Enzymatic Degradation of Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composite Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enzymatic Degradation with Proteinase K
2.2. Lactic acid Concentration Measurement
- V = final volume [mL]
- = sample volume [mL]
- = molecular weight of the substance to be assayed [g/mol]
- d = light path [cm]
- ε = extinction coefficient of NADH at: 340 nm = 6.3 [l × mmol−1 × cm−1]
- = ∆Asample − ∆Ablank
- ∆Asample = A2 − A1
- ∆Ablank = A2 − A1
3. Results and Discussion
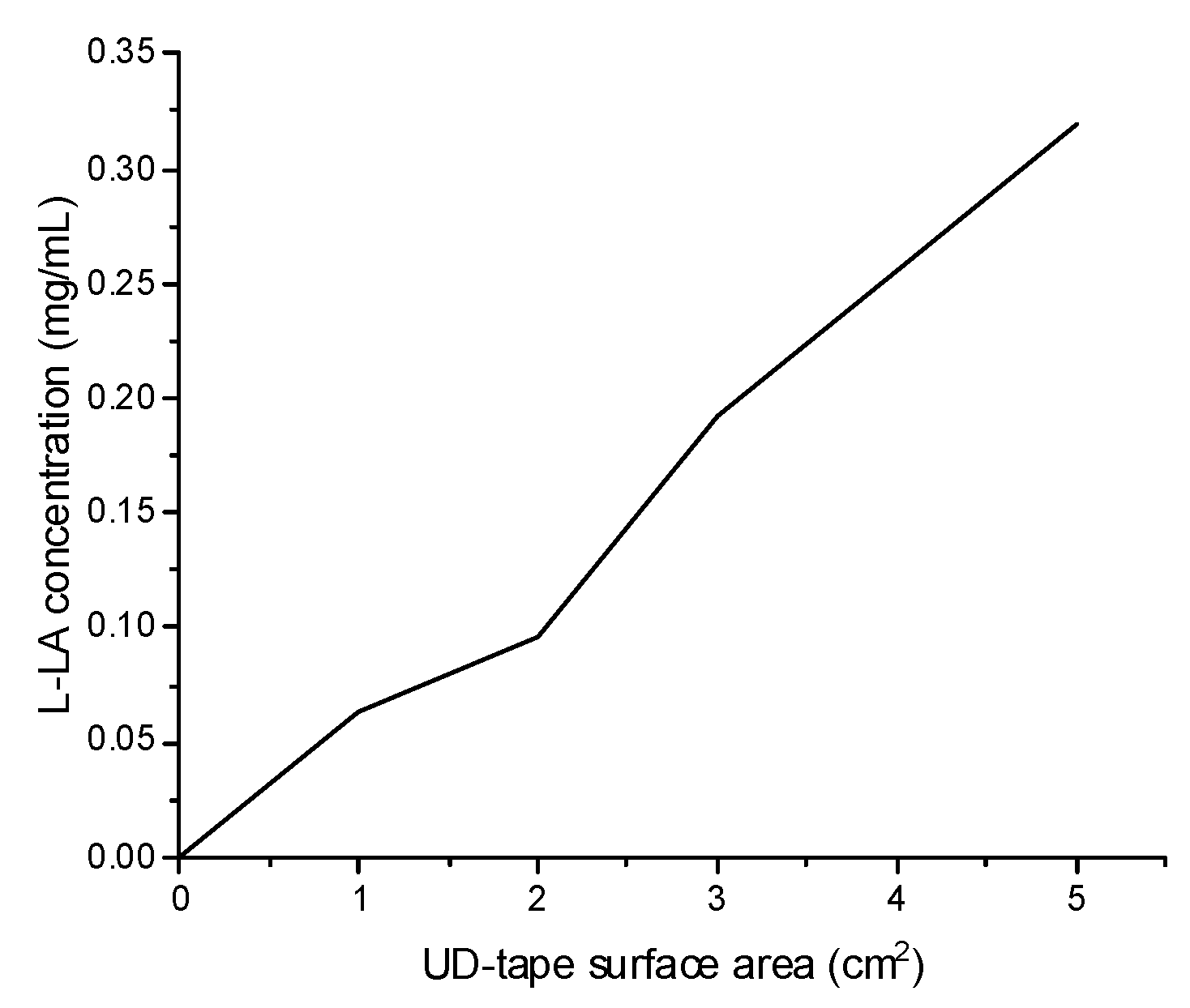
3.1. Enzymatic Degradation of PLA-UD Tapes
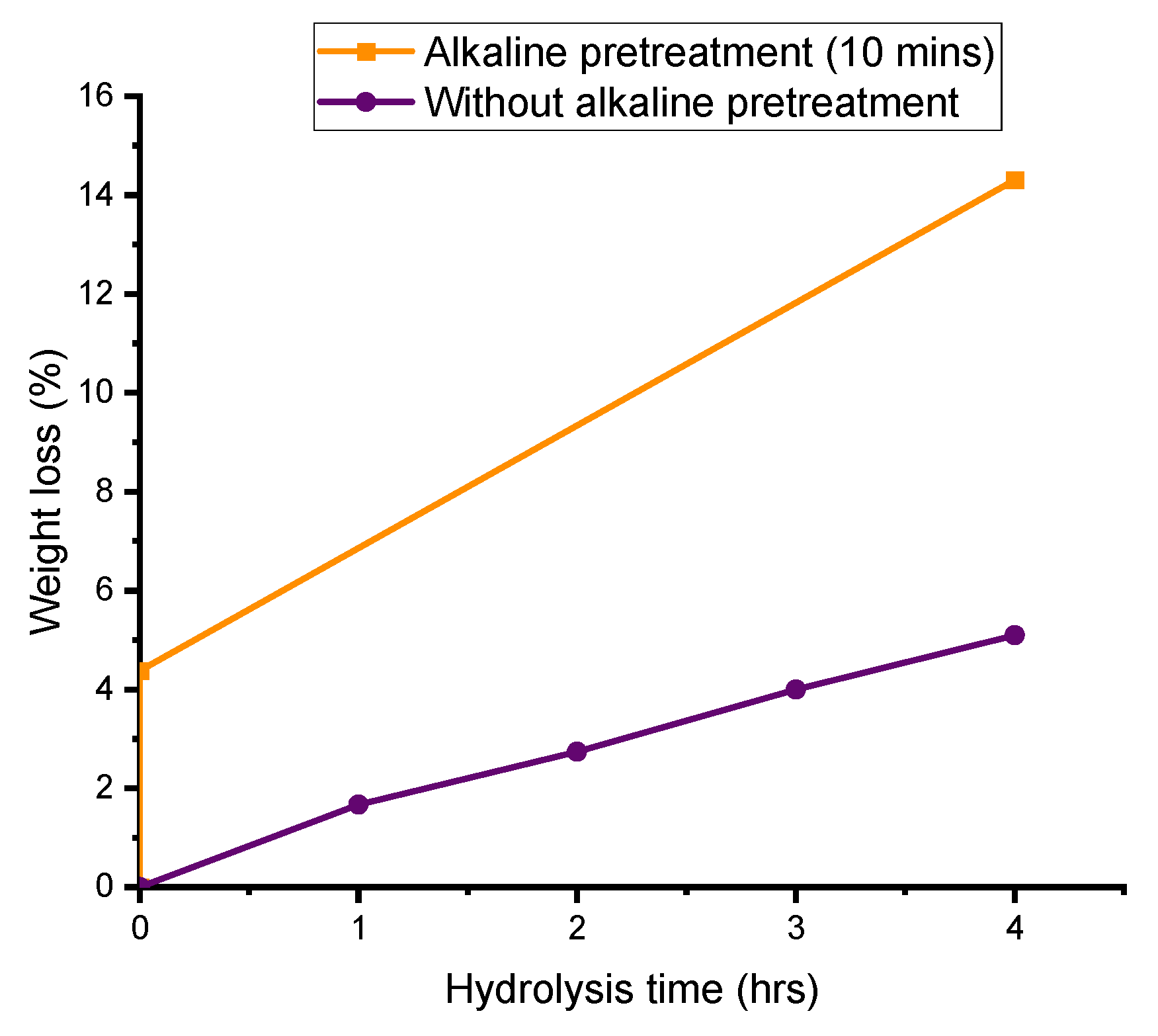
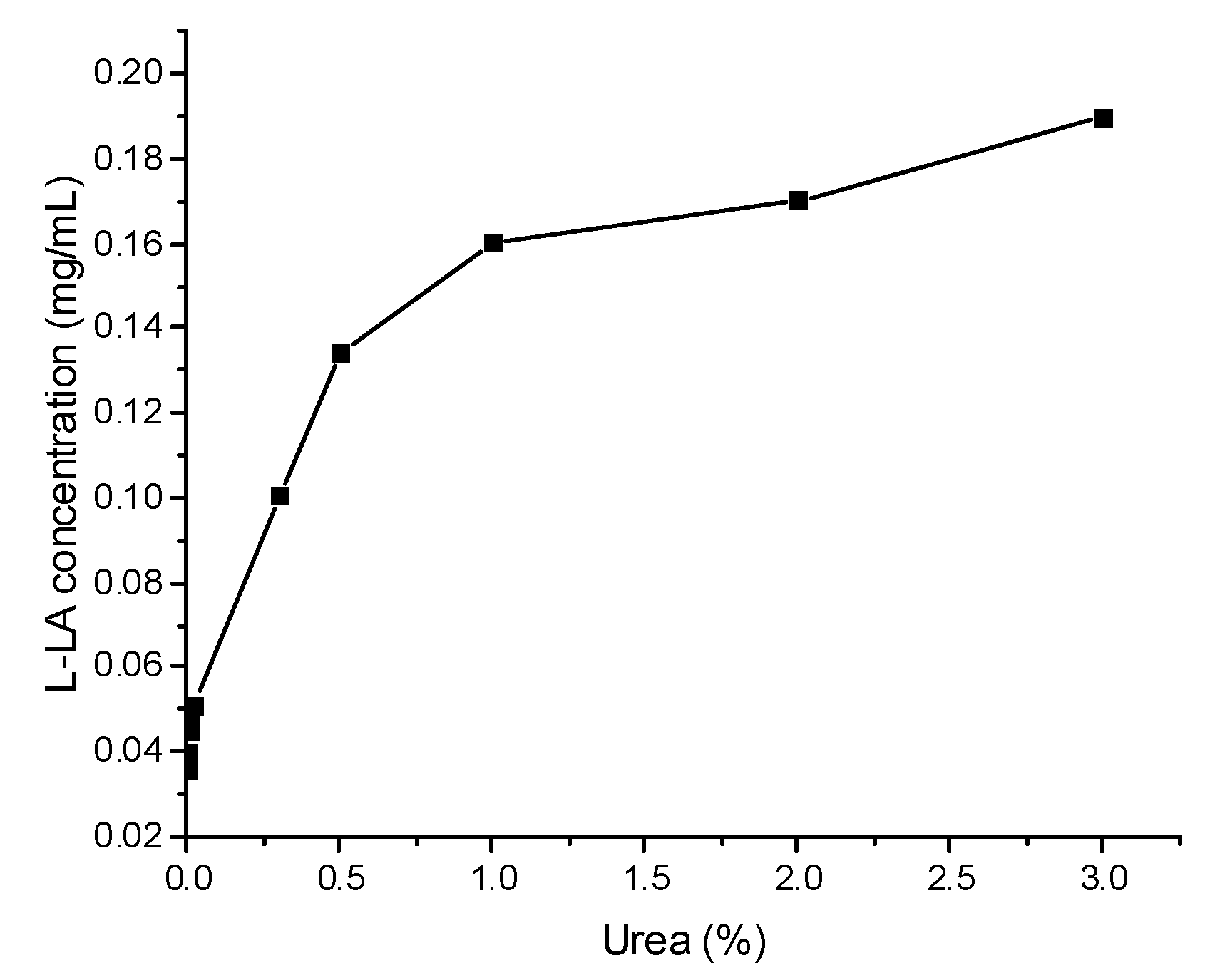
3.2. Enhancement of Enzymatic Degradation by Alkali Pretreatment and Urea
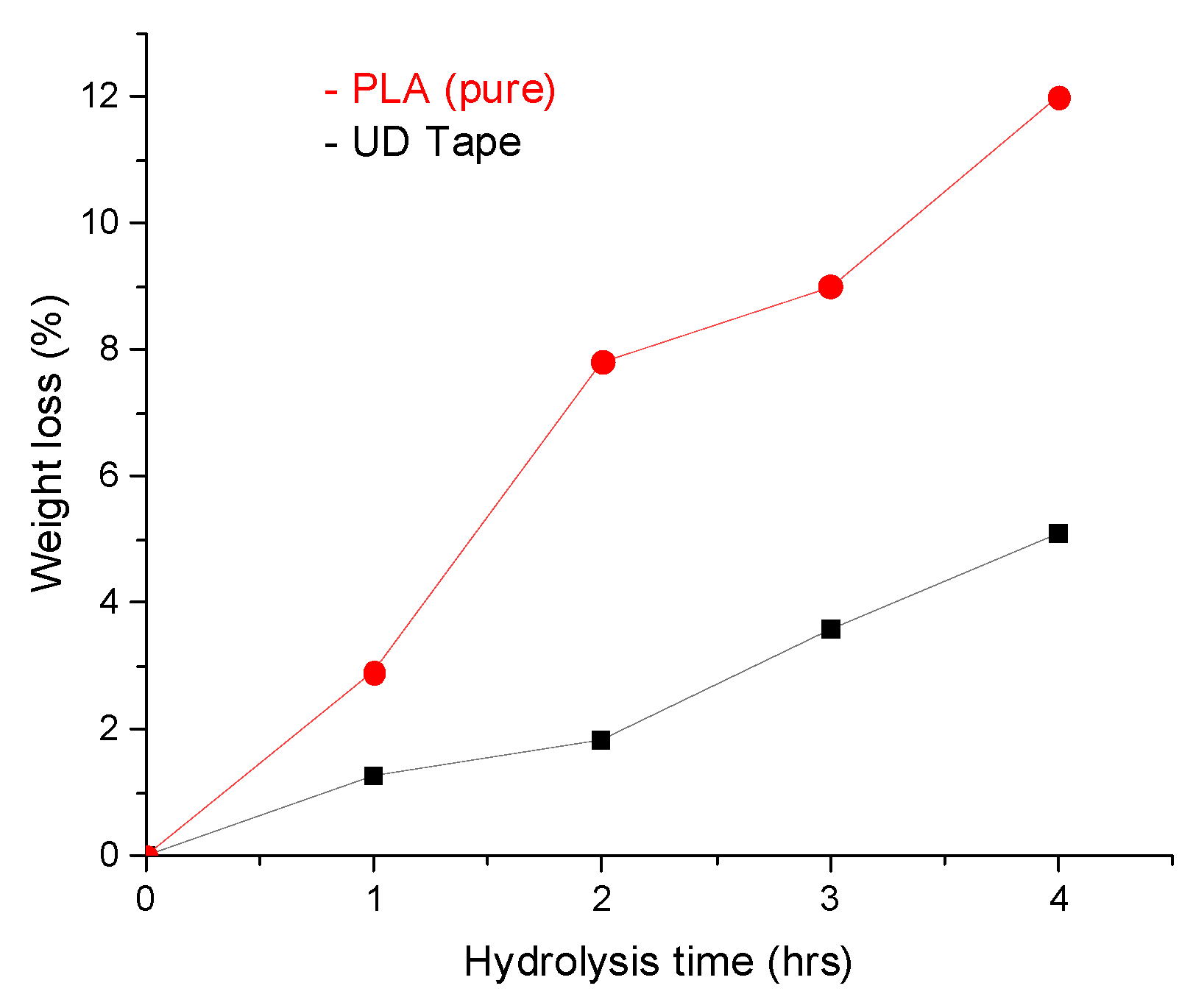
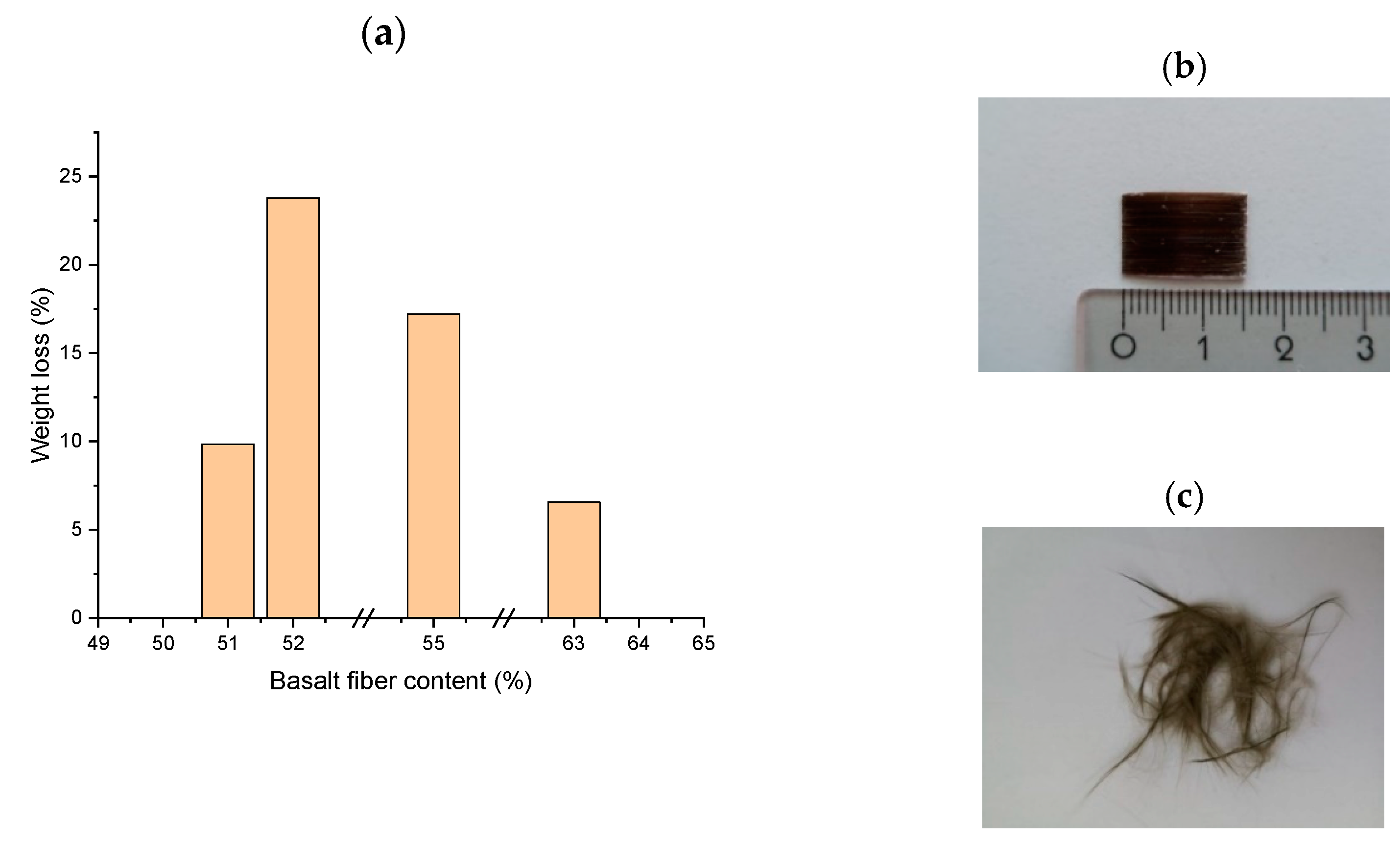
3.3. Effect of Fiber Content and PLA Type on the Degradation of PLA
3.4. Estimates for Industrial-Scale Hydrolysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bledzki, A.K.; Seidlitz, H.; Goracy, K.; Urbaniak, M.; Rösch, J.J. Recycling of carbon fiber reinforced composite polymers—Review—Part 1: Volume of production, recycling technologies, legislative aspects. Polymers 2021, 13, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlioglu, M.; Preziosi, R.; Robson, G. Abiotic and biotic environmental degradation of the bioplastic polymer poly (lactic acid): A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 137, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Cui, J. Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of Basalt Fibers in Sodium Hydroxide Solution. Materials 2018, 11, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Jaafar, M. A review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: Hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Deng, S.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Polylactic acid (PLA) synthesis and modifications: A review. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avérous, L. Polylactic Acid: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. In Monomers, Polymers and Composites from Renewable Resources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 433–450. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Aguirre, E.; Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Samsudin, H.; Fang, X.; Auras, R. Poly(lactic acid)-Mass production, processing, industrial applications, and end of life. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 333–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M.; Dolan, K.; Soto-Valdez, H.; Selke, S. Control of Hydrolytic Degradation of Poly(Lactic Acid) by Incorporation of Chain Extender: From Bulk to Surface Erosion. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 146, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.B.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.Z. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the long-term hydrolytic degradation behavior of PLA. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husárová, L.; Pekařová, S.; Stloukal, P.; Kucharzcyk, P.; Verney, V.; Commereuc, S.; Ramone, A.; Koutny, M. Identification of important abiotic and biotic factors in the biodegradation of poly(l-lactic acid). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X. New advances in the biodegradation of Poly(lactic) acid. Inter Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 117, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ogiwara, M.; Saha, S.K.; Sakaki, T. Enzymatic, Alkaline, and Autocatalytic Degradation of Poly(L-lactic acid): Effects of Biaxial Orientation. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegyesi, N.; Zhang, Y.; Kohári, A.; Polyák, P.; Sui, X.; Pukánszky, B. Enzymatic degradation of PLA/cellulose nanocrystal composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, M.; Chen, L. Interface and bonging mechanism of plant fiber composites: An overview. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 101, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruffen, C.; Mahltig, B. Basalt fibers as functional additives in coating of textiles. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2021, 18, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghini, M.C.; Touchard, F.; Sarasini, F.; Cech, V.; Chocinski-Arnault, L.; Mellier, D.; Tirillo, J.; Bracciale, M.P.; Zvonek, M. Interfacial Adhesion of Basalt Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites. In Proceedings of the Twenty Second International Conference on Composite Materials (ICCM22), Melbourne, Australia, 11–16 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Chen, X.; Liang, Q.; Xu, X.; Jing, X. Enzymatic Degradation of Poly(L-lactide) and Poly(ε-caprolactone) Electrospun Fibers. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Cimmino, S.; Silvestre, C. Effect of TiO2 and ZnO on PLA degradation in various media. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Crawford, K.; Gorman, C.B. Effects of temperature and pH on the degradation of poly(lactic acid) brushes. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4777–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillner, B.; Moser, K.; Hanstein, S. Sustainable Light-Weight Solutions Based on PLA and Basalt Fibers. AVK Compos. Rep. 2021, 4, 16–17. Available online: https://www.avk-tv.de/files/publications/files/avk_compositesreport4_gb_komprimiert.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Ku, H.; Wang, H.; Pattarachaiyakoop, N.; Trada, M. A review on the tensile properties of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos. Part B 2011, 42, 856–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Matsuzawa, H.; Ohta, T. Stability of thermostable enzyme, aqualysin I; a subtilisin-type serine protease from Thermus aquaticus YT-1. Biosc. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1998, 62, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansson, O.; Valgren, C.; Wester, S. Proteinase K challenged by a novel protease. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 2008, 1, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genov, N.; Filippi, B.; Dolashka, P.; Wilson, K.S.; Betzel, C. Stability of subtilisins and related proteinases (subtilases). Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1995, 45, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazawa, K.; Sugahara, M.; Yutani, K.; Takehira, M.; Numata, K. Derivatization of Proteinase K with Heavy Atoms Enhances Its Thermal Stability. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3036–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urinov, E.; Hanstein, S.; Weidenkaff, A. Enzymatic Degradation of Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composite Material. Macromol 2022, 2, 522-530. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2040033
Urinov E, Hanstein S, Weidenkaff A. Enzymatic Degradation of Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composite Material. Macromol. 2022; 2(4):522-530. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2040033
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrinov, Eldor, Stefan Hanstein, and Anke Weidenkaff. 2022. "Enzymatic Degradation of Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composite Material" Macromol 2, no. 4: 522-530. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2040033
APA StyleUrinov, E., Hanstein, S., & Weidenkaff, A. (2022). Enzymatic Degradation of Fiber-Reinforced PLA Composite Material. Macromol, 2(4), 522-530. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol2040033






