Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Concurrent EGFR Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of the Double Dilemma
Abstract
1. Introduction
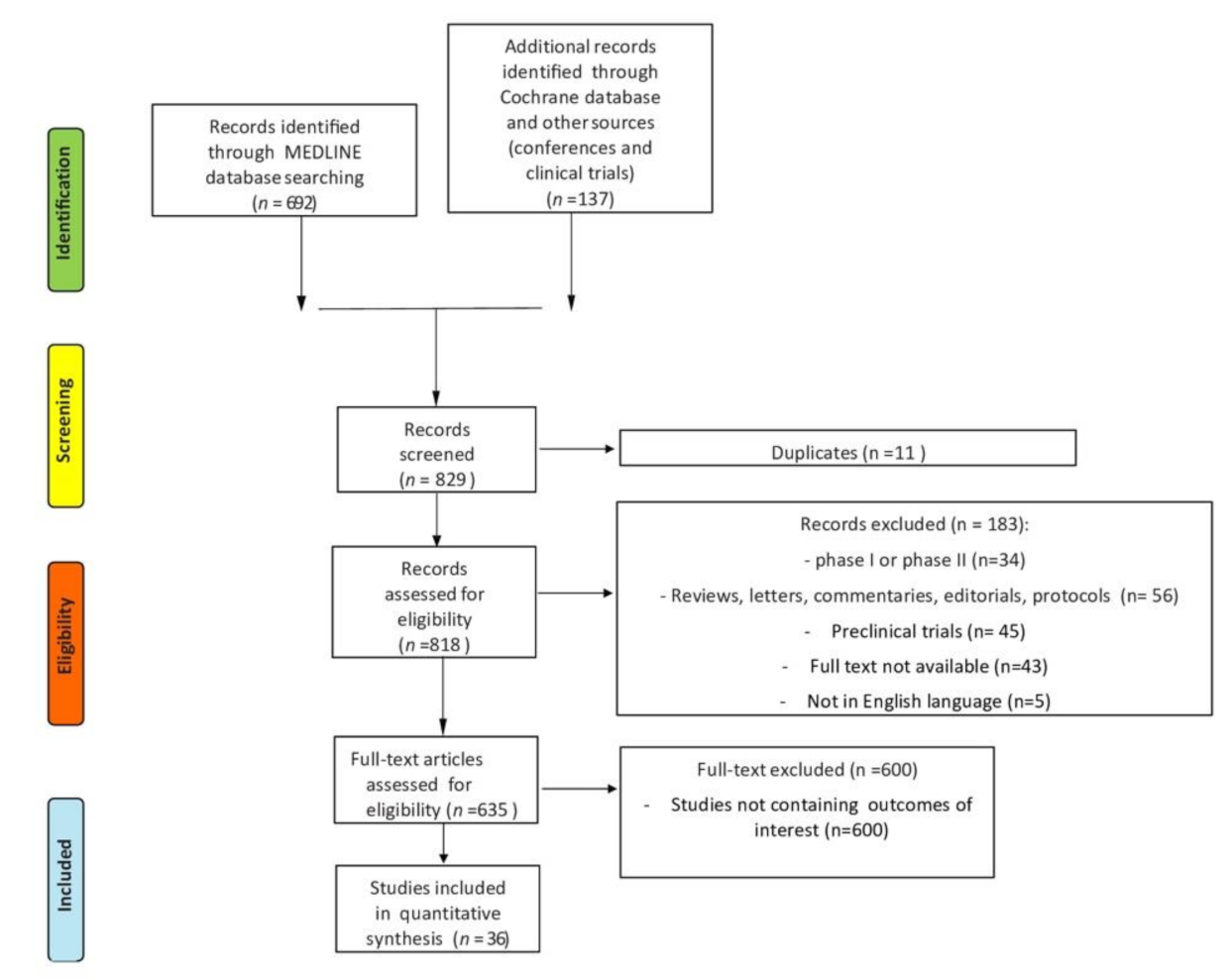
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Complex EGFR Mutations
3.2. Actionable Concomitant Oncogenic Driver Mutations
3.2.1. ALK
3.2.2. KRAS
3.2.3. ROS-1
3.2.4. MET
3.2.5. BRAF
3.2.6. RET
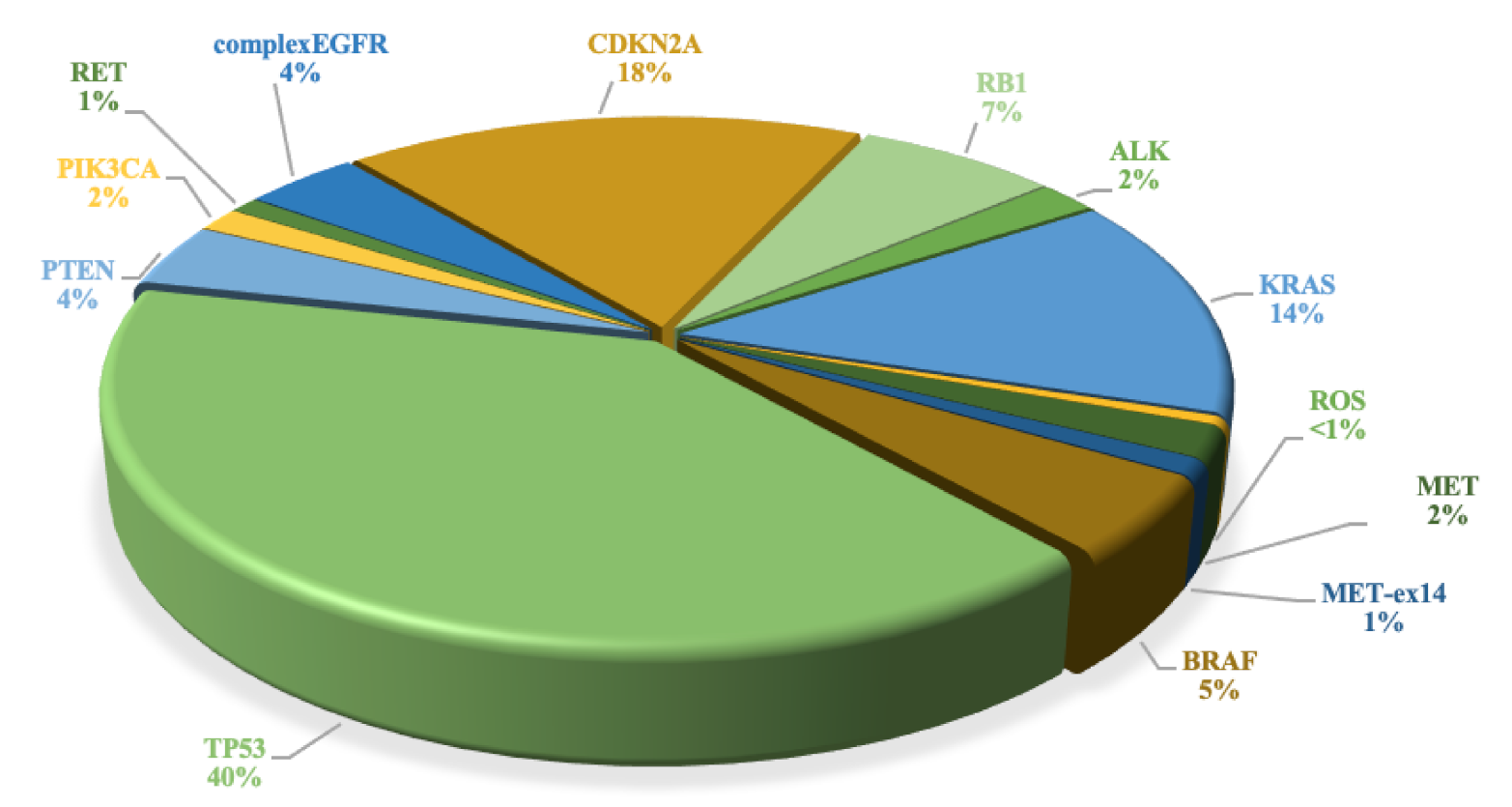
3.3. TP53, PTEN, PIK3CA, CDKN2A and RB1
3.4. Methods of Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkala, S.; Ramalingam, S.S. Personalized therapy for lung cancer: Striking a moving target. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacchio, M.; Sgariglia, R.; Gristina, V.; Pisapia, P.; Pepe, F.; De Luca, C.; Migliatico, I.; Clery, E.; Greco, L.; Vigliar, E.; et al. KRAS mutations testing in non-small cell lung cancer: The role of Liquid biopsy in the basal setting. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 3836–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passiglia, F.; Galvano, A.; Castiglia, M.; Incorvaia, L.; Calò, V.; Listì, A.; Mazzarisi, S.; Perez, A.; Gallina, G.; Rizzo, S.; et al. Monitoring blood biomarkers to predict nivolumab effectiveness in NSCLC patients. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919839928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yang, P.-C. Precision Management of Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2020, 71, 117–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtivelman, E.; Hensing, T.; Simon, G.R.; Dennis, P.A.; Otterson, G.A.; Bueno, R.; Salgia, R. Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1392–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Russano, M.; Franchina, T.; Migliorino, M.R.; Aprile, G.; Mansueto, G.; Berruti, A.; Falcone, A.; Aieta, M.; Gelibter, A.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR), Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR), and Outcomes with Nivolumab in Pretreated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Large Retrospective Multicenter Study. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, V.; Malapelle, U.; Galvano, A.; Pisapia, P.; Pepe, F.; Rolfo, C.; Tortorici, S.; Bazan, V.; Troncone, G.; Russo, A. The significance of epidermal growth factor receptor uncommon mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and critical appraisal. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 85, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, G.; Passiglia, F.; Galvano, A.; Barraco, N.; Listì, A.; Castiglia, M.; Rizzo, S.; Fiorentino, E.; Bazan, V.; Russo, A. Nintedanib in NSCLC: Evidence to date and place in therapy. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2016, 8, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yamamoto, N.; Obyrne, K.J.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III Study of Afatinib or Cisplatin Plus Pemetrexed in Patients With Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma With EGFR Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Okamoto, I.; Sriuranpong, V.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Imamura, F.; Lee, J.S.; Pang, Y.-K.; Cobo, M.; Kasahara, K.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Tissue and Plasma EGFR Mutation Analysis in the FLAURA Trial: Osimertinib versus Comparator EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor as First-Line Treatment in Patients with EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6644–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, C.; Pepe, F.; Iaccarino, A.; Pisapia, P.; Righi, L.; Listì, A.; Greco, L.; Gragnano, G.; Campione, S.; De Dominicis, G.; et al. RNA-Based Assay for Next-Generation Sequencing of Clinically Relevant Gene Fusions in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malapelle, U.; Pepe, F.; Pisapia, P.; Sgariglia, R.; Nacchio, M.; Barberis, M.; Bilh, M.; Bubendorf, L.; Büttner, R.; Cabibi, D.; et al. TargetPlex FFPE-Direct DNA Library Preparation Kit for SiRe NGS panel: An international performance evaluation study. J. Clin. Pathol 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, F.; Pisapia, P.; Gristina, V.; Rocco, D.; Bs, M.M.; Micheli, P.; Iaccarino, A.; Tufano, R.; Bs, G.G.; De Luca, C.; et al. Tumor mutational burden on cytological samples: A pilot study. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Steen, N.; Mentens, Y.; Ramael, M.; Leon, L.G.; Germonpré, P.; Ferri, J.; Gandara, D.R.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J.; Pauwels, P.; et al. Double Trouble: A Case Series on Concomitant Genetic Aberrations in NSCLC. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belardinilli, F.; Gradilone, A.; Gelibter, A.; Zani, M.; Occhipinti, M.; Ferraro, S.; Nicolazzo, C.; Coppa, A.; Giannini, G. Coexistence of three EGFR mutations in an NSCLC patient: A brief report. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2018, 33, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesova, L.; Minarik, M.; Jancarikova, D.; Belsanova, B.; Pesek, M. Multiplicity of EGFR and KRAS mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Anticancer. Res. 2010, 30, 1667–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Wu, J.; Huang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, H.; Dai, X.; Nie, X. Concomitant EGFR mutation and ALK rearrangement in multifocal lung adenocarcinoma: A case report. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 15, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammers, P.E.; Lovly, C.; Horn, L. A patient with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma harboring concurrent EGFR L858R, EGFR germline T790M, and PIK3CA mutations: The challenge of interpreting results of comprehensive mutational testing in lung cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2014, 12, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Lee, B.; Choi, Y.-L.; Han, J.; Ahn, M.-J.; Um, S.-W. Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Concomitant EGFR, KRAS, and ALK Mutation: Clinicopathologic Features of 12 Cases. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2016, 50, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanaga, A.; Shimizu, K.; Noro, R.; Seike, M.; Kitamura, K.; Kosaihira, S.; Minegishi, Y.; Shukuya, T.; Yoshimura, A.; Kawamoto, M.; et al. Activity of EGFR-tyrosine kinase and ALK inhibitors for EML4–ALK-rearranged non–small–cell lung cancer harbored coexisting EGFRmutation. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweis, R.F.; Thomas, S.; Bank, B.; Fishkin, P.; Mooney, C.; Salgia, R. Concurrent EGFR Mutation and ALK Translocation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cureus 2016, 8, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thumallapally, N.; Yu, H.; Farhan, M.; Ibrahim, U.; Odiami, M. Concomitant Presence of EGFR and ALK Fusion Gene Mutation in Adenocarcinoma of Lung: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Pharm. Pr. 2017, 31, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.-W.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Ye, X.-Q.; Yin, M.-X.; Zhang, J.-X.; Du, K.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Hu, J. Lung cancer with concurrent EGFR mutation and ROS1 rearrangement: A case report and review of the literature. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, ume 9, 4301–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-J.; Zhang, X.-C.; Su, J.; Xu, C.-R.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, H.-X.; Xie, Z.; Chen, H.-J.; Huang, Y.-S.; Jiang, B.-Y.; et al. Lung Cancers with Concomitant EGFR Mutations and ALK Rearrangements: Diverse Responses to EGFR-TKI and Crizotinib in Relation to Diverse Receptors Phosphorylation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Qin, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J.; Lv, H.; Li, T.; et al. Concurrent TP53 mutations predict poor outcomes of EGFR-TKI treatments in Chinese patients with advanced NSCLC. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, ume 11, 5665–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cai, L.; Yang, H.; Wen, Y.; Wang, J.; Rong, T.; Shao, J.; Zhang, L. Echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearrangement and epidermal growth factor receptor mutation coexisting in Chinese patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac. Cancer 2014, 5, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Qin, Y.; Liu, H.; Renheidenreich, L.; Shi, B.; Ren, H.; Chu, X.; et al. Coexistence of EGFR with KRAS, or BRAF, or PIK3CA somatic mutations in lung cancer: A comprehensive mutation profiling from 5125 Chinese cohorts. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2812–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Huang, J.; Cai, X.; Cheng, B.; Xiong, S.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Concomitant Mutations in EGFR 19Del/L858R Mutation and Their Association with Response to EGFR-TKIs in NSCLC Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, ume 12, 8653–8662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, K.; Jiang, R.; Chen, P.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, M.; Ma, Y.; Xie, Y.; et al. Frequency, clinical features and differential response to therapy of concurrent ALK/EGFR alterations in Chinese lung cancer patients. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, ume 13, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, G.; Carlet, J.; Marra, L.; Bonanno, L.; Boscolo, A.; Maso, A.D.; Bragadin, A.B.; Indraccolo, S.; Zulato, E. Detection of Low-Frequency KRAS Mutations in cfDNA From EGFR-Mutated NSCLC Patients After First-Line EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachiglio, A.M.; Fenizia, F.; Piccirillo, M.C.; Galetta, D.; Crinò, L.; Vincenzi, B.; Barletta, E.; Pinto, C.; Ferraù, F.; Lambiase, M.; et al. The Presence of Concomitant Mutations Affects the Activity of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Nagahashi, M.; Koike, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Shimada, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Takada, K.; Nakanishi, R.; Oki, E.; et al. Impact of Concurrent Genomic Alterations Detected by Comprehensive Genomic Sequencing on Clinical Outcomes in East-Asian Patients with EGFR-Mutated Lung Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanderLaan, P.A.; Rangachari, D.; Mockus, S.M.; Spotlow, V.; Reddi, H.V.; Malcolm, J.; Huberman, M.S.; Joseph, L.J.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. Mutations in TP53, PIK3CA, PTEN and other genes in EGFR mutated lung cancers: Correlation with clinical outcomes. Lung Cancer 2017, 106, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-G.; Chang, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-J.; Yang, P.-C.; Shih, J.-Y. The Role of PIK3CA Mutations among Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients with Primary and Acquired Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, B. Coexisting EGFR and TP53 Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Are Associated With COMP and ITGB8 Upregulation and Poor Prognosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Su, C.; Chen, X.; Ren, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, C. Clinical features and therapeutic options in non-small cell lung cancer patients with concomitant mutations of EGFR, ALK, ROS1, KRAS or BRAF. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2858–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Zhong, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Wang, L. Study of anlotinib combined with icotinib as the first-line treatment in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients harboring activating EGFR mutations (ALTER-L004). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, W.; Min, X.; Gu, K.; Yu, G.; Cheng, C.; Cui, J.; Miao, L.; et al. LBA50 ACTIVE: Apatinib plus gefitinib versus placebo plus gefitinib as first-line treatment for advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant (EGFRm) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A multicentered, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial (CTONG1706). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Petracci, E.; Delmonte, A.; Bronte, G.; Chiadini, E.; Ludovini, V.; Dubini, A.; Papi, M.; Baglivo, S.; De Luigi, N.; et al. Concomitant TP53 Mutation Confers Worse Prognosis in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with TKIs. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.-C.; Lai, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Huang, L.-K.; Chen, S.-J.; Tan, K.T.; Yu, P.-N.; Lai, J.-I. Concomitant Genetic Alterations are Associated with Worse Clinical Outcome in EGFR Mutant NSCLC Patients Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Dai, Z.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, W.; Cai, W.; Yang, D.; Huang, J.; et al. Concomitant genetic alterations are associated with response to EGFR targeted therapy in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, F.; Haley, L.; Fryer, H.; Ibrahim, J.; Beierl, K.; Zheng, G.; Gocke, C.D.; Eshleman, J.R.; Belchis, D.; Illei, P.; et al. Clinical Validation of Coexisting Activating Mutations Within EGFR, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathways in Lung Cancers. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S.; Plodkowski, A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Chaft, J.E.; Kris, M.; Arcila, M.E.; Ladanyi, M.; Drilon, A. Impact of Concurrent PIK3CA Mutations on Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers and on Prognosis in Oncogene-Driven Lung Adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevallier, M.; Tsantoulis, P.; Addeo, A.; Friedlaender, A. Influence of Concurrent Mutations on Overall Survival in EGFR-mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2020, 17, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Concurrent gene alterations with EGFR mutation and treatment efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in Chinese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25046–25054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, L.; Bi, Y.; Wang, M. Concurrent Driver Gene Mutations as Negative Predictive Factors in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. EBioMedicine 2019, 42, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Shin, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, C.; Kim, J.-Y.; Koh, Y.; Keam, B.; Min, H.S.; Kim, T.M.; et al. Primary resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harboring TKI-sensitive EGFR mutations: An exploratory study. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2080–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, T.; Kang, P.; Qian, K.; Deng, B.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Jiang, B.; Li, K.; Liu, F.; et al. Combined analysis of rearrangement of ALK, ROS1, somatic mutation of EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, and mRNA expression of ERCC1, TYMS, RRM1, TUBB3, EGFR in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and their clinical significance. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Cai, D.; Sun, Y.; et al. PIK3CA Mutations Frequently Coexist with EGFR/KRAS Mutations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Suggest Poor Prognosis in EGFR/KRAS Wildtype Subgroup. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempner, S.J.; Bazhenova, L.A.; Braiteh, F.S.; Nikolinakos, P.G.; Gowen, K.; Cervantes, C.M.; Chmielecki, J.; Greenbowe, J.R.; Ross, J.S.; Stephens, P.J.; et al. Emergence of RET rearrangement co-existing with activated EGFR mutation in EGFR -mutated NSCLC patients who had progressed on first- or second-generation EGFR TKI. Lung Cancer 2015, 89, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-H.; Fang, Y.-F.; Chang, W.-C.; Kuo, H.-P.; Lin, S.-Y.; Liu, H.-P.; Liu, C.-L.; Chen, H.-C.; Ku, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; et al. Complex mutation patterns of epidermal growth factor receptor gene associated with variable responses to gefitinib treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2006, 53, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Qian, J.; Yang, W.; Qian, F.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, R.; Han, B. Complex epidermal growth factor receptor mutations and their responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in previously untreated advanced lung adenocarcinomas. Cancer 2018, 124, 2399–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gristina, V.; La Mantia, M.; Iacono, F.; Galvano, A.; Russo, A.; Bazan, V. The Emerging Therapeutic Landscape of ALK Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Franchina, T.; Ricciardi, G.R.R.; Ferraro, G.; Scimone, A.; Bronte, G.; Russo, A.; Rolfo, C.; Adamo, V. Central nervous system involvement in ALK-rearranged NSCLC: Promising strategies to overcome crizotinib resistance. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2016, 16, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, B.; Palmer, R.H. The role of the ALK receptor in cancer biology. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, iii4–iii15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Lin, J.; Liao, G.; Tian, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, M.; Yuan, Y. ALK Inhibitors in the Treatment of ALK Positive NSCLC. Front. Oncol. 2019, 8, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Varghese, A.M.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Kabraji, S.; Awad, M.M.; Katayama, R.; Pawlak, A.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Yeap, B.Y.; Riely, G.J.; et al. ALK Rearrangements Are Mutually Exclusive with Mutations in EGFR or KRAS: An Analysis of 1,683 Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4273–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, G.; Incorvaia, L.; Rizzo, S.; Passiglia, F.; Galvano, A.; Rizzo, F.; Rolfo, C.; Fanale, D.; Listì, A.; Natoli, C.; et al. The resistance related to targeted therapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Why has not the target been hit yet? Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2016, 107, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarakonda, S.; Morgensztern, D.; Govindan, R. Genomic alterations in lung adenocarcinoma. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e342–e351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, C.; Zhuang, W.; Wei, J.; Du, K. Dual drive coexistence of EML4-ALK and TPM3-ROS1 fusion in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. Thoracic Cancer 2017, 9, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, N.; Boyer, J.L.; Herbst, R.S. A RAS Renaissance: Emerging Targeted Therapies for KRAS-Mutated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3921–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B. Crizotinib in ROS1-Rearranged Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lung, J.; Hung, M.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lee, K.-F.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Huang, S.-L.; Fang, Y.H.; Lu, M.-S.; Lin, C.-K.; Yang, T.-M.; et al. MET exon 14 skipping mutations and gene amplification in a Taiwanese lung cancer population. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zejnullahu, K.; Mitsudomi, T.; Song, Y.; Hyland, C.; Park, J.O.; Lindeman, N.; Gale, C.-M.; Zhao, X.; Christensen, J.; et al. MET Amplification Leads to Gefitinib Resistance in Lung Cancer by Activating ERBB3 Signaling. Science 2007, 316, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Sun, K.D.; Gu, J.; Chen, Z.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sun, S.-Y. The novel MET inhibitor, HQP8361, possesses single agent activity and enhances therapeutic efficacy of AZD9291 (osimertinib) against AZD9291-resistant NSCLC cells with activated MET. Am. J. Cancer Res 2020, 10, 3316–3327. [Google Scholar]
- Sequist, L.V.; Han, J.-Y.; Ahn, M.-J.; Cho, B.C.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Su, W.-C.; Kowalski, D.; et al. Osimertinib plus savolitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive, MET-amplified, non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Interim results from a multicentre, open-label, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Soo, R.A.; Kim, S.-W.; Pan, H.; et al. Tepotinib plus gefitinib in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer with MET overexpression or MET amplification and acquired resistance to previous EGFR inhibitor (INSIGHT study): An open-label, phase 1b/2, multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helena, A.Y.; Suzawa, K.; Jordan, E.J.; Zehir, A.; Ni, A.; Kim, H.R.; Kris, M.G.; Hellmann, M.D.; Li, B.T.; Somwar, R.; et al. Concurrent Alterations in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers Associated with Resistance to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors and Characterization of MTOR as a Mediator of Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3108–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Asthana, S.; Chan, E.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Martins, M.M.; Olivas, V.; Yan, J.J.; Pham, L.; Wang, M.M.; Bollag, G.; et al. Mapping the molecular determinants of BRAF oncogene dependence in human lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, E748–E757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Smit, E.; Groen, H.; Mazieres, J.; Besse, B.; Helland, Å.; Giannone, V.; D’Amelio, A.; Zhang, P.; Mookerjee, B.; et al. Phase 2 trial (BRF113928) of dabrafenib (D) plus trametinib (T) in patients (pts) with previously untreated BRAF V600E–mutant metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, v637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minari, R.; Bordi, P.; La Monica, S.; Squadrilli, A.; Leonetti, A.; Bottarelli, L.; Azzoni, C.; Lagrasta, C.A.M.; Gnetti, L.; Campanini, N.; et al. Concurrent Acquired BRAF V600E Mutation and MET Amplification as Resistance Mechanism of First-Line Osimertinib Treatment in a Patient with EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, e89–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, P.; Koopman, B.; Kok, K.; ter Elst, A.; Schuuring, E.; van Kempen, L.C.; Timens, W.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Groen, H.J.; Berg, A.V.D.; et al. Combined osimertinib, dabrafenib and trametinib treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with an osimertinib-induced BRAF V600E mutation. Lung Cancer 2020, 146, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Totoki, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Hiramoto, M.; Nammo, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Tsuta, K.; Furuta, K.; Shimada, Y.; et al. KIF5B-RET fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipson, D.; Capelletti, M.; Yelensky, R.; Otto, G.; Parker, A.; Jarosz, M.; A Curran, J.; Balasubramanian, S.; Bloom, T.; Brennan, K.W.; et al. Identification of new ALK and RET gene fusions from colorectal and lung cancer biopsies. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Subbiah, V.; Wirth, L.; Schuler, M.; Mansfield, A.; Brose, M.; Curigliano, G.; Leboulleux, S.; Zhu, V.; Keam, B.; et al. 1913O Results from the registrational phase I/II ARROW trial of pralsetinib (BLU-667) in patients (pts) with advanced RET mutation-positive medullary thyroid cancer (RET+ MTC). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.; Loong, H.H.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Hazar-Rethinam, M.; Rizzo, C.; Nadres, B.; Van Seventer, E.E.; Shahzade, H.A.; Lennes, I.T.; Iafrate, A.J.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Leshchiner, I.; et al. Heterogeneity and Coexistence of T790M and T790 Wild-Type Resistant Subclones Drive Mixed Response to Third-Generation Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors in Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.; Puri, S.; Negrao, M.V.; Nilsson, M.B.; Robichaux, J.P.; A Boyle, T.; Hicks, J.K.; Lovinger, K.L.; Roarty, E.B.; Rinsurongkawong, W.; et al. Landscape of EGFR-Dependent and -Independent Resistance Mechanisms to Osimertinib and Continuation Therapy Beyond Progression in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6195–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Search Results 05/12/2021. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03944772 (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Mogi, A.; Kuwano, H. TP53 Mutations in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deben, C.; Deschoolmeester, V.; Lardon, F.; Rolfo, C.; Pauwels, P. TP53 and MDM2 genetic alterations in non-small cell lung cancer: Evaluating their prognostic and predictive value. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2016, 99, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viktorsson, K.; De Petris, L.; Lewensohn, R. The role of p53 in treatment responses of lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Le Teuff, G.; Lacas, B.; Tsao, M.; Graziano, S.; Pignon, J.-P.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Le Chevalier, T.; Seymour, L.; Filipits, M.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Effect of TP53 Mutations in Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer from Adjuvant Cisplatin–Based Therapy Randomized Trials: A LACE-Bio Pooled Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, G.; Cicero, G.; Cusenza, S.; Galvano, A.; Musso, E.; Rizzo, S.; Sortino, G.; Roselli, M.; Bazan, V.; Fiorentino, E.; et al. Monoclonal antibodies in gastrointestinal cancers. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrendt, S.A.; Hu, Y.; Buta, M.; McDermott, M.P.; Benoit, N.; Yang, S.C.; Wu, L.; Sidransky, D. p53 Mutations and Survival in Stage I Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of a Prospective Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, R.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, T.; Takano, A.; Khng, A.J.; Lee, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Lim, C.H.; Koh, T.P.T.; Aung, Z.W.; et al. Elucidating the genomic architecture of Asian EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma through multi-region exome sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvano, A.; Peri, M.; Guarini, A.A.; Castiglia, M.; Grassadonia, A.; De Tursi, M.; Irtelli, L.; Rizzo, S.; Bertani, A.; Gristina, V.; et al. Analysis of systemic inflammatory biomarkers in neuroendocrine carcinomas of the lung: Prognostic and predictive significance of NLR, LDH, ALI, and LIPI score. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920942378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Na, I.I.; Yang, S.H.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, J.C. p53 Enhances Gefitinib-Induced Growth Inhibition and Apoptosis by Regulation of Fas in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinavila, M.A.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Gascó, A.; Mayo-De-Las-Casas, C.; Sánchez-Ronco, M.; Pujantell-Pastor, L.; Bonanno, L.; Favaretto, A.G.; Cardona, A.F.; Vergnenègre, A.; et al. Nondisruptive p53 Mutations Are Associated with Shorter Survival in Patients with Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4647–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, O.; Derakhshani, A.; Baradaran, B.; Galvano, A.; Russo, A.; Silvestris, N. COVID-19 Infection in Cancer Patients: How Can Oncologists Deal With These Patients? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, T.; Sontag, E.; Chen, P.; Levine, A. Transcriptional control of human p53-regulated genes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Jin, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Xu, C.; Ying, L.; Su, D. Non-disruptive mutation in TP53 DNA-binding domain is a beneficial factor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Pregartner, G.; Rücker, F.G.; Heitzer, E.; Zebisch, A.; Bullinger, L.; Berghold, A.; Döhner, K.; Sill, H. Functional Classification of TP53 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2020, 12, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offin, M.; Rizvi, H.; Tenet, M.; Ni, A.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Li, B.T.; Drilon, A.; Kris, M.G.; Rudin, C.M.; Schultz, N.; et al. Tumor Mutation Burden and Efficacy of EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Hong, S.; Yang, Y.; Fang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H. The ACTIVE study protocol: Apatinib or placebo plus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer (CTONG1706). Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkareem, I.H.; Blair, M. Phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10. Niger. Med J. 2013, 54, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emilella, M.; Efalcone, I.; Econciatori, F.; Incani, U.E.; DEL Curatolo, A.; Einzerilli, N.; Nuzzo, C.C.; Evaccaro, V.; Evari, S.; Cognetti, F.; et al. PTEN: Multiple Functions in Human Malignant Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incorvaia, L.; Fanale, D.; Bono, M.; Calò, V.; Fiorino, A.; Brando, C.; Corsini, L.R.; Cutaia, S.; Cancelliere, D.; Pivetti, A.; et al. BRCA1/2 pathogenic variants in triple-negative versus luminal-like breast cancers: Genotype–phenotype correlation in a cohort of 531 patients. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920975326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Hu, C.-P.; He, B.-X.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.-X.; Xie, M.-X.; Li, W.; He, S.-Y.; You, S.-J.; Chen, Q. PTEN expression is a prognostic marker for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57832–57840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGranahan, N.; Favero, F.; De Bruin, E.C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Szallasi, Z.; Swanton, C. Clonal status of actionable driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer evolution. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 283ra54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, J.; Parry, D.; Aagaard, L.; Mann, D.J.; Bartkova, J.; Strauss, M.; Peters, G.; Bartek, J. Retinoblastoma-protein-dependent cell-cycle inhibition by the tumour suppressor p16. Nat. Cell Biol. 1995, 375, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakawa, R.; Kohno, T.; Anami, Y.; Noguchi, M.; Suzuki, K.; Matsuno, Y.; Mishima, K.; Nishikawa, R.; Tashiro, F.; Yokota, J. Association of p16 Homozygous Deletions with Clinicopathologic Characteristics and EGFR/KRAS/p53 Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oliveira, M.; Ruiz-Pace, F.; Matito, J.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Suñol, A.; Bellet, M.; Escriva-De-Romani, S.; Zamora, E.; Gomez, P.; Garrigós, L.; et al. Determinants of concordance in clinically relevant genes (CRG) from synchronously acquired tumor biopsies (tBx) and ctDNA in metastatic breast cancer (MBC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augereau, P.; Patsouris, A.; Bourbouloux, E.; Gourmelon, C.; Lacourtoisie, S.A.; Rigaud, D.B.; Soulié, P.; Frenel, J.S.; Campone, M. Hormonoresistance in advanced breast cancer: A new revolution in endocrine therapy. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2017, 9, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Gu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, R.; Fu, L.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Y. Coexistence of p16/CDKN2A homozygous deletions and activating EGFR mutations in lung adenocarcinoma patients signifies a poor response to EGFR-TKIs. Lung Cancer 2016, 102, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.-P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunnissen, E.; Borczuk, A.C.; Flieder, D.B.; Witte, B.; Beasley, M.B.; Chung, J.-H.; Dacic, S.; Lantuejoul, S.; Russell, P.A.; Bakker, M.D.; et al. The Use of Immunohistochemistry Improves the Diagnosis of Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Differential Diagnosis. An International Reproducibility Study in a Demanding Set of Cases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Caldon, C.E.; Barraclough, J.; Stone, A.; Sutherland, R.L. Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, B.; Shim, J.H.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, W.-Y.; Choi, Y.-L.; Sun, J.-M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, K. Concurrent Genetic Alterations Predict the Progression to Target Therapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peifer, M.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Sos, M.L.; George, J.; Seidel, D.; Kasper, L.H.; Plenker, D.; Leenders, F.; Sun, R.; Zander, T.; et al. Integrative genome analyses identify key somatic driver mutations of small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaozhang, Z.; Ming, Z.; Haiyan, P.; Aiping, Z.; Qitao, Y.; Xiangqun, S. Comparison of ARMS and direct sequencing for detection of EGFR mutation and prediction of EGFR-TKI efficacy between surgery and biopsy tumor tissues in NSCLC patients. Med Oncol. 2014, 31, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Q.-Q.; Yang, R.; Shi, J.-F.; Zeng, N.-Y.; Liang, D.-Y.; Sha, S.; Chang, Q. Effect of preservation time of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues on extractable DNA and RNA quantity. J. Int. Med Res. 2020, 48, 300060520931259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-W.; Stefaniuk, C.; Jakubowski, M.A. Real-time PCR and targeted next-generation sequencing in the detection of low level EGFR mutations: Instructive case analyses. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 28, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, C.-W.; Shao, Y.; Wang, H.-T.; Wu, Y.-F.; Song, Y.-Y.; Li, X.-B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.-J.; Li, L.-Q.; et al. Comparison of droplet digital PCR and conventional quantitative PCR for measuring EGFR gene mutation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.W.; Brannigan, B.W.; Matsuo, K.; Finkelstein, D.M.; Sordella, R.; Settleman, J.; Mitsudomi, T.; Haber, D.A. Increased Prevalence of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer in Women and in East Asian Populations: Analysis of Estrogen-Related Polymorphisms. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4079–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, A.; Le, X.; Cornelissen, R.; Shum, E.; Suga, J.; Socinski, M.; Molina, J.R.; Haura, E.; Clarke, J.; Bhat, G.; et al. 36MO Safety, tolerability and preliminary efficacy of poziotinib with twice daily strategy in EGFR/HER2 Exon 20 mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-C.; Tseng, G.-C.; Tu, C.-Y.; Chen, W.-C.; Liao, W.-C.; Li, C.-H.; Chen, H.-J.; Hsia, T.-C. Comparing the effects of afatinib with gefitinib or Erlotinib in patients with advanced-stage lung adenocarcinoma harboring non-classical epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. Lung Cancer 2017, 110, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Schuler, M.H.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.V.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M.J.; et al. LUX-Lung 3: A randomized, open-label, phase III study of afatinib versus pemetrexed and cisplatin as first-line treatment for patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the lung harboring EGFR-activating mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, LBA7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Tsai, T.-H.; Wu, S.-G.; Liu, Y.-N.; Yu, C.-J.; Shih, J.-Y. Complex EGFR mutations with secondary T790M mutation confer shorter osimertinib progression-free survival and overall survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Shih, J.-Y.; Su, W.-C.; Hsia, T.-C.; Tsai, C.-M.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Yu, C.-J.; Chang, G.-C.; Ho, C.-L.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. Afatinib for patients with lung adenocarcinoma and epidermal growth factor receptor mutations (LUX-Lung 2): A phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Lim, S.H.; An, H.J.; Kim, K.H.; Park, K.U.; Kang, E.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Ahn, M.S.; Lee, M.H.; Sun, J.-M.; et al. Osimertinib for Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase II Trial (KCSG-LU15-09). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Sueoka-Aragane, N.; Nakamura, T.; Takeda, Y.; Mitsuoka, M.; Yamasaki, F.; Hayashi, S.; Sueoka, E.; Kimura, S. Co-existence of positive MET FISH status with EGFR mutations signifies poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Lung Cancer 2012, 75, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Aragane, N.; Nakamura, T.; Sato, A.; Takeda, Y.; Mitsuoka, M.; Yamasaki, F.; Hayashi, S.; Sueoka, E.; Kimura, S. Abstract 1737: Co-existence of positiveMETFISH status withEGFRmutations signifies poor prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Clinical Trials 2012, 72, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.G.; Lim, T.H.; Lim, J.; Liew, P.J.; Kwang, X.L.; Nahar, R.; Aung, Z.W.; Takano, A.; Lee, Y.Y.; Lau, D.P.; et al. Clonal MET Amplification as a Determinant of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Mutant Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Cappuzzo, F.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Camidge, D.R. Targeting MET in Lung Cancer: Will Expectations Finally Be MET? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Ungerer, V.; Holdenrieder, S. The emerging role of cell-free DNA as a molecular marker for cancer management. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2019, 17, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Diao, X.-Y.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Q.; Feng, Y.-F.; An, X.; Wang, H.-Y. Identification of genetic alterations associated with primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR sensitive mutations. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, Y.; Ballesteros, P. Álvarez; García, M.O.; Rueda, A.G.; de la Fuente, E.C.; Jiménez, J.T.; Navas, E.V.; Castillo, J.S.; Lario, M.; Berlinches, A.B.; et al. 6P Clinical and molecular characteristics in non-small cell lung cancer patients with alteration in PIK3 pathway. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passiglia, F.; Rizzo, S.; Rolfo, C.; Galvano, A.; Bronte, E.; Incorvaia, L.; Listi, A.; Barraco, N.; Castiglia, M.; Calò, V.; et al. Metastatic Site Location Influences the Diagnostic Accuracy of ctDNA EGFR- Mutation Testing in NSCLC Patients: A Pooled Analysis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 18, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Study Type | Race | No. of Pts | Concurrent Genomic Alteration | Detection Method | Sample | VAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belardinilli et al. [17] | Case Report | Caucasian | 1 | EGFR complex | NGS | tumor tissue | 40.30% 41.30% 67.50% |
| Benesova et al. [18] | Case Series | Caucasian | 4 | EGFR+KRAS EGFR complex | Sanger | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Fan et al. [19] | Case Report | Asian | 1 | EGFR+ALK | NGS | tumor tissue | EGFR 15.58% ALK 6.42% |
| Lammers et al. [20] | Case Report | Caucasian | 1 | EGFR+PIK3CA | SNapShot PCR | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Lee et al. [21] | Case Series | Asian | 12 | EGFR+KRAS EGFR+ALK | Sanger; Real Time PCR after PNA; FISH and IHC | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Miyanaga et al. [22] | Case Report | Asian | 1 | EGFR+ALK | PNA-LNA PCR clamp method, FISH and IHC | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Sweis et al. [23] | Case Series | Caucasian | 4 | EGFR+ALK | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Thumallapally et al. [24] | Case Report | Caucasian | 1 | EGFR+ALK | FISH, direct sequencing | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Zhu et al. [25] | Case Report | Asian | 1 | EGFR+ROS-1 | NGS, PCR and FISH | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Yang et al. [26] | Case Series | Asian | 13 | EGFR+ALK | IHC, FISH, Sanger, RT-PCR and RACE-PCR sequencing | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Hou et al. [27] | Retrospective | Asian | 59 | EGFR+TP53 EGFR+RB1 | NGS | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Zhu et al. [28] | Retrospective | Asian | 2 | EGFR+ALK | FISH, RT-PCR | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Li et al. [29] | Retrospective | Asian | 149 | EGFR+ PIK3CA EGFR complex EGFR+KRAS EGFR+BRAF | SurPlex®-xTAG70plex-EGFR liquidchip | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Liang et al. [30] | Retrospective | Asian | 403 | EGFR complex | NGS | tumor tissue + plasma | N/A |
| Liu et al. [31] | Retrospective | Asian | 21 | EGFR+ALK | NGS | tumor tissue + plasma | N/A |
| Nardo et al. [32] | Retrospective | Caucasian | 3 | EGFR+KRAS | ddPCR | tumor tissue + plasma | KRAS <0.2 |
| Rachiglio et al. [33] | Retrospective | Caucasian | 38 | EGFR+KRAS EGFR+BRAF EGFR+MET EGFR+TP53 EGFR+PIK3CA | NGS, ddPCR | tumor tissue + plasma | KRAS 2–38% EGFR ≥ 2% |
| Sato et al. [34] | Retrospective | Asian | 43 | EGFR complex EGFR+TP53 EGFR+RB1 | NGS | tumor tissue | N/A |
| VanderLaan et al. [35] | Retrospective | Caucasian | 19 | EGFR+TP53 EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+PTEN | NGS, Sanger | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Wu et al. [36] | Retrospective | Asian | 12 | EGFR+PIK3CA | Sanger, RT-PCR | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Zheng et al. [37] | Retrospective | Asian | 11 | EGFR+TP53 | NGS | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Zhuang et al. [38] | Retrospective | Asian | 43 | EGFR+ALK EGFR+ROS-1 EGFR+KRAS EGFR+BRAF | ARMS | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Huang et al. [39] | Prospective | Asian | 18 | EGFR+TP53/PTEN EGFR+PIK3CA | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Zhang et al. [40] | Prospective | Asian | N/A | EGFR+TP53 | NGS | N/A | N/A |
| Canale et al. [41] | Retrospective | Caucasian | 136 | EGFR+TP53 | Sanger, MassARRAY, NGS | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Chang et al. [42] | Retrospective | Asian | 26 | EGFR+ALK EGFR+TP53 EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+CDKN2A | NGS, CNV | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Chen et al. [43] | Retrospective | Asian | 16 | EGFR complex EGFR+ALK EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+TP53 | NGS | tumor tissue + plasma | N/A |
| De Marchi et al. [44] | Retrospective | Caucasian | 47 | EGFR complex EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA | NGS, Sanger, SNP array | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Eng et al. [45] | Retrospective | Caucasian | 13 | EGFR+PIK3CA | mutation hotspot testing, FISH, multiplex sizing assays | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Chevallier et al. [46] | Retrospective | Caucasian | 20 | EGFR+TP53 EGFR+MET EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+PTEN | NGS | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Hu et al. [47] | Retrospective | Asian | 21 | EGFR+ALK EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+KRAS EGFR+ROS-1 EGFR+RET EGFR+HER2 | ARMS; adx-RT, mutation detection kit; fusion gene detection kit | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Chen et al. [48] | Retrospective | Asian | 71 | EGFR complex EGFR+TP53 EGFR+ALK EGFR+BRAF EGFR+MET | NGS, ARMS | tumor tissue + plasma | N/A |
| Lee et al. [49] | Retrospective | Asian | 7 | EGFR+ALK EGFR+MET EGFR+TP53 EGFR complex | FISH, NGS, Sanger | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Zhang et al. [50] | Retrospective | Asian | 9 | EGFR complex EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA | FISH, liquid chip platform | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Wang et al. [51] | Retrospective | Asian | 17 | EGFR+PIK3CA | Sanger, FISH, IHC | tumor tissue | N/A |
| Klempner et al. [52] | Case report | Asian | 2 | EGFR+RET | NGS | tumor tissue | 53% 54% 62% 18% |
| Study | Concurrent Genomic Alteration | TKI | mPFS (mo.) | mOS (mo.) | Best Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belardinilli et al. [17] | EGFR complex | Afatinib | 8 | N/A | PR |
| Benesova et al. [18] | EGFR+KRAS EGFR complex | Gefitinib Erlotinib | 6–12 | 5-23 | 3 PR 1 CR |
| Fan et al. [19] | EGFR+ALK | Gefitinib Crizotinib | 18 | N/A | PR/SD |
| Lammers et al. [20] | EGFR+PIK3CA | Erlotinib Afatinib PI3K inhibitor | 1–4 | N/A | SD/PR |
| Lee et al. [21] | EGFR+KRAS EGFR+ALK | Gefitinib Erlotinib Crizotinib | 4–29 | N/A | SD/PR |
| Miyanaga et al. [22] | EGFR+ALK | Gefitinib Erlotinib Crizotinib | 2–7 | N/A | SD |
| Sweis et al. [23] | EGFR+ALK | Erlotinib Crizotinib | 2–12 | N/A | PR/PD |
| Thumallapally et al. [24] | EGFR+ALK | Crizotinib | N/A | 3 wk | N/A |
| Zhu et al. [25] | EGFR+ROS-1 | Adj CT | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Yang et al. [26] | EGFR+ALK | Gefitinib Erlotinib Crizotinib Afatinib | 12–27.4 | N/A | SD/PR/PD |
| Hou et al. [27] | EGFR+TP53 EGFR+RB1 | Erlotinib Gefitinib Icotinib | 4–11 | 10–59 | N/A |
| Zhu et al. [28] | EGFR+ALK | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Li et al. [29] | EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR complex EGFR+KRAS EGFR+BRAF | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Liang et al. [30] | EGFR Complex | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Liu et al. [31] | EGFR+ALK | Osimertinib Crizotinib Afatinib | 6–15 | N/A | N/A |
| Nardo et al. [32] | EGFR+KRAS | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib | 5 | 6 | PR |
| Rachiglio et al. [33] | EGFR+KRAS EGFR+BRAF EGFR+MET EGFR+TP53 EGFR+PIK3CA | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib | 7 | 15.5 | N/A |
| Sato et al. [34] | EGFR complex EGFR+TP53 EGFR+RB1 | Gefitinib Erlotinib | N/A | N/A | PR |
| VanderLaan et al. [35] | EGFR+TP53 EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+PTEN | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib | 6.5 | 15.5 | N/A |
| Wu et al. [36] | EGFR+PIK3CA | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib | 12 | 5.1 | PR |
| Zheng et al. [37] | EGFR+TP53 | N/A | N/A | 23.9 | N/A |
| Zhuang et al. [38] | EGFR+ALK EGFR+ROS-1 EGFR+KRAS EGFR+BRAF | Gefitinib Erlotinib Afatinib Icotinib Crizotinib Alectinib | 9.6 | N/A | PR |
| Huang et al. [39] | EGFR+TP53/PTEN EGFR+PIK3CA | Anlotinib Icotinib | N/A | N/A | PR |
| Zhang et al. [40] | EGFR+TP53 | Gefitinib Afatinib | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Canale et al. [41] | EGFR+TP53 | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib | 5.8–12.9 | 29.7–19.5 | CR |
| Chang et al. [42] | EGFR+ALK EGFR+TP53 EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+CDKN2A | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib | 1–24.2 | 5.4–57.6 | N/A |
| Chen et al. [43] | EGFR complex EGFR+ALK EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+TP53 | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib Osimertinib | 18.7 | N/A | CR |
| De Marchi et al. [44] | EGFR complex EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Eng et al. [45] | EGFR+PIK3CA | Gefitinib | 7.8 | 18 | PR |
| Chevallier et al. [46] | EGFR+TP53 EGFR+MET EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+PTEN | Erlotinib Gefitinib Afatinib Osimertinib | 6.8–11.6 | 7.7–16.8 | N/A |
| Hu et al. [47] | EGFR+ALK EGFR+PIK3CA EGFR+KRAS EGFR+ROS-1 EGFR+RET EGFR+HER2 | Erlotinib Gefitinib Crizotinib Icotinib | 1–24 | 10–43 | PR/PD |
| Chen et al. [48] | EGFR complex EGFR+TP53 EGFR+ALK EGFR+BRAF EGFR+MET | Erlotinib Gefitinib Icotinib | 6–24 | N/A | N/A |
| Lee et al. [49] | EGFR+ALK EGFR+MET EGFR+TP53 EGFR complex | Erlotinib Gefitinib Crizotinib | 1–2.1 | 1–21.8 | N/A |
| Zhang et al. [50] | EGFR complex EGFR+KRAS EGFR+PIK3CA | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Wang et al. [51] | EGFR+PIK3CA | Gefitinib | N/A | N/A | PR |
| Klempner et al. [52] | EGFR+RET | Erlotinib | N/A | N/A | PR/PD |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gristina, V.; La Mantia, M.; Galvano, A.; Cutaia, S.; Barraco, N.; Castiglia, M.; Perez, A.; Bono, M.; Iacono, F.; Greco, M.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Concurrent EGFR Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of the Double Dilemma. J. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 2, 173-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp2020016
Gristina V, La Mantia M, Galvano A, Cutaia S, Barraco N, Castiglia M, Perez A, Bono M, Iacono F, Greco M, et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Concurrent EGFR Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of the Double Dilemma. Journal of Molecular Pathology. 2021; 2(2):173-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp2020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleGristina, Valerio, Maria La Mantia, Antonio Galvano, Sofia Cutaia, Nadia Barraco, Marta Castiglia, Alessandro Perez, Marco Bono, Federica Iacono, Martina Greco, and et al. 2021. "Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Concurrent EGFR Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of the Double Dilemma" Journal of Molecular Pathology 2, no. 2: 173-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp2020016
APA StyleGristina, V., La Mantia, M., Galvano, A., Cutaia, S., Barraco, N., Castiglia, M., Perez, A., Bono, M., Iacono, F., Greco, M., Calcara, K., Calò, V., Rizzo, S., Incorvaia, L., Lisanti, M. C., Santanelli, G., Sardo, D., Inguglia, S., Insalaco, L., ... Bazan, V. (2021). Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Concurrent EGFR Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of the Double Dilemma. Journal of Molecular Pathology, 2(2), 173-196. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmp2020016









