Abstract
The present study aims at comparing the two most promising water treatment technologies for selenium removal. A techno-economical comparison of Se(IV) uptake between the laboratory synthesized iron oxy hydroxide (FeOOH/2.5) with the highest positive surface density of 3.25 mmol [OH−]/g and adsorption capacity 4.3 μg Se(IV)/mg FeOOH/2.5 at pH 7, and coagulation/precipitation with the use of Fe(III) presenting an uptake capacity 3.2 μg Se(IV)/mg Fe was attempted based on the laboratory scale results. The evaluation showed that coagulation/precipitation treatment appears to be economically advantageous in comparison to adsorption process that was applied in Rapid Small Scale Column Tests (RSSCTs) with the FeOOH/2.5. It must be pointed out that for selection of the optimum removal method, other criteria should also be considered, such as post treatment requirements, water flow, labor cost, and maintenance requirements.
1. Introduction
Several works of research have pointed out that though selenium is a micronutrient of vital importance for human growth and reproducibility, it bears numerous health hazards when bioaccumulated in the human body [1]. Unfortunately, there is a narrow range between daily necessary selenium uptake and intake quantities that result, in some cases, to fatal toxicity [2]. Although selenium is a micronutrient, when surpassing homeostatic levels, it becomes toxic for living organisms [3]. Selenate (SeO4−) predominates in oxidizing conditions and is very soluble with low adsorption and precipitation capacities, while selenite (SeO32−) is present in moderate redox potential ranges and neutral pH environments [4]. Increasing reports on water pollution by selenium verify that excess consumption leads to the potential of bioaccumulation to humans and causes adverse health effects, such as selenosis and cancer, which has forced the European Commission to set a Drinking Water Regulation Limit (DWRL) for selenium at 10 μg/L [5,6].
Both Se(IV) and Se(VI) are toxic, with the first species being more toxic than the second one. The dominant species of selenium in water depends on physicochemical factors, including redox conditions and pH. SeO32− (Se(IV)) is presented as the dominant species, since moderate redox potential ranges and neutral pH environments are mostly met in nature [7,8]. Research on selenium removal is ongoing, with a variety of treatment methods being examined that include: chemical reduction techniques either with nanoparticles such as zero valent iron [9] and inorganic sulfur reductants such as Na2S and Na2S2O4 [10,11]; co-precipitation with barite during the crystallization phase [12]; coagulation-flocculation with Fe/Al based inorganic coagulants [13]; adsorption with inorganic adsorbents such as natural or synthesized iron-based adsorbents [14,15], apatites [16], layered double hydroxides [17], activated carbon [18], graphene oxide [19], and organic-based adsorbents such as chitosan [20] and conjugate adsorbents [21,22]; ion-exchange with resins [23]; membrane technologies [24]; bioremediation with thauera selenatis [25]; and phytoremediation using ashydrilla, duckweed, swamp lily, cattail and phragmites [26]. In order to apply the optimum water treatment process for selenium removal—apart from the removal effectiveness criteria such as the removal capacity at Ce = 10 μg/L (Q10 value), maintaining (not modification) the physicochemical characteristics of the water, and estimation of treatment cost—the water flow rate and specific requirements of treatment process should be also considered.
The majority of selenium removal treatment technologies are suitable for wastewater treatment rather than treatment of potable water. Research focuses on acidic conditions with high initial selenium concentrations that do not correspond to the physicochemical characteristics of natural waters. Acidic conditions and membrane processes lead to the deterioration of the physicochemical characteristics of the treated water. Among the water treatment processes, the most promising methods are considered to be the adsorption and coagulation/precipitation, because they fulfil the above mentioned criteria of processes evaluation along with economic benefits.
This study aims at the evaluation of Se(IV) removal from a techno–economic point of view by comparing the optimum uptake capacity shown by adsorption onto iron oxy hydroxides (FeOOH/2.5) and by coagulation/precipitation with Fe(III). These two treatment technologies take advantage of the Se(IV) affinity to Fe(III). Conditions that simulate natural water matrix, pH 7 and initial concentration of 100 μg Se(IV)/L were used at the laboratory experiments. The techno economic evaluation was based on the removal efficiency that was determined according to the uptake capacity at a residual concentration equal to DWRL of 10 μg/L—henceforth abbreviated as Q10.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Water Characteristics
For both the adsorption and coagulation experiments, tap water (Table 1) of the city of Thessaloniki, Greece, was used after chlorine removal by filtering through a fixed bed of activated carbon. Water samples were spiked daily with Se(IV) and were used in the experiments after at least 24 h.

Table 1.
Main (yearly) physicochemical characteristics of Thessaloniki tap water.
