Multiscale Correlation Analysis between Wind Direction and Meteorological Parameters in Guadeloupe Archipelago
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Description
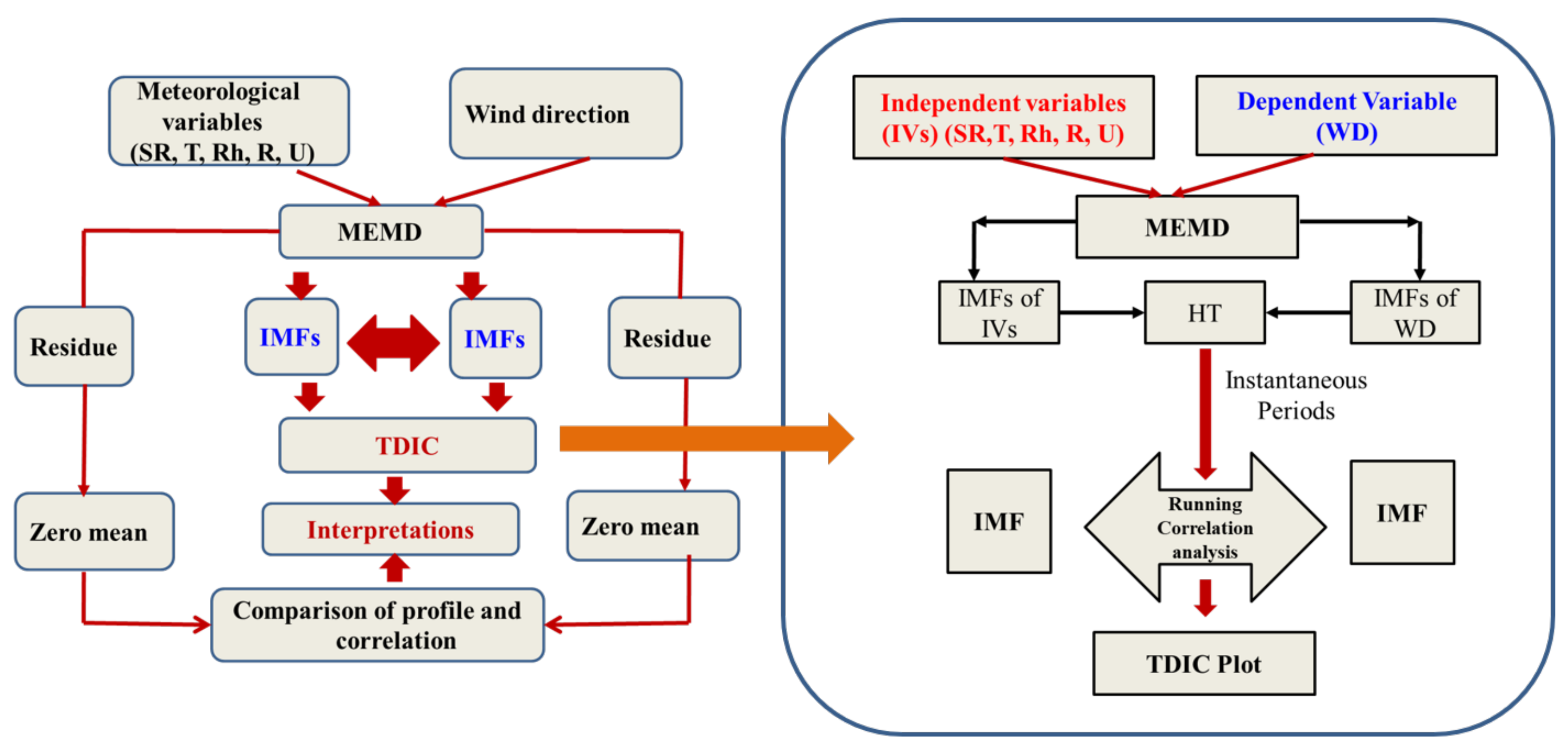
2.2. Multi-Scale Multidimensional Correlation Analysis
2.2.1. MEMD
- 1.
- A suitable set of direction vectors are generated by sampling on a unit hyper-sphere;
- 2.
- The projection of the dataset are calculated along the direction vector for all k;
- 3.
- Temporal instants are identified corresponding to the maxima of projection for all k;
- 4.
- is interpolated to obtain multivariate envelope curves for all k;
- 5.
- The mean of envelope curves is calculated by ;
- 6.
- The “detail” is extracted using . If fulfils the stoppage criterion for a multivariate IMF, the above procedure from step (1) onwards is applied upon the residue series (i.e., ). Otherwise, steps from (2) onwards are repeated upon the series .
2.2.2. HSA
2.2.3. TDIC
- 1.
- All time series data are decomposed using MEMD;
- 2.
- The periodicities of the IMFs of the two time series of concern are compared and the IMFs with nearly same mean periodicity are selected;
- 3.
- The ITs of both IMFs (of similar scale) are identified by HT;
- 4.
- The minimum sliding window size () is identified as the maximum of ITs between the two signals at the current position , i.e., ;
- 5.
- The sliding window is then fixed as where n is any positive number (a multiplication factor for minimum sliding window size). In general, n is selected as 1 [46];
- 6.
- IMF1 and IMF2 are given as two IMFs of nearly the same mean period pertaining to two different time series. The TDIC of the pair of IMFs can be found out as at any , where is the correlation coefficient of two time series;
- 7.
- Student’s t-tests are performed to investigate whether the difference between the correlation coefficient and zero is statistically significant or not;
- 8.
- Steps 4 to 7 are repeated iteratively till the boundary of the sliding window exceeds the end points of the time series.
