Innovations in Proteomic Technologies and Artificial Neural Networks: Unlocking Milk Origin Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
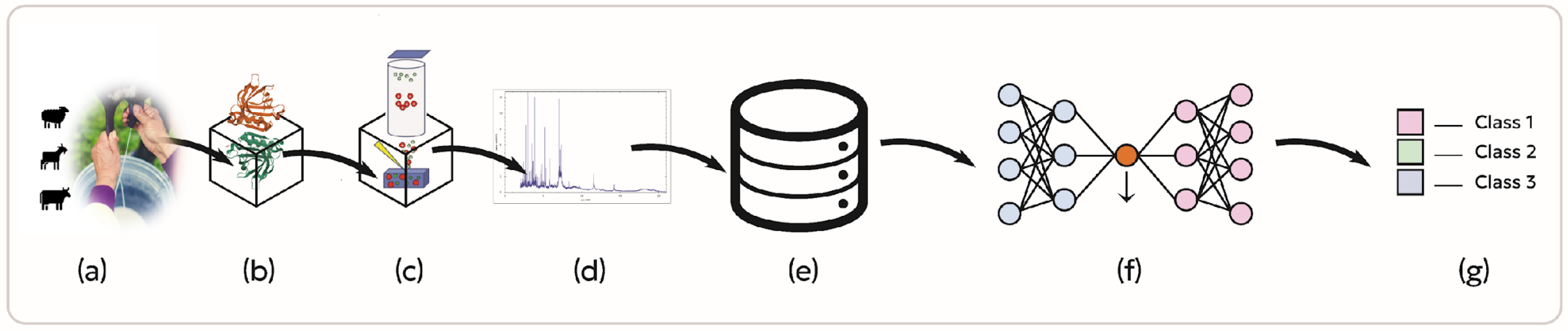
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
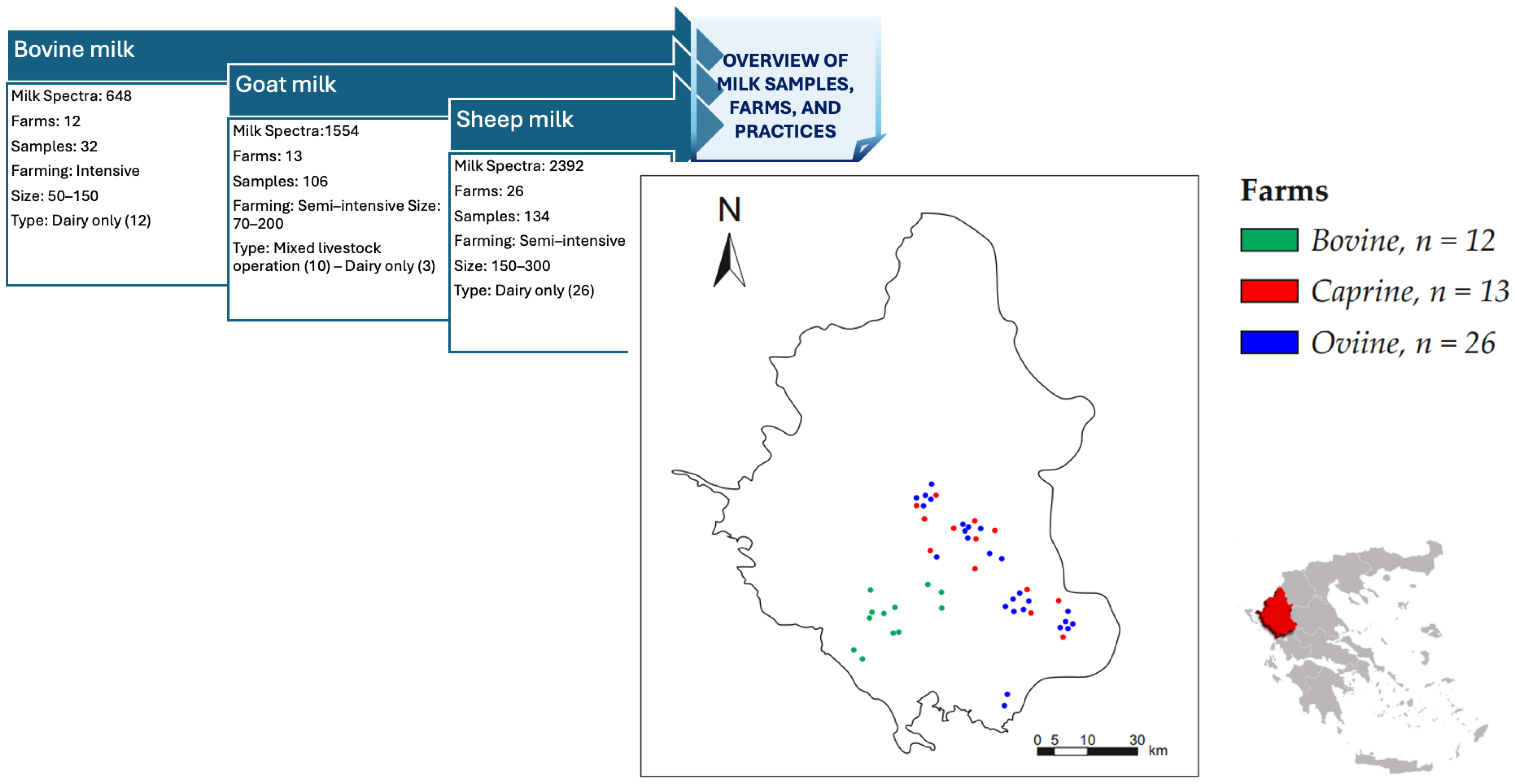
2.1.1. Milk Sampling and Laboratory Acquisition
2.1.2. Protein/Peptide Precipitation
2.1.3. Protein Extraction and Isolation Process
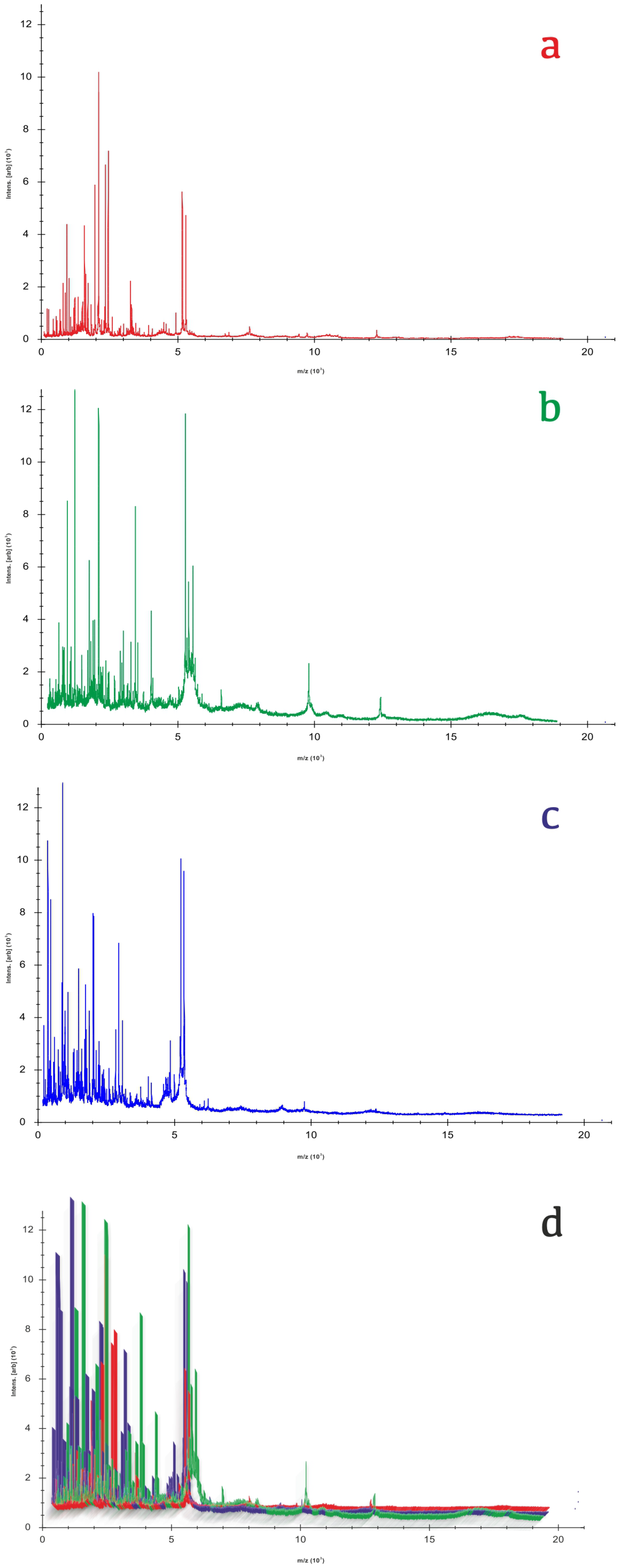
2.2. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Data Preprocessing
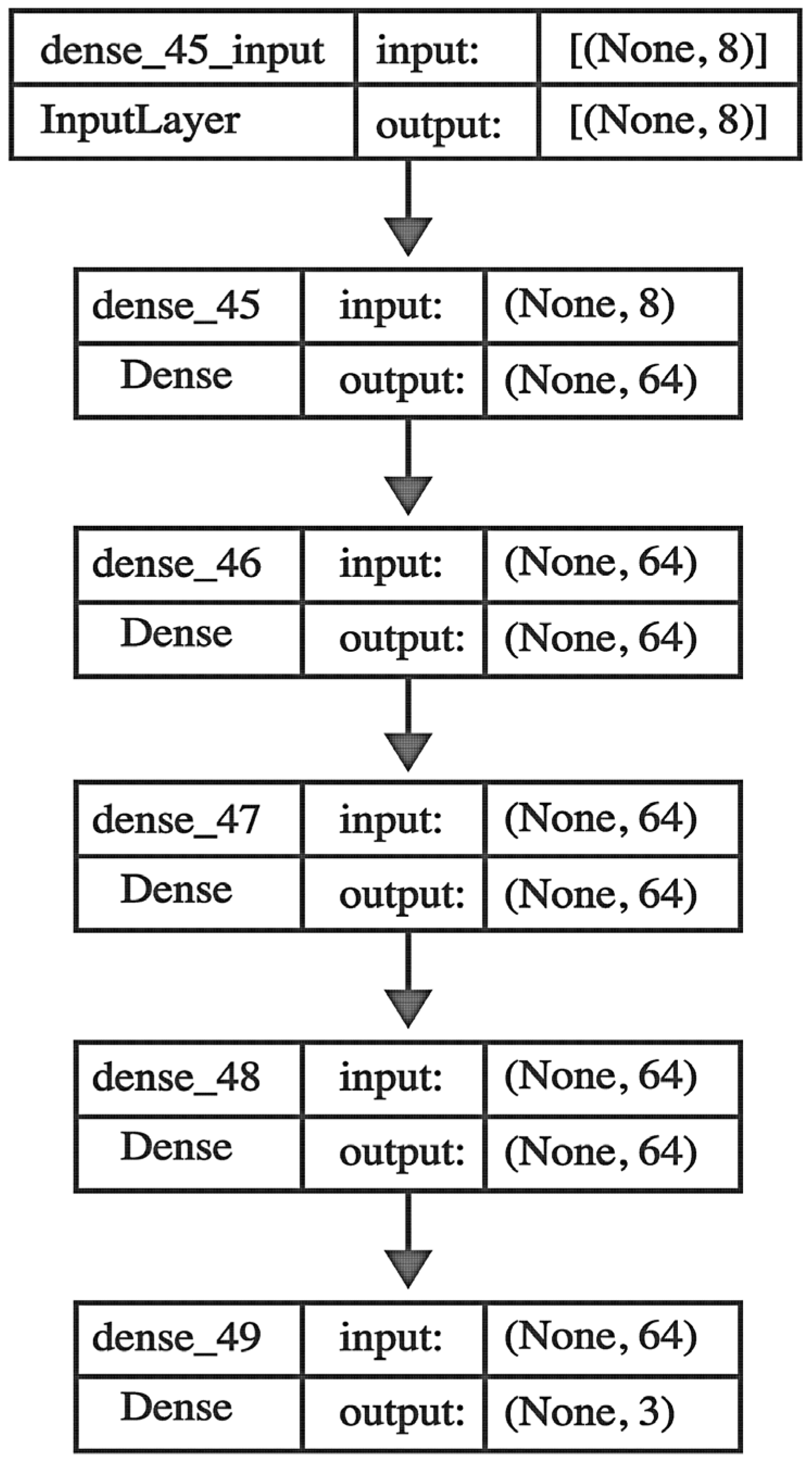
