Abstract
This study examined the trends and key themes of artificial intelligence in the field of tourism and hospitality research. On 5 March 2025, a search was performed using “artificial intelligence” and related terms in the “Title, Abstract, and Keywords”, focusing on tourism and hospitality journals indexed in Scopus. The identified documents were subjected to performance analysis and science mapping techniques. The search yielded 921 documents, comprising 882 articles and 39 reviews. The number of documents increased from 3 in 1987 to 277 in 2024. R. Law from the University of Macau was the most prolific author, while the Hong Kong Polytechnic University recorded the highest publication count. Chinese researchers produced the most documents, totaling 262 articles and reviews. A keyword co-occurrence analysis revealed four key themes: “machine learning and sentiment analysis of online reviews”, “adoption of AI including robots and ChatGPT in the hospitality industry”, “artificial neural networks for tourism management and demand analysis”, and “random forest models in travel”. Additionally, the study noted a shift in research focus from tourism demand forecasting and sentiment analysis to using service bots and applying artificial intelligence to enhance service quality, with a recent emphasis on generative AI tools like ChatGPT.
1. Introduction
Travel and tourism have become major parts of the global economy in recent decades (World Travel & Tourism Council, 2021). This sector generates jobs, boosts spending, imports, and exports, and leads to worldwide prosperity. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, travel and tourism accounted for 10.3% of the world’s gross domestic product (GDP) at about USD 9 trillion and created over 10% of all jobs, i.e., 334 million jobs (World Travel & Tourism Council, 2021). In some economies, like Aruba, British Virgin Islands, Macao, and US Virgin Islands, the travel and tourism sector contributed to over 50% of their GDP and 60% of their total employment (Lim & To, 2022; World Travel & Tourism Council, 2021). However, the COVID-19 pandemic severely affected this sector, leading to travel bans, quarantine, and social distancing measures worldwide (Varzakas & Metaxas, 2024). As such, the number of air passengers plummeted in February, March, and April 2023 (Iacus et al., 2020; Monmousseau et al., 2020; To & Lee, 2024). Although air travel began to recover in the summer of 2020 in the US and Europe, the world’s travel and tourism GDP fell to USD 4.7 trillion, or 5.5% of the world’s GDP in 2020 (World Travel & Tourism Council, 2021), while the number of all travel- and tourism-related jobs fell to 272 million. Within a year, 62 million jobs were lost. Fortunately, as COVID-19 has transitioned to an endemic phase, the travel and tourism sector has rebounded quickly over the past two years. It was projected that GDP and employment would reach about 90% of the levels seen before the pandemic in 2023 (World Travel & Tourism Council, 2023). In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, chatbots, and service robots, have been deployed in hotels, malls, restaurants, shops, and airports, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic (Berezina et al., 2019; Fusté-Forné & Jamal, 2021; Leung, 2020; Saputra et al., 2024; Song et al., 2024; X. Zhang et al., 2022). Specifically, researchers investigate how AI technologies can be utilized in tourism and hospitality settings (Berezina et al., 2019; Buhalis & Moldavska, 2022; Chang et al., 2020; Leung, 2020; Lin & Mattila, 2021; Melián-González et al., 2021; Orden-Mejia & Huertas, 2022; Pillai & Sivathanu, 2020; Saputra et al., 2024; X. Zhang et al., 2022). Additionally, the emergence of generative AI provides vast opportunities and challenges to the tourism and hospitality industry (Carvalho & Ivanov, 2024; Gursoy et al., 2023; Shi et al., 2024). However, how many research efforts have been devoted to AI in tourism and hospitality over the years? What are the trends and key themes of these efforts? Finding answers to these questions is crucial for the field.
More specifically, this study seeks to identify how many core academic publications have been devoted to AI in tourism and hospitality using a bibliometric approach. Additionally, it aims to reveal trends and significant contributors, while utilizing science mapping to illustrate the evolution and key areas of interest in AI research within tourism and hospitality over recent decades. On 5 March 2025, a search about “artificial intelligence”, including its key technological terms in the “Title, Abstract, and Keywords” in tourism and hospitality journals, was performed using Scopus. The search yielded 942 documents. After excluding 21 irrelevant documents, a total of 921 documents, including 882 articles and 39 reviews, were retained. These documents were then carefully analyzed through performance analysis and science mapping. Performance analysis identified the trend (i.e., efforts) of AI in tourism and hospitality research. It also highlighted the most productive authors, affiliations, and countries, the most supportive funding bodies, and the most cited publications among the identified documents. Science mapping revealed the underlying themes of AI in tourism and hospitality. The paper contains a specific section focusing on how generative AI tools, like ChatGPT and possibly DeepSeek, will bring about significant changes in tourism and hospitality research. Specifically, the novelty of this study lies in its application of science mapping and trend analysis to uncover the progression of AI in tourism and hospitality research, highlighting recent focal points like deep learning, generative AI, and ChatGPT.
2. Review of AI in Tourism and Hospitality and Bibliometric Analysis
AI is a very broad concept. It encompasses the study and application of various disciplines, such as applied mathematics, computer science and engineering, logic, modeling and simulation, linguistics, psychology, and many others. Its origins can be traced back to the 1950s, when pioneers like John McCarthy and Marvin Minsky proposed that machines, specifically computers, could perform intelligence tasks similarly to human beings (McCarthy et al., 1956; Minsky, 1956). The investment and development of AI experienced notable fluctuations throughout the subsequent four decades (Grudin, 2009). While AI held great promise in advancing a country’s competitive edge, the development of computational power during the 1970s and 1980s lagged behind the demands of AI, despite notable advancements in processor technology with the introduction of integrated circuits (Valverde, 2016). However, in the 1990s, efficient machine learning algorithms, such as recurrent neural networks (Levin, 1990) and support vector machines (Cortes & Vapnik, 1995), were developed and deployed to handle the ever-increasing size of datasets while computer power continued to improve. Over the past two decades, various deep learning technologies have been developed and utilized for purposes including statistical data and visual image analysis, text and natural language processing, and the generation of audio–visual content generation (LeCun et al., 2015). Specifically, AI, such as deep learning, has been employed to forecast tourism demand (Law et al., 2019; G. Yu & Schwartz, 2006), understand tourists’ perceptions and behaviors (K. Zhang et al., 2019), and analyze visitor feedback, comments, and reviews (Chang et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2021). Since the beginning of 2023, generative AI tools, such as ChatGPT, have attracted significant attention in both practical and research communities, including their application in tourism and hospitality research (Carvalho & Ivanov, 2024; Dwivedi et al., 2024).
Bibliometrics is a branch of information and library science that uses a structural and quantitative approach to analyze bibliographical data in a specific research area or topic (Donohue, 1972; Donthu et al., 2021). It entails identifying relevant documents from an academic indexing database and utilizing performance analysis and science mapping to uncover the research personnel and units’ performance, as well as the trend and underlying structure of the research area or topic (To et al., 2024; Zhong et al., 2023). In contrast to systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses that primarily focus on in-depth qualitative analysis of individual publications and statistical analysis of results from multiple related research publications (which can only be conducted on a limited number of identified documents, such as a few tens or up to one or two hundreds), a bibliometric study is more suitable when the research topic is broad, like the current one, and the number of identified documents is too large for manual review, such as close to a thousand in the current study (Donthu et al., 2021). Thus, this study opted for a bibliometric analysis.
3. Methods
3.1. Data Source and Data
Scopus and the Web of Science are widely recognized as the leading academic indexing databases in bibliometric studies (Mishra et al., 2022; Singh et al., 2021). Both of them have strict criteria for the inclusion and exclusion of journals, books, and conference proceedings (Clarivate, 2025; Scopus, 2025). Scopus, although relatively newer than the Web of Science, has continually expanded its coverage over the past two decades. As of March 2025, Scopus contained over 100 million academic publication records from around 28,900 journals, 167 thousand conference events, and 3.56 million book items, larger than the Web of Science Core Collection of 95 million academic publication records from around 22,000 journals, over 300 thousand conferences, and 143 thousand books. Scopus covered 155 journals in the subject area of tourism, leisure, and hospitality management, while the Web of Science Core Collection covered 140 journals with 58 Social Science Citation Index journals and 82 Emerging Science Citation Index journals. Notably, Scopus actively collaborates with researchers, institutions, funding bodies, and higher education ranking bodies to curate its database (Baas et al., 2020). Additionally, Scopus offers essential features for basic bibliometric analysis and provides a user-friendly interface for exporting data in various formats. Therefore, this study utilized Scopus as the primary data source.
On 5 March 2025, a comprehensive search was conducted on Scopus, using (“artificial intelligence” OR “machine learning” OR “deep learning” OR “vector machine” OR “neural network” OR “long short-term memory” OR “supervised learning” OR “unsupervised learning” OR “reinforcement learning” OR “Naive Bayes” OR “random forest” OR “supervised classification” OR “unsupervised classification” OR “dimensionality reduction” OR “dimensional reduction” OR “dimension reduction” OR “natural language processing” OR “generative artificial intelligence” OR “generative AI” OR “ChatGPT”) in the “Article Title, Abstract, and Keywords” and (tourism OR hospitality OR travel OR leisure OR tourist OR vacation OR destination) in the “Source Title”. This search yielded a total of 1523 documents, which included 1132 journal articles, 49 reviews in journals, 16 notes, 14 letters, 3 editorials, 1 retracted paper, 1 erratum, 7 conference papers, 267 book chapters, and 33 books.
