An Introduction to Atmospheric Pollutant Dispersion Modelling †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Basics of Dispersion Modelling
2.1. Data Input
2.2. Data Processing—The “Black Box”
2.3. Data Output
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Simulation Timeframe
3. Box Models
3.1. Introduction
3.2. Examples of Simple Box Models
EKMA
3.3. Uses
4. Eulerian Models
4.1. Introduction
4.2. Examples
4.2.1. TAPM
4.2.2. Variable K-Theory Model
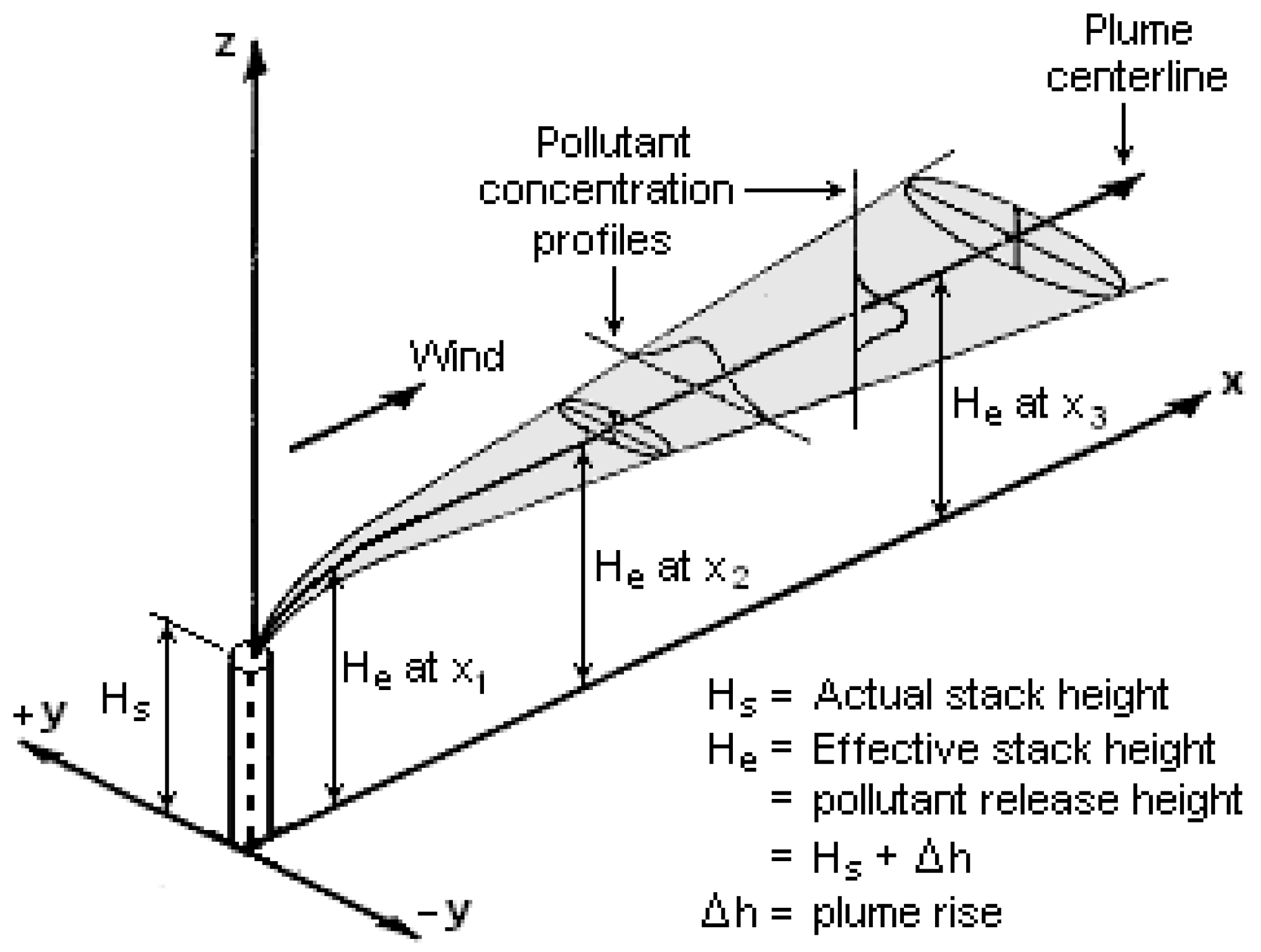
5. Gaussian Models
5.1. Introduction
5.2. Gaussian Plume Models
5.2.1. AEOLIUSF
5.2.2. AERMOD
5.2.3. AUSPLUME
5.2.4. CALINE3
5.2.5. CAL3QHC and CAL3QHCR
5.2.6. CTDMPLUS
5.2.7. ISC
5.2.8. OCD
6. Lagrangian Models
6.1. Introduction
6.2. Examples
6.2.1. AFTOX
6.2.2. CALPUFF
6.2.3. Hybrid Eulerian–Lagrangian Dispersion Models (HDMs)
7. Computational Fluid Dynamics Models
7.1. Introduction
7.2. Examples and Uses
8. Street Network Models
8.1. Introduction
8.2. Examples
SIRANE
9. Other Models
10. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Huang, F.; Gao, Q.; Wu, L.; Tao, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, W. Fine particulate air pollution and hospital emergency room visits for respiratory disease in urban areas in Beijing, China, in 2013. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horne, B.D.; Joy, E.A.; Hofmann, M.G.; Gesteland, P.H.; Cannon, J.B.; Lefler, J.S.; Blagev, D.P.; Korgenski, E.K.; Torosyan, N.; Hansen, G.I. Short-term elevation of fine particulate matter air pollution and acute lower respiratory infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannson, K.A.; Balmes, J.R.; Collard, H.R. Air pollution exposure: A novel environmental risk factor for interstitial lung disease? Chest 2015, 147, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Li, G.; Zhao, D.; Xie, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Sun, J. Relationship between fine particulate air pollution and ischaemic heart disease morbidity and mortality. Heart 2015, 101, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope III, C.A.; Turner, M.C.; Burnett, R.T.; Jerrett, M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; Krewski, D.; Brook, R.D. Relationships between fine particulate air pollution, cardiometabolic disorders, and cardiovascular mortality. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.G.; Xia, Y.; Shang, K.Z.; Cheng, Y.F.; Xu, L.; Ning, G.C.; Zhao, W.J.; LI, N.R. Association between ambient air pollution and hospital emergency admissions for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in Beijing: A time series study. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 352–363. [Google Scholar]
- Gharibvand, L.; Shavlik, D.; Ghamsary, M.; Beeson, W.L.; Soret, S.; Knutsen, R.; Knutsen, S.F. The association between ambient fine particulate air pollution and lung cancer incidence: Results from the AHSMOG-2 study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 125, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, L.-w.; Huang, J.-j.; Song, F.-j.; Zhang, L.-p.; Qian, Z.-m.; Trevathan, E.; Mao, H.-j.; Han, B.; Vaughn, M. Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and lung cancer mortality: A 12-year cohort study in Northern China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 571, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatsky, S.; Smargiassi, A.; Barnabe, C.; Svenson, L.W.; Brand, A.; Martin, R.V.; Hudson, M.; Clarke, A.E.; Fortin, P.R.; van Donkelaar, A. Fine particulate air pollution and systemic autoimmune rheumatic disease in two Canadian provinces. Environ. Res. 2016, 146, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.G.F.; de Azevedo Giacomin, M.F.; Braga, A.L.F.; Sallum, A.M.E.; Pereira, L.A.A.; Farhat, L.C.; Strufaldi, F.L.; Lichtenfels, A.J.d.F.C.; de Santana Carvalho, T.; Nakagawa, N.K. Influence of air pollution on airway inflammation and disease activity in childhood-systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.A.; Martin, R.V.; Boys, B.L.; van Donkelaar, A. Long-term trends worldwide in ambient NO2 concentrations inferred from satellite observations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 124, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalabi, Z.; Milojevic, A.; Doherty, R.M.; Stevenson, D.S.; MacKenzie, I.A.; Milner, J.; Vieno, M.; Williams, M.; Wilkinson, P. Applying air pollution modelling within a multi-criteria decision analysis framework to evaluate UK air quality policies. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Patil, R.S.; Dikshit, A.K.; Islam, S.; Kumar, R. Evaluation of control strategies for industrial air pollution sources using American Meteorological Society/Environmental Protection Agency Regulatory Model with simulated meteorology by Weather Research and Forecasting Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 116, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Baksi, S. Air Pollutant Dispersion Models: A Review. In Advances in Health and Environment Safety; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, T. Public concerns about transboundary haze: A comparison of Indonesia, Singapore, and Malaysia. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 25, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Zhao, J.; Fan, S.; Wang, X. Sources of formaldehyde and their contributions to photochemical O3 formation at an urban site in the Pearl River Delta, southern China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Po, L.; Rollo, F.; Viqueira, J.R.R.; Lado, R.T.; Bigi, A.; López, J.C.; Nesi, P. TRAFAIR: Understanding Traffic Flow to Improve Air Quality. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE African Workshop on Smart Sustainable Cities and Communities (IEEE ASC2 2019)-In conjunction with the 5th IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2 2019), Casablanca, Morocco, 14–17 October 2019; pp. 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L. Haze in China: Current and future challenges. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khreis, H.; Kelly, C.; Tate, J.; Parslow, R.; Lucas, K.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M. Exposure to traffic-related air pollution and risk of development of childhood asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2017, 100, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gehring, U.; Hoek, G.; Keuken, M.; Jonkers, S.; Beelen, R.; Eeftens, M.; Postma, D.S.; Brunekreef, B. Air pollution and lung function in dutch children: A comparison of exposure estimates and associations based on land use regression and dispersion exposure modeling approaches. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, L. Identification of long-range transport pathways and potential sources of PM10 in Tibetan Plateau uplift area: Case study of Xining, China in 2014. Aerosol Air Qual. Res 2016, 16, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squizzato, S.; Masiol, M. Application of meteorology-based methods to determine local and external contributions to particulate matter pollution: A case study in Venice (Italy). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godish, T.; Davis, W.T.; Fu, J.S. Air quality; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dezzutti, M.; Berri, G.; Venegas, L. Intercomparison of Atmospheric Dispersion Models Applied to an Urban Street Canyon of Irregular Geometry. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, A.; Zannetti, P. Air pollution modeling–An overview. In Ambient Air Pollution; Zannetti, P., Al-Ajmi, D., Al-Rashied, S., Eds.; The EnviroComp Institute: Half Moon Bay, CA, USA, 2007; pp. 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, R. Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling: An Introduction to Practical Applications; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Colls, J.; Tiwary, A. Air Pollution: Measurement, Modelling and Mitigation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Forehead, H.; Huynh, N. Review of modelling air pollution from traffic at street-level-The state of the science. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.; Ketzel, M.; Kakosimos, K.; Sørensen, M.; Jensen, S.S. Road traffic air and noise pollution exposure assessment–A review of tools and techniques. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 634, 661–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cécé, R.; Bernard, D.; Brioude, J.; Zahibo, N. Microscale anthropogenic pollution modelling in a small tropical island during weak trade winds: Lagrangian particle dispersion simulations using real nested LES meteorological fields. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 139, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, A.; Carotenuto, F.; Di Gennaro, F.; Gioli, B.; Gualtieri, G.; Martelli, F.; Matese, A.; Toscano, P.; Vagnoli, C.; Zaldei, A. Development of Low-Cost Air Quality Stations for Next Generation Monitoring Networks: Calibration and Validation of PM2.5 and PM10 Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Castell, N.; Vogt, M.; Dauge, F.R.; Lahoz, W.A.; Bartonova, A. Mapping urban air quality in near real-time using observations from low-cost sensors and model information. Environ. Int. 2017, 106, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffee, A.F.; Rahmat, S.N.; Hamid, H.A.; Jaffar, M.I. A Review on Short-Term Prediction of Air Pollutant Concentrations. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gronwald, F.; Chang, S.-Y. Evaluation of the Precision and Accuracy of Multiple Air Dispersion Models. J. Atmos. Pollut. 2018, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, W.P.; Winer, A.M.; Pitts Jr, J.N. Effects of kinetic mechanisms and hydrocarbon composition on oxidant-precursor relationships predicted by the EKMA isopleth technique. Atmos. Environ. 1982, 16, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.; Maxwell, C.; Javitz, H.; Bowol, R. Evaluation of the Empirical Kinetic Modeling Approach (EKMA); NTIS: Springfield, VA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.R.; Maxwell, C.; Javitz, H.S.; Bawol, R. Performance evaluation of the Empirical Kinetic Modeling Approach (EKMA). In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application II; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 1983; pp. 199–211. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Duan, Y. Source-based dynamic control strategies of ozone in different functional areas in Shanghai, China. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 8–13 April 2018; p. 3237. [Google Scholar]
- Collet, S.; Kidokoro, T.; Karamchandani, P.; Shah, T. Future-Year Ozone Isopleths for South Coast, San Joaquin Valley, and Maryland. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Lu, K.; Yu, J.; Tan, Z.; Jiang, M.; Li, J.; Xie, S.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Zhai, C. Exploration of the formation mechanism and source attribution of ambient ozone in Chongqing with an observation-based model. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K. Air pollution modeling. Int. J. Adv. Res. Ideas Innov. Technol. 2018, 4, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-W.; Jwo, C.-S.; Ho, H.-J.; Chen, L.-Y. Using box modeling to determine photodegradation coefficients describing the removal of gaseous formaldehyde from indoor air. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocho, P.; Desauziers, V.; Plaisance, H.; Sauvat, N. Improvement of the performance of a simple box model using CFD modeling to predict indoor air formaldehyde concentration. Build. Environ. 2017, 124, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Cai, X.-M.; Bloss, W.J. Modelling photochemical pollutants in a deep urban street canyon: Application of a coupled two-box model approximation. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 143, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Cai, X.-M.; Bloss, W.J. Modelling the dispersion and transport of reactive pollutants in a deep urban street canyon: Using large-eddy simulation. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 200, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.; Dal Maso, M.; Koivisto, A.; Belut, E.; Meyer-Plath, A.; Van Tongeren, M.; Sánchez Jiménez, A.; Tuinman, I.; Domat, M.; Toftum, J. Comparison of geometrical layouts for a multi-box aerosol model from a single-chamber dispersion study. Environments 2018, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.; Ludwig, F.; Dabberdt, W.; Allen, R. An urban diffusion simulation model for carbon monoxide. J. Air Pollut. Control. Assoc. 1973, 23, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, C.; Lewyckyj, N. A simple model for the assessment of air quality in streets. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2001, 27, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, S.D.; Roth, P.M.; Seinfeld, J.H. Mathematical modeling of photochemical air pollution—I: Formulation of the model. Atmos. Environ. 1973, 7, 1033–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ničeno, B.; Dhotre, M.; Deen, N. One-equation sub-grid scale (SGS) modelling for Euler–Euler large eddy simulation (EELES) of dispersed bubbly flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 3923–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P.J.; Edwards, M.; Physick, W.L.; Luhar, A.K. TAPM V3-model description and verification. Clean Air Environ. Qual. 2005, 39, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, P. Development and verification of TAPM. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XIX; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Matthaios, V.N.; Triantafyllou, A.G.; Albanis, T.A.; Sakkas, V.; Garas, S. Performance and evaluation of a coupled prognostic model TAPM over a mountainous complex terrain industrial area. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 132, 885–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.Q.; Nguyen, H.D.; Vu, K.; Hien, T.T. Photochemical Smog Modelling Using the Air Pollution Chemical Transport Model (TAPM-CTM) in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Environ. Modeling Assess. 2019, 24, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieu, T.; Duc, H.N.; Scorgie, Y. Performance of TAPM-CTM as an airshed modelling tool for the sydney region. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Clean Air & Environment Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 20–23 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, A.S.; Williamson, B.J.; Taylor, M.; Purvis, W.O.; Goossens, M.; Reis, S.; Aminov, P.; Udachin, V.; Osborne, N.J. Integrating dispersion modelling and lichen sampling to assess harmful heavy metal pollution around the Karabash copper smelter, Russian Federation. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhosh, M.; Shamsipour, A.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Nabizadeh, R.; Naddafi, K.; Mohseni, S.M. Dispersion modeling and health risk assessment of VOCs emissions from municipal solid waste transfer station in Tehran, Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwstadt, F.; van Dop, H. Atmospheric Turbulence and Air Pollution Modeling; D. Reidel Publishing Company: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1982; p. 358. [Google Scholar]
- Buckland, A. Validation of a street canyon model in two cities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1998, 52, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Air Quality Dispersion Modeling-Preferred and Recommended Models. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/scram/air-quality-dispersion-modeling-preferred-and-recommended-models (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Goldstone, M. AERMOD; assessment of meteorlogical files and comparison with Ausplume for Area Source Modelling. Air Qual. Clim. Chang. 2015, 49, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Gulia, S.; Kumar, A.; Khare, M. Performance evaluation of CALPUFF and AERMOD dispersion models for air quality assessment of an industrial complex. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2015, 74, 302–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdi, M.N.; Arhami, M.; Ketabchy, M.; Delavarrafeei, M. Modeling of Cement Factory Air Pollution Dispersion by AERMOD. In Proceedings of the A&WMA’s 109th Annual Conference & Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 20–23 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jayadipraja, E.; Daud, A.; Assegaf, A.; Maming, M. The application of the AERMOD model in the environmental health to identify the dispersion area of total suspended particulate from cement industry stacks. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 4, 2044–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, D.; MukeshSharma, A.; Shukla, S. Ambient Air Quality Modeling of 355 MW Gas Based Combined Cycle Power Plant in Complex Terrain. Indian J. Air Pollut. Control. 2016, 16, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Askariyeh, M.H.; Kota, S.H.; Vallamsundar, S.; Zietsman, J.; Ying, Q. AERMOD for near-road pollutant dispersion: Evaluation of model performance with different emission source representations and low wind options. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 57, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ul Haq, A.; Nadeem, Q.; Farooq, A.; Irfan, N.; Ahmad, M.; Ali, M.R. Assessment of AERMOD modeling system for application in complex terrain in Pakistan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madear, G.; Traista, E.; Pop, I. Radon Dispersion Air Modeling in Banat Mining Area. In Mine Planning and Equipment Selection 2000; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2018; pp. 919–924. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, N.; Kamarulzaman, N.; Nor, Z.M. Odour Dispersion Modelling for Raw Rubber Processing Factories. J. Rubber Res. 2017, 20, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, P.E. A review of the development and application of the CALINE3 and 4 models. Atmos. Environment. Part B. Urban Atmos. 1992, 26, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S. Emission load distribution and prediction of NO2 and PM10 using ISCST3 and CALINE4 line source modeling. Appl. J. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 5, 2121–2135. [Google Scholar]