3. Results and Discussion
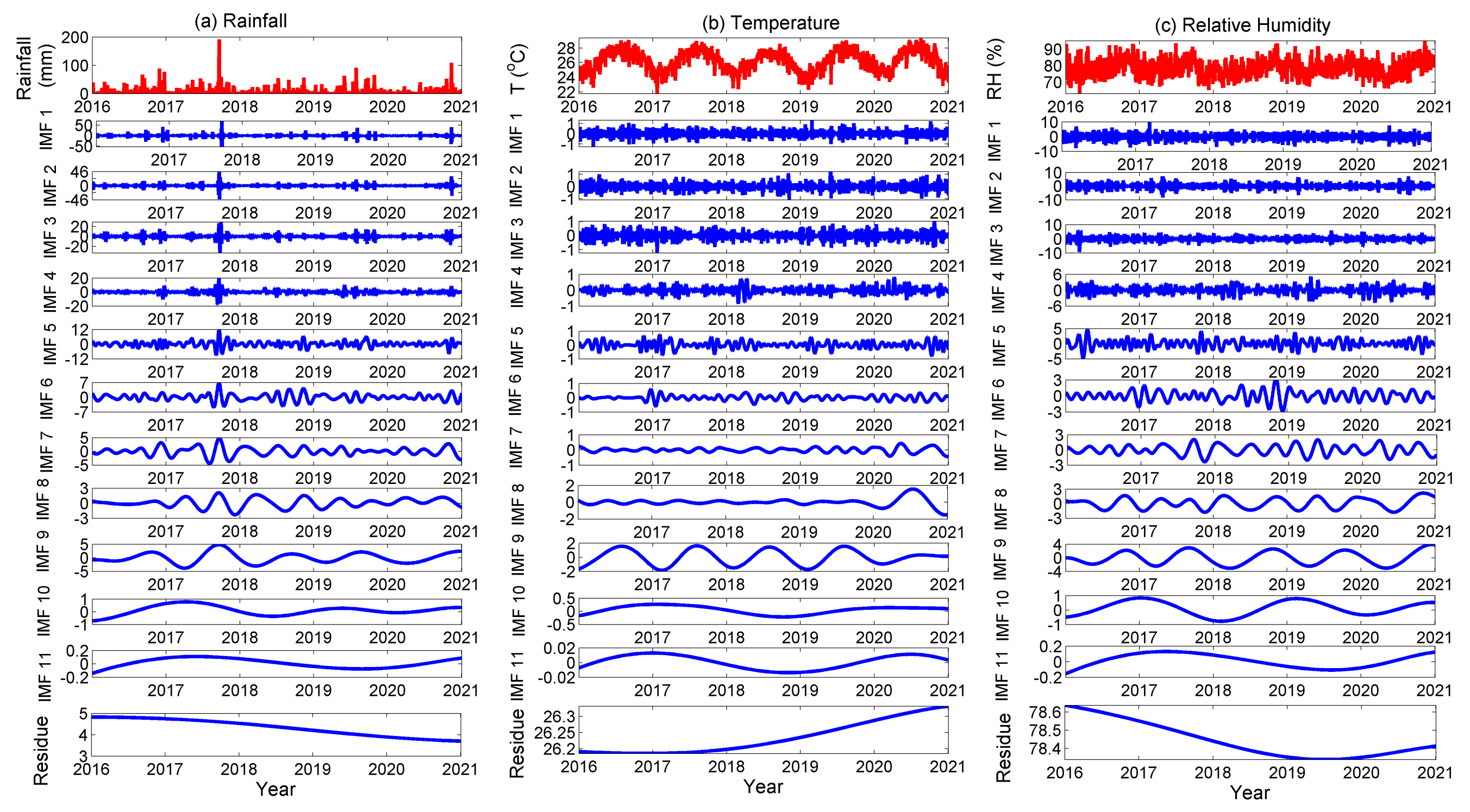
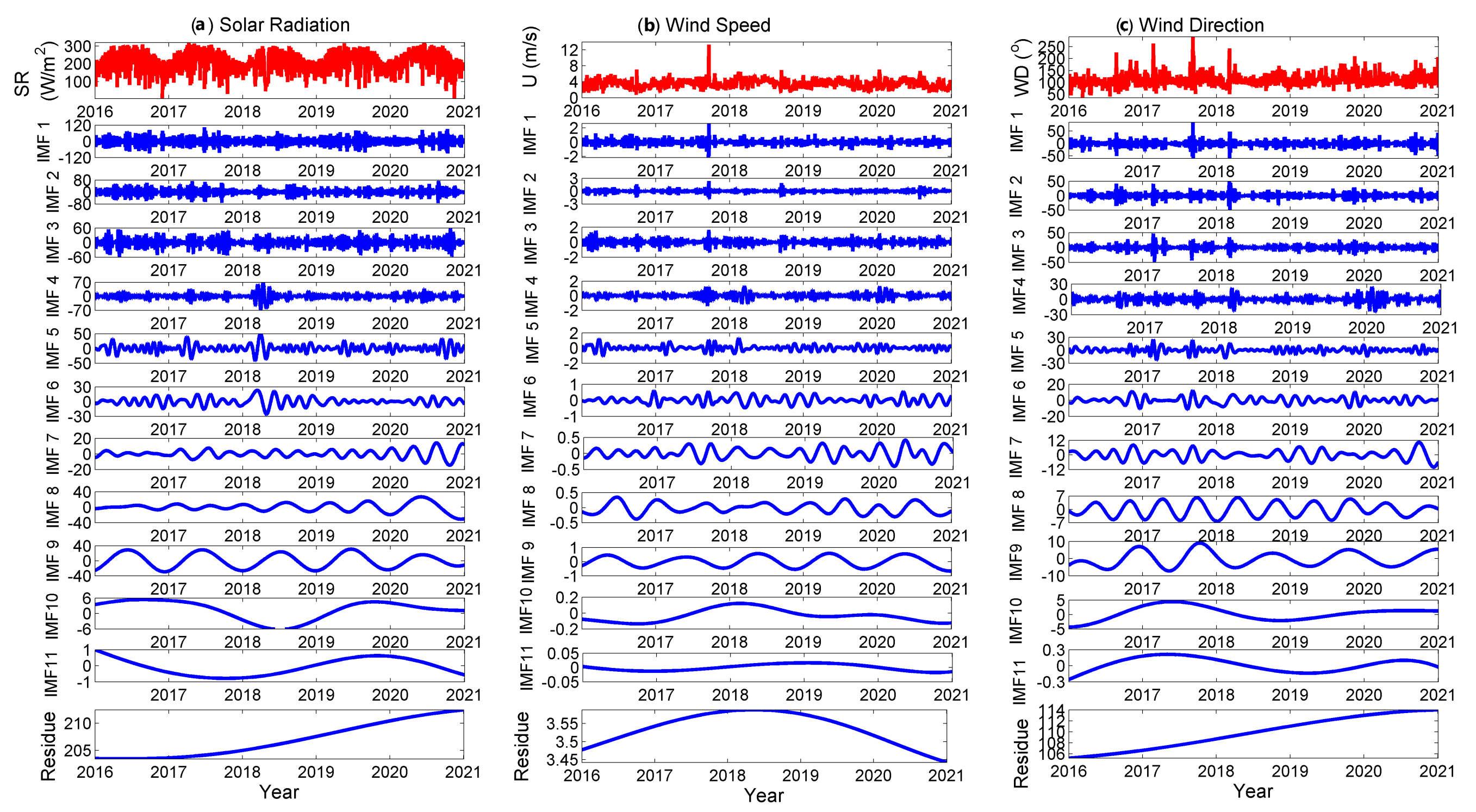
3.1. MEMD Analysis
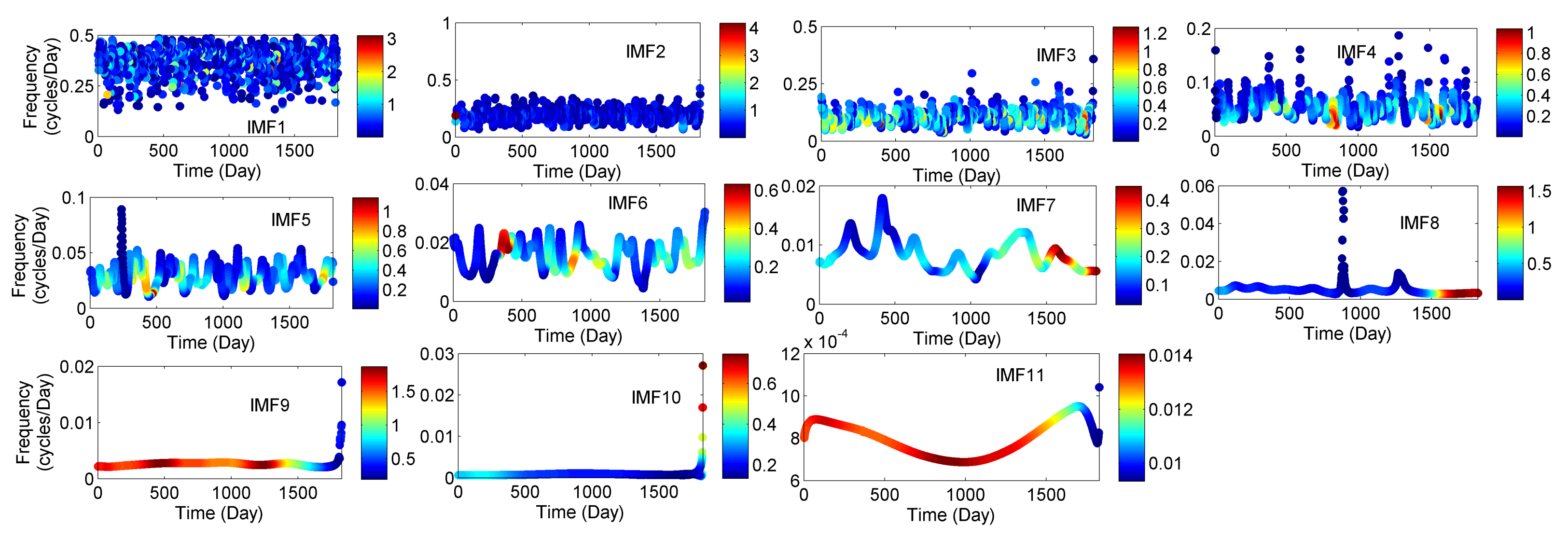
3.2. Instantaneous Frequency of Meteorological Parameters (IMFs)
3.3. TDIC Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharholy, M.; Ahmad, K.; Mahmood, G.; Trivedi, R. Municipal solid waste management in Indian cities—A review. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaia, R.G.d.S.M.; Costa, A.M.; Campos, J.C. Municipal solid waste in Brazil: A review. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 1195–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yadav, P.; Samadder, S. A global prospective of income distribution and its effect on life cycle assessment of municipal solid waste management: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9123–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanda, S.; Berruti, F. Municipal solid waste management and landfilling technologies: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1433–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Jacoby-Koaly, S.; Petit, R.H.; Roussas, A. Estimation of methane emission from a waste dome in a tropical insular area. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Jacoby-Koaly, S.; Bernard, M.; Molinié, J.; Roussas, A. Impact of a new legislation on volatile organic compounds emissions in an open landfill in tropical insular climate. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul, S. Environmental and health impact of solid waste disposal at Mangwaneni dumpsite in Manzini: Swaziland. J. Sustain. Dev. Afr. 2010, 12, 64–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sankoh, F.P.; Yan, X.; Tran, Q. Environmental and health impact of solid waste disposal in developing cities: A case study of granville brook dumpsite, Freetown, Sierra Leone. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 2013, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Sun, P.; Lin, B.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Xiang, M.; Li, H.; Guo, S. Effects of ambient air pollution from municipal solid waste landfill on children’s non-specific immunity and respiratory health. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinn-Gofroń, A.; Strzelczak, A.; Wolski, T. The relationships between air pollutants, meteorological parameters and concentration of airborne fungal spores. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ying, Q.; Hu, X.M. Relationships between meteorological parameters and criteria air pollutants in three megacities in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindra, K.; Goyal, A.; Mor, S. Influence of meteorological parameters and air pollutants on the airborne pollen of city Chandigarh, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzworth, G.C. Mixing depths, wind speeds and air pollution potential for selected locations in the United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1967, 6, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.L.; Dong, G.; Leung, C.W.; Cheung, C.S.; Hung, W. Validation of a two-dimensional pollutant dispersion model in an isolated street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Dorville, J.F.; Monjoly, S.; Jacoby-Koaly, S.; André, M. Assessment of Nitrogen Oxides and Ground-Level Ozone behavior in a dense air quality station network: Case study in the Lesser Antilles Arc. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 1278–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coccia, M. The effects of atmospheric stability with low wind speed and of air pollution on the accelerated transmission dynamics of COVID-19. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 78, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccia, M. How do low wind speeds and high levels of air pollution support the spread of COVID-19? Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Wang, Y.; Su, W.; Yang, H. A varying-coefficient regression approach to modeling the effects of wind speed on the dispersion of pollutants. Environ. Ecol. Stat. 2022, 29, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, M.C.; Mukerjee, S.; Fox, D.L. Estimating the wind direction of maximum air pollutant concentration. Environmetrics 1996, 7, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statheropoulos, M.; Vassiliadis, N.; Pappa, A. Principal component and canonical correlation analysis for examining air pollution and meteorological data. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.C.; Chang, Y.S.; Spiegelman, C.H. Locating nearby sources of air pollution by nonparametric regression of atmospheric concentrations on wind direction. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardoulakis, S.; Valiantis, M.; Milner, J.; ApSimon, H. Operational air pollution modelling in the UK–Street canyon applications and challenges. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4622–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Corr, D.; Deluca, P.; Kanaroglou, P.; McCarry, B. Mobile monitoring of air pollution in cities: The case of Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.B.; Woo, D.; Bae, G.N. Influence of wind direction and speed on the transport of particle-bound PAHs in a roadway environment. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleke, T.B.; Si, B.C. Characterizing scale-dependent spatial relationships between soil properties using multifractal techniques. Geoderma 2006, 134, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Euphrasie-Clotilde, L.; Calif, R.; Brute, F. Quantifying spatio-temporal dynamics of African dust detection threshold for PM10 concentrations in the Caribbean area using multiscale decomposition. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, N.; Mandic, D.P. Multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Proc. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 466, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. The time-dependent intrinsic correlation based on the empirical mode decomposition. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 233–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T. Detecting the Causal Nexus between Particulate Matter (PM10) and Rainfall in the Caribbean Area. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peel, M.C.; Finlayson, B.L.; McMahon, T.A. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plocoste, T.; Jacoby-Koaly, S.; Petit, R.; Molinié, J.; Roussas, A. In situ quantification and tracking of volatile organic compounds with a portable mass spectrometer in tropical waste and urban sites. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2280–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T. Multiscale analysis of the dynamic relationship between particulate matter (PM10) and meteorological parameters using CEEMDAN: A focus on “Godzilla” African dust event. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, S.; Reddy, M.J. Multi-Scale Spectral Analysis in Hydrology: From Theory to Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, Z.; Long, S.R.; Arnold, K.C.; Chen, X.; Blank, K. On instantaneous frequency. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 177–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.E.; Colominas, M.A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Flandrin, P. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 4144–4147. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Ouarda, T.B. Prediction of climate nonstationary oscillation processes with empirical mode decomposition. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iyengar, R.; Raghu Kanth, S. Intrinsic mode functions and a strategy for forecasting Indian monsoon rainfall. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 90, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massei, N.; Fournier, M. Assessing the expression of large-scale climatic fluctuations in the hydrological variability of daily Seine river flow (France) between 1950 and 2008 using Hilbert–Huang Transform. J. Hydrol. 2012, 448, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antico, A.; Schlotthauer, G.; Torres, M.E. Analysis of hydroclimatic variability and trends using a novel empirical mode decomposition: Application to the Paraná River Basin. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1218–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E.; Long, S.R.; Peng, C.K. On the trend, detrending, and variability of nonlinear and nonstationary time series. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14889–14894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Si, B.C. Soil water prediction based on its scale-specific control using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Geoderma 2013, 193, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, S.; Janga Reddy, M. Evaluation of trends and predictability of short-term droughts in three meteorological subdivisions of India using multivariate EMD-based hybrid modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, G.; Su, Y.; Kareem, A.; Liao, H. Time-frequency analysis of nonstationary process based on multivariate empirical mode decomposition. J. Eng. Mech. 2016, 142, 04015065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, R.P. Linear Integral Equations; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Schmitt, F.G. Time dependent intrinsic correlation analysis of temperature and dissolved oxygen time series using empirical mode decomposition. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 130, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, D.K.B.; Lazure, P.; Puillat, I. Advanced spectral analysis and cross correlation based on the empirical mode decomposition: Application to the environmental time series. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1968–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derot, J.; Schmitt, F.G.; Gentilhomme, V.; Morin, P. Correlation between long-term marine temperature time series from the eastern and western English Channel: Scaling analysis using empirical mode decomposition. C. R. Geosci. 2016, 348, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Calif, R.; Jacoby-Koaly, S. Multi-scale time dependent correlation between synchronous measurements of ground-level ozone and meteorological parameters in the Caribbean Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 211, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, S.; Reddy, M.J. Multiscale characterization and prediction of monsoon rainfall in India using Hilbert—Huang transform and time-dependent intrinsic correlation analysis. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2018, 130, 667–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Calif, R.; Euphrasie-Clotilde, L.; Brute, F.N. Investigation of local correlations between particulate matter (PM10) and air temperature in the Caribbean basin using Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1692–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Pavón-Domínguez, P. Multifractal detrended cross-correlation analysis of wind speed and solar radiation. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2020, 30, 113109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzwiller, M.C. Moon-Earth-Sun: The oldest three-body problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plocoste, T.; Jacoby-Koaly, S.; Molinié, J.; Petit, R. Evidence of the effect of an urban heat island on air quality near a landfill. Urban Clim. 2014, 10, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Wen, F.; Gong, X. Time-dependent intrinsic correlation analysis of crude oil and the US dollar based on CEEMDAN. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2021, 26, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 13, p. 666. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, T.T. Downbursts: Meteorological features and wind field characteristics. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1990, 36, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johny, K.; Pai, M.L.; Adarsh, S. A multivariate EMD-LSTM model aided with Time Dependent Intrinsic Cross-Correlation for monthly rainfall prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 123, 108941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


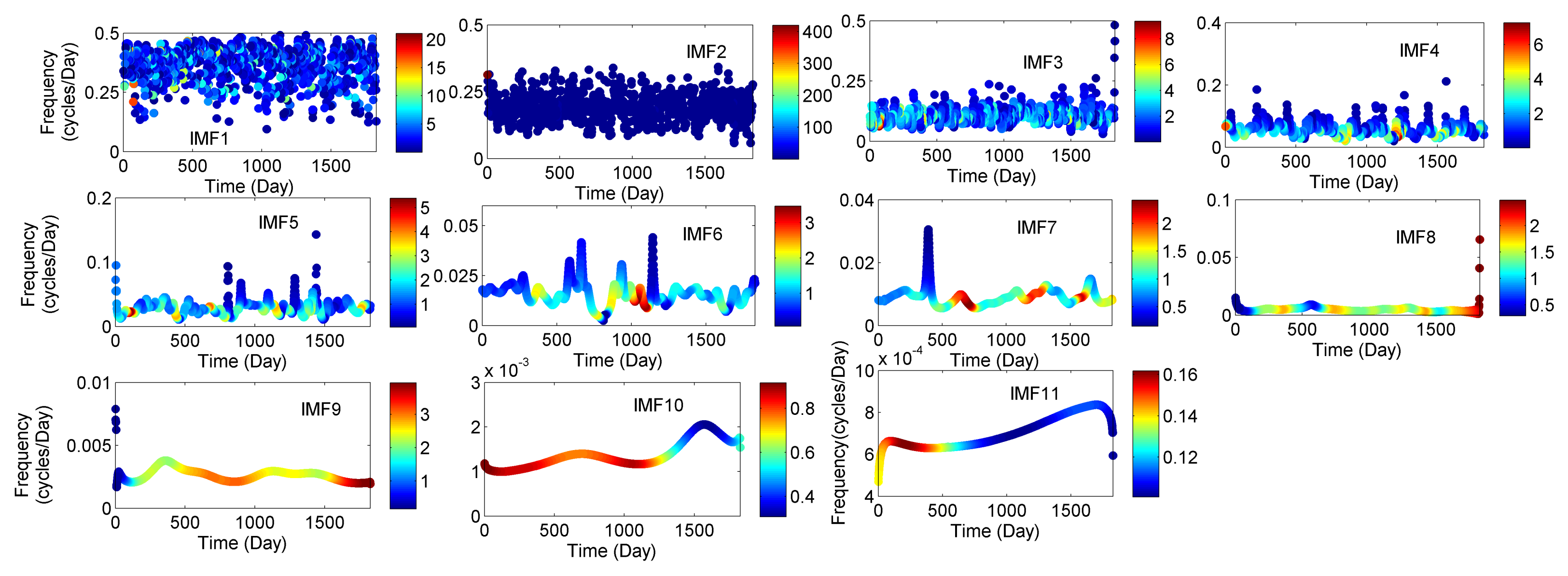
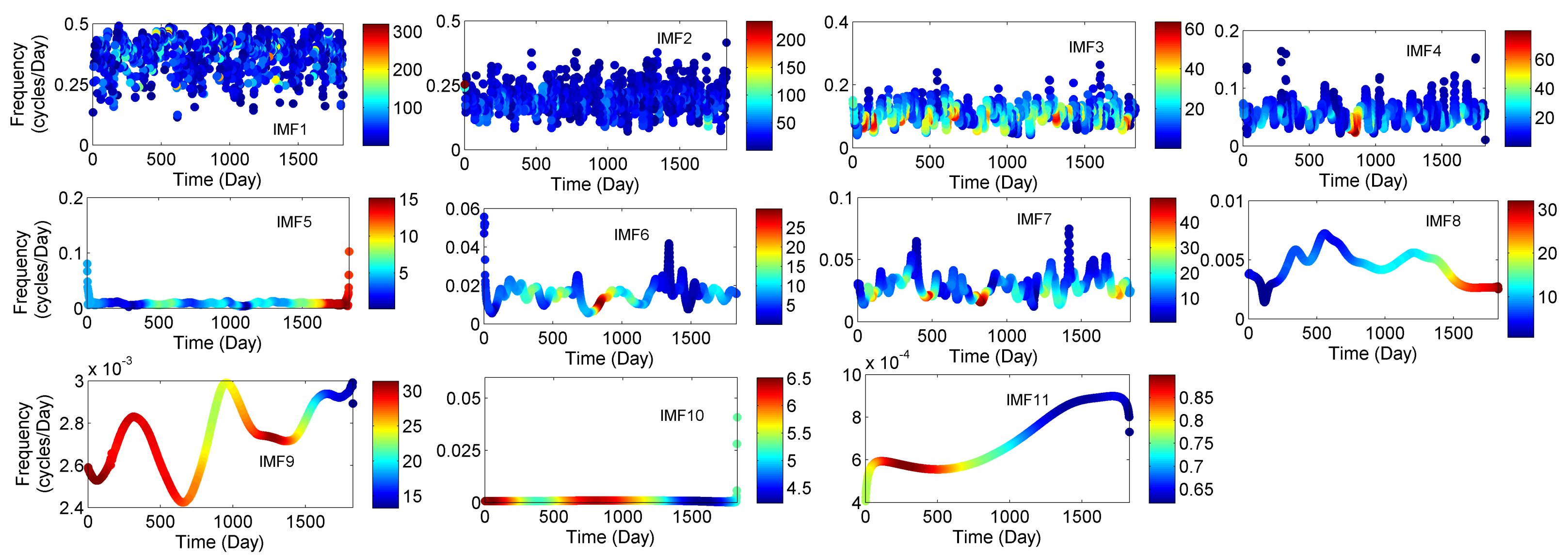
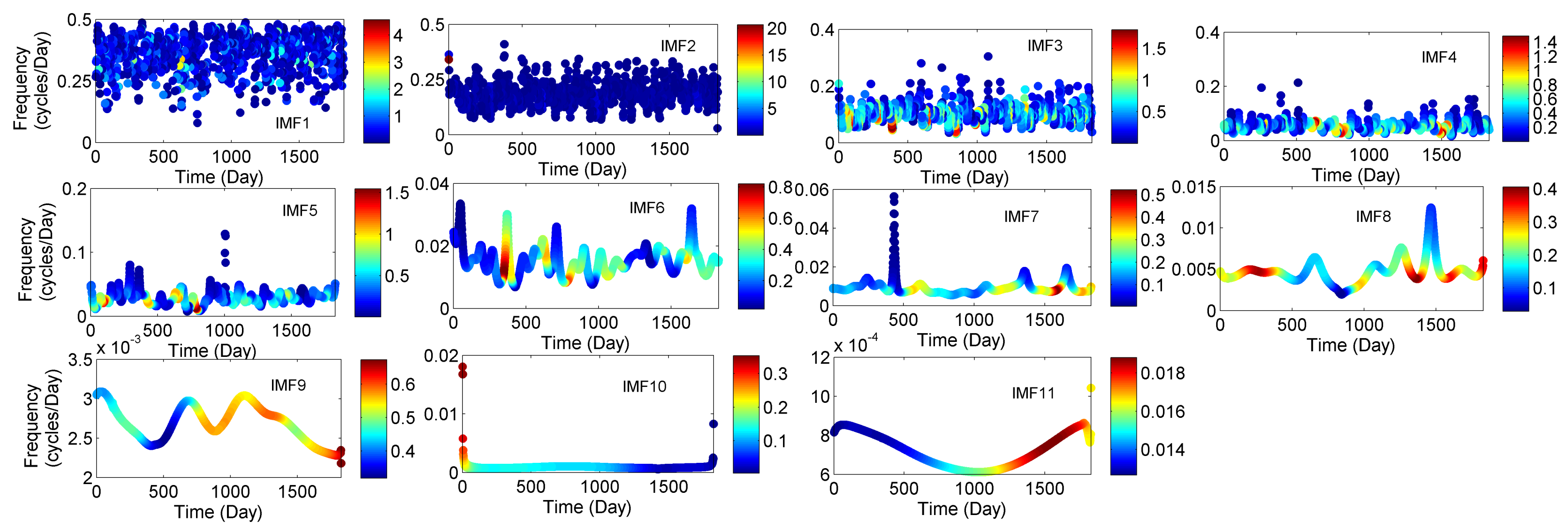

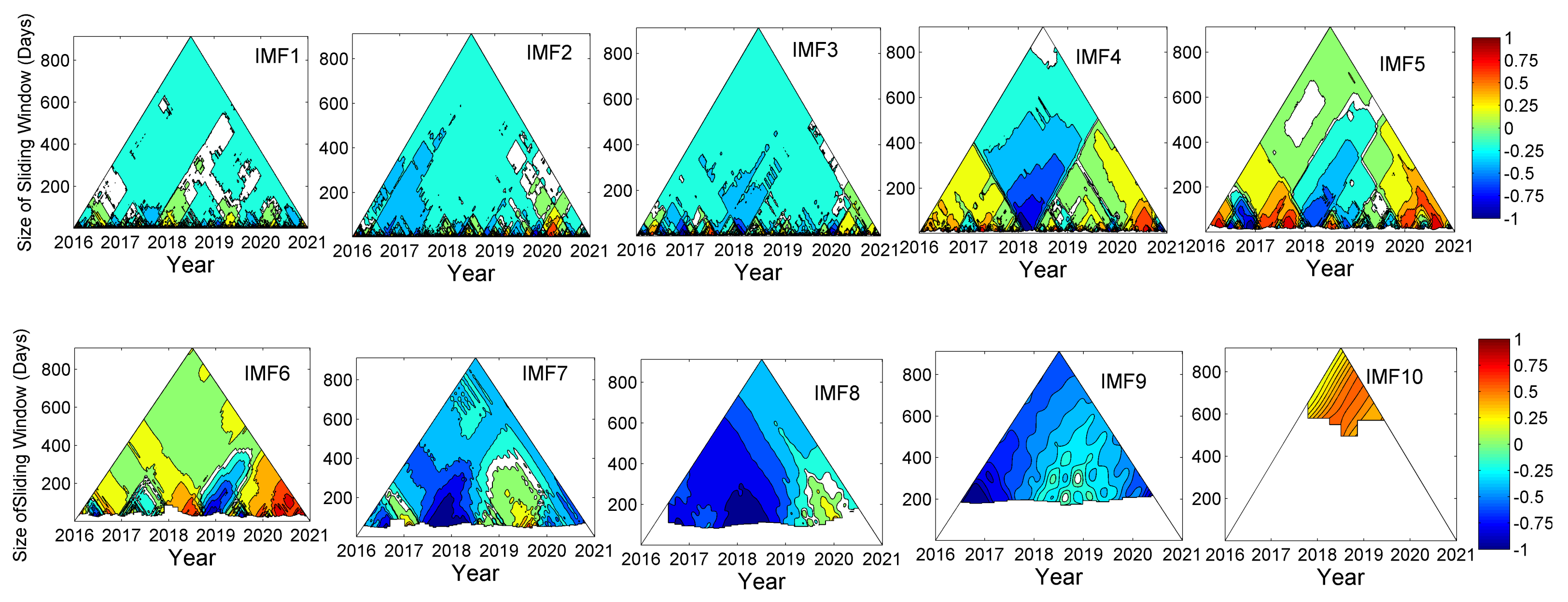
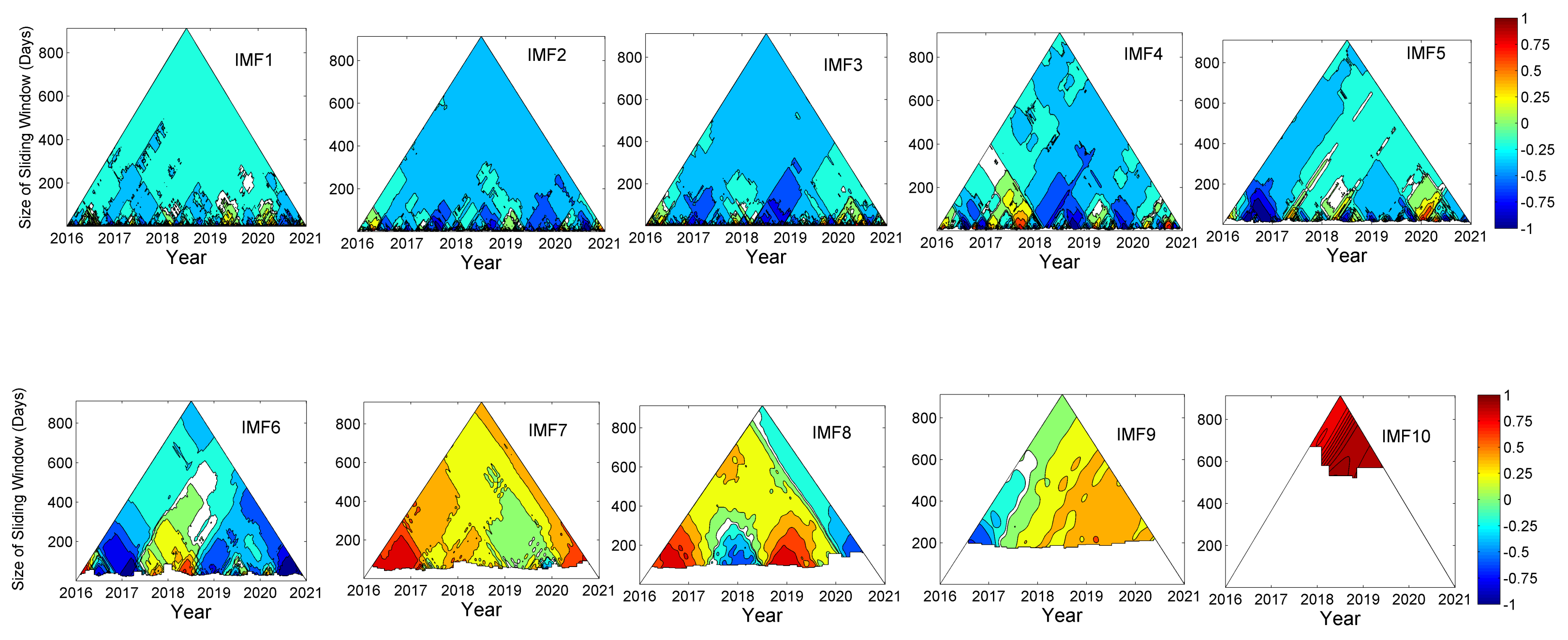
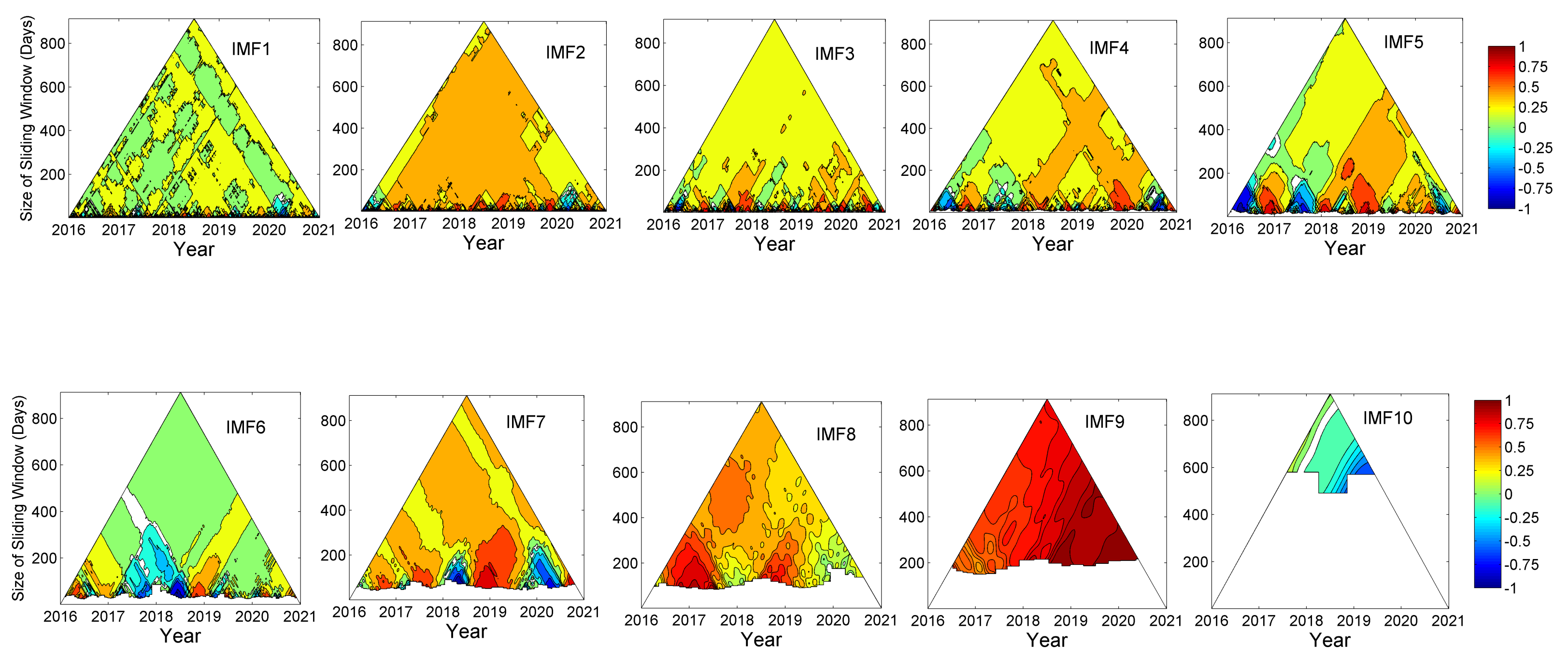

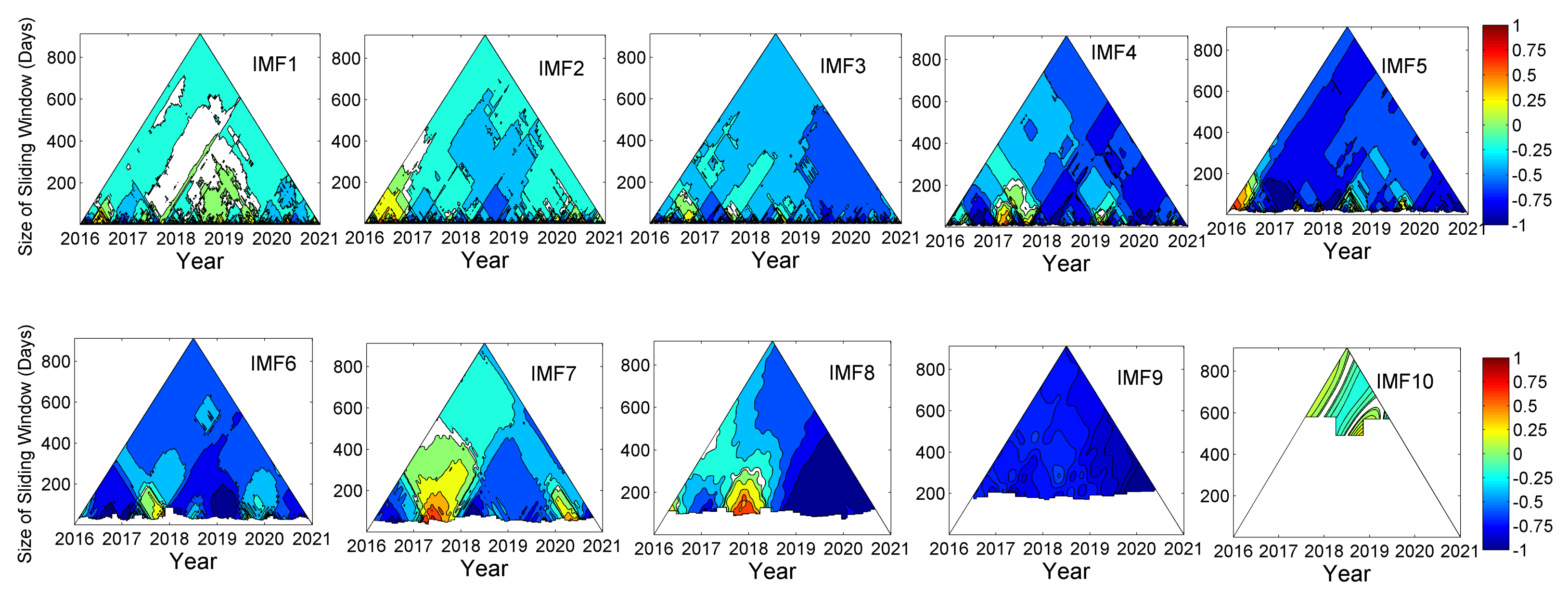
| Rainfall | Temperature | Relative Humidity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modes | (Days) | V (%) | (Days) | V (%) | (Days) | V (%) |
| IMF1 | 2.905 | 38.974 | 2.671 | 5.536 | 2.687 | 19.992 |
| IMF2 | 4.885 | 20.720 | 4.872 | 5.000 | 4.978 | 16.638 |
| IMF3 | 8.742 | 17.364 | 8.659 | 5.550 | 8.659 | 13.764 |
| IMF4 | 16.459 | 8.236 | 15.887 | 2.911 | 16.917 | 9.980 |
| IMF5 | 31.500 | 5.265 | 31.500 | 3.656 | 33.218 | 8.820 |
| IMF6 | 60.900 | 2.547 | 57.094 | 1.584 | 60.900 | 3.796 |
| IMF7 | 101.500 | 2.202 | 114.188 | 1.259 | 114.188 | 4.085 |
| IMF8 | 203.000 | 0.776 | 203.000 | 12.268 | 203.000 | 5.074 |
