Characterization of the Planetary Boundary Layer Height in Huelva (Spain) During an Episode of High NO2 Pollutant Concentrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Area Characteristics
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Data from Air Quality Stations
2.2.2. Data from Radiosondes
2.2.3. Data from Reanalysis
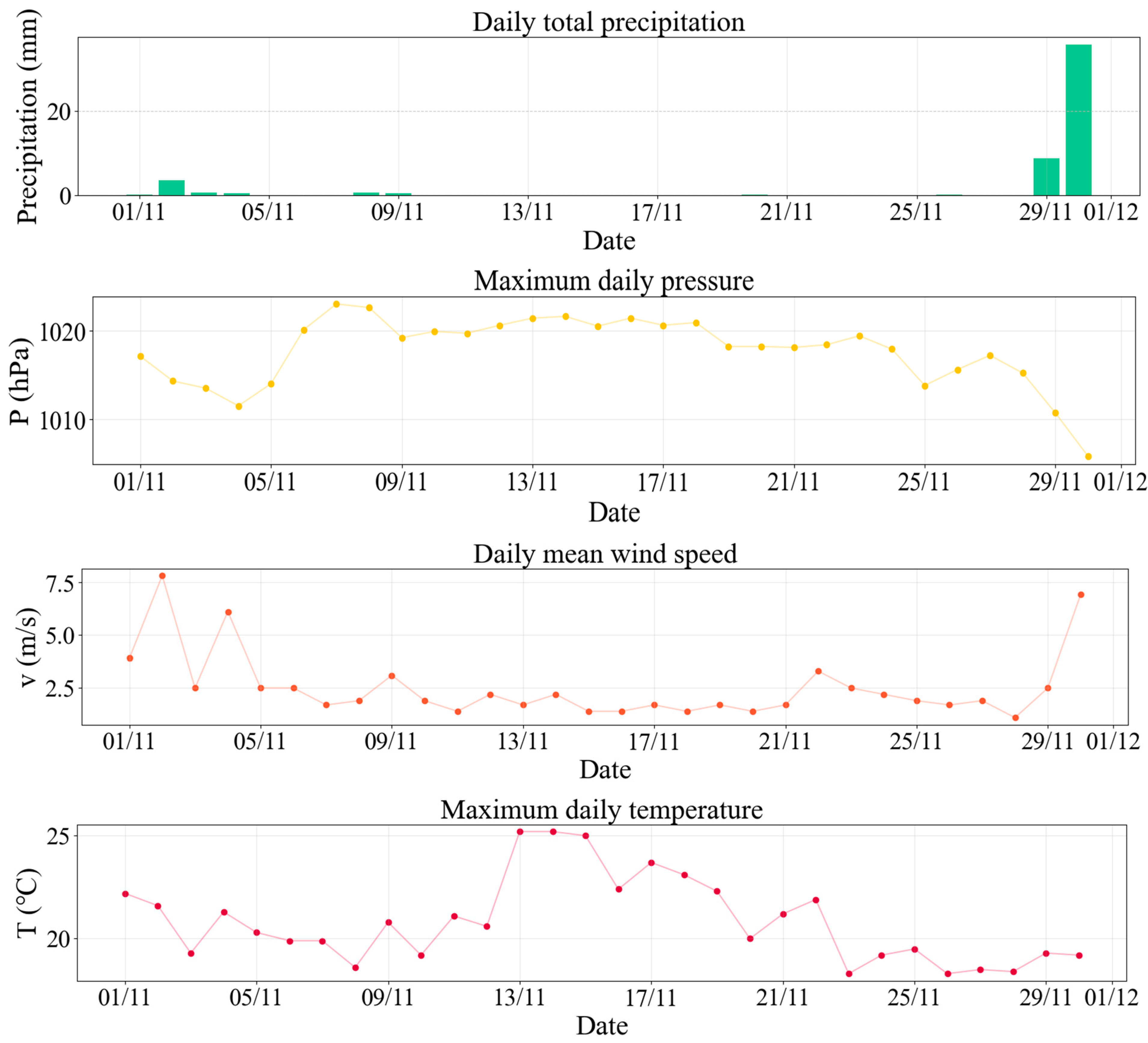
2.3. Episode Selection
2.4. PBLH Estimation
2.4.1. Richardson Number
2.4.2. Humidity Gradient Method
2.4.3. Refractivity Gradient Method
3. Results
3.1. PBLH Estimation
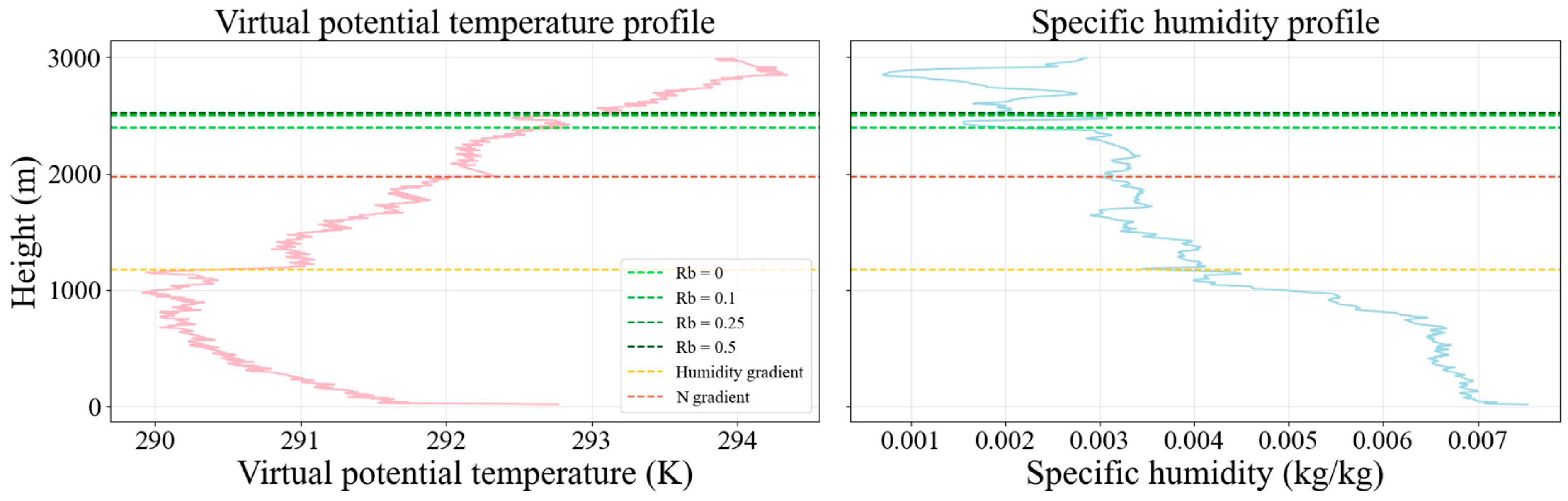
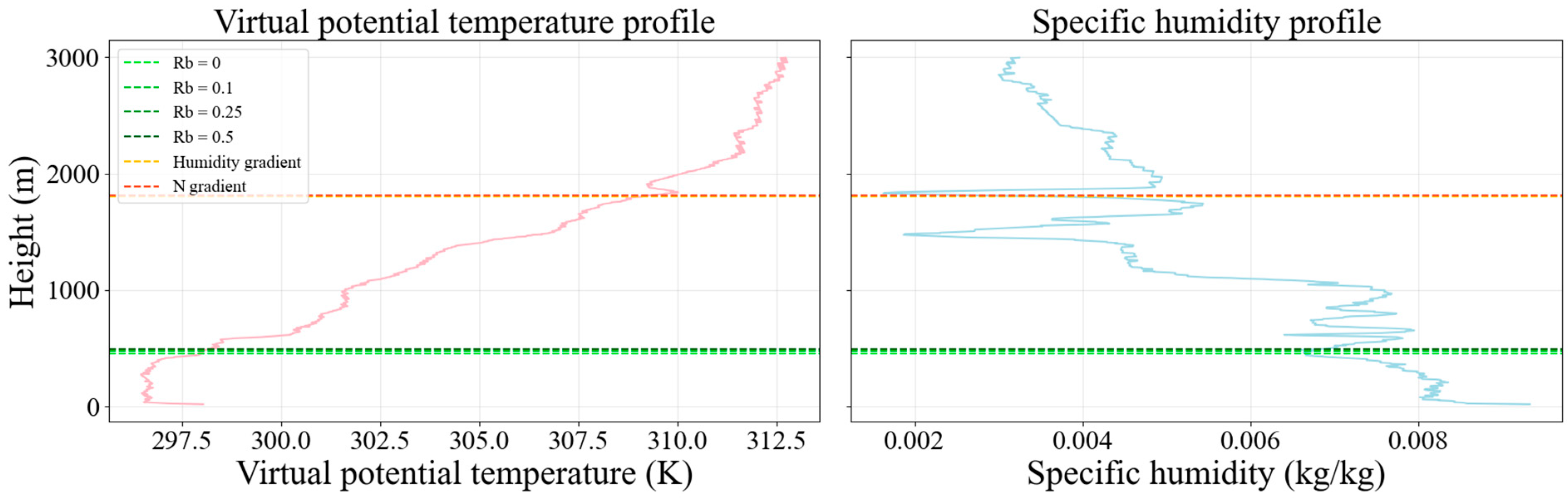
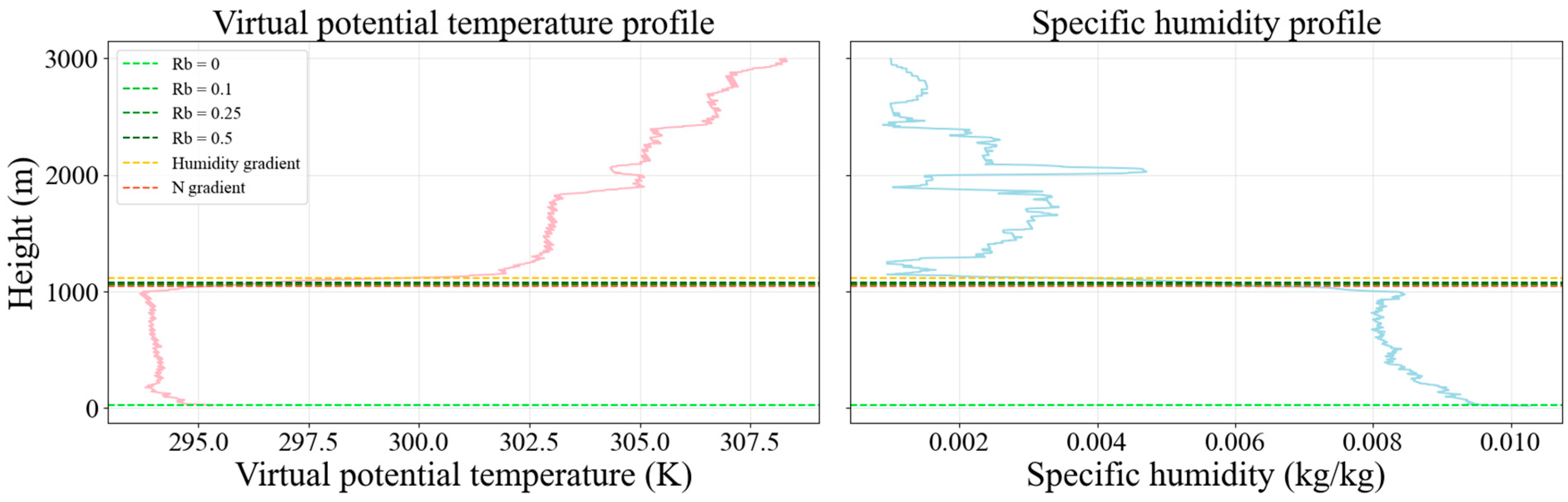
3.1.1. Daytime Values
- A-type profiles;
- B-type profiles;
- C-type profiles;
3.1.2. Nighttime Values
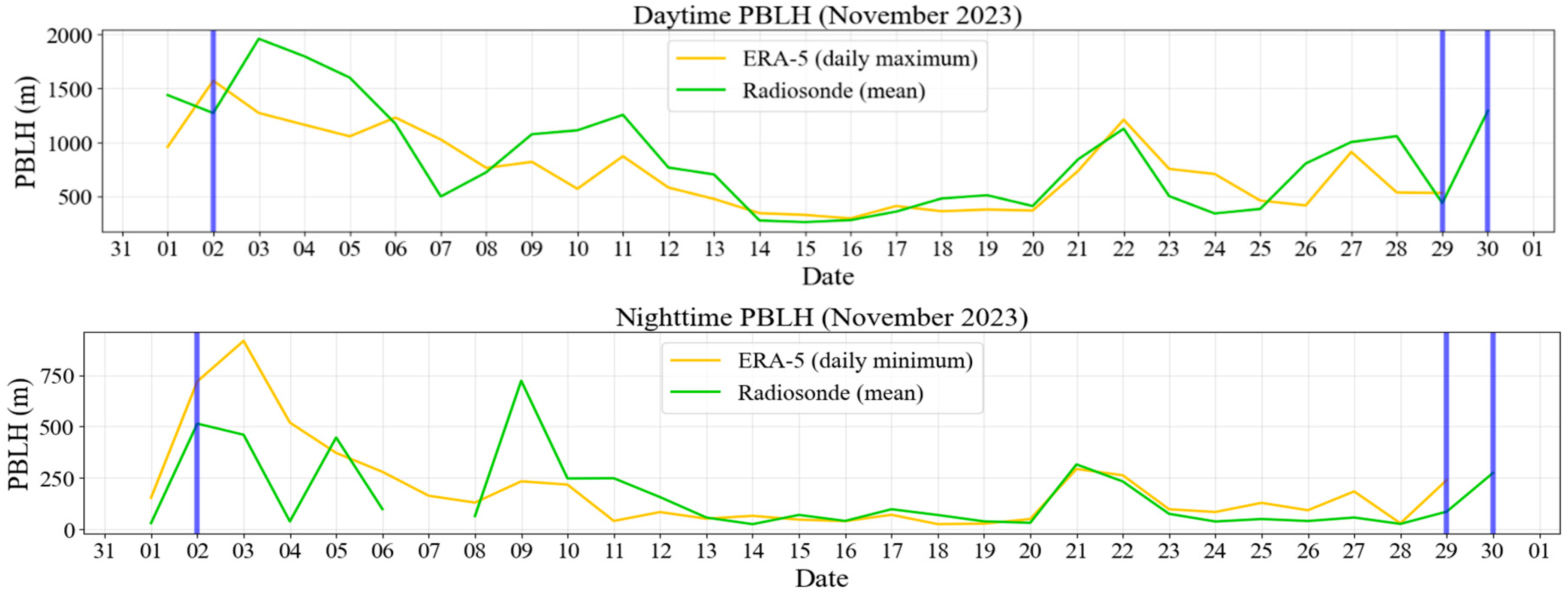
3.2. Comparison Between PBLH Estimation and ERA5
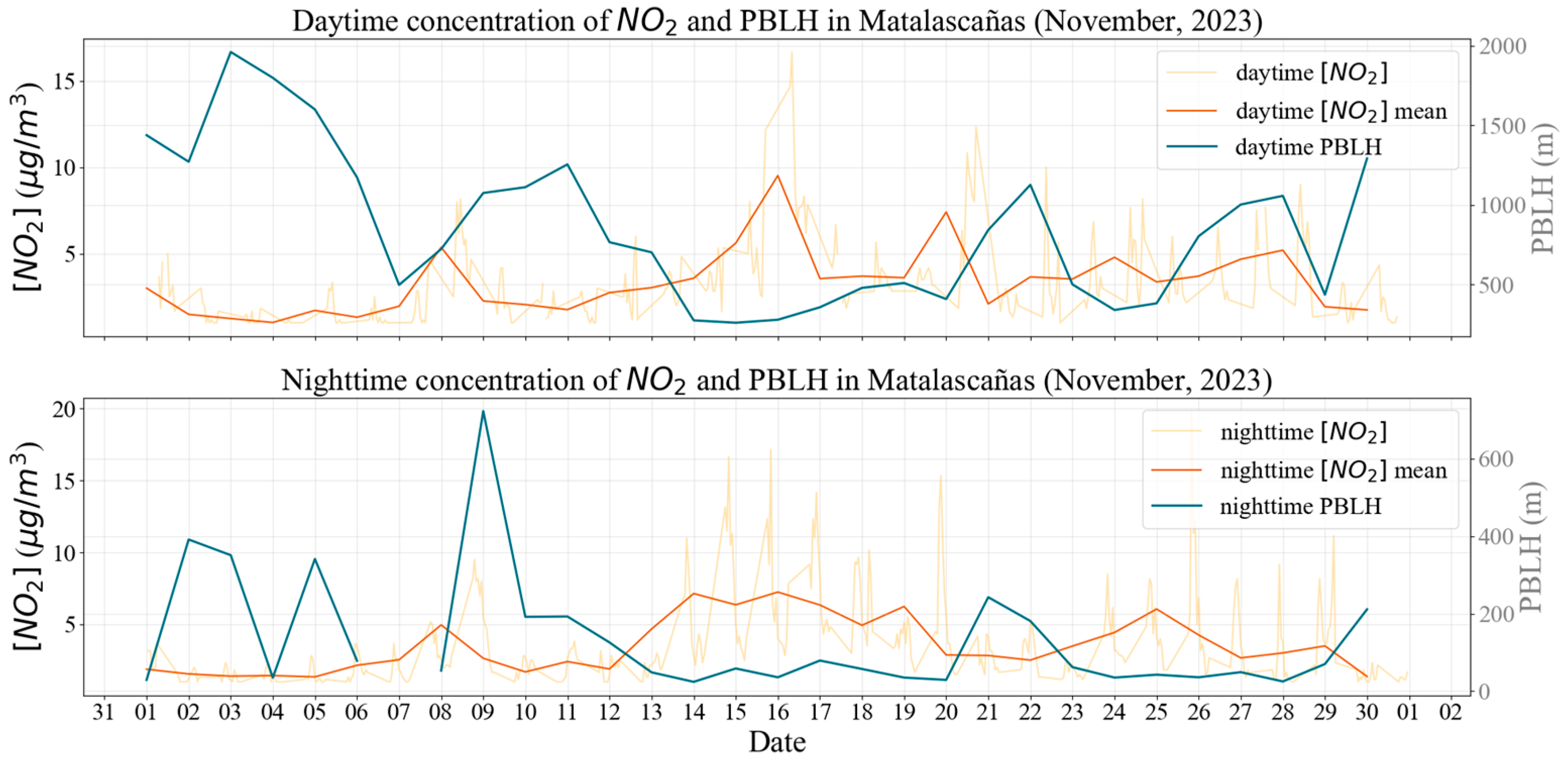
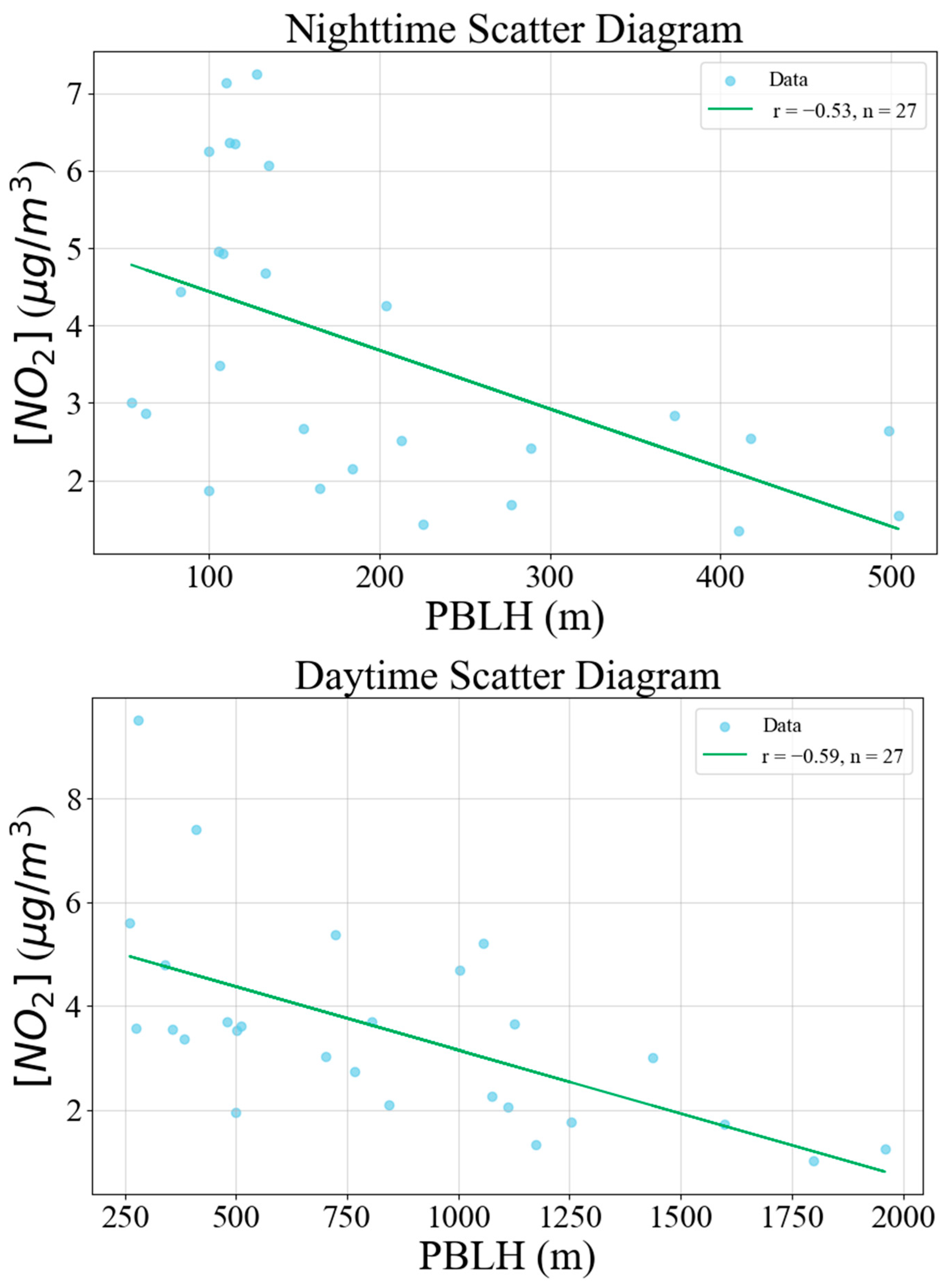
3.3. Correlation Between PBLH and NO2 Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABL | Atmospheric Boundary Layer |
| AEMET | National Spanish Meteorological Agency |
| CIQSO | Center for Research in Sustainable Chemistry |
| ECMWF | European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts |
| ERA5 | ECMWF Reanalysis V5 |
| PBL | Planetary Boundary Layer |
| PBLH | Planetary Boundary Layer Height |
| UHU | University of Huelva |
References
- EEA. How Air Pollution Affects Our Health; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2024; Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/topics/in-depth/air-pollution/eow-it-affects-our-health (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- WHO. Air Pollution: The Invisible Health Threat; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/air-pollution--the-invisible-health-threat (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Newby, D.E.; Manucci, P.M.; Grethe, S.T.