Biotechnological Solutions for Recycling Synthetic Fibers †
Abstract
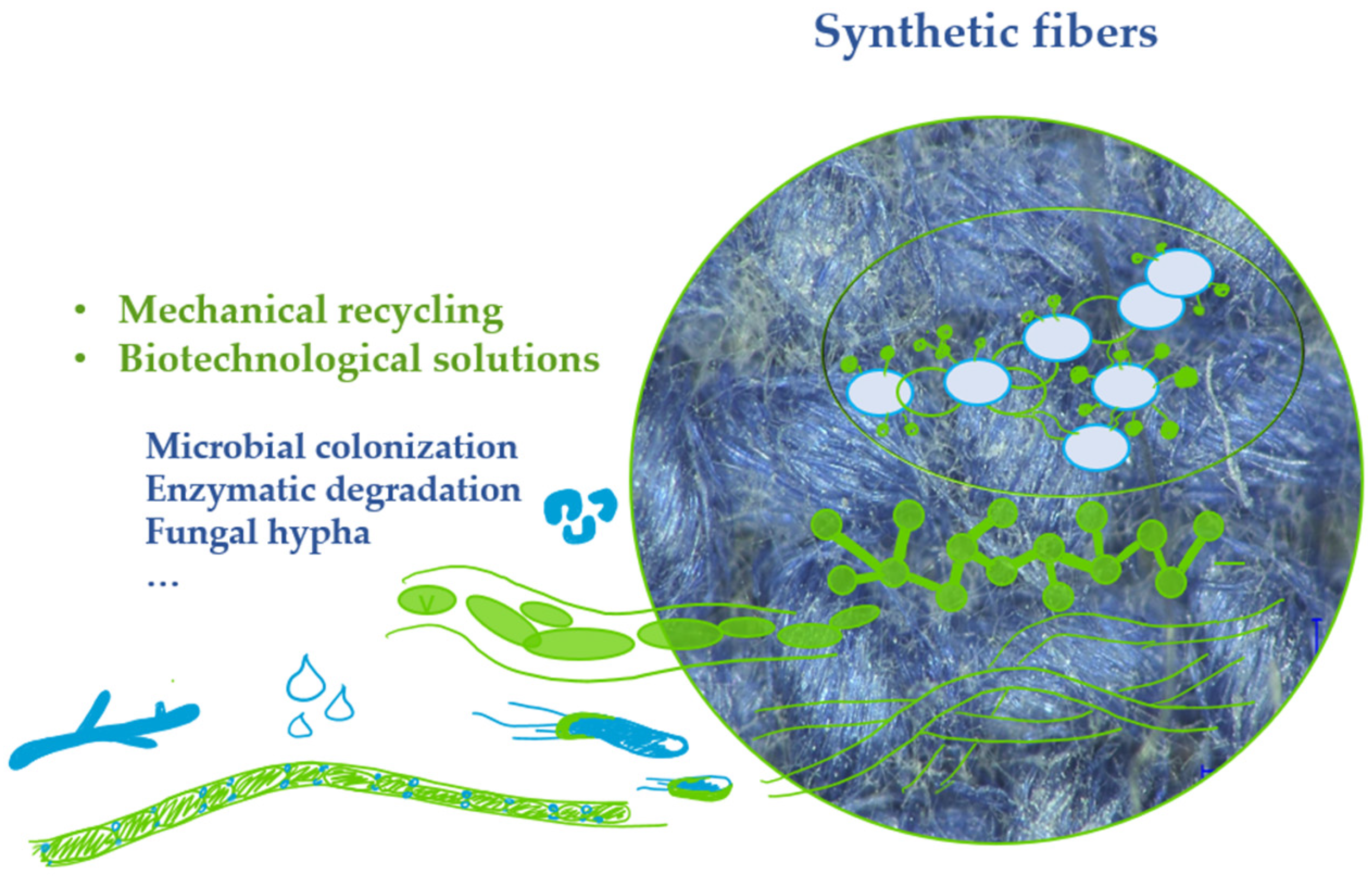
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanical Recycling Processes and Limitations
3. Biotechnological Perspectives for Synthetic Fiber Recycling
3.1. Enzymatic Degradation
3.2. Microbial Biodegradation
4. Current Challenges and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, P.; Bhadra, S.; Ray, S.S. Combination of Mechanical and Chemical Recycling of Polyamide 6 and Polyamide 66 Fibers: Effect of 35 6-Membered-Ring Monomer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 8, 11818–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, D.; Wulandari, L.A.; Bagaskoro, A.; Rianjanu, A.; Wu, H.-S. Possibility Routes for Textile Recycling Technology. Polymers 2021, 13, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Beneit, F.; Chen, L.M.; Bordel, S.; Frutos de la Flor, R.; García-Depraect, O.; Lebrero, R.; Rodriguez-Vega, S.; Muñoz, R.; Börner, R.A.; Börner, T. Screening Enzymes That Can Depolymerize Commercial Biodegradable Polymers: Heterologous Expression of Fusarium solani Cutinase in Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafatti-Picca, L.; Bucioli, E.C.; de Barros Chaves, M.R.; de Castro, A.M.; Valoni, É.; de Oliveira, V.M.; Marsaioli, A.J.; Govone, J.S.; de Franceschi de Angelis, D.; Brienzo, M.; et al. Fungal Screening for Potential PET Depolymerization. Polymers 2023, 15, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo, P.; Marín, A.; Samaniego-Aguilar, K.; Sánchez-Safont, E.; Lagarón, J.M.; Gámez-Pérez, J.; Cabedo, L. Effect of the Presence of Lignin from Woodflour on the Compostability of PHA-Based Biocomposites: Disintegration, Biodegradation and Microbial Dynamics. Polymers 2023, 15, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, J.; Salmon, S. Strategies and progress in synthetic textile fiber biodegradability. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcona, J.; Olguín, C.; Durán, A.; Fernández-Rodríguez, J. Approach to anaerobic bio-degradation of natural and synthetic fabrics: Physico-chemical study of the alteration processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marqués-Calvo, M.S.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Kint, D.P.R.; Bou, J.J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Enzymatic and microbial biodegradability of poly(ethylene terephthalate) copolymers containing nitrated units. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, N.; Montazer, Z.; Sharma, P.; Levin, D. Microbial and Enzymatic Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, S.; Bartoli, F.; Bruni, C.; Fernandez-Avila, C.; Rodriguez-Turienzo, L.; Mellado-Carretero, J.; Spinelli, D.; Coltelli, M.-B. Opportunities and Limitations in Recycling Fossil Polymers from Textiles. Macromol 2023, 3, 120–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Feng, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.-H. Recycling and Reutilization of Waste Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics: Current Status and Prospects. Polymers 2023, 15, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klose, L.; Meyer-Heydecke, N.; Wongwattanarat, S.; Chow, J.; Pérez García, P.; Carré, C.; Streit, W.; Antranikian, G.; Romero, A.M.; Liese, A. Towards Sustainable Recycling of Epoxy-Based Polymers: Approaches and Challenges of Epoxy Biodegradation. Polymers 2023, 15, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, D. Research Progress on Fiber-Reinforced Recycled Brick Aggregate Concrete: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Geem, K.V. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boondaeng, A.; Keabpimai, J.; Srichola, P.; Vaithanomsat, P.; Trakunjae, C.; Niyomvong, N. Optimization of Textile Waste Blends of Cotton and PET by Enzymatic Hydrolysis with Reusable Chemical Pretreatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Chatterjee, K.; and Madras, G. Enzymatic degradation of polymers: A brief review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, M.; Yehia, A.; Yehia, S.; Abuzaid, W. Shear Strength of Fiber Reinforced Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraveas, C. Production of Sustainable and Biodegradable Polymers from Agricultural Waste. Polymers 2020, 12, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strik, D.P.B.T.B.; Heusschen, B. Microbial Recycling of Polylactic Acid Food Packaging Waste into Carboxylates via Hydrolysis and Mixed-Culture Fermentation. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teacă, C.-A.; Shahzad, A.; Duceac, I.A.; Tanasă, F. The Re-/Up-Cycling of Wood Waste in Wood–Polymer Composites (WPCs) for Common Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agüero, Á.; Corral Perianes, E.; Abarca de las Muelas, S.S.; Lascano, D.; de la Fuente García-Soto, M.d.M.; Peltzer, M.A.; Balart, R.; Arrieta, M.P. Plasticized Mechanical Recycled PLA Films Reinforced with Microbial Cellulose Particles Obtained from Kombucha Fermented in Yerba Mate Waste. Polymers 2023, 15, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Su, T.; Wang, Z. Effect of Hydroxyl Monomers on the Enzymatic Degradation of Poly(ethylene succinate), Poly(butylene succinate), and Poly(hexylene succinate). Polymers 2018, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navone, L.; Moffitt, K.; Hansen, K.A.; Blinco, J.; Payne, A.; Speight, R. Closing the textile loop: Enzymatic fibre separation and recycling of wool/polyester fabric blends. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, J.; Wang, S.; Shen, J.; Baars, O.; Moxley, G.; Salmon, S. Enzymatic textile fiber separation for sustainable waste processing, Resources. Environ. Sustain. 2023, 13, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiso, T.; Narancic, T.; Wei, R.; Pollet, E.; Beagan, N.; Schröder, K.; Honak, A.; Jiang, M.; Kenny, S.T.; Wierckx, N.; et al. Towards bio-upcycling of polyethylene terephthalate. Metab. Eng. 2021, 66, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadaleta, G.; De Gisi, S.; Sorrentino, A.; Sorrentino, L.; Notarnicola, M.; Kuchta, K.; Picuno, C.; Oliviero, M. Effect of Cellulose-Based Bioplastics on Current LDPE Recycling. Materials 2023, 16, 4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Koller, M. Microbial PolyHydroxyAlkanoate (PHA) Biopolymers—Intrinsically Natural. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabisa, E.W.; Ratanatamskul, C.; Gheewala, S.H. Recycling of Plastics as a Strategy to Reduce Life Cycle GHG Emission, Microplastics and Resource Depletion. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zimmermann, W. Microbial enzymes for the recycling of recalcitrant petroleum-based plastics: How far are we? Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1308–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiros, T.N.; Mosher, C.Z.; Zhu, Y.; Bina, T.; Gomez, V.; Lee, C.L.; Lu, H.H.; Obermeyer, A.C. Bioengineering textiles across scales for a sustainable circular economy. Chem 2021, 7, 2913–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, W. Biocatalytic recycling of polyethylene terephthalate plastic. R. Soc. 2020, 378, 20190273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazli, A.; Rodrigue, D. Sustainable Reuse of Waste Tire Textile Fibers (WTTF) as Reinforcements. Polymers 2022, 14, 3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruuth, E.; Sanchis-Sebastiá, M.; Larsson, P.T.; Teleman, A.; Jiménez-Quero, A.; Delestig, S.; Sahlberg, V.; Salén, P.; Sanchez Ortiz, M.; Vadher, S.; et al. Reclaiming the Value of Cotton Waste Textiles: A New Improved Method to Recycle Cotton Waste Textiles via Acid Hydrolysis. Recycling 2022, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opálková Šišková, A.; Pleva, P.; Hrůza, J.; Frajová, J.; Sedlaříková, J.; Peer, P.; Kleinová, A.; Janalíková, M. Reuse of Textile Waste to Production of the Fibrous Antibacterial Membrane with Filtration Potential. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukoje, M.; Itrić Ivanda, K.; Kulčar, R.; Marošević Dolovski, A. Spectroscopic Stability Studies of Pressure Sensitive Labels Facestock Made from Recycled Post-Consumer Waste and Agro-Industrial By-Products. Forests 2021, 12, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, E.; Chrysafi, I.; Polychronidis, P.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Evaluation of Eco-Friendly Hemp-Fiber-Reinforced Recycled HDPE Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tošić, N.; de la Fuente, A. Recycling of Macro-Synthetic Fiber-Reinforced Concrete and Properties of New Concretes with Recycled Aggregate and Recovered Fibers. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, X. Preparation of flame retardant, smoke suppression and reinforced polyacrylonitrile composite fiber by using fully biomass intumescent flame retardant system and its sustainable recycle application. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 173, 107705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Nie, X.; Chen, J. Bio-based epoxy vitrimer for recyclable and carbon fiber reinforced materials: Synthesis and structure-property relationship. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 227, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Gao, J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H. Efficient preparation of chemically crosslinked recyclable photodeformable azobenzene polymer fibers with high processability and reconstruction ability via a facile post-crosslinking method. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 139, 109998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamun, A.; Kuntz, F.; Golle, C.; Sabantina, L. Biotechnological Solutions for Recycling Synthetic Fibers. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16301
Mamun A, Kuntz F, Golle C, Sabantina L. Biotechnological Solutions for Recycling Synthetic Fibers. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 56(1):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16301
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamun, Al, Friederike Kuntz, Cornelia Golle, and Lilia Sabantina. 2023. "Biotechnological Solutions for Recycling Synthetic Fibers" Engineering Proceedings 56, no. 1: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16301
APA StyleMamun, A., Kuntz, F., Golle, C., & Sabantina, L. (2023). Biotechnological Solutions for Recycling Synthetic Fibers. Engineering Proceedings, 56(1), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-16301







