Abstract
The energy demand in Pakistan is escalating owing to the growing population, rapid urbanization, and industrial growth. Therefore, the development and execution of Energy Efficiency and Conservation (EE&C) policies and initiatives are critical for the Government in order to enhance energy efficiency and to address the country’s increasing energy demand. In this study, the Low Emission Analysis Platform (LEAP) tool is used to develop and analyze the effects of load control, energy efficiency, and conservation-based measures. Based on the policy analysis and energy consumption patterns, macro-economic modeling has been undertaken using LEAP for the study period 2020–2050. The two scenarios developed are Business-As-Usual (BAU) and Demand-Side-Management (DSM). The model results forecast 1910.2 TWh electricity demand by 2050 under the BAU scenario, with an average annual growth rate of 5.5%, which is eighteen times greater than energy demand in the base year. The sustainable electricity generation path followed under the DSM scenario ensures a lower demand of 1597.5 TWh and an average annual growth rate of 4.5%. This scenario will reduce energy use by 16% compared to the BAU scenario. Therefore, it is proposed that policy may be envisaged using infrastructural and consumer engagement approaches to encourage DSM development in Pakistan. The proposed LEAP model can be used to undertake the supply policy selection and demand assumption for future power production in Pakistan.
1. Introduction
Having access to reliable and efficient energy sources is essential for economic development and progression in every sector. Every country endeavors to develop an energy supply model that can support positive growth at all levels. Given the current environmental scenario, energy sources are required to be sustainable with less or at least a balanced effect on the environment. Pakistan is also moving towards environmental sustainability in line with its National Development Agenda. However, Pakistan’s energy sector has limited access to sustainable energy and heavily relies on traditional oil and gas sources. The country has already seen a boom in energy demand. The economic growth in recent years has translated to increasing demand. In these conditions, the country needs to revisit its existing energy supply system and develop an efficient model to meet the demand. For an early solution, demand side management will play a vital role in balancing the country’s increasing energy demand.
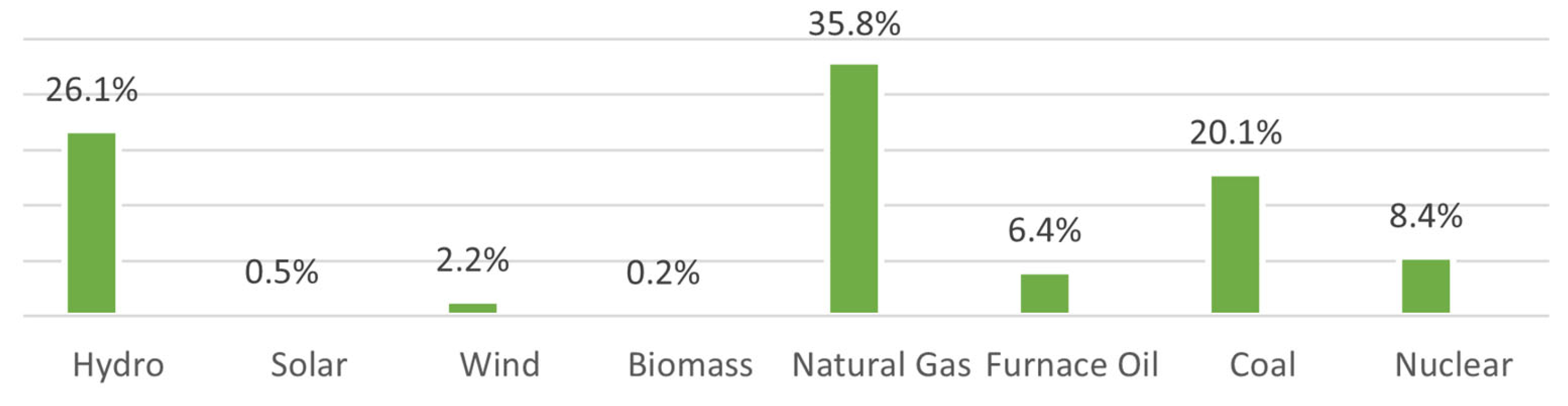
Currently, Pakistan’s total power generation capacity is coming from various energy resources. The energy mix, as shown in Figure 1, comprises natural gas 35.8%, hydroelectric 26.1%, bituminous coal 20.1%, furnace oil 6.4%, nuclear power 8.4%, wind power 2.2%, and solar PV 0.5%, respectively [1]. As per the Economic Survey 2020–21, Pakistan’s installed capacity to generate electricity increased to 37,261 MW by July 2020 from 22,812 MW in June 2013 [2]. Pakistan is still facing an energy crisis, even though it has a power generation capacity that is larger than the demand capacity of power. According to the Pakistan Economic Survey 2019–20, the installed power generation capacity in 2020 was 37,402 MW. The greatest total demand from domestic and industrial estates was nearly 25,000 MW, whereas the transmission and distribution capacity was roughly 22,000 MW. When demand is at its highest, this results in a 3000 MW deficit. Even though the country’s peak demand is significantly below its installed capacity of 37,402 MW, the additional 3000 MW required cannot be supplied to consumers.
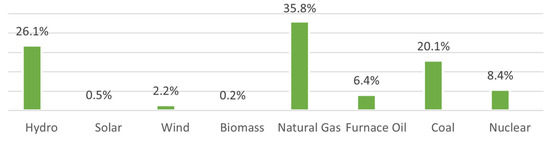
Figure 1.
Fuel used for energy generation.
