A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study on Characteristics of Flow Separation in Flow Rate Measurement Using Multi-Hole Plates †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geometry of the Fluid Flow Domain
2.2. Turbulence Model and Analysis Method
2.3. Boundary Condition
2.4. Grid Independency Study
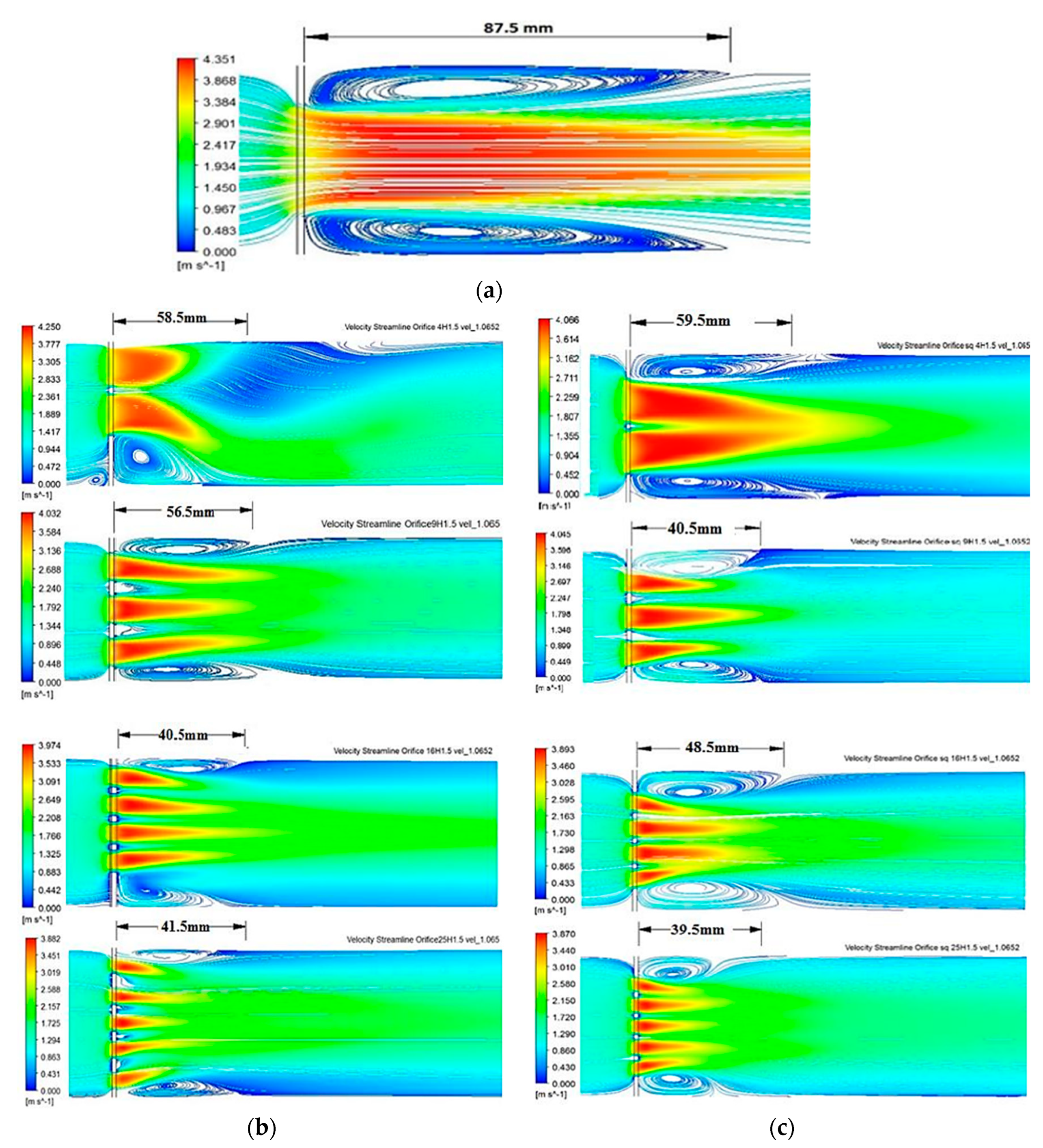
3. Results
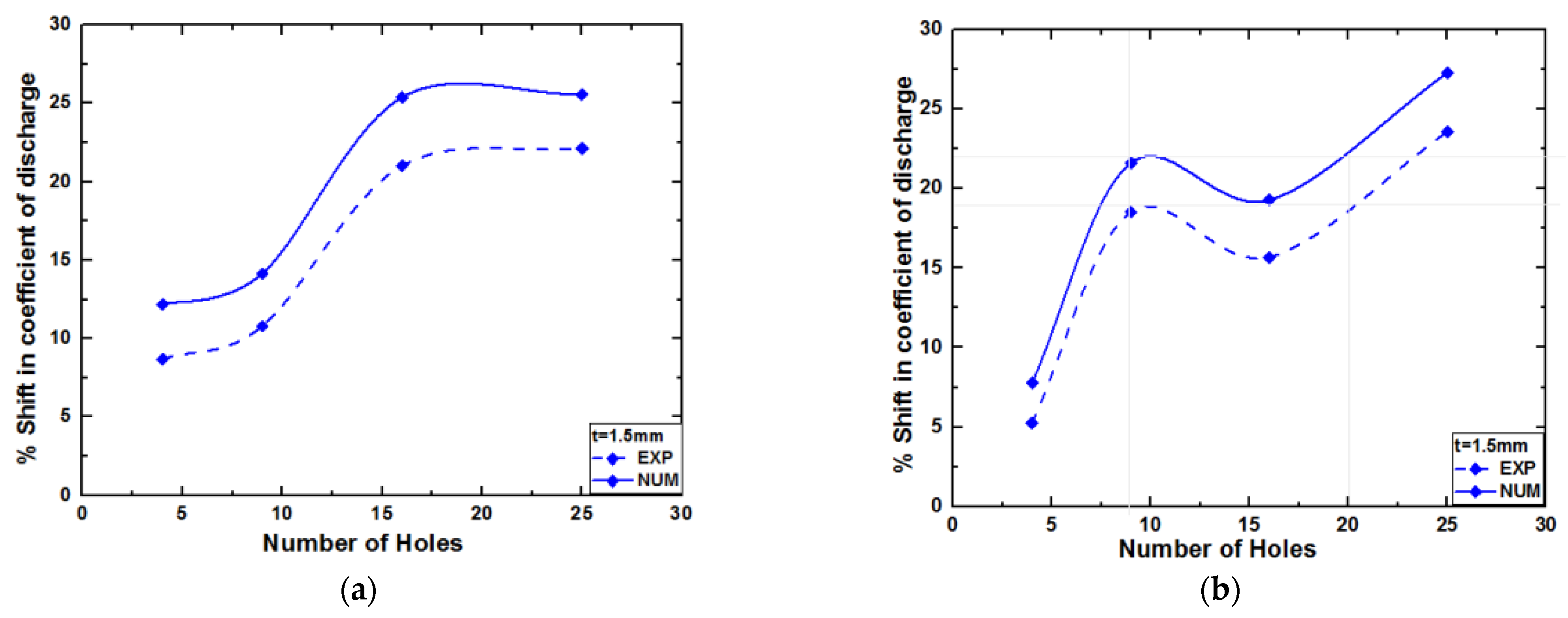
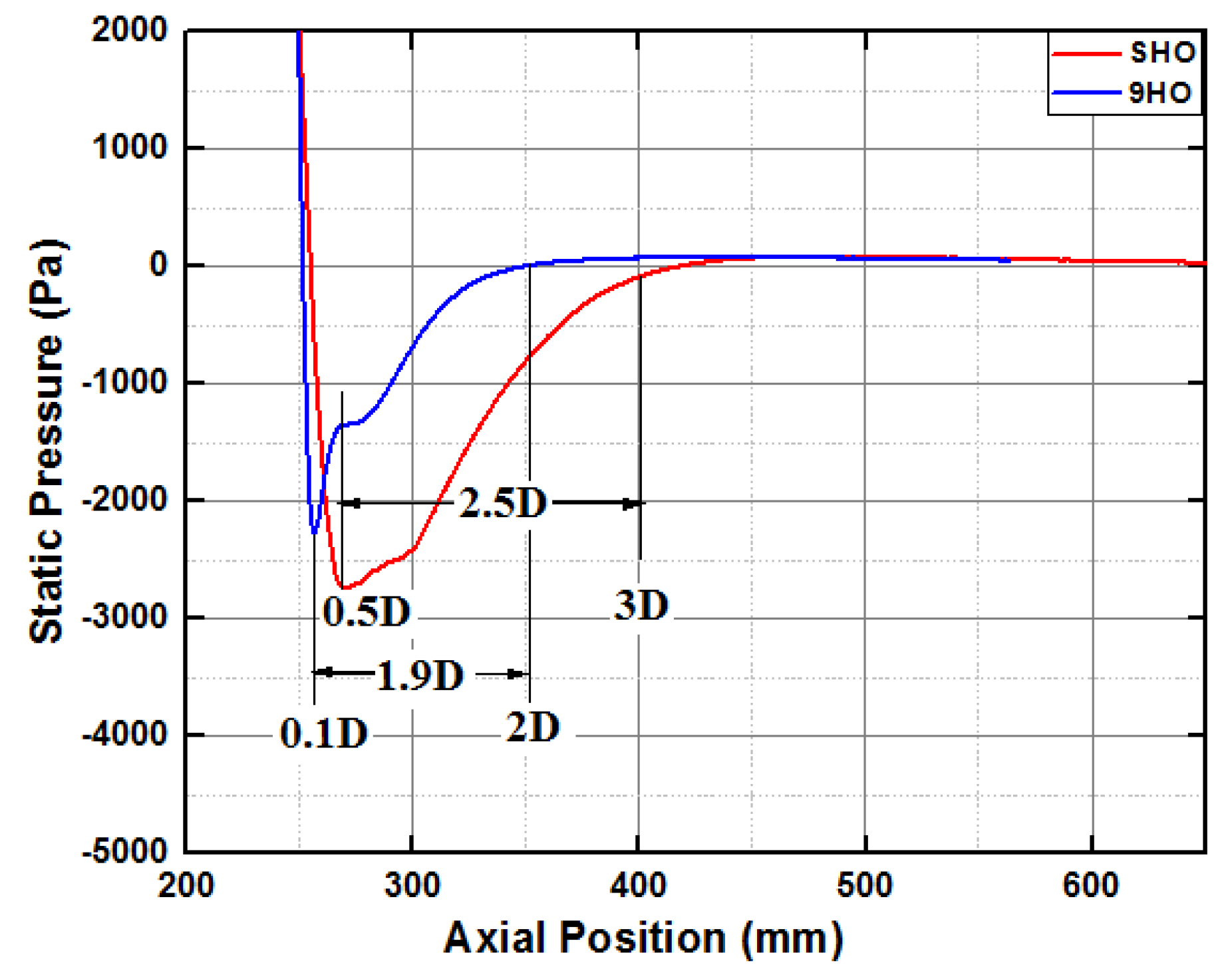
4. Discussion
Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolodzie, P.A.; Winkle, M.V. Discharge coefficients through perforated plates. Aiche J. 1957, 3, 305–312 . [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, L. A general structural design methodology for multi-hole orifices and its experimental application. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 2237–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ma, T.; Wang, D.; Lin, Z. Study on discharge coefficient of perforated orifices as a new kind of flowmeter. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2012, 46, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavasi, S.; Messa, G.; Fratino, U.; Pagano, A. On the pressure losses through perforated plates. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2012, 28, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra Babu, K.J.; Gangadhara Gowda, C.J.; Ranjith, K. Discharge Coefficient Prediction for Multi hole Orifice Plate in a Turbulent Flow through Pipe:Experimental and Numerical Investigation. Int. J. Eng. Res. Mech. Civ. Eng. 2017, 2, 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Laribi, B.; Mehdi, M. Effectiveness