CT-Based Defect Analysis in Aluminium Rotor End Rings †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method, Results, and Discussion
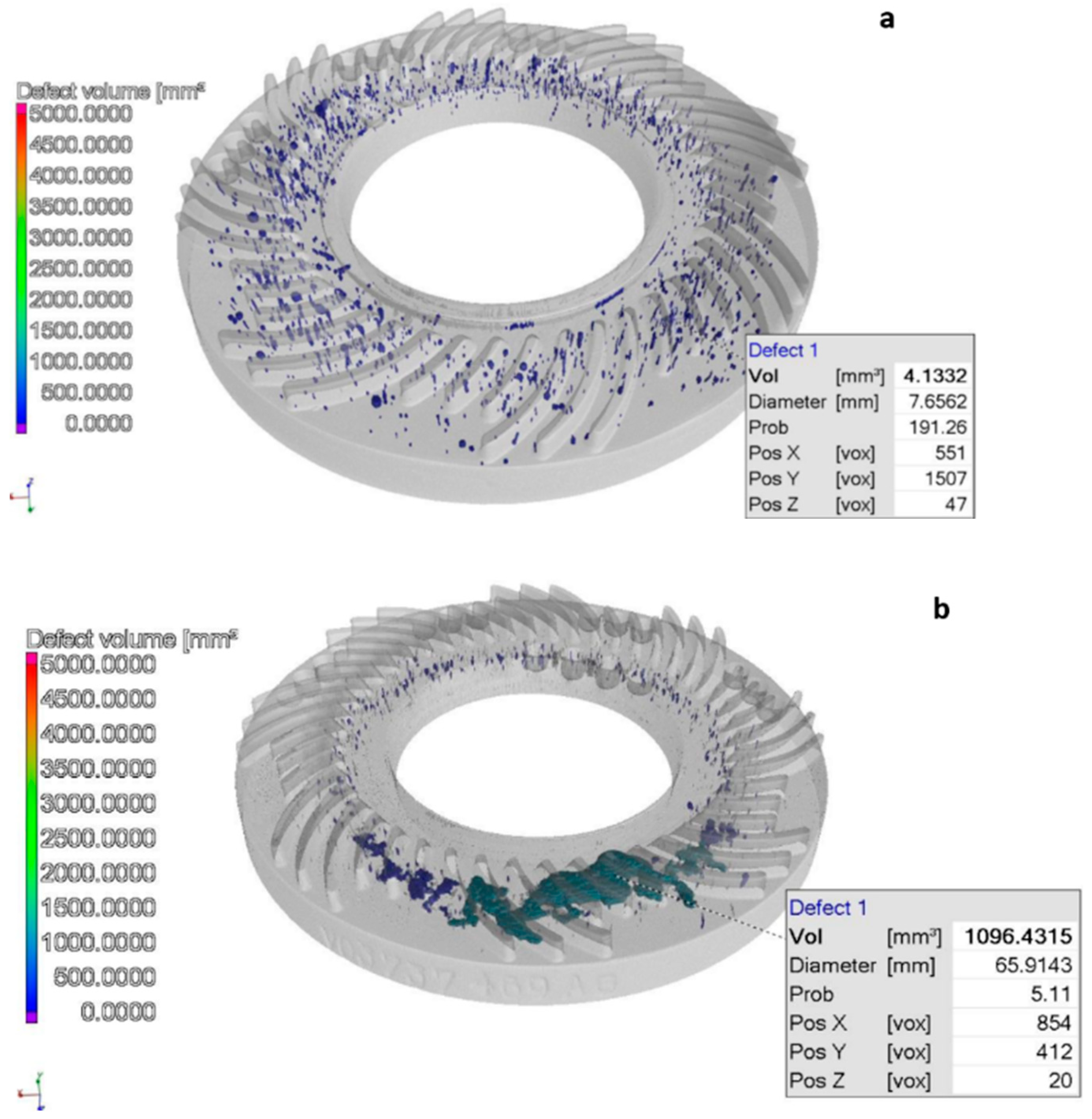
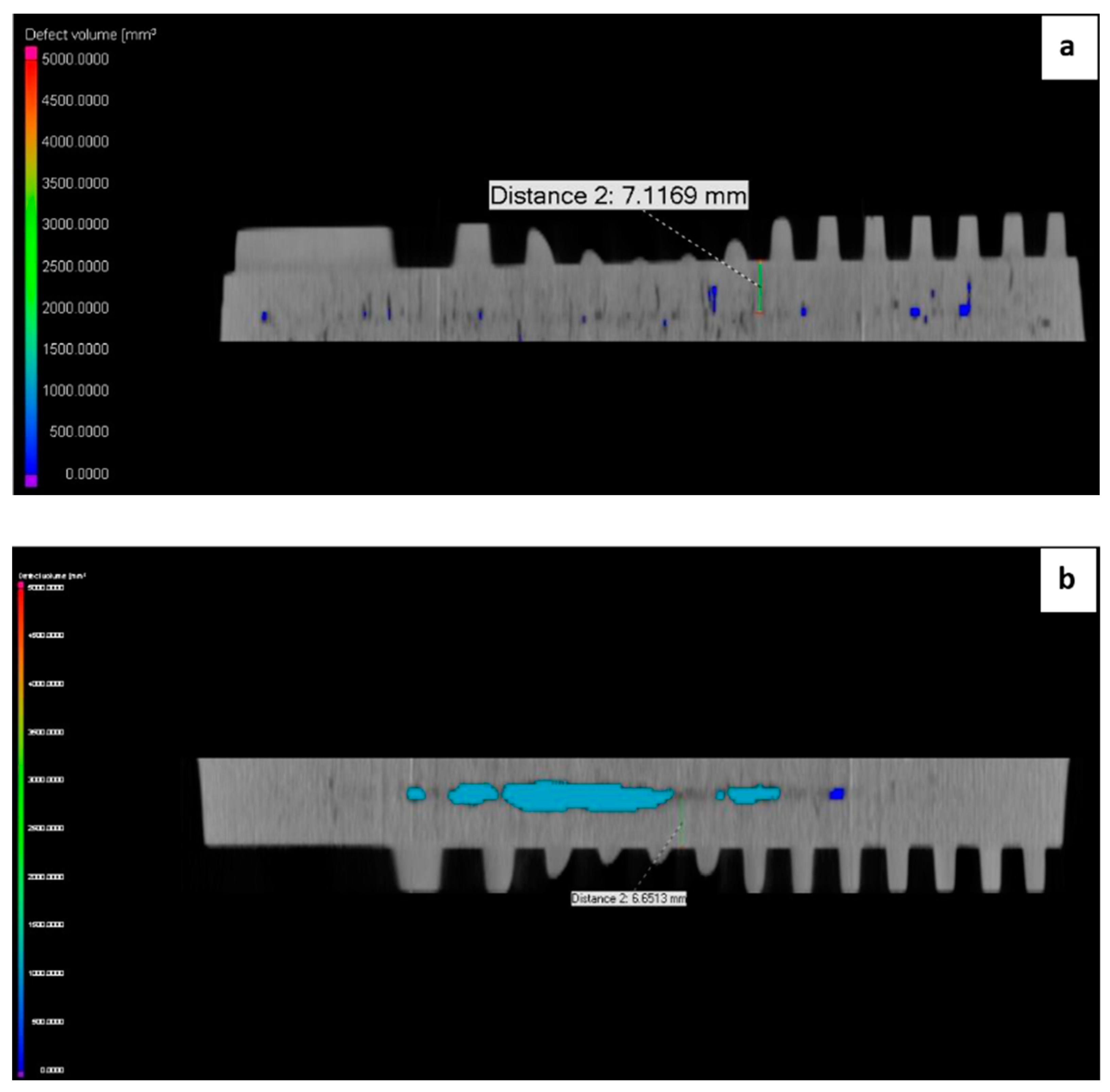
- A total of 123 porosities were found;
- The majority of the porosities was smaller than 0.5 mm3;
- The largest porosity was also smaller than 1.5 mm3.
- In the part marked “B”:
- We found much more, a total of 360 porosities;
- Only less than half of this quantity (168 pieces) was smaller than 0.5 mm3;
- The quantity (18 pieces) of larger porosities—with a volume between 3 mm3 and 4.5 mm3—was also significant.
3. Conclusions
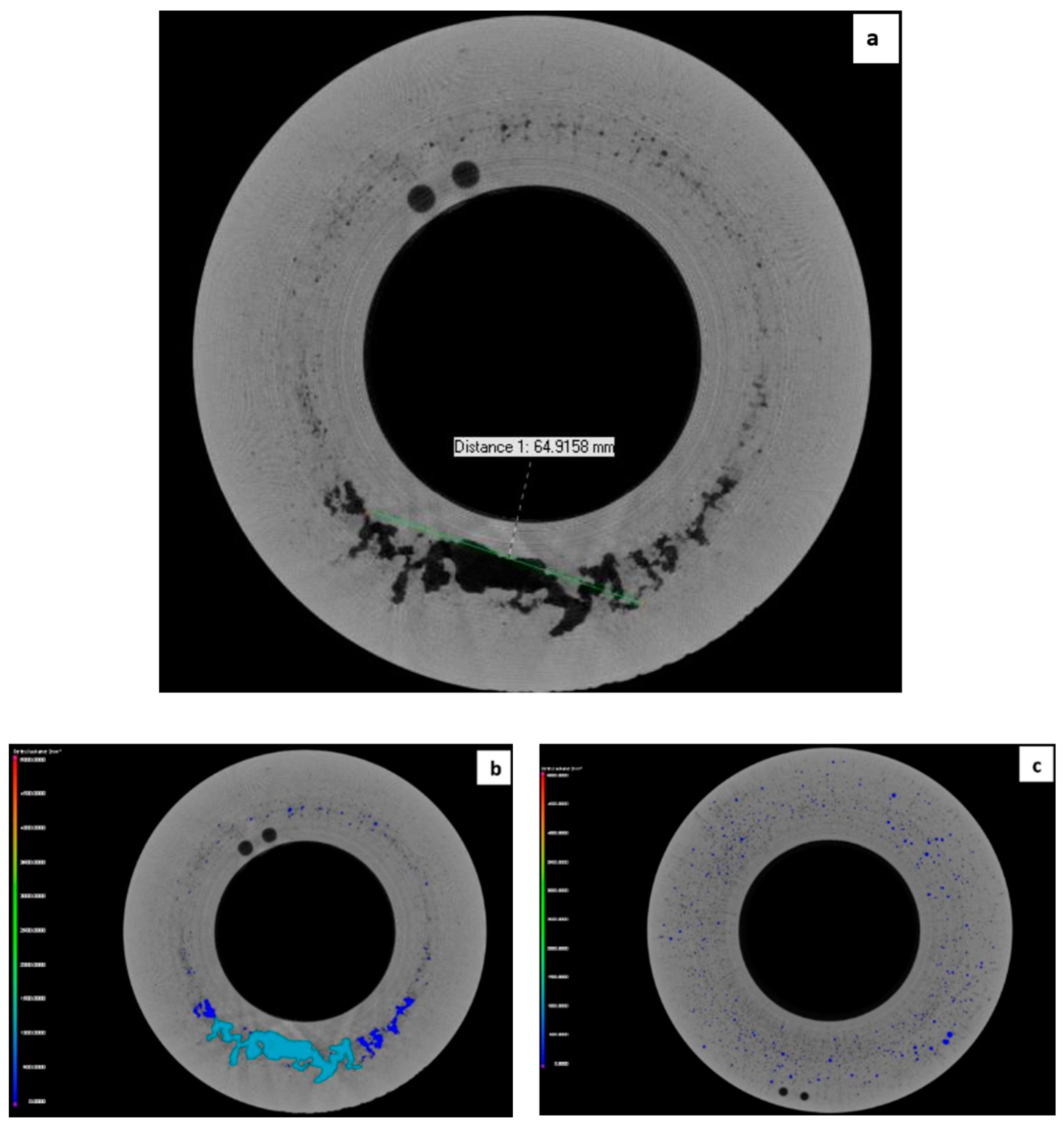
- Discontinuities, volume lunkers, and porosities appeared in the middle part of the volume and in the vicinity of the centre lines, both in the case of good- and poor-quality casting.
- There were large differences in the number and size of porosities. With proper casting technology, only about 120 porosities were found, and the volume of all of them was less than 1.5 mm3. We experienced a rapid increase in the number of porosities and their size in the second examined part, and this indicates an inadequate technological implementation. There were 360 porosities, where the number of volumes between 3–4.5 mm3 was still significant.
- We also found a big difference in the distribution of porosities. In the case of the first examined part, the uniform, homogeneous distribution indicates appropriate technology, while in the case of the second examined part, highly inhomogeneous porosities indicate improper technology.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.C.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, C.W.; Cho, J.I.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, C.S. Limitation of Shrinkage Porosity in Aluminum Rotor Die Casting. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Aluminum Alloys (ICAA 13), Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 3 June 2012; pp. 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.B.; Hyun, D.; Kang, T.J.; Yang, C.; Shin, S.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Kong, T.S.; Kim, H.D. Identification of False Rotor Fault Indications Produced by Online MCSA for Medium-Voltage Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Lee, S.B. Influence of Aluminum Die-Cast Rotor Porosity on the Efficiency of Induction Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8104905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Yun, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.B.; Gyftakis, K. Quality Assurance Testing for Screening Defective Aluminum Die-cast Rotors of Squirrel Cage Induction Machines. In Proceedings of the 11th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED) IEEE, Tinos, Greece, 9 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubonyi, T.; Barkóczy, P.; Gácsi, Z. Comparison of CT and metallographic method for evaluation of microporosities of dye cast aluminum parts. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 903, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, R.; Réger, M.; Oláh, F. Characterisation of defects in die cast aluminium parts. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1246, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réger, M.; Gáti, J.; Oláh, F.; Horváth, R.; Fábián, E.R.; Bubonyi, T. Detection of Porosity in Impregnated Die-Cast Aluminum Alloy Piece by Metallography and Computer Tomography. Crystals 2023, 13, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozma, I.; Zsoldos, I. CT-Based Defect Analysis in Aluminium Rotor End Rings. Eng. Proc. 2024, 79, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024079093
Kozma I, Zsoldos I. CT-Based Defect Analysis in Aluminium Rotor End Rings. Engineering Proceedings. 2024; 79(1):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024079093
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozma, István, and Ibolya Zsoldos. 2024. "CT-Based Defect Analysis in Aluminium Rotor End Rings" Engineering Proceedings 79, no. 1: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024079093
APA StyleKozma, I., & Zsoldos, I. (2024). CT-Based Defect Analysis in Aluminium Rotor End Rings. Engineering Proceedings, 79(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2024079093





