Kim, B. Towards a rigorous science of interpretable machine learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.08608. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, Z.C. The mythos of model interpretability: In machine learning, the concept of interpretability is both important and slippery. Queue 2018, 16, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, A.; Kampik, T.; Pannu, H.; Madhikermi, M.; Främling, K. Explaining machine learning-based classifications of in-vivo gastral images. In Proceedings of the 2019 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Perth, WA, Australia, 2–4 December 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 4768–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Psychoula, I.; Gutmann, A.; Mainali, P.; Lee, S.H.; Dunphy, P.; Petitcolas, F. Explainable machine learning for fraud detection. Computer 2021, 54, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, D.; Naik, H.; Singhal, S.; Patel, P. Explainable ai meets healthcare: A study on heart disease dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.03195. [Google Scholar]
- Karpathy, A.; Johnson, J.; Fei-Fei, L. Visualizing and understanding recurrent networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.02078. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, S. Memory visualization for gated recurrent neural networks in speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2017; pp. 2736–2740. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What uncertainties do we need in bayesian deep learning for computer vision? In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5580–5590. [Google Scholar]
- Shapley, L. 7. A Value for n-Person Games. Contributions to the Theory of Games II (1953) 307–317. In Classics in Game Theory; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Molnar, C. Interpretable Machine Learning. A Guide for Making Black Box Models Explainable. Available online: https://originalstatic.aminer.cn/misc/pdf/Molnar-interpretable-machine-learning_compressed.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Vergara, A.; Martinelli, E.; Llobet, E.; D’Amico, A.; Di Natale, C. Optimized feature extraction for temperature-modulated gas sensors. J. Sens. 2009, 2009, 716316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembhurne, J.V.; Diwan, T. Sentiment analysis in textual, visual and multimodal inputs using recurrent neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 6871–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, Y.; Ghahramani, Z. Dropout as a bayesian approximation: Representing model uncertainty in deep learning. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 1050–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, N.; Hinton, G.; Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Salakhutdinov, R. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2014, 15, 1929–1958. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakraborty, S.; Mittermaier, S.; Carbonelli, C. Understanding the Behavior of Gas Sensors Using Explainable AI. Eng. Proc. 2022, 27, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13350
Chakraborty S, Mittermaier S, Carbonelli C. Understanding the Behavior of Gas Sensors Using Explainable AI. Engineering Proceedings. 2022; 27(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13350
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakraborty, Sanghamitra, Simon Mittermaier, and Cecilia Carbonelli. 2022. "Understanding the Behavior of Gas Sensors Using Explainable AI" Engineering Proceedings 27, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13350
APA StyleChakraborty, S., Mittermaier, S., & Carbonelli, C. (2022). Understanding the Behavior of Gas Sensors Using Explainable AI. Engineering Proceedings, 27(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsa-9-13350