| IMF9 | 304.500 | 3.633 | 365.400 | 60.834 | 304.500 | 16.740 |
| IMF10 | 609.000 | 0.130 | 913.500 | 1.260 | 609.000 | 1.039 |
| IMF11 | 1827.000 | 0.004 | 913.500 | 0.005 | 1827.000 | 0.031 |
| Residue | LT | 0.150 | LT | 0.139 | LT | 0.041 |
| Solar radiation | Wind speed | Wind direction | ||||
| Modes | (Days) | V (%) | (Days) | V (%) | (Days) | V (%) |
| IMF1 | 2.687 | 31.998 | 2.659 | 13.060 | 2.699 | 29.116 |
| IMF2 | 4.885 | 15.998 | 4.911 | 14.761 | 4.885 | 18.601 |
| IMF3 | 8.869 | 12.871 | 8.659 | 17.381 | 8.659 | 17.494 |
| IMF4 | 17.075 | 9.077 | 16.761 | 15.065 | 16.917 | 10.567 |
| IMF5 | 34.472 | 7.192 | 32.053 | 13.015 | 32.625 | 8.337 |
| IMF6 | 60.900 | 2.249 | 63.000 | 5.008 | 60.900 | 3.432 |
| IMF7 | 107.471 | 0.941 | 107.471 | 2.962 | 101.500 | 3.068 |
| IMF8 | 228.375 | 4.901 | 203.000 | 3.214 | 182.700 | 2.666 |
| IMF9 | 365.400 | 13.829 | 365.400 | 14.635 | 365.400 | 3.752 |
| IMF10 | 913.500 | 0.547 | 913.500 | 0.685 | 913.500 | 1.121 |
| IMF11 | 1827.000 | 0.011 | 1827.000 | 0.014 | 913.500 | 0.003 |
| Residue | LT | 0.388 | 1827.000 | 0.200 | LT | 1.842 |
| Parameters | Pearson Correlation |
|---|---|
| vs. R | 0.11 |
| vs. T | −0.04 |
| vs. | 0.32 |
| vs. | −0.08 |
| vs. U | −0.29 |
| Rainfall | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Direction | IMF1 | IMF2 | IMF3 | IMF4 | IMF5 | IMF6 | IMF7 | IMF8 | IMF9 | IMF10 | IMF11 | Residue |
| IMF1 | 0.085 | −0.003 | −0.009 | 0.003 | −0.009 | −0.008 | −0.015 | −0.003 | −0.006 | −0.005 | −0.004 | 0.006 |
| IMF2 | −0.004 | 0.166 | 0.023 | −0.004 | −0.006 | 0.006 | −0.001 | 0.011 | −0.003 | −0.003 | −0.001 | 0.002 |
| IMF3 | −0.008 | 0.004 | 0.101 | 0.021 | 0.000 | −0.015 | −0.006 | −0.001 | −0.007 | −0.004 | −0.005 | 0.010 |
| IMF4 | 0.003 | 0.000 | −0.016 | −0.050 | 0.040 | 0.003 | 0.004 | −0.003 | −0.016 | −0.017 | −0.011 | −0.019 |
| IMF5 | 0.012 | −0.015 | 0.016 | −0.007 | −0.050 | 0.047 | 0.010 | 0.022 | 0.002 | 0.017 | 0.000 | 0.006 |
| IMF6 | −0.009 | −0.020 | 0.021 | 0.015 | −0.045 | 0.023 | 0.038 | 0.045 | −0.002 | −0.020 | −0.019 | 0.007 |
| IMF7 | −0.010 | −0.007 | −0.019 | −0.008 | −0.016 | 0.009 | 0.288 | 0.054 | −0.066 | 0.031 | 0.044 | −0.008 |
| IMF8 | −0.004 | −0.006 | −0.007 | 0.007 | 0.028 | 0.056 | 0.178 | 0.690 | −0.104 | 0.036 | 0.041 | 0.144 |
| IMF9 | −0.038 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.016 | 0.031 | −0.071 | −0.006 | 0.744 | 0.115 | 0.038 | 0.056 |
| IMF10 | −0.018 | −0.002 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.026 | −0.024 | 0.014 | 0.233 | 0.816 | 0.664 | −0.014 |
| IMF11 | −0.018 | −0.001 | 0.012 | −0.002 | 0.001 | −0.002 | −0.051 | −0.004 | 0.184 | 0.765 | 0.880 | −0.318 |
| Residue | 0.004 | −0.005 | −0.015 | 0.015 | 0.007 | −0.004 | 0.048 | −0.047 | −0.097 | −0.007 | 0.228 | −0.993 |
| Wind direction | Temperature | |||||||||||
| IMF1 | −0.153 | 0.012 | 0.020 | −0.027 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.023 | 0.011 | −0.002 | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.008 |
| IMF2 | 0.003 | −0.204 | −0.057 | 0.000 | 0.005 | −0.008 | 0.012 | −0.013 | 0.005 | −0.007 | −0.009 | 0.012 |
| IMF3 | 0.020 | −0.039 | −0.228 | −0.045 | −0.009 | −0.005 | 0.017 | −0.001 | −0.002 | 0.000 | −0.001 | 0.003 |
| IMF4 | 0.002 | 0.011 | −0.006 | −0.186 | −0.008 | 0.030 | 0.015 | −0.004 | −0.001 | 0.015 | 0.019 | 0.015 |