It is examined that any utility across the world, including in Pakistan, does not wish to overspend large sums to enhance transmission and distribution capacity or add up costly generation resources to meet a manageable demand. Over the years, the day-to-day electricity consumption has been increasing, given the excess usage of cooling and heating systems and other appliances. The newly developing trend of electric vehicles is also adding to this increasing demand. Within the next 10 to 15 years, the demand will be quadrupled. In this regard, it is quite important for our ambitious electricity consumption plan that we optimize our demand before developing our systems [2,3].
The Demand Side Management (DSM) program is one of the foremost solutions to be implemented. It consists of prescribed rules through which consumers transfer their loads from peak hours to off-peak hours to meet their needs and enhance power system efficiency [4].
Electricity Demand Side Management (DSM) is one of the most cost-effective and durable solutions to decrease power consumption and is most significant when available capacity is short and fuel cost is high. This program has become a vital element in utility planning to reduce the demand at the consumer level without minimizing or maximizing the level of output and the consumer’s comfort. By implementing DSM programs, the demand on power stations can be reduced; consequently, the construction of new facilities can be deferred, and a substantial saving in capital expenditure can be achieved, resulting in lowering the cost of supplying electricity to consumers. This can be achieved through two principles of DSM: load shifting and efficient energy conservation response. These two techniques will make a power system more reliable and stable and will equalize supply–demand load requirements.
Demand Side Management (DSM) in the power distribution system started in the 1970s; DSM came under the study of the world in 1973. Due to an oil embargo by oil-producing countries, it was necessary to decrease oil utilization to meet the power demand of consumers. Then, it was decided to introduce a technique, program, or subject that would cover all these problems with future energy management after having banned the exportation of oil [5]. It is important to mention the name of the guide written by Barney LB Capehart and Wayne C. Tuner, “Energy Management”, as it is most-informative literature that covers all areas of energy management [5]. There is other literature that is written about developed energy-efficient programs, including Energy Efficiency Demand Response and Energy Utilization. All these programs have been applied in different leading countries to stabilize their power sectors. These strategies can also be adopted to enhance the efficiency of the Pakistan power system [6]. As we are all aware, consumers do not all have the same connected load. They also have different loads and