Biomass Burning and Water Balance Dynamics in the Lake Chad Basin in Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
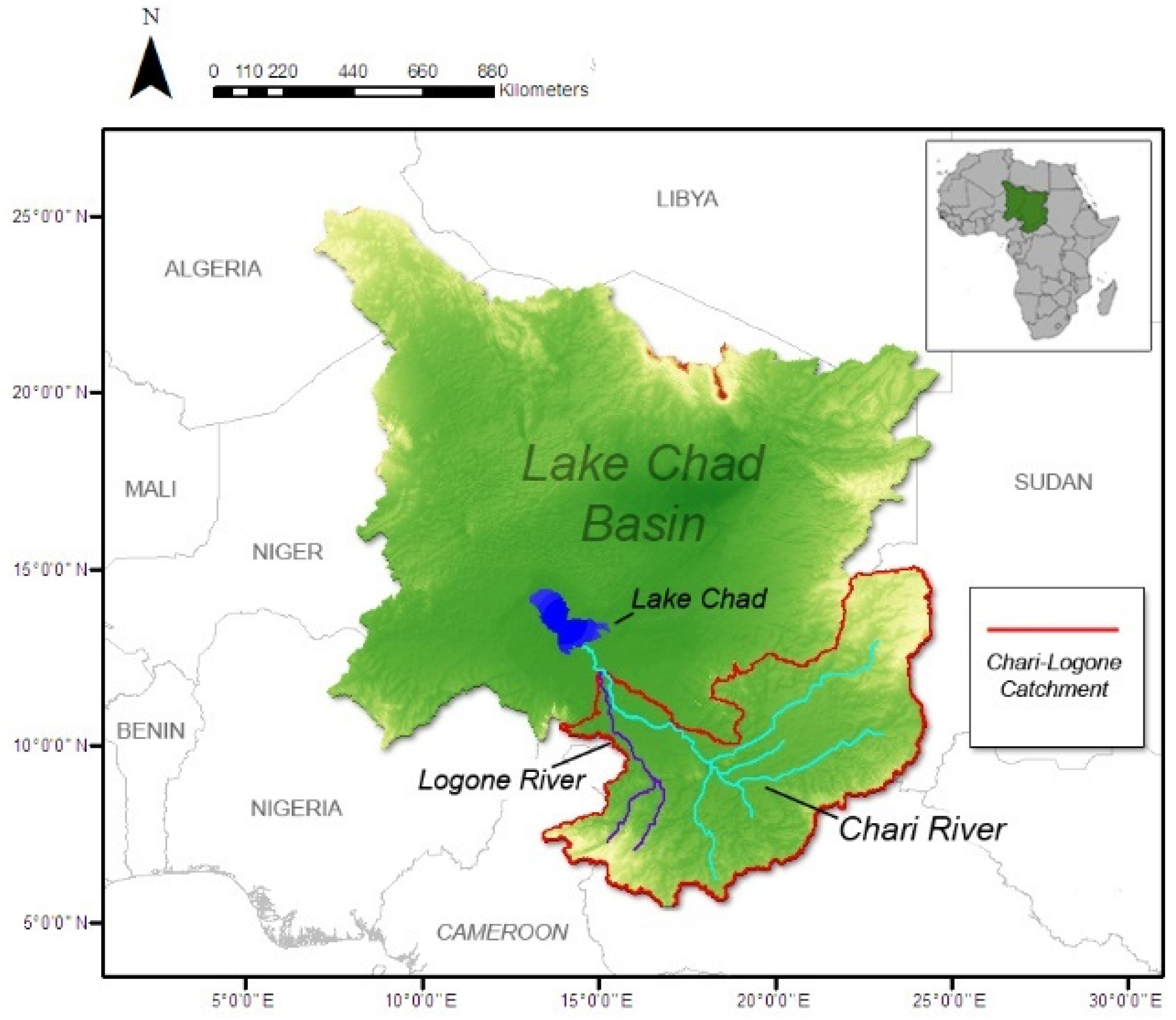
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The WetSpass-M: The Water Balance Model
3.2. Datasets and Parameters for Burning
4. Results
4.1. Validation
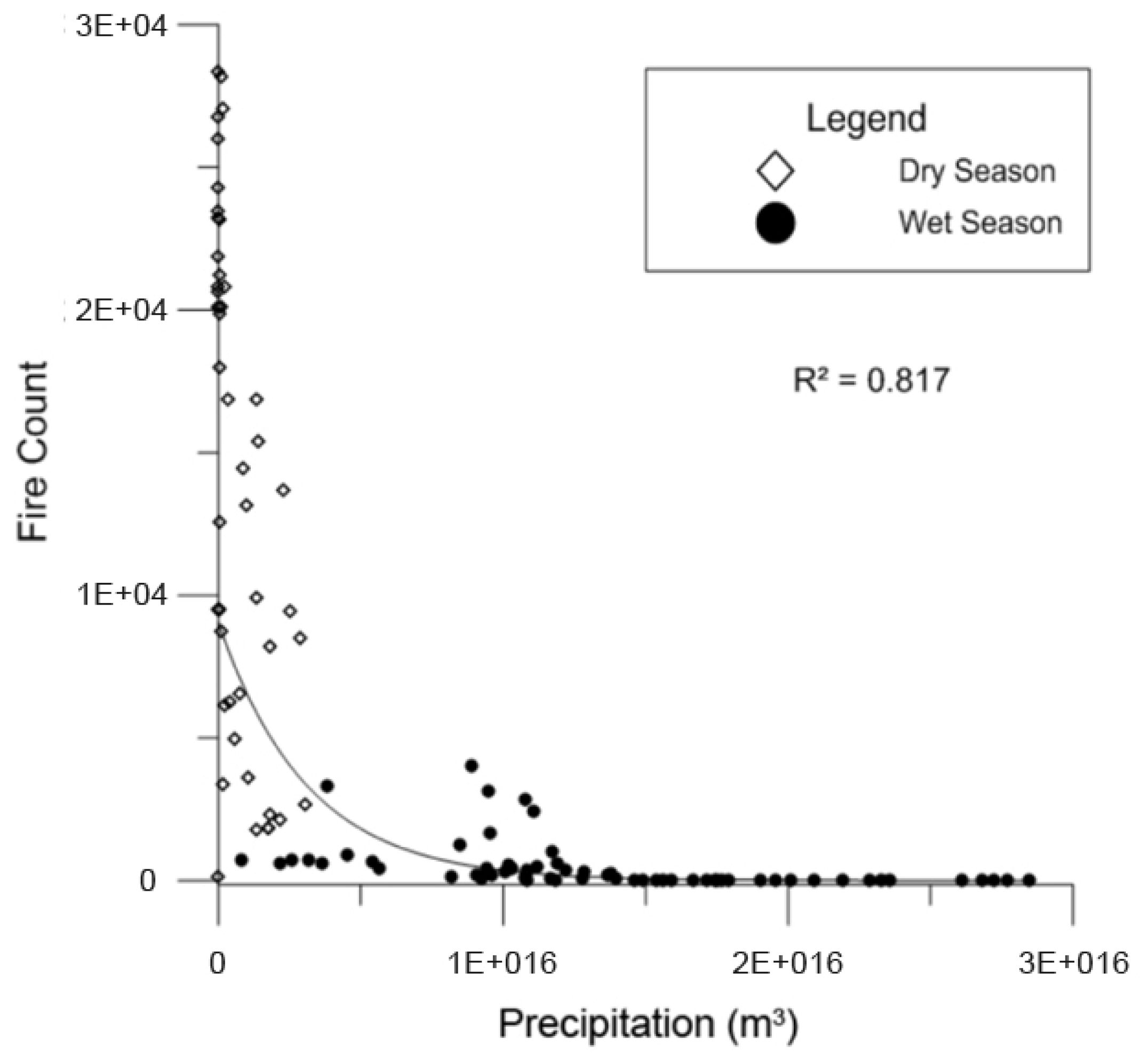
4.2. Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okonkwo, C.; Demoz, B.; Sakai, R.; Ichoku, C.; Anarado, C.; Adegoke, J.; Amadou, A.; Abdullahi, S.I. Combined effect of El Niño southern oscillation and Atlantic multidecadal oscillation on Lake Chad level variability. Cogent Geosci. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, I.K. Saving Lake Chad. Proceedings of Sirte Roundtable. Available online: http://afrwg.icidonline.org/save_lakechad.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- Sarch, M.T. Fishing and farming at Lake Chad: Institutions for access to natural resources. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 62, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimmage, K.; Adams, W.M. Wetland agricultural production and river basin development in the Hadejia-Jama’are Valley, Nigeria. Geogr. J. 1992, 158, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agricultural Organization. Adaptive water management in the Lake Chad Basin: Addressing current challenges and adapting to future needs. In Proceedings of the Water Seminar Proceedings, World Water Week, Stockholm, Sweden, 16–22 August 2009; pp. 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Babamaaji, R.A.; Lee, J. Land use/land cover classification of the vicinity of Lake Chad using NigeriaSat-1 and Landsat data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4309–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchez, C.; Goncalves, J.; Deschamps, P.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Hamelin, B.; Doumnang, J.-C.; Sylvestre, F. Hydrological, chemical, and isotopic budgets of Lake Chad: A quantitative assessment of evaporation, transpiration and infiltration fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 1599–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, S.E. The West African Sahel: A review of recent studies on the rainfall regime and its interannual variability. ISRN Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Some, B.; Kone, B. An analysis of recent rainfall conditions in West Africa, including the rainy seasons of the 1997 El Niño and the 1998 La Niña Years. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2628–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policelli, F.; Hubbard, A.; Jung, H.C.; Zaitchik, B.; Ichoku, C. Lake Chad total surface water area as derived from land surface temperature andradar remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thonicke, K.; Venevsky, S.; Sitch, S.; Cramer, W. The role of fire disturbance for global vegetation dynamics: Coupling fire into a dynamic global vegetation model. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2001, 10, 661–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyons, E.; Jin, Y.; Randerson, J. Changes in surface albedo after fire in boreal forest ecosystems of interior Alaska assessed using MODIS satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, G02012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, D.; Balch, J.; Artaxo, P.; Bond, W.; Carlson, J.; Cochrane, M.; Pyne, S. Fire in the earth system. Science 2009, 324, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Ellison, L. Global top-down smoke-aerosol emissions estimation using satellite fire radiative power measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 6643–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Collatz, G.J.; Mu, M.