2.5. Neural Network Model Development
3. Results
3.1. Loss and Accuracy
3.2. Precision and Recall
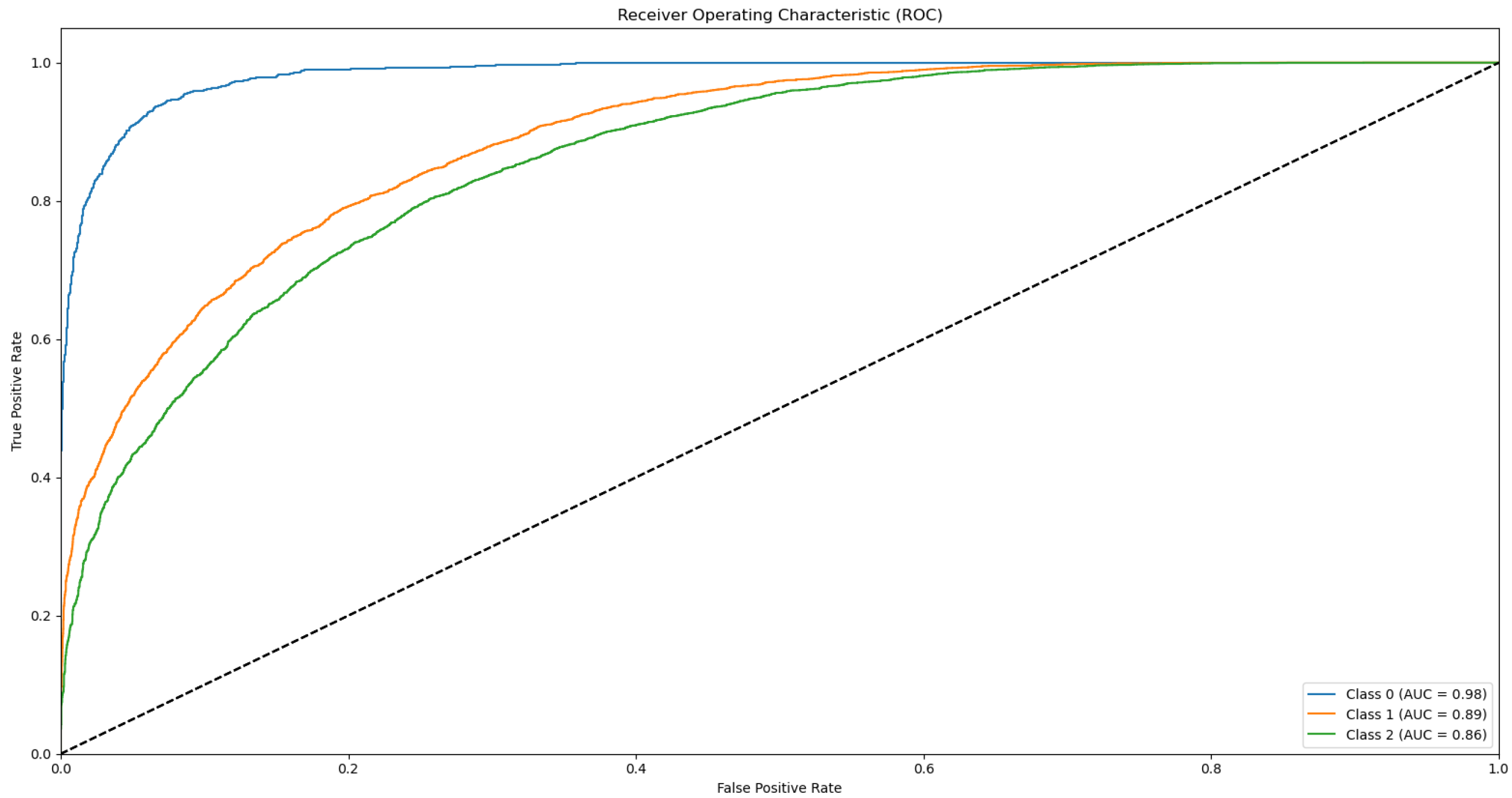
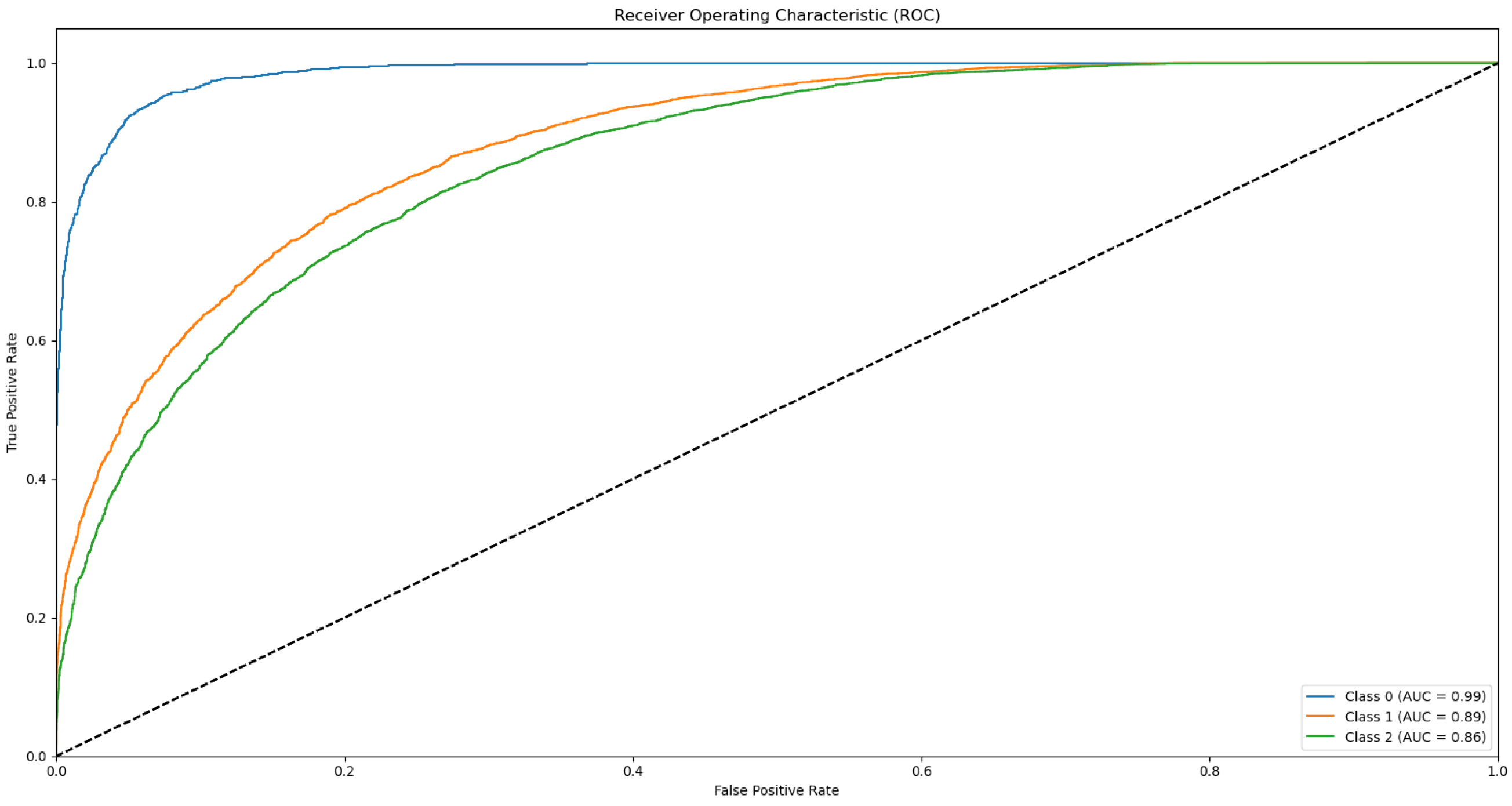
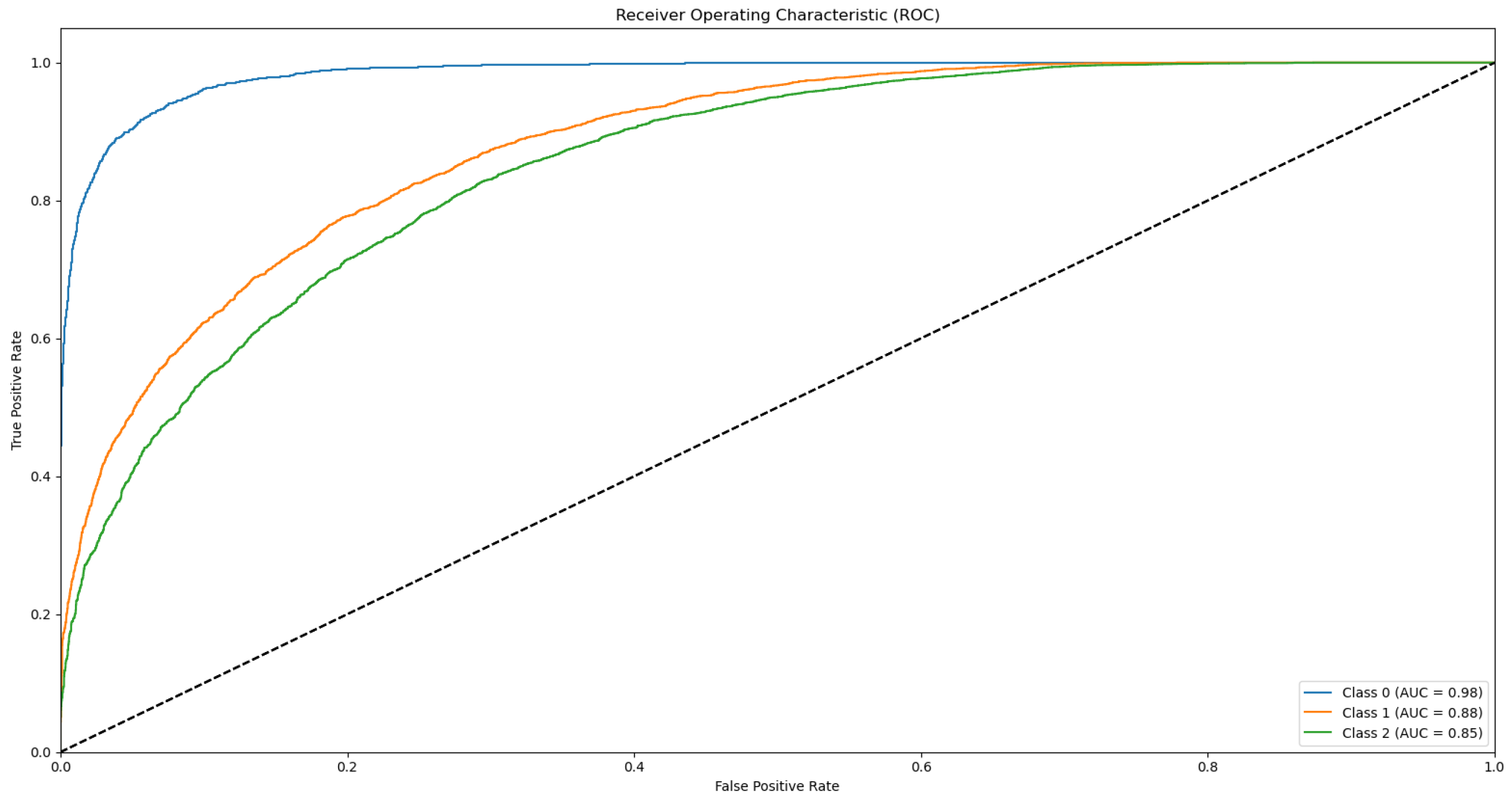
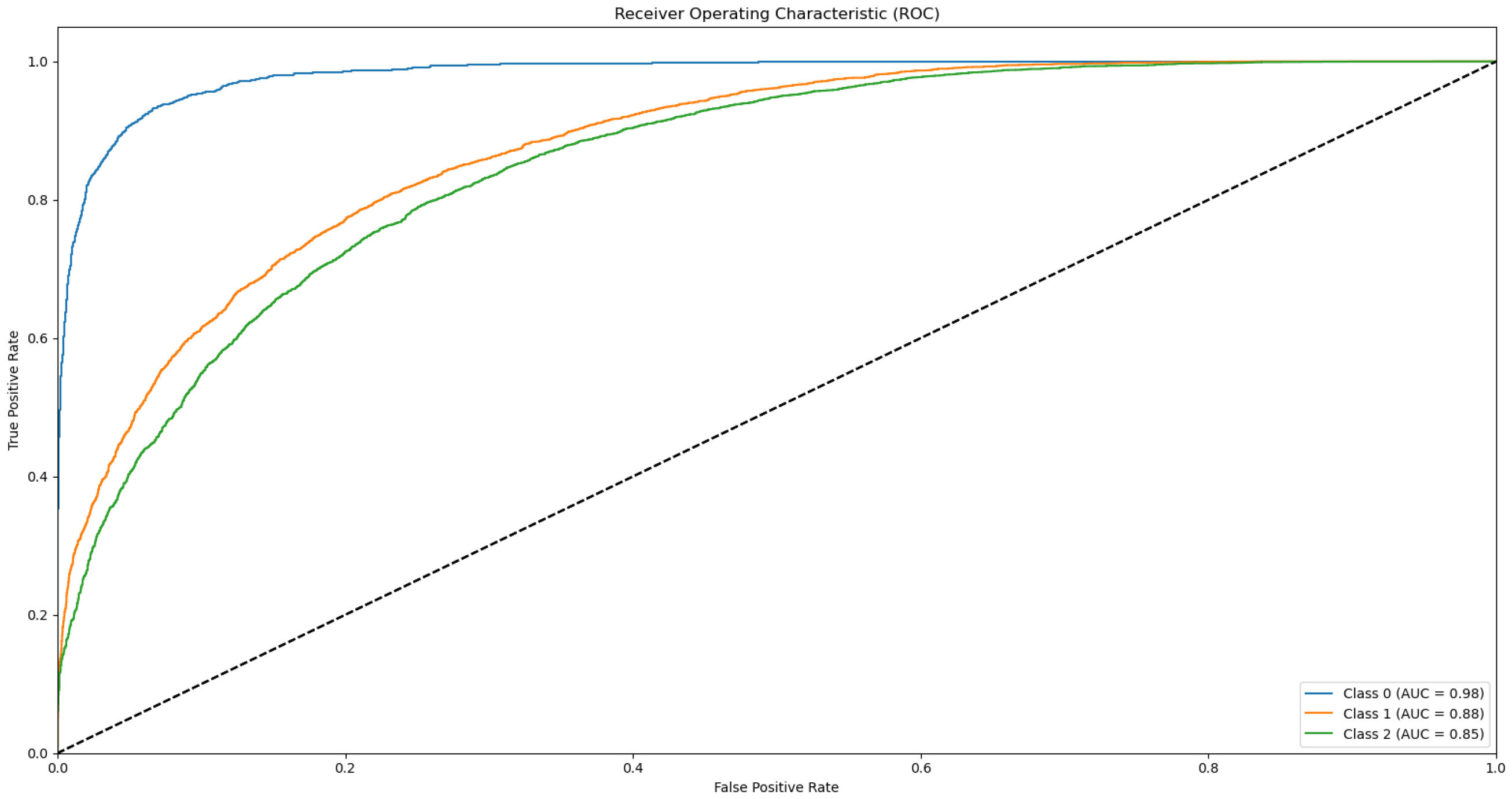
3.3. ROC and AUC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| MALDI—TOF MS | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry |
| MSP | Main Spectral Profile |
| CE | Capillary Electrophoresis |
| LC | Liquid Chromatography |
| UA | Ultraviolet Absorption |
| FNN | Feedforward Neural Network |