switch the times of operation. Accidentally, this may result in a load on the Power System that is less at a particular time than the generated capacity, and sometimes it may be higher than the generated capacity. This will lead to a Power System in low- or high-power factor operation. To avoid these issues, some techniques are described to convert the irregular shape of the load curve into a flat line so that the Power System will operate smoothly on the rated power factor [7].
1.1. Problem Statement
The Pakistan population is growing rapidly, and so is electric power demand. Pakistan’s future energy needs would be met by developing new power infrastructures. However, Pakistan is a developing country, and as such, it does not have the economic strength to achieve this goal. As a result, to overcome the supply and demand gap, the country should develop significant energy conservation and management programs (DSM) across energy sectors.
1.2. Aim and Objectives
Due to increasing consumer demand for power, sometimes insufficient power is generated for a durable period. Because of the resulting power shortages, we present and provide a complete solution to resolving energy crises through Demand Side Management (DSM). The strategies are based on energy efficiency, reducing electricity consumption, and shifting the load curve through conservation and load management with the implementation of DSM measures.
2. Research Methodology
Pakistan’s Leap Model Framework
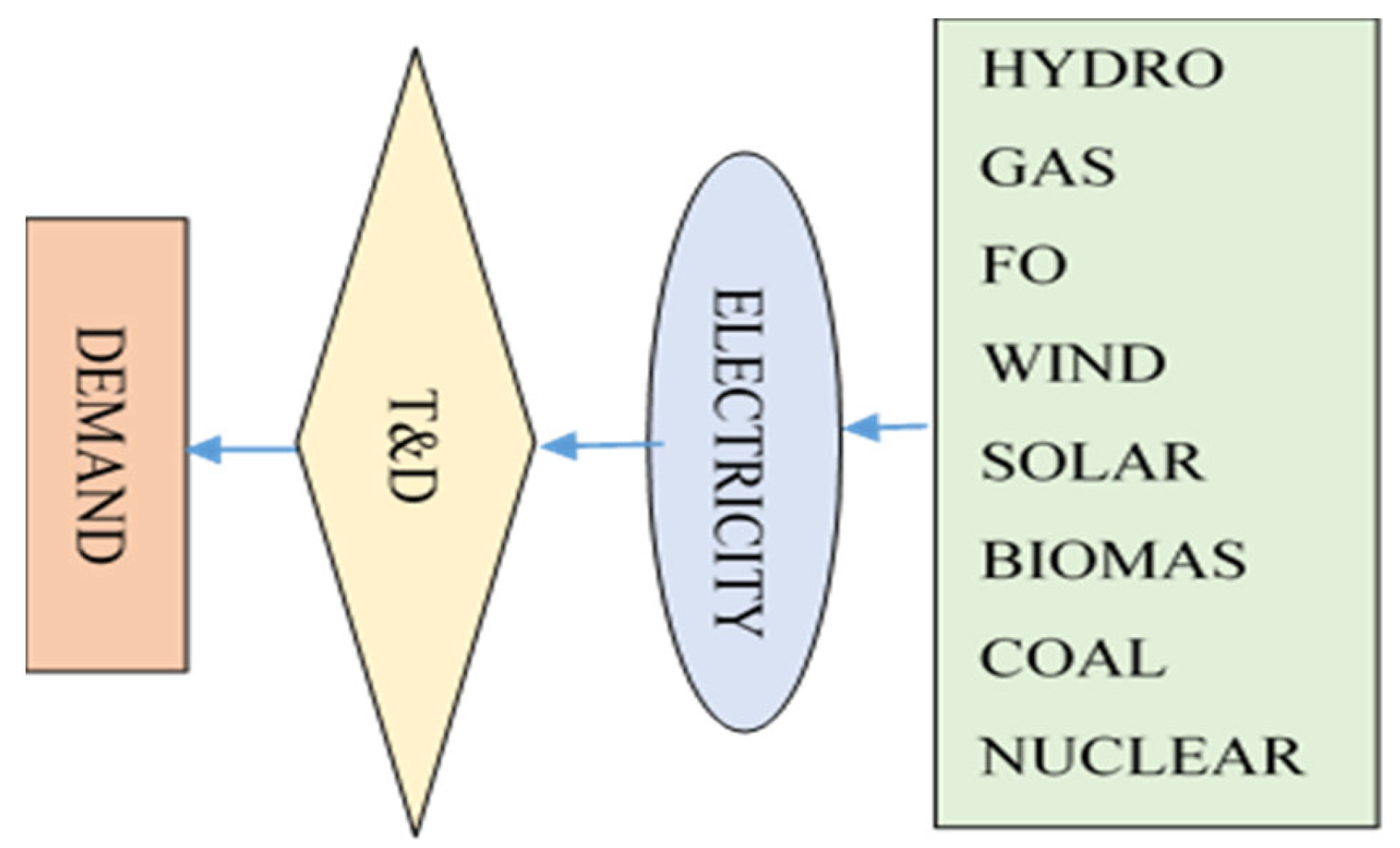
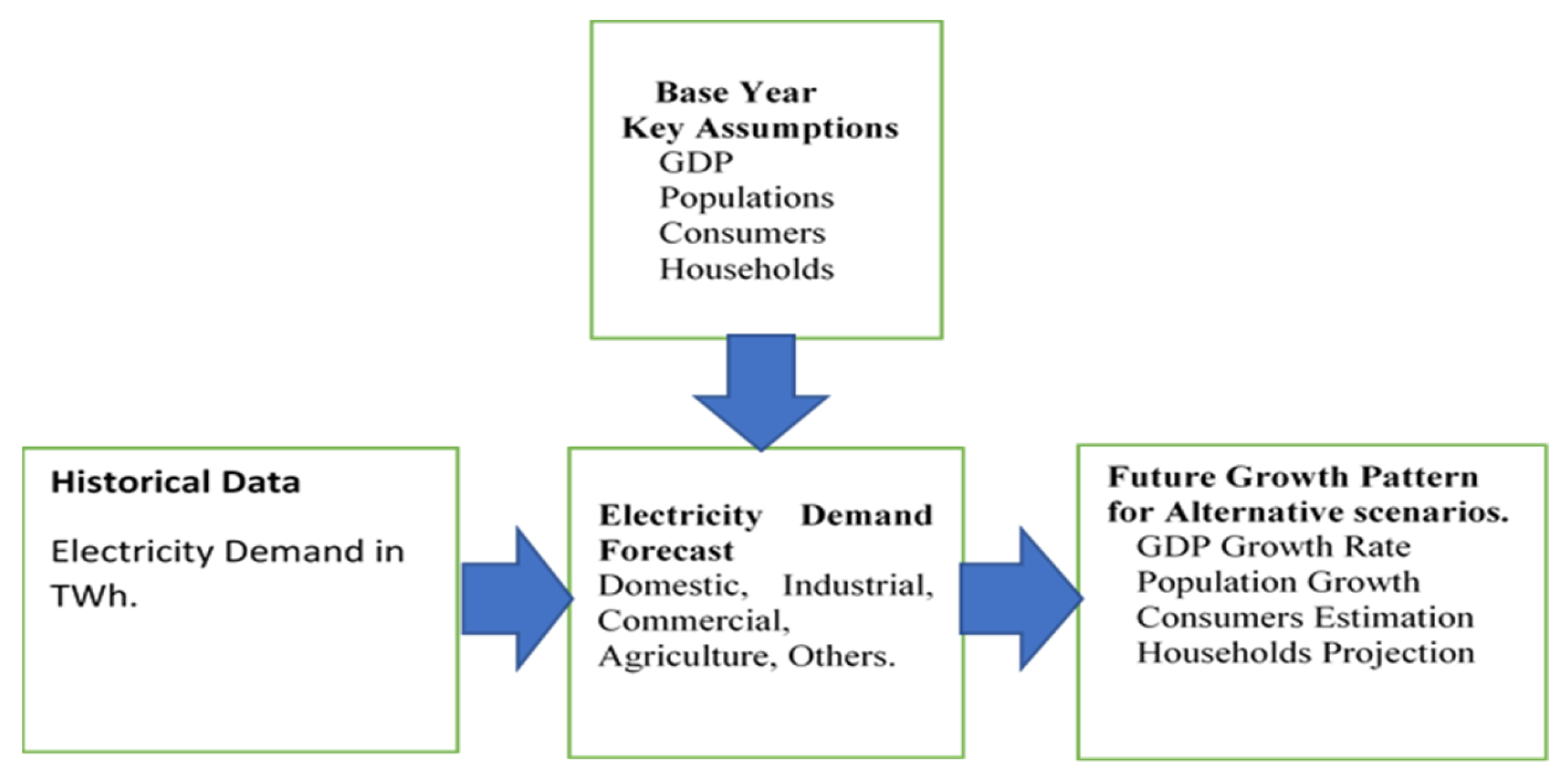
Various energy modeling tools are used throughout the entire world for energy planning and policy making. These modeling tools include the low emission analysis platform (LEAP) system, which is employed as a modeling tool for energy accounting to predict electricity demand and pair it with available generation capacity [8]. Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the structure of LEAP for predicting energy demand and generating energy. In LEAP, the energy demand module predicts energy demand by examining demand. In order to predict the energy demand, the bottom line of the various sectors of energy consumption is taken into account, which includes domestic, industrial, commercial, agriculture, and others. A key input for the energy demand module is the total population, household, consumer, and historical data on energy consumption, Gross Domestic Product (GDP), growth rates, and projections [9,10]. The energy production module in LEAP forecasts energy production utilizing the transformation module. Domestic energy assets are used for energy production, and transformed energy as an input to energy products is modeled using a variety of energy production technologies. The data required for the energy production module include base year exogenous capacity, energy production, system efficiency, maximum availability, system lifetime, and technology selection [11].