- Beamer, P.I.; Guerra, S.; Lothrop, N.; Stern, D.A.; Lu, Z.; Billheimer, D.; Halonen, M.; Wright, A.L.; Martinez, F.D. B46 Health effects of air pollution and nanoparticles: Childhood Cc16 Levels Are Associated with Diesel Exposure At Birth. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Dhyani, R.; Sharma, N.; Advani, M. Estimation of fuel loss and spatial-temporal dispersion of vehicular pollutants at a signalized intersection in Delhi City, India. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2019, 236, 233–243. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, S.G. CTDMPLUS: A dispersion model for sources near complex topography. Part I: Technical formulations. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1992, 31, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, J.; Anderson, A.J.; Huber, A. Evaluation study of the industrial source complex (ISC) dispersion model. Paper 81.20. 4. In Proceedings of the 74th APCA Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 21–26 June 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.-H.; Yuan, C.-S.; Wang, L.-C. A feasible approach to quantify fugitive VOCs from petrochemical processes by integrating open-path fourier transform infrared spectrometry measurements and industrial source complex (ISC) dispersion model. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, P.; Senatore, A. Appraisal of pollutant emissions and air quality state in a critical I talian region: Methods and results. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iodice, P.; Senatore, A. Air pollution and air quality state in an Italian National Interest Priority Site. Part 2: The pollutant dispersion. Energy Procedia 2015, 81, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Singh, G.; Yadav, P. Identification and elucidation of anthropogenic source contribution in PM10 pollutant: Insight gain from dispersion and receptor models. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 48, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esbrí, J.M.; López-Berdonces, M.A.; Fernández-Calderón, S.; Higueras, P.; Díez, S. Atmospheric mercury pollution around a chlor-alkali plant in Flix (NE Spain): An integrated analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4842–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel-García, M.; Cerón-Bretón, R.M.; Cerón-Bretón, J.G. Air pollution in the Gulf of Mexico. Open J. Ecol. 2016, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rodhe, H. Some aspects of the use of air trajectories for the computation of large-scale dispersion and fallout patterns. In Advances in Geophysics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 18, pp. 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rodhe, H. A study of the sulfur budget for the atmosphere over Northern Europe. Tellus 1972, 24, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inthavong, K.; Tian, L.; Tu, J. Lagrangian particle modelling of spherical nanoparticle dispersion and deposition in confined flows. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 96, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monin, A. Smoke propagation in the surface layer of the atmosphere. In Advances in Geophysics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1959; Volume 6, pp. 331–343. [Google Scholar]
- Boughton, B.; Delaurentis, J.; Dunn, W. A stochastic model of particle dispersion in the atmosphere. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1987, 40, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, B. User’s Guide for the Air Force Toxic Chemical Dispersion Model (AFTOX); Interim report, October 1985–December 1987; Air Force Geophysics Lab: Hanscom Air Force Base, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, T.; Tauseef, S.; Suganya, R.; Abbasi, S. Types of accidents occurring in chemical process industries and approaches to their modeling. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Math 2017, 6, 424–455. [Google Scholar]
