Monitoring and Evaluation: The Foundation for Lake and Reservoir Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Water Quality Monitoring
2.1. Water Quality Modelling
2.2. Citizen Science and Water Quality Monitoring
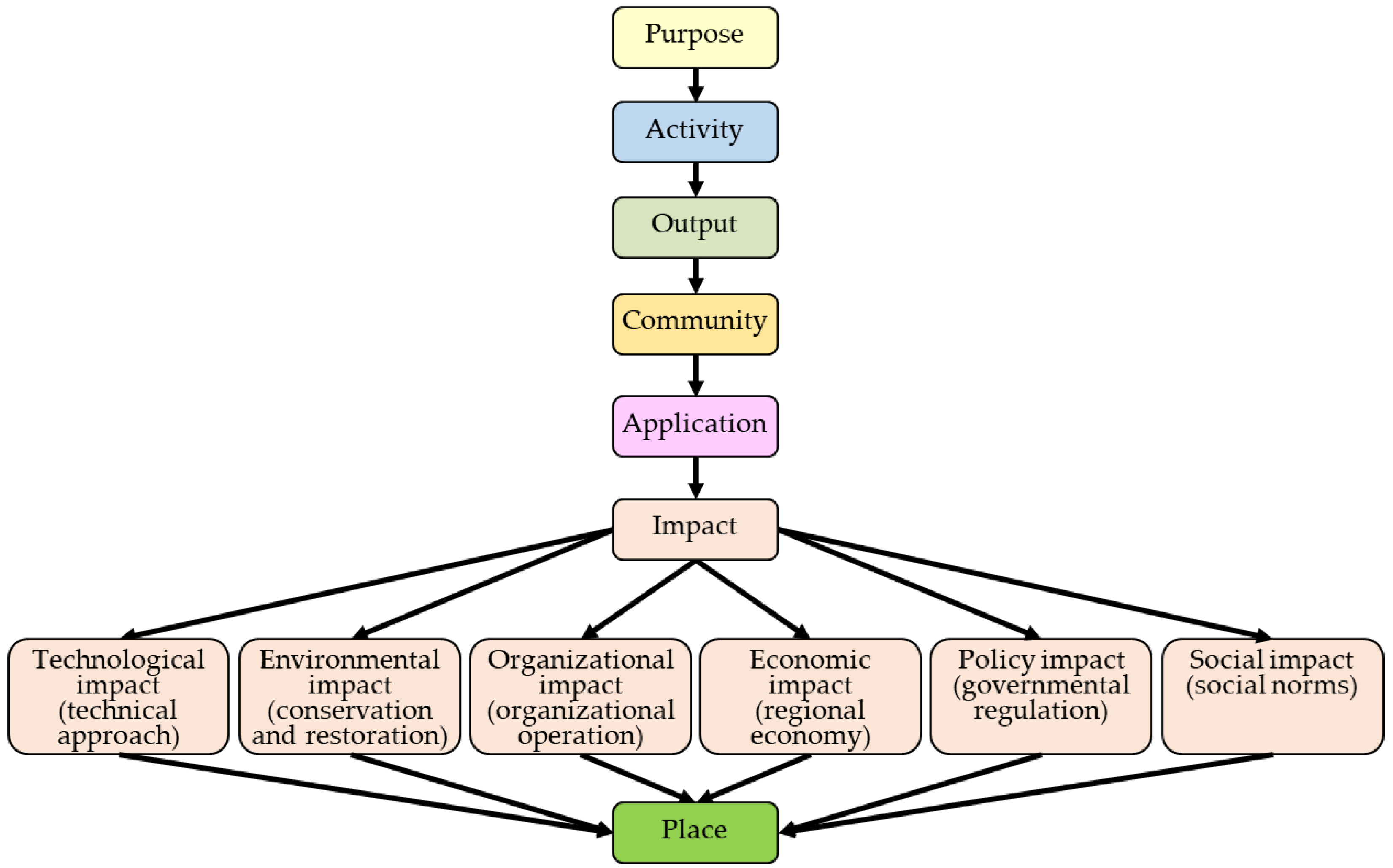
3. Project and Program Monitoring
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allum, M.O.; Glessner, R.E.; Gakstatter, J.H. An Evaluation of the National Eutrophication Survey Data; Working Paper No. 900; US Environmental Protection Agency: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1977.
