Impact of Filler Electrodes on Welding Properties of Dissimilar Welded 316L/201 Austenitic Stainless Steels †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microstructural and Mechanical Studies
2.2. Electrochemical Studies
3. Results
3.1. Microstructural Analysis
3.1.1. Solidification Mode and δ-Ferrite Content Estimation
3.1.2. Microstructural Evolution
3.2. Mechanical and Corrosion Properties
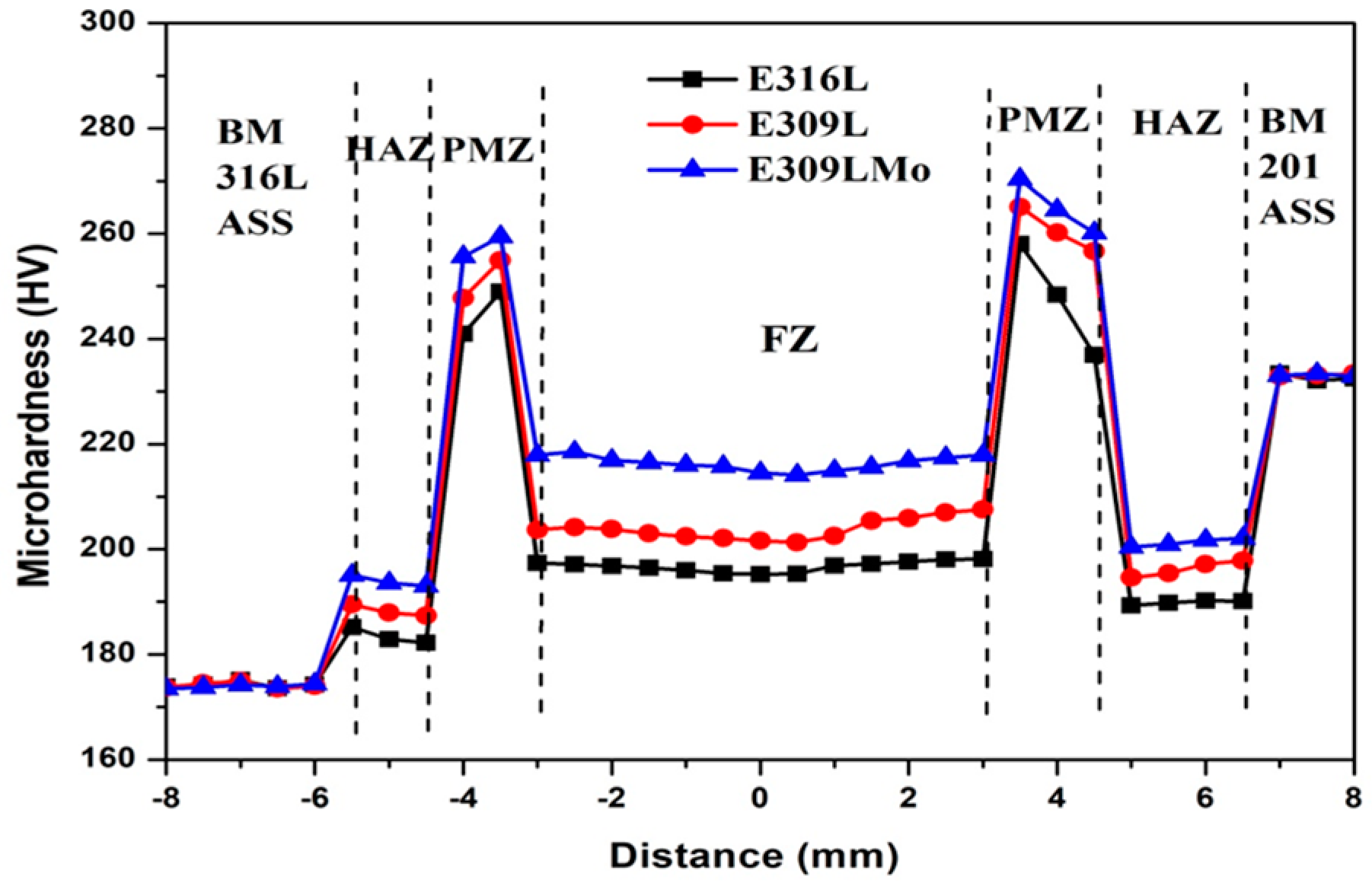
3.2.1. Microhardness Analysis
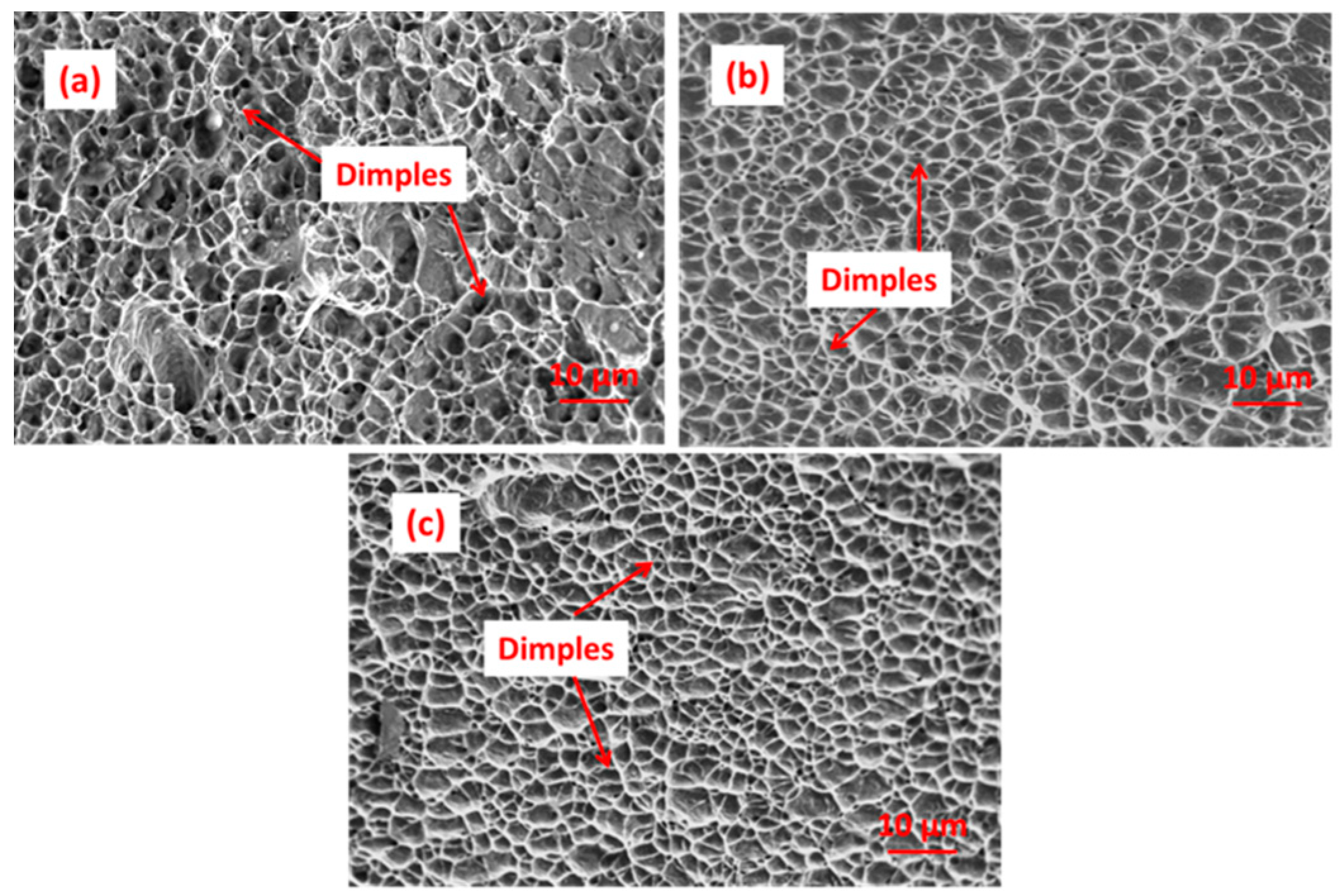
3.2.2. Tensile Test Analysis
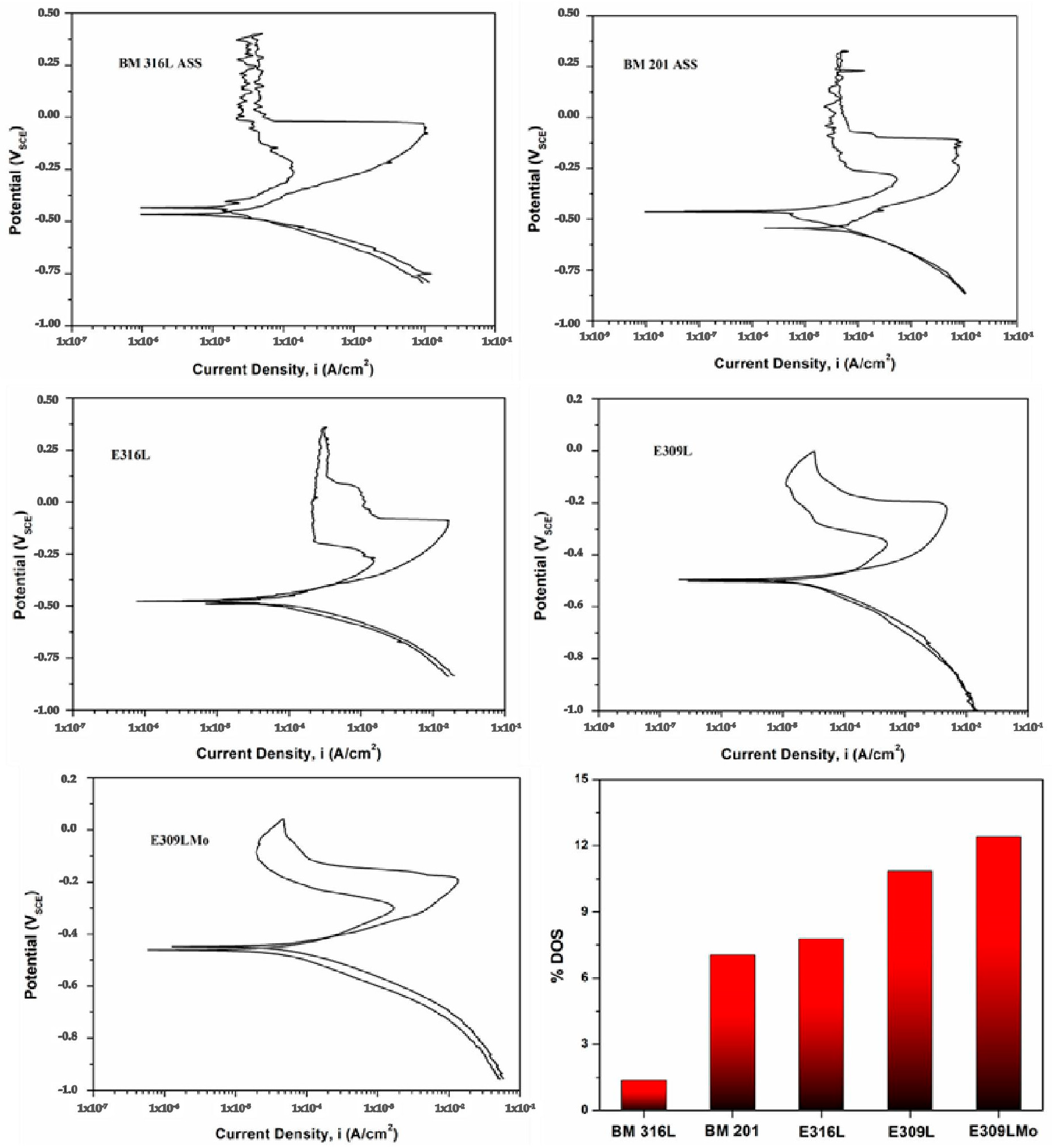
3.2.3. Electrochemical Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (i)
- In all of the weldments, a microstructure featuring skeletal ferrite and lathy ferrite was observed. A minimal amount of lathy ferrite was evident in welds made with the E316L filler electrode. Conversely, the lathy ferrite content increased when using the E309L and E309LMo filler electrodes, primarily due to their higher Cr content.
- (ii)
- The HAZ width was greater for the 201 ASS BM compared to the 316L ASS BM.
- (iii)
- The weldment employing the E309LMo filler electrode exhibited higher tensile strength, which can be attributed to the increased δ-ferrite content.
