Effect of Wild Blueberry Metabolites on Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal and Immune Health In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Migration and Formation of Junctional Complexes
2.4. Nitric Oxide Production and Gene Expression in Macrophages
2.5. RNA Extraction, Purification, and cDNA Synthesis
2.6. Quantitative PCR Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physiological Dose Ranges of Gastrointestinal Metabolites
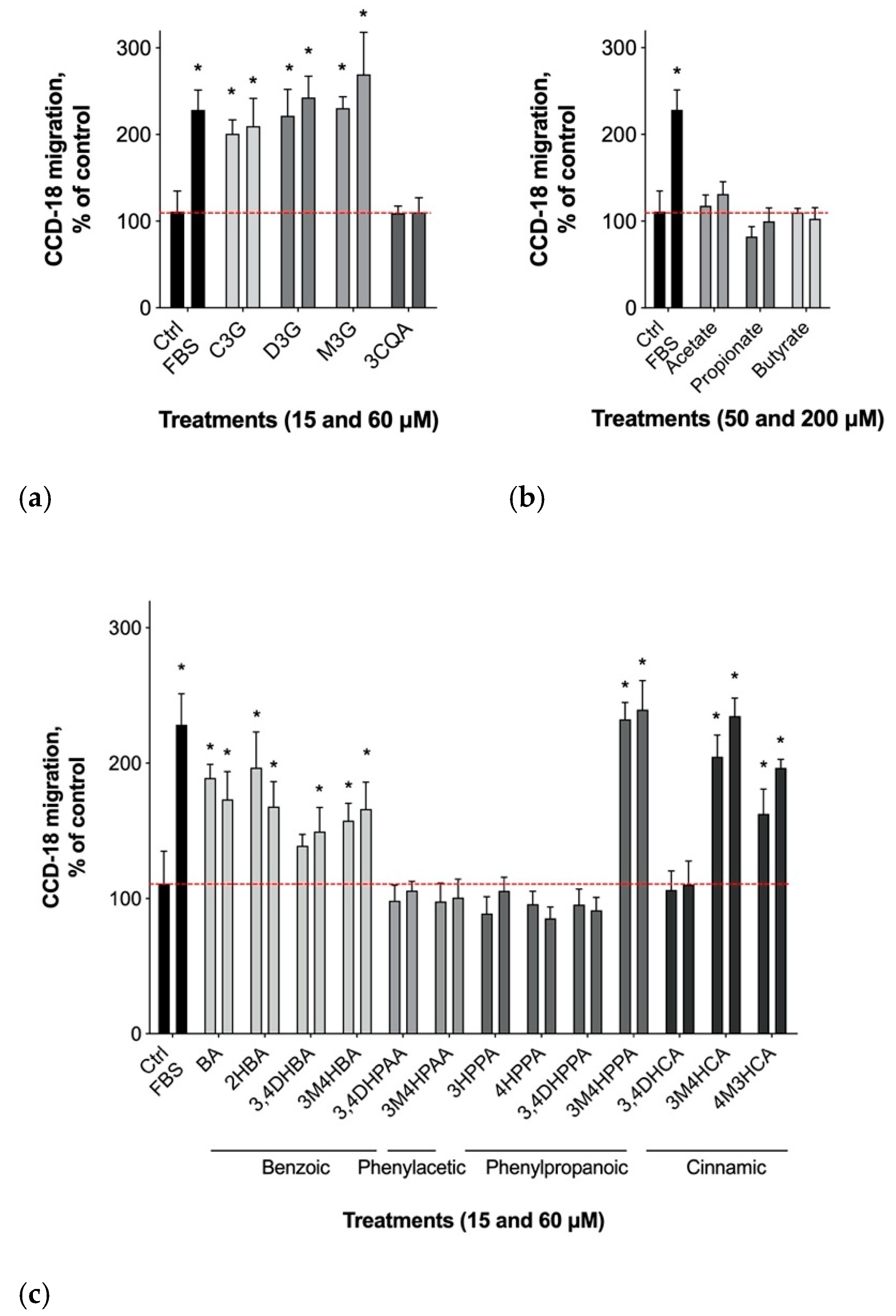
3.2. Gastrointestinal Epithelial Cell Migration
3.3. Formation of Epithelial Cell Monolayers
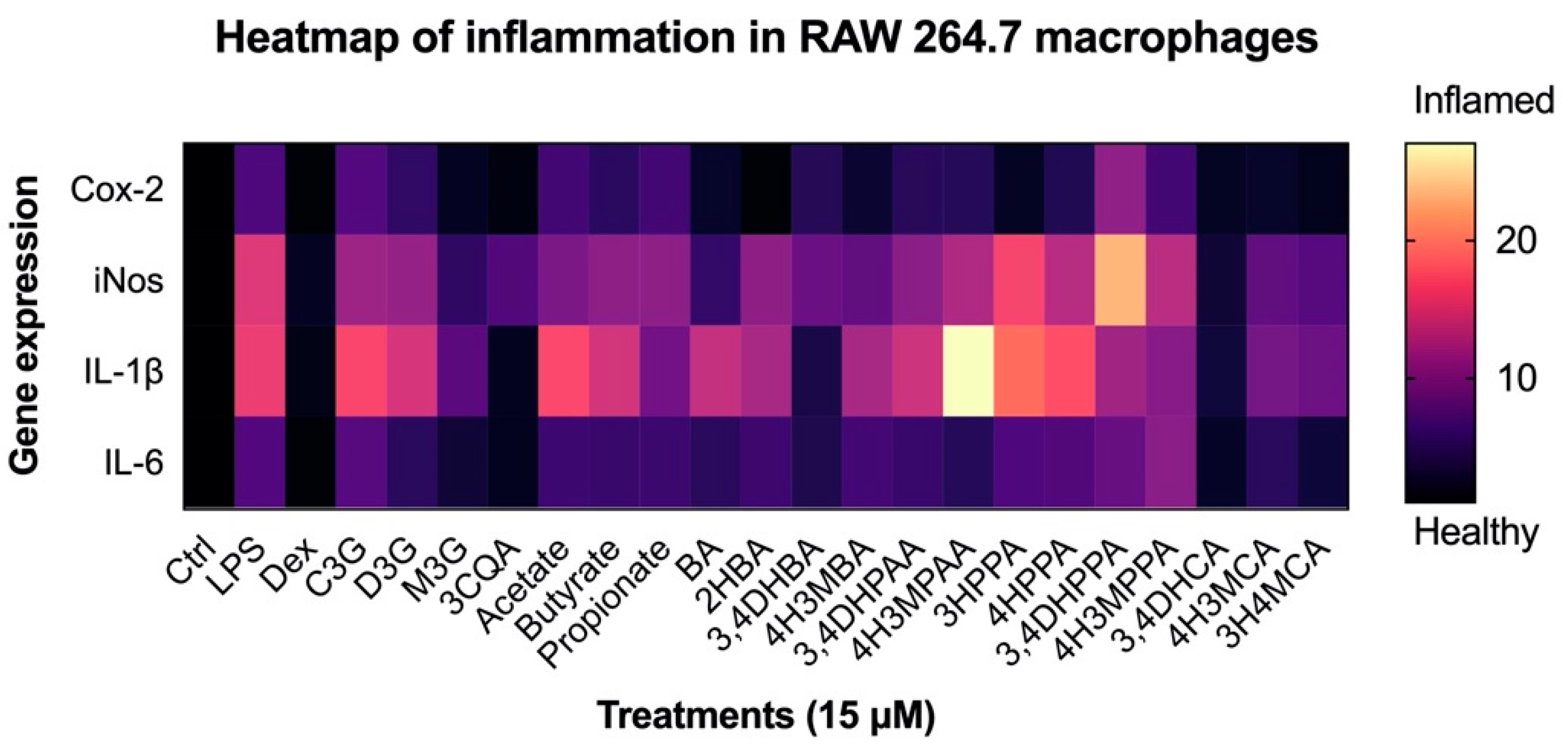
3.4. Reduction in Inflammatory Response in Macrophages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Edible Berries: Bioactive Components and Their Effect on Human Health. Nutrition 2014, 30, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, G.G.; Brown, A.F.; Funakoshi, Y.; Mbeunkui, F.; Grace, M.H.; Ballington, J.R.; Loraine, A.; Lila, M.A. Efficient Quantification of the Health-Relevant Anthocyanin and Phenolic Acid Profiles in Commercial Cultivars and Breeding Selections of Blueberries (Vaccinium Spp.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4806–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Cifuentes-Gomez, T.; Tabatabaee, S.; Lecras, C.; Spencer, J.P.E. Procyanidin, Anthocyanin, and Chlorogenic Acid Contents of Highbush and Lowbush Blueberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5772–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J. Classification of Fruits Based on Anthocyanin Types and Relevance to Their Health Effects. Nutrition 2015, 31, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fong, S.K.; Singh, A.P.; Vorsa, N.; Johnson-Cicalese, J. Variation of Anthocyanins, Proanthocyanidins, Flavonols, and Organic Acids in Cultivated and Wild Diploid Blueberry Species. HortScience 2019, 54, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.-L.; Yu, Y.-Q.; Chen, Z.-J.; Wen, G.-S.; Wei, F.-G.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, C.-D.; Xiao, X.-L. Stability-Increasing Effects of Anthocyanin Glycosyl Acylation. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Betanzo, J.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; McDonald, J.; Schroeter, K.; Corredig, M.; Paliyath, G. Stability and Biological Activity of Wild Blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) Polyphenols during Simulated in Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. Food Chem. 2014, 165, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilich, A.C.; Clevidence, B.A.; Britz, S.J.; Simon, P.W.; Novotny, J.A. Plasma and Urine Responses Are Lower for Acylated vs Nonacylated Anthocyanins from Raw and Cooked Purple Carrots. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6537–6542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, C.D.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Ludwig, I.A.; Clifford, M.N.; Crozier, A. Anthocyanins and Flavanones Are More Bioavailable than Previously Perceived: A Review of Recent Evidence. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, D.; Damsud, T.; Wilson, M.; Grace, M.H.; Strauch, R.; Li, X.; Lila, M.A.; Komarnytsky, S. Black Currant Anthocyanins Attenuate Weight Gain and Improve Glucose Metabolism in Diet-Induced Obese Mice with Intact, but Not Disrupted, Gut Microbiome. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6172–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Du, M.; Leyva, M.J.; Sanchez, K.; Betts, N.M.; Wu, M.; Aston, C.E.; Lyons, T.J. Blueberries Decrease Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Obese Men and Women with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Ferrars, R.M.; Czank, C.; Zhang, Q.; Botting, N.P.; Kroon, P.A.; Cassidy, A.; Kay, C.D. The Pharmacokinetics of Anthocyanins and Their Metabolites in Humans. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3268–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Feliciano, R.P.; Cifuentes-Gomez, T.; Spencer, J.P.E. Bioavailability of Wild Blueberry (Poly)Phenols at Different Levels of Intake. J. Berry Res. 2016, 6, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stull, A.J.; Cash, K.C.; Johnson, W.D.; Champagne, C.M.; Cefalu, W.T. Bioactives in Blueberries Improve Insulin Sensitivity in Obese, Insulin-Resistant Men and Women. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Rendeiro, C.; Bergillos-Meca, T.; Tabatabaee, S.; George, T.; Heiss, C.; Spencer, J. Intake and Time Dependence of Blueberry Flavonoid-Induced Improvements in Vascular Function: A Randomized, Controlled, Double-Blind, Crossover Intervention Study with Mechanistic Insights into Biological Activity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, S.A.; Feresin, R.G.; Navaei, N.; Figueroa, A.; Elam, M.L.; Akhavan, N.S.; Hooshmand, S.; Pourafshar, S.; Payton, M.E.; Arjmandi, B.H. Effects of Daily Blueberry Consumption on Circulating Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Antioxidant Defense in Postmenopausal Women with Pre- and Stage 1-Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.J.; van der Velpen, V.; Berends, L.; Jennings, A.; Feelisch, M.; Umpleby, A.M.; Evans, M.; Fernandez, B.O.; Meiss, M.S.; Minnion, M.; et al. Blueberries Improve Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Function in Participants with Metabolic Syndrome-Results from a 6-Month, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowtell, J.L.; Aboo-Bakkar, Z.; Conway, M.E.; Adlam, A.-L.R.; Fulford, J. Enhanced Task-Related Brain Activation and Resting Perfusion in Healthy Older Adults after Chronic Blueberry Supplementation. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vermeire, S. The Intestinal Barrier: A Fundamental Role in Health and Disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal Mucosal Barrier Function in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Lammers, K.M.; Goldblum, S.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Netzel-Arnett, S.; Buzza, M.S.; Antalis, T.M.; Vogel, S.N.; Zhao, A.; Yang, S.; et al. Identification of Human Zonulin, a Physiological Modulator of Tight Junctions, as Prehaptoglobin-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16799–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zak-Gołąb, A.; Kocełak, P.; Aptekorz, M.; Zientara, M.; Juszczyk, L.; Martirosian, G.; Chudek, J.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M. Gut Microbiota, Microinflammation, Metabolic Profile, and Zonulin Concentration in Obese and Normal Weight Subjects. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 674106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliviero, S.; Cortese, R. The Human Haptoglobin Gene Promoter: Interleukin-6-Responsive Elements Interact with a DNA-Binding Protein Induced by Interleukin-6. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Sabater, M.; Ortega, F.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Circulating Zonulin, a Marker of Intestinal Permeability, is Increased in Association with Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massier, L.; Chakaroun, R.; Kovacs, P.; Heiker, J.T. Blurring the Picture in Leaky Gut Research: How Shortcomings of Zonulin as a Biomarker Mislead the Field of Intestinal Permeability. Gut 2021, 70, 1801–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendrame, S.; Guglielmetti, S.; Riso, P.; Arioli, S.; Klimis-Zacas, D.; Porrini, M. Six-Week Consumption of a Wild Blueberry Powder Drink Increases Bifidobacteria in the Human Gut. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12815–12820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, S.; Fracassetti, D.; Taverniti, V.; Del Bo’, C.; Vendrame, S.; Klimis-Zacas, D.; Arioli, S.; Riso, P.; Porrini, M. Differential Modulation of Human Intestinal Bifidobacterium Populations after Consumption of a Wild Blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) Drink. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8134–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, S.N.; Mastaloudis, A.; Gray, R.; Antony, J.M.; Evans, M.; Wood, S.M. Efficacy of an Anthocyanin and Prebiotic Blend on Intestinal Environment in Obese Male and Female Subjects. J. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 2018, 7497260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, J.M.; Crowley, S.M.; Law, H.T.; Chang, S.-Y.; Ko, H.-J.; Vallance, B.A. The Intestinal Epithelium: Central Coordinator of Mucosal Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, D.; Chen, A.; Grace, M.H.; Komarnytsky, S.; Lila, M.A. Inhibitory Effects of Wild Blueberry Anthocyanins and Other Flavonoids on Biomarkers of Acute and Chronic Inflammation in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7022–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.M.P.; Rathinasabapathy, T.; Esposito, D.; Komarnytsky, S. Structural Constraints and Importance of Caffeic Acid Moiety for Anti-Hyperglycemic Effects of Caffeoylquinic Acids from Chicory. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1601118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skates, E.; Overall, J.; DeZego, K.; Wilson, M.; Esposito, D.; Lila, M.A.; Komarnytsky, S. Berries Containing Anthocyanins with Enhanced Methylation Profiles Are More Effective at Ameliorating High Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaid, F.; Sukhotnik, I.; Matter, I.; Berkowitz, D.; Hadjittofi, C.; Pollak, Y.; Lavy, A. Dietary Glutamine Supplementation Prevents Mucosal Injury and Modulates Intestinal Epithelial Restitution Following Acetic Acid Induced Intestinal Injury in Rats. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andou, A.; Hisamatsu, T.; Okamoto, S.; Chinen, H.; Kamada, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Okutsu, T.; Shimbo, K.; Takeda, T.; et al. Dietary Histidine Ameliorates Murine Colitis by Inhibition of Proinflammatory Cytokine Production from Macrophages. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 564–574.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.; Duthie, G. Plant Secondary Metabolites and Gut Health: The Case for Phenolic Acids. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2011, 70, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, P.; Flint, H.J. Formation of Propionate and Butyrate by the Human Colonic Microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venegas, D.P.; De la Fuente, M.K.; Landskron, G.; González, M.J.; Quera, R.; Dijkstra, G.; Harmsen, H.J.M.; Faber, K.N.; Hermoso, M.A. Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahle, K.; Kraus, M.; Scheppach, W.; Ackermann, M.; Ridder, F.; Richling, E. Studies on Apple and Blueberry Fruit Constituents: Do the Polyphenols Reach the Colon after Ingestion? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krndija, D.; Marjou, F.E.; Guirao, B.; Richon, S.; Leroy, O.; Bellaiche, Y.; Hannezo, E.; Vignjevic, D.M. Active Cell Migration is Critical for Steady-State Epithelial Turnover in the Gut. Science 2019, 365, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarnytsky, S.; Retchin, S.; Vong, C.I.; Lila, M.A. Gains and Losses of Agricultural Food Production: Implications for the Twenty-First Century. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vong, C.I.; Rathinasabapathy, T.; Moncada, M.; Komarnytsky, S. All Polyphenols Are Not Created Equal: Exploring the Diversity of Phenolic Metabolites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 2077–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.; Blaak, E.E. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Control of Body Weight and Insulin Sensitivity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, J.H.; Macfarlane, G.T. The Control and Consequences of Bacterial Fermentation in the Human Colon. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1991, 70, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, M.C.; Brennan, L.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Sébédio, J.-L.; Scalbert, A.; Fagan, A.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibney, M.J. Influence of Acute Phytochemical Intake on Human Urinary Metabolomic Profiles. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieber, R.; Bütikofer, U.; Bosset, J.O. Benzoic Acid as a Natural Compound in Cultured Dairy Products and Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 1995, 5, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halas, D.; Hansen, C.F.; Hampson, D.J.; Mullan, B.P.; Kim, J.C.; Wilson, R.H.; Pluske, J.R. Dietary Supplementation with Benzoic Acid Improves Apparent Ileal Digestibility of Total Nitrogen and Increases Villous Height and Caecal Microbial Diversity in Weaner Pigs. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 160, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halas, D.; Hansen, C.F.; Hampson, D.J.; Mullan, B.P.; Wilson, R.H.; Pluske, J.R. Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Inulin and/or Benzoic Acid on the Incidence and Severity of Post-Weaning Diarrhoea in Weaner Pigs after Experimental Challenge with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2009, 63, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.R.; Cox, I.J.; Walker, D.G.; Cobbold, J.F.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Marshall, S.E.; Orchard, T.R. Differences in Gut Microbial Metabolism Are Responsible for Reduced Hippurate Synthesis in Crohn’s Disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. Ferulic Acid Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Barrier Dysfunction via MicroRNA-200c-3p-Mediated Activation of PI3K/AKT Pathway in Caco-2 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascale, A.; Marchesi, N.; Marelli, C.; Coppola, A.; Luzi, L.; Govoni, S.; Giustina, A.; Gazzaruso, C. Microbiota and Metabolic Diseases. Endocrine 2018, 61, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohata, A.; Usami, M.; Miyoshi, M. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Alter Tight Junction Permeability in Intestinal Monolayer Cells via Lipoxygenase Activation. Nutrition 2005, 21, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, R.; Ma, X. Role of Metabolic Changes of Mucosal Layer in the Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction Following Trauma/Hemorrhagic Shock. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannenas, I.; Papaneophytou, C.P.; Tsalie, E.; Pappas, I.; Triantafillou, E.; Tontis, D.; Kontopidis, G.A. Dietary Supplementation of Benzoic Acid and Essential Oil Compounds Affects Buffering Capacity of the Feeds, Performance of Turkey Poults and Their Antioxidant Status, PH in the Digestive Tract, Intestinal Microbiota and Morphology. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pu, J.; Chen, D.; Tian, G.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Mao, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Luo, J.; et al. Protective Effects of Benzoic Acid, Bacillus Coagulans, and Oregano Oil on Intestinal Injury Caused by Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli in Weaned Piglets. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1829632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Sousa, J.R.; Da Costa Vasconcelos, P.F.; Quaresma, J.A.S. Functional Aspects, Phenotypic Heterogeneity, and Tissue Immune Response of Macrophages in Infectious Diseases. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2589–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novoselov, V.V.; Sazonova, M.A.; Ivanova, E.A.; Orekhov, A.N. Study of the Activated Macrophage Transcriptome. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, G.A. Lipids as Bioeffectors in the Immune System. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Rathore, A.S.; Kay, K.L.; Everhart, J.L.; Curtis, P.; Burton-Freeman, B.; Cassidy, A.; Kay, C.D. Contribution of Berry Polyphenols to the Human Metabolome. Molecules 2019, 24, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warner, E.F.; Rodriguez-Ramiro, I.; O’Connell, M.A.; Kay, C.D. Cardiovascular Mechanisms of Action of Anthocyanins May Be Associated with the Impact of Microbial Metabolites on Heme Oxygenase-1 in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, A.F.; Palatini, K.; Komarnytsky, S.; Gianfagna, T.J.; Munafo, J.P. Phenylpropanoid Glycerol Glucosides Attenuate Glucose Production in Hepatocytes. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 10670–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, J.; Dinis, T.C.P.; Almeida, L.M. Malvidin-3-Glucoside Protects Endothelial Cells up-Regulating Endothelial NO Synthase and Inhibiting Peroxynitrite-Induced NF-KB Activation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2012, 199, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Series | Common Name | Chemical Name | Abbr. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benzoic | Benzoic | Benzoic | BA |
| Salicylic | 2-Hydroxybenzoic | 2HBA | |
| Protocatechuic | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic | 3,4DHBA | |
| Vanillic | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic | 4H3MBA | |
| Phenylacetic | DOPAC | 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic | 3,4DHPAA |
| Homovanillic | 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxyphenylacetic | 4H3MPAA | |
| Phenylpropionic | m-Dihydrocoumaric | 3-Hydroxyphenylpropionic | 3HPPA |
| p-Dihydrocoumaric | 4-Hydroxyphenylpropionic | 4HPPA | |
| Dihydrocaffeic | 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylpropionic | 3,4DHPPA | |
| Dihydroferulic | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylpropionic | 4H3MPPA | |
| Cinnamic | Caffeic | 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic | 3,4DHCA |
| Isoferulic | 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic | 3H4MCA | |
| Ferulic | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic | 4H3MCA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rathinasabapathy, T.; Lomax, J.; Srikanth, K.; Esposito, D.; Kay, C.D.; Komarnytsky, S. Effect of Wild Blueberry Metabolites on Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal and Immune Health In Vitro. Immuno 2022, 2, 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2020019
Rathinasabapathy T, Lomax J, Srikanth K, Esposito D, Kay CD, Komarnytsky S. Effect of Wild Blueberry Metabolites on Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal and Immune Health In Vitro. Immuno. 2022; 2(2):293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleRathinasabapathy, Thirumurugan, Jade Lomax, Kavin Srikanth, Debora Esposito, Colin D. Kay, and Slavko Komarnytsky. 2022. "Effect of Wild Blueberry Metabolites on Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal and Immune Health In Vitro" Immuno 2, no. 2: 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2020019
APA StyleRathinasabapathy, T., Lomax, J., Srikanth, K., Esposito, D., Kay, C. D., & Komarnytsky, S. (2022). Effect of Wild Blueberry Metabolites on Biomarkers of Gastrointestinal and Immune Health In Vitro. Immuno, 2(2), 293-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/immuno2020019