of Perforated Plate in the Development and Establishment of Turbulent Flow for Better Metrological Performances. Int. J. Appl. Phys. Math. 2012, 2, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynes, D.; Holt, G.J.; Blotter, J. Cavitation Inception and Head Loss Due to Liquid Flow Through Perforated Plates of Varying Thickness. ASME. J. Fluids Eng. 2013, 135, 031302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridevi, T.; Sekhar, D.; Subrahmanyam, V. Comparision of flow analysis through a different geometry of flowmeters using fluent software. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, M.H.; Kumaresh, S.K.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, C. A numerical study on the flow performance inside the straight pipe with perforated plates. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 3183–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosa, M.; Hekmat, M.H. Numerical investigation of turbulence characteristics and upstream disturbance of flow through standard and multi-hole orifice flowmeters. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2019, 65, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.N.; Ghanem, A.A. A novel comprehensive correlation for discharge coefficient of square-edged concentric orifice plate at low Reynolds numbers. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2020, 73, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Nitter, B.; Ong, M.C. Numerical simulations of turbulent flow through an orifice plate in a pipe. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2021, 143, 041903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahariea, D. Numerical Analysis of Eccentric Orifice Plate Using ANSYS Fluent Software. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 161, 012041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, A.; Przybylinski, T.; Lackowski, M. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of Multi-Hole Orifice Flow Meter: Investigation of the Relationship between Pressure Drop and Mass Flow Rate. Sensors 2020, 20, 7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrowiec, A. Uncertainty Assessment for Determining the Discharge Coefficient C for a Multi-Opening Orifice. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurga, A.P.; Janocha, M.J.; Yin, G.; Giljarhus, K.E.T.; Ong, M.C. Validation and assessment of different RANS turbulence models for simulating turbulent flow through an orifice plate. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1201, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golijanek-Jędrzejczyk, A.; Mrowiec, A.; Kleszcz, S.; Hanus, R.; Zych, M.; Jaszczur, M. A Numerical and Experimental Analysis of Multi-hole Orifice in Turbulent Flow. Measurement 2022, 193, 110910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska-Wach, B. Numerical Analysis of the Differential Flowmeter: Standard Orifice and Slotted Orifices. Energies 2023, 16, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5167-2:2003; Measurement of Fluid Flow by Means of Pressure Differential Devices Inserted in Circular Cross-Section Conduits Running Full—Part 2: Orifice Plates. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2003.