| IMF5 | 0.013 | 0.015 | −0.001 | −0.074 | −0.188 | 0.007 | 0.018 | −0.002 | 0.004 | −0.018 | −0.005 | −0.027 |
| IMF6 | 0.006 | −0.005 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.059 | −0.245 | −0.078 | 0.046 | −0.027 | 0.023 | 0.016 | −0.005 |
| IMF7 | 0.003 | −0.004 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.019 | −0.022 | 0.505 | 0.088 | 0.003 | −0.019 | −0.002 | −0.007 |
| IMF8 | 0.020 | −0.002 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.018 | −0.004 | 0.171 | −0.059 | −0.225 | 0.038 | 0.134 | 0.044 |
| IMF9 | −0.019 | 0.001 | 0.003 | −0.008 | 0.022 | 0.080 | −0.039 | −0.023 | 0.117 | −0.004 | 0.028 | 0.001 |
| IMF10 | −0.012 | −0.005 | −0.002 | −0.016 | 0.009 | 0.036 | −0.018 | 0.001 | 0.134 | 0.776 | 0.780 | −0.162 |
| IMF11 | −0.005 | −0.007 | −0.007 | −0.016 | 0.010 | 0.048 | −0.003 | −0.026 | 0.028 | 0.630 | 0.721 | −0.147 |
| Residue | −0.003 | 0.002 | 0.010 | −0.013 | −0.004 | 0.015 | −0.054 | 0.031 | 0.076 | 0.002 | −0.197 | 0.941 |
| Wind direction | Relative humidity | |||||||||||
| IMF1 | 0.199 | −0.004 | −0.008 | 0.014 | −0.007 | 0.005 | −0.021 | 0.004 | 0.005 | −0.012 | −0.011 | 0.002 |
| IMF2 | 0.014 | 0.386 | 0.057 | −0.004 | −0.001 | 0.002 | −0.004 | 0.012 | −0.004 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| IMF3 | −0.016 | 0.041 | 0.304 | 0.063 | −0.009 | −0.004 | 0.007 | 0.018 | −0.007 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.012 |
| IMF4 | 0.000 | −0.006 | 0.029 | 0.345 | 0.081 | −0.007 | −0.016 | 0.014 | 0.002 | −0.021 | −0.013 | −0.029 |
| IMF5 | 0.007 | −0.013 | 0.012 | 0.045 | 0.200 | 0.088 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.009 | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.019 |
| IMF6 | 0.007 | −0.004 | 0.005 | 0.009 | −0.012 | 0.151 | 0.155 | 0.017 | 0.010 | 0.017 | 0.015 | −0.003 |
| IMF7 | −0.013 | −0.004 | −0.012 | −0.008 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.454 | 0.084 | −0.063 | −0.001 | 0.016 | −0.017 |
| IMF8 | −0.004 | −0.003 | −0.013 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.007 | 0.055 | 0.398 | 0.123 | 0.003 | −0.061 | 0.119 |
| IMF9 | −0.033 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.015 | 0.039 | −0.068 | 0.030 | 0.760 | 0.111 | 0.015 | 0.093 |
| IMF10 | −0.004 | −0.010 | 0.001 | 0.017 | 0.007 | 0.075 | −0.011 | −0.014 | 0.042 | 0.107 | 0.022 | 0.010 |
| IMF11 | −0.017 | −0.003 | 0.009 | −0.002 | 0.002 | 0.003 | −0.051 | −0.016 | 0.165 | 0.753 | 0.889 | −0.309 |
| Residue | 0.003 | −0.010 | −0.025 | 0.015 | 0.012 | 0.023 | 0.020 | −0.073 | −0.119 | 0.001 | 0.271 | −0.894 |
| Wind direction | Solar radiation | |||||||||||
| IMF1 | −0.056 | −0.002 | 0.014 | −0.012 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.007 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.008 | −0.010 |
| IMF2 | 0.007 | −0.128 | −0.026 | 0.003 | 0.001 | −0.006 | −0.009 | −0.008 | 0.001 | −0.004 | −0.002 | −0.007 |
| IMF3 | 0.003 | −0.008 | −0.093 | 0.002 | −0.006 | 0.000 | 0.004 | −0.004 | 0.002 | 0.013 | 0.013 | −0.002 |
| IMF4 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.004 | −0.015 | −0.005 | 0.005 | −0.003 | −0.008 | 0.013 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.006 |
| IMF5 | −0.002 | −0.001 | −0.022 | 0.051 | 0.152 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.017 | −0.023 | −0.006 | 0.006 | −0.018 |