- Elperin, T.; Fominykh, A.; Krasovitov, B. Effect of raindrop size distribution on scavenging of aerosol particles from Gaussian air pollution plumes and puffs in turbulent atmosphere. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 102, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, E.; Giovannini, L.; Falocchi, M.; Zardi, D.; Antonacci, G.; Ferrero, E.; Bisignano, A.; Alessandrini, S.; Mortarini, L. Dispersion Modeling Over Complex Terrain in the Bolzano Basin (IT): Preliminary Results from a WRF-CALPUFF Modeling System. In Proceedings of the 35th International Technical Meeting on Air Pollution Modelling and Its Application, Crete, Greece, 3–7 October 2016; pp. 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Exponent Engineering and Science Consulting. CALPUFF Modeling System. Available online: http://www.src.com/ (accessed on 3 July 2022).
- Yaacof, N.; Qamaruzzaman, N.; Yusup, Y. Comparison method of odour impact evaluation using calpuff dispersion modelling and on-site odour monitoring. Eng. Herit. J. 2017, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin Doğruparmak, Ş.; Pekey, H.; Arslanbaş, D. Odor dispersion modeling with CALPUFF: Case study of a waste and residue treatment incineration and utilization plant in Kocaeli, Turkey. Environ. Forensics 2018, 19, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formentin, G. Estimating the Dispersion of Shipping Emissions from Fremantle Port, Western Australia; Murdoch University: Perth, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- García, G.F.; Álvarez, H.B.; Echeverría, R.S.; de Alba, S.R.; Rueda, V.M.; Dosantos, E.C.; Cruz, G.V. Spatial and temporal variability of atmospheric mercury concentrations emitted from a coal-fired power plant in Mexico. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagan, V.; Pasken, R.; Zarauz, J.; Krotkov, N. SO2 trajectories in a complex terrain environment using CALPUFF dispersion model, OMI and MODIS data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 69, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrén, A. A meso-scale plume dispersion model. Preliminary evaluation in a heterogeneous area. Atmos. Environ. Part A. Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlali, M.; Dupont, E.; Carissimo, B. Adaptation of the Lagrangian module of a CFD code for atmospheric dispersion of pollutants in complex urban geometries and comparison with existing Eulerian results. In Proceedings of the 18th International conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Bologna, Italy, 9–12 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bonafé, G.; Montanari, F.; Stel, F. A hybrid Eulerian-Lagrangian-statistical approach to evaluate air quality in a mixed residential-industrial environment. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 64, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusca, S.; Famoso, F.; Lanzafame, R.; Mauro, S.; Messina, M.; Strano, S. PM10 Dispersion Modeling by means of CFD 3D and Eulerian–Lagrangian models: Analysis and comparison with experiments. Energy Procedia 2016, 101, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlali, M.L.; Dupont, E.; Carissimo, B. A hybrid CFD RANS/Lagrangian approach to model atmospheric dispersion of pollutants in complex urban geometries. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 64, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.J.; Gowardhan, A.A.; Nelson, M.A.; Williams, M.D.; Pardyjak, E.R. QUIC transport and dispersion modelling of two releases from the Joint Urban 2003 field experiment. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 52, 263–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Stathopoulos, T. CFD simulations of near-field pollutant dispersion with different plume buoyancies. Build. Environ. 2018, 131, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, B.; Santiago, J.-L.; Martilli, A.; Palacios, M.; Kirchner, F. CFD modeling of reactive pollutant dispersion in simplified urban configurations with different chemical mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12143–12157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Nguyen, C.V.; Volta, P.; Salizzoni, P. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion. PART III: Validation against NO2 yearly concentration measurements in a large urban agglomeration. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulhac, L.; Salizzoni, P.; Cierco, F.-X.; Perkins, R. The model SIRANE for atmospheric urban pollutant dispersion; part I, presentation of the model. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7379–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.B.; Garbero, V.; Salizzoni, P.; Lamaison, G.; Soulhac, L. Modelling pollutant dispersion in a street network. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2015, 155, 157–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Fallah-Shorshani, M.; Xu, J.; Hatzopoulou, M. Characterizing near-road air pollution using local-scale emission and dispersion models and validation against in-situ measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, C.; Kihal-Talantikit, W.; Vieira, V.; Deguen, S. City-specific spatiotemporal infant and neonatal mortality clusters: Links with socioeconomic and air pollution spatial patterns in France. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouidir, M.; Giorgis-Allemand, L.; Lyon-Caen, S.; Morelli, X.; Cracowski, C.; Pontet, S.; Pin, I.; Lepeule, J.; Siroux, V.; Slama, R. Estimation of exposure to atmospheric pollutants during pregnancy integrating space–time activity and indoor air levels: Does it make a difference? Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, X.; Rieux, C.; Cyrys, J.; Forsberg, B.; Slama, R. Air pollution, health and social deprivation: A fine-scale risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2016, 147, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wu, Y.; Seigneur, C.; Roustan, Y. Multi-scale modeling of urban air pollution: Development and application of a Street-in-Grid model (v1. 0) by coupling MUNICH (v1. 0) and Polair3D (v1. 8.1). Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, O.; Berkowicz, R.; Larssen, S. The operational street pollution model (OSPM). In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application VIII; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 1991; pp. 741–750. [Google Scholar]
- Ciarelli, G.; Aksoyoglu, S.; Crippa, M.; Jimenez, J.-L.; Nemitz, E.; Sellegri, K.; Äijälä, M.; Carbone, S.; Mohr, C.; O’Dowd, C. Evaluation of European air quality modelled by CAMx including the volatility basis set scheme. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10313–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, G.; Nunnari, G. Air Quality Forecast and Alarm Systems. Chapter 16A. In Air Quality Modelling—Theories, Methodologies, Computational Techniques and Available Databases and Software; Zannetti, P., Ed.; AWMA: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2005; Volume II, pp. 397–452. [Google Scholar]
- Shaban, K.B.; Kadri, A.; Rezk, E. Urban air pollution monitoring system with forecasting models. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 2598–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, Q. ModOdor: 3D numerical model for dispersion simulation of gaseous contaminants from waste treatment facilities. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 113, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Emission Characteristics | Source Characteristics | Location Characteristics | Meteorological Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pollutants | Source types (e.g., point, line, area, volume) | Location (e.g., urban vs. rural) | Temperature |
| Pollutant characteristics | Source dimensions (if applicable) | Terrain (simple vs. complex) | Wind speed |
| Distribution of source(s) | Volume emission rates | Surface roughness (z0) | Wind direction |
| Emission rates | Temperature | Interfaces of land & water (if any) | Atmospheric stability/turbulence |
| Moisture content | Existing (background) pollutant levels | Solar radiation (particularly important for photochemical modelling) | |
| Presence of buildings or other infrastructure | Cloud cover | ||
| Moisture |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, J.B. An Introduction to Atmospheric Pollutant Dispersion Modelling. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2022, 19, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12826
Johnson JB. An Introduction to Atmospheric Pollutant Dispersion Modelling. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2022; 19(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12826
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Joel B. 2022. "An Introduction to Atmospheric Pollutant Dispersion Modelling" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 19, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12826
APA StyleJohnson, J. B. (2022). An Introduction to Atmospheric Pollutant Dispersion Modelling. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 19(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecas2022-12826