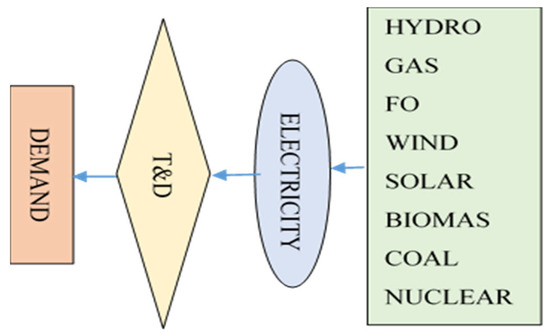
Figure 2.
Structure of electricity production forecast.
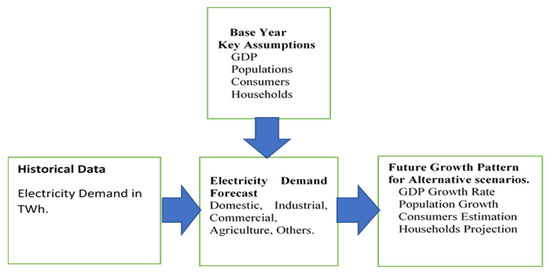
Figure 3.
Structure of electricity demand forecast.
2.1. Business as Usual (BAU) Scenario
This scenario depicts the power grid in the context of current trends and government policies. In this scenario, it is assumed that Pakistan’s policies won’t change and that ongoing development will proceed similarly to how it does now. Generation technology, efficiency, losses of distribution and transmission lines, percentage share in electricity generation, fuel, installation of plants, growth rate of electricity utilization, and economic growth will all stay the same [2,10,12].
2.2. Demand Side Management (DSM) Scenario
For the sake of long-term resource security and environmental sustainability, this scenario was developed to illustrate the potential for energy savings that would result from modifying power consumption patterns across all sectors and cutting down on transmission and distribution losses.
DSM has typically been viewed as a means of lowering peak demand, allowing utilities to put off constructing additional capacity. This is crucial in postponing costly investments in G&T&D infrastructure. Therefore, DSM has reduced the financial and fuel dependability for the environment when applied to electric systems [10].
