Investigation of Machining Parameters and Surface Quality of AZ-31 Magnesium Alloy Subjected to Spark Machining †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Selection
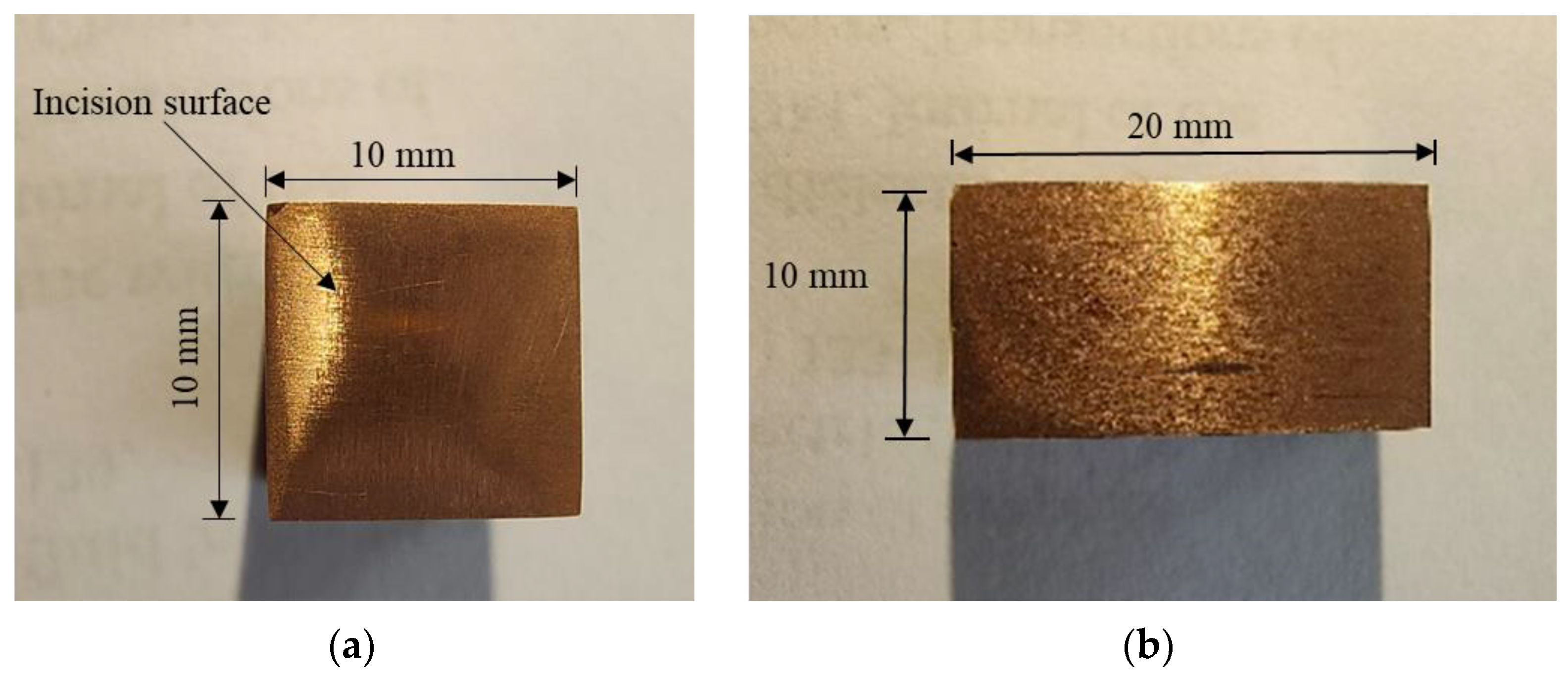
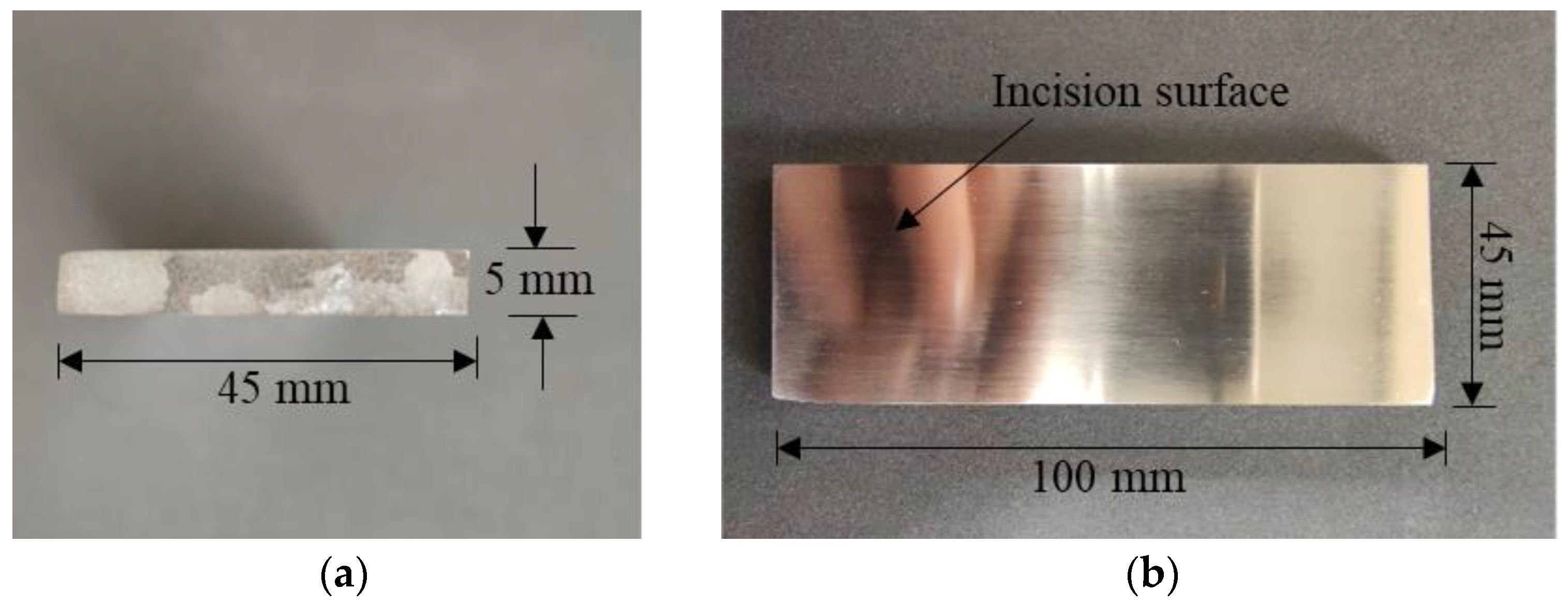
2.2. Tool and Specimen Preparation
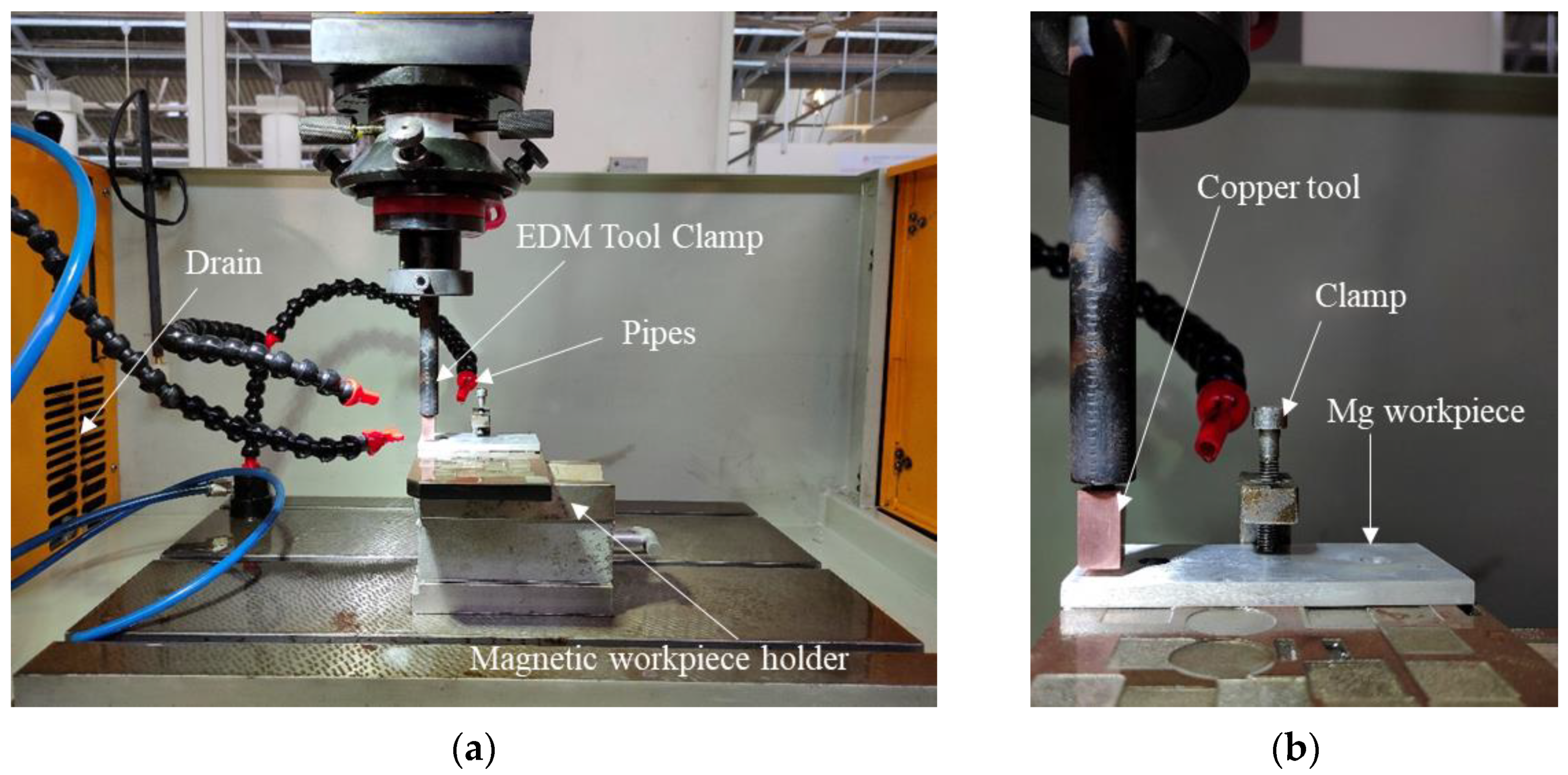
2.3. Experimental Setup and Machining Using EDM
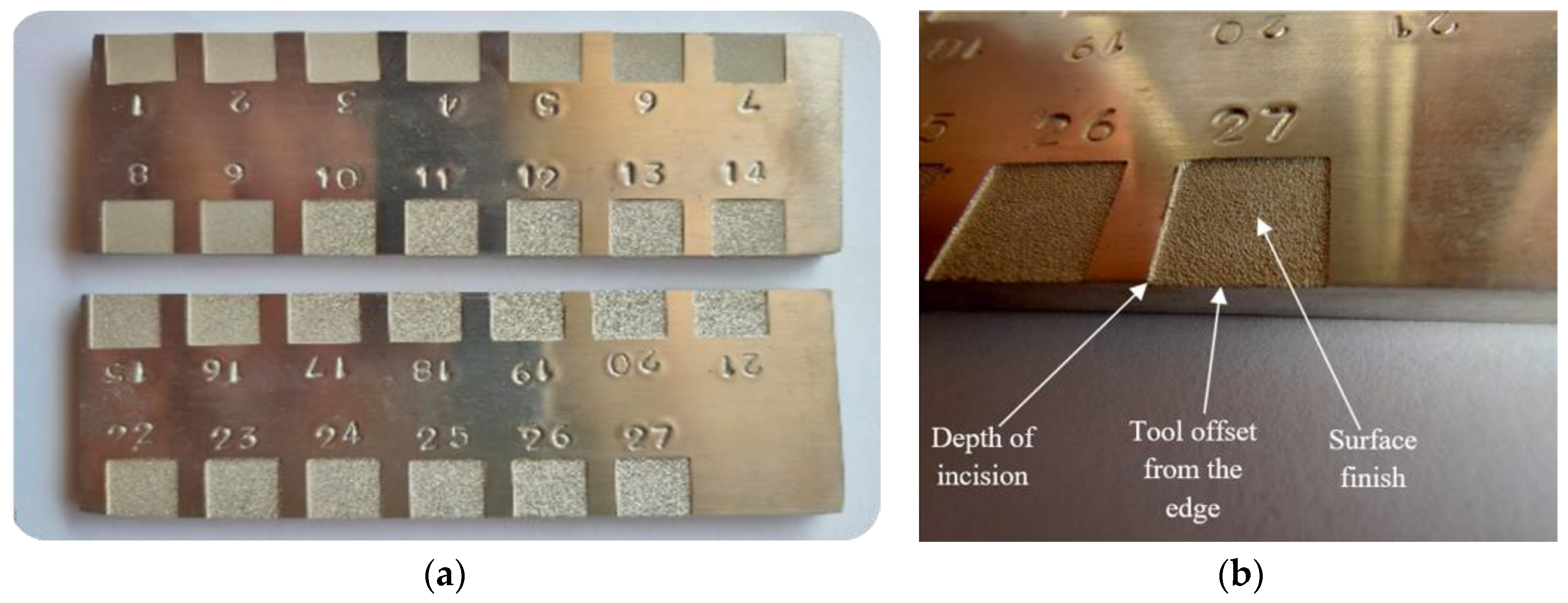
2.4. Surface Analysis Using Optical Microscope
2.5. Surface Analysis Using Profilometer
3. Results
3.1. Surface Analysis Using Optical Microscope
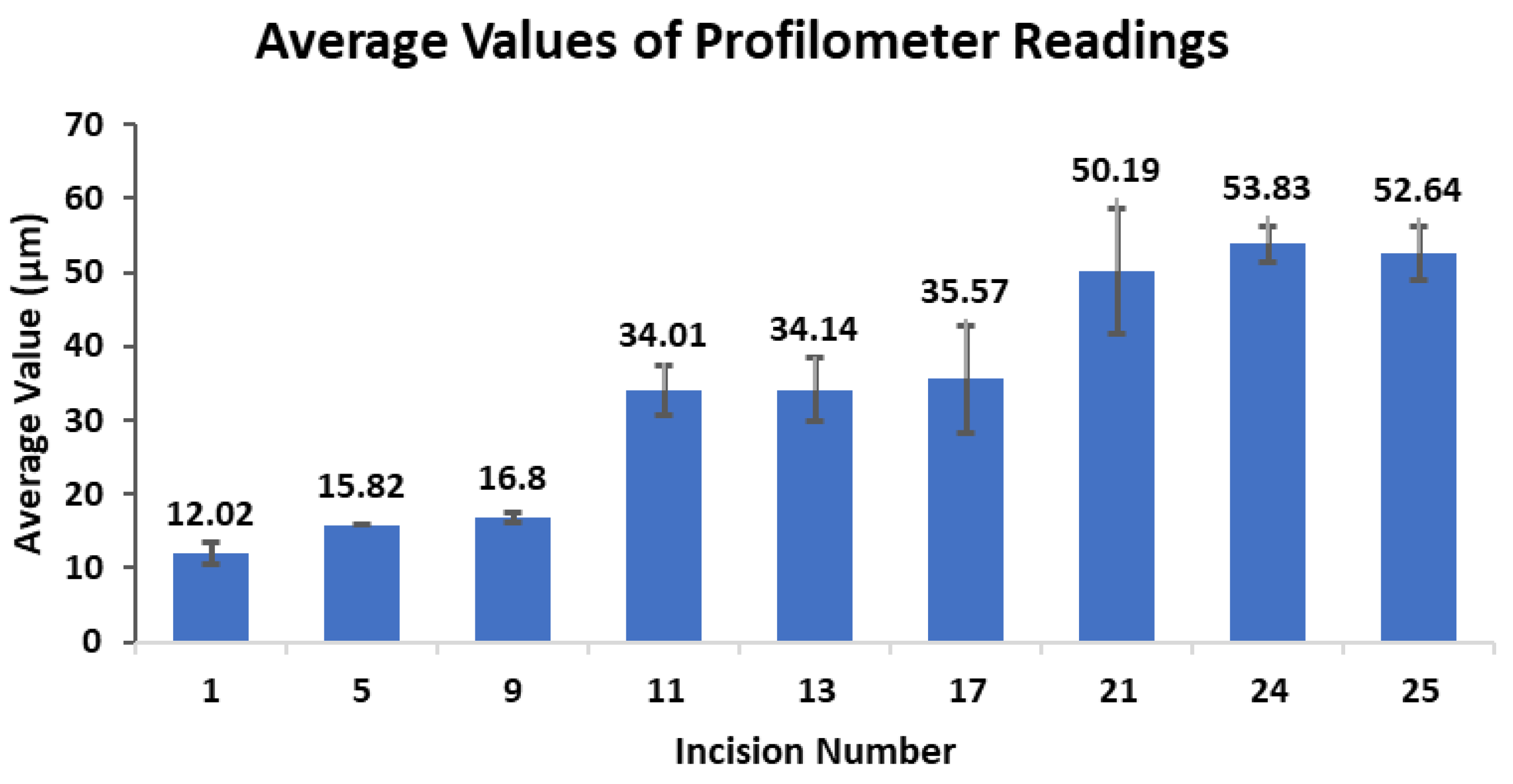
3.2. Surface Analysis Using Profilometer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crane, F.A.A.; Charles, J.A.; Furness, J.A.G. Selection and Use of Engineering Materials, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Massachusetts, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 45–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Research advances in magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2020. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 705–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Applications of Magnesium and Its Alloys: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaeian-Naeini, M.; Sedighi, M.; Hashemi, R.; Delavar, H. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and fracture toughness of ECAPed magnesium matrix composite reinforced with hydroxyapatite ceramic particulates for bioabsorbable implants. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 17074–17090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekguleryuz, M.O.; Kaya, A.A. Creep Resistant Magnesium Alloys for Powertrain Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2003, 5, 866–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghion, E.; Bronfín, B.; Von Buch, F. Newly developed magnesium alloys for powertrain applications. JOM 2003, 55, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyuz, B. Influence of Al content on machinability of AZ series Mg alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Yasir, M.; Mia, M.; Nazir, K.; Ahmed, T.; Ahmad, M.A.R. High speed machining of magnesium and its alloys. High Speed Mach. 2020, 10, 263–282. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, N.; Batra, U.; Kumar, K. Experimental investigation and optimization of wire electrical discharge machining for surface characteristics and corrosion rate of biodegradable Mg alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 4117–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Li, C.; Tong, W.; Xiong, D.; Li, Z.; Wu, Z. High-speed wire electrical discharge machining to create superhydrophobic surfaces for magnesium alloys with high corrosion and wear resistance. Mater. Corros. 2020, 71, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darras, B.M.; Khraisheh, M.K.; Abu-Farha, F.K.; Omar, M.A. Friction Stir Processing of Commercial AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2007, 191, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily, M.; Svensson, J.E.; Fajardo, S.; Birbilis, N.; Frankel, G.S.; Virtanen, S.; Arrabal, R.; Thomas, S.; Johansson, L.G. Fundamentals and advances in magnesium alloy corrosion. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 92–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoren, S.A.; Solomon, M.M.; Madhankumar, A.; Obot, I.B. Exploration of natural polymers for use as green corrosion inhibitors for AZ31 magnesium alloy in saline environment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.L. The Effect of Texture on the Corrosion Behavior of AZ31 Mg Alloy. JOM 2012, 64, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Katyal, P.; Mandhania, S. Grey relational analysis based multiresponse optimization for WEDM of ZE41A magnesium alloy. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2022, 5, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.S.; Kumar, K.; Batra, U. Surface Characteristics and Corrosion Behavior of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining Processed Mg-4Zn Alloy. J. Materi. Eng Perform 2021, 30, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rani, A.M.; Razak, M.A.; Littlefair, G.; Gibson, I.; Nanimina, A.M. Improving EDM Process on AZ31 Magnesium Alloy towards Sustainable Biodegradable Implant Manufacturing. Procedia Manuf. 2016, 7, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaram, M.; Kumar, J.P. Multi response optimization of EDM process parameters for biodegradable AZ31 magnesium alloy using TOPSIS and grey relational analysis. Sādhanā 2022, 47, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Constituents | Mg | Al | Zn | Mn | Si | Cu | Ca | Fe | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content % | 97 | 3.2 | 1.0 | 0.45 | <0.1 | 0.003 | <0.01 | <0.005 | <0.003 |
| Incision Number | Peak Current (A) | Pulse On-Time (µs) | Pulse Off-Time (µs) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 90 | 50 |
| 5 | 1 | 120 | 70 |
| 9 | 1 | 150 | 90 |
| 11 | 3 | 90 | 70 |
| 13 | 3 | 120 | 50 |
| 17 | 3 | 150 | 70 |
| 21 | 5 | 90 | 90 |
| 24 | 5 | 120 | 90 |
| 25 | 5 | 150 | 50 |
| Incision No. | Optical Microscopy Image | Surface Roughness Profile |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 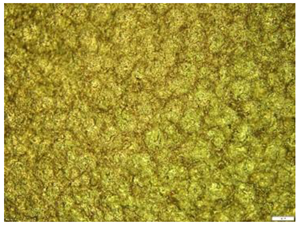 |  Avg. Roughness = 12.021 µm |
| 11 | 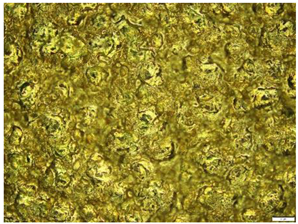 |  Avg. Roughness = 34.011 µm |
| 21 |  | 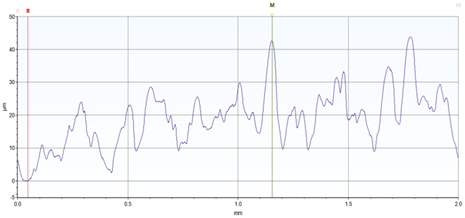 Avg. Roughness = 50.192 µm |
| 25 | 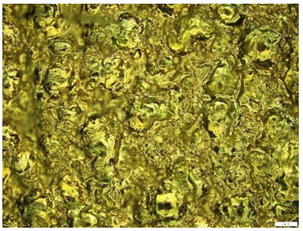 | 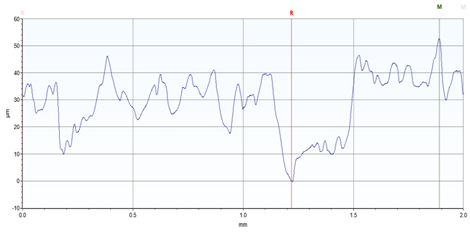 Avg. Roughness = 52.64 µm |
| Incision No. | Reading 1 (µm) | Reading 2 (µm) | Reading 3 (µm) | Average Value (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.352 | 12.269 | 13.443 | 12.02 ± 1.56 |
| 5 | 15.841 | 15.768 | 15.847 | 15.82 ± 0.04 |
| 9 | 17.477 | 16.739 | 16.186 | 16.80 ± 0.65 |
| 11 | 37.71 | 31.032 | 33.292 | 34.01 ± 3.40 |
| 13 | 35.906 | 37.27 | 29.241 | 34.14 ± 4.30 |
| 17 | 28.408 | 43.019 | 35.287 | 35.57 ± 7.31 |
| 21 | 48.787 | 42.49 | 59.279 | 50.19 ± 8.48 |
| 24 | 53.007 | 52.029 | 56.451 | 53.83 ± 2.32 |
| 25 | 49.162 | 52.488 | 56.275 | 52.64 ± 3.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhardwaj, S.; Agarwal, A.; Tibdewal, I.; Bolar, G.; Managuli, V. Investigation of Machining Parameters and Surface Quality of AZ-31 Magnesium Alloy Subjected to Spark Machining. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059135
Bhardwaj S, Agarwal A, Tibdewal I, Bolar G, Managuli V. Investigation of Machining Parameters and Surface Quality of AZ-31 Magnesium Alloy Subjected to Spark Machining. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 59(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059135
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhardwaj, Shouryha, Arnav Agarwal, Ishriit Tibdewal, Gururaj Bolar, and Vishwanath Managuli. 2023. "Investigation of Machining Parameters and Surface Quality of AZ-31 Magnesium Alloy Subjected to Spark Machining" Engineering Proceedings 59, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059135
APA StyleBhardwaj, S., Agarwal, A., Tibdewal, I., Bolar, G., & Managuli, V. (2023). Investigation of Machining Parameters and Surface Quality of AZ-31 Magnesium Alloy Subjected to Spark Machining. Engineering Proceedings, 59(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059135