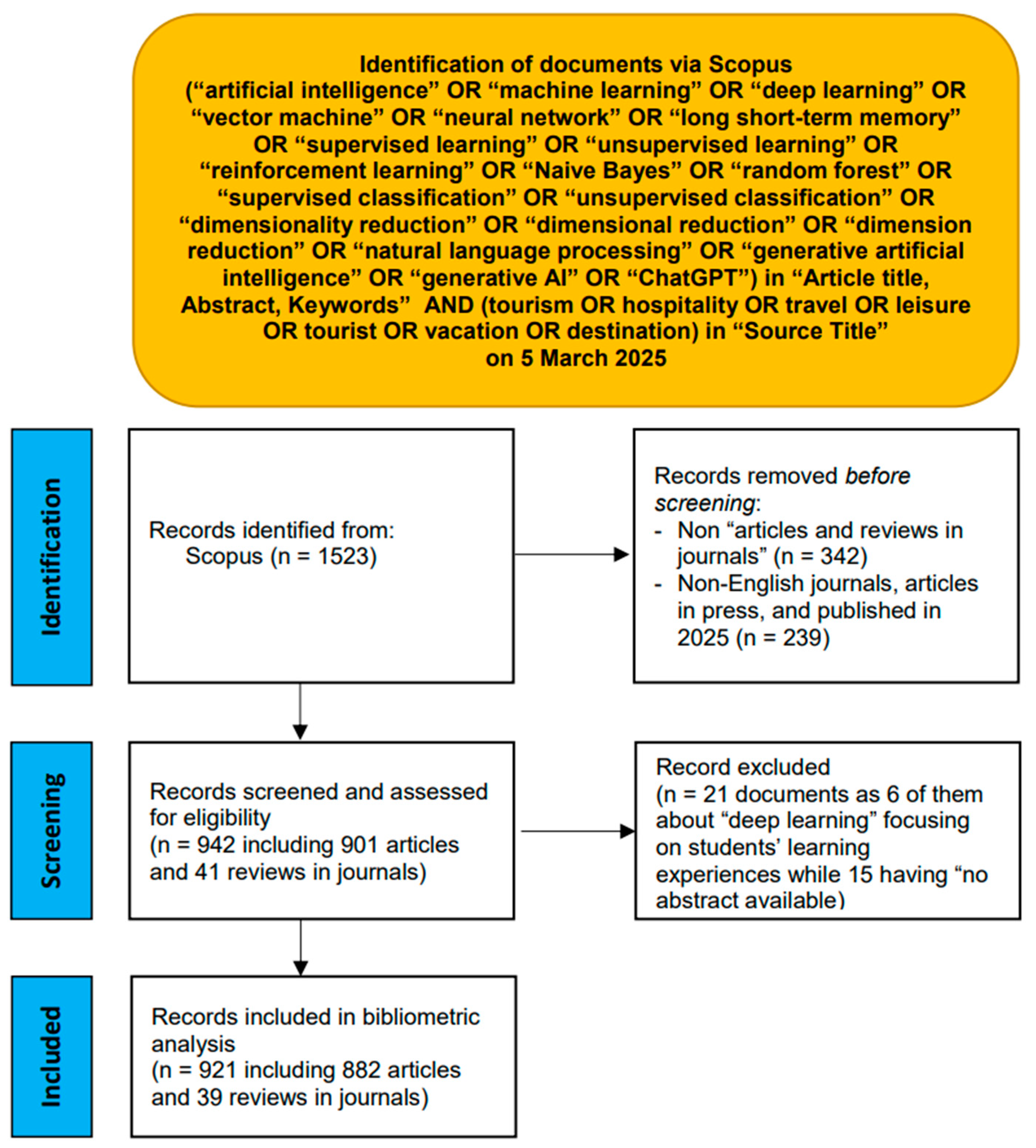
Subsequently, the search was refined to focus exclusively on articles and reviews published in English-language journals that had reached the final publication stage and were dated up to 2024, resulting in the identification of 942 documents. A meticulous review of all abstracts led to the exclusion of 21 documents. The exclusions were based on the presence of “deep learning” in 6 documents that pertained to students’ learning experience in tourism and hospitality management education (e.g., Ruhanen, 2006; Murphy & de Jongh, 2011), rather than the application of deep learning techniques in AI. Additionally, 15 documents were excluded due to “no abstract available”. Consequently, a total of 921 documents, comprising 882 articles and 39 reviews, were analyzed using various bibliometric methods. The process used in this study closely followed the guidelines set forth by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA, 2020; Page et al., 2021), as depicted in Figure 1.
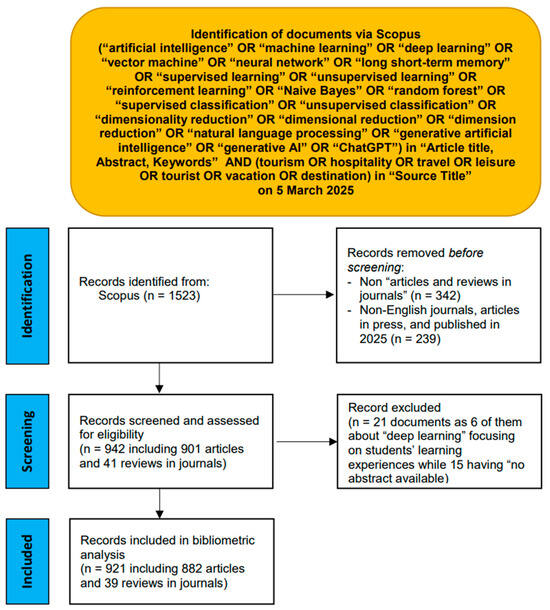
Figure 1.
Bibliometric search using Scopus.
3.2. Data Analysis Approach
The study focused on performance analysis and science mapping. Scopus, which offers various bibliometric functions, was utilized to uncover the most productive authors, affiliations, and countries, as well as the funding bodies that provided the most support among the 921 selected documents. Furthermore, the study identified the most popular source titles and the top 10 highly cited publications. Science mapping involves examining the connections between the selected publications through co-authorship and keywords. This method can help identify the underlying structure, important research topics, and emerging themes. To create different types of maps, two widely used bibliometric visualization tools, VOSviewer version 1.6.20 (Van Eck & Waltman, 2010) and Biblioshiny version 4.0 (Belfiore et al., 2022), were employed.
4. Results
4.1. Trend Analysis Using Scopus
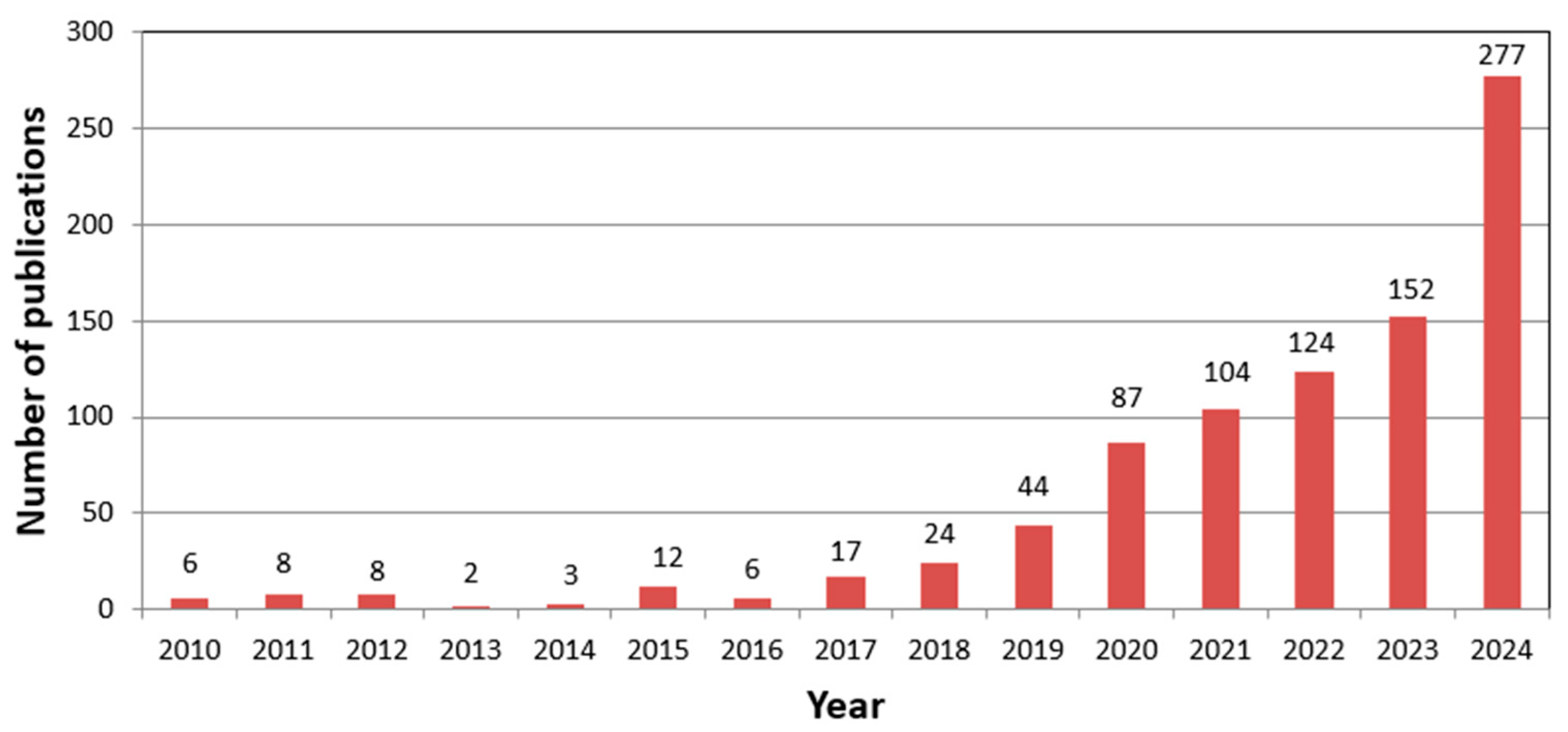
According to the Scopus results, the first three documents were published in 1987, where the first two were about the use of expert systems for gastronomy and food processing (Garber et al., 1987; Nissan, 1987). In total, there were 7 publications in the 1980s, 9 publications in the 1990s, and 31 publications in the 2000s. Figure 2 shows the number of publications about AI for tourism and hospitality research during the period 2010 to 2014. As this figure illustrates, there were no more than 24 publications per year before 2018. The number of publications increased to 104 in 2021 and 277 in 2024.
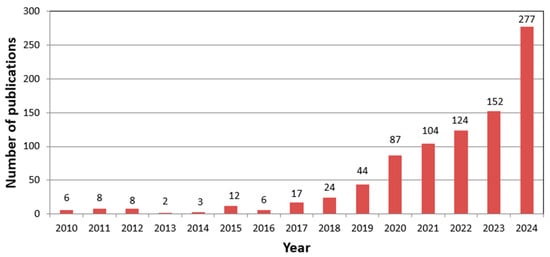
Figure 2.
The number of publications from 2010 to 2024.