- Reader-Harris, M.; Reader-Harris, M. Orifice Discharge Coefficient. In Orifice Plates and Venturi Tubes. Experimental Fluid Mechanics; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
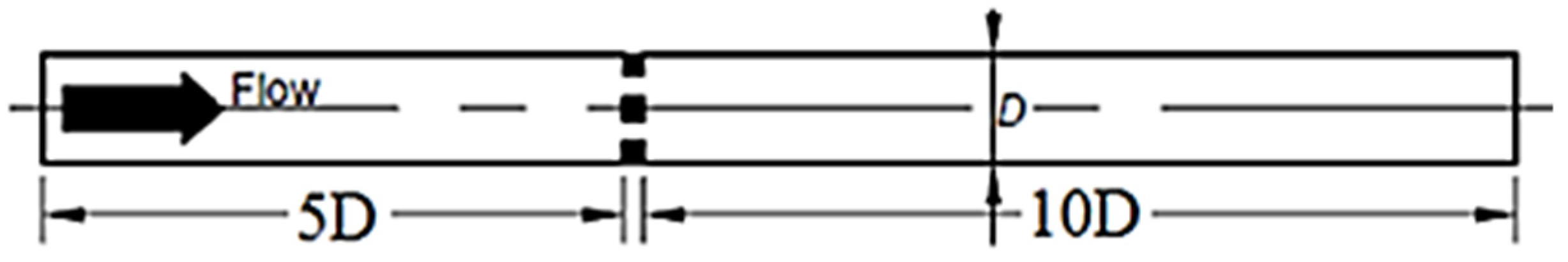
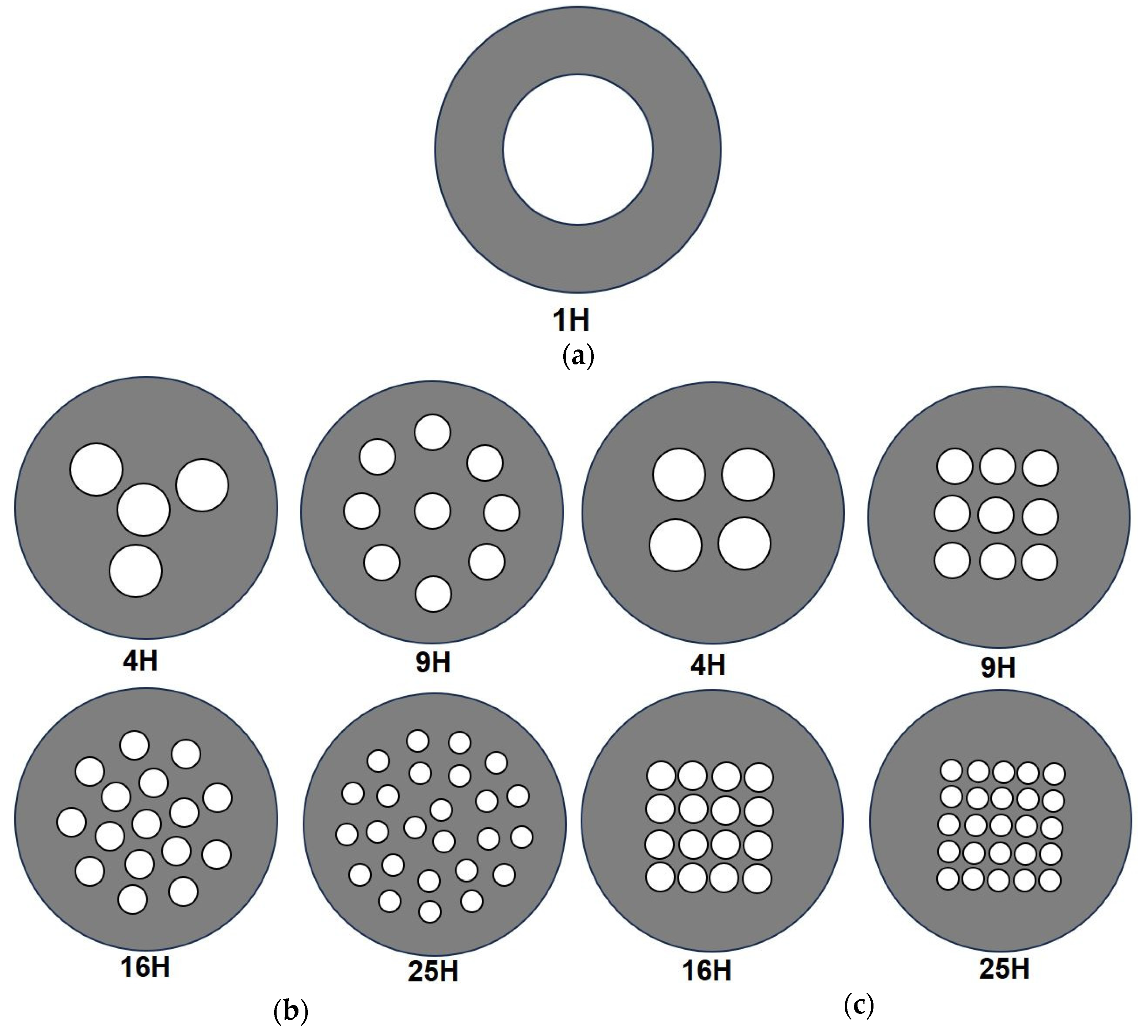
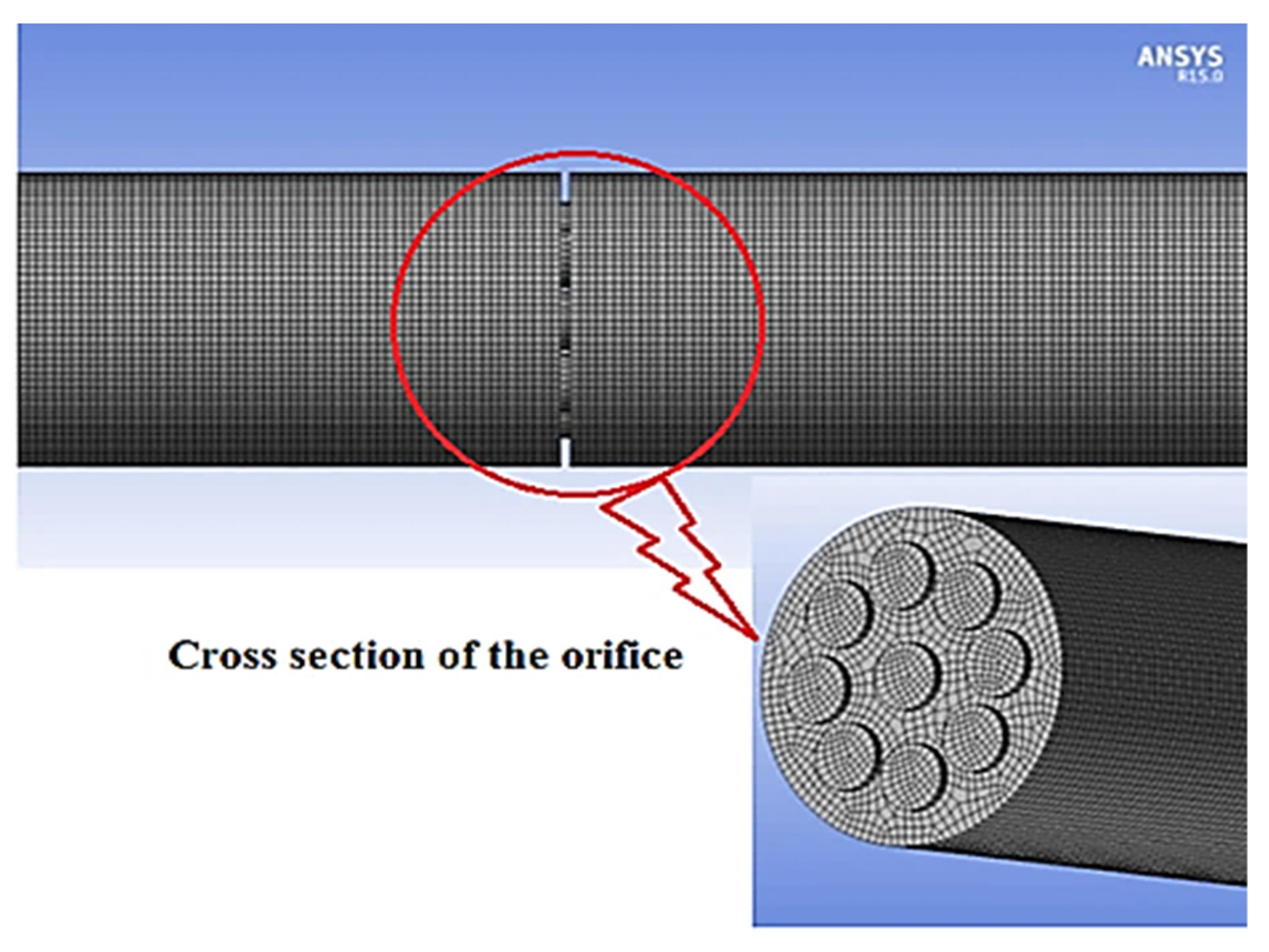
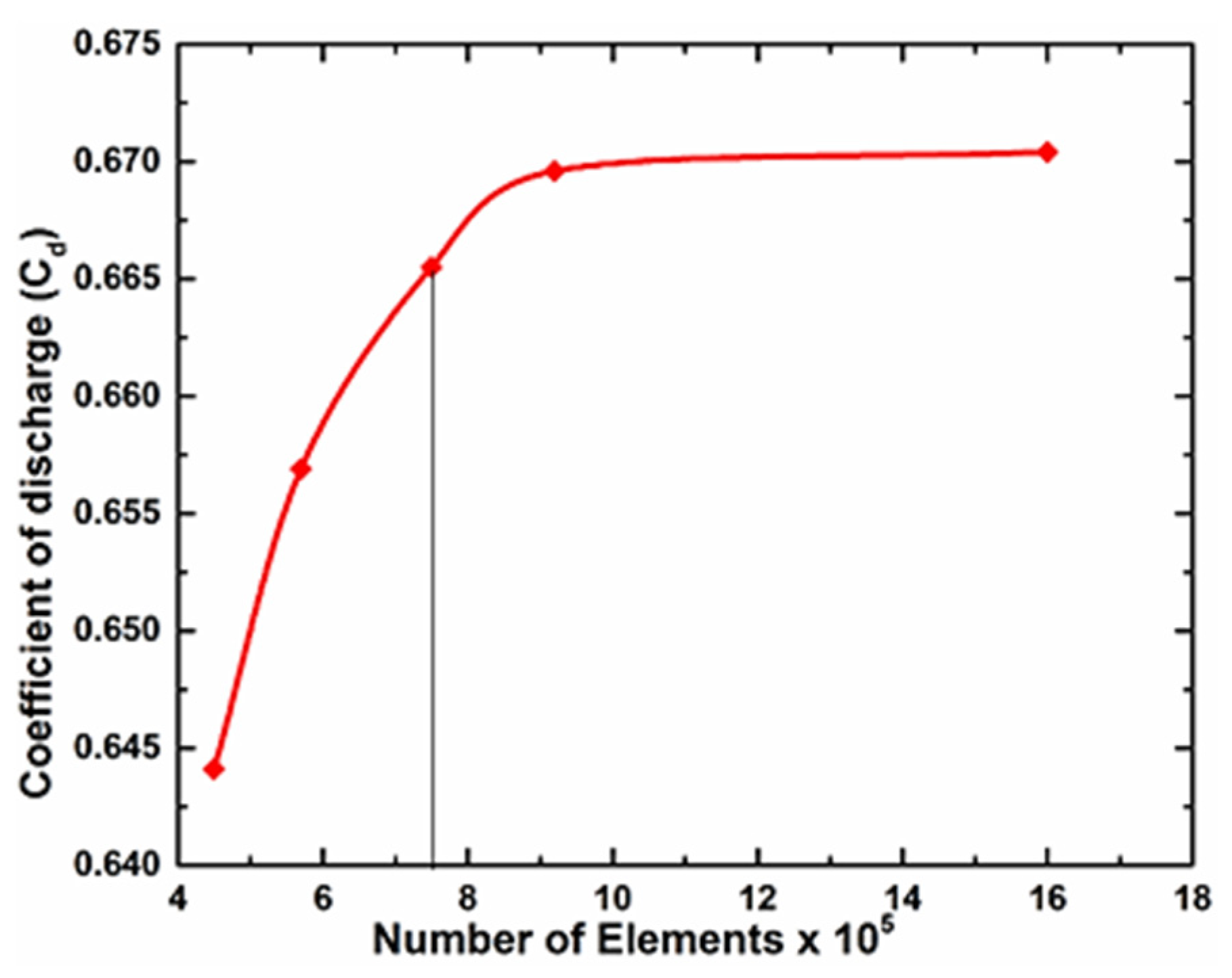

| Number of Holes | Orifice Plate Thickness, t (mm) | Diameter of Hole, d (mm) | Aspect Ratio, t/d | Beta Ratio β = d/D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 30 | 0.05 | 0.6 |