2.2. Reagents and Adsorbents
The 10 mg/L stock solutions of Se(IV) were prepared by the dissolution of analytical grade Na2SeO3. Then, 12 g of 12.5% w/w FeClSO4 solution was used to prepare a stock solution of 1500 mg Fe(III)/L by dilution in 1 L distilled water. The pH of the stock solution was adjusted to 1–1.5 by the addition of 6 M HCl. The Fe concentrations (1500 ± 50 mg/L) were verified by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The FeOOH adsorbents evaluated were laboratory synthesized following the procedure of Tresintsi et al., 2012, by the oxidation-hydrolysis of FeSO4·H2O at pH values 2.5 [27]. The main physicochemical characteristics of the qualified adsorbents [14] are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Main physicochemical characteristics of laboratory synthesized FeOOH/2.5.
2.3. Coagulation Tests
The treatment tests were performed on a Wisestir JT-M6C jar tester with six paddle stirrers at 20 ± 1 °C. The water pH was adjusted to 7 via the addition of either 0.1 M HCl or 0.1 M NaOH. A 1500 mL water sample was transferred into a 2000 mL glass beaker. Under initial rapid stirring at 230 rpm, the predetermined coagulant dose ranging between 1 and 30 mg/L was added. After 2 min of rapid mixing, the stirring speed was reduced to 80 rpm and the solution was stirred continuously for 60 min. A 100 mL sample was collected, filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane filter and acidified at pH ≤ 2 to determine the residual selenium concentration.
2.4. Adsorption Tests
For the evaluation of the adsorbent rapid small-scale column tests (RSSCTs) were applied in glass columns of 1.1 cm diameter and 50 cm height with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) valves and caps, and a glass frit at the base of each column. The columns were filled with FeOOH/2.5 adsorbent of particle size 0.25–0.50 mm to the height of 23.6 cm and were fed from the top with 100 μg Se(IV)/L solution in tap water of Thessaloniki at pH 7 ± 0.1 via a dosing pump. Effluent samples were collected periodically and analyzed for residual selenium concentration. The laboratory experiment simulates full-scale processes and was designed to achieve an Empty Bed Contact Time (EBCT) of 3–4 min at 20 °C which corresponds to 5–6.5 min of EBCT of the respective large scale column (Table 3).

Table 3.
Experimental conditions of RSSCTs for evaluation of FeOOH/2.5 adsorption capacity.
2.5. Analytical Procedure
Initial and residual selenium concentrations were determined by graphite atomic absorption spectrophotometry using a Perkin-Elmer Analyst 800 instrument. The method’s detection limit for selenium was 1 μg Se/L.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Coagulation Tests
The experimental results (Figure 1) for Se(IV) coagulation/precipitation by Fe(III) at pH 7 delivered a Q10 value of 3.2 μg Se(IV)/mg Fe(III) with the data best fitted in a BET adsorption model (Table 4) that indicated the Se(IV) removal by a physisorption process [28]. In order to estimate the cost of treatment, the Fe(III) dose required for the removal of Se(IV) from natural water at an initial concentration of 100 μg Se(IV)/L and pH 7 can be calculated as follows:
Fe(III) dose = [(100 × 10 μg Se(IV)/L]/[3.2 μg Se(IV)/mg Fe(III)] = 28.1 mg Fe(III)/L
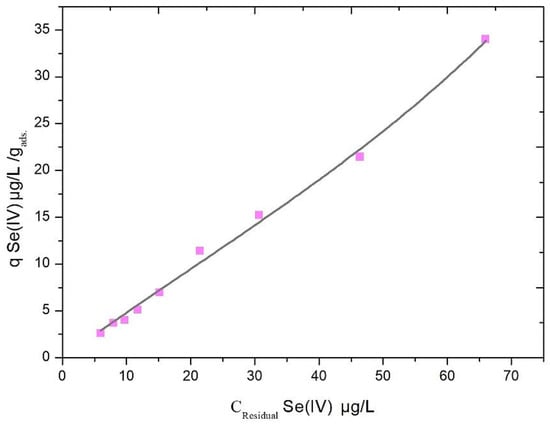
Figure 1.
Se(IV) adsorption isotherm by Fe(III) coagulant. Experimental conditions: pH 7, Fe(III) dose range 1–15 mg/L, initial Se(IV) concentration range 25–100 μg/L.

Table 4.
BET fitting parameters for Se(IV) adsorption isotherms with Fe(III) (according to the equation: Q = aC/(1 + bC + dC2)).
