Abstract
Interstitial pneumonia is a general term for diseases in which inflammation occurs mainly in the interstitium of the lung. It is also pointed out that interstitial pneumonia reduces alveolar function and makes it difficult to take in oxygen through inspiration, causing symptoms such as dyspnea and coughing, which may eventually lead to respiratory failure. At present, there is no effective treatment, and only conservative treatment exists. This time, we report that the therapeutic effect was confirmed in patients with interstitial pneumonia who took platinum palladium. In this case, improvement tendencies were observed in patients with Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), but improvement tendencies were also observed in many other lung diseases. In order to explore the mechanism, AMPK was measured at the in vitro level, and blood KL-6 and hydrogen peroxide levels in the patient were measured at the in vivo level. AMPK values were significantly elevated by more than 800%, and KL-6 and hydrogen peroxide levels were also significantly decreased by drinking platinum palladium. Platinum palladium exhibits a strong antioxidant effect and is the only substance in the world that can approach all four types of active oxygen. In addition, when it was actually administered to patients, there were cases of dramatic improvement, and it was confirmed that KL-6, a parameter of lung function, decreased in 16 out of 32 patients, and furthermore, oxygen inhalation was completed. Patients were also seen. It was suggested that increasing the number of cases in the future may help improve interstitial pneumonia.
1. Introduction
The alveoli are covered with pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and capillaries, and “gas exchange” takes place, exchanging oxygen needed by the body for carbon dioxide that is no longer needed. The “interstitium” exists in the part called the alveolar wall that is on the outside of the alveoli. Interstitial pneumonia is a general term for diseases in which the interstitium becomes inflamed and fibrotic due to some cause [1].
Currently, interstitial pneumonia is classified according to the cause as follows [2,3,4,5,6,7].
- Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia
The medical term for the inability to identify the cause of onset is “idiopathic”. As the name suggests, idiopathic interstitial pneumonia is a disease that develops with unknown causes, and it is said to account for 80 to 90% of interstitial pneumonia patients.
- Autoimmune interstitial pneumonia
This is interstitial pneumonia that occurs in conjunction with autoimmune diseases, mainly collagen diseases. It develops as one of the immune abnormalities in which the immune system attacks its own cells.
- Drug-induced interstitial pneumonia
It has been pointed out that interstitial pneumonia is more likely to develop due to the influence of anticancer drugs and other therapeutic drugs.
- Occupational/environmental interstitial pneumonia (hypersensitivity pneumonitis)
This type of interstitial pneumonia develops when foreign substances, such as dust, mold, pet hair, and chemicals, are inhaled due to the influence of occupation or lifestyle.
- Interstitial pneumonia caused by other factors
This type of interstitial pneumonia includes pneumonia caused by the influence of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, and sarcoidosis, which causes inflammation in cells throughout the body.
In all types of interstitial pneumonia, the interstitial pneumonia that has chronic inflammation gradually hardens. When it progresses to a state called fibrosis, it affects the supply of oxygen and the excretion of carbon dioxide, which are essential for maintaining life, and the entire body becomes oxygen-deficient, leading to shortness of breath, coughing, and difficulty in breathing.
In this study, we investigated the possibility of new treatments, particularly for patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). In interstitial pneumonia, inflammation gradually causes the fibrosis of the alveolar walls [8] and increases pulmonary surfactant protein-D (SP-D) levels [9,10]. As lung function declines, oxygen supply becomes difficult, causing coughing and shortness of breath, and ultimately leading to respiratory failure and death [11]. As of now, there is no effective treatment, and steroids and other treatments for interstitial lung disease are the only symptomatic treatments [12].
On the other hand, COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) is a chronic respiratory disease that progresses irreversibly and is characterized by inflammation and destruction of the alveoli due to smoking and environmental chemicals [13,14]. As with interstitial pneumonia, there is no effective treatment for COPD, and only symptomatic treatment is applicable. Symptomatic treatments include conservative oxygen inhalation, maintenance of ADL, and maintenance and improvement of QOL [15]. According to the WHO, COPD is the third most common cause of death in the world, so measures to combat it are urgently needed [16]. COPD is also said to be a possible background risk for lung cancer, so measures must be taken [17]. Until now, the main treatments for COPD have been smoking cessation, antioxidants, dietary therapy, and alternative therapies, but these have been aimed at slowing down the disease’s progression [18]. In our clinical experience, approximately 40–50% of patients with COPD have shown improvement in symptoms after administration of platinum-palladium. Although COPD was not directly studied in this study, it is possible that it may improve respiratory disease. Although no data have been collected yet, when platinum-palladium was administered to COPD patients, some improvement was observed, so this report was made. In this study, because it was expected that the treatment would be effective for interstitial pneumonia, cases were examined as a pilot study from multiple perspectives. For these reasons, we expected that the same therapeutic effect would be seen in interstitial pneumonia, so we examined cases.
Platinum-palladium is generally available as a soft drink (functional nutritional water), but this is a colloidal solution of platinum and palladium mixed at a ratio of 1:3 (Figure 1 and Figure 2). It has also been confirmed to induce apoptosis in stomach cancer and colon cancer, and is the world’s first functional nutrient water that is expected to have various effects, including activating immune cells (unpublished).
Figure 1.
Platinum colloid.
Figure 2.
Palladium colloid.
Platinum is a chemically very stable element and is used for various purposes. In the medical field, its complexes are used as anticancer drugs [19]. Other uses focusing on the antioxidant properties of platinum have been reported [20]. Palladium is also one of the platinum group elements, and is widely used in industrial materials and dentistry, and in Japan, it is also treated as a food additive [21,22]. It is known that platinum causes a reduction reaction, and when palladium is added to it, it causes a reduction reaction again [23]. This time, the mixture of platinum and palladium is used in various situations [24]. Based on the chemical reaction and various properties of platinum and palladium, the mixture of platinum and palladium is expected to be useful as a material with sustained antioxidant properties compared to platinum alone [24]. Furthermore, it is known that platinum palladium moderately removes all four types of active oxygen [25]. According to a literature survey, there is no other substance that can remove all four types of reactive oxygen species (generally superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, and singlet oxygen [26]). In addition, platinum-palladium is considered to have a low absorption rate in the intestinal tract due to its colloidal nature [27,28]. It is possible that platinum-palladium may act as a catalyst and activate AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) at the cellular level in the digestive tract, thereby contributing to the improvement of symptoms and lesions of interstitial pneumonia and COPD. In this study, we reported cases and measured blood KL-6 [29] and hydrogen peroxide levels [30] in patients with interstitial pneumonia and COPD. At the same time, we confirmed whether platinum-palladium activates AMPK at the in vivo and in vitro levels.
2. Materials and Methods: A Case of Interstitial Pneumonia Improved
2.1. Patient
- -
- 90-year-old male.
- -
- Height 172.3 cm, weight 68.3 kg, body surface area 1800 m2.
- -
- Smoking history: None.