| BTS | Bacterial Test Standard |
| QC | Quality Control |
| m/z | Mass to Charge ratio |
| SN | Signal to noise ratio |
| FWHM | Full-width-at-half-maximum |
| OHE | One Hot Encoding |
| ReLU | Rectified Linear Unit |
| TPR | True Positive Rate |
| FPR | False Positive Rate |
| AUC | Area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
Appendix A
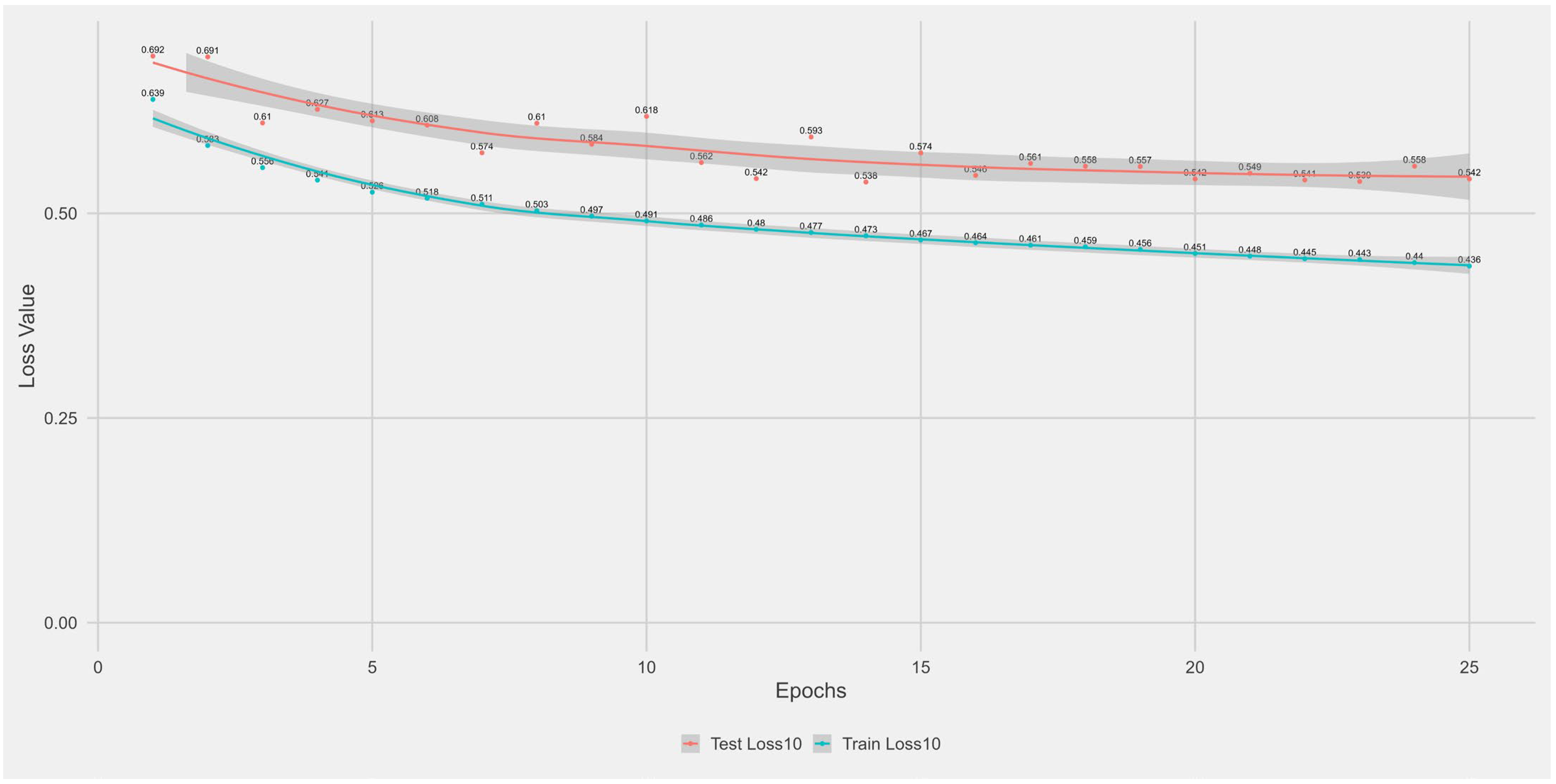
Appendix A.1. Supplementary Data 1: Loss Function per Epoch
- The training loss (solid blue line), reflecting the model’s error on the training data after each epoch.