According to a study by the Asian Development Bank [13], Pakistan has the potential to save 20–25% of its total energy consumption across its domestic, industrial, commercial, agricultural, and other sectors, which is 20–23%, 10–14%, 41%, and 6%, respectively. We estimate that the efficiency and conservation measures implemented in this scenario will reduce electricity demand by 29% relative to the total projected demand under the reference scenario.
3. Results
In this section, we present our findings regarding the Baseline and DSM scenarios for projecting energy demand and production from 2020 to 2050.
3.1. Energy Demand Forecasting
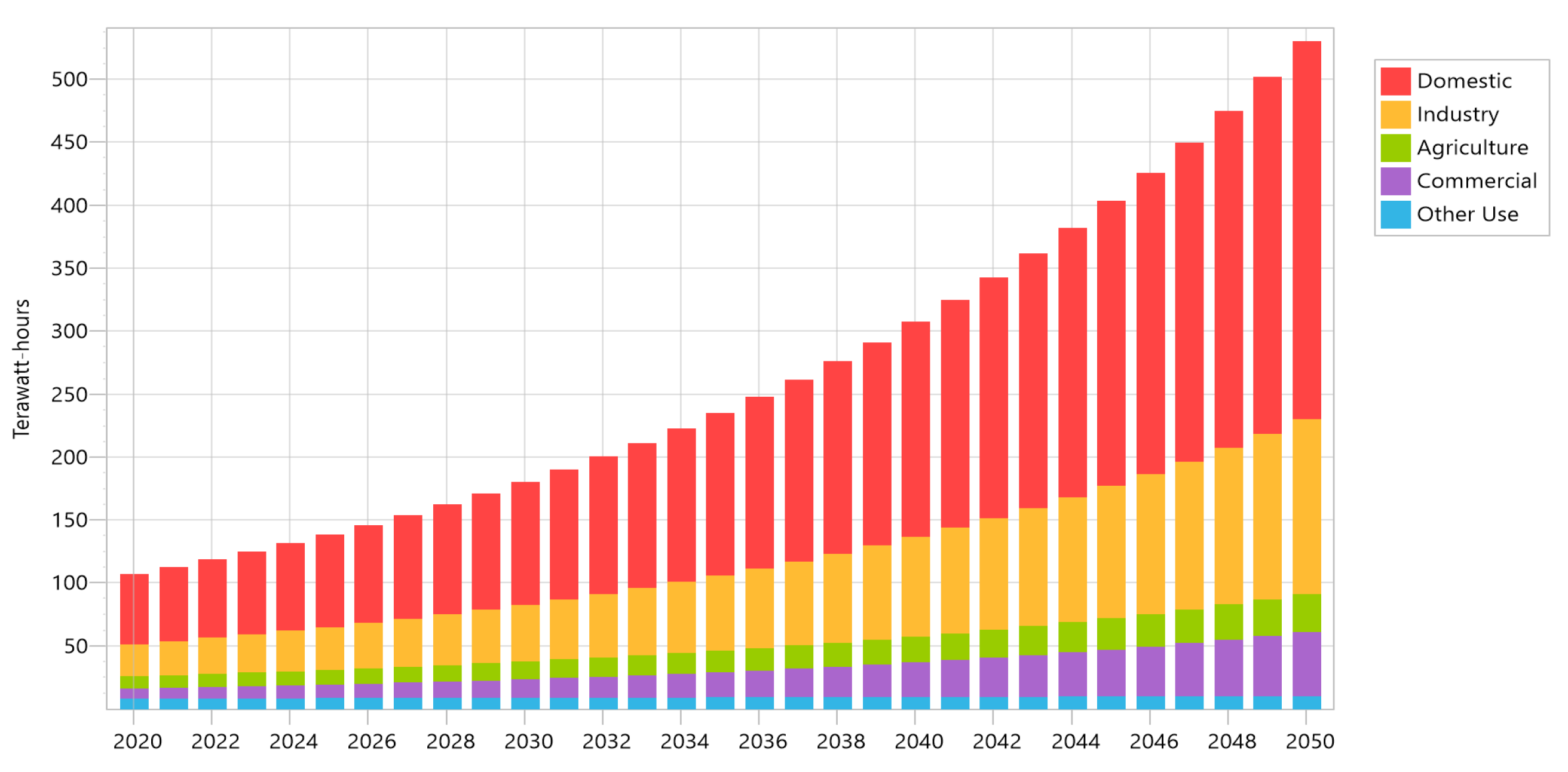
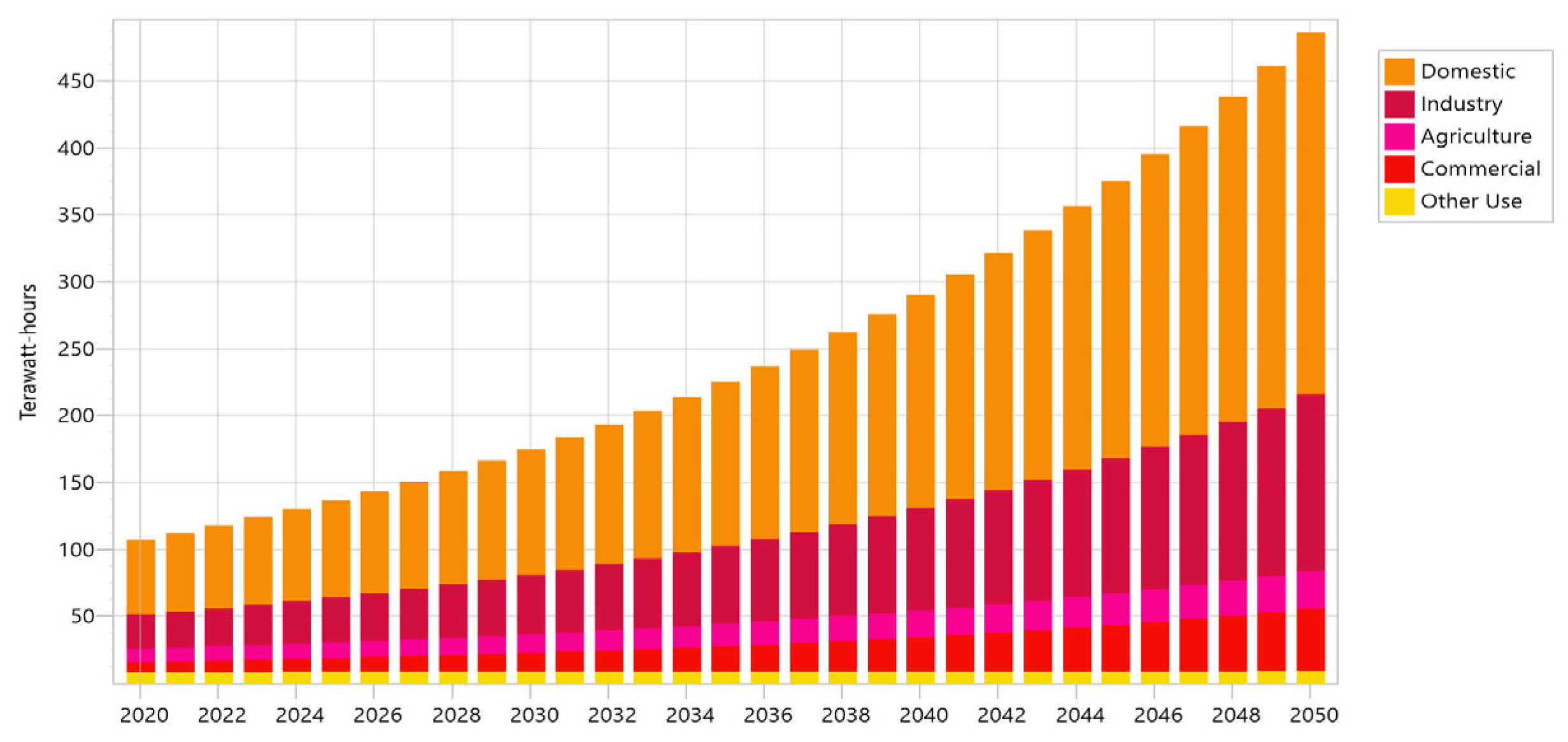
We ran projections for both scenarios’ electricity consumption from 2020 (the “base year”) to 2050 (the “target year”). The two futures share a trend of rising electricity demand due to rising populations, rising living standards, and expanding economies. These trends will continue until 2050. Figure 4 displays the increase in electricity demand from 2020 to 2050 under the BAU scenario (107 to 530 thousand GWh), while Figure 5 displays the increase in electricity demand under the DSM scenario (107 to 403.4 thousand GWh) from 2020 to 2050. DSM tends to result in a 29% decrease in electricity generation compared to the BAU scenario in 2050.
