Assessing the Friction and Wear Behavior of AZ91-Based Hybrid Composites Reinforced with Nano hBN/Micron TiB2 Ceramic Particles Using WASPAS and ARAS Techniques †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
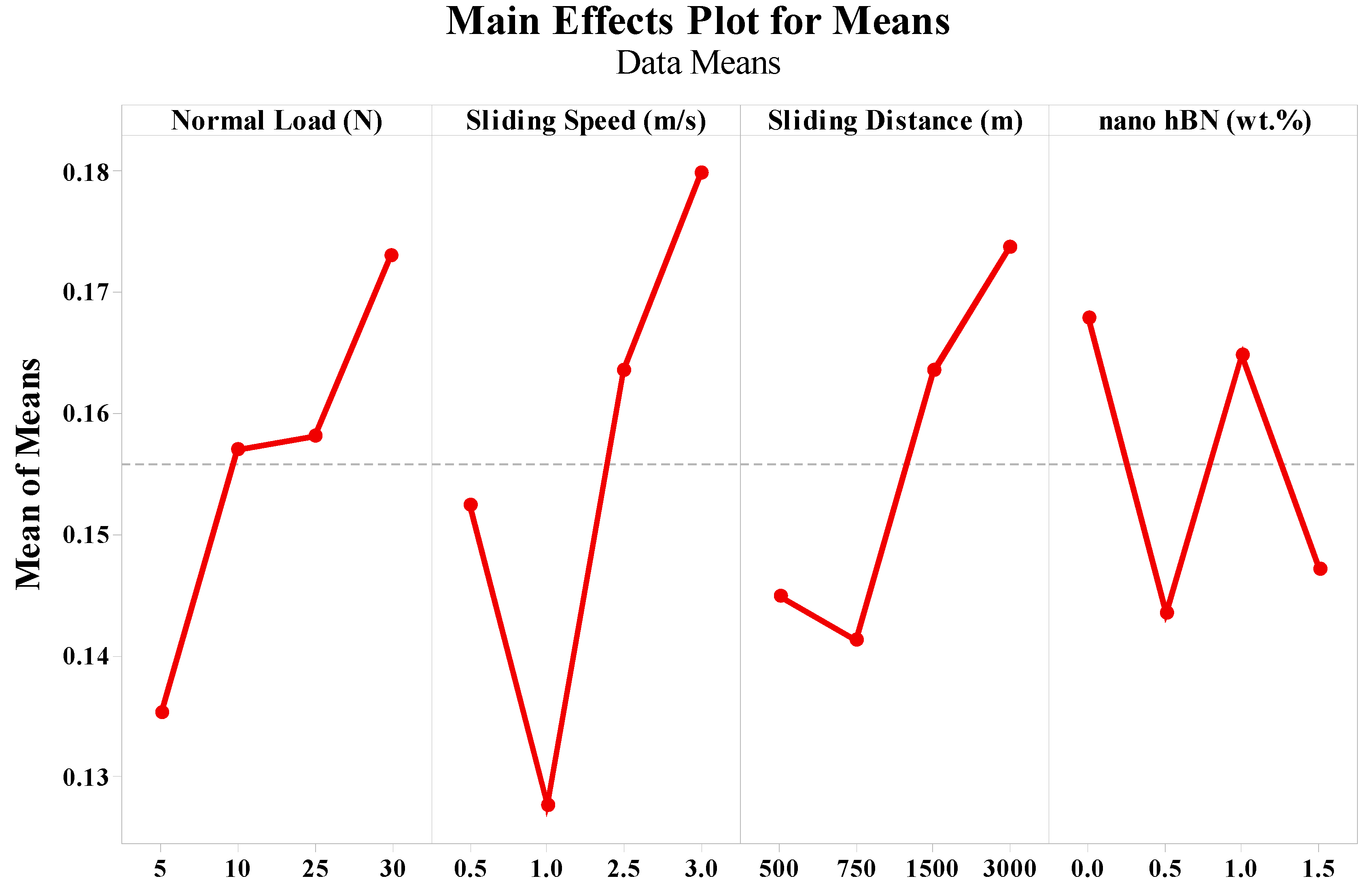
3.1. Effect of Normal Load, Sliding Speed, Sliding Distance, and hBN wt.% on Wear Loss and COF
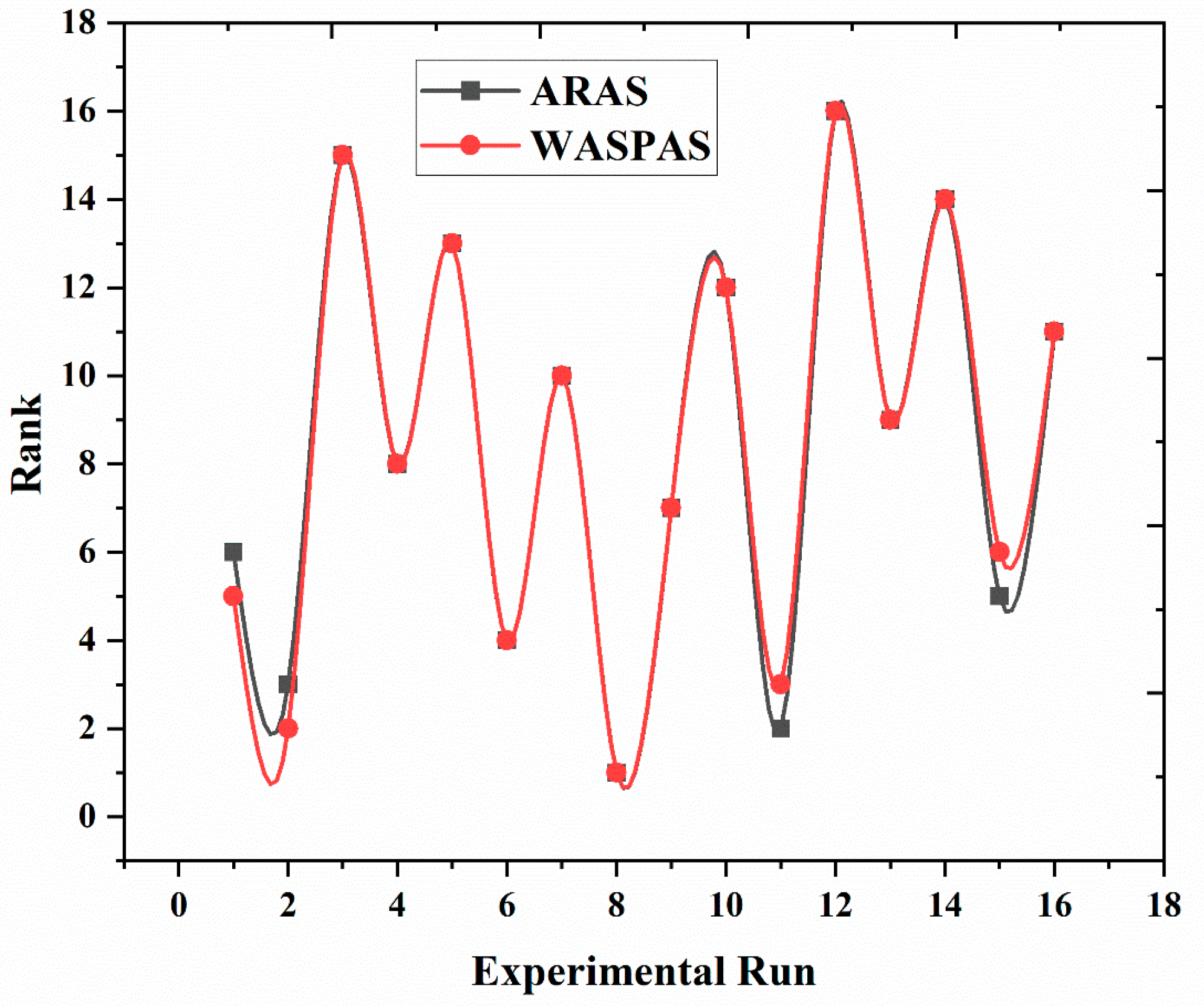
3.2. ARAS Method
- Step 1: Establish the decision matrix of criteria and alternatives.
- Step 2: Normalize the values in the decision matrix.
- Step 3: Calculate the weighted normalized values.
- Step 4: Compute the optimality function values.
- Step 5: Determine the utility degree of alternative.
3.3. WASPAS
- Step 1: Normalize the values in the decision matrix.
- Step 2: Calculating the weighted sum and weighted product of values.
- Step 3: Determine the overall relative index.