4.2. Performance Analysis Based on Scopus Bibliometric Tools
Scopus results indicated that R. Law, affiliated with the University of Macau and formerly with the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, stood out as the most productive author, having published a total of 38 works. Following him was G. Li from Deakin University, who has 15 publications, and S. Wang from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, with 14 publications. R. Law’s 38 works have garnered an impressive 2498 citations, resulting in an h-index of 23. G. Li’s 15 publications have accumulated 902 citations, yielding an h-index of 10, while S. Wang’s 14 publications have received 781 citations, leading to an h-index of 11. Additionally, D. Gursoy from Washington State University has 11 publications that have collectively amassed 1776 citations, resulting in a citations per publication ratio exceeding 160. Table 1 illustrates the top nine authors who have authored or co-authored nine or more publications, providing details on their total citations and citations per publication. Moreover, five researchers have authored or co-authored eight publications: D. Buhalis, S. Ivanov, M.J. Kim, P. Rita, and I.K.A. Wong.

Table 1.
The most productive authors.
In the assessment of the most productive institutions, the Hong Kong Polytechnic University distinguished itself by leading with a total of 65 publications. It was followed by Nankai University and the University of Macau, each of which recorded 27 publications. Griffith University contributed 24 publications, while both the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Sun Yat-Sen University produced 22 publications each. Kyung Hee University generated 19 publications, and the University of Johannesburg along with the University of Surrey each had 17 publications. It is noteworthy that among the top six most productive institutions, five are higher education and research institutions situated in China, including those in Hong Kong and Macao, both of which are recognized as two prominent tourism destinations in Asia.
Regarding the most productive countries or regions, China ranked first with 262 publications, followed by the United States with 201 publications and the United Kingdom with 105 publications. Spain, Australia, and Hong Kong ranked fourth to sixth, with 68, 67, and 62 publications, respectively. They were succeeded by India with 54 publications, Turkey with 46, South Korea with 43, and Portugal with 41 publications.
An examination of funding bodies revealed that the National Natural Science Foundation of China emerged as the most prominent supporter, being acknowledged in 160 publications. The next four leading funding bodies were all distinct entities within China: The Ministry of Science and Technology, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the National Office for Philosophy and Social Sciences, and the Ministry of Education, which were recognized in 61, 32, 26, and 25 publications, respectively.
In terms of publication numbers by source title, Tourism Management was identified as the foremost journal, with an impressive total of 80 publications. It was closely followed by The International Journal of Hospitality Management, which secured the second position with 77 publications, and The International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, which ranked third with 73 publications. Collectively, these journal articles and reviews received a substantial number of citations, with Tourism Management amassing 8573 citations, The International Journal of Hospitality Management receiving 4227 citations, and The International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management obtaining 4146 citations. Table 2 shows the top ten source titles that had 26 or more publications each, along with the total number of citations, h-index, and citations per publication based on the search results.

Table 2.
AI publication by source titles.
4.3. Top Ten Highly Cited Publications
When citations were considered, the article “A comparative analysis of major online review platforms: Implications for social media analytics in hospitality and tourism” by Xiang et al. (2017) ranked first with 672 citations, as illustrated in Table 3. This paper used text analytics to compare three online review platforms: TripAdvisor, Expedia, and Yelp. The authors created a machine learning procedure to determine a helpfulness score for each review, finding that review length was a strong predictor of helpfulness on TripAdvisor and Yelp. The second highly cited document, “Effects of COVID-19 on hotel marketing and management: A perspective article” by Jiang and Wen (2020), examined how COVID-19 impacted hotel marketing and management. It proposed that the pandemic would accelerate the adoption of AI and robotics in the hospitality industry, as hygiene and cleanliness became top priorities for travelers. This article attracted 600 citations, with the highest citations per year at 125. The third highly cited document was “Developing and validating a service robot integration willingness scale” by Lu et al. (2019). The authors provided examples of service robots in hotels, airports, and restaurants. With the growing demand for service robots in the hospitality industry, they created a scale to measure consumers’ willingness to integrate robots into service interactions. The scale was validated using four consumer samples in the US. This paper received 548 citations. The fourth highly cited document was “Real-time co-creation and newness service: Lessons from tourism and hospitality” by Buhalis and Sinarta (2019). The authors emphasized the role of real-time marketing in the tourism and hospitality industry. They conducted qualitative research to examine how brands use social media technology, like dynamic big data mining, to improve consumer experiences. They specifically looked at how Marriott MLive helps Marriott and its consumers create value together. This paper attracted 526 citations. The fifth highly cited document was “Adoption of AI-based chatbots for hospitality and tourism” by Pillai and Sivathanu (2020). In this study, the authors investigated the intention and behavior of consumers regarding chatbot usage for tourism, employing an extended technology adoption model. Using responses from 1480 travelers across various locations in India, they found that factors such as perceived ease of use, perceived trust, perceived intelligence, perceived usefulness, and anthropomorphism served as positive predictors of the intention to adopt tourism chatbots. Additionally, stickiness to human travel agents was found to negatively influence the relationship between intention and actual behavior. This article has garnered 492 citations.

Table 3.
The most highly cited publications.
The sixth highly cited document was a review on automation, including artificial intelligence and robotics in tourism, published by Tussyadiah (2020) in Annals of Tourism Research, with 471 citations. The seventh highly cited document was “From high-touch to high-tech: COVID-19 drives robotics adoption” by Zeng et al. (2020). The authors discussed how COVID-19 impacted the tourism industry, which is known for its personal interactions, before April 2020. They proposed using various types of robots, like telerobots, teleoperators, and social robots, to reduce human contacts in different settings. They concluded that integrating AI and robotics could significantly improve the tourism and hospitality industry. This article received 448 citations. The eighth highly cited document was “Hotel employees’ artificial intelligence and robotics awareness and its impact on turnover intention: The moderating roles of perceived organizational support and competitive psychological climate” by Li et al. (2019), attracting 445 citations. The authors noted that using AI and robotics in hotels greatly influenced service delivery and impacted the turnover intention of frontline employees. Using responses from 468 full-time employees in five-star hotels in Guangzhou, Li et al. (2019) discovered that awareness of AI and robotics was closely linked to turnover intention, with perceived organizational support and competitive psychological climate affecting this relationship. The ninth highly cited document was “Sentiment analysis in tourism: Capitalizing on big data” by Alaei et al. (2019). The authors explored different sentiment analysis techniques, like supervised machine learning, unsupervised machine learning, dictionary-based, semantic, and hybrid approaches, within the tourism industry. They argued that the rapid increase in tourist reviews on social media calls for automated methods, developed in collaboration with tourism experts and IT specialists. Alaei et al.’s (2019) review attracted 435 citations. The tenth highly cited document was “What do Airbnb users care about? An analysis of online review comments” by Cheng and Jin (2019). The authors explored factors affecting Airbnb user experiences using big data techniques, analyzing 181,263 review comments from Inside Airbnb that focused on 23,615 listings in Sydney. Their analysis revealed three main factors: location, amenities, and host, which significantly influenced the reviews. This article attracted 391 citations.
4.4. Science Mapping
4.4.1. Co-Authorship Relationships Between Authors
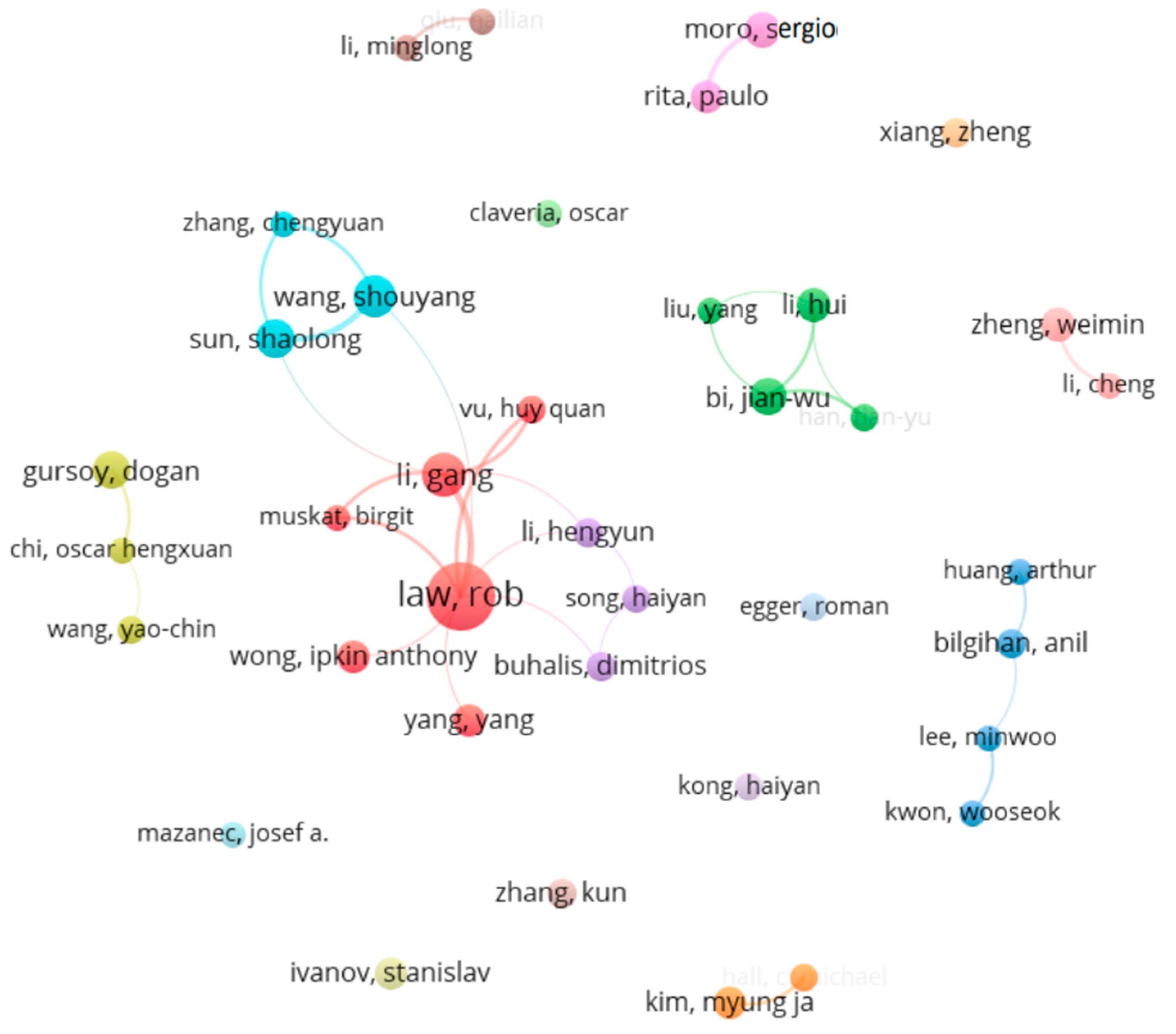
VOSviewer was used to explore co-authorship relationships between authors. When the minimum number of publications was set to 5, 38 out of the 2306 identified authors met the threshold and formed 17 clusters, in which 10 clusters had 2 members or more and 7 clusters had a single member. As shown in Figure 3 (red cluster and the largest one with 6 members), R. Law was the one producing the largest number of publications and he actively collaborated with G. Li—the second most productive author—and H.Q. Vu of Deakin University, with 13 and 6 co-authored publications, respectively. S. Wang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences was the third most productive author. He collaborated frequently with S. Sun of Xi’an Jiaotong University and C. Zhang of Xidian University, forming a cluster of three members (light blue cluster). The second and third largest clusters had four authors each. J.W. Bai, H. Li, Y. Liu, and T.-Y. Han of Nankai University formed a cluster of four members (green cluster), while A. Huang of the University of Central Florida, A. Bilgihan of Florida Atlantic University, M. Lee of the University of Houston, and W. Kwon of Sejong University formed another cluster of four members (blue cluster).
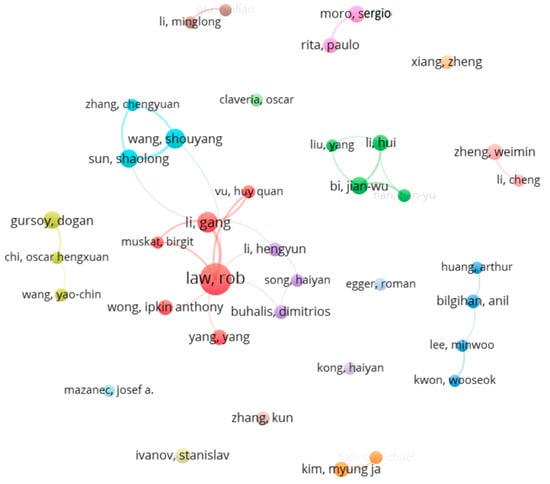
Figure 3.
Co-authorship networks formed between authors.
4.4.2. Bibliographic Coupling
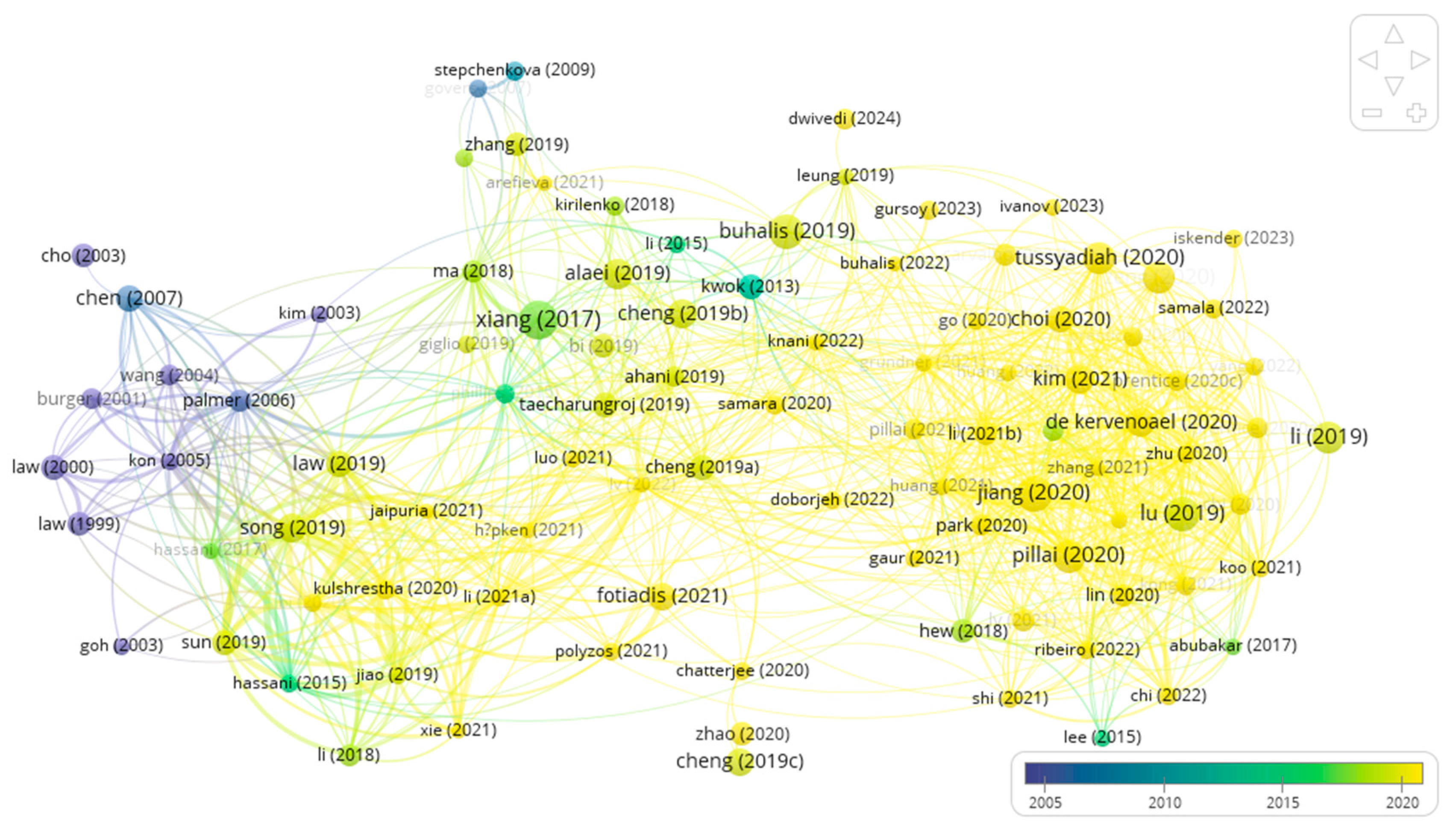
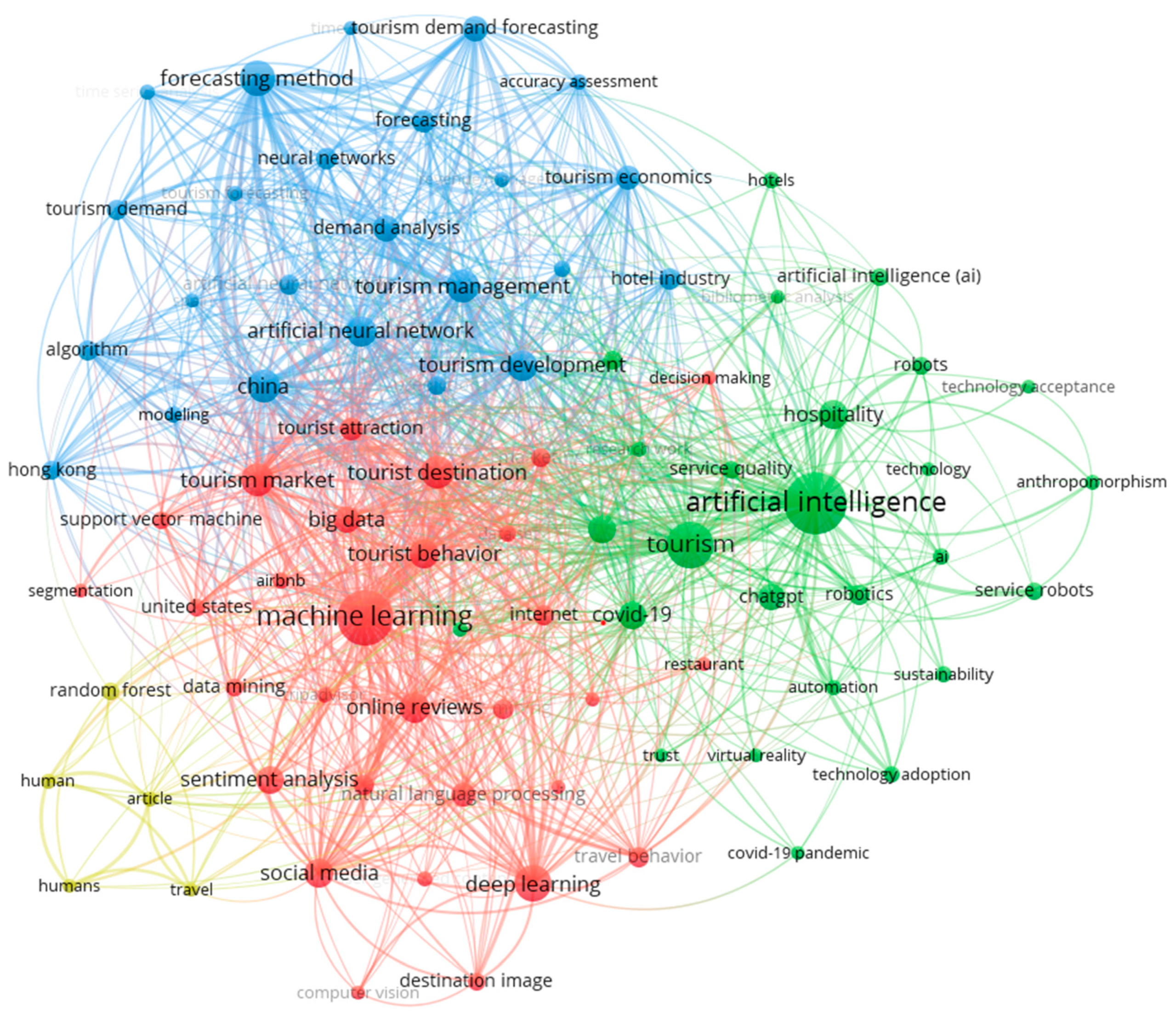
Bibliographic coupling occurs when two documents cite a common third document in their references, implying that the studies are closely related. Figure 4 shows bibliographic coupling from VOSviewer. When the minimum number of citations was set to 100, 98 of the 921 identified documents met the threshold. Figure 5 showed that some early applications of AI technologies in tourism and hospitality were the use of neural network models (Law, 2000; Law & Au, 1999) and support vector regression (Chen & Wang, 2007) to forecast tourism demand (see the purple circles). During the 2010s, there was a shift in research focus toward utilizing machine learning techniques for the purpose of detecting sentiment and extracting important information from social media platforms. Notable studies in this area included the works of Kwok and Yu (2013), Xiang et al. (2017), Alaei et al. (2019), and Buhalis and Sinarta (2019). Recently, the COVID-19 pandemic has sparked a surge in research focusing on the use of service robots in the tourism and hospitality industry (Pillai & Sivathanu, 2020; Jiang & Wen, 2020; Tussyadiah, 2020; Zeng et al., 2020).
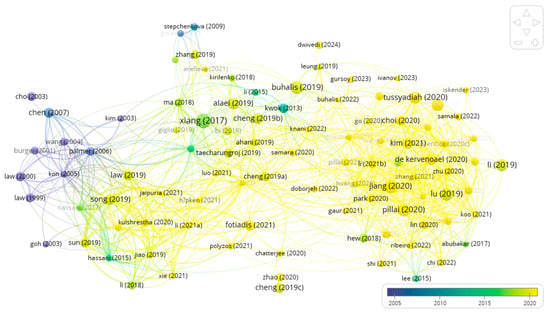
Figure 4.
Bibliographic coupling.
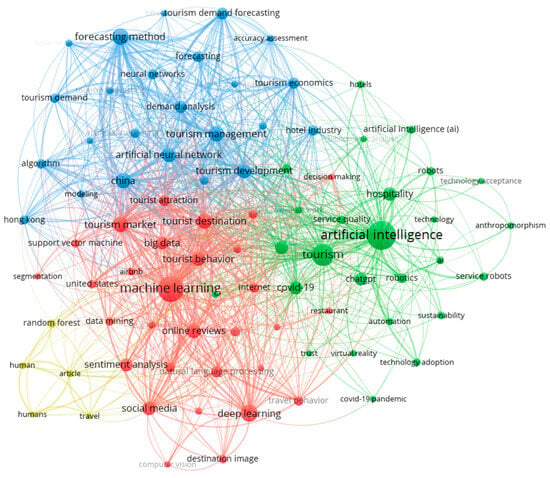
Figure 5.
Keyword co-occurrences in the 921 documents.
4.4.3. Research Themes and Their Evolution
Cluster analysis was conducted on all keywords, including author keywords and index keywords, based on their co-occurrence frequencies. When the minimum number of occurrences of a keyword was set to 10, 85 out of the 3455 identified keywords met the threshold. The relatedness of keywords was determined by the number of documents in which they appeared together in this analysis. VOSviewer identified four clusters, as shown in Figure 5, and Table 4 presents the top ten keywords of the first three clusters and the five keywords of the fourth cluster, along with their frequency of occurrences. In Figure 5, the size of the nodes represents the frequency of occurrences, while the relative distance between nodes indicates the strength of their relationship. Figure 5 and Table 4 reveal that the largest cluster (red) consisted of 30 keywords, primarily focusing on machine learning (199 occurrences, 74 links, and 513 total links strength), deep learning, tourism market, tourist destination, online reviews, social media, sentiment analysis, and natural language processing. The second largest cluster (green) comprised 26 keywords, with a focus on “artificial intelligence” (218 occurrences, 77 links, and 487 total links strength), tourism, hospitality, hospitality industry, COVID-19, ChatGPT, robotics, and robots. The third cluster (blue) included 24 keywords, focusing on forecasting method (69 occurrences, 47 links, and 398 total links strength), China, tourism management, artificial neural network, tourism development, and demand analysis. The fourth cluster (yellow) had 5 items, with a focus on random forest, human, humans, travel, and article. These four clusters were collectively labeled as “machine learning and sentiment analysis of online reviews” (red), “adoption of AI including robots and ChatGPT in the hospitality industry” (green), “artificial neural network for tourism management and demand analysis” (blue), and “random forest models in travel” (yellow).

Table 4.
Top 10 keywords of the identified clusters (except Cluster 4, which had 5 keywords).
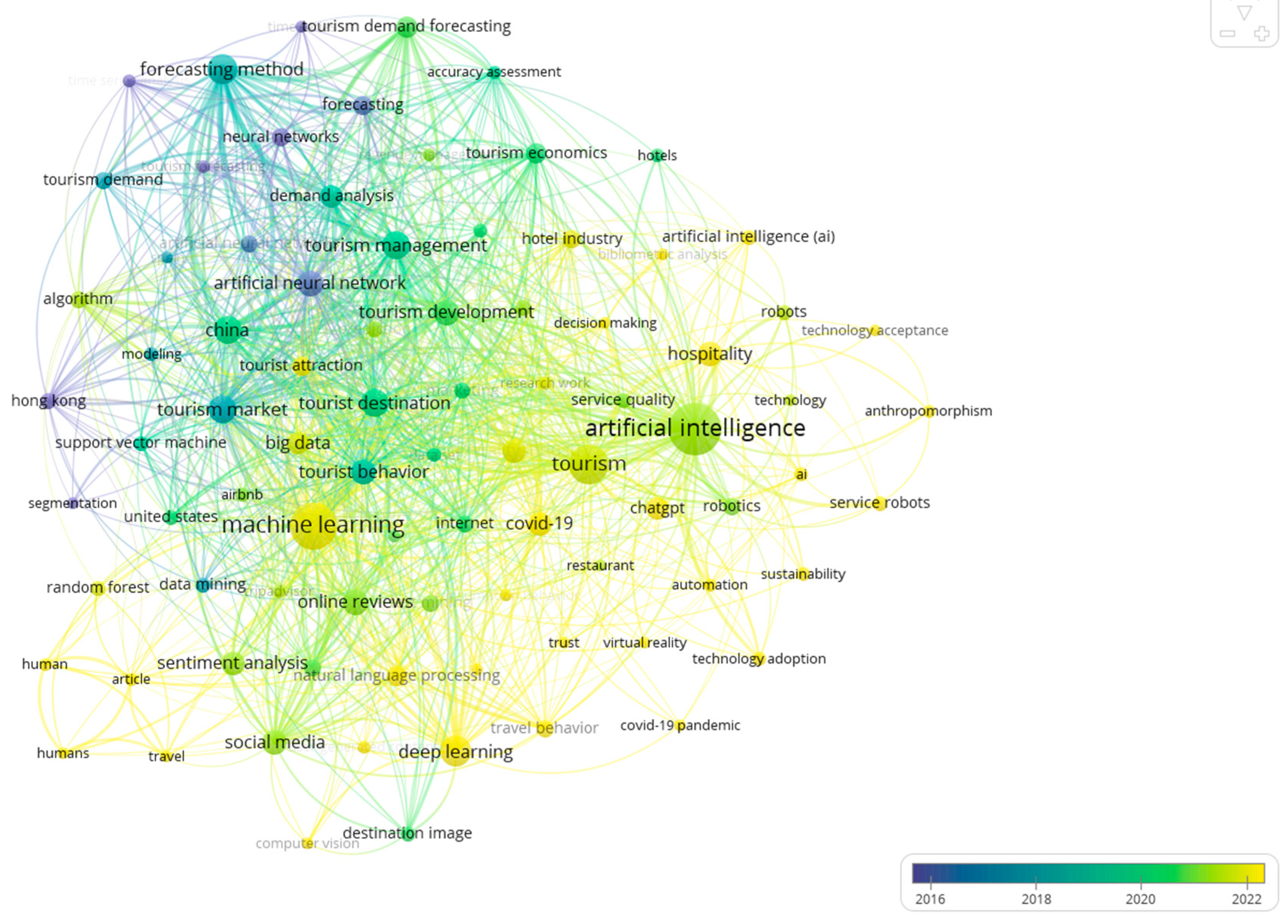
Figure 6 shows the overlay visualization map of the most frequently used keywords identified in the study. Keywords that appeared earlier are represented in purple, while those with a more recent appearance are colored in yellow. In the initial phase, specifically in 2016 or earlier, the predominant topics included “time series analysis”, forecasting”, “tourism forecasting”, “artificial neural network”, and “neural networks”. As time progressed, particularly around 2018, topics such as “forecasting method”, “tourism management”, “tourist destination”, and “China” gained popularity, represented in green. More recent keywords, like “artificial intelligence”, “social media”, “sentiment analysis”, and “online reviews”, were colored in light green, indicating their recent rise in popularity around 2021. Finally, keywords such as “machine learning”, “deep learning”, “COVID-19”, “hospitality”, “technology adoption”, and “ChatGPT” were colored in yellow, particularly around 2023–2024, suggesting that these topics have garnered increasing attention and will become research hotspots in the near future.
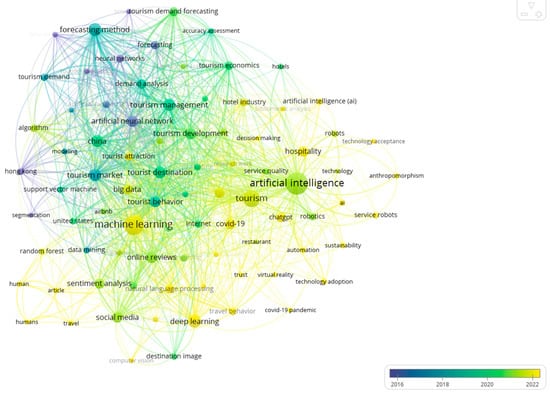
Figure 6.
Overlay visualization map of the most frequently used keywords.
4.4.4. Trend Topics
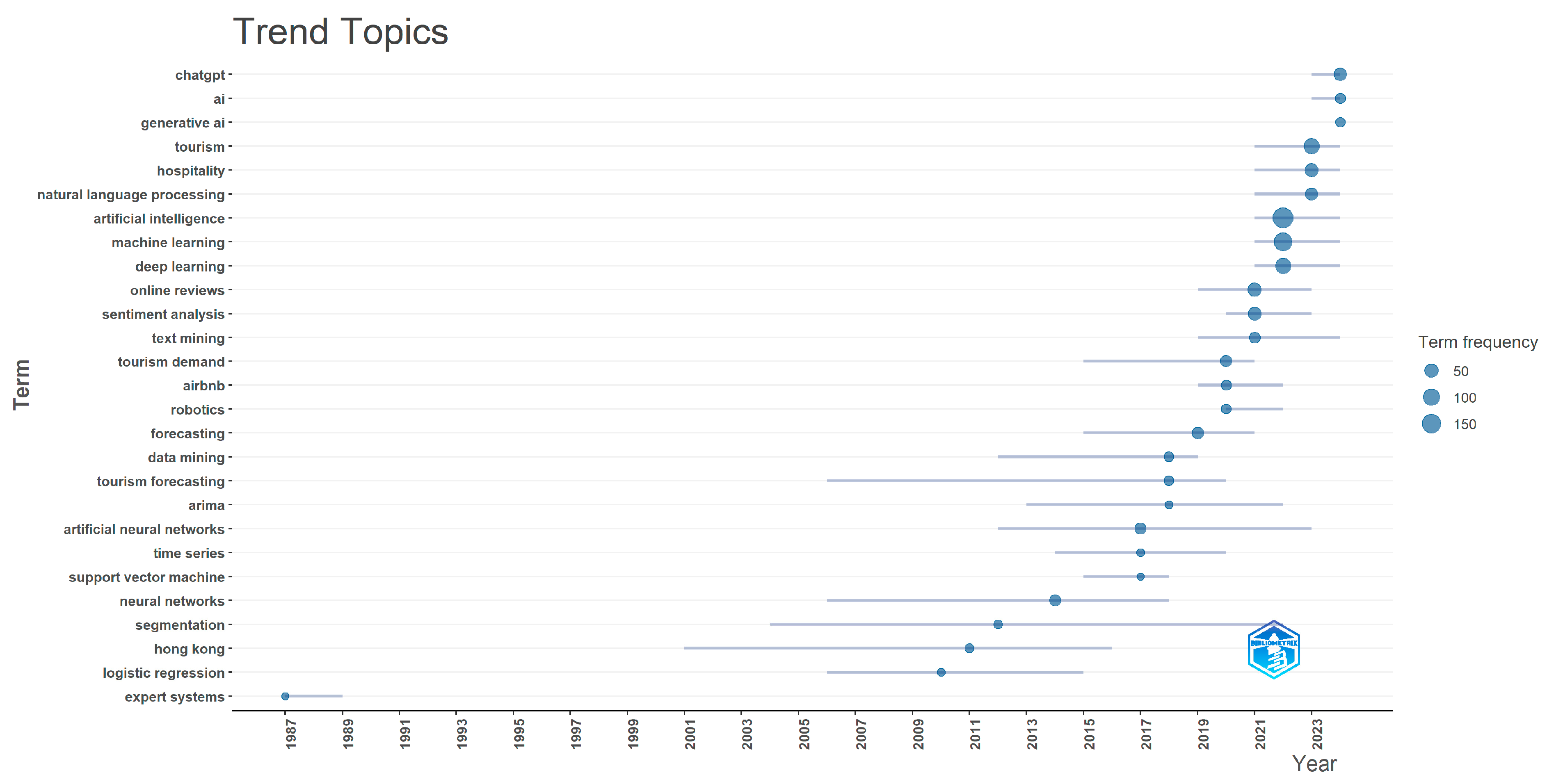
Figure 7 depicts the trend topics derived from author keywords generated by Biblioshiny. It demonstrates that the majority of previous research endeavors, specifically before 2016, concentrated on the use of expert systems, logistic regression, and neural networks within the field of tourism research. However, following 2016, there was a shift toward exploring artificial neural networks for forecasting tourism demand, as well as engaging in data mining, text mining of online reviews, and sentiment analysis. Recently, research attention has been directed toward deep learning, machine learning, natural language processing, ChatGPT, and generative AI, which have merged as prominent areas of study.
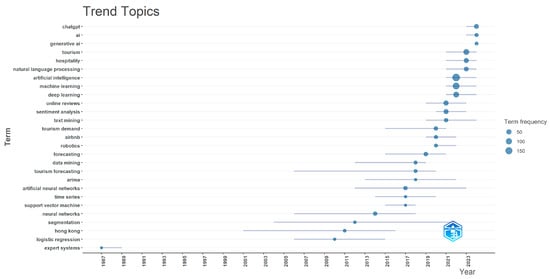
Figure 7.
Trend topics.
4.5. The Rise of Generative AI
When the search was focused on (“generative artificial intelligence” OR “generative AI” OR “ChatGPT”), specifically the last three key terms mentioned in Section 3.1, in the “Title, Abstract, and Keywords” AND (tourism OR hospitality OR travel OR leisure OR tourist OR vacation OR destination) in the “Source Title”, it yielded a total of 50 documents (48 articles and 2 reviews in journals). Among these, 15 were published in 2023 and 35 in 2024. The launch of ChatGPT on 30 November 2022 generated considerable interest in generative AI. Its applications and potential have been extensively discussed across various disciplines, including tourism and hospitality research, over the past two years. When the number of documents was considered, it was found that four researchers, namely, Y.K. Dwivedi, S. Ivanov, J. Kim, and R. Law, have authored or co-authored three publications each about generative AI. Additionally, another 13 researchers have authored or co-authored two publications each about this topic.
Among the 50 identified articles, the article titled “ChatGPT for tourism: Applications, benefits and risks” became the most cited article on ChatGPT in tourism and hospitality research (Carvalho & Ivanov, 2024). It was first published online in April 2023 and officially released with volume and page numbers in February 2024 in Tourism Review. This article has garnered 208 citations. Additionally, four other notable articles (Dwivedi et al., 2024; Gursoy et al., 2023; Iskender, 2023; Ivanov & Soliman, 2023) had citations ranging from 122 to 180, as detailed in Table 5. Carvalho and Ivanov (2024), Dwivedi et al. (2024), and Gursoy et al. (2023) examined how ChatGPT can be applied in the tourism and hospitality industry. They highlighted the potential advantages of using ChatGPT and other large language models to improve productivity and efficiency in both frontline and back-office tasks, while also facilitating the creation and delivery of personalized services in tourism businesses. Moreover, tourists can find engaging tourism-related information, receive helpful tips, and make better travel choices (Carvalho & Ivanov, 2024). Conversely, Iskender (2023) and Ivanov and Soliman (2023) investigated ChatGPT’s impact on tourism education and research, particularly in academic writing and publishing tasks.

Table 5.
The most highly cited generative AI publications in tourism and hospitality research.
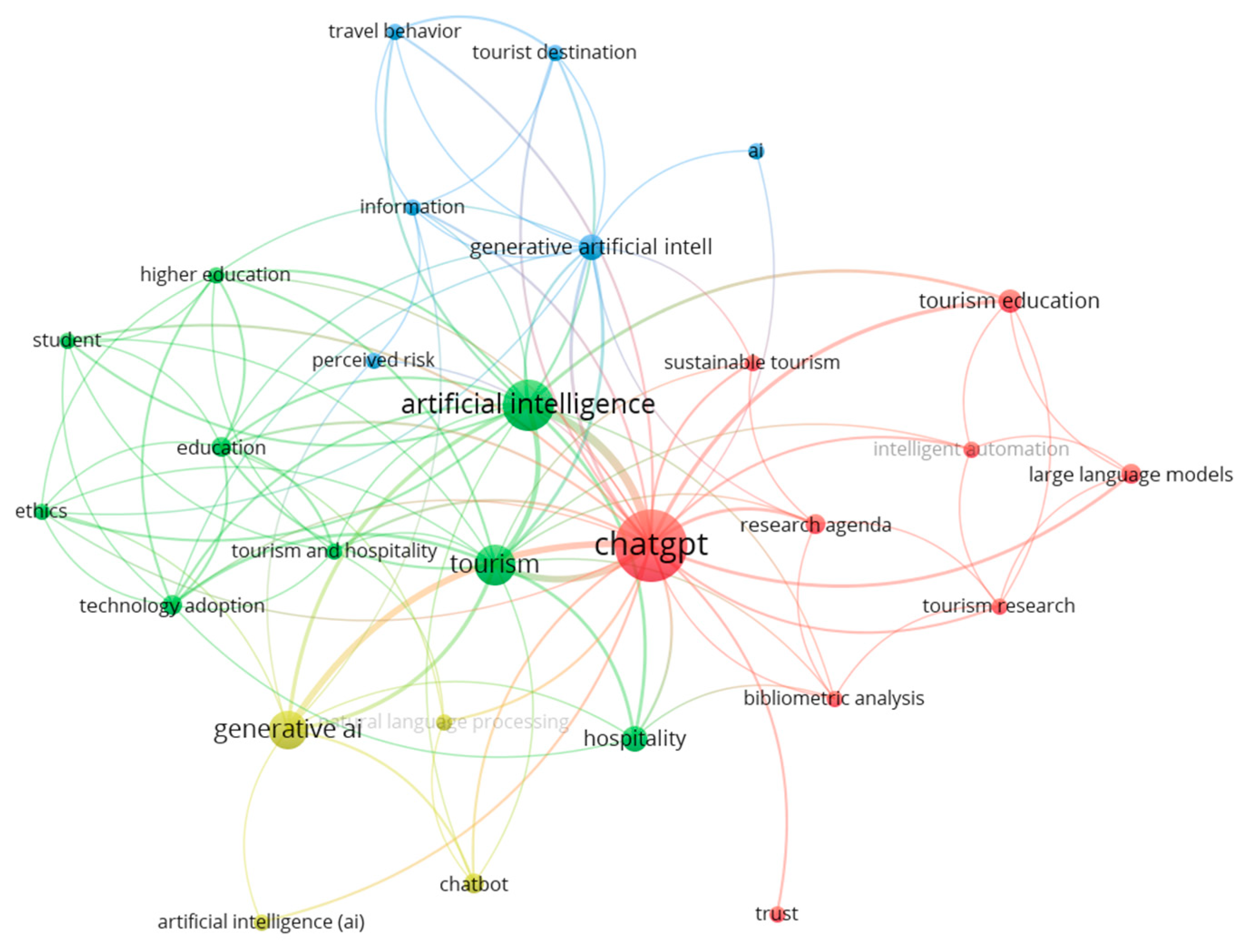
Cluster analysis was performed on keyword co-occurrences within the 50 generative AI documents. When the minimum number of keyword occurrences was set to 2, 28 out of the 207 identified keywords met the threshold. Figure 8 reveals the formation of four clusters. The largest cluster (red) consisted of nine keywords, primarily centered on ChatGPT, tourism education, large language models, research agenda, bibliometric analysis, intelligent automation, sustainable tourism, tourism research, and trust. The second largest cluster (green) also comprised nine keywords, focusing on artificial intelligence, tourism, hospitality, education, technology adoption, ethics, higher education, student, and tourism and hospitality. The third cluster (blue) included six keywords, emphasizing generative artificial intelligence, AI, information, perceived risk, tourist destination, and travel behavior. The fourth cluster (yellow) contained four keywords, with a focus on generative AI, chatbot, artificial intelligence (AI), and natural language processing. The first two clusters primarily addressed the applications and impacts of ChatGPT and artificial intelligence on tourism research and education. The third cluster emphasized the effects of generative AI and perceived risk on travel behavior, while the fourth cluster focused on chatbots and natural language processing. When the frequency of occurrences was considered, 12 keywords were identified to occur at least 3 times. Among the 50 documents, the keyword “ChatGPT” was the most popular, appearing 41 times. It was followed by “artificial intelligence” with 20 occurrences, “tourism” with 13, and “generative AI” with 11 occurrences. Additionally, the keywords “hospitality” and “generative artificial intelligence” each appeared five times, while the other keywords, “large language models”, “research agenda”, “education”, “technology adoption”, and “chatbot”, each appeared three times.
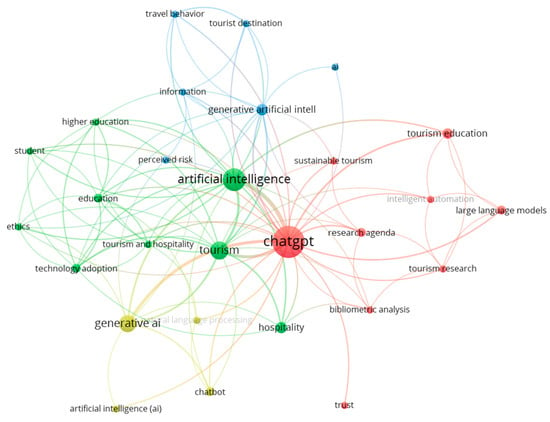
Figure 8.
Keyword co-occurrences of generative AI-related articles.
5. Discussion
The use of AI in tourism and hospitality has gone through a prolonged period of development and it started to take off in 2018 (Figure 2). Performance analysis showed that China is a major player in this field, having the most productive author and the top three institutions. China also leads in the number of publications, with 262 papers and reviews, while the United States and the United Kingdom follow with 201 and 105 publications, respectively. Among the journals, Tourism Management was found to be the most popular journal with 80 publications, followed by The International Journal of Hospitality Management (77 publications) and The International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management (73 publications), as shown in Table 2.
Table 3 presents an overview of the most highly cited publications in tourism and hospitality research, shedding light on key topics and their implications for the industry. It demonstrates the significance of specific studies, particularly the one with the highest citation counts per year, which delved into the impact of COVID-19 on hotel marketing and management (Jiang & Wen, 2020). Another article entitled “Adoption of robotics in response to the pandemic” by Zeng et al. (2020) also received around 90 citations per year, with the total citations at 448. These two works underscore the strategies for crisis management through technological innovation in the tourism and hospitality industry. The emphasis on big data signifies a growing trend toward utilizing data-driven insights to understand consumer behavior and enrich the overall tourism experience (Alaei et al., 2019; Cheng & Jin, 2019; Xiang et al., 2017). Additionally, the comprehensive reviews published by a reputable journal acknowledge the importance of automation in shaping the future of tourism (Tussyadiah, 2020), offering valuable insights into upcoming industry trends.
The co-occurrence of keywords analysis indicated closely related concepts grouped in clusters (see Figure 5 and Table 4). The foundation of utilizing present-day technologies involves “machine learning and sentiment analysis of online reviews” (red cluster) and the exploration of “random forest models in travel” (yellow cluster). These two clusters collectively utilized data analytics to obtain actionable insights into consumer preferences and explore the potential applications of demand forecasting. These modeling techniques also help in risk assessment and consumer segmentation, providing valuable information for strategic decision-making, thereby enhancing service quality and service design, as well as improving the overall tourism experience. Figure 7 further highlights that the latest applications revolve around deep learning, machine learning, generative AI, and natural language processing, such as chatbots.
The performance analysis of Chinese researchers aligned with the overlay visualization map presented in Figure 6, which illustrates the increasing prominence of China in the research landscape. This observation reflects the surge in academic publications authored by Chinese researchers (To & Yu, 2023). The theme “adoption of AI including robots and ChatGPT in the hospitality industry” highlights a transition from traditional methodologies to emerging trends. Notably, keywords like “time series analysis”, “artificial neural network”, and “neural networks” were prominent in the early stage (around 2015–2017), while newer topics, like “machine learning”, “deep learning”, and “natural language processing”, are gaining attention recently. This transition was further supported by an in-depth examination of the rise of generative AI in tourism and hospitality research, as illustrated in Table 5 and the studies by Carvalho and Ivanov (2024), Dwivedi et al. (2024), and Gursoy et al. (2023). Each of these articles has garnered nearly or over 100 citations annually. On the one hand, the idea of implementing chatbots and generative AI emphasizes the need for increased automation. However, their main focus lies in business-related initiatives. They aim to tackle challenges in the tourism and hospitality industry, particularly in response to crises, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Their overall emphasis is on data-driven decision-making in management, with the goal of optimizing resource allocation, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns to maximize revenue and enhance destination competitiveness. Conversely, the inevitable trend of incorporating chatbots and service robots necessitates a transparent application of generative AI and automation technologies in the tourism and hospitality settings (R. Yu et al., 2024).
5.1. Implications
This study on artificial intelligence in tourism and hospitality research highlighted significant progress made in this field. The emergence of generative AI offers tourism enterprises an opportunity to improve their operational efficiency. The analysis indicated that AI has become a crucial tool for strategic decision-making, risk assessment, consumer segmentation, service quality enhancement, and overall service design improvement (Tussyadiah, 2020; Alaei et al., 2019). The findings also underscore the importance of AI and automation in shaping the future of tourism, which is acknowledged by reputable journals, such as Tourism Management, The International Journal of Hospitality Management, and Annals of Tourism Research (Lu et al., 2019; Tussyadiah, 2020; Xiang et al., 2017). This trend points to the increasing reliance on data-driven insights to understand consumer behavior and enhance the tourism experience. It suggests that contemporary technologies are pivotal for promising business growth and are increasingly relevant in tourism and hospitality research (Carvalho & Ivanov, 2024; Dwivedi et al., 2024), with 15 AI-related publications out of 152 (10%) in 2023 and 35 out of 277 (12%) in 2024. Additionally, it is important to emphasize the necessity for transparent implementation of generative AI and automation technologies to maintain customer trust and satisfaction (R. Yu et al., 2024).
The methodological approach utilized in this study can be applied to other disciplines, such as business administration and marketing. The use of performance analysis, overlay visualization maps, and keyword co-occurrence analysis provided a comprehensive understanding of the current trends and key themes in AI research (see also B. T. W. Yu & Liu, 2024). The implications of this research extend beyond tourism and hospitality—it may be used for fostering student-centered learning and teaching within the fields of tourism, hospitality, and general business education (Ip & To, 2025; Ivanov & Soliman, 2023).
5.2. Limitations and Future Research
Performance analysis and science mapping depend greatly on the completeness, accuracy, and consistency of keywords from bibliometric databases. This reliance means there can be issues like missing terms, errors, and inconsistencies, such as variations in spellings and homonyms. To mitigate these issues, precautionary measures were taken during data collection and processing, including using comprehensive terms related to AI and manually checking for any omissions or mistakes. This approach aimed to reduce any negative effects on the results, leading to a more accurate representation and interpretation of the data. Additionally, the study used bibliometric data from Scopus as of 5 March 2025. The application of AI in the tourism and hospitality industry is an ongoing development, with new publications regularly appearing, which may result in slightly different bibliometric analysis outcomes. Therefore, researchers who want to track development may consider utilizing Scopus as the data source at a future time. Researchers can also validate the findings with bibliometric data from other platforms, like Web of Science or Dimensions. Lastly, it is crucial to recognize that this analysis may not have thoroughly examined certain emerging topics, such as the transition from traditional AI applications to generative AI. Although this shift was touched upon, the understanding of generative AI’s development and use was limited due to the limited availability of publications. Thus, further research is needed to fully grasp the implications and complexities of this transition, potentially through a more in-depth exploration based on geography or demographics. While there have been many successful examples of AI applications in customer relationship management (Cheng & Jin, 2019; Zeng et al., 2020), more breakthroughs are anticipated with the rise of generative AI.
6. Conclusions
This bibliometric study offered a timely analysis of the application of AI in tourism and hospitality research, as published in pertinent academic journals, utilizing both performance analysis and science mapping techniques. A search for “artificial intelligence” and related terms in the “Title, Abstract, and Keywords” within tourism and hospitality journals was performed on 5 March 2025 using Scopus. The search identified 921 documents, showing an increase in publications from 24 in 2018 to 277 in 2024. R. Law emerged as the most productive author, while D. Gursoy attained the highest citation rate per publication. The Hong Kong Polytechnic University was the top institution, and China led in contributions. The citation-based analysis showed a growing focus on using advanced AI for crisis responses, particularly highlighted by the highly cited publications discussing COVID-19’s effects on the tourism and hospitality industry. Keyword co-occurrence analysis and the overlay visualization map indicated a transition in AI-related research from the use of neural networks for forecasting to sentiment analysis, and subsequently to the adoption of deep learning, machine learning, and natural language processing. Stakeholders are encouraged to focus on technology innovation and adoption while keeping social connections. The emphasis on big data analytics underlines the importance of using data to understand consumer behavior and preferences. The success of targeted marketing strategies in providing personalized services was reaffirmed. By encouraging collaboration among tourism research, data analytics, and technology, stakeholders can better meet consumer needs and improve the overall tourism experience.
Furthermore, there has been a significant rise in generative AI research in tourism and hospitality, with many publications on its tools, such as ChatGPT, appearing in the last two years and continuing to grow. Similarly, DeepSeek may appear soon in the literature. Our findings suggested that tourism stakeholders should focus on adopting AI, utilizing data analytics, and developing crisis management strategies to adapt to the changing industry landscape and promote sustainable growth and resilience.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.M.T. and B.T.W.Y.; methodology, W.M.T.; formal analysis, W.M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, W.M.T. and B.T.W.Y.; writing—review and editing, W.M.T. and B.T.W.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Alaei, A. R., Becken, S., & Stantic, B. (2019). Sentiment analysis in tourism: Capitalizing on big data. Journal of Travel Research, 58(2), 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, J., Schotten, M., Plume, A., Côté, G., & Karimi, R. (2020). Scopus as a curated, high-quality bibliometric data source for academic research in quantitative science studies. Quantitative Science Studies, 1(1), 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, A., Cuccurullo, C., & Aria, M. (2022). IoT in healthcare: A scientometric analysis. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 184, 122001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, K., Ciftci, O., & Cobanoglu, C. (2019). Robots, artificial intelligence, and service automation in restaurants. In S. Ivanov, & C. Webster (Eds.), Robots, artificial intelligence, and service automation in travel, tourism and hospitality (pp. 185–219). Emerald Publishing Limited. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhalis, D., & Moldavska, I. (2022). Voice assistants in hospitality: Using artificial intelligence for customer service. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 13(3), 386–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhalis, D., & Sinarta, Y. (2019). Real-time co-creation and nowness service: Lessons from tourism and hospitality. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 36(5), 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I., & Ivanov, S. (2024). ChatGPT for tourism: Applications, benefits and risks. Tourism Review, 79(2), 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y. C., Ku, C. H., & Chen, C. H. (2020). Using deep learning and visual analytics to explore hotel reviews and responses. Tourism Management, 80, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K. Y., & Wang, C. H. (2007). Support vector regression with genetic algorithms in forecasting tourism demand. Tourism Management, 28(1), 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M., & Jin, X. (2019). What do Airbnb users care about? An analysis of online review comments. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 76, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarivate. (2025). Web of science core collection—Editorial selection process. Clarivate. Available online: https://clarivate.com/products/scientific-and-academic-research/research-discovery-and-workflow-solutions/webofscience-platform/web-of-science-core-collection/editorial-selection-process/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Support-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, J. C. (1972). A bibliometric analysis of certain information science literature. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 23(5), 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N., Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, Y. K., Pandey, N., Currie, W., & Micu, A. (2024). Leveraging ChatGPT and other generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based applications in the hospitality and tourism industry: Practices, challenges and research agenda. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 36(1), 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusté-Forné, F., & Jamal, T. (2021). Co-creating new directions for service robots in hospitality and tourism. Tourism and Hospitality, 2(1), 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, S., Nissan, E., & Shur, A. (1987). The ‘Wining and dining’ project—I. ‘The wine adviser’, a deductive database. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 6(4), 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudin, J. (2009). AI and HCI: Two fields divided by a common focus. AI Magazine, 30(4), 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy, D., Li, Y., & Song, H. (2023). ChatGPT and the hospitality and tourism industry: An overview of current trends and future research directions. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 32(5), 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacus, S. M., Natale, F., Santamaria, C., Spyratos, S., & Vespe, M. (2020). Estimating and projecting air passenger traffic during the COVID-19 coronavirus outbreak and its socio-economic impact. Safety Science, 129, 104791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, S. W. S., & To, W. M. (2025). Effects of online learning readiness and online self-regulated English learning on satisfaction with online English learning experience during the COVID-19 pandemic. Behavioral Sciences, 15(1), 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskender, A. (2023). Holy or unholy? Interview with open AI’s ChatGPT. European Journal of Tourism Research, 34, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, S., & Soliman, M. (2023). Game of algorithms: ChatGPT implications for the future of tourism education and research. Journal of Tourism Futures, 9(2), 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y., & Wen, J. (2020). Effects of COVID-19 on hotel marketing and management: A perspective article. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 32(8), 2563–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, L., & Yu, B. (2013). Spreading social media messages on Facebook: An analysis of restaurant business-to-consumer communications. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 54(1), 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R. (2000). Back-propagation learning in improving the accuracy of neural network-based tourism demand forecasting. Tourism Management, 21(4), 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R., & Au, N. (1999). A neural network model to forecast Japanese demand for travel to Hong Kong. Tourism Management, 20(1), 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R., Li, G., Fong, D. K. C., & Han, X. (2019). Tourism demand forecasting: A deep learning approach. Annals of Tourism Research, 75, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, X. Y. (2020). Technology-enabled service evolution in tourism: A perspective article. Tourism Review, 75(1), 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E. (1990). A recurrent neural network: Limitations and training. Neural Networks, 3(6), 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. J., Bonn, M. A., & Ye, B. H. (2019). Hotel employee’s artificial intelligence and robotics awareness and its impact on turnover intention: The moderating roles of perceived organizational support and competitive psychological climate. Tourism Management, 73, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W. M., & To, W. M. (2022). The economic impact of a global pandemic on the tourism economy: The case of COVID-19 and Macao’s destination-and gambling-dependent economy. Current Issues in Tourism, 25(8), 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I. Y., & Mattila, A. S. (2021). The value of service robots from the hotel guest’s perspective: A mixed-method approach. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 94, 102876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L., Cai, R., & Gursoy, D. (2019). Developing and validating a service robot integration willingness scale. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 80, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, J., Minsky, M. L., Rochester, N., & Shannon, C. E. (1956). A proposal for the Dartmouth summer research project on artificial intelligence. Dartmouth College. Available online: https://250.dartmouth.edu/highlights/artificial-intelligence-ai-coined-dartmouth (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Melián-González, S., Gutiérrez-Taño, D., & Bulchand-Gidumal, J. (2021). Predicting the intentions to use chatbots for travel and tourism. Current Issues in Tourism, 24(2), 192–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minsky, M. L. (1956). Heuristic aspects of the artificial intelligence problem. Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lincoln Laboratory. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, H. G., Pandita, S., Bhat, A. A., Mishra, R. K., & Sharma, S. (2022). Tourism and carbon emissions: A bibliometric review of the last three decades: 1990–2021. Tourism Review, 77(2), 636–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monmousseau, P., Marzuoli, A., Feron, E., & Delahaye, D. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 on passengers and airlines from passenger measurements: Managing customer satisfaction while putting the US Air Transportation System to sleep. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, 7, 100179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, H. C., & de Jongh, H. (2011). Student perceptions of information system subject learning in hospitality management degree programmes: A study of contexts for “deep learning”. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 23(3), 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissan, E. (1987). The ‘Wining and dining’ project—II. ‘Fidel-Gastro’ an expert system for gastronomy and terminal food-processing. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 6(4), 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orden-Mejia, M., & Huertas, A. (2022). Analysis of the attributes of smart tourism technologies in destination chatbots that influence tourist satisfaction. Current Issues in Tourism, 25(17), 2854–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J. M., & Moher, D. (2021). Updating guidance for reporting systematic reviews: Development of the PRISMA 2020 statement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 134, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R., & Sivathanu, B. (2020). Adoption of AI-based chatbots for hospitality and tourism. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 32(10), 3199–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhanen, L. (2006). Bridging the divide between theory and practice: Experiential learning approaches for tourism and hospitality management education. Journal of Teaching in Travel & Tourism, 5(4), 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputra, F. E., Buhalis, D., Augustyn, M. M., & Marangos, S. (2024). Anthropomorphism-based artificial intelligence (AI) robots typology in hospitality and tourism. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 15(5), 790–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopus. (2025). Content policy and selection. Scopus. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/products/scopus/content/content-policy-and-selection (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Shi, J., Lee, M., Girish, V. G., Xiao, G., & Lee, C.-K. (2024). Embracing the ChatGPT revolution: Unlocking new horizons for tourism. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 15(3), 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. K., Singh, P., Karmakar, M., Leta, J., & Mayr, P. (2021). The journal coverage of Web of Science, Scopus and Dimensions: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics, 126, 5113–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X., Li, Y., Leung, X. Y., & Mei, D. (2024). Service robots and hotel guests’ perceptions: Anthropomorphism and stereotypes. Tourism Review, 79(2), 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W. M., & Lee, P. K. C. (2024). Modeling of the COVID-19 impact on air passenger traffic in the US, European countries, and China. Journal of Air Transport Management, 115, 102556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W. M., & Yu, B. T. W. (2023). Rise in higher education researchers and academic publications. Emerald Open Research, 1(3), 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, W. M., Yu, B. T. W., Chung, A. W. L., & Chung, W. K. (2024). Metaverse: Trend, emerging themes, and future directions. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 35(1), e4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tussyadiah, I. (2020). A review of research into automation in tourism: Launching the Annals of Tourism Research Curated Collection on artificial intelligence and robotics in tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 81, 102883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, S. (2016). Major transitions in information technology. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371(1701), 20150450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varzakas, I. P., & Metaxas, T. (2024). Pandemic and economy: An econometric analysis investigating the impact of COVID-19 on the global tourism market. Tourism and Hospitality, 5(2), 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Travel & Tourism Council. (2021). Travel & tourism—Global economic impact & trends 2021. World Travel & Tourism Council. [Google Scholar]
- World Travel & Tourism Council. (2023). Travel & tourism—Economic impact 2023. World Travel & Tourism Council. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z., Du, Q., Ma, Y., & Fan, W. (2017). A comparative analysis of major online review platforms: Implications for social media analytics in hospitality and tourism. Tourism Management, 58, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B. T. W., & Liu, S. T. X. (2024). Deep learning application for marketing engagement–its thematic evolution. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G., & Schwartz, Z. (2006). Forecasting short time-series tourism demand with artificial intelligence models. Journal of Travel Research, 45(2), 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R., Feng, J., Wang, K., Yang, L., & Feng, J. (2024). Who are you talking to? How chatbot identity disclosure affects service satisfaction. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 41(8), 1090–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z., Chen, P. J., & Lew, A. A. (2020). From high-touch to high-tech: COVID-19 drives robotics adoption. Tourism Geographies, 22(3), 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K., Chen, Y., & Li, C. (2019). Discovering the tourists’ behaviors and perceptions in a tourism destination by analyzing photos’ visual content with a computer deep learning model: The case of Beijing. Tourism Management, 75, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Ouyang, S., & Tavitiyaman, P. (2022). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on generation Z employees’ perception and behavioral intention toward advanced information technologies in hotels. Tourism and Hospitality, 3(2), 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T., Wu, F., Law, R., Qiu, W., & Wu, R. (2021). Identifying unreliable online hospitality reviews with biased user-given ratings: A deep learning forecasting approach. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 92, 102658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L., Sun, S., Law, R., Li, X., & Deng, B. (2023). Health tourism in China: A 40-year bibliometric analysis. Tourism Review, 78(1), 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).