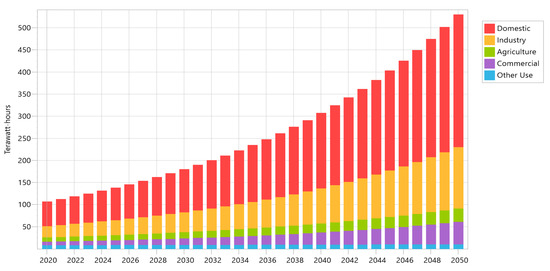
Figure 4.
Energy demand under Baseline scenario.
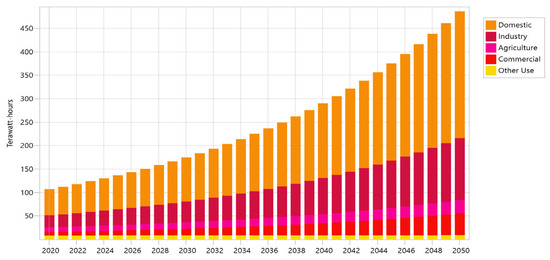
Figure 5.
Energy demand under DSM scenario.
3.2. Energy Production Forecasting
For the years 2020–2050, the study takes a model that incorporates a wide range of technologies and fuel mixes to predict energy production under the Baseline (BAU) and Demand Side Management (DSM) scenarios. In the base year, there is an insufficient supply of energy due to a gap between the actual demand of 125,635 GWh and the supply of 107,066 GWh. Power interruptions in Pakistan are caused by this deficit. As mentioned in the BAU and DSM scenarios, they will ensure that power supply and demand are in balance.
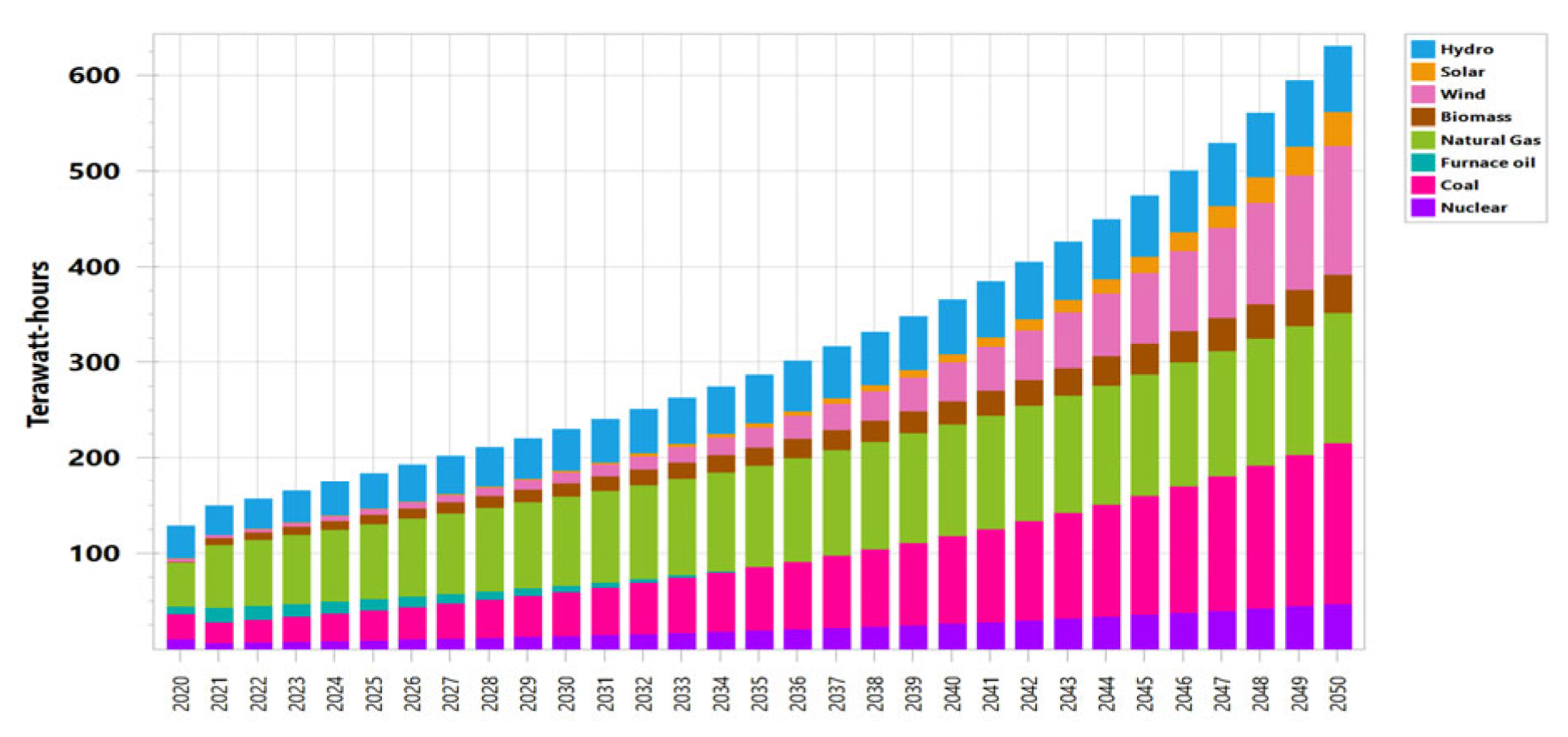
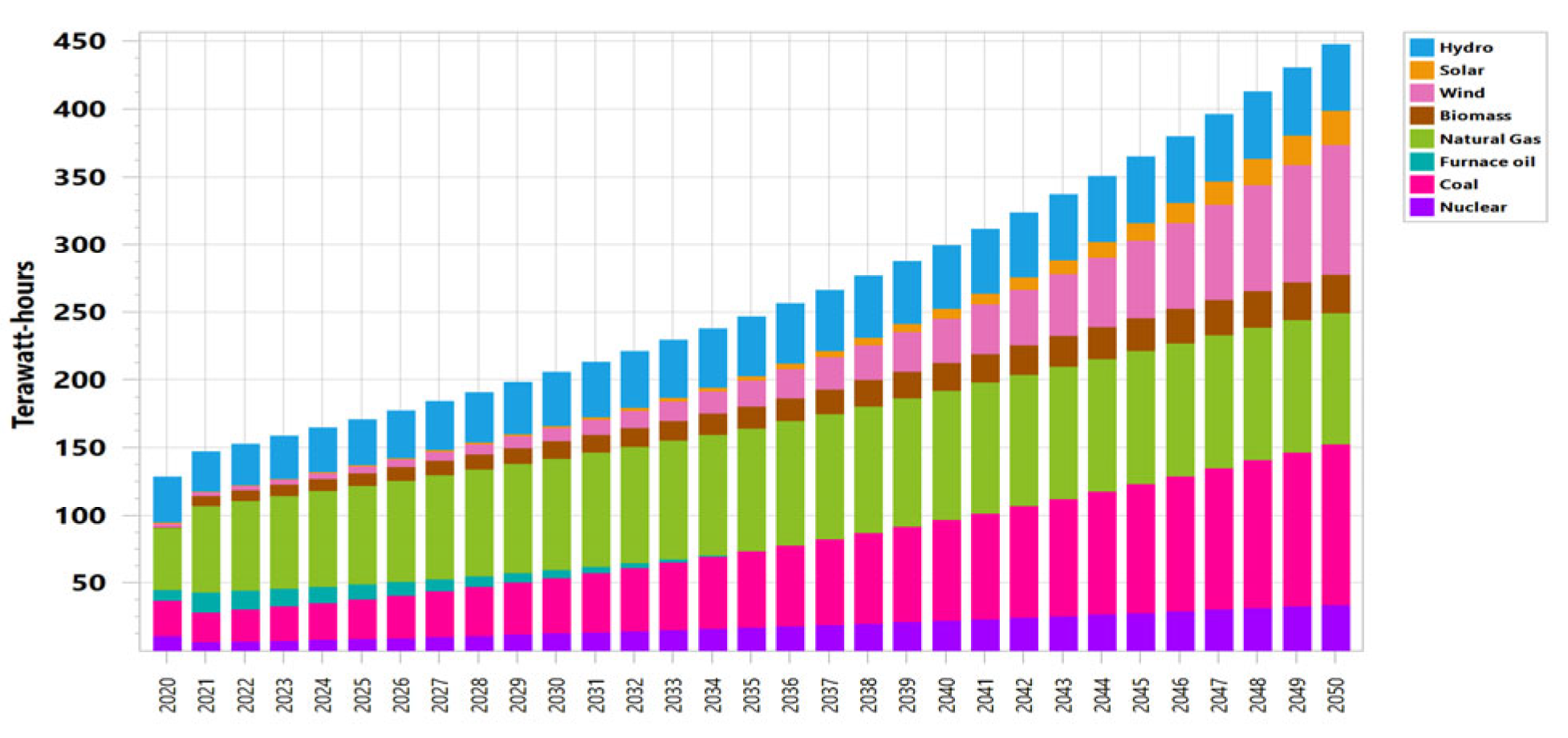
Hydropower facilities, biomass power plants, solar PV, nuclear power plants, and wind power plants were all part of the energy supply mix in 2020, yielding a total of 107,066 GWh for the BAU scenario. In 2020, oil will account for 6.4% of the energy mix; by 2034, this percentage will have decreased to 2%, while by 2035, it is going to decrease to 0%. Hydro’s share will increase from 26.1% in 2020 to 51% in 2050. As can be seen in Figure 6, the BAU scenario results in an increase in the supply of electricity from 107.066 TWh in 2020 to 631 TWh in 2050. Demand side management, or DSM, is a technique often used to close the supply and demand mismatch. According to ENERCON (National Energy Conservation Center), Pakistan’s sectors have enough saving potential. It follows that no energy-saving measures are implemented in the first BAU scenario and that by 2050, the DSM scenario’s electricity supply has reached 447.8 TWh, as shown in Figure 7. Compared to the BAU scenario’s 631 TWh in 2050, this shows a massive decline in power supply of 183.2 TWh.