- The test loss (solid orange line), indicating how well the model generalises to unseen data.
- The grey area is the Confidence interval.
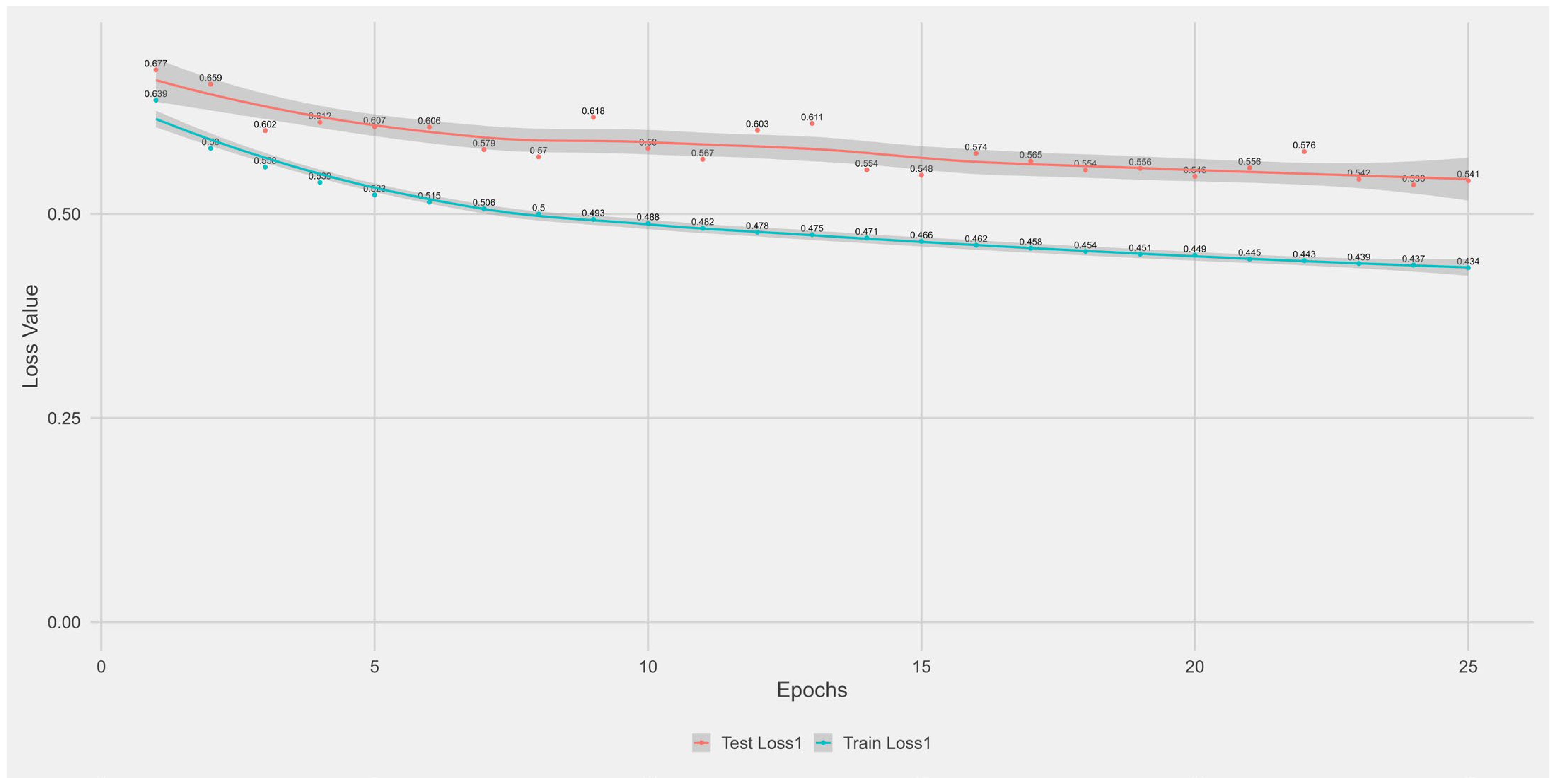
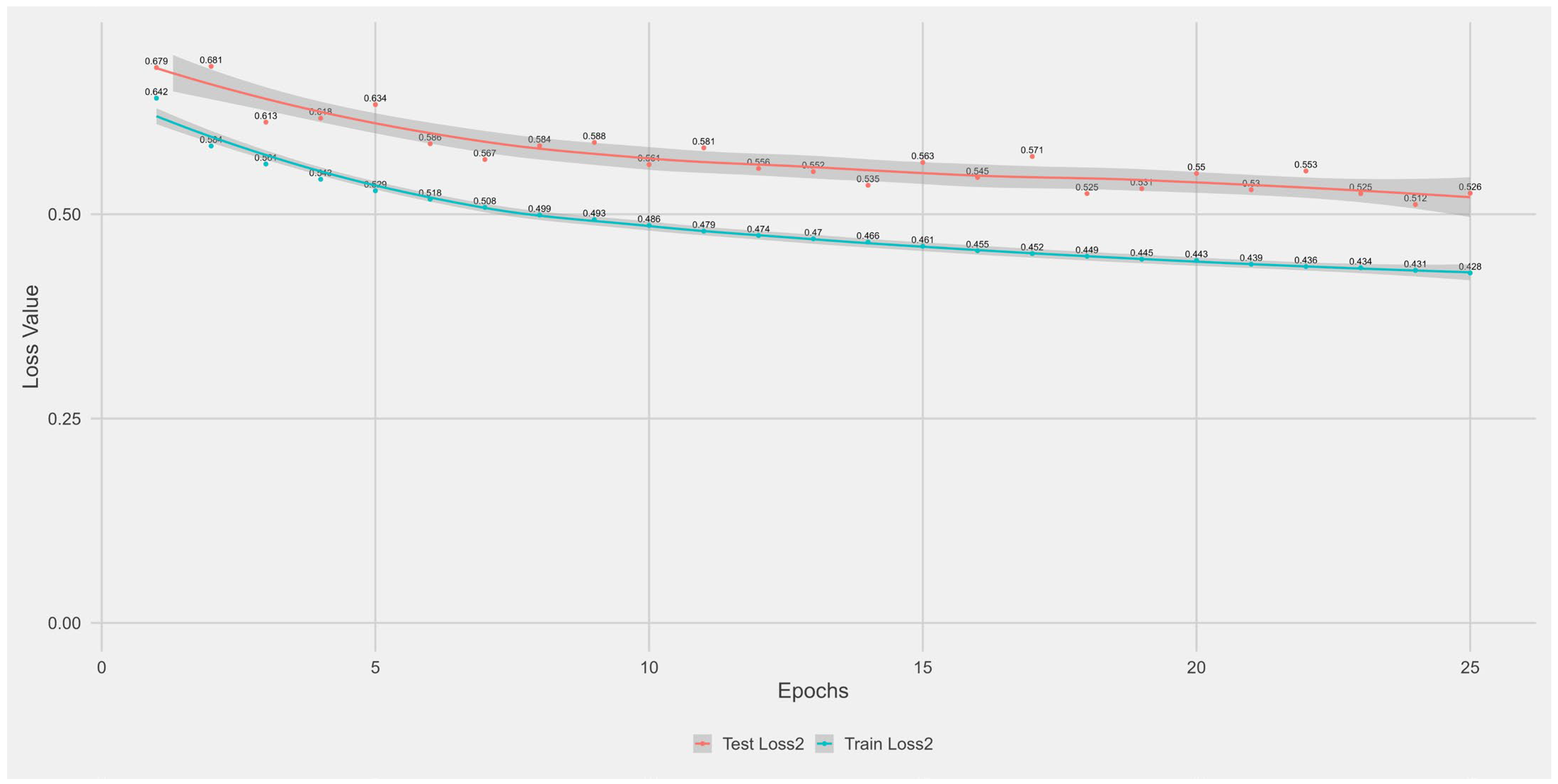