| 4 | 1.5 | 15 | 0.1 | 0.6 |
| 9 | 1.5 | 10 | 0.15 | 0.6 |
| 16 | 1.5 | 7.5 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| 25 | 1.5 | 6 | 0.25 | 0.6 |
| Parameter | Type | Value/Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Working Fluid | Water | Incompressible |
| Inlet | Velocity inlet | 0.5–1.5 m/s |
| Outlet | Pressure outlet | 0 pascals |
| Surrounding | Wall | No slip |
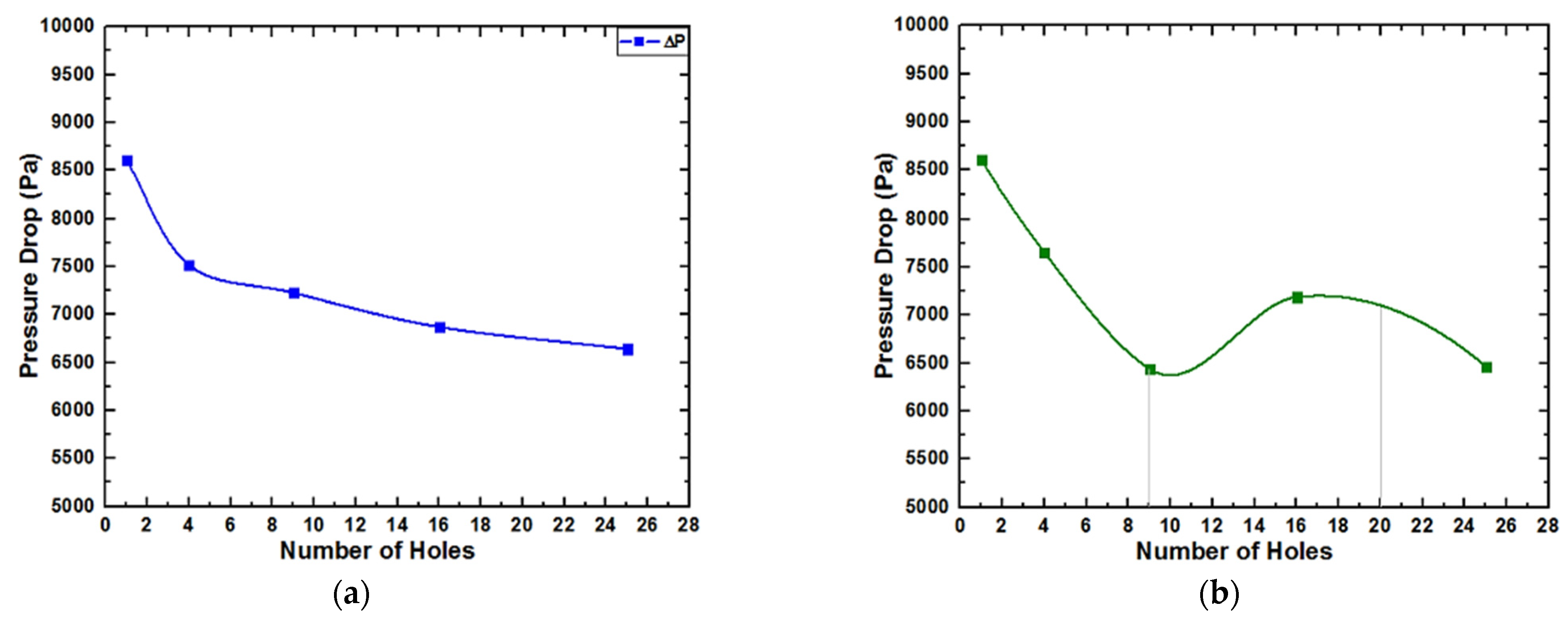
| Number of Holes | Pressure Drop (Pa) | |
|---|---|---|
| Circular Arrangement | Square Arrangement | |