| IMF6 | 0.006 | 0.010 | −0.009 | −0.016 | 0.059 | 0.202 | −0.071 | 0.026 | −0.043 | −0.001 | 0.009 | 0.000 |
| IMF7 | 0.007 | −0.002 | 0.005 | 0.018 | −0.001 | −0.031 | −0.349 | −0.144 | 0.023 | −0.010 | −0.018 | 0.007 |
| IMF8 | 0.013 | 0.005 | 0.005 | −0.010 | 0.010 | −0.049 | 0.048 | −0.270 | −0.261 | 0.000 | 0.089 | −0.047 |
| IMF9 | 0.005 | −0.001 | −0.002 | −0.005 | 0.015 | 0.066 | −0.004 | −0.030 | −0.533 | −0.047 | −0.008 | −0.063 |
| IMF10 | 0.000 | −0.008 | −0.020 | −0.002 | 0.014 | 0.051 | 0.007 | −0.014 | −0.015 | 0.215 | 0.171 | −0.203 |
| IMF11 | 0.017 | −0.002 | −0.017 | −0.002 | 0.003 | 0.026 | 0.048 | −0.003 | −0.183 | −0.612 | −0.707 | 0.254 |
| Residue | −0.004 | 0.004 | 0.013 | −0.014 | −0.006 | 0.008 | −0.050 | 0.040 | 0.087 | −0.003 | −0.224 | 0.977 |
| Wind direction | Wind speed | |||||||||||
| IMF1 | −0.085 | 0.012 | 0.007 | −0.025 | 0.001 | 0.012 | 0.002 | 0.011 | −0.010 | 0.008 | 0.013 | 0.004 |
| IMF2 | 0.000 | −0.096 | −0.066 | −0.002 | 0.002 | −0.009 | 0.000 | −0.006 | 0.005 | 0.009 | 0.010 | −0.006 |
| IMF3 | 0.021 | −0.035 | −0.294 | −0.058 | −0.030 | −0.014 | 0.000 | −0.014 | −0.010 | −0.015 | −0.014 | −0.004 |
| IMF4 | −0.006 | 0.011 | −0.012 | −0.465 | −0.014 | 0.039 | 0.024 | −0.009 | −0.018 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.011 |
| IMF5 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.010 | −0.098 | −0.489 | −0.065 | −0.002 | 0.002 | 0.009 | −0.018 | −0.018 | −0.019 |
| IMF6 | −0.003 | −0.009 | 0.016 | 0.019 | −0.061 | −0.480 | −0.093 | −0.066 | −0.011 | −0.001 | −0.009 | 0.002 |
| IMF7 | 0.003 | 0.001 | −0.006 | 0.018 | −0.026 | −0.097 | −0.265 | −0.076 | −0.022 | 0.031 | 0.015 | 0.020 |
| IMF8 | 0.001 | −0.002 | 0.001 | −0.008 | −0.035 | −0.006 | −0.039 | −0.383 | −0.111 | 0.026 | 0.084 | −0.080 |
| IMF9 | 0.022 | 0.000 | −0.006 | −0.011 | −0.004 | 0.042 | 0.041 | −0.003 | −0.749 | −0.104 | −0.029 | −0.060 |
| IMF10 | −0.003 | 0.014 | 0.018 | −0.008 | −0.013 | −0.086 | 0.012 | 0.049 | 0.083 | 0.065 | 0.023 | 0.059 |
| IMF11 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 0.010 | 0.008 | −0.010 | −0.044 | 0.027 | 0.048 | −0.025 | −0.532 | −0.675 | 0.157 |
| Residue | −0.001 | 0.008 | 0.018 | −0.001 | −0.009 | −0.047 | 0.046 | 0.042 | 0.055 | 0.089 | 0.056 | −0.256 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plocoste, T.; Sankaran, A. Multiscale Correlation Analysis between Wind Direction and Meteorological Parameters in Guadeloupe Archipelago. Earth 2023, 4, 151-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4010008
Plocoste T, Sankaran A. Multiscale Correlation Analysis between Wind Direction and Meteorological Parameters in Guadeloupe Archipelago. Earth. 2023; 4(1):151-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4010008
Chicago/Turabian StylePlocoste, Thomas, and Adarsh Sankaran. 2023. "Multiscale Correlation Analysis between Wind Direction and Meteorological Parameters in Guadeloupe Archipelago" Earth 4, no. 1: 151-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4010008
APA StylePlocoste, T., & Sankaran, A. (2023). Multiscale Correlation Analysis between Wind Direction and Meteorological Parameters in Guadeloupe Archipelago. Earth, 4(1), 151-167. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth4010008