- Walmsley, R.D.; Butty, M. The Limnology of Some Selected South African Impoundments; National Institute for Water Research, Council for Scientific and Industrial Research: Pretoria, South Africa, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Water Quality for Environment and Human Health, 2nd ed.; United Nations Environment Programme Global Environment Monitoring System/Water Programme: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2008; 120p. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Regional Water Quality Management Plan for Southeastern Wisconsin—2000, Volume One, Inventory Findings; Planning Report No. 30; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Analysis of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Golterman, H.L.; Clymo, R.S. Methods for Chemical Analysis of Fresh Waters; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider, R.A.; Talling, J.F.; Westlake, D.F. A Manual on Methods for Measuring Primary Production in Aquatic Environments, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie, J.E.; Sorokin, Y.I.; Kadota, H. Techniques for the Assessment of Microbial Production and Decomposition in Fresh Waters; IBP Handbook 23; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Ricker, W.E. Methods for Assessment of Fish Production in Fresh Waters; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Global Environment Facility. Framework and Work Program for GEF’s Monitoring, Evaluation and Dissemination Activities; Global Environment Facility Council Document GEF/C.8/4; Global Environment Facility: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Thienemann, A. Untersuchungen uber die Beziehungen zwischen dem Sauerstoffgehalt des Wassers under der Zusammensetzung der Fauna in norddeutschen Seen. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1918, 12, 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Naumann, E. Nagra synpunkter angarnde limnoplanktons ekologi med sarskild hansyn till fytoplankton. Sven. Bot. Tidskr. 1919, 13, 129–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttner, F. Hydrographische und hydrochemische Beobachtungen auf Java, Sumatra und Bali. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1930, 8, 197–454. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, G.E.; Pickford, G.L.; Schuurman, J.F.M. A contribution to the hydrobiology of pans and other inland waters of South Africa. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1933, 24, 1–136. [Google Scholar]
- Egerton, F.N. Part 57: Aspects of Limnology in America, 1930s to about 1990, Led by Hutchinson and Hasler. Bull. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2016, 97, 228–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Eighty years of Redfield. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 849. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, M. Primary production by the phytoplankton community in some Japanese lakes and its dependence on lake depth. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1966, 62, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Vollenweider, R.A. Scientific Fundamentals of The Eutrophication of Lakes and Flowing Waters, with Particular Reference to Nitrogen and Phosphorus as Factors in Eutrophication; Publication No. DAS/CSI/68.27; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD): Paris, France, 1968; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Eutrophication of Waters. Monitoring, Assessment, Control; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD): Paris, France, 1982; p. 154. [Google Scholar]
- David, E.L. Public perceptions of water quality. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooyoomijian, K.H.; Clesceri, N.L. Perceptions of water quality by selected respondent groupings in inland-water-based recreational environments. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 10, 728–744. [Google Scholar]
- Barnard, J.L. Biological denitrification. Water Pollut. Control 1973, 72, 705–720. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, J.A.; Rast, W.; Holland, M.M.; Jolankai, G.; Ryding, S.-O. Assessment and Control of Nonpoint Source Pollution of Aquatic Ecosystems: A Practical Approach; UNESCO Man and the Biosphere Series; Parthenon Press: London, UK, 1999; Volume 23. [Google Scholar]
- Health Professionals Advisory Board. The Great Lakes Water Quality Centennial Study—Phase I Report; International Joint Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, J.P.S. Water Microbiology: Bacterial pathogens and water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3657–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Developing Drinking-Water Quality Regulations and Standards: General Guidance with a Special Focus on Countries with Limited Resources; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.J.; Bootsma, M.J.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; McLellan, S.L. A microbial signature approach to identify fecal pollution in the waters off an urbanized coast of Lake Michigan. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, H.B.N. The Ecology of Running Waters; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1970; p. 555. [Google Scholar]
