Prediction of Machining Characteristics and Machining Performance for Grade 2 Titanium Material in a Wire Electric Discharge Machine Using Group Method of Data Handling and Artificial Neural Network †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Setup
2.1. Material Details
2.2. Experimental Details
2.3. Acoustic Emission (AE)
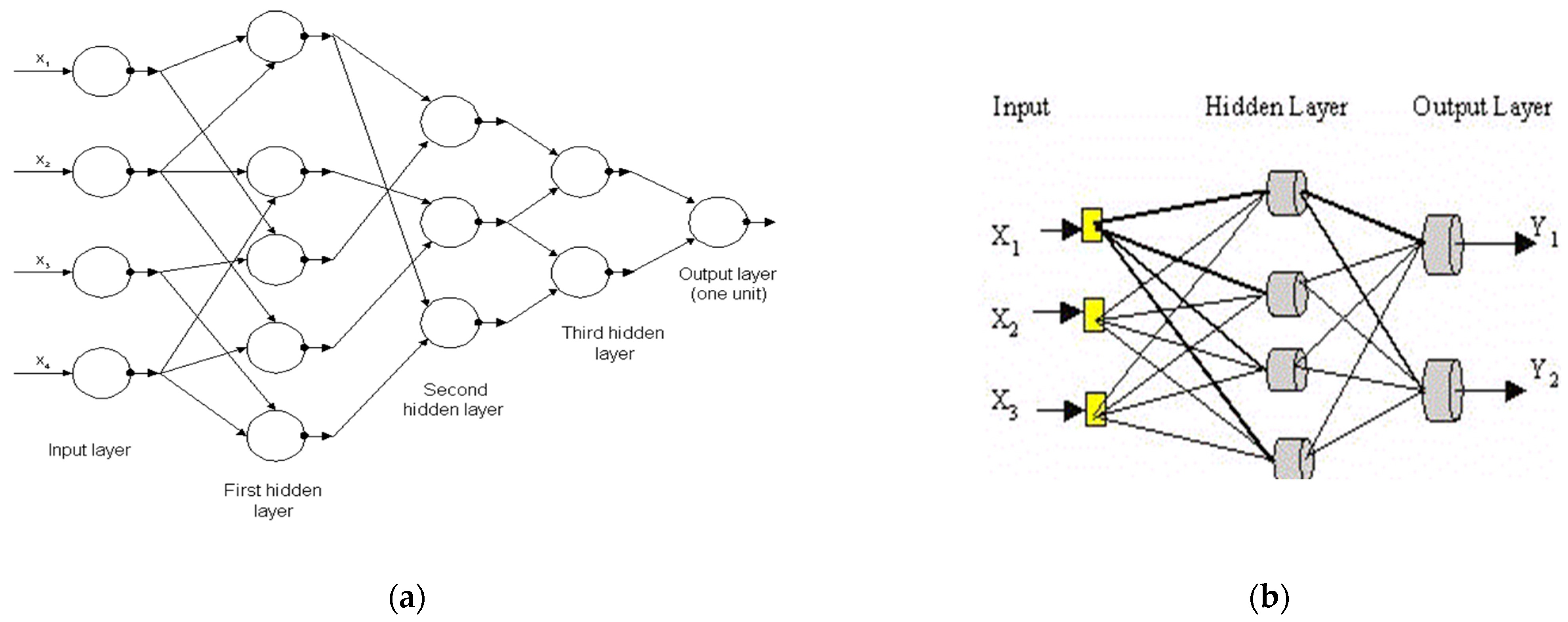
2.4. Theoretical Estimation: Group Method of Data Handling (GMDH) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Response Parameter: AE Signals
3.2. Parametric Influence on SR, EW and AE Signals on Grade-2 Titanium Material
3.3. Raw Data Analysis for Variation of Pulse on Time (Pon) and Current (C) to Know the Workpiece Status, Electrode Status and Machining Performance Status for Grade-2 Titanium Material
3.4. Theoretical Estimation of Machining Characteristics and Machining Performance Using the GMDH and ANN
3.4.1. Prediction of Minimum and Maximum Pulse on Time and Current for the EW and AERMS of Grade-2 Titanium Material Using the GMDH
3.4.2. Prediction of Minimum and Maximum Pulse on Time and Current for the EW and AERMS of Grade-2 Titanium Material Using ANN
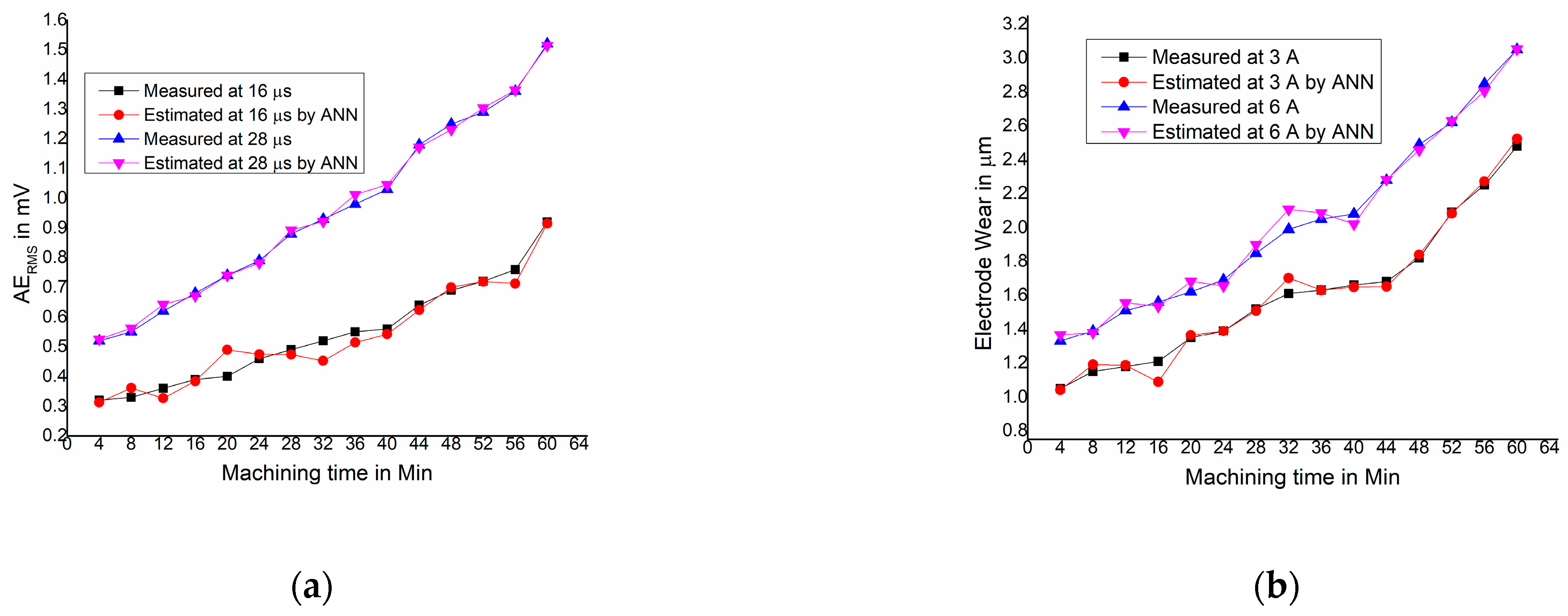
3.5. Comparative Study of the GMDH and ANN Estimates for Grade-2 Titanium Material
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sai, P.V.; Madhukar, S.; Reddy, M.K.P.; Ramachandra Rao, N.V.S. A review on machinability aspects of titanium grade-2. Int. J. Sci. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Rahul, V.; Balaji, V.; Narendranath, S. Optimization of wire-EDM process parameters for Ni-Ti-Hf shape memory alloy through particle swarm optimization and CNN-based SEM-image classification. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nain, S.S.; Garg, D.; Kumar, S. Investigation for obtaining the optimal solution for improving the performance of WEDM of super alloy Udimet-L605 using particle swarm optimization. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, P.; Vijayaraghavan, L.; Ramesh Babu, N. Assessment of material removal capability with vibration-assisted wire electrical discharge machining. J. Manuf. Processes 2017, 26, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukey, K.; Sahu, A.R.; Gajghate, S.S.; Behera, A.K.; Limbadri, C.; Majumder, H. Wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) review on current optimization research trends. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, K.; Zahoor, S.; Ali Khan, S.; Rehman, M.; Alfaify, A.; Anwar, S. Minimizing the corner errors (top and bottom) at optimized cutting rate and surface finish during WEDM of Al6061. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2021, 24, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram Prasad, A.V.S.; Ramji, K.; Datta, G.L. An experimental study of Wire-EDM on Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2567–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourbakhsh, F.; Rajurkar, K.P.; Malshe, A.P.; Cao, J. Wire electro-discharge machining of titanium alloy. Procedia CIRP 2013, 5, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Kumar, S.; Khan, Z.A.; Siddiquee, A.N. An investigation on effects of wire electrical discharge machining parameters on surface roughness of newly developed hybrid metal matrix composite. J. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 228, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A. Investigation of material removal rate and surface roughness during wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM) of Inconel 625 super alloy by cryogenic treated tool electrode. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2017, 29, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Khanna, R.; Gupta, R. Multi quality characteristics of WEDM process parameters with RSM. Procedia Eng. 2013, 64, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Uthayakumar, M.; Kumaran, S.T.; Parameswaran, P.; Hannef, T.K.; Mukhopadhyay, C.K.; Pao, B.P.C. Performance Monitoring of WEDM Using Online Acoustic Emission Technique. Silicon 2018, 10, 2635–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathik Jain, S.; Ravindra, H.V.; Ugrasen, G.; Naveen Prakash, G.V.; Rammohan, Y.S. Study of Surface Roughness and AE Signals while Machining Titanium Grade-2 Material using ANN in WEDM. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 9557–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.M.R.; Cheruku, S.; Pasunuri, V.P.K.; Salike, S.; Reddy, N.S.; Srija, C. Machine learning and statistical approach in modeling and optimization of surface roughness in wire electrical discharge machining. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 6, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, D.; Yang, L.; Xiong, W. Formation mechanism of surface topography in low-speed wire electrical discharge machining Inconel 718 and its on-line prediction based on acoustic emission technology. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017694579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasa Rao, P.; Ramji, K.; Satyanarayana, B. Experimental investigation and optimization of wire edm parameters for surface roughness, MRR and white layer in machining of aluminium alloy. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2197–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitonde, V.N.; Manjaiah, M.; Maradi, S.; Karnik, S.R.; Petkar, P.M.; Paulo Davim, J. 7-Multiresponse optimization in wire electric discharge machining (WEDM) of HCHCr steel by integrating response surface methodology (RSM) with differential evolution (DE). In Computational Methods and Production Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, B.K.; Agarwal, S. Optimization of machining parameters in WEDM of AISI D3 steel using taguchi technique. Procedia CIRP 2014, 14, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Ali MB, M.; Shaffiar NB, M. Relationship of surface roughness with current & voltage during wire EDM. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 6, 2317–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.V.; Krishna, P.V.; Kumar, B.S.; Shashidhar, M. Optimization of process parameters during EDM of Stainless Steel 304 using taguchi method. Int. J. Eng. Trends Technol. 2016, 31, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Pandey, A.; Sharma, P. Investigation of surface roughness for Inconel 625 using wire electric discharge machining. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 377, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| S. No. | Particular | % of Composition |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | C | 0.1 |
| 2 | Fe | 0.3 |
| 3 | H | 0.015 |
| 4 | N | 0.03 |
| 5 | O | 0.25 |
| 6 | Ti | 99.2 |
| S. No. | Pon | Poff | C | BS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 20 |
| 2 | 16 | 6 | 4 | 25 |
| 2 | 16 | 8 | 5 | 30 |
| 4 | 16 | 10 | 6 | 35 |
| 5 | 20 | 4 | 4 | 30 |
| 6 | 20 | 6 | 3 | 35 |
| 7 | 20 | 8 | 6 | 20 |
| 8 | 20 | 10 | 5 | 25 |
| 9 | 24 | 4 | 5 | 35 |
| 10 | 24 | 6 | 6 | 30 |
| 11 | 24 | 8 | 3 | 25 |
| 12 | 24 | 10 | 4 | 20 |
| 13 | 28 | 4 | 6 | 25 |
| 14 | 28 | 6 | 5 | 20 |
| 15 | 28 | 8 | 4 | 35 |
| 16 | 28 | 10 | 3 | 30 |
| Parameter | SR | EW | AESS | AERMS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimized Value | F-Value | Optimized Value | F-Value | Optimized Value | F-Value | Optimized Value | F-Value | |
| Pulse on time (µs) | 20 | 12.51 | 20 | 18.39 | 16 | 54.39 | 20 | 10.10 |
| Pulse off time (µs) | 4 | 4.49 | 4 | 3.69 | 4 | 14.10 | 8 | 3.33 |
| Current (Amps) | 4 | 6.27 | 4 | 9.17 | 5 | 21.48 | 4 | 5.57 |
| Bedspeed (µm/s) | 30 | 2.52 | 25 | 2.88 | 25 | 2.23 | 35 | 2.12 |
| R-Square Value | 95.91% | 96.31% | 99.36% | 93.66% | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prathik, S.J.; Sundaramahalingam, A.; Nithyashree, M.E.; Rudreshi, A.; Ugrasen, G. Prediction of Machining Characteristics and Machining Performance for Grade 2 Titanium Material in a Wire Electric Discharge Machine Using Group Method of Data Handling and Artificial Neural Network. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059085
Prathik SJ, Sundaramahalingam A, Nithyashree ME, Rudreshi A, Ugrasen G. Prediction of Machining Characteristics and Machining Performance for Grade 2 Titanium Material in a Wire Electric Discharge Machine Using Group Method of Data Handling and Artificial Neural Network. Engineering Proceedings. 2023; 59(1):9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059085
Chicago/Turabian StylePrathik, Sudhir Jain, Athimoolam Sundaramahalingam, Maddur Eswara Nithyashree, Addamani Rudreshi, and Gonchikar Ugrasen. 2023. "Prediction of Machining Characteristics and Machining Performance for Grade 2 Titanium Material in a Wire Electric Discharge Machine Using Group Method of Data Handling and Artificial Neural Network" Engineering Proceedings 59, no. 1: 9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059085
APA StylePrathik, S. J., Sundaramahalingam, A., Nithyashree, M. E., Rudreshi, A., & Ugrasen, G. (2023). Prediction of Machining Characteristics and Machining Performance for Grade 2 Titanium Material in a Wire Electric Discharge Machine Using Group Method of Data Handling and Artificial Neural Network. Engineering Proceedings, 59(1), 9085. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2023059085