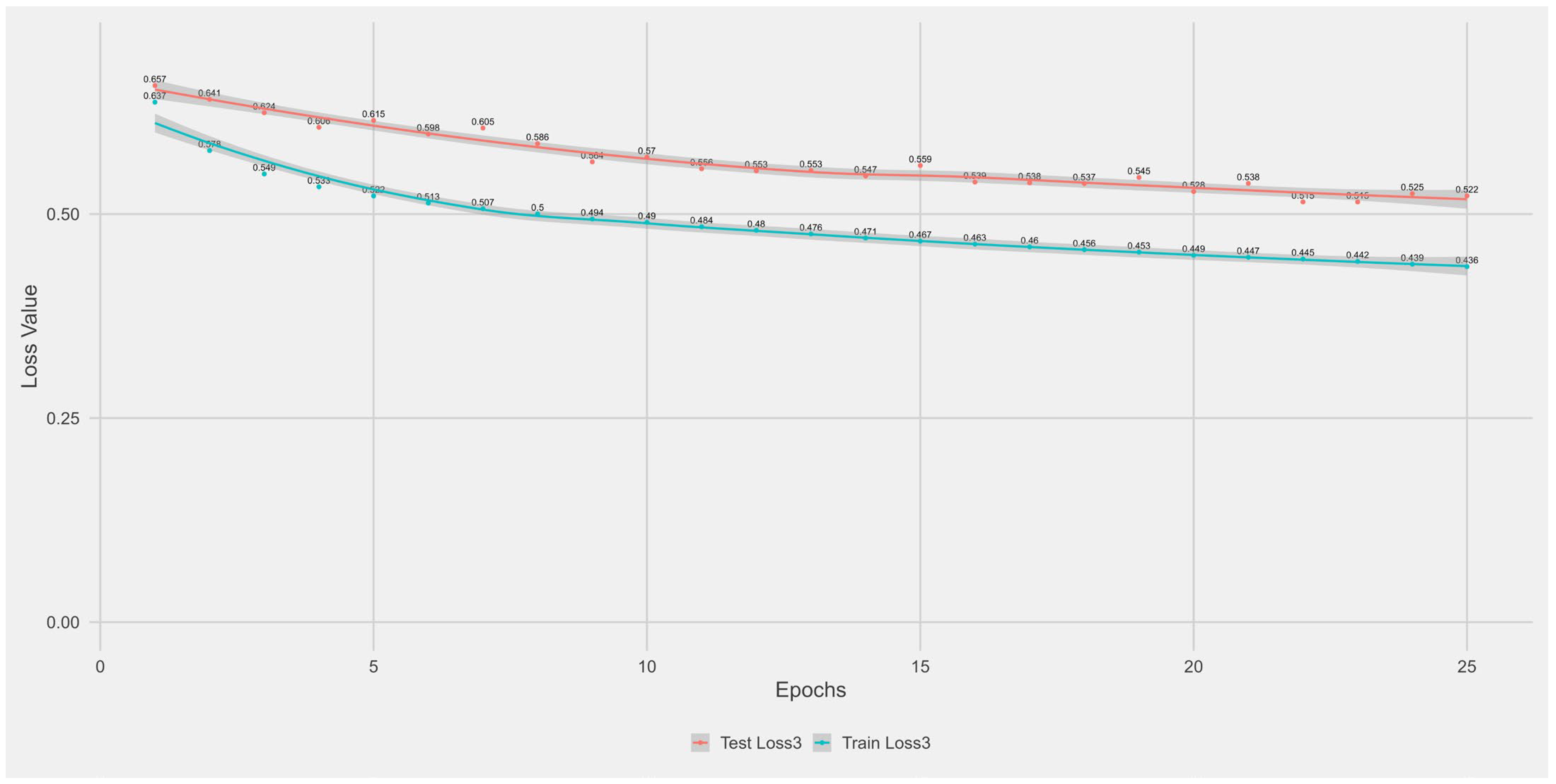
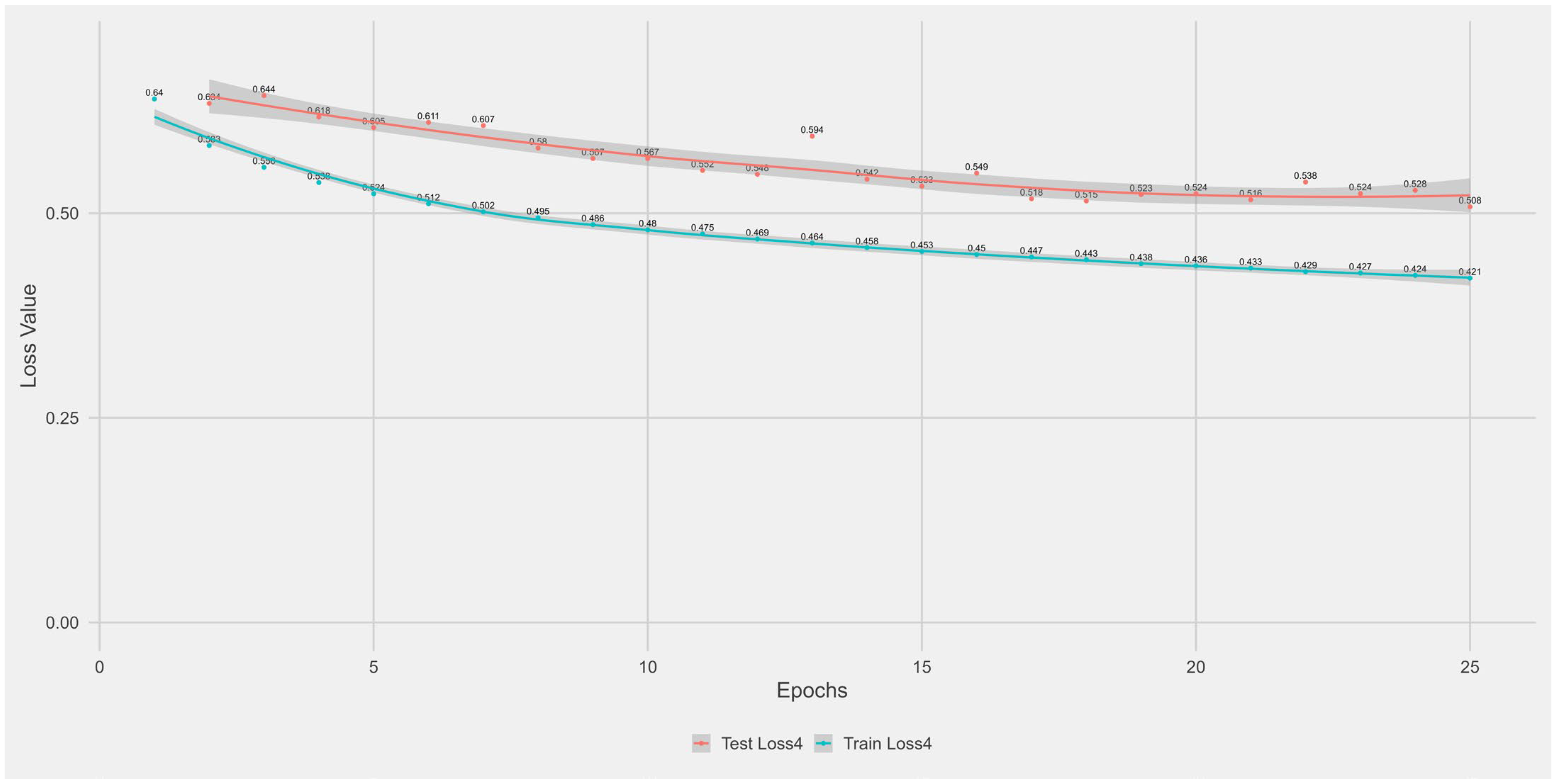
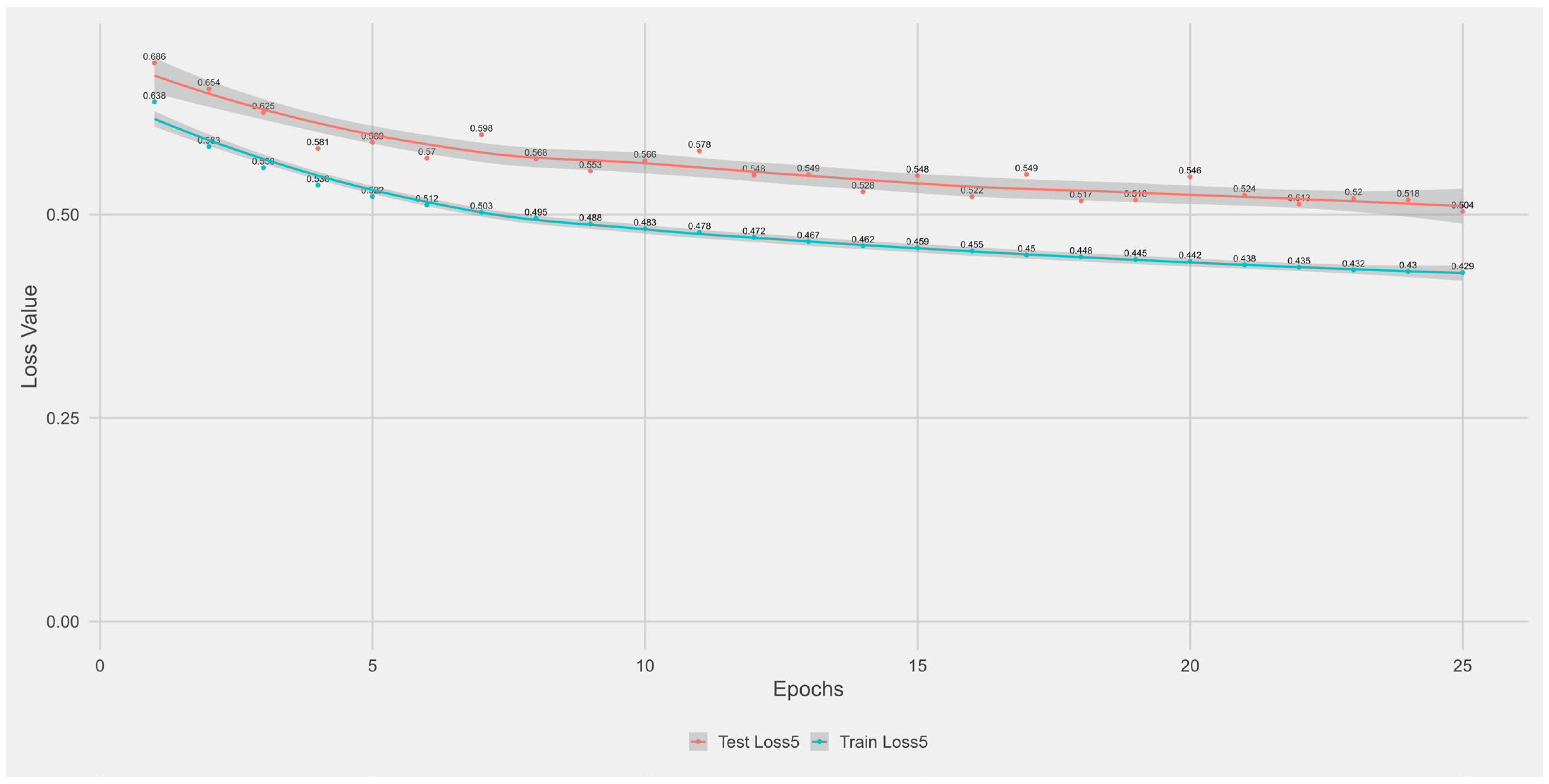
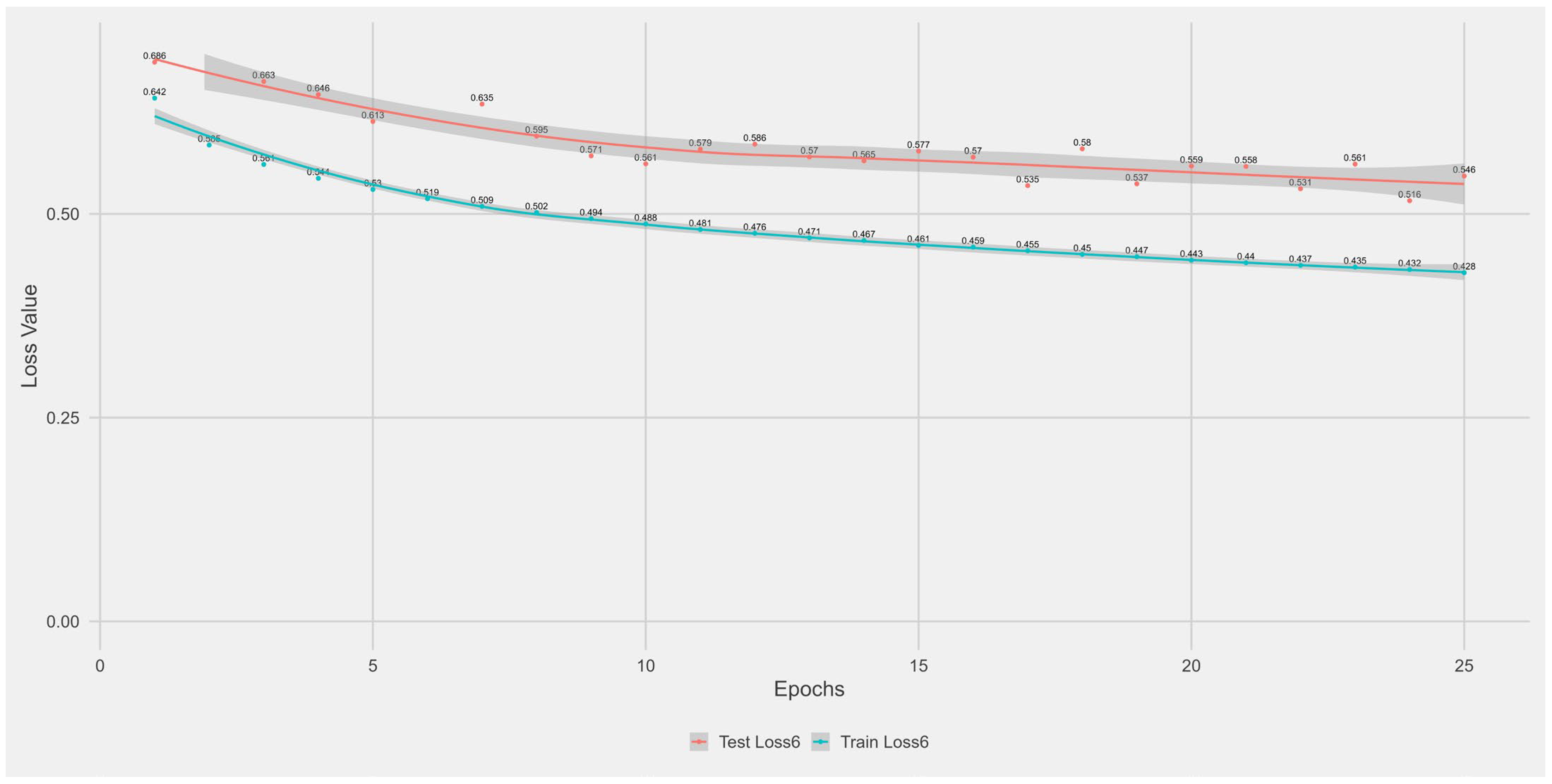
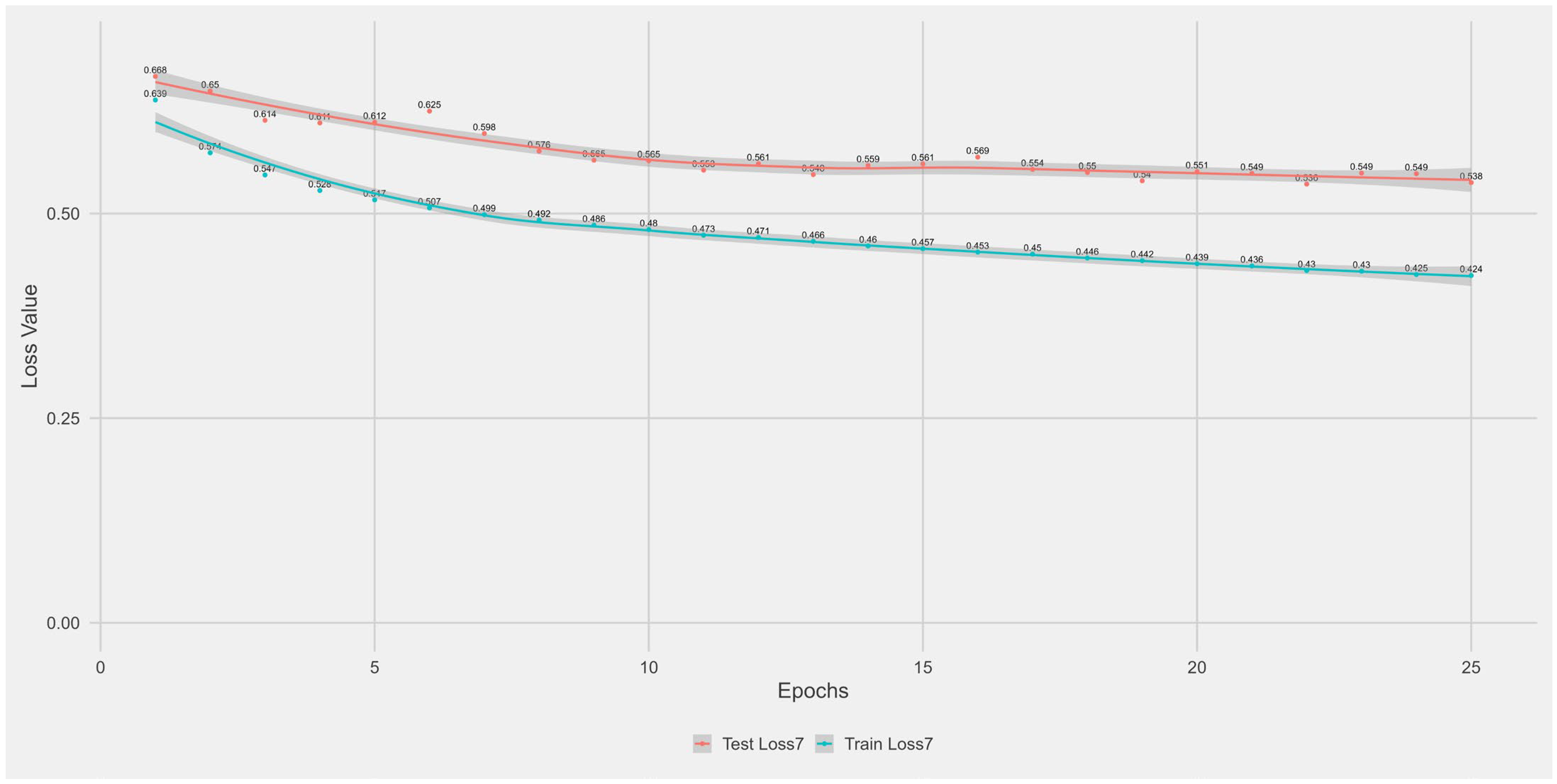

