A Hybrid Graph Hydrodynamic Method for Modelling Multiple Pipe Failure in Stormwater Networks †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Graph Theory Method
2.2. Hydrodynamic Modelling
2.3. Case Studies
3. Results and Discussion
Computational Time
4. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Möderl, M.; Kleidorfer, M.; Sitzenfrei, R.; Rauch, W. Identifying weak points of urban drainage systems by means of VulNetUD. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2507–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, D.; Van Bijnen, M.; Langeveld, J.; Korving, H.; Post, J.; Clemens, F. Identifying Critical Elements in Sewer Networks Using Graph-Theory. Water 2018, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, M.; Sitzenfrei, R.; Kleidorfer, M.; Möderl, M.; Rauch, W. GIS-based applications of sensitivity analysis for sewer models. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.E.; Bacak-Turan, G.; Cetin, T.; Aslan, E. Feasible Sanitary Sewer Network Generation Using Graph Theory. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8527180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgir, A.; Hesarkazzazi, S.; Oberascher, M.; Hajibabaei, M.; Sitzenfrei, R. Graph method for critical pipe analysis of branched and looped drainage networks. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 87, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

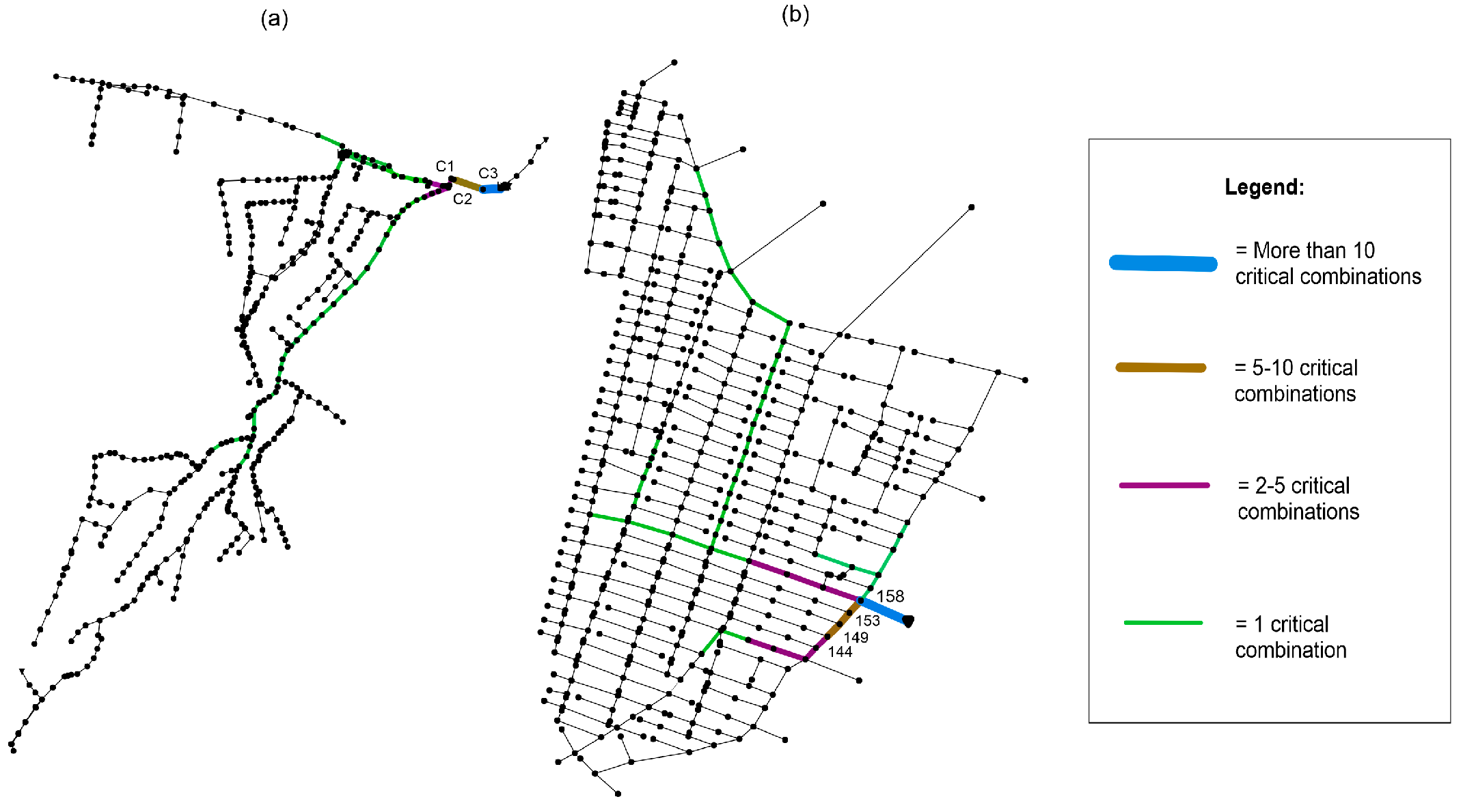
| Networks | Critical Combinations | Flooding Volumes |
|---|---|---|
| Alpine Network | 1. Pipe C3, Pipe C2 | 5520 m3 |
| 2. Pipe C3, Pipe C1 | 5431 m3 | |
| 3. Pipe C2, Pipe C1 | 5296 m3 | |
| Ahvaz Network | 1. Pipe 158, Pipe 153 | 4436 m3 |
| 2. Pipe 158, Pipe 149 | 4412 m3 | |
| 3. Pipe 158, Pipe 144 | 4366 m3 |
| Networks | GHM (hrs) | HMM (hrs) | Computational Time Gain Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpine Network | 1.68 | 172 | 102 |
| Ahvaz Network | 1.83 | 243 | 133 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dastgir, A.; Satish, R.; Hajibabaei, M.; Oberascher, M.; Sitzenfrei, R. A Hybrid Graph Hydrodynamic Method for Modelling Multiple Pipe Failure in Stormwater Networks. Eng. Proc. 2024, 69, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069097
Dastgir A, Satish R, Hajibabaei M, Oberascher M, Sitzenfrei R. A Hybrid Graph Hydrodynamic Method for Modelling Multiple Pipe Failure in Stormwater Networks. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 69(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069097
Chicago/Turabian StyleDastgir, Aun, Rahul Satish, Mohsen Hajibabaei, Martin Oberascher, and Robert Sitzenfrei. 2024. "A Hybrid Graph Hydrodynamic Method for Modelling Multiple Pipe Failure in Stormwater Networks" Engineering Proceedings 69, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069097
APA StyleDastgir, A., Satish, R., Hajibabaei, M., Oberascher, M., & Sitzenfrei, R. (2024). A Hybrid Graph Hydrodynamic Method for Modelling Multiple Pipe Failure in Stormwater Networks. Engineering Proceedings, 69(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024069097