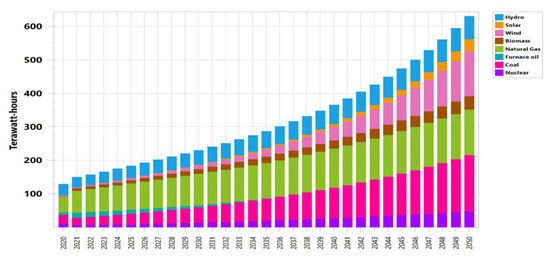
Figure 6.
Energy production under Baseline (BAU) scenario.
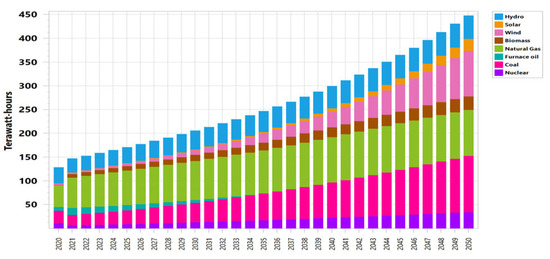
Figure 7.
Energy production under DSM scenario.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the existing electricity consumption and supply have been examined. Using existing data and assumptions, the electricity demand of Pakistan’s various sectors has been estimated, and it has been concluded that the demand will increase by 143% by 2020. This study successfully modeled the BAU scenario and alternative DSM scenarios for power generation using the LEAP model for the period of 2020 to 2050. Environmental impacts and cost–benefit analysis indicate that alternative scenarios are superior to the current situation. The alternative scenarios, therefore, provide an alternative option to Pakistan’s current electrical problem by decreasing the high import expenditure for imported resources and refocusing on indigenous resources. The DSM scenario describes the utilization of current technology and energy-efficient appliances, as well as energy conservation initiatives, to reduce electricity demand without establishing new generating and transmission infrastructure.
As such, it is predicted that the efficiency and conservation measures of the DSM scenario will lower energy consumption by 18% of the entire forecasted demand under the BAU scenario.
- The Government of Pakistan must prioritize harnessing power potential through efficient technologies and effective strategies that contribute to achieving sustainable power capacity objectives.
- The Government of Pakistan should implement DSM reforms in the power sector and improve electricity bill collection.
- DSM has not yet been considered as a viable option for enhancing the performance of the power sector.
- Failure on the part of the government to advise customers of the potential benefits of DSM.
- DSM measures are not understood by consumers.
- DSM technology solutions and a greater understanding of power are not adequately promoted to the general public, academic institutions, and researchers.
- Encourage companies to use clean conversion technologies and promote technological advancements that enhance energy efficiency.
Author Contributions
M.A.B.: investigation, conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft, writing—review & editing, formal analysis and validation. N.H.M.: supervision, project administration, resources. S.A.K.: formal analysis, visualization, validation. A.M.: formal analysis. M.A.R.: formal analysis, visualization, validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of NED University of Engineering and Technology.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- HDIP. Pakistan Energy Year Book (2020); Government of Pakistan: Islamabad, Pakistan, 2020.
- Finance Division Government of Pakistan. Pakistan Economic Survey 2019–20. Economic Survey. 2020. Available online: https://www.finance.gov.pk/survey_1920.html (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Akpojedje, F.O.; Ogujor, E.A.; Folorunso, O. A comprehensive review of optimal demand side management and its influence on enhancing distribution network congestion management. IJRET Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabir, H.J.; Teh, J.; Ishak, D.; Abunima, H. Impacts of Demand-Side Management on Electrical Power Systems: A Review. Energies 2018, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, P. A review of demand-side management policy in the UK. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshell, F.; Veloza, O.P. Review of developed demand side management programs including different concepts and their results. In Proceedings of the Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition: Latin America, Bogota, Columbia, 13–15 August 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, C.M.; Bhongade, S. Load Management. 2019. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Kishor%2C+C.+M.%2C+%26+Bhongade%2C+S.+%282019%29.+Load+Management+Techniques+and+Pricing+Model+for+Demand+Side+Management-A+Review.+International+Journal+on+Emerging+Technologies%2C+10%281%29%2C+42-46.&btnG= (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Stockholm Environment Institute. User Guide for LEAP 2020. September 2020. Available online: https://leap.sei.org/default.asp?action=trainingmaterials (accessed on 11 June 2020).
- Raza, M.A.; Khatri, K.L.; Hussain, A. Transition from fossilized to defossilized energy system in Pakistan. Renew. Energy 2022, 190, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjat, N.; Uqaili, M.; Harijan, K. Energy and undefined 2018. In Long-Term Electricity Demand Forecast and Supply Side Scenarios for Pakistan (2015–2050): A LEAP Model Application for Policy Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Perwez, U.; Sohail, A.; Hassan, S.F.; Zia, U. The long-term forecast of Pakistan’s electricity supply and demand: An application of long range energy alternatives planning. Energy 2015, 93, 2423–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NTDC. Indicative Generation Capacity Expansion Plan 2021–30 by National Transmission and Dispatch Company (NTDC). Available online: https://nepra.org.pk/Admission%20Notices/2021/06%20June/IGCEP%202021.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- International Energy Agency. World Energy Outlook 2012; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).