- -
- Diagnosis: Interstitial pneumonia.
- -
- Age at onset of interstitial pneumonia: 85 years old (as of 2020)
- -
- Underlying diseases: None.
- -
- Platinum-palladium intake: 18 mL/day (6 mL/1 vial × 3 vials).
- -
- Duration: 44 months.
- -
- Drug treatment: None.
- -
- Oxygen inhalation: None.
2.2. Progress
In daily life, the patient walked 2–3 km every day to maintain and improve his health. No smoking history, alcohol history. Suddenly, frequent coughing was confirmed, and cough suppressants were prescribed, but there was no sign of improvement. When he returned to the city hospital for a follow-up visit, chest X-rays and other tests showed findings specific to interstitial pneumonia, and he was diagnosed with interstitial pneumonia. His doctor told him he had two years to live. His condition gradually progressed, and he experienced difficulty breathing even when performing everyday activities such as climbing the stairs at home or going to the toilet, and he would often collapse. He lost the will to move, but by taking platinum-palladium, his respiratory function improved on the 18th day, his coughing almost disappeared, and his difficulty breathing decreased. At his final visit, he had improved to the point where he was able to resume walking. However, during a period when he temporarily stopped taking platinum-palladium, he experienced difficulty breathing again.
3. Measurements at In Vitro and In Vivo Levels
3.1. AMPK Measurement
Examination of AMPK activity by platinum-palladium.
In this experiment, the aim was to measure activity at an in vitro level without using humans. The reason for this is that in order to observe the time-dependent AMPK activity of platinum-palladium, if humans are used, AMPK activity will change due to eating and sleep, so the experiment was performed using cell cultures that can be measured under certain conditions. Using the CycLex® AMPK Kinase Assay Kit (MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LABORATORIES Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), AMPK activity was examined in the platinum-palladium addition group (final concentration 1%). The PBS addition group was used as a control. Since the kit’s instructions stated that measurements were performed using breast cancer cell lines, a comparative evaluation was performed using the purchased human breast cancer cell line (MCF-7). In addition, in order to measure the current activity of AMPK in this kit, three flasks were prepared, and AMPK activity was confirmed 1 h, 12 h, and 24 h after addition. In addition, the evaluation was performed using statistical processing software (IBM SPSS Statistics Ver. 29) and, since there was no correspondence, a statistical evaluation was performed using the Mann–Whitney U test. The investigation of AMPK activity was conducted by platinum-palladium.
