Field Spectroscopy Applied to the Kaolinite Polytypes Identification †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
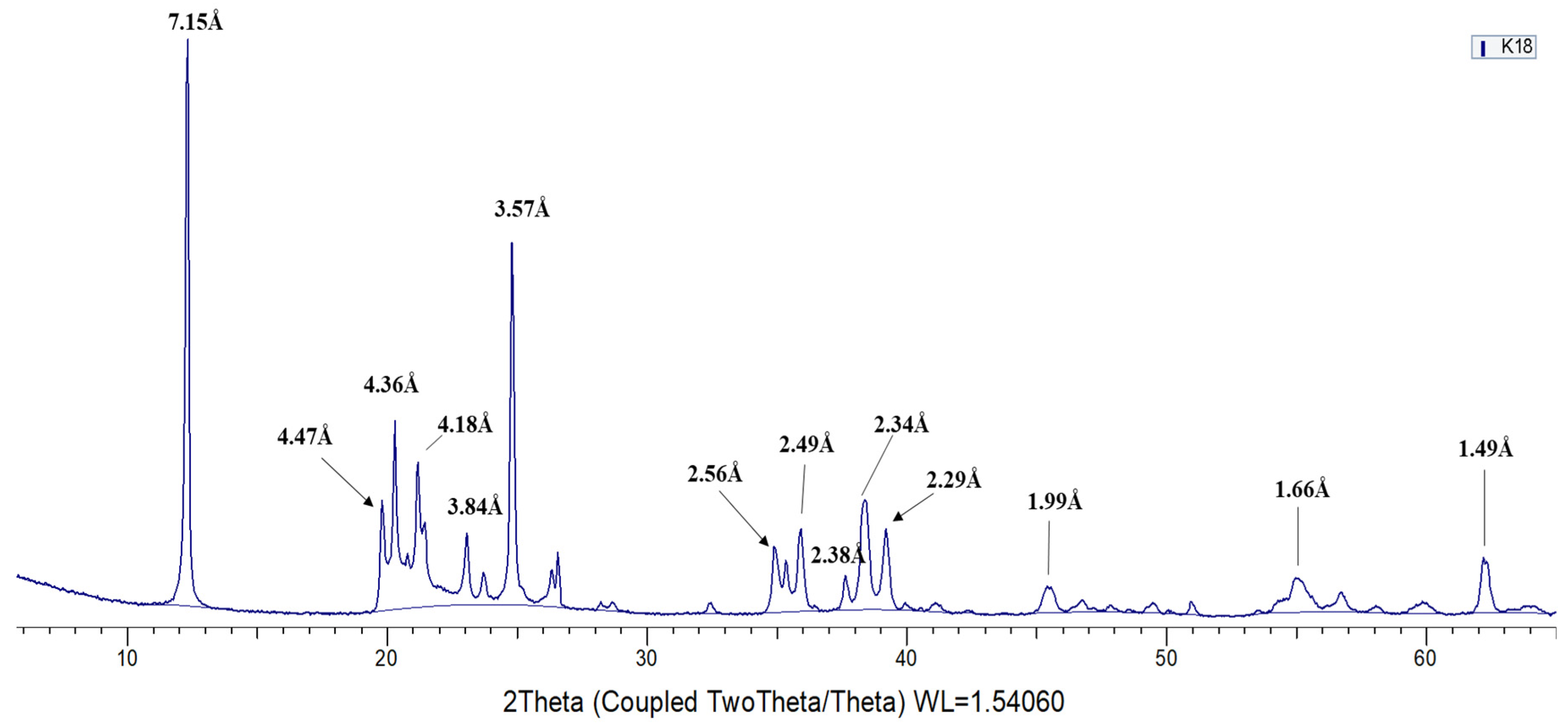
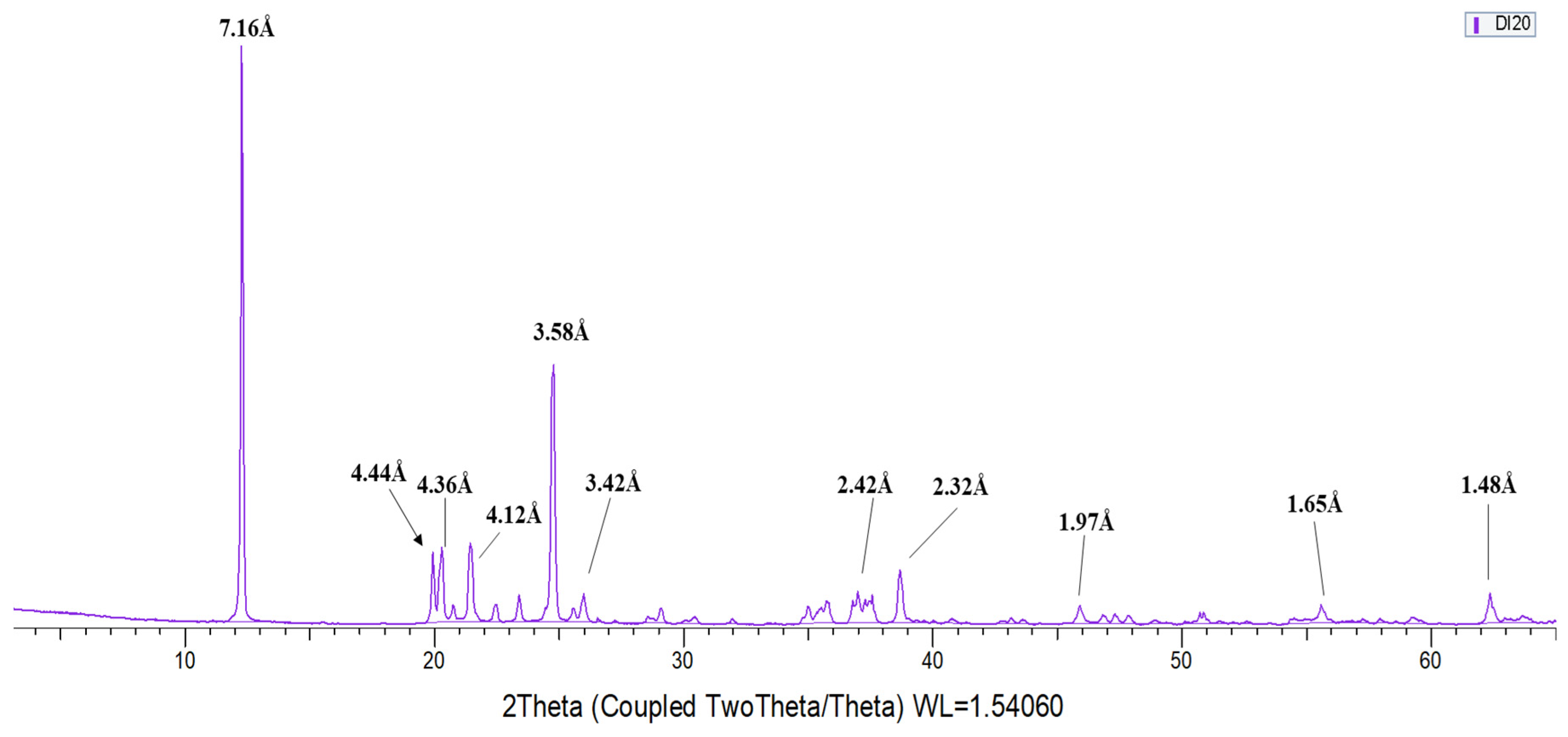
3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
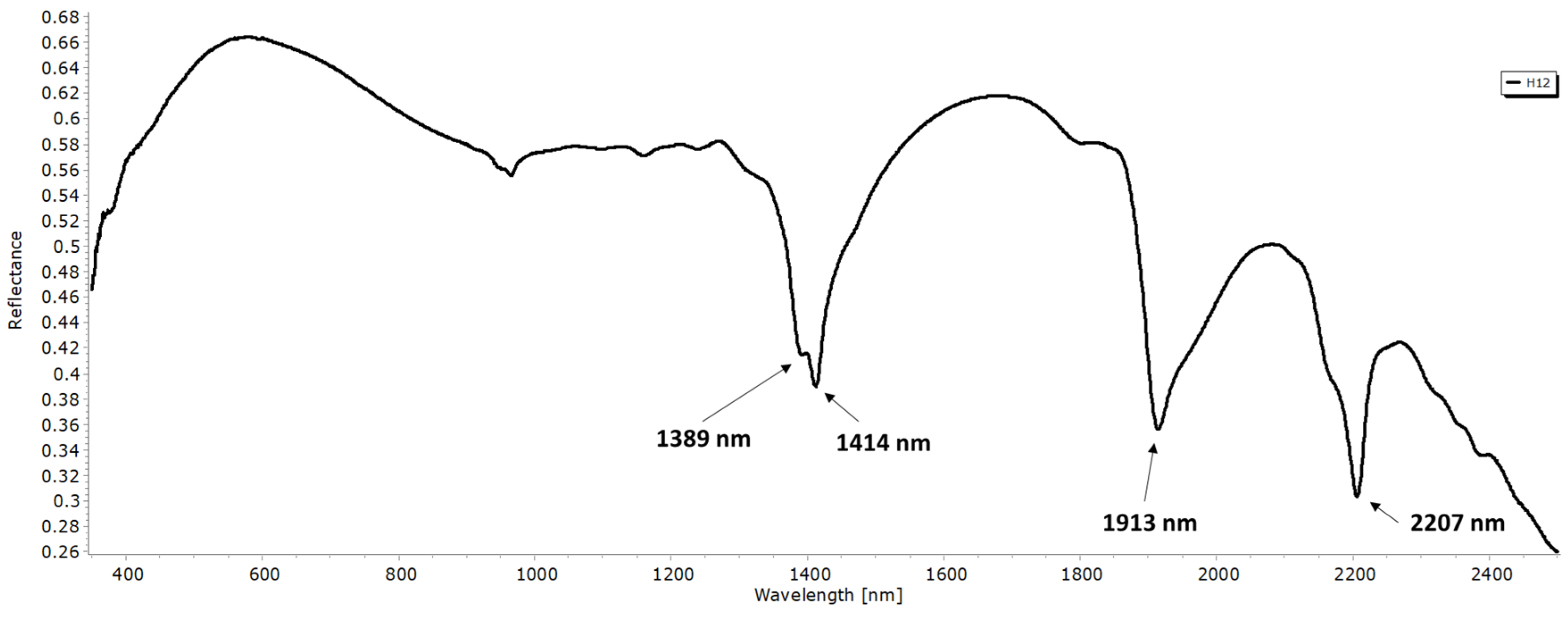