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; van Leeuwen, T.T. Global fire emissions and the contribution of deforestation, savanna, forest, agricultural, and peat fires (1997–2009). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11707–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatebe, C.K.; Ichoku, C.M.; Poudyal, R.; Román, M.O.; Wilcox, E. Surface albedo darkening from wildfires in Northern Sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sales, F.; Xue, Y.; Okin, G.S. Impact of burned areas on the northern African seasonal climate from the perspective of regional modeling. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 3393–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dintwe, K.; Okin, G.S.; Xue, Y. Fire-induced albedo change and surface radiative forcing in sub-Saharan Africa savanna ecosystems: Implications for the energy balance. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 6186–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atchley, A.L.; Kinoshita, A.M.; Lopez, S.R.; Trader, L.; Middleton, R. Simulating surface and subsurface water balance changes due to burn severity. Vadose Zone J. 2018, 17, 180099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodnebrog, Ø.; Myhre, G.; Forster, P.M.; Sillmann, J.; Samset, B.H. Local biomass burning is a dominant cause of the observed precipitation reduction in southern Africa. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichoku, C.; Ellison, L.T.; Willmot, K.E.; Matsui, T.; Dezfuli, A.K.; Gatebe, C.K.; Wang, J.; Wilcox, E.; Lee, J.; Adegoke, J.; et al. Biomass burning, land-cover change, and the hydrological cycle in Northern sub-Saharan Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 095005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Govaerts, Y.M. Impact of fires on surface albedo dynamics over the African continent. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Berntsen, T.K.; Govaerts, Y.; Haywood, J.M.; Lattanzio, A. Radiative effect of surface albedo change from biomass burning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saha, M.V.; D’Odorico, P.; Scanlon, T.M. Albedo changes after fire as an explanation of fire-induced rainfall suppression. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 3916–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bano, L.F. Water Repellent Soils: A State-of-the-Art; General Technical Report, (PSW-46); US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Rulli, M.C.; Offeddu, L.; Santini, M. Modeling post-fire water erosion mitigation strategies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2323–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nyman, P.; Smith, H.; Sherwin, C.B.; Langhans, C.; Lane, P.N.; Sheridan, G. Predicting sediment delivery from debris flows after wildfire. Geomorphology 2015, 250, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buma, W.G.; Lee, S.