Since the current commercial cost of Fe(III) coagulants in Greece is 1.5 ± 0.1 EUR/kg Fe(III), the cost of the reagent required for the removal of 1 kg Se(IV) and treatment 103 m3 using FeClSO4 solution at pH 7 can be calculated as follows:
Fe(III) consumption for removal 1 kg Se(IV):
[1 kg Se(IV)/3.2 μg Se(IV)/mg Fe(III)] = [1000 g Se(IV)/3.2 g Se(IV)/kg Fe(III)] = 312.5 kg Fe(III)/kg Se(IV)
Reagent cost = [312.5 kg Fe(III)/kg Se(IV)] × [1.5 ± 0.1 EUR/kg Fe(III)] = 469± 32 EUR/kg Se(IV)
Fe(III) consumption for treatment 103 m3:
[103 m3 × (100 − 10) mg Se(IV)/m3]/[3.2 × 103 mg Se(IV)/kg Fe(ΙΙΙ)] = 28.1 kg Fe(III)/103 m3
Reagent cost/103 m3 = [28.1 kg Fe(III)/103 m3] × [1.5 ± 0.1 EUR/kg Fe(III)] = 42.1 ± 2.8 EUR/103 m3
Energy and labor costs of the treatment process do not depend on initial Se(IV) concentrations, but rather the water quantity and energy/labor prices of each individual country/state. An approximation of the energy and labor cost based on current Greek market prices is estimated to be 50 ± 20 EUR/103 m3 treated water.
3.2. Adsorption Tests
According to Kalaitzidou et al. 2019, the implementation of the RSSCTs breakthrough curve for an initial concentration of 100 μg Se(IV)/L resulted in a Q10 value of 4.3 μg Se(IV)/mg FeOOH/2.5 [14]. The commercial cost of adsorbents is estimated to 8 EUR/kg. The estimated cost of adsorbents according to adsorption capacities estimated by the RSSCTs (Figure 2), which simulate the full-scale adsorption process, for Se(IV) removal from natural water at an initial concentration of 100 μg Se(IV)/L and pH 7 were calculated as follows:

Figure 2.
Breakthrough curves of: Se(IV) adsorption by FeOOH/2.5 in RSSCTs (initial concentrations: 100 μg Se(IV)/L, pH = 7, T = 20 °C).
FeOOH/2.5 consumption for removal 1 kg Se(IV):
[1 kg Se (IV)/(4.3 μg Se(IV)/mg FeOOH/2.5)] = [1000 g Se(IV)/(4.3 g Se(IV)/kg FeOOH/2.5)] = 232.6 kg FeOOH/2.5/kg Se(IV)
Cost of FeOOH/2.5 adsorbent:
Adsorbent cost = [232.6 kg FeOOH/2.5/kg Se(IV)] × [8.0 EUR/kg FeOOH/2.5] = 1860.8 EUR/kg Se(IV)
Furthermore, the adsorbent cost, e.g., for treatment 103 m3: natural water, with an initial concentration of 100 μg/L at pH 7.0 ± 0.1 is:
Spent FeOOH/2.5/103 m3 = [103 m3 × (100 − 10) mg Se(IV)/m3]/[4.3 × 103 mg Se(IV)/kg FeOOH/2.5] = 20.9 kg FeOOH/2.5
Adsorbent cost = (20.9 kg FeOOH/2.5/103 m3) x (8.0 EUR/kg FeOOH/2.5) = 167.2 EUR/103 m3
4. Conclusions
Coagulation/precipitation with the application of Fe(III) and adsorption onto FeOOH water treatment processes are both effective and techno–economically viable for selenite removal. Adsorption has many advantages that include the reusability of the adsorbent, safe disposal and low labor cost, with the main disadvantage being the significantly higher treatment cost. Although uptake capacities (Q10) were similar for both processes, the comparison between the coagulation/precipitation and the adsorption water treatment process indicated the superiority of the first method to reduce Se(IV) below the regulated drinking water limit of 10 μg/L in terms of economic aspects. However, for the installation of the optimum drinking water treatment process, sludge production, post treatment requirements, water flow rate, and initial selenite concentration, along with labor and maintenance requirements, should also be considered. The major disadvantage of the coagulation/precipitation process is the production and management of a high amount of sludge.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and A.Z.; methodology, K.K.; validation, M.M., formal analysis, K.K.; investigation, A.-A.N. and L.B.; data curation, K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.; writing—review and editing, M.M., K.S. and A.Z.; visualization, M.M.; supervision, M.M.; project administration, M.M. All authors have read and agree to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been co-financed by the European Union and Greek national funds through the Operational Program Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation, under the call RESEARCH—CREATE—INNOVATE (project code: T1EDK-03543).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tan, L.C.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Lens, P.N.L. Selenium: Environmental significance, pollution, and biological treatment technologies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 886–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Shang, C.; Luo, L.; Gao, J.; Tang, L. Selenium contamination, consequences and remediation techniques in water and soils: A review. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, S.; Kumar, P.S. An investigation of adsorption parameters on ZVI-AC nanocomposite in the displacement of Se(IV) ions through CCD analysis. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 211–223. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, S.; Ungureanu, G.; Boaventura, R.; Botelho, C. Selenium contaminated waters: An overview of analytical methods, treatment options and recent advances in sorption methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etteieb, S.; Magdouli, S.; Zolfaghari, M.; Brar, S.K. Monitoring and analysis of selenium as an emerging contaminant in mining industry: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 698, 134339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive, C. The Council of the European Union Council Directive 98/93/EC of November 1998 on the quality of water intended for human consumption. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1998, 330, 32–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pettine, M.; McDonald, T.J.; Sohn, M.; Anquandah, G.A.K.; Zboril, R.; Sharma, V.K. A critical review of selenium analysis in natural water samples. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabelin, C.B.; Igarashi, T.; Villacorte-Tabelin, M.; Park, I.; Opiso, E.M.; Ito, M.; Hiroyoshi, N. Arsenic, selenium, boron, lead, cadmium, copper, and zinc in naturally contaminated rocks: A review of their sources, modes of enrichment, mechanisms of release, and mitigation strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1522–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Dong, H.; Luo, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X. Selenite removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron (ZVI) in combination with oxidants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, N.; Demopoulos, G.P. The elimination of selenium(IV) from aqueous solution by precipitation with sodium sulfide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoffroy, N.; Demopoulos, G.P. Reductive precipitation of elemental selenium from selenious acidic solutions using sodium dithionite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 10240–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, K.; Takahashi, Y. Effective Removal of Selenite and Selenate Ions from Aqueous Solution by Barite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9194–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, Q.; Chen, G.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Removal of Se(IV) and Se(VI) from drinking water by coagulation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 142, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzidou, K.; Nikoletopoulos, A.A.; Tsiftsakis, N.; Pinakidou, F.; Mitrakas, M. Adsorption of Se(IV) and Se(VI) species by iron oxy-hydroxides: Effect of positive surface charge density. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.T.; Fan, M. Evaluation of natural goethite on the removal of arsenate and selenite from water. J. Environ. Sci. (China) 2019, 76, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.C.; Rigali, M.J.; Brady, P. Selenite sorption by carbonate substituted apatite. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, L.V.; Quirino, J.N.; Monteiro, A.M.; Abrão, T.; Parreira, P.S.; Urbano, A.; Santos, M.J. Sorption-desorption of selenite and selenate on Mg-Al layered double hydroxide in competition with nitrate, sulfate and phosphate. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Gang, D.D.; McDonald, L.; Lin, L.S. Background electrolytes and pH effects on selenate adsorption using iron-impregnated granular activated carbon and surface binding mechanisms. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Yan, B.; Zeng, H.; Liu, Q. Dendrimer functionalized graphene oxide for selenium removal. Carbon 2016, 105, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Shen, Q. High performance of selenium cathode by encapsulating selenium into the micropores of chitosan-derived porous carbon framework. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 746, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Khaleque, M.A. Efficient selenium(IV) detection and removal from water by tailor-made novel conjugate adsorbent. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awual, M.R.; Hasan, M.M.; Ihara, M.; Yaita, T. Mesoporous silica based novel conjugate adsorbent for efficient selenium (IV) detection and removal from water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Nakayama, M. Removal of selenium (VI) from aqueous solution with polyamine-type weakly basic ion exchange resin. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 3155–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, M.; Pal, M.; Pal, P. A response surface optimized nanofiltration-based system for efficient removal of selenium from drinking Water. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantafio, A.W.; Hagen, K.D.; Lewis, G.E.; Bledsoe, T.L.; Nunan, K.M.; Macy, J.M. Pilot-scale selenium bioremediation of San Joaquin drainage water with Thauera selenatis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3298–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, K.S.; Bañuelos, G.S. Selenium in Plants; Overview and Prospects of Selenium Phytoremediation Approaches; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 11, pp. 277–321. [Google Scholar]
- Tresintsi, S.; Simeonidis, K.; Vourlias, G.; Stavropoulos, G.; Mitrakas, M. Kilogram-scale synthesis of iron oxy-hydroxides with improved arsenic removal capacity: Study of Fe(II) oxidation-precipitation parameters. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5255–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzidou, K.; Bakouros, L.; Mitrakas, M. Techno-economic evaluation of iron and aluminum coagulants on Se(IV) removal. Water 2020, 12, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).