3.2. Measurement of Blood KL-6
Study of KL-6 fluctuations due to platinum-palladium.
This study involved 16 patients (hereafter referred to as subjects) who visited Hino Kosei Clinic, were diagnosed with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, and agreed to participate in this study. As this was a pilot study, no control group was set up. KL-6 was measured before and after administration and compared. The evaluation was performed using statistical software (IBM SPSS Statistics Ver. 29) with the paired t-test.
KL-6 was measured by enzyme immunoassay (EIA) as per the standard method, with a standard value of less than 500 U/mL [31,32].
3.3. Measurement of Blood Hydrogen Peroxide (Figure 3)
Study of changes in hydrogen peroxide due to platinum-palladium.
This study included 12 subjects (hereafter referred to as subjects) who visited Hino Kosei Clinic and agreed to participate in this study. Each subject was given platinum-palladium for 28 days (4 weeks). The subjects were given three vials in the first week, two vials in the second week, and one vial in the last 2 weeks. Hydrogen peroxide was measured before and after administration and compared. In addition, the results were statistically evaluated using a paired t-test with statistical processing software (IBM SPSS Statistics Ver. 26).
Qualitative measurement of hydrogen peroxide was performed using the peroxidase-diaminobenzidine method.
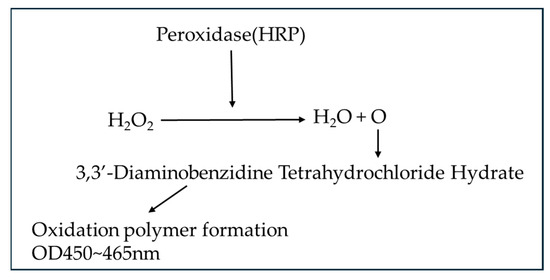
Figure 3.
Hydrogen peroxide measurement principle.
Figure 3.
Hydrogen peroxide measurement principle.
3.4. Study on the Effect of Platinum-Palladium on Symptom Improvement in Patients with Interstitial Pneumonia
A total of 32 patients with interstitial pneumonia were given platinum-palladium for one to three months, three vials for the first week, two vials for the second week, and one vial for the last two weeks, and clinical judgment was made. In this study, the subjects were patients with KL-6 > 500 U/mL, crepitus + in breath sounds, and + in X-ray reading. It should be noted that since this is a pilot study, no control group was set up.
4. Results
4.1. AMPK Measurement
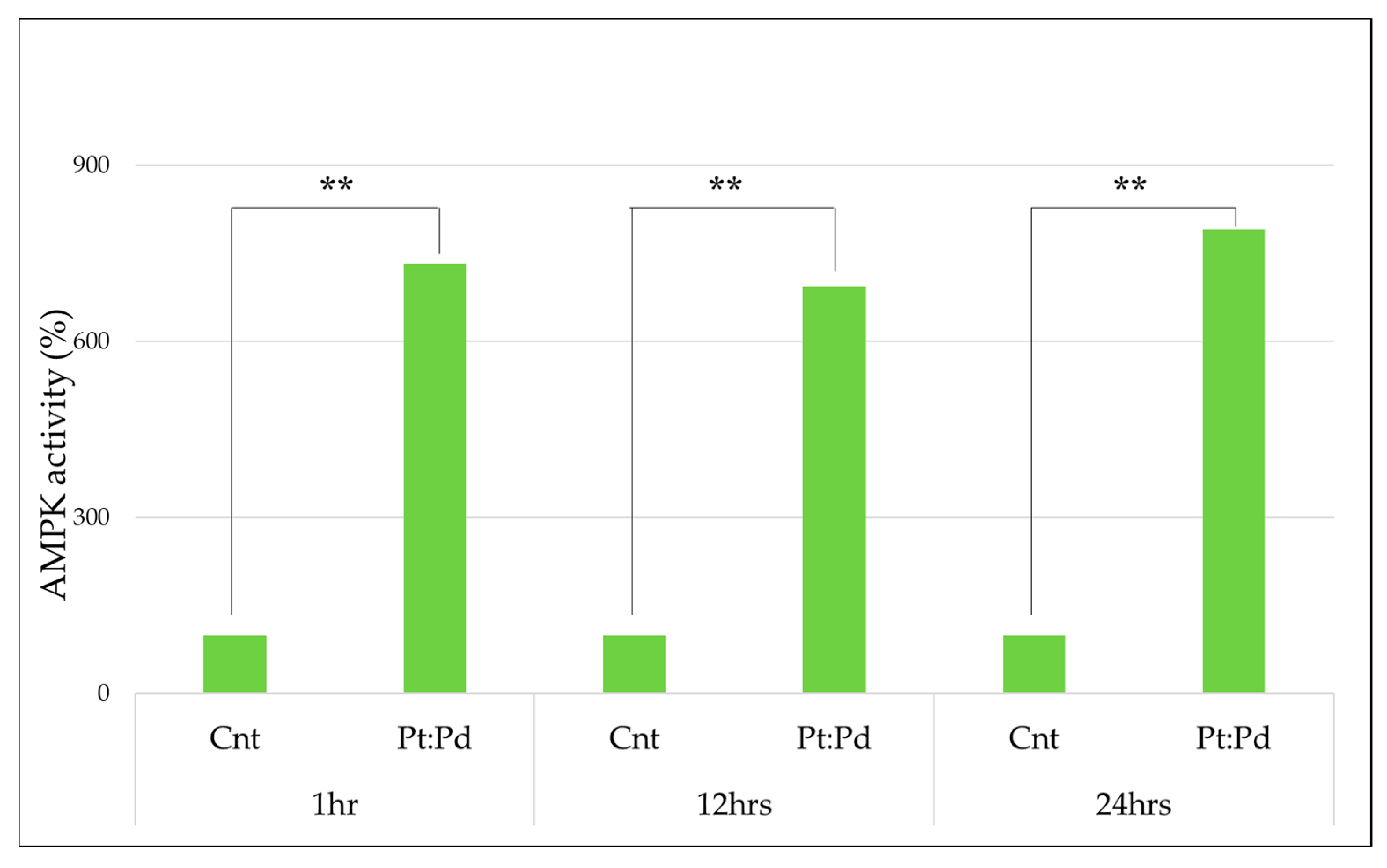
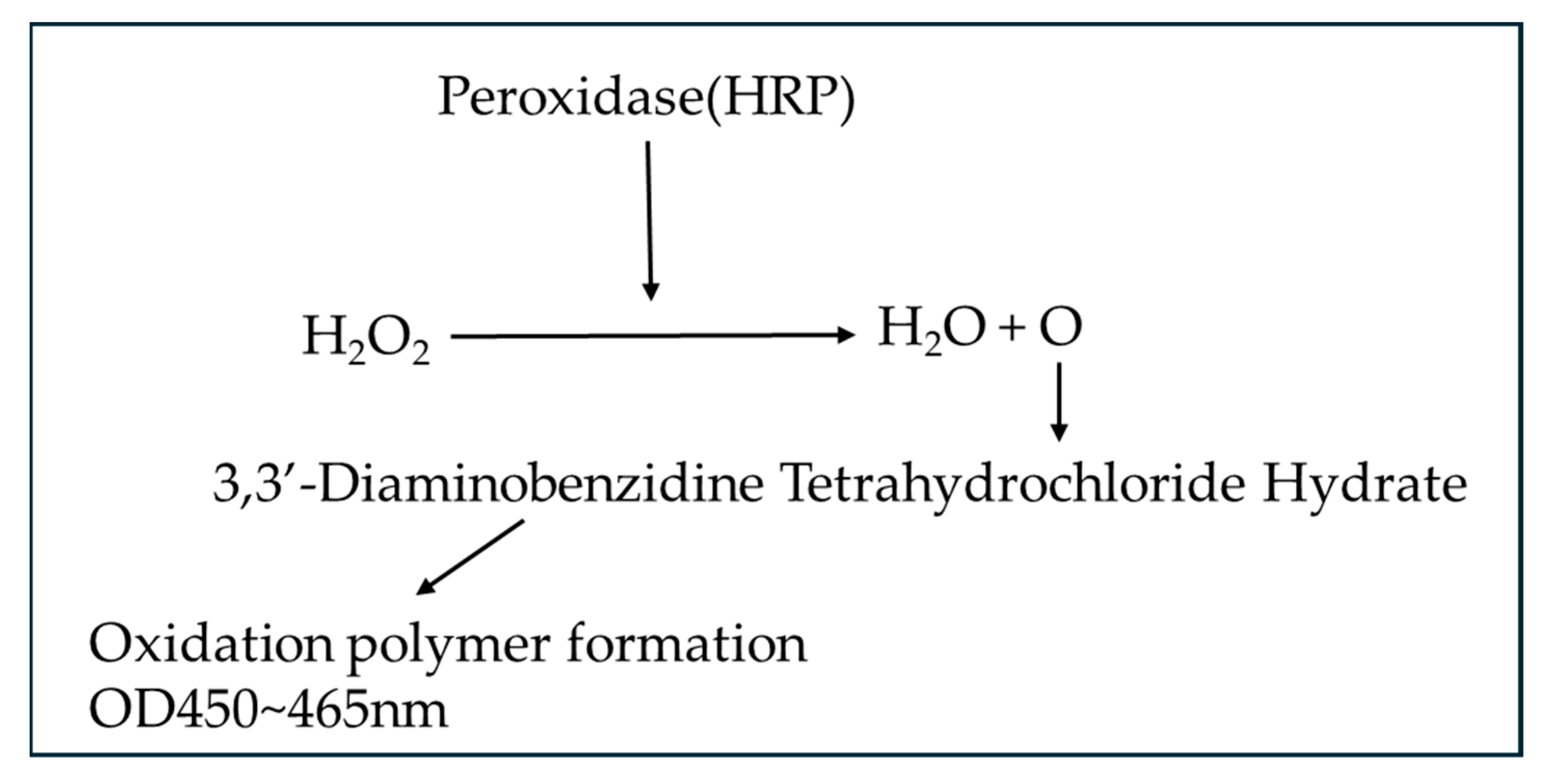
To measure the activity of MPK, platinum palladium was administered to MCF-7, and the percentage was calculated from the absorbance, with the following results being obtained. With the control group taken as 100%, it was confirmed that the activity had increased significantly in all groups at a significance level of 1%. (Table 1 and Figure 4)

Table 1.
AMPK activity when compared to the control group (100%).
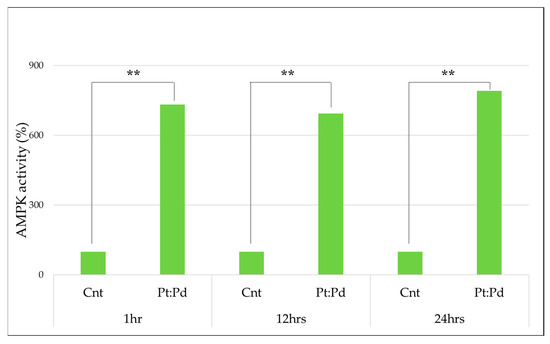
Figure 4.
AMPK activity in platinum-palladium compared to the control group (100%) (Mann–Whitney U test., **: p < 0.01).