- Karr, J.R. Assessment of biotic integrity using fish communities. Fisheries 1981, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Volunteer Stream Monitoring: A Methods Manual; US Environmental Protection Agency Report No. EPA841-B-97-003; US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Cleiton Rocha, F.; Maia Andrade, E.; Bezerra Lopes, F. Water quality index calculated from biological, physical and chemical attributes. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, J.C.; Bae, Y.J.; Munkhjargal, G.; Narumon, S.; Tanida, K.; Vshivkova, T.S.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Yule, C.M. Freshwater biomonitoring with macroinvertebrates in East Asia. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, V.; Olem, H. Water Quality: Prevention, Identification and Management of Diffuse Pollution; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, W.V.; Mooney, H.A.; Cropper, A.; Capistrano, D.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chopra, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Hassan, R.; et al. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker, L.; Lahlou, M.; Bryer, M.; Kumar, D.; Kratt, K. Compendium of Tools for Watershed Assessment and TMDL Development; US Environmental Protection Agency Report No. EPA841-B-97-006; US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Handbook for Developing Watershed Plans to Restore and Protect Our Waters; US Environmental Protection Agency Report No. EPA841-B-08-002; US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Larsen, D.P.; Malueg, K.W. Whatever became of Shagawa Lake? In Restoration of Lakes and Inland Waters; US Environmental Protection Agency Report No. EPA440-5-81-010; US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1980; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Gura, T. Citizen science: Amateur experts. Nature 2013, 496, 259–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steven, R.; Barnes, M.; Garnett, S.T.; Garrard, G.; O’Connor, J.; Oliver, J.L.; Robinson, C.; Tulloch, A.; Fuller, R.A. Aligning citizen science with best practice: Threatened species conservation in Australia. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2019, 1, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graham, M.; Taylor, J. Development of Citizen Science Water Resource Monitoring Tools and Communities of Practice for South Africa, Africa and the World; WRC Report No. TT 763/18; Water Research Commission: Gezina, South Africa, 2018; p. 141. [Google Scholar]
- Franzoni, C.; Sauermann, H. Crowd science: The organization of scientific research in open collaborative projects. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report: 2020; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, L. The case for cross-media environmental policy. Contemp. Econ. Policy 2005, 23, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangley, L. Tackling “Cross-Media” pollution. BioScience 1985, 35, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borys, D.S.; Skarzinskas, R.D.; Green, L.D. Assessing Cross-Media impacts: A comparative risk approach. Risk Anal. 1996, 16, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.C.; Bergstrom, J.; Pemberton, C. Measuring values for wetlands protection in a developing country from domestic and international citizen groups. In Proceedings of the Agricultural and Applied Economics Association (AAEA) Conferences, Montreal, QC, Canada, 27–30 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Howley, P.; Hynes, S.; O’Donoghue, C. The citizen versus consumer distinction: An exploration of individual’s preferences in contingent valuation studies. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlheim, M.; Ekasingh, B.; Frör, O.; Kitchaicharoen, J.; Neef, A.; Sangkapitux, C.; Sinphurmsukskul, N. Better than their reputation: Enhancing the validity of contingent valuation mail survey results through citizen expert groups. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2010, 53, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrício, J.; Elliott, M.; Mazik, K.; Papadopoulou, K.-N.; Smith, C.J. DPSIR—Two Decades of Trying to Develop a Unifying Framework for Marine Environmental Management? Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motew, M.; Chen, X.; Carpenter, S.R.; Booth, E.G.; Seifert, J.; Qiu, J.; Loheide, S.P.; Turner, M.G.; Zipper, S.C.; Kucharik, C.J. Comparing the effects of climate and land use on surface water quality using future watershed scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteufel, S.B.; Robertson, D.M. Water-Quality and Lake-Stage Data for Wisconsin Lakes, Water Year 2014; U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2016–1131; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; p. 170.
- Dantoin, E.D.; Robertson, D.M. Evaluation of the Effects of Changes in the Timing of Water-Level Drawdowns on the Export of Phosphorus from Little St. Germain Lake, Wisconsin; U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2018–5078; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; p. 14.