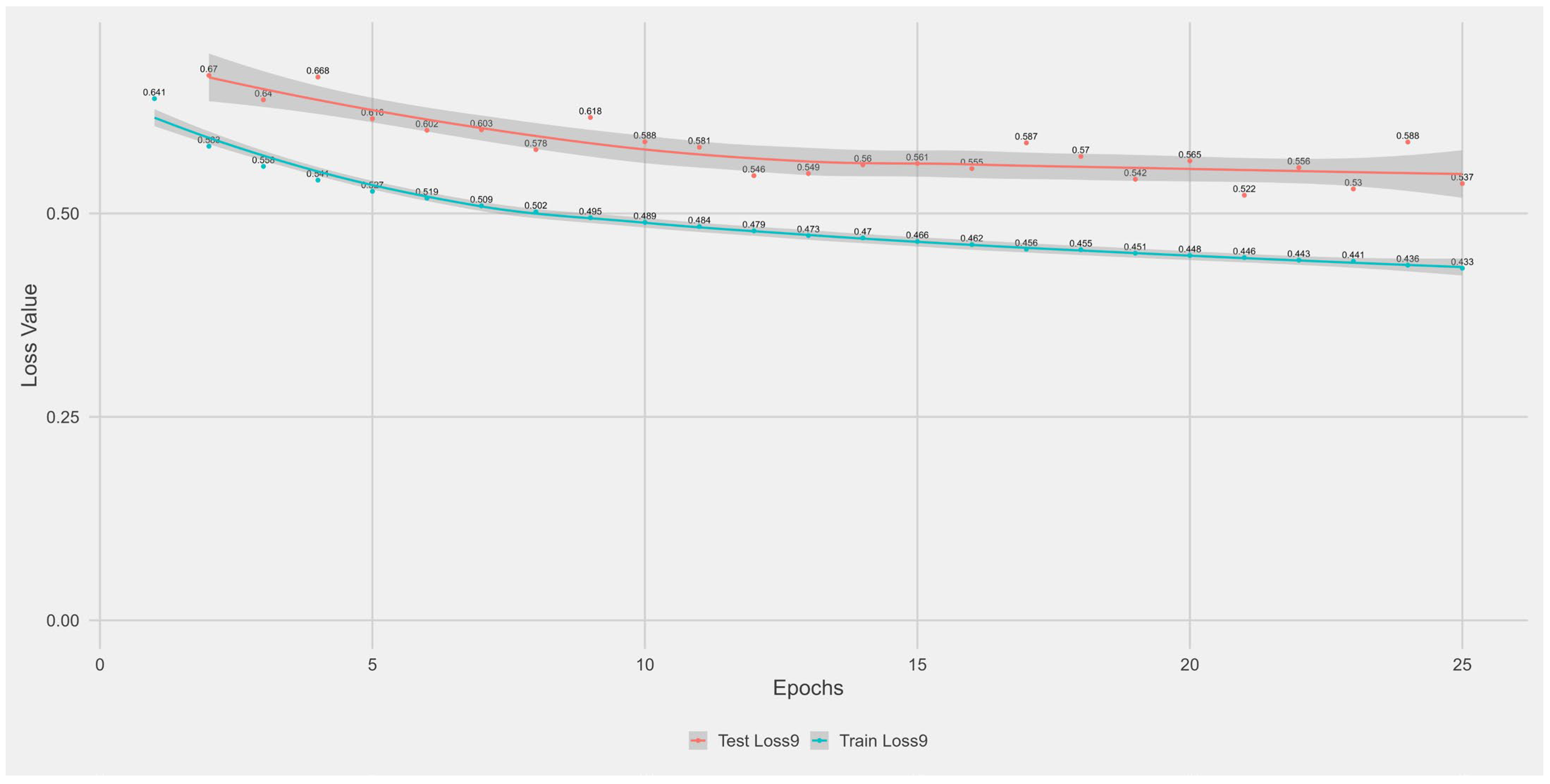
Appendix B
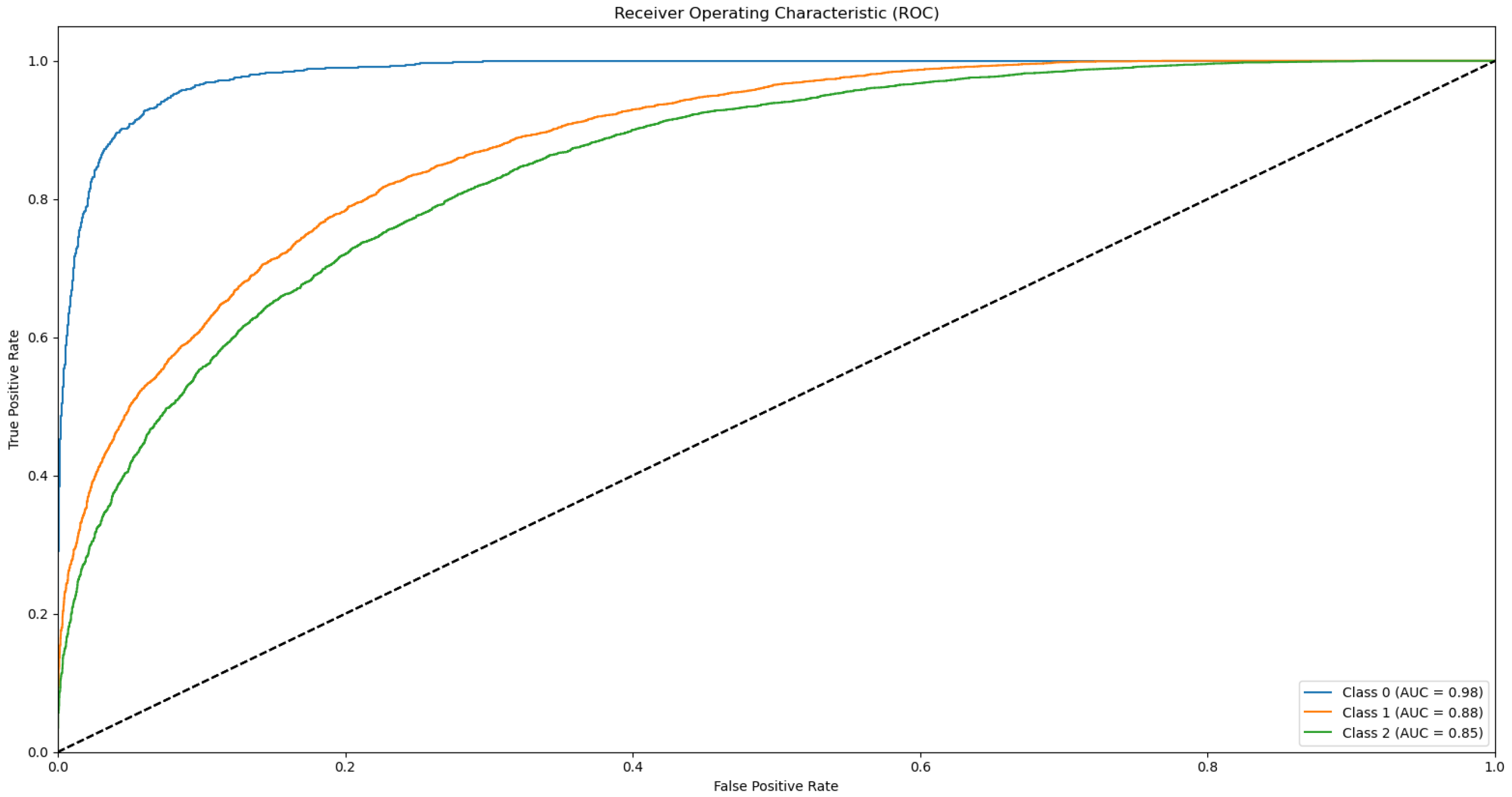
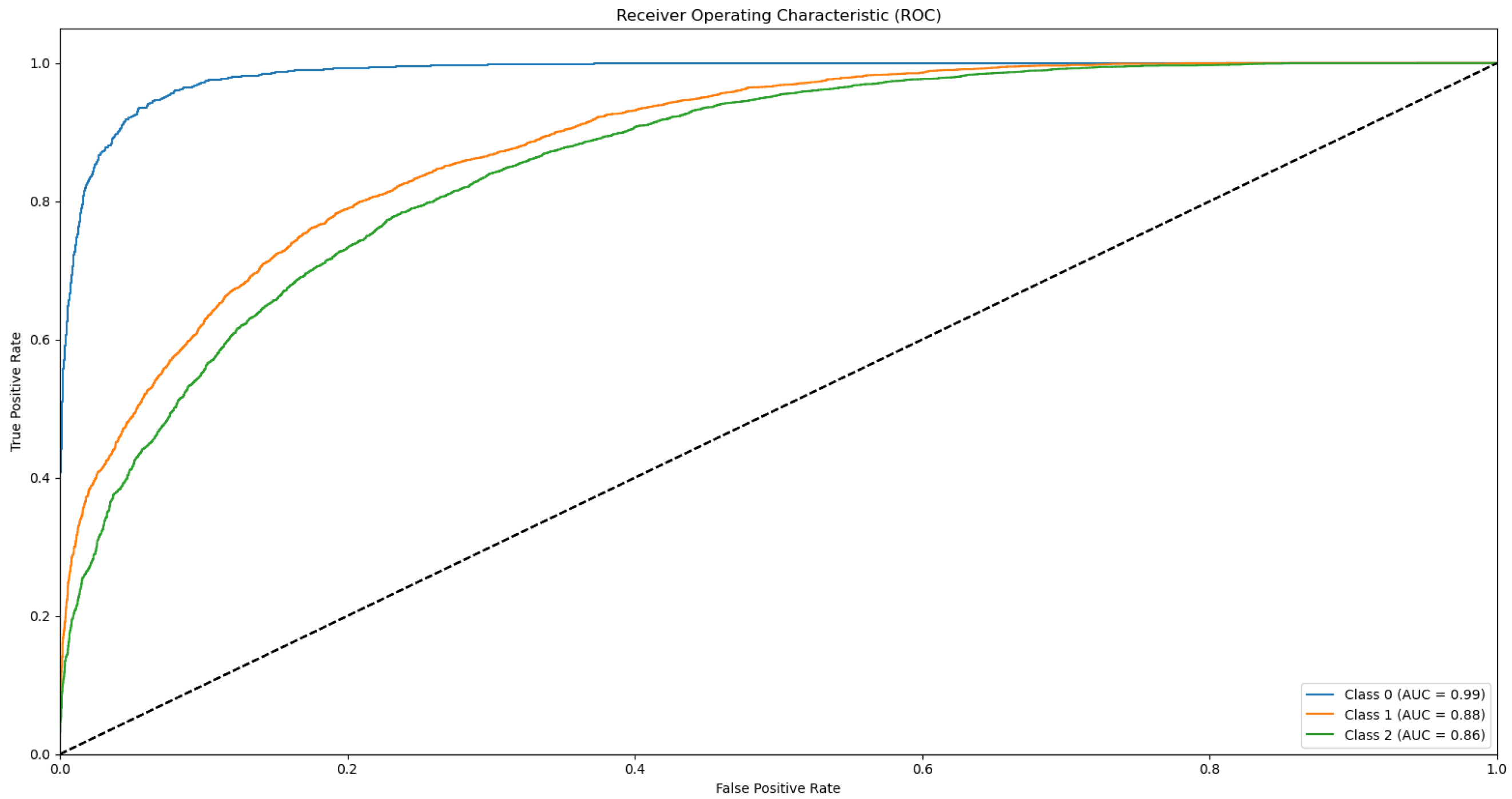
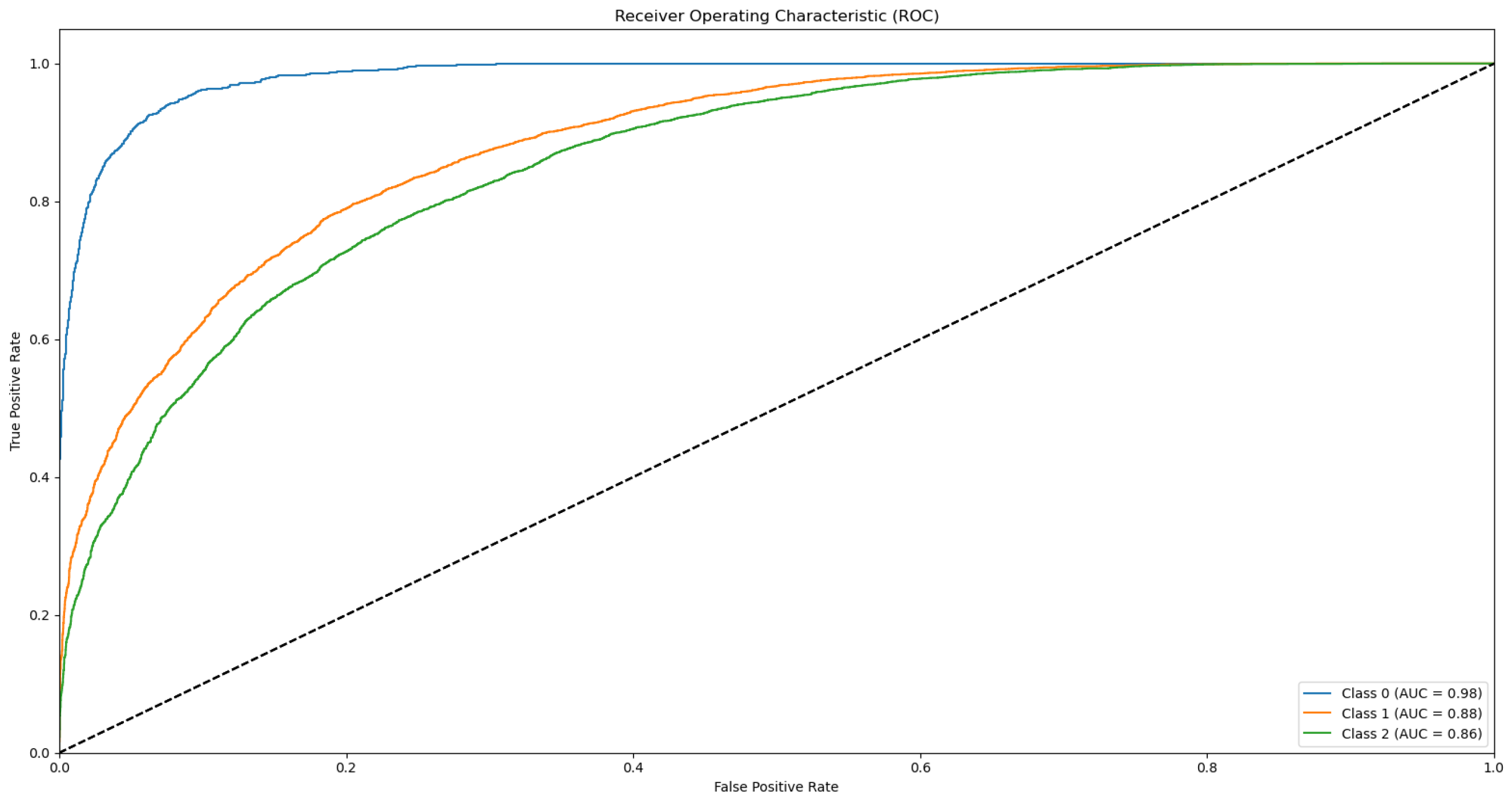
Appendix B.1. Supplementary Data 2: ROC Curves
- The ROC curve of Bovine Milk (Class 0) is depicted as a blue solid line,
- The ROC curve of Goat Milk (Class 1) is represented as an orange solid line, and
- The ROC curve of Sheep Milk (Class 2) is illustrated as a green solid line.