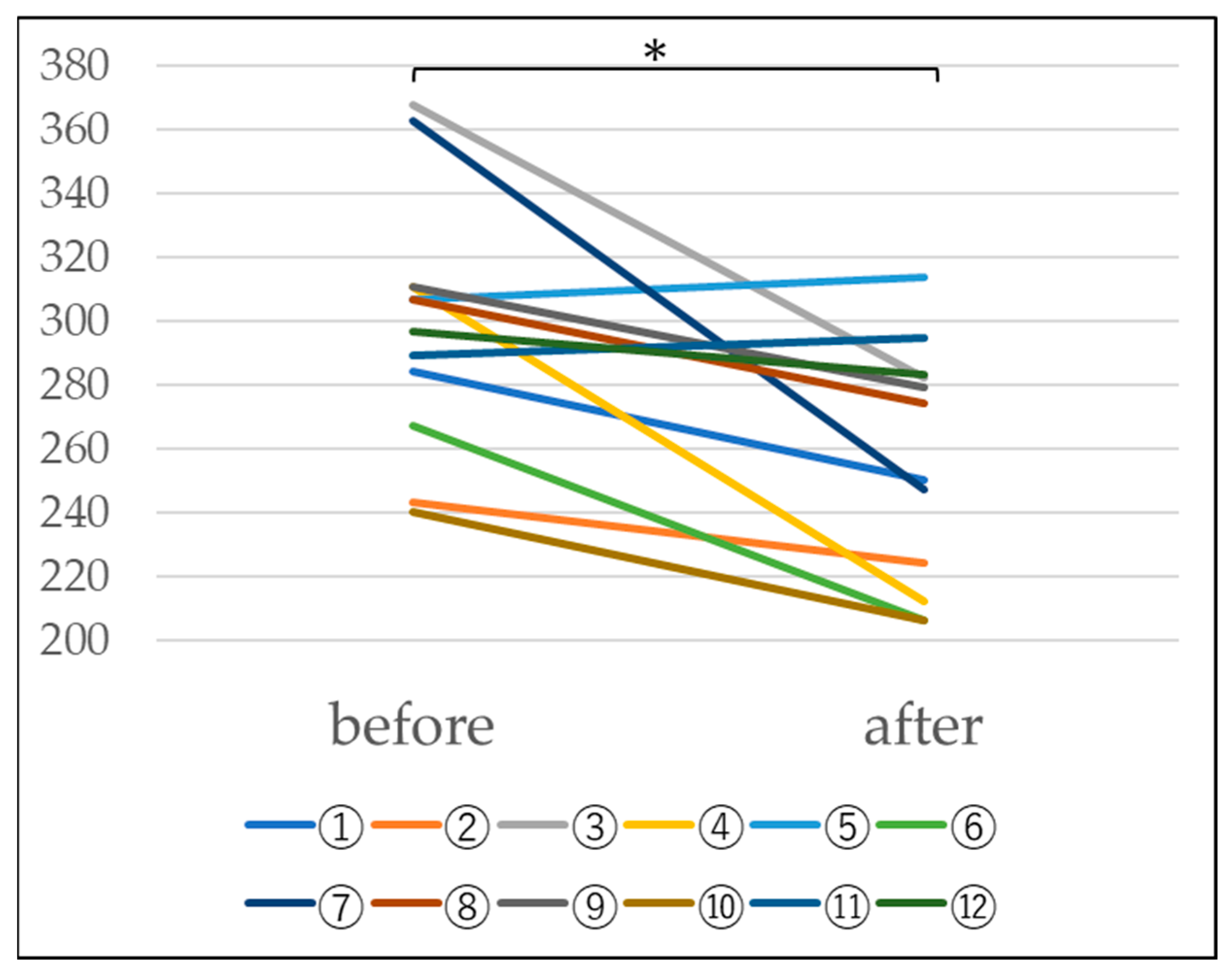
4.2. Measurement of Blood KL-6
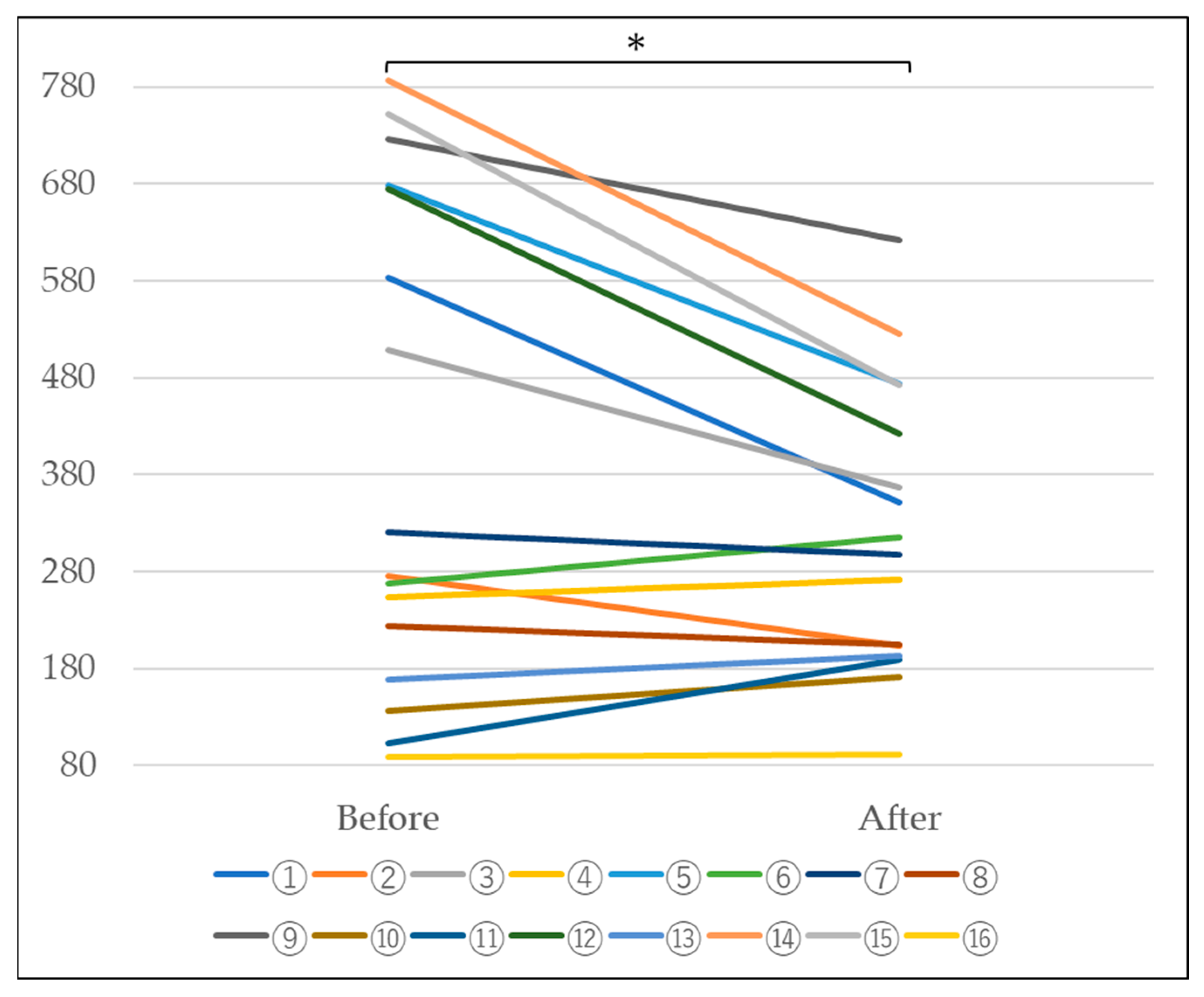
In n = 16 subjects, a tendency for the KL-6 value to decrease was observed, as shown in Table 2 and Figure 5 below. Furthermore, statistical processing revealed a significant decrease at a significance level of 5%. This suggests that the escape of KL-6 from the alveoli is suppressed, suggesting the possibility of improved alveolar function (Table 2 and Figure 5).

Table 2.
Comparison of KL-6 before and after administration of platinum-palladium (n = 16) KL-6 (IU/mL).
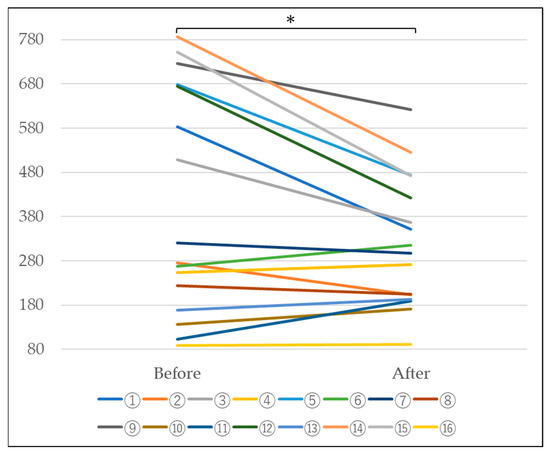
Figure 5.
Changes in KL-6 before and after platinum-palladium administration (Paired-samples t-test, *: p < 0.05).
4.3. Measurement of Blood Hydrogen Peroxide
When blood hydrogen peroxide levels were measured in n = 12 subjects, a decrease was observed at a significance level of 5%, as shown in Table 3 and Figure 6. Since there is thought to be a relationship between interstitial pneumonia and hydrogen peroxide, these results suggest that interstitial pneumonia caused by hydrogen peroxide may improve (Table 3 and Figure 6).

Table 3.
Changes in blood hydrogen peroxide levels due to platinum-palladium (U).
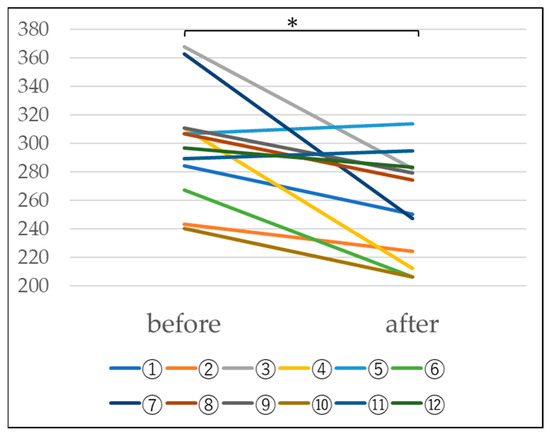
Figure 6.
Changes in blood hydrogen peroxide levels before and after administration of platinum-palladium (Paired-samples t-test, *: p < 0.05).
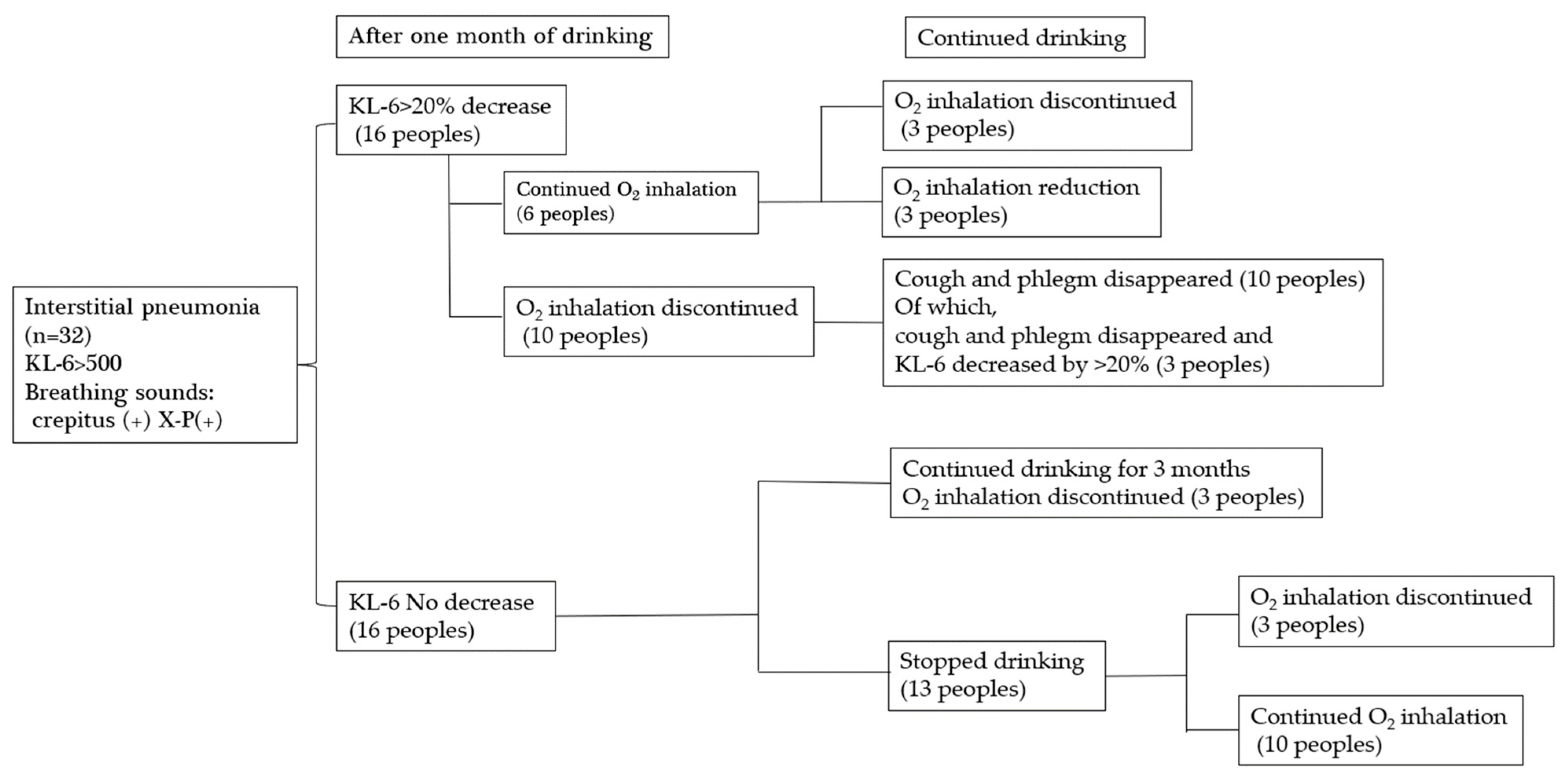
4.4. Investigation into the Effectiveness of Platinum-Palladium in Improving
Symptoms in patients with interstitial pneumonia (Figure 7).
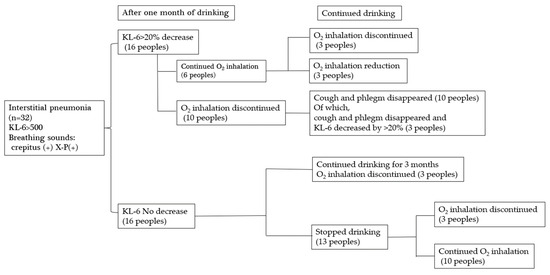
Figure 7.
Changes after drinking platinum-palladium.
Thirty-two patients with interstitial pneumonia who visited Hino Kosei Clinic and Kisaragi Soken Clinic took platinum palladium supplements, and their progress was monitored. Sixteen of the 32 patients showed a 20% or greater decrease in KL-6 after one month. Ten of them stopped inhaling oxygen after one month, and all ten patients also stopped coughing and sputum. Three of them showed a further 20% decrease in KL-6. Six patients continued to take oxygen after one month, even though their KL-6 had decreased by more than 20%, but three of them stopped taking oxygen, and three had their dose reduced after continued intake. This suggests the need to continue taking the platinum palladium supplement. Sixteen of the 32 patients showed no decrease in KL-6 after one month, but they were able to stop taking oxygen after three more months of continued intake. Of the patients who stopped drinking the water after one month, three subsequently stopped oxygen inhalation, and ten continued oxygen inhalations; however, this does not mean that the platinum-palladium solution was ineffective, but rather that the patients discontinued the solution due to unavoidable circumstances. Therefore, it is possible that their condition would have improved if they had continued drinking the solution.
5. Discussion
This is a case report of platinum-palladium improving the condition of interstitial pneumonia. In addition to this case, there have been many reports of improvement in interstitial pneumonia and COPD at other clinics, and platinum-palladium has been used in many cases. Therefore, platinum-palladium may be an effective treatment for interstitial pneumonia. Currently, symptomatic treatment for interstitial pneumonia is focused on preventing the progression of interstitial pneumonia or administering oxygen inhalation to treat symptoms as they arise, but it is difficult to improve the condition. However, in this case, the patient was finally able to drive a car and perform daily activities, so it is possible that the lung function itself may have improved. Although the mechanism is still largely unknown, we have considered the possibility. Although the cause of interstitial pneumonia is often unknown, it is thought that interstitial pneumonia may produce reactive oxygen species in the interstitium, causing inflammation [33]. Reactive oxygen species, such as superoxide present in neutrophils, act as a defense mechanism against antigens, while excessive reactive oxygen species have a detrimental effect on normal cells, causing lifestyle-related diseases, aging, and chronic inflammation [34,35]. In this case, platinum-palladium was used, but it is possible that platinum-palladium does not completely act as an antioxidant, but rather removes only the amount of reactive oxygen species necessary for the body, and removes only the excess. In addition, it was statistically found that platinum-palladium activates AMPK, although at an in vitro level. AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is an enzyme that maintains homeostasis in the body and is a serine/threonine kinase in the metabolism of carbohydrates and lipids [36]. Generally, AMPK is activated in starvation, but it is said that the passive activation of AMPK, as in this case, maintains energy homeostasis and is currently attracting attention as a potential treatment for metabolic diseases, including diabetes and chronic inflammation-related cancer [36]. Energy is essential for human beings to maintain biological functions, and the source of this energy is ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is generated when ATP is hydrolyzed and converted to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) [37]. AMPK regulates this ATP level to maintain homeostasis and is expected to be effective against metabolic diseases such as cancer, type 2 diabetes, and obesity [38,39,40]. It is thought that AMPK regulates metabolism by inhibiting the ATP consumption pathway [41,42]. Therefore, AMPK contributes to maintaining health in the body by suppressing chronic inflammation [43,44]. It promotes autophagy [45]. It contributes to the production of NAD+, which in turn activates mitochondria [46], and may increase intracellular ATP levels by activating mitochondrial biosynthesis [47,48].
In other words, it is expected that increased AMPK activity can prevent lifestyle-related diseases, including cancer. It is thought that AMPK regulates metabolism by blocking the process of consuming ATP, an energy source. It has been reported that AMPK activation suppresses chronic inflammatory responses, and further reduces cellular aging due to the activation of autophagy, which can lead to the treatment of interstitial pneumonia [49], so it was suggested that this effect could be used to play a part in the improvement of interstitial pneumonia caused by platinum-palladium.
In addition, blood tests were performed on patients at the in vivo level to measure the aforementioned KL-6 and blood hydrogen peroxide levels. KL-6 is a high molecular weight sialylated glycoprotein contained mainly in type II alveolar epithelial cells that is strongly involved in the production and secretion of pulmonary surfactant [50]. It correlates with the activity (severity) of chronic respiratory diseases [51] and is released into the blood due to inflammatory damage to the alveoli [52], so it is widely used clinically to determine the severity [53]. It is strongly correlated with the severity of interstitial pneumonia, but it has also been reported to correlate with the severity of lung cancer and mixed disorders (combined with emphysema) [54] and is used clinically [55]. In this experiment, the KL-6 value was significantly decreased, suggesting that the severity of the disease had improved. In the future, we plan to examine what action in the body’s dynamics is suppressing the deviation of KL-6, but we hypothesize that the alveolar function in patients with interstitial pneumonia has improved. At the same time, we examined hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is one of the representative reactive oxygen species (ROS) [56]. In normal physiological actions, it plays an important role in cell signaling, etc. [57], but on the other hand, it induces oxidative stress in the body and causes cell and tissue damage [58,59]. When glucose is ingested in the body, it enters the TCA cycle through the glycolysis process and produces ATP through the electron transport chain [60], but when glucose cannot be ingested, ATP is produced by burning fat and protein. In other words, ATP is essential for human life-sustaining activities [61]. A lot of oxygen is required to produce this ATP, and of course, this oxygen is taken in through breathing. Most of them are involved in energy production, but a few percent are transformed into reactive oxygen species (ROS) [62]. ROS has advantages and disadvantages for the body. The advantage is that they play a role in the body’s defense mechanism, destroying bacteria and cancer cells in granules contained in neutrophils [63]. The disadvantage is that they are known to be involved in various lifestyle-related diseases, including malignant neoplasms and aging [64]. Currently, the following four types of ROS are known to exist as representatives: ① Superoxide (O2−), ② Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), ③ Hydroxyl radical (·OH), ④ Singlet oxygen (1O2) [65]. In recent years, methods for removing ROS for the purpose of preventing disease and combating aging have been studied both domestically and internationally [66]. Since aging has been treated as a disease since ICD-11 [67], it is expected that further research will be conducted on antioxidants in the future. In this context, platinum-palladium has been confirmed to be the only substance in the world that can remove all four types of reactive oxygen species mentioned above [25]. In this study, the plasma hydrogen peroxide level was qualitatively measured from the viewpoint that hydrogen peroxide may be generated in large amounts in patients with interstitial pneumonia before and after taking platinum-palladium [68]. A significant difference was observed in this experiment, and a tendency for hydrogen peroxide to decrease in the body was confirmed with platinum-palladium. Hydrogen peroxide is a type of reactive oxygen species [69], and it is possible that hydrogen peroxide affects the alveoli in patients with interstitial pneumonia and COPD [70]. Therefore, the fact that a decreasing trend was observed this time confirms that platinum-palladium significantly reduced KL-6 and reduced hydrogen peroxide in patients with interstitial pneumonia, suggesting that platinum-palladium may have a protective effect on the alveoli in the reduction of KL-6, suppress the effects of ROS caused by hydrogen peroxide, and also increase mitochondrial activity, thereby improving interstitial pneumonia.
6. Conclusions
In this study, the use of platinum-palladium resulted in some improvement in patients with idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. When examining the mechanism, it was found that patients with interstitial pneumonia generate a lot of reactive oxygen in their lungs [33], and the purpose of this study was to determine the need to remove this reactive oxygen. As a result, although there are four types of reactive oxygen, the use of platinum-palladium, which moderately removes all of them, was able to remove hydrogen peroxide, which is said to be closely related to interstitial pneumonia, and is thought to have led to the improvement of interstitial pneumonia. In addition, since it will be necessary to prevent and treat diseases based on “mitochondrial activity” not only in interstitial pneumonia but in all diseases in the future, AMPK was also measured as part of this. There, it was confirmed that AMPK was significantly active at the in vitro level, so it is thought that mitochondrial activity can also be expected with platinum-palladium. Since this is a pilot study, we would like to conduct further studies at the in vivo level in the future. At this stage, a certain degree of effectiveness has been observed for interstitial pneumonia, so we would like to conduct large-scale intervention trials in the future.
Author Contributions
S.K. designed this study, the main conceptual ideas, and the proof outline. T.S. and S.K. collected the data. K.S., S.W. and Y.S. aided in interpreting the results and worked on the manuscript. S.K. supervised the project. S.K. wrote the manuscript with support from S.K. and Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
In this study, testing fees and reagents were provided by Hinokosei Clinic. In conducting this research, research funds and test products were provided by Hinokosei Clinic (Tokyo, Japan), and collaborative research was conducted.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This clinical research was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki, the “Ethical Guidelines for Life Science and Medical Research Involving Human Subjects”, and the research implementation plan. This study was conducted with the approval of the Hino Kosei Clinic Ethics Committee. Ethics Review Numbers HKC_N10023001 (Approved 2022/06/01), HKC_N10023002 (Approved 1 February 2023), HKC_N10023003 (Approved 3 June 2023), and HKC_N10023004 (Approved 11 July 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to the university staff and clinic staff who cooperated with in vivo and in vitro research in conducting this study, and to Yoshitaka Fukuzawa of Aichi Medical University and the Center for Preemptive and Integrated Medical Care for his advice.
Conflicts of Interest
This study was conducted at the clinic and university to which the authors belong, and there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lamb, Y.N. Nintedanib: A Review in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases [published correction appears in Drugs. Drugs 2021, 81, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzoni, E.A.; Poletti, V.; Mackintosh, J.A. Disease pathology in fibrotic interstitial lung disease: Is it all about usual interstitial pneumonia? Lancet 2021, 398, 1437–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graney, B.A.; Fischer, A. Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.; Feary, J.; Cullinan, P. Occupational Contributions to Interstitial Lung Disease. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vourlekis, J.S. Acute interstitial pneumonia. Clin. Chest Med. 2004, 25, 739–747, vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloli, E.A.; Beckford, R.; Hadley, R.; Flaherty, K.R. Idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonia. Respirology 2016, 21, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society; European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, T.M.; Wuyts, W. Management of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Adv. Ther. 2019, 36, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- akahashi, H.; Fujishima, T.; Koba, H.; Murakami, S.; Kurokawa, K.; Shibuya, Y.; Shiratori, M.; Kuroki, Y.; Abe, S. Serum surfactant proteins A and D as prognostic factors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and their relationship to disease extent. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162 Pt 1, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, H.; Otsuka, M.; Takahashi, H. Significance of molecular biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A mini review. Respir. Investig. 2018, 56, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasch, F. Interstitial pulmonary diseases. Pathologe 2006, 27, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.W.; Ryerson, C.J.; Guler, S.A. Progression of fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turino, G.M. TURIN: Natural History and Clinical Management of Emphysema in Patients with and without Alpha1-Antitrypsin Inhibitor Deficiency. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 624, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Detels, R.; Simmons, M.; Liu, H.; Coulson, A.H.; Sayre, J.; Rokaw, S. The UCLA population studies of chronic obstructive respiratory disease. XI. Impact of air pollution and smoking an annual change in forced expiratory volume in one second. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, J.K.; Panos, R.J.; Krachman, S.; Doherty, D.E.; Make, B.; Long-term Oxygen Treatment Trial Research Group. Oxygen therapy for patients with COPD: Current evidence and the long-term oxygen treatment trial. Chest 2010, 138, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2010; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&q=Organization+WH.+World+health+statistics+2010.+World+Health+Organization%2C+Geneva%2C+2010 (accessed on 8 June 2022).
- Young, R.P.; Hopkins, R.J.; Christmas, T.; Black, P.N.; Metcalf, P.; Gamble, G.D. COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 34, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.M.; Voynow, J.A.; Ghio, A.J. COPD: Balancing oxidants and antioxidants. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2015, 10, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Pais, A.; Ferreira, R.; da Costa, R.G. Platinum-induced muscle wasting in cancer chemotherapy: Mechanisms and potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Life Sci. 2018, 208, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katarzyna, M.; Anna, S.; Zielinska-Blizniewska, H.; Ireneusz, M. An Evaluation of the Antioxidant and Anticancer Properties of Complex Compounds of Copper (II), Platinum (II), Palladium (II) and Ruthenium (III) for Use in Cancer Therapy. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Yu, Y.; Jung, H.J.; Naik, S.S.; Yeon, S.; Choi, M.Y. Efficient recovery of palladium nanoparticles from industrial wastewater and their catalytic activity toward reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucar, Y.; Brantley, W.A.; Bhattiprolu, S.N.; Johnston, W.M.; McGlumphy, E.A. Characterization of cast-to implant components from five manufacturers. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2009, 102, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Horii, K.; Fujisawa, A.; Yamamoto, Y. Oxidative deterioration of platinum nanoparticle and its prevention by palladium. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, S.; Ozawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Izuo, N.; Toda, T.; Yokote, K.; Shimizu, T. Palladium and platinum nanoparticles attenuate aging-like skin atrophy via antioxidant activity in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Sato, T.; Kataoka, H.; Ide, T.; Terayama, H.; Sakabe, K. Antioxidant ability of platinum-palladium-Study using soft drinks containing platinum-palladium-. J. Jpn. Soc. Oral Funct. Water 2021, 22, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Based Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4881–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, S.P.; Dobrota, M. Kinetics and mechanism of uptake of platinum-based pharmaceuticals by the rat small intestine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 40, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable, V.; Maindan, K.; Kapdi, A.R.; Shejwalkar, P.S.; Hara, K. Active Palladium Colloids via Palladacycle Degradation as Efficient Catalysts for Oxidative Homocoupling and Cross-Coupling of Aryl Boronic Acids. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, E.Y.; Ha, Y.J.; Kang, E.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Song, Y.W. Serum KL-6 levels reflect the severity of interstitial lung disease associated with connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Bai, S.; He, N.; Wang, R.; Xing, Y.; Lv, C.; Yu, F. Real-Time Evaluation of Hydrogen Peroxide Injuries in Pulmonary Fibrosis Mice Models with a Mitochondria-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuraba, N.; Togami, Y. Fundamental and clinical evaluation of KL—6 measurement by chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay system “Lumipulse Presto KL—6 Eisai”. Jpn. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 61, 629–635. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara, T.; Hirano, K.; Morinobu, T.; Ogawa, S.; Hiroi, M.; Ban, R.; Ogihara, H.; Tamai, H. KL-6, a mucinous glycoprotein, as an indicator of chronic lung disease of the newborn. J. Pediatr. 2000, 137, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Z.; Venardos, K.; Chin-Dusting, J.; Kaye, D.M. Adverse effects of cigarette smoke on NO bioavailability: Role of arginine metabolism and oxidative stress. Hypertension 2006, 48, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R. ROS Are Good. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D. AMPK signalling in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 45, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, P.D.; Chance, B.; Ernster, L.; Mitchell, P.; Racker, E.; Slater, E.C. Oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1977, 46, 955–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cool, B.; Zinker, B.; Chiou, W.; Kifle, L.; Cao, N.; Perham, M.; Dickinson, R.; Adler, A.; Gagne, G.; Iyengar, R.; et al. Identification and characterization of a small molecule AMPK activator that treats key components of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordanetto, F.; Karis, D. Direct AMP-activated protein kinase activators: A review of evidence from the patent literature. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Sanders, M.J.; Carmena, D.; Bright, N.J.; Haire, L.F.; Underwood, E.; Patel, B.R.; Heath, R.B.; Walker, P.A.; Hallen, S.; et al. Structural basis of AMPK regulation by small molecule activators. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, M.M.; Shaw, R.J. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nature Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.M.; Hardie, D.G. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase: Do We Need Activators or Inhibitors to Treat or Prevent Cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zou, M.H. AMPK, Mitochondrial Function, and Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Sun, X.; Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Luo, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. AMPK regulates autophagy by phosphorylating BECN1 at threonine 388. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, R.; Ren, J.M.; Cadman, K.S.; Moore, I.K.; Perret, P.; Pypaert, M.; Young, L.H.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Shulman, G.I. Chronic activation of AMP kinase results in NRF-1 activation and mitochondrial biogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 281, E1340–E1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Noh, J.-R.; Choi, D.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Lee, C.-H. Enhanced Production of Adenosine Triphosphate by Pharmacological Activation of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Ameliorates Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G.; Schaffer, B.E.; Brunet, A. AMPK: An energy-sensing pathway with multiple inputs and out-puts. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, C.; Li, J.; Yao, H.W. AMP-activated protein kinase reduces inflammatory responses and cellular senescence in pulmonary emphysema. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22513–22523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaka, A.; Yanagihara, K.; Yamada, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Inokuchi, N.; Hayashi, T.; Komoda, M.; Nakamura, S.; Aoyama, M.; Sawada, T.; et al. Elevation of serum KL-6 glycoprotein or surfactant protein-D in adult T-cell leukemia with distinct pulmonary complications. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2009, 218, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Fujii, M.; Furusawa, H.; Tsuchiya, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Inase, N. The usefulness of KL-6 and SP-D for the diagnosis and management of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, M.; Haruta, T. The role of serum KL-6 measurement in common pediatric respiratory infections. J. Infect. Chemother. 2006, 12, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kaminski, N. Biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2012, 18, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Pieroni, M.; Refini, R.M.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Serum Concentrations of KL-6 in Patients with IPF and Lung Cancer and Serial Measurements of KL-6 in IPF Patients Treated with Antifibrotic Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Kurishima, K.; Kagohashi, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Satoh, H.; Hizawa, N. Serum KL-6 levels in lung cancer patients with or without interstitial lung disease. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2010, 24, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaus, U.G. Oxidants in Physiological Processes. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2021, 264, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, B.E.; Proudfoot, A.T.; Vale, J.A. Hydrogen peroxide poisoning. Toxicol. Rev. 2004, 23, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vliet, A.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M. Hydrogen peroxide as a damage signal in tissue injury and inflammation: Murderer, mediator, or messenger? J. Cell Biochem. 2014, 115, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.L. Glucose, glycolysis, and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 7653–7662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, A.; Dodd, M.S. Metabolism. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 607–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress; Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: Tokyo, Japan. (In Japanese)
- Beck-Schimmer, B.; Bonvini, J.M. Bronchoaspiration: Incidence, consequences and management. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2011, 28, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: Role and Response of Short Guanine Tracts at Genomic Locations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madreiter-Sokolowski, C.T.; Thomas, C.; Ristow, M. Interrelation between ROS and Ca in aging and age-related diseases. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N. Autophagy as a second level protective process in conferring resistance to environmentally-induced oxidative stress. Autophagy 2008, 4, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calimport, S.R.G.; Bentley, B.L. Aging Classified as a Cause of Disease in ICD-11. Rejuvenation Res. 2019, 22, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraja, C.; Shashibhushan, B.L.; Sagar; Asif, M.; Manjunath, P.H. Hydrogen peroxide in exhaled breath condensate: A clinical study. Lung India 2012, 29, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.D. Mitochondrial generation of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide as the source of mitochondrial redox signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Prieto, M.T.; García-Río, F.; Villamor, J. Role of oxidative stress in respiratory diseases and its monitoring. Med. Clin. 2006, 127, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).