3.2. Spectroscopy VNIR–SWIR
3.2.1. Kaolinite
3.2.2. Dickite
3.2.3. Halloysite
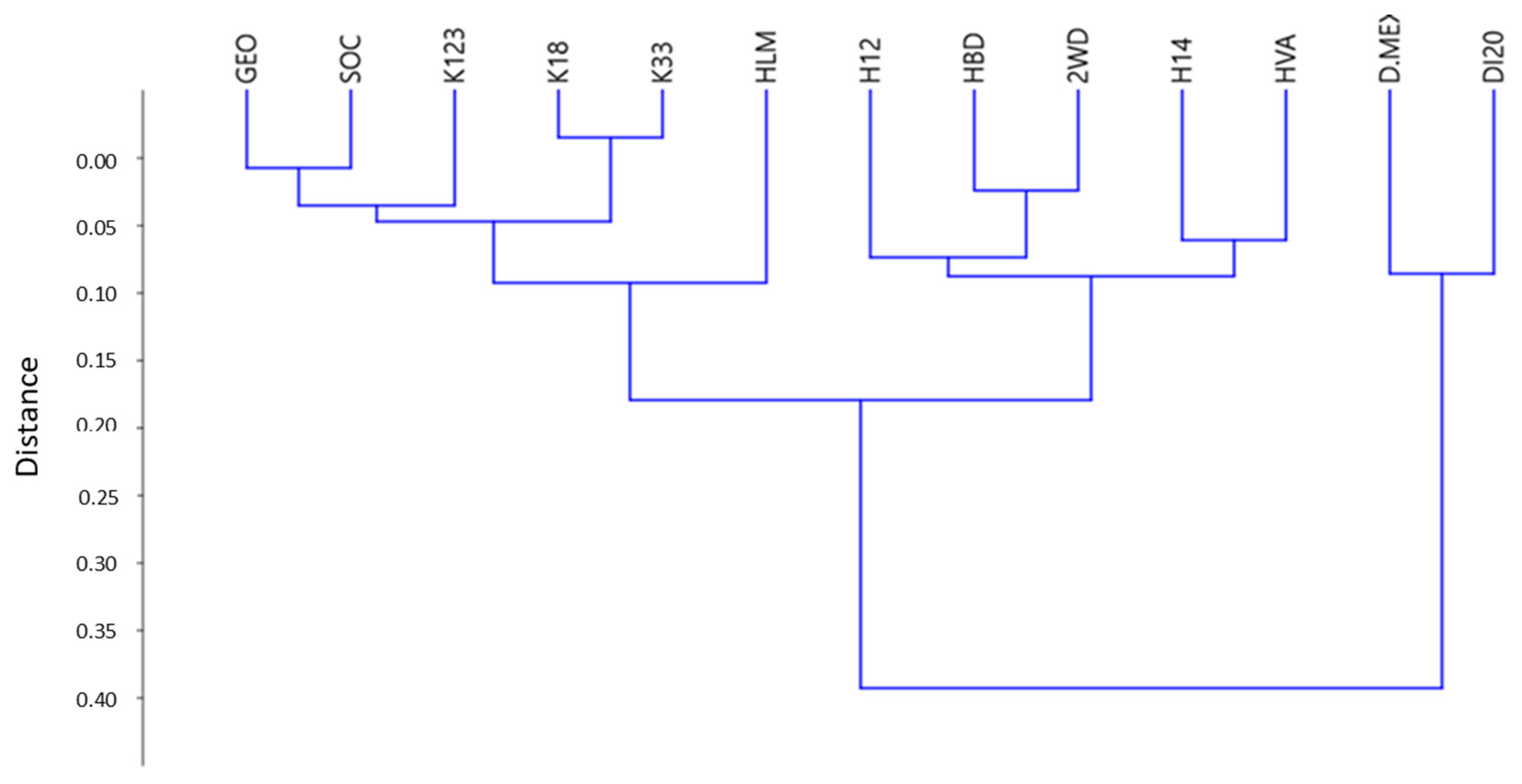
3.2.4. Statistical Treatment
4. Conclusions
- −
- From the 13 samples studied, 5 have been identified as kaolinite, 2 as dickite and 6 as halloysite. Diagnostic XRD peaks for kaolinite, not found in dickite, appear in 4.47Å, 4.36 Å, 4.18 Å, 3.84 Å, 3.73 Å, 2.75 Å, and 2.29 Å. On the other hand, the diagnostic peaks of dickite, not found in kaolinite, appear in 4.44 Å, 4.26 Å, 4.12 Å, 3.95 Å, 3.79 Å, and 2.32 Å. Halloysite diagnostic reflections correspond to 7.20–7.6 Å, 2.53 Å and 1.68 Å.