References
- Tzora, A.; Nelli, A.; Voidarou, C.; Fthenakis, G.; Rozos, G.; Theodorides, G.; Bonos, E.; Skoufos, I. Microbiota “Fingerprint” of Greek Feta Cheese through Ripening. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, M.M.; Chang, Y.S. Traceability in a Food Supply Chain: Safety and Quality Perspectives. Food Control 2014, 39, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L. Food Fraud: Policy and Food Chain. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 10, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Leon, E.; Emons, H.; O’Connor, G.; Nørgaard, J.; Robouch, P. Food Allergen Analysis: Considerations for Establishing a Reference Measurement System to Implement EU Legislation. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Croguennec, T.; Pochet, S. Milk Proteins-Analytical Methods. Ref. Modul. Food Sci. 2018, 2018, 9780081005965. [Google Scholar]
- Fuerer, C.; Jenni, R.; Cardinaux, L.; Andetsion, F.; Wagnière, S.; Moulin, J.; Affolter, M. Protein Fingerprinting and Quantification of β-Casein Variants by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoori, Z.; Tehrani, T.; Pont, L.; Benavente, F. Separation and Characterization of Bovine Milk Proteins by Capillary Electrophoresis-mass Spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 3614–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, J.M.L.; Olieman, C.; Schennink, A.; Van Valenberg, H.J.F.; Visker, M.; Meuldijk, R.C.R.; Van Hooijdonk, A.C.M. Estimation of Variation in Concentration, Phosphorylation and Genetic Polymorphism of Milk Proteins Using Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbaix, H.; Budinger, D.; Dieu, M.; Fumière, O.; Gillard, N.; Delahaut, P.; Mauro, S.; Raes, M. Identification of Proteins and Peptide Biomarkers for Detecting Banned Processed Animal Proteins (PAPs) in Meat and Bone Meal by Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bargen, C.; Brockmeyer, J.; Humpf, H.-U. Meat Authentication: A New HPLC–MS/MS Based Method for the Fast and Sensitive Detection of Horse and Pork in Highly Processed Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9428–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valletta, M.; Ragucci, S.; Landi, N.; Di Maro, A.; Pedone, P.V.; Russo, R.; Chambery, A. Mass Spectrometry-Based Protein and Peptide Profiling for Food Frauds, Traceability and Authenticity Assessment. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuollo, M.; Caira, S.; Fierro, O.; Pinto, G.; Picariello, G.; Addeo, F. Toward milk speciation through the monitoring of casein proteotypic peptides. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzolino, R.; Passalacqua, S.; Salemi, S.; Garozzo, D. Identification of Adulteration in Water Buffalo Mozzarella and in Ewe Cheese by Using Whey Proteins as Biomarkers and Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 37, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, J.; Korte, N.; Dyk, M.; Wenninger, O.; Schreiter, P.; Hiller, E. Rapid Animal Species Identification of Feta and Mozzarella Cheese Using MALDI-TOF Mass-Spectrometry. Food Control 2020, 117, 107349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, M.; Huber, I.; Konrad, R.; Busch, U. Application of MALDI-TOF MS for the Identification of Food Borne Bacteria. Open Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintela-Baluja, M.; Böhme, K.; Fernández-No, I.C.; Alnakip, M.E.; Caamano, S.; Barros-Velázques, J.; Calo-Mata, P. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry, a Rapid and Reliable Method for the Identification of Bacterial Species in Food-Microbiology Laboratories. Nov. Food Preserv. Microb. Assess. Tech. 2014, 2014, 353–385. [Google Scholar]
- Tzora, A.; Skoufos, S.; Bonos, E.; Fotou, K.; Karamoutsios, A.; Nelli, A.; Giannenas, I.; Tsinas, A.; Skoufos, I. Identification by MALDI-TOF MS and Antibiotic Resistance of Riemerella Anatipestifer, Isolated from a Clinical Case in Commercial Broiler Chickens. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenning, M.; Breitenwieser, F.; Konrad, R.; Huber, I.; Busch, U.; Scherer, S. Identification and Differentiation of Food-Related Bacteria: A Comparison of FTIR Spectroscopy and MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 103, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzora, A.; Voidarou, C.; Giannenas, I.; Bonos, E.; Fotou, K.; Nelli, A.; Grigoriadou, K.; Karamoutsios, A.; Basdagianni, Z.; Dokou, S. Effects of Dietary Omega-3 Enrichment on the Chemical Composition and the Pathogenic Microbiota of Ovine Milk. Foods 2022, 11, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelli, A.; Voidarou, C.; Venardou, B.; Fotou, K.; Tsinas, A.; Bonos, E.; Fthenakis, G.C.; Skoufos, I.; Tzora, A. Antimicrobial and Methicillin Resistance Pattern of Potential Mastitis-Inducing Staphylococcus Aureus and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolates from the Mammary Secretion of Dairy Goats. Biology 2022, 11, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaudrops, C.; Armstrong, N.; Raoult, D.; Chabriere, E. Determination of the Animal Origin of Meat and Gelatin by MALDI-TOF-MS. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 41, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, E.; Maennig, A.; Rau, J. Animal Type Differentiation in Meat With MALDI-TOF-MS from the Database for Validation. Dtsch. Lebensm.-Rundsch. 2017, 113, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Stahl, A.; Schroder, U. Development of a MALDI–TOF MS-Based Protein Fingerprint Database of Common Food Fish Allowing Fast and Reliable Identification of Fraud and Substitution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7519–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephan, R.; Johler, S.; Oesterle, N.; Näumann, G.; Vogel, G.; Pflüger, V. Rapid and Reliable Species Identification of Scallops by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Food Control 2014, 46, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, S.; Kühn, U.; Biermaier, B.; Piacenza, N.; Schwaiger, K.; Gottschalk, C.; Gareis, M. Direct Identification of Edible Insects by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Food Control 2017, 76, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, S.; Salzano, A.M.; Scaloni, A. Identification of Protein Markers for the Occurrence of Defrosted Material in Milk through a MALDI-TOF-MS Profiling Approach. J. Proteom. 2016, 147, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caira, S.; Pinto, G.; Nicolai, M.A.; Chianese, L.; Addeo, F. Simultaneously Tracing the Geographical Origin and Presence of Bovine Milk in Italian Water Buffalo Mozzarella Cheese Using MALDI-TOF Data of Casein Signature Peptides. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2016, 408, 5609–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvano, C.D.; De Ceglie, C.; Monopoli, A.; Zambonin, C.G. Detection of Sheep and Goat Milk Adulterations by Direct MALDI–TOF MS Analysis of Milk Tryptic Digests. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Girolamo, F.; Masotti, A.; Salvatori, G.; Scapaticci, M.; Muraca, M.; Putignani, L. A Sensitive and Effective Proteomic Approach to Identify She-Donkey’s and Goat’s Milk Adulterations by MALDI-TOF MS Fingerprinting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 13697–13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, N.; Xu, Y.; Goodacre, R. MALDI-MS and Multivariate Analysis for the Detection and Quantification of Different Milk Species. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 3491–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Rega, C.; Chambery, A. Rapid Detection of Water Buffalo Ricotta Adulteration or Contamination by Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionisation Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassi, M.; Arena, S.; Scaloni, A. MALDI-TOF-MS Platform for Integrated Proteomic and Peptidomic Profiling of Milk Samples Allows Rapid Detection of Food Adulterations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 6157–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunsolo, V.; Muccilli, V.; Saletti, R.; Foti, S. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry for the Monitoring of She-donkey’s Milk Contamination or Adulteration. J. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 48, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, C.; Hale, O.J.; Reynolds, C.K.; Jones, A.K.; Taylor, N.; Morris, M.; Cramer, R. Speciation and Milk Adulteration Analysis by Rapid Ambient Liquid MALDI Mass Spectrometry Profiling Using Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, T.; Pont, L.; Benavente, F. Rapid Detection and Quantification of Milk Adulteration Using MALDI-MS Protein Profiling and Multivariate Calibration. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 130, