Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles Using Waste Natural Materials and Its Application for Wastewater Treatment †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of the Extracts of Waste Natural Materials and Iron Nanoparticles
2.2. Characterization of the Synthesized Fe/NPs
2.3. Characteristics of Raw Wastewater
2.3.1. Sample Sites and Analysis of Raw Samples
2.3.2. Reagents
2.3.3. Instruments and Characterization Techniques
2.4. Batch Experiments Fe/NPs
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization
3.1.1. UV–Vis Spectral Analysis of Fe/NPs
3.1.2. Appearance of Synthesized Fe/NPs
3.1.3. XRD Pattern Analysis of Fe/NPs
3.1.4. Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis
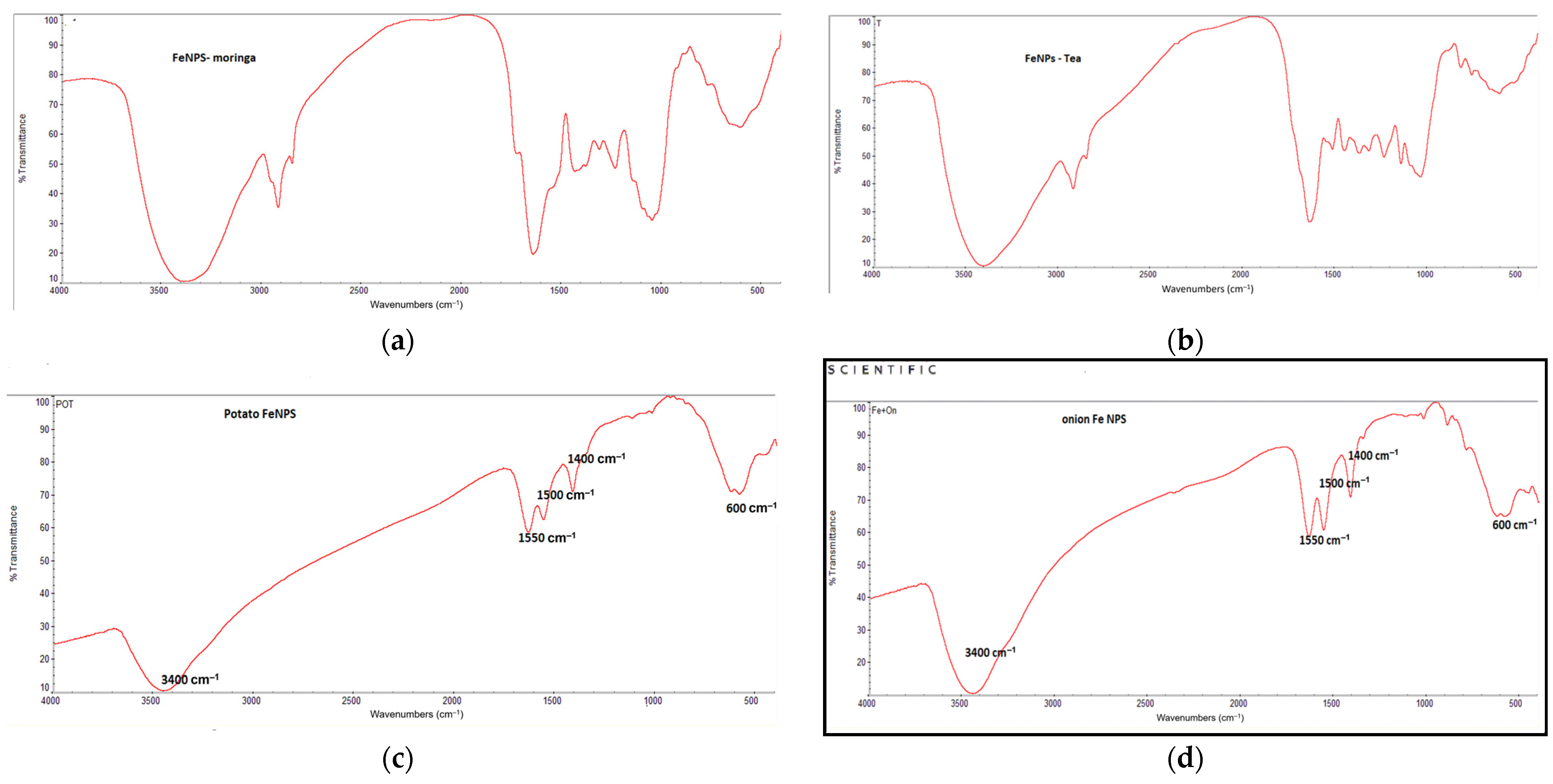
3.1.5. The FT-IR Spectra of Fe/NPs
3.1.6. XRF Analysis of Banana, Orange, and Pomegranate
3.1.7. Yield of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
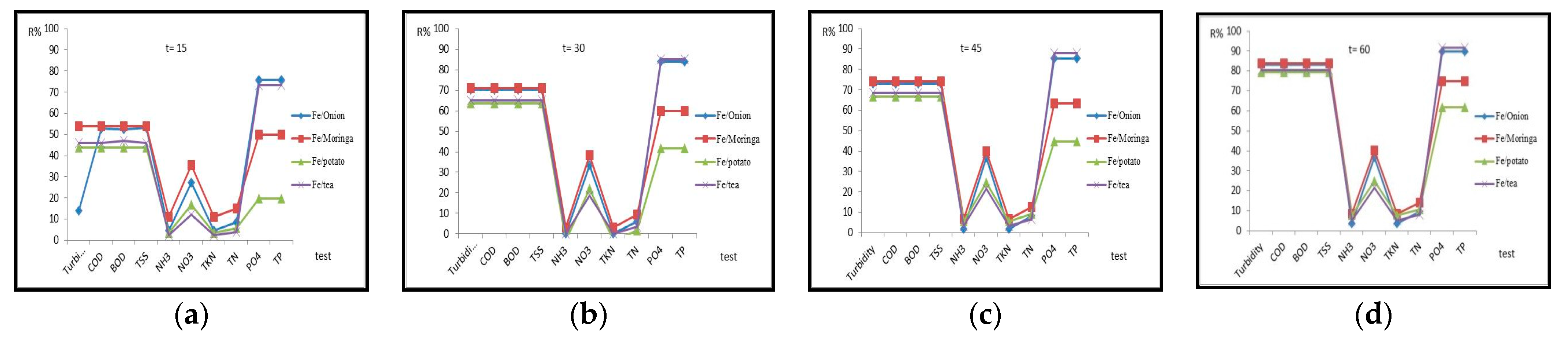
3.2. Effect of Contact Time
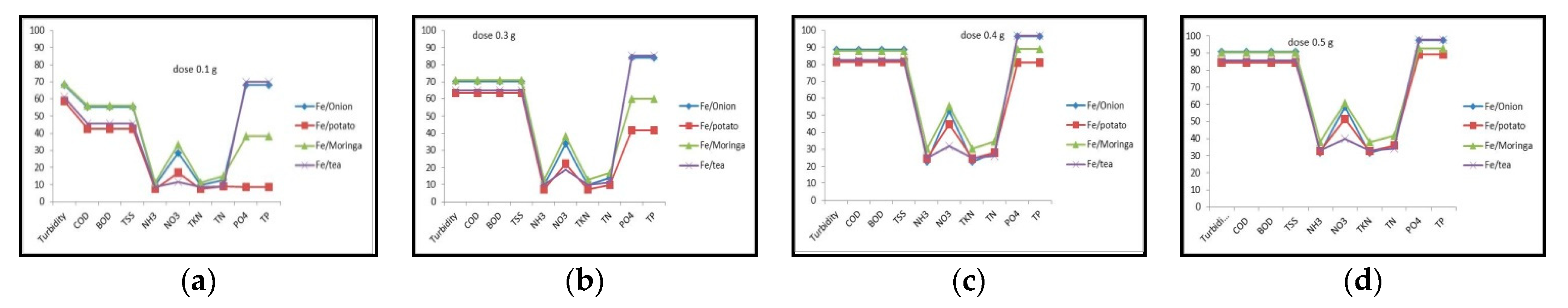
3.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kakavandi, B.; Kalantary, R.R.; Farzadkia, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Esrafili, A.; Azari, A.; Yari, A.R.; Javid, A.B. Enhanced chromium (VI) removal using activated carbon modified by zero valent iron and silver bimetallic nanoparticles. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, R.D.; Barwar, S.; Kane, P.; Bhatt, L. Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles using Banana Leaves. Eur. J. Sci. 2018, 1, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, S.; Rajendran, S.P. Methods of synthesis of nano particles and its applications. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Das, G.; Shin, H.-S.; Kumar, A.; Vishnuprasad, C.N.; Patra, J.K. Photo-mediated optimized synthesis of silver nanoparticles using the extracts of outer shell fibre of cocos nucifera L. fruit and detection of its antioxidant, cytotoxicity and antibacterial potential. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles from Natural Resources and Food Waste and Their Environmental Application. In Green Metal Nanoparticles; Scrivener Publishing: Beverly, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 321–385. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Mohamed, F.M.; Marzouq, M.H.; Mustafa, A.B.E.; Alsoudi, A.M.; Ali, O.A.; Mohamed, M.A.; Mahmoud, F.A. Review of Green Methods of Iron Nanoparticles Synthesis and Applications. Bionanoscience 2018, 8, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, N. Physical Properties of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Ph.D. Thesis, Maine University, Orono, ME, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Al Rawi, O.; Balarak, D. Capacity and Modeling of Acid Blue 113 Dye Adsorption onto Chitosan Magnetized by Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amany, R.G.; Nagwa, M.S.; Ahmed, S.H.; Abdelmoteleb, Y.A. Biosynthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by fungi. Az. J. Pharm Sci. 2020, 62, 164–178. [Google Scholar]
- Badmus, K.O.; Coetsee-Hugo, E.; Swart, H.; Petrik, L. Synthesis and characterisation of stable and efficient nano zero valent iron. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23667–23684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da’na, E.; Taha, A.; Afkar, E. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles by Acacia nilotica Pods Extract and Its Catalytic, Adsorption, and Antibacterial Activities. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-P.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.P. Characterization of zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 120, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majlesi, M. Preparation and adsorption properties of chitosan-bound Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for phenol removal from aqueous solution. World Rev. Sci. Technol. Sust. Dev. 2016, 12, 371–380. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, D.; Behari, J.; Sen, P. Application of nanoparticles in waste water treatment. World Appl. Sci. J. 2008, 3, 417–433. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Elah Mohammad, D.; Mohammad Taher, E. Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles fabricated from some vegetable plants. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1294, 062048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheilkordi, Z.; Ziarani, M. Recent advances in the application of magnetic bio-polymers as catalysts in multicomponent. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 12672–12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egyptian Environmental Association Affair (EEAA). Book, Law 48, 1982, Permissible Values for Wastes in River Nile and Law 44, Law of the Environmental Protection 1994, Updating 2000. Available online: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/egy18642.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Ahmed, H.; El-Khateeb, M.; Ahmed, N. Effective Granular Activated Carbon for Greywater Treatment Prepared from Corncobs. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A. Thermodynamics and Kinetics Studies of Mn (II) Removal from Aqueous Solution onto Powder Corn Cobs (PCC). J. Chromatogr. Sep. Techol. 2015, 6, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadon, F.N.; Ibrahem, A.S.; Ismail, K.N. An overview of rice husk applications and modification techniques in wastewater treatment. J. Purity, Util. React. Environ. 2012, 1, 308–334. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Removal of pyrene and benzo(a)pyrene micropollutant from water via adsorption by green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Mubarak, N.M.; Baloch, H.A.; Abdullah, E.C.; Mazari, S.A.; Griffin, G.J.; Srinivasan, M.P.; Tanksale, A. Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes From Wastewater. In Nanoscale Materials in Water Purification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 447–472. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.U.; Zaidi, R.; Hassan, S.Z.; Farooqi, I.H.; Azam, A. Application of Fe-Cu binary oxide nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Test | Unit | * Average Values of Raw Samples |
|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.2 |
| TDs | mg/L | 611 |
| EC | µs/cm | 1099 |
| ORP | mV | −19.7 |
| Turbidity | NTU | 89.5 |
| COD | mg/L | 560 |
| BOD | mg/L | 302 |
| TSS | mg/L | 330 |
| NH3 | mg/L | 13.2 |
| NO3 | mg/L | 5.4 |
| TKN | mg/L | 28.2 |
| TN | mg/L | 33.6 |
| PO4 | mg/L | 3.3 |
| TP | mg/L | 0.66 |
| Sample Name | Fe2O3 | Na2O | MnO | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | K2O | SO3− | Cr2O3 | MgO | Cl− | LOI | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-Tea | 40.86 | 19.8 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 15.6 | 22.2 | 99.99 |
| Fe-Potato | 53.92 | 16.1 | 0.53 | 0.3 | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 9.63 | 18.8 | 99.98 |
| Fe-Onion | 67.3 | 8.39 | 0.63 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 11.6 | 9.51 | 99.94 |
| Fe-Moringa | 46.62 | 22.1 | 0.46 | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.07 | 0.07 | - | - | 0.04 | 14.9 | 15.1 | 99.99 |
| Iron Oxide Nanoparticle | Weight (g) |
|---|---|
| Fe-Metal | 7.625 |
| Fe-Moringa | 38.235 |
| Fe-Potato | 19.116 |
| Fe-Onion | 16.114 |
| Fe-Tea | 12.899 |
| Parameter | Unit | Raw | Residual Concentration (mg/L) of Pollutants at Optimum Contact Time 45 min—Turbidity as NTU | Removal Efficiency of Adsorbents (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/onion | Fe/moringa | Fe/potato | Fe/tea | Fe/onion | Fe/moringa | Fe/potato | Fe/tea | |||
| pH | --- | 7.2 | 8.3 | 8.19 | 8.6 | 8.4 | - | - | - | - |
| TDS | mg/L | 611 | 688 | 745 | 752 | 978 | - | - | - | - |
| EC | µs/cm | 1099.8 | 1238.4 | 1341 | 1353.6 | 1760.4 | - | - | - | - |
| ORP | mV | −19.7 | −80 | −72 | −95 | −83 | - | - | - | - |
| Turbidity | NTU | 89.5 | 24.31 | 23.19 | 29.75 | 28.15 | 72.85 | 74.10 | 66.78 | 68.57 |
| COD | mg/L | 560 | 152 | 145 | 186 | 176 | 72.85 | 74.10 | 66.78 | 68.57 |
| BOD | mg/L | 302 | 82.08 | 78.3 | 100.44 | 95.04 | 72.85 | 74.10 | 66.78 | 68.57 |
| TSS | mg/L | 330 | 89.68 | 85.55 | 109.74 | 103.84 | 72.85 | 74.10 | 66.78 | 68.57 |
| NH3 | mg/L | 13.2 | 12.98 | 12.34 | 12.45 | 12.79 | 1.66 | 6.51 | 5.68 | 3.10 |
| NO3 | mg/L | 6.4 | 4.05 | 3.85 | 4.82 | 5.03 | 36.71 | 39.84 | 24.68 | 21.40 |
| TKN | mg/L | 28.24 | 27.7 | 26.4 | 26.6 | 27.3 | 1.66 | 6.51 | 5.68 | 3.10 |
| TN | mg/L | 34.64 | 31.8 | 30.2 | 31.4 | 32.4 | 8.14 | 12.67 | 9.19 | 6.48 |
| PO4 | mg/L | 3.3 | 0.489 | 1.205 | 1.8 | 0.398 | 85.18 | 63.48 | 44.57 | 87.93 |
| TP | mg/L | 0.66 | 0.097 | 0.241 | 0.36 | 0.079 | 85.18 | 63.48 | 44.57 | 87.93 |
| Parameter | Raw | Residual Concentration (mg/L) of Pollutants at Optimum Dose 0.4—Turbidity as NTU | Removal Efficiency of Adsorbents (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe/onion | Fe/potato | Fe/moringa | Fe/tea | Fe/onion | Fe/potato | Fe/moringa | Fe/tea | ||
| pH | 7.2 | 8.35 | 8.6 | 8.25 | 8.52 | - | - | - | - |
| TDS | 611 | 703 | 750 | 752 | 1005 | - | - | - | - |
| EC | 1099 | 1265 | 1350 | 1353 | 1809 | - | - | - | - |
| ORP | −19.7 | −85 | −105 | −75 | −89 | - | - | - | - |
| Turbidity | 89.5 | 10 | 16 | 10. | 15 | 88.39 | 81.25 | 87.85 | 82.5 |
| COD | 560 | 65 | 105 | 68 | 98 | 88.39 | 81.25 | 87.85 | 82.5 |
| BOD | 302 | 35 | 56 | 36 | 52 | 88.39 | 81.25 | 87.85 | 82.5 |
| TSS | 330 | 38 | 61 | 40 | 57 | 88.39 | 81.25 | 87.85 | 82.5 |
| NH3 | 14.6 | 11.3 | 11.05 | 10.2 | 11 | 22.86 | 24.57 | 30.17 | 24.91 |
| NO3 | 6.4 | 3.02 | 3.54 | 2.85 | 4.3 | 52.81 | 44.68 | 55.46 | 31.87 |
| TKN | 31.3 | 24.1 | 23.6 | 21.8 | 23.5 | 22.86 | 24.57 | 30.17 | 24.91 |
| TN | 37.7 | 27.2 | 27.1 | 24.7 | 27.9 | 27.94 | 27.98 | 34.45 | 26.09 |
| PO4 | 3.3 | 0.11 | 0.62 | 0.36 | 0.097 | 96.66 | 81.06 | 88.93 | 97.06 |
| TP | 0.66 | 0.022 | 0.125 | 0.073 | 0.0194 | 96.66 | 81.06 | 88.93 | 97.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, H.M.; El-khateeb, M.A.; Sobhy, N.A.; Hefny, M.M.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M. Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles Using Waste Natural Materials and Its Application for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 25, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14181
Ahmed HM, El-khateeb MA, Sobhy NA, Hefny MM, Abdel-Haleem FM. Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles Using Waste Natural Materials and Its Application for Wastewater Treatment. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2023; 25(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14181
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Hussein M., Mohamed A. El-khateeb, Neama A. Sobhy, Mohamed M. Hefny, and Fatehy M. Abdel-Haleem. 2023. "Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles Using Waste Natural Materials and Its Application for Wastewater Treatment" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 25, no. 1: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14181
APA StyleAhmed, H. M., El-khateeb, M. A., Sobhy, N. A., Hefny, M. M., & Abdel-Haleem, F. M. (2023). Green Synthesis of Magnetite Nanoparticles Using Waste Natural Materials and Its Application for Wastewater Treatment. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 25(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECWS-7-14181