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Lake Management Plan for Nagawicka Lake, Waukesha County, Wisconsin, 2nd ed.; Community Assistance Planning Report No. 262; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 2021; p. 380. [Google Scholar]
- Government of the United States. United States Code: Title 33—Navigation and Navigable Waters; Supplement 1, Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Kent, P.G.; Dudiak, T.A. Wisconsin Water Law: A Guide to Water Rights and Regulations, 2nd ed.; Publication No G3622; University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Regional Water Quality Management Plan for Southeastern Wisconsin–2000, Volume Three, Recommended Plan; Planning Report No. 30; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 1979; p. 309. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Regional Water Quality Management Plan for Southeastern Wisconsin: An Update and Status Report; Memorandum Report No. 93; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 1995; p. 259. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Regional Water Quality Management Plan Update for the Greater Milwaukee Watersheds; Planning Report No. 50; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 2007; p. 1072. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, C.A.; Crawford, J.K.; Otto, K.L.; Manning, R.L.; Meyer, M.T.; Furlong, E.T. Concentrations of Selected Pharmaceuticals and Antibiotics in South-Central Pennsylvania Waters, March through September 2006; US Geological Survey Data Series 300; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2007; p. 101.
- Sciacca, S.; Oliveri Conti, G. Mutagens and carcinogens in drinking water. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 2, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Pharmaceuticals in Drinking-Water; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Water Quality Management Plan for Pewaukee Lake, Waukesha County, Wisconsin; Community Assistance Planning Report No. 58; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Lake Management Plan for Pewaukee Lake, Waukesha County, Wisconsin, 2nd ed.; Community Assistance Planning Report No. 58; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 2003; p. 242. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Lake Management Plan for Pewaukee Lake, Waukesha County, Wisconsin, 3rd ed.; Community Assistance Planning Report No. 58; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 2020; p. 380. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Lakefront Recreational Use and Waterway Protection Plan for the Village of Pewaukee; Memorandum Report No. 56; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 1996; p. 68. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). Pewaukee River Watershed Protection Plan; Community Assistance Planning Report No. 313; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 2013; p. 408. [Google Scholar]
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources and University of Wisconsin-Extension. Quality Assurance Project Plan for Citizen Lake Monitoring Network for Water Clarity, Water Chemistry, Dissolved Oxygen and Native Aquatic Plant Monitoring; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources and University of Wisconsin-Extension: Rhinelander, WI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Panuska, J.C.; Kreider, J.C. Wisconsin Lake Modeling Suite Program Documentation and User’s Manual, Version 3.3 for Windows; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources Publication No. PUBL-WR-363-94; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources: Madison, WI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, The Cadmus Group, and US Geological Survey. Estimations of Sources of Water Quality Impairments at Ungaged Sites in the Upper Wisconsin River Basin: A SWAT Model in Support of the Wisconsin River TMDL; Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Bureau of Water Quality: Madison, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC). A Lake Management Plan for George Lake, Kenosha County, Wisconsin; Community Assistance Planning Report No. 300; Southeastern Wisconsin Regional Planning Commission (SEWRPC): Waukesha, WI, USA, 2007; p. 166. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thornton, J.A.; Harding, W.R.; Slawski, T.M.; Lin, H. Monitoring and Evaluation: The Foundation for Lake and Reservoir Management. Earth 2022, 3, 115-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3010008
Thornton JA, Harding WR, Slawski TM, Lin H. Monitoring and Evaluation: The Foundation for Lake and Reservoir Management. Earth. 2022; 3(1):115-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleThornton, Jeffrey A., William R. Harding, Thomas M. Slawski, and Hebin Lin. 2022. "Monitoring and Evaluation: The Foundation for Lake and Reservoir Management" Earth 3, no. 1: 115-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3010008
APA StyleThornton, J. A., Harding, W. R., Slawski, T. M., & Lin, H. (2022). Monitoring and Evaluation: The Foundation for Lake and Reservoir Management. Earth, 3(1), 115-124. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth3010008