- (iv)
- Higher IGC (%DOS) was noticed in the FZ of welds made with the E309LMo filler electrode, attributable to the higher δ-ferrite content. The presence of larger interphase regions composed of ferrite and austenite accelerated the sensitization phenomenon.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Tandon, V.; Patil, A.P.; Rathod, R.C. Correlation of martensite content and dislocation density of cold worked 316L on defect densities of passivating film in acidic environment. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 086515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, V.; Patil, A.P.; Rathod, R.C. Enhanced corrosion resistance of Cr-Mn ASS by low temperature salt bath nitriding technique for the replacement of convectional Cr-Ni ASS. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2019, 66, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalipi, R.; Borgese, L.; Casaroli, A.; Boniardi, M.; Fittschen, U.; Tsuji, K.; Depero, L.E. Study of metal release from stainless steels in simulated food contact by means of total reflection X-ray fluorescence. J. Food Eng. 2016, 173, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, N.; Hirakawa, N.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Takaki, S. Grain refinement of nickel-free high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel by reversion of eutectoid structure. Scr. Mater. 2007, 57, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, X.; Han, E.-H.; Ke, W.; Yang, K.; Jiang, Z. Effects of nitrogen on the passivation of nickel-free high nitrogen and manganese stainless steels in acidic chloride solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 4005–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, S.S.M.; Pardal, J.M.; da Silva, M.J.G.; Abreu, H.F.G.; da Silva, M.R. Deformation induced martensitic transformation in a 201 modified austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2009, 60, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Mi, G. Effect of parameters on microstructure and mechanical property of dissimilar joints between 316L stainless steel and GH909 alloy by laser welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 65, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, H.; Taiwade, R.V.; Sharma, S.; Patil, A.P. Effect of welding processes on microstructural and mechanical properties of dissimilar weldments between conventional austenitic and high nitrogen austenitic stainless steels. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.R.; Khedr, M.; Mahmoud, T.S.; Abdel-Aleem, H.A.; Hamada, A. Study on the Mechanical Performance of Dissimilar Butt Joints between Low Ni Medium-Mn and Ni-Cr Austenitic Stainless Steels Processed by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding. Metals 2021, 11, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishtha, H.; Taiwade, R.V.; Sharma, S. Effect of Electrodes and Post Weld Solution Annealing Treatment on Microstructures, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Dissimilar High Nitrogen Austenitic and Conventional Austenitic Stainless Steel Weldments. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaiphan, W.; Srijaroenpramong, L. Optimization of gas tungsten arc welding parameters for the dissimilar welding between AISI 304 and AISI 201 stainless steels. Def. Technol. 2019, 15, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, V.; Thombre, M.A.; Patil, A.P.; Taiwade, R.V.; Vashishtha, H. Effect of Heat Input on the Microstructural, Mechanical, and Corrosion Properties of Dissimilar Weldment of Conventional Austenitic Stainless Steel and Low-Nickel Stainless Steel. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. 2020, 9, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Taiwade, R.V. Effect of Austenitic and Austeno-Ferritic Electrodes on 2205 Duplex and 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Dissimilar Welds. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 4706–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Patil, A.P.; Rathod, R.C.; Tandon, V.; Vashishtha, H. Tailoring the Process Parameters for Ti-Stabilized 439 Ferritic Stainless Steel Welds by Cold Metal Transfer Process. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 32, 6042–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.K.; Patil, A.P.; Rathod, R.C.; Tandon, V.; Gupta, A.; Chavhan, J. Influence of filler variation on microstructural evolution, mechanical and corrosion performance of Ti-stabilized 439 ferritic stainless steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Ha, H.-Y.; Lee, T.-H. Corrosion behavior in high heat input welded heat-affected zone of Ni-free high-nitrogen Fe–18Cr–10Mn–N austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2013, 82, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Materials | C | Ni | Mo | Cr | Mn | P | Si | S | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | 0.018 | 10.62 | 2.15 | 16.85 | 1.32 | 0.02 | 0.29 | 0.01 | - | Bal. |
| 201 | 0.09 | 4.12 | - | 17.39 | 5.24 | 0.03 | 0.26 | 0.01 | 0.15 | Bal. |
| Materials | C | Ni | Mo | Cr | Mn | P | Si | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316L | 0.016 | 11.12 | 2.11 | 17.41 | 1.57 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.01 | Bal. |
| 309L | 0.03 | 12.7 | 0.07 | 23.24 | 1.21 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.01 | Bal. |
| 309LMo | 0.03 | 12.4 | 2.42 | 23.76 | 1.56 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 0.01 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tandon, V.; Patil, A.P.; Kowshik, S. Impact of Filler Electrodes on Welding Properties of Dissimilar Welded 316L/201 Austenitic Stainless Steels. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059090
Tandon V, Patil AP, Kowshik S. Impact of Filler Electrodes on Welding Properties of Dissimilar Welded 316L/201 Austenitic Stainless Steels. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 59(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059090
Chicago/Turabian StyleTandon, Vipin, Awanikumar P. Patil, and Suhas Kowshik. 2023. "Impact of Filler Electrodes on Welding Properties of Dissimilar Welded 316L/201 Austenitic Stainless Steels" Engineering Proceedings 59, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059090
APA StyleTandon, V., Patil, A. P., & Kowshik, S. (2023). Impact of Filler Electrodes on Welding Properties of Dissimilar Welded 316L/201 Austenitic Stainless Steels. Engineering Proceedings, 59(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059090