-I.; Seo, J.Y. Hydrological evaluation of Lake Chad basin using space borne and hydrological model observations. Water 2016, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ndehedehe, C.E.; Awange, J.L.; Kuhn, M.; Agutu, N.O.; Fukuda, Y. Climate teleconnections influence on West Africa’s terrestrial water storage. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3206–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramillien, G.; Frappart, F.; Seoane, L. Application of the regional water mass variations from GRACE satellite gravimetry to large-scale water management in Africa. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 737977–867405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skaskevych, A.; Lee, J.; Jung, H.C.; Bolten, J.; David, J.L.; Policelli, F.S.; Goni, I.B.; Favreau, G.; San, S.; Ichoku, C.M. Application of GRACE to the estimation of groundwater storage change in a data-poorregion: A case study of Ngadda catchment in the Lake Chad Basin. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 941–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, L.; Romankiewicz, C.; Brandt, M.; Doevenspeck, M.; Samimi, C. Data and methods in the environment-migration nexus: A scale perspective. Erde 2016, 147, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanogo, S.; Fink, A.H.; Omotosho, J.A.; Ba, A.; Redl, R.; Ermert, V. Spatio-temporal characteristics of the recent rainfall recovery in West Africa. Int. J. Clim. 2015, 35, 4589–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Brandt, M.; Guichard, F.; Tian, Q.; Fensholt, R. Using long-term daily satellite based rainfall data (1983–2015) to analyze spatio-temporal changes in the sahelian rainfall regime. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batelaan, O.; De Smedt, F. GIS-based recharge estimation by coupling surface–subsurface water balances. J. Hydrol. 2007, 337, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, K.; Bashir, I.; Verbeiren, B.; Harouna, M.R.; Van Griensven, A.; Huysmans, M.; Batelaan, O. A distributed monthly water balance model: Formulation and application on Black Volta Basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Bohn, T.; Podest, E.; McDonald, K.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. On the causes of the shrinking of Lake Chad. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 034021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vuillaume, G. Bilanhydrologiquemensuel et modélisationsommaire du régime hydrologique du lac Tchad. Paris. Cah. ORSTOM. Série Hydrol. 1981, 18, 23–72, ISSN 0008-0381. [Google Scholar]
- Candela, L.; Elorza, F.J.; Tamoh, K.; Jiménez-Martínez, J.; Aureli, A. Groundwater modelling with limited data sets: The Chari-Logone area (Lake Chad Basin, Chad). Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 3714–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouché, P.; Douglas-Hamilton, I.; Wittemyer, G.; Nianogo, A.J.; Doucet, J.-L.; Lejeune, P.; Vermeulen, C. Will elephants soon disappear from west African Savannahs? PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguis, L.; Cappelaere, B.; Milesi, G.; Peugeot, C.; Massuel, S.; Favreau, G. Simulated impacts of climate change and land-clearing on runoff from a small Sahelian catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 3401–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulain, N.; Cappelaere, B.; Seguis, L.; Gignoux, J.; Peugeot, C. Hydrologic and land use impacts on vegetation growth and NPP at the watershed scale in a semi-arid environment. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2006, 6, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulain, N.; Cappelaere, B.; Seguis, L.; Favreau, G.; Gignoux, J. Water balance and vegetation change in the Sahel: A case study at the watershed scale with an eco-hydrological model. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, C.; Favreau, G.; Schroeter, P. Long-term rise in a Sahelian water-table: The Continental Terminal in South-West Niger. J. Hydrol. 2001, 243, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melki, A.; Abdollahi, K.; Fatahi, R.; Abida, H. Groundwater recharge estimation under semi arid climate: Case of Northern Gafsa watershed, Tunisia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 132, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shao, Q. An improved statistical approach to merge satellite rainfall estimates and raingauge data. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo, S.M.; de Oliveira, R.P. Evaluation of extreme precipitation estimates from TRMM in Angola. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, J.; Omotosho, T. Comparison of 1-min rain rate derived from TRMM satellite data and raingauge data for microwave applications in Nigeria. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2013, 102, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; McIver, D.K.; Hodges, J.C.; Zhang, X.; Muchoney, D.; Strahler, A.H.; Cooper, A. Global land covermapping from MODIS: Algorithms and early results. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, M.A.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Tan, B.; Schneider, A.; Ramankutty, N.; Sibley, A.; Huang, X. MODIS collection 5 global land cover: Algorithm refinements and characterization of new datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Oduor, P.; Flores, A.I.; Kotikot, S.M.; Mugo, R.; Ababu, J.; Farah, H. Evaluating land cover changes in Eastern and Southern Africa from 2000 to 2010 using validated Landsat and MODIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 62, 8–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessner, U.; Bliefernicht, J.; Rahmann, M.; Dech, S. Land cover maps for regional climate modeling in West Africa—A comparison of datasets. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual EARSeL Symposium, Mykonos, Greece, 21–25 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Vintrou, E.; Desbrossea, A.; Beguea, A.; Traoreb, S.; Barona, C.; Seena, D. Crop area mapping in West Africa using landscape stratification of MODIS time series and comparison with existing global land products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 14, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Feng, X.; Li, H. Accuracy assessment of seven global land cover datasets over China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Descloitres, J.; Justice, C.O.; Kaufman, Y.J. An enhanced contextual fire detection algorithm for MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 87, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.; Giglio, L.; Korontzi, S.; Owens, J.; Morisette, J.; Roy, D.; Descloitres, J.; Alleaume, S.; Petitcolin, F.; Kaufman, Y. The MODIS fire products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 244–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, E.-D. Short-term and long-term effects of plant water deficits on stomatal response to humidity in Corylus avellana L. Planta 1979, 146, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Lawrence, D.M.; Bond-Lamberty, B. Human impacts on 20th century fire dynamics and implications for global carbon and water trajectories. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 162, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilovich, M.G. A comparison of MODIS land surface temperature with in situ observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, C.; Wan, Z.; Galve, J.M. Temperature-based and radiance-based validations of the V5 MODIS land surface temperature product. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Z. Radiance-based validation of the V5 MODIS land-surface temperature product. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5373–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulley, G.C.; Hook, S.J. Intercomparison of versions 4, 4.1 and 5 of the MODIS Land Surface Temperature and Emissivity products and validation with laboratory measurements of sand samples from the Namib desert, Namibia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1313–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelstaedter, S.; Washington, R. Evaluation of reanalysis near-surface winds over northern Africa in Boreal summer. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; EGU General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2014; p. 13169. [Google Scholar]
- Mughal, M.; Lynch, M.; Yu, F.; McGann, B.; Jeanneret, F.; Sutton, J. Wind modelling, validation and sensitivity study using Weather Research and Forecasting model in complex terrain. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 90, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M.A.; Webster, R. Kriging: A method of interpolation for geographical information systems. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1990, 4, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lu, C. Urban percent impervious surface and its relationship with land surface temperature in Yantai City, China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valiantzas, J.D. Simplified versions for the Penman evaporation equation using routine weather data. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegetation and hydrology. H. L. Penman (Technical Communication No. 53, Commonwealth Bureau of Soils, Harpenden) Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Farham Royal, 1963. Pp. v, 124: 72 Tables. 20s. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1963QJRMS..89..565./abstract (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- Shuttleworth, W.J. Evaporation. In Maidment; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 4.1–4.53. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Smith, M.; Pereira, L.S.; Perrier, A. An update for the calculation of reference evapotranspiration. ICID Bull. 1994, 43, 35–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zomer, R.J.; Bossio, D.A.; Trabucco, A.; Yuanjie, L.; Gupta, D.C.; Singh, V.P. Trees and Water: Smallholder Agroforestry on Irrigated Lands in Northern India. Colombo, Sri Lanka; IWMI Research Report; International Water Management Institute: Cairo, Egypt, 2007; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Zomer, R.J.; Trabucco, A.; Bossio, D.A.; van Straaten, O.; Verchot, L.V. Climate change mitigation: A spatial analysis of global land suitability for clean development mechanism afforestation and reforestation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 126, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zyl, J.J. The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM): A breakthrough in remote sensing of topography. Acta Astronaut 2001, 48, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ranson, K.; Kharuk, V.; Kovacs, K. Validation of surface height from shuttle radar topography mission using shuttle laser altimeter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Institute of Geosciences and Natural Resources & Lake Chad Commission. Lake Chad Sustainable Water Management Project Activities—Report N° 3. 2010. Available online: https://www.whymap.org/EN/Themen/Wasser/Projekte/abgeschlossen/TZ/Tschad/report_3.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=3 (accessed on 4 February 2019).
- Seeber, K. 2nd Mission on Discharge Measurements at Chari, Logone and Koulambou River, Chad; Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development: Hanovra, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver FC &Singels, A. The effect of crop residue layers on evapotranspiration, growth and yield of irrigated sugarcane. Water SA 2012, 38, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Notaro, M.; Wyrwoll, K.-H.; Chen, G. Did aboriginal vegetation burning impact on the Australian summer monsoon? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vadilonga, T.; Úbeda, X.; Germann, P.F.; Lorca, M. Effects of prescribed burnings on soil hydrological parameters. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 4249–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, Y.; Dietrich, W.E.; Booker, F. Evolution of overland flow after a severe forest fire, Point Reyes, California. Catena 2008, 72, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| MODIS | WetSpass-M | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Label | Number | Label | Number |
| Rainfed Cropland | 12, 14 | Agriculture | 21 |
| Mosaic Vegetation | 12, 14 | Reference Grassland | 307 |
| Forest | 6, 7 | Mixed Forest | 33 |
| Shrubland | 6, 7 | Shrub | 36 |
| Grassland | 9, 10 | Reference Grassland | 307 |
| Sparse Vegetation | 9, 10 | Reference Grassland | 307 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Black, F.W.; Lee, J.; Ichoku, C.M.; Ellison, L.; Gatebe, C.K.; Babamaaji, R.; Abdollahi, K.; San, S. Biomass Burning and Water Balance Dynamics in the Lake Chad Basin in Africa. Earth 2021, 2, 340-356. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth2020020
Black FW, Lee J, Ichoku CM, Ellison L, Gatebe CK, Babamaaji R, Abdollahi K, San S. Biomass Burning and Water Balance Dynamics in the Lake Chad Basin in Africa. Earth. 2021; 2(2):340-356. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth2020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlack, Forrest W., Jejung Lee, Charles M. Ichoku, Luke Ellison, Charles K. Gatebe, Rakiya Babamaaji, Khodayar Abdollahi, and Soma San. 2021. "Biomass Burning and Water Balance Dynamics in the Lake Chad Basin in Africa" Earth 2, no. 2: 340-356. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth2020020
APA StyleBlack, F. W., Lee, J., Ichoku, C. M., Ellison, L., Gatebe, C. K., Babamaaji, R., Abdollahi, K., & San, S. (2021). Biomass Burning and Water Balance Dynamics in the Lake Chad Basin in Africa. Earth, 2(2), 340-356. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth2020020