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Brook, R.D.; Donaldson, K.; Forastiere, F.; Franchini, M.; Franco, O.H.; Graham, I.; et al. Expert Position Paper on Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutzen, P.J. New Directions: The Growing Urban Heat and Pollution Island Effect-Impact on Chemistry and Climate. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3539–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, M.; Müller, D.; Tsai, M.-Y.; Parlow, E. Air Pollution Modeling over Very Complex Terrain: An Evaluation of WRF-Chem over Switzerland for Two 1-Year Periods. Atmos. Res. 2013, 132–133, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA (European Environment Agency). Air Quality in Europe 2022; Report No. 05/2022; EEA (European Environment Agency): Copenhagen, Denmark, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gu, J.; Wang, X. The impact of Sahara dust on air quality and public health in European Countries. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuval Tritscher, T.; Raz, R.; Levi, Y.; Levy, I.; Broday, D.M. Emissions vs. turbulence and atmospheric stability: A study of their relative importance in determining air pollutant concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, C.D.; Hoch, S.W.; Horel, J.D.; Charland, A. Relationship between particulate air pollution and meteorological variables in Utah’s Salt Lake Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, M.R.; Arasa, R.; Merino, M.T.; Ortega, S. Modelling Local Sea-Breeze Flow and Associated Dispersion Patterns Over a Coastal Area in North-East Spain: A Case Study. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2011, 140, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udina, M.; Soler, M.R.; Arasa, R. Effects of nocturnal thermal circulation and boundary layer structure on pollutant dispersion in complex terrains areas: A case study. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 48, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemel, C.; Burns, P. Pollutant Dispersion in a Developing Valley Cold-Air Pool. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2015, 154, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; 670p. [Google Scholar]
- Sudeepkumar, B.L.; Babu, C.A.; Varikoden, H. Atmospheric boundary layer height and surface parameters: Trends and relationships over the west coast of India. Atmos. Res. 2020, 245, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yang, Q.; Shupe, M.D.; Xi, X.; Han, B.; Chen, D.; Dahlke, S.; Liu, C. The characteristics of atmospheric boundary layer height over the Arctic Ocean during MOSAiC. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 8683–8703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, R.F.; Tiana-Alsina, J.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Baldasano, J.M. Performance Evaluation of the Boundary-Layer Height from Lidar and the Weather Research and Forecasting Model at an Urban Coastal Site in the North-East Iberian Peninsula. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2015, 157, 265–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Dalmau, M.; Udina, M.; Bech, J.; Sola, Y.; Montolio, J.; Jaén, C. Pollutant concentration changes during the COVID-19 lockdown in Barcelona and surrounding regions: Modification of diurnal cycles and limited role of meteorological conditions. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2022, 183, 273–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthaus, S.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Collaud Coen, M.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Costa, M.J.; Cimini, D.; O’Connor, E.J.; Hervo, M.; Alados-Arboledas, L.; Jiménez-Portaz, M.; et al. Atmospheric boundary layer height from ground-based remote sensing: A review of capabilities and limitations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 433–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; De la Rosa, J.; Sánchez-de-la-Campa, A.M.; Plana, F.; Ruiz, C.R. Source apportionment analysis of atmospheric particulates in an industrialised urban site in southwestern Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3113–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachorro, V.E.; Toledano, C.; Prats, N.; Sorribas, M.; Mogo, S.; Berjón, A.; Torres, B.; Rodrigo, R.; De la Rosa, J.D.; De Frutos, A.M. The strongest desert Dust intrusion mixed with smoke over the Iberian Peninsula registered with Sun photometry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cayuela, M.Á.; Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Bermejo-Pantaleón, D.; Sicard, M.; Salgueiro, V.; Molero, F.; Carvajal-Pérez, C.V.; Granados-Muñoz, M.J.; Comerón, A.; Couto, F.T.; et al. Vertical characterization of fine and coarse dust particles during an intense Saharan dust outbreak over the Iberian Peninsula in springtime 2021. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; De la Rosa, J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Mantilla, E. Geochemistry and origino f PM10 in the Huelva región, Southwestern Spain. Environ. Res. 2007, 103, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Camacho, R.; De la Rosa, J.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Rodríguez, S. Geochemical characterization of Cu-smelter emission plumes with impact in an urban area of SW Spain. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castanedo, G.; Moreno, T.; Fernández-Camacho, R.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; De la Rosa, J. Size distribution and chemical composition of particulate matter stack emissions in and around a copper smelter. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Stein, A.F.; Castell, N.; Gonzalez-Castanedo, Y.; Sanchez de la Campa, A.M.; De la Rosa, J.D. Modeling and evaluation of urban pollution events of atmospheric heavy metals from a large Cu-smelter. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.; Alsioufi, L.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; de la Rosa, J.D. Air quality trends in an industrialised area of SW Spain. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, B.; de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; de la Rosa, J.D. 2005–2014 trends of PM10 source contributions in an industrialized area of southern Spain. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán-Martínez, M.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; De la Rosa, J.D. Source contribution and origin of PM and arsenic in a complex industrial region (Huelva, SW Spain). Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Macías, E.; Pérez-Vizcaíno, P.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.; Sánchez-Rodas, D.A.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; De la Rosa, J.D. Extreme historic SO2 levels in an industrial city (Huelva, SW Spain). Air quality implications. In Proceedings of the RICTA2024: 8th Iberian Meeting on Aerosol Science and Technology, A Coruña, Spain, 26–28 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, Z. Influencing Factors on Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion around buildings under the Combined Effect of Wind and Buoyancy—A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunis, P.; Clappier, A.; Tarrason, L.; Cuvelier, C.; Monteiro, A.; Pisoni, E.; Wesseling, J.; Belis, C.A.; Pirovano, G.; Janssen, S.; et al. Source apportionment to support air quality planning: Strengths and weaknesses of existing approaches. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, K.; Gao, Z.; Pan, Z.; Shook, M.A.; Li, D. Diurnal climatology of planetary boundary layer height over the contiguous United States derived from AMDAR and reanalysis data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, M.G.; Brown, T.J.; Curcio, G.M. Establishing a national standard method for operational mixing height determination. J. Oper. Meteorol. 2015, 3, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Jin, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, W. Evaluation of retrieval methods for planetary boundary layer height based on radiosonde data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, P.; Beyrich, F.; Gryning, S.E.; Joffre, S.; Rasmussen, A.; Tercier, P. Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1001–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B. A time-split nonhydrostatic atmospheric model for weather research and forecasting applications. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3465–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, C.; McFarlane, S.; Chapman, E.; Jensen, M.; Toto, T.; Liu, S.; Fischer, M. Planetary Boundary Layer Height (PBL) Value Added Product (VAP): Radisonde Retrievals. DOE/SC-ARM-TR-132; US Department of Energy, Climate & Environmental Science Division: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.arm.gov/publications/tech_reports/doe-sc-arm-tr-132.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Sorensen, J.H.; Rasmussen, A.; Ellermann, T.; Luck, E. Mesoscale influence on long-range transport evidence from ETEX modelling and observations. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 4207–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMS American Meteorological Society. Glossary of Meteorology. Available online: https://glossary.ametsoc.org/wiki/Welcome (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Richardson, H.; Basu, S.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Improving stable boundary-layer height estimation using a stability-dependent critical bulk Richardson number. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2013, 148, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Ao, C.O.; Li, K. Estimating climatological planetary boundary layer heights from radiosonde observations: Comparison of methods and uncertainty analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D16113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, C.O.; Chan, T.K.; Iijima, B.A.; Li, J.-L.; Mannucci, A.J.; Teixeira, J.; Tian, B.; Waliser, D.E. Planetary boundary layer information from GPS radio occultation measurements. In Proceedings of the GRAS SAF Workshop on Applications of GPSRO Measurements, Reading, UK, 16–18 June 2008; pp. 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Thayer, G. An improved equation for radiorefractive index of air. Radio Sci. 1974, 9, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V. Identification of atmospheric boundary layer height over a tropical station using high-resolution radiosonde refractivity profiles: Comparison with GPS radio occultation measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D16101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.A.; McKay, S.J.; Nagel, D.E.; Piepho, T.; Rorig, M.L.; Anderson, C.; Kellog, L. Assessing Values of Air Quality and Visibility at Risk from Wildland Fires. 2003. Available online: http://walker.dgf.uchile.cl/IndiceRemocion/doc/FergusonEtAl2003.pdf (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Ministerio del Medio Ambiente, Gobierno de Chile. Pronóstico de las Condiciones de Ventilación. Available online: https://airecqp.mma.gob.cl/pronostico-de-ventilacion (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- National Weather Service; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Smoke Dispersal (Ventilation Rate). Available online: https://www.weather.gov/riw/fire_smoke_dispersal (accessed on 18 December 2024).
- Ministerio del Medio Ambiente, Gobierno de Chile. Resolución que Establece los Criterios para Determinar las Condiciones de Ventilación en las Comunas de Concón, Quintero y Puchuncaví para la Gestión de Episodios Críticos. 2023. Available online: https://www.bcn.cl/leychile/navegar?i=1187779 (accessed on 18 December 2024).




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comas Muguruza, A.; Arasa Agudo, R.; Udina, M. Characterization of the Planetary Boundary Layer Height in Huelva (Spain) During an Episode of High NO2 Pollutant Concentrations. Earth 2025, 6, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020026
Comas Muguruza A, Arasa Agudo R, Udina M. Characterization of the Planetary Boundary Layer Height in Huelva (Spain) During an Episode of High NO2 Pollutant Concentrations. Earth. 2025; 6(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleComas Muguruza, Ainhoa, Raúl Arasa Agudo, and Mireia Udina. 2025. "Characterization of the Planetary Boundary Layer Height in Huelva (Spain) During an Episode of High NO2 Pollutant Concentrations" Earth 6, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020026
APA StyleComas Muguruza, A., Arasa Agudo, R., & Udina, M. (2025). Characterization of the Planetary Boundary Layer Height in Huelva (Spain) During an Episode of High NO2 Pollutant Concentrations. Earth, 6(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/earth6020026