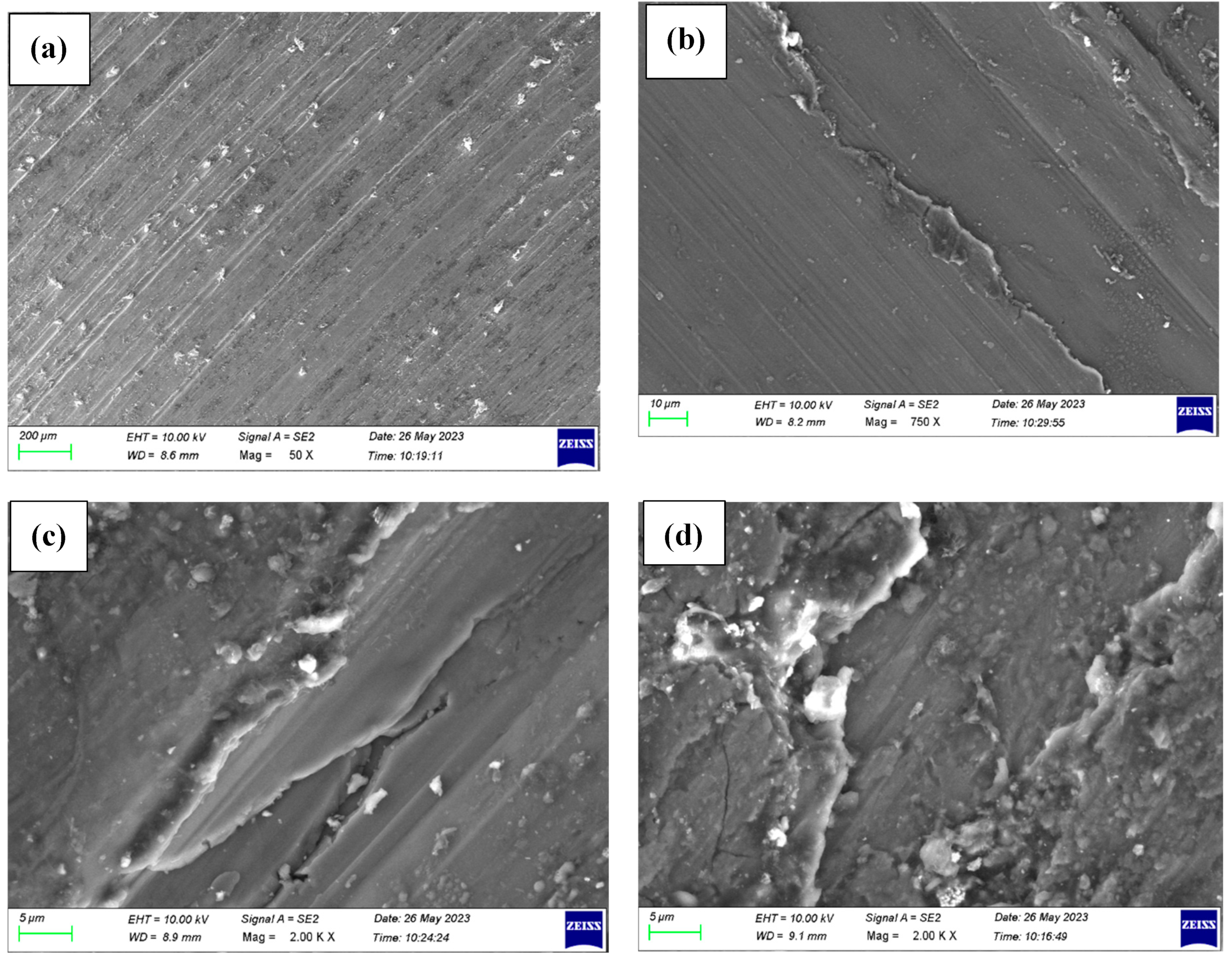
3.4. Wear Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meher, A.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Samal, P.; Vundavilli, P.R. Study on effect of TiB2 reinforcement on the microstructural and mechanical properties of magnesium RZ5 alloy based metal matrix composites. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 8, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, L.; Yin, M.; Xu, S.; Liang, Z. Review on magnesium and magnesium-based alloys as biomaterials for bone immobilization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 4396–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanavelbabu, A.; Prahadeeswaran, M.; Rai, R.; Ross, N.S.; Gupta, M.K. Tribo-Corrosive Wear Behaviour of Squeeze-Casted MG/TIN/HBN Composite under Different Ageing Temperature. Tribol. Int. 2023, 187, 108748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, S.V.; Singh, S.P.; Sinha, P.; Bhingole, P.P.; Chaudhari, G.P. Microstructural evolution in ultrasonically processed in situ AZ91 matrix composites and their mechanical and wear behavior. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez, S.; Torres, B.; Maroto, A.; López, A.J.; Otero, E.; Rams, J. Dry sliding wear behavior of globular AZ91 magnesium alloy and AZ91/SiCp composites. Wear 2017, 390–391, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.R.; Liu, J.D.; Han, Z.W.; Yuan, D.S. Microstructure and wear resistance of electrodeposited Ni-SiO2 nano-composite coatings on AZ91HP magnesium alloy substrate. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2011, 21 (Suppl. 2), s483–s488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aatthisugan, I.; Rose, A.R.; Jebadurai, D.S. Mechanical and wear behaviour of AZ91D magnesium matrix hybrid composite reinforced with boron carbide and graphite. J. Magnes. Alloys 2017, 5, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, P.; Selvakumar, N. Tensile, compressive and wear behaviour of self-lubricating sintered magnesium based composites. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2017, 27, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasathyakawin, S.; Ravichandran, M. Fabrication and wear behaviour of Mg-3wt.%Al-x wt. % SiC composites. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moheimani, S.K.; Keshtgar, A.; Khademzadeh, S.; Tayebi, M.; Rajaee, A.; Saboori, A. Tribological behaviour of AZ31 magnesium alloy reinforced by bimodal size B4C after precipitation hardening. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 3267–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavimani, V.; Prakash, K.S.; Thankachan, T. Experimental investigations on wear and friction behaviour of SiC@r-GO reinforced Mg matrix composites produced through solvent-based powder metallurgy. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 162, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, B.; Marimuthu, P.; Narayanasamy, R.; Anandakrishnan, V.; Tun, K.S.; Gupta, M.; Kamaraj, M. Dry sliding wear behaviour of zinc oxide reinforced magnesium matrix nano-composites. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Sahoo, B.N.; Panigrahi, S.K. Investigation into machining performance of microstructurally engineered in-situ particle reinforced magnesium matrix composite. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 916–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.Y.H.; Lim, S.C.; Gupta, M. Wear behaviour of SiCp-reinforced magnesium matrix composites. Wear 2003, 255, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacikowski, M.; Betiuk, M.; Cymerman, K.; Pisarek, M.; Pokorska, I.; Wierzchoń, T. High performance corrosion and wear resistant composite titanium nitride layers produced on the AZ91D magnesium alloy by a hybrid method. J. Magnes. Alloys 2014, 2, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Abbas, A.; Ballóková, B. Effect of CNT on microstructure, dry sliding wear and