- −
- The main discriminatory absorption bands of the different polytypes are the following: 1397 nm, 1414 nm, and 2208 nm with kaolinite, 1381 nm and 2178 nm with dickite; and finally, 1913 nm and 2138 nm with halloysite.
- −
- Groups of diagnostic peaks for kaolinite, dickite, and halloysite polytypes were identified in the VNIR–SWIR spectrum and, in good agreement to XRD mineralogical identification, allow an unequivocal classification of kaolinite polytypes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guggenheim, S.; Adams, J.M.; Bain, D.C.; Bergaya, F.; Brigatti, M.F.; Drits, V.A.; Formoso, M.L.L.; Galán, E.; Kogure, T.; Stanjek, H. Summary of recommendations of Nomenclature Committees relevant to clay mineralogy: Report of the association Internationale pour l’Etude des Argiles (AIPEA) Nomenclature Committee for 2006. Clays Clay Miner. 2006, 54, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.S.; Kerr, P.F. The kaolin minerals. U. S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1931, 165E, 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- Zvyagin, B.B.; Drits, V.A. Interrelated features of structure and stacking of kaolin mineral layers. Clays Clay Miner. 1996, 44, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, G.W.; Robinson, K. Structure of kaolinite. Nature 1945, 156, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, G.W.; Robinson, K. Randomness in the structures of kaolinitic clay minerals. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1946, 42, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W. Polymorphism of the kaolin minerals. Am. Mineral. 1963, 48, 1196–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Bookin, A.S.; Drits, V.A.; Plançon, A.Y.; Tchoubar, C. Stacking faults in kaolin-group minerals in the light of real structural features. Clays Clay Miner. 1988, 37, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloprogge, J.T. Spectroscopic Methods in the Study of Kaolin Minerals and Their Modifications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 434. [Google Scholar]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, G.J.; Theng, B.K.G.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite clay minerals—A review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File, P.D. Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards; ASTM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1967; pp. 9–185. [Google Scholar]
- Menges, F. Spectragryph-Optical Spectroscopy Software. 2019. Available online: http://www.effemm2.de/spectragryph/ (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Bradley, W.F.; Grim, R.E.; Brown, G. X-ray Identification and Crystal Structures of Clay Minerals; Mineralogical Society, Clay Minerals Group: London, UK, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.M.; Reynolds, R.C., Jr. X-ray Diffraction and the Identification and Analysis of Clay Minerals; Oxford University Press (OUP): Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, G.R.; Ashley, R.P. Spectra of altered rocks in the visible and near infrared. Econ. Geol. 1979, 74, 1613–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.R. Spectral signatures of particulate minerals in the visible and near infrared. Geophysics 1977, 42, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Vicente, A.; Lorenzo, A.; Morales, J.; García-Romero, E.; Suárez, M. Field Spectroscopy Applied to the Kaolinite Polytypes Identification. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 6, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09353
García-Vicente A, Lorenzo A, Morales J, García-Romero E, Suárez M. Field Spectroscopy Applied to the Kaolinite Polytypes Identification. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2021; 6(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09353
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Vicente, Andrea, Adrián Lorenzo, Juan Morales, Emilia García-Romero, and Mercedes Suárez. 2021. "Field Spectroscopy Applied to the Kaolinite Polytypes Identification" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 6, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09353
APA StyleGarcía-Vicente, A., Lorenzo, A., Morales, J., García-Romero, E., & Suárez, M. (2021). Field Spectroscopy Applied to the Kaolinite Polytypes Identification. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 6(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/iecms2021-09353