| 1 | 8602.70 | 8602.70 |
| 4 | 7516.67 | 7651.14 |
| 9 | 7227.20 | 6440.14 |
| 16 | 6870.48 | 7186.89 |
| 25 | 6642.44 | 6467.27 |
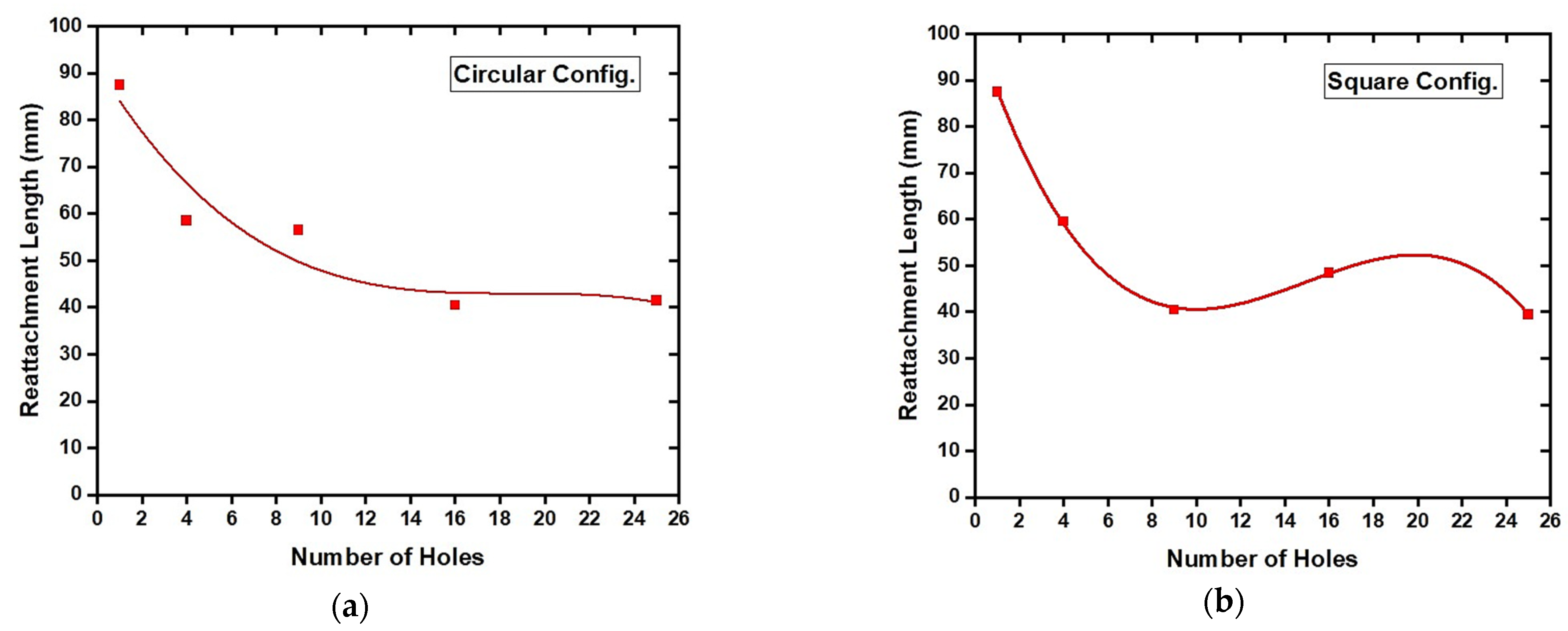
| Number of Holes | Reattachment Length (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Circular Arrangement | Square Arrangement | |
| 1 | 87.5 | 87.5 |
| 4 | 58.5 | 59.5 |
| 9 | 56.5 | 40.5 |
| 16 | 40.5 | 48.5 |
| 25 | 41.5 | 39.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Babu, K.J.M.; Gowda, C.J.G.; Ranjith, K. A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study on Characteristics of Flow Separation in Flow Rate Measurement Using Multi-Hole Plates. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059048
Babu KJM, Gowda CJG, Ranjith K. A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study on Characteristics of Flow Separation in Flow Rate Measurement Using Multi-Hole Plates. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 59(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059048
Chicago/Turabian StyleBabu, K. J. Mahendra, C. J. Gangadhara Gowda, and K. Ranjith. 2023. "A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study on Characteristics of Flow Separation in Flow Rate Measurement Using Multi-Hole Plates" Engineering Proceedings 59, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059048
APA StyleBabu, K. J. M., Gowda, C. J. G., & Ranjith, K. (2023). A Computational Fluid Dynamics Study on Characteristics of Flow Separation in Flow Rate Measurement Using Multi-Hole Plates. Engineering Proceedings, 59(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059048