compressive mechanical properties of AZ61 magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4273–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.Z.; Shamsuri, S.R.B.; Chang, S.Y.; Rashid, M.W.A.; Ahsan, Q. Effect of sliding velocity on wear behavior of magnesium composite reinforced with SiC and MWCNT. Procedia Eng. 2013, 68, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, M.; Loganathan, C.; Kamaraj, M.; Nguyen, Q.B.; Gupta, M.; Narayanasamy, R. Sliding wear behaviour of AZ31B magnesium alloy and nano-composite. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China Engl. Ed. 2012, 22, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.K.; Kumar, S. Dry sliding wear behaviour of magnesium alloy based hybrid composites in the longitudinal direction. Wear 2009, 267, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z. A new additive ratio assessment (ARAS) method in multicriteria decision-making. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 2010, 16, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavadskas, E.K.; Turskis, Z.; Antucheviciene, J. Optimization of weighted aggregated sum product assessment. Elektronika Ir Elektrotechnika 2012, 122, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, N.; Shivamurthy, B.; Thimmappa, B.H.; Gupta, A.; Guo, J.Z.; Seok, I. A review on processing methods and characterization techniques of green composites. Eng. Sci. 2022, 20, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, P.; Ranjan, R.; DeSouza, V.; Bhat, R.; Patil, S.; Maddodi, B.; Shivamurthy, B.; Perez, T.C.; Naik, N. Enhanced Wear Resistance in Carbon Nanotube-Filled Bio-Epoxy Composites: A Comprehensive Analysis via Scanning Electron Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, B.R.N.; Rao, U.S.; Naik, N.; Potti, S.R.; Nambiar, S.S. A Study to Investigate the Influence of Machining Parameters on Delamination in the Abrasive Waterjet Machining of Jute-Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: An Integrated Taguchi and Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Optimization to Minimize Delamination. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, R.; Hegde, A.; Shetty SV, U.K.; Nayak, R.; Naik, N.; Nayak, M. Processing and Mechanical Characterisation of Titanium Metal Matrix Composites: A Literature Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
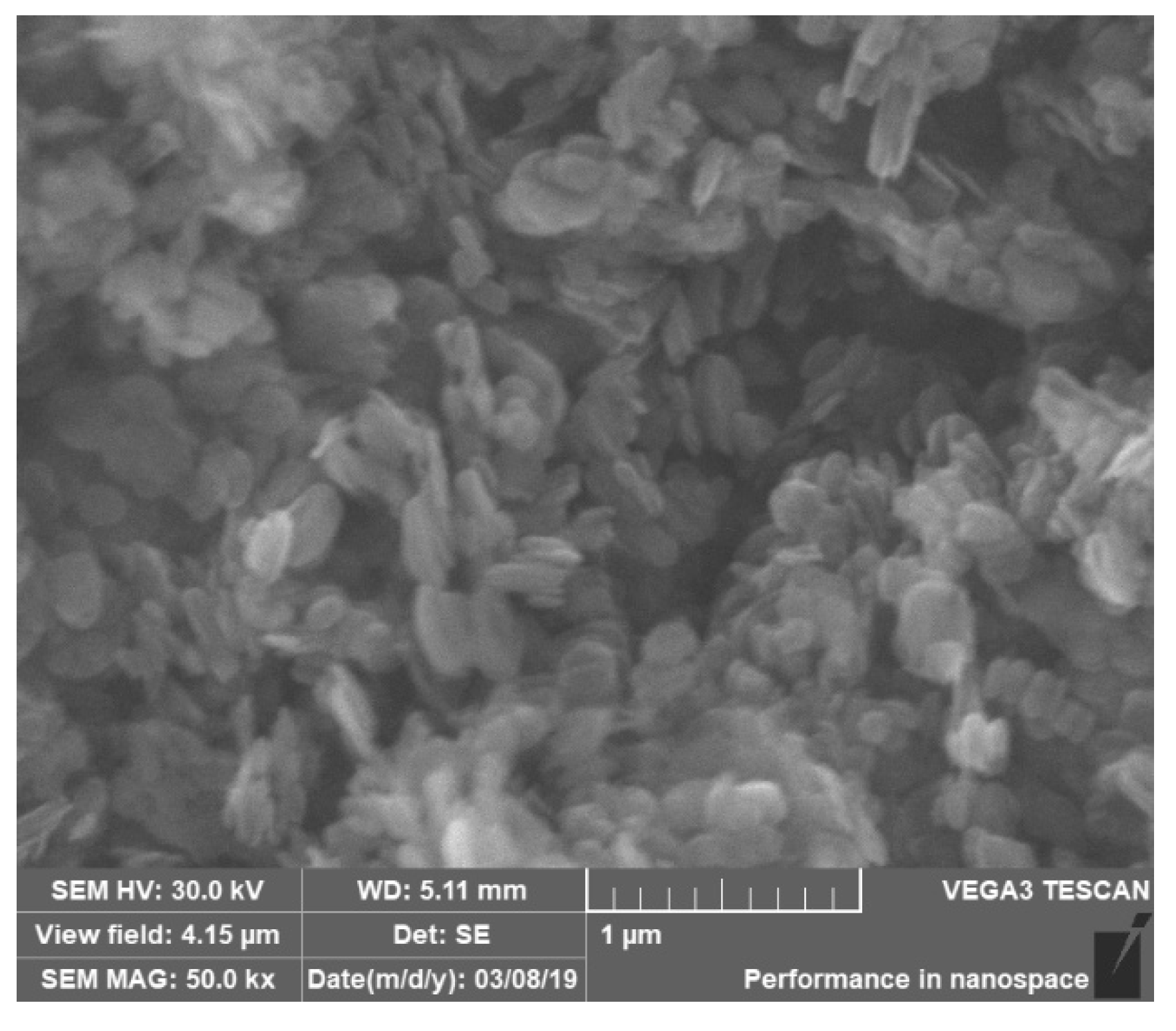
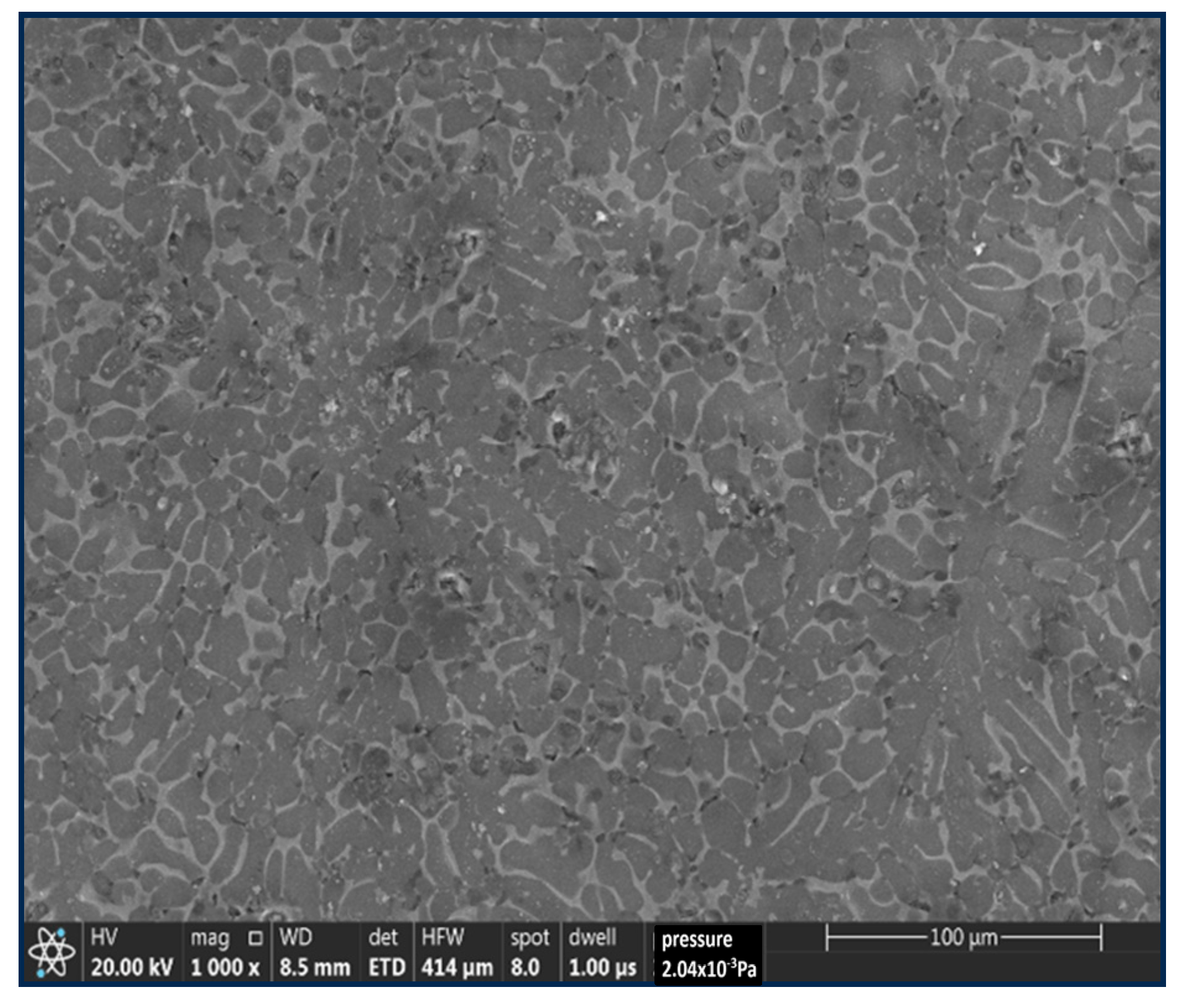

| Element | Al | Zn | Mn | Si | Fe | Cu | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt.% | 8.6 | 0.9 | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.005 | 0.003 | Balance |
| S. No. | Factors | Levels |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Normal load (N) | 5, 10, 25, 30 |
| 2. | Sliding speed (m/s) | 0.5, 1, 2.5, 3 |
| 3. | Sliding distance (m) | 500, 750, 1500, 3000 |
| 4. | Nano hBN (Wt.%) | 0, 0.5, 1, 1.5 |
| Exp. No. | Normal Load (N) | Sliding Speed (m/s) | Sliding Distance (m) | Nano hBN (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 5 | 0.5 | 500 | 0 |
| 2. | 5 | 1 | 750 | 0.5 |
| 3. | 5 | 2.5 | 1500 | 1 |
| 4. | 5 | 3 | 3000 | 1.5 |
| 5. | 10 | 0.5 | 750 | 1 |
| 6. | 10 | 1 | 500 | 1.5 |
| 7. | 10 | 2.5 | 3000 | 0 |
| 8. | 10 | 3 | 1500 | 0.5 |
| 9. | 25 | 0.5 | 1500 | 1.5 |
| 10. | 25 | 1 | 3000 | 1 |
| 11. | 25 | 2.5 | 500 | 0.5 |
| 12. | 25 | 3 | 750 | 0 |
| 13. | 30 | 0.5 | 3000 | 0.5 |
| 14. | 30 | 1 | 1500 | 0 |
| 15. | 30 | 2.5 | 750 | 1.5 |
| 16. | 30 | 3 | 500 | 1 |
| Exp. No. | Wear Loss (mg) | COF |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0.005 | 0.23 |
| 2. | 0.007 | 0.15 |
| 3. | 0.025 | 0.32 |
| 4. | 0.005 | 0.34 |
| 5. | 0.014 | 0.29 |
| 6. | 0.004 | 0.24 |
| 7. | 0.006 | 0.38 |
| 8. | 0.002 | 0.32 |
| 9. | 0.004 | 0.3 |
| 10. | 0.013 | 0.27 |
| 11. | 0.003 | 0.29 |
| 12. | 0.045 | 0.34 |
| 13. | 0.006 | 0.37 |
| 14. | 0.027 | 0.31 |
| 15. | 0.004 | 0.28 |
| 16. | 0.007 | 0.38 |
| Level | Normal Load (N) | Sliding Speed (m/s) | Sliding Distance (m) | Nano hBN (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.13 | 13.66 | 14.09 | 13.16 |
| 2 | 13.37 | 15.60 | 14.90 | 14.45 |
| 3 | 13.48 | 13.03 | 13.10 | 13.10 |
| 4 | 12.57 | 12.25 | 12.45 | 13.83 |
| Delta | 2.56 | 3.35 | 2.45 | 1.34 |
| Rank | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| Level | Normal Load (N) | Sliding Speed (m/s) | Sliding Distance (m) | Nano hBN (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1353 | 0.1524 | 0.1449 | 0.1679 |
| 2 | 0.1570 | 0.1276 | 0.1413 | 0.1435 |
| 3 | 0.1581 | 0.1635 | 0.1635 | 0.1649 |
| 4 | 0.1730 | 0.1799 | 0.1738 | 0.1471 |
| Delta | 0.0377 | 0.0522 | 0.0325 | 0.0244 |
| Rank | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ponnarengan, H.; Kannan, S.; Kamaraj, L. Assessing the Friction and Wear Behavior of AZ91-Based Hybrid Composites Reinforced with Nano hBN/Micron TiB2 Ceramic Particles Using WASPAS and ARAS Techniques. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059156
Ponnarengan H, Kannan S, Kamaraj L. Assessing the Friction and Wear Behavior of AZ91-Based Hybrid Composites Reinforced with Nano hBN/Micron TiB2 Ceramic Particles Using WASPAS and ARAS Techniques. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 59(1):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059156
Chicago/Turabian StylePonnarengan, Hariharasakthisudhan, Sathish Kannan, and Logesh Kamaraj. 2023. "Assessing the Friction and Wear Behavior of AZ91-Based Hybrid Composites Reinforced with Nano hBN/Micron TiB2 Ceramic Particles Using WASPAS and ARAS Techniques" Engineering Proceedings 59, no. 1: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059156
APA StylePonnarengan, H., Kannan, S., & Kamaraj, L. (2023). Assessing the Friction and Wear Behavior of AZ91-Based Hybrid Composites Reinforced with Nano hBN/Micron TiB2 Ceramic Particles Using WASPAS and ARAS Techniques. Engineering Proceedings, 59(1), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059156






