Abstract
Using biochar/δ-MnO2 as an adsorbent, heavy metals in soil were immobilized to prevent further pollution. When biochar/δ-MnO2 was thoroughly mixed with contaminated soil in a ratio of 2:8, the residual fractions of As, Cu, Pb, and Zn increased by 9.78, 39.0, 61.6, and 15.7%. The addition of biochar/δ-MnO2 significantly immobilized Cu and Pb. Since biochar/δ-MnO2 fixed As, Cu, Pb, and Zn in the soil, soil contamination was prevented effectively.
1. Introduction
Taiwan’s rapid economic development has indirectly increased soil pollution in farmland with heavy metals such as arsenic (As), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), and cadmium (Cd). Unlike organic pollutants, heavy metals cannot be easily removed through self-purification from the soil. Instead, they accumulate over time, polluting the soil and infiltrating groundwater. The treatment methods for heavy-metal-contaminated soil include solidification/stabilization, vitrification, phytoremediation, and separation/concentration. The waste generated by these treatment methods affects soil quality. Therefore, adsorbents are used to adsorb heavy metals in the soil as an environmentally friendly approach.
Biochar is a solid material rich in carbon produced by the thermochemical conversion of biomass in a low-oxygen environment []. Biochar serves as an adsorbent as it substitutes fuel, catalyst, and soil amendment, which makes biochar available for soil quality improvement. In this study, agricultural waste peanut vines were used as raw material for biochar production. Traditionally, peanut vines are disposed of through burning, causing air pollution. By transforming them into biochar, resource recycling and zero waste can be achieved. δ-type manganese dioxide (MnO2) is known for its natural oxidizing property. It possesses a unique adsorption-friendly two-dimensional layered structure, large surface area, high porosity, high adsorption activity, small particle size, surface charge, and oxidation capability. Its low production cost and minimal environmental impact allow δ-type MnO2 to be a useful chemical in the biogeochemical cycles of inorganic and organic compounds. The oxidation mechanism of MnO2 involves the formation of free radicals through electron transfer. Therefore, manganese dioxide is used for the remediation of polluted groundwater. However, limited research has been conducted for its application in soil pollution control.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of δ-MnO2/Biochar Composite Material
The raw material for biochar in this study was peanut vines, a common agricultural waste in Yunlin County, a major agricultural county in Taiwan. The peanut vines were crushed into powder, soaked in 0.5 M calcium chloride for 24 h, and then dried in an oven at 105 °C. Subsequently, the dried peanut vine charcoal (biochar) was placed in a high-temperature furnace at 600 °C for 1 h. After cooling, the activated biochar was ground to 100 mesh and treated with 0.1 M hydrochloric acid and acetone to remove surface tars. A solution of tetrahydrate manganese acetate was added to the biochar, and the mixture was stirred with a magnetic stirrer for 10 min and then ultrasonicated for 30 min. The mixture was then placed on a heating plate, and potassium permanganate solution was slowly added while stirring at 80 °C for 1 h. After precipitating solids, the upper liquid was removed with a pipette, and the remaining sample was washed with deionized water. After drying in an oven, the precipitates were ground into powder using an agate mortar to obtain δ-MnO2-coated biochar (biochar/δ-MnO2). The specific surface area and pore size analysis (BET), surface imaging analysis (SEM), surface element analysis (EDS), and surface functional group analysis (FTIR) were performed to investigate the properties of biochar/δ-MnO2.
2.2. Sequential Extraction
Sequential extraction was conducted to obtain different forms of heavy metals in extractants at different pH values. The extraction was performed using the method proposed by Tessier []. In the method, heavy metal forms are classified into exchangeable, carbonate, iron-manganese oxide, organic matter-bound, and residual forms. Heavy metals in exchangeable and carbonate forms are more easily released into the environment and absorbed by organisms than in other forms, while organic matter-bound forms are more likely to be released in anaerobic environments.
2.3. Bioaccessibility
Bioaccessibility refers to the ratio of heavy metal concentration ingested into the body of organisms. Therefore, bioaccessibility is used to confirm the release of heavy metals into the human body when contaminated soil is inadvertently ingested. Bioaccessibility is estimated by simulating the dissolution of heavy metals in acidic conditions similar to the stomach and comparing the total amount of heavy metals with the sequentially extracted amount. It is calculated using (1).
2.4. Evaluation of Soil Pollution
2.4.1. Enrichment Factor
The enrichment factor (EF) is a measure used in the assessment of soil pollution. In the natural weathering process. EF values are typically around 1.5. If the EF value exceeds 1.5, the primary source of heavy metals is regarded as anthropogenic. The value is a criterion for assessing the degree of influence []. The degree of pollution is classified based on the enrichment level of heavy metals. In the classification, no pollution (EF ≤ 2), slight pollution (2 ≤ EF < 5), moderate pollution (5 ≤ EF < 20), severe pollution (20 ≤ EF < 40), and extremely severe pollution (EF > 40) are defined []. The calculation formula of EF is as follows.
Cn: Concentration of heavy metals in the sample.
Cref: Reference concentration of heavy metals in the sample.
Bn: Background concentration of heavy metals.
Bref: Reference background concentration of heavy metals.
2.4.2. Geo-Accumulation Index
The geo-accumulation index (Igeo) is used to assess the impact of heavy metals on soil quality. Due to potential variations in background values related to lithospheric effects, a background correction factor (k = 1.5) is incorporated into the calculation. Igeo is used to categorize pollution levels as no pollution (Igeo < 1), slight pollution (1 < Igeo < 2), moderate pollution (2 < Igeo < 3), moderately severe pollution (3 < Igeo < 4), severe pollution (4 < Igeo < 5), and extremely severe pollution (Igeo > 5) (3) [].
K: Correction factor.
Cn: Concentration of heavy metals in the sample.
Bn: Background concentration of heavy metals.
2.4.3. Contamination Factor
The contamination factor (CF) serves as an assessment criterion for the degree of soil pollution caused by a single metal. The calculation formula for the contamination factor is as follows.
Cn: heavy metal concentration in sample.
Bn: background heavy metal concentration.
2.4.4. Pollution Load Index
The pollution load index (PLI) serves as an assessment criterion for the overall degree of soil pollution caused by multiple metals. The calculation formula for the pollution load index is as follows.
CF: Contamination Factor.
2.4.5. Single Metal Pollution Factor and Global Metal Pollution Factor
The individual contamination factor (ICF) and the global contamination factor (GCF) are used to represent the potential ecological risk of a single metal in the soil. A higher value indicates a higher ecological pollution risk, and vice versa. GCF represents the overall metal pollution situation. The calculation formulas are as follows.
CFi: sum of non-residual concentrations (mg/kg).
CFE: residual concentration (mg/kg).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization Analysis
3.1.1. Specific Surface Area and Pore Size
The specific surface area and total pore volume of biochar were 94.9 m2/g and 0.09 c.c/g, respectively. For δ-MnO2, the specific surface area and total pore volume were 245 m2/g and 0.79 c.c/g, respectively. The biochar/δ-MnO2 composite had a specific surface area and total pore volume of 216 m2/g and 0.45 c.c/g, respectively. Micropores exist on the biochar’s surface, accounting for 79.9% of the total surface area. In δ-MnO2, the proportions of mesopores and micropores were similar. Mesopores accounted for 57.3% of the total surface area. Biochar/δ-MnO2 had numerous mesopores, constituting 81.8% of the total surface area. The addition of KMnO4 in the coating process disrupted the micropore structure, transforming it into mesopores or macropores. After coating, the specific surface area of biochar increased by 2.27 times, with the mesopores being the main contributor as the area of the mesopores increased by 9.26 times. This result was consistent with previous studies []. The increase in mesopore volume contributes to the enhancement of the specific surface area, thereby improving the adsorption capacity for pollutants []. An increase in specific surface area and pore volume is beneficial for the adsorption capacity of pollutants [], while excessively small pore sizes result in poor adsorption efficiency [].
3.1.2. Surface Element Analysis
Figure 1 shows the surface image of biochar/δ-MnO2, revealing distinct spherical particles adhering to biochar. This result is similar to the findings in Ref. []. The pores of the biochar/δ-MnO2 surface are increased, consistent with the pore size analysis results (Table 1). The oxidative action of KMnO4 disrupts the micropore structure in the coating process, transforming it into mesopores. Thus, the specific surface area of biochar increased by 2.27 times after coating []. In the coating process, KMnO4 reacts with Mn(CH3COO)2·4H2O to deposit δ-MnO2 on the surface of biochar, forming a layered and flocculent structure, which provides a larger specific surface area and highly reactive void structure []. Before coating, the elements of the biochar surface included C, O, Cl, and Ca with C and O being the major elements. After thermal decomposition, peanut vines became carbon-rich solid materials, similar to the characteristics of biochar []. The presence of Cl and Ca is attributed to the use of CaCl2 as an activator in the thermal decomposition process of peanut vines. Surface elements of biochar/δ-MnO2 included C, O, Ca, Mn, and K, with C, O, and Ca having the same origins. Mn and K in biochar/δ-MnO2 originated from the precipitation reaction in coating using KMnO4 and Mn(CH3COO)2·4H2O [].
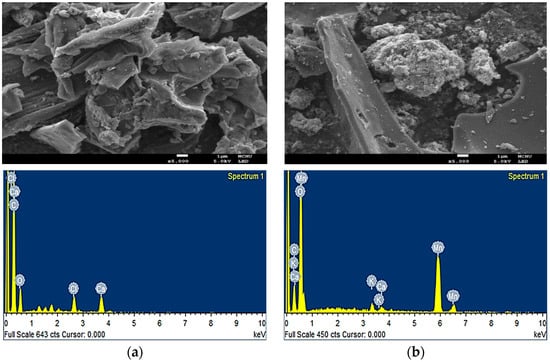
Figure 1.
(a) Surface imaging and elemental analysis of biochar; (b) surface imaging and elemental analysis of biochar/δ-MnO2.

Table 1.
Specific surface area and pore size analysis.
3.1.3. Functional Group Analysis (Figure 2)
The absorption by biochar/δ-MnO2 was observed at 1635 cm−1 due to the internal pores in the δ-MnO2 structure and the bending vibration of -OH and H2O []. This indicates that the Mn identified in the surface element analysis originated from δ-MnO2. In the range of 1725–1680 cm−1, absorption is related to carboxyl groups (C=O) that stretch vibrations at the wavelengths. Absorption at 1699, 1716, and 1733 cm−1 indicates the presence of C=O in biochar/δ-MnO2 []. Conjugated C=O structures dissociate H+, which increases the alkalinity of the soil by combining with metal oxides, hydroxides, and carbonate dissolved substances in the soil. With H+ dissociation, C=O transforms from -COOH to -COO and binds heavy metal ions, which causes heavy metal adsorption. In the range of 3800–2200 cm−1, stretched vibrations of water molecules and hydroxyl groups are observed []. Absorption occurs at 3565, 3627, and 3647 cm−1, indicating the presence of -OH. These -OH groups are protonated during the adsorption process and bind heavy metal ions to immobilize them.
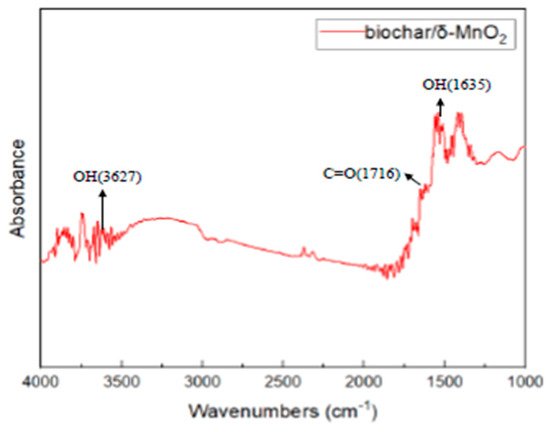
Figure 2.
Surface functional group analysis of biochar/δ-MnO2.
3.1.4. Bioavailability
Table 2 presents the bioavailability of different concentrations of biochar/δ-MnO2 for heavy metals in soil. The bioavailability of As, Cu, Pb, and Zn in polluted soil decreased with the addition of biochar/δ-MnO2 [], indicating that the addition of biochar/δ-MnO2 to polluted soil reduced the bioavailability of heavy metals. The reduction was more pronounced for As and Pb, suggesting that biochar/δ-MnO2 is more effective in inhibiting the absorption of As and Pb by the human body.

Table 2.
Bioavailability of metals with the addition of different concentrations of biochar/δ-MnO2.
3.2. Heavy Metal Forms in Soil
Sequential extraction results of As, Cu, Pb, and Zn revealed that the addition of biochar/δ-MnO2 had a pronounced effect on the fixation of Cu and Pb (Figure 3). Upon the addition of biochar/δ-MnO2 to the soil, soil organic matter (SOM) and MnO2 increased. SOM exhibited a higher selectivity for divalent metal ions, with varying bond strengths for different metals. The bond strength follows the order Cu > Pb > Zn. With prolonged mixing time, Cu and Pb transformed into more stable compounds, resulting in stable forms. Therefore, the residual form increased, achieving an enhancement in fixation.
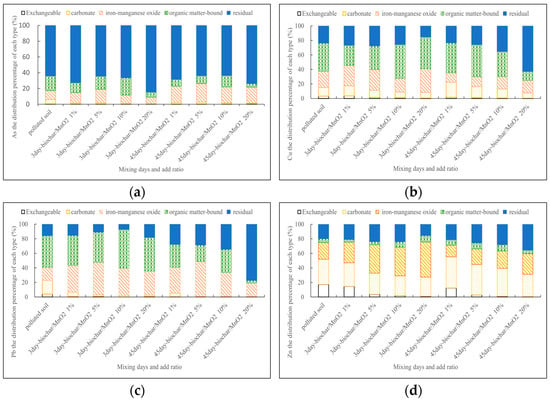
Figure 3.
Changes form after adding different concentrations of biochar/δ-MnO2 at different times (a) As; (b) Cu; (c) Zn; (d) Pb.
Zn showed less change in the concentration in the organic matter-bound form, while the iron-manganese oxide form showed significant change. The strong adsorption capability of iron-manganese oxides/hydroxides for Zn caused biochar/δ-MnO2 to initially adsorb exchangeable Zn ions on the surface, which later transformed into internal spherical complexes. This makes it less susceptible to release, thus enhancing its fixation ability.
Heavy metals in the residual form predominantly existed in polluted soil, exhibiting higher stability. The adsorption capacity of As(V) on δ-MnO2 surfaces is weaker than Cu, Pb, and Zn. Consequently, the changes in forms were less significant for As than Cu, Pb, and Zn, resulting in a less pronounced fixation of biochar/δ-MnO2 on As.
The sequential extraction results of heavy metals confirmed that the addition of biochar/δ-MnO2 significantly enhanced the fixation of Cu and Pb, while the effect on Zn and As was less significant. Exchangeable and carbonate forms pose ecological risks and iron-manganese oxide forms are indicative of potential ecological risks. Therefore, the changes in the proportion in the residual form can be used for assessing heavy metal properties. When adding biochar/δ-MnO2 to the soil in a ratio of 2:8, the best effect was observed with an increase in the residual form proportions by 9.78, 39.0, 61.6, and 15.7% for As, Cu, Pb, and Zn, respectively. This substantiates the significant effectiveness of biochar/δ-MnO2 in enhancing the fixation of Cu and Pb.
3.3. Soil Pollution Assessment
3.3.1. EF
Table 3 presents the soil exhibiting moderate contamination for As, Cu, Zn, and mild contamination for Pb. After the addition of biochar/δ-MnO2, the contamination levels decreased. The optimal proportion was 10% to transform Pb from mild to non-contamination and Cu and Zn from moderate to mild contamination. As maintained a moderate contamination level. Biochar/δ-MnO2 alleviated contamination with a better effect observed for Pb, Cu, and Zn, indicating its potential effectiveness in remediating Pb, Cu, and Zn pollution.

Table 3.
Enrichment factor of heavy metals in soil.
3.3.2. Igeo
Table 4 shows that As and Cu exhibited higher pollution levels. With biochar/δ-MnO2, a significant decrease in Igeo was observed. The decrease was significant for Pb, transitioning from mild to non-contamination. As and Cu maintained a moderate contamination level, while Zn remained similar. The changes in As forms were less pronounced with biochar/δ-MnO2, as As was associated with the iron-manganese oxide and organic matter-bound forms. δ-MnO2 increased As in the iron-manganese oxide form over time. In acidic environments, As is usually present as As(V), and biochar/δ-MnO2 exhibits weaker adsorption capacity for As(V). Consequently, As is less adsorbed. Pb and Cu showed more adsorption to organic matter, forming stable organic compounds. Zn exhibited more adsorption on iron-manganese oxides/hydroxides.

Table 4.
Geo-accumulation index (Igeo).
3.3.3. CF and PLI
CF reveals the potential risk of individual heavy metals in the soil. Before adding biochar/δ-MnO2, the concentrations of As, Cu, and Zn were high, while that of Pb was moderate. After the addition of biochar/δ-MnO2, CF decreased for all heavy metals. Although As maintained a high CF, the CF of Pb remained low, and the CFs of Cu and Zn were still high. The CF values of As, Cu, and Zn were reduced by 20%, while that of Pb was reduced by 30%. Biochar/δ-MnO2 reduced the CFs of those heavy metals considerably. PLI is used to estimate the impact of heavy metals on pollution. When PLI > 1, it indicates pollution, with a higher value indicating severe pollution. After adding biochar/δ-MnO2, PLI values decreased, indicating a reduction in pollution levels (Table 5).

Table 5.
Contamination factor (CF) and pollution load index (PLI).
3.3.4. Mobility, ICF, and GCF
Table 6 presents the mobility of heavy metals in the soil: Zn > Pb > Cu > As. After adding biochar/δ-MnO2, the order of the mobility was Zn > Cu > As > Pb. Mobility presents the degree of the potential for heavy metal pollution. The results aligned with EF, Igeo, CF, and PLI. ICF and GCF are standards for assessing potential ecological risks. In the polluted soil, Zn and Pb had higher ICF, indicating higher potential mobility and bioavailability. After adding biochar/δ-MnO2, all ICF values decreased. The ICF of As, Cu, and Pb decreased to the level of no contamination, and that of Zn decreased to moderate contamination. In GCF, pollution levels decreased from heavy to low contamination. Table 7 presents the ICF and GCF and the potential ecological risk. Residual forms, composed of primary and secondary minerals, are less affected by external factors and pose no potential risk to the environment. Exchangeable and carbonate forms present ecological risks, while iron-manganese oxide and organic matter-bound forms present potential ecological risks. Therefore, exchangeable, carbonate, iron-manganese oxide, and organic matter-bound forms affect ICF and GCF.

Table 6.
Mobility of each metal.

Table 7.
Mobility, individual contamination factor (ICF), and global contamination factor (GCF).
4. Conclusions
After coating with δ-MnO2, the biochar’s specific surface area increased by 2.27 times, and functional groups such as OH, C-O, C=O, and C=C contributed to the adsorption of heavy metal ions. Biochar/δ-MnO2 increased pH and SOM. The pH increase was induced by the precipitation of metals and enhanced soil’s negative charge, thereby increasing its adsorption capacity for heavy metal elements. Meanwhile, SOM, with functional groups, binds heavy metal ions, altering their bonding forms to organic matter-bound forms. The optimal effect was observed for As, Cu, Pb, and Zn when adding biochar/δ-MnO2 to the soil in a ratio of 2:8. The residual fraction for As, Cu, Pb, and Zn increased by 9.78, 39.0, 61.6, and 15.7%, respectively, confirming the significant effectiveness of biochar/δ-MnO2 in enhancing the fixation of Cu and Pb. Biochar/δ-MnO2 reduced the bioavailability of As, Cu, Pb, and Zn, with a pronounced decrease in As and Pb bioavailability from 68.5 to 21.4 and from 2.92 to 2.58%, respectively. Biochar/δ-MnO2 is beneficial for mitigating soil pollution, with the most notable effect for Pb, Cu, and Zn.
Author Contributions
S.-W.C.C.: Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources. P.-Q.L.: Conceptualizations, Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing—original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- He, E.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Qiu, H.; Yang, F.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, R.; Wang, S. Two years of aging influences the distribution and lability of metal(loid)s in a contaminated soil amended with different biochars. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Wiechuła, D.; Korus, I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.; Couto, C.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Maia, A.S.; Santos, M.; Tiritan, M.E.; Pinto, E.; Almeida, A.A. Distribution and environmental assessment of trace elements contamination of water, sediments and flora from Douro River estuary, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the Elements in Some Major Units of the Earth’s Crust. GSA Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Yuan, B.; Fu, M.-L. A facile foaming-polymerization strategy to prepare 3D MnO2 modified biochar-based porous hydrogels for efficient removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.; Fang, J.; Xue, Y.; Yang, K. Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Gao, H.; Wang, M.; Xue, J. Remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil by ball milling and reuse as heavy metal adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Quinlivan, P.A.; Knappe, D.R.U. Effects of activated carbon surface chemistry and pore structure on the adsorption of organic contaminants from aqueous solution. Carbon 2002, 40, 2085–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Z.; Song, Z. Adsorption Properties of Nano-MnO2–Biochar Composites for Copper in Aqueous Solution. Mol. A J. Synth. Chem. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2017, 22, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, R.M. The adsorption of lead and other heavy metals on oxides of manganese and iron. Soil Res. 1980, 18, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, L. Locking carbon up in soil makes more sense than storing it in plants and trees that eventually decompose, argues Johannes Lehmann. Can this idea work a large scale? Nature 2007, 447, 143–144. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Ruoff, R.S.; Wen, Z.; Liu, Q. Self-Assembly of Mesoporous Nanotubes Assembled from Interwoven Ultrathin Birnessite-type MnO2 Nanosheets for Asymmetric Supercapacitors. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, L. Transitional Adsorption and Partition of Nonpolar and Polar Aromatic Contaminants by Biochars of Pine Needles with Different Pyrolytic Temperatures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5137–5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, T.; Tombácz, E.; Illés, E.; Dékány, I. Enhanced acidity and pH-dependent surface charge characterization of successively oxidized graphite oxides. Carbon 2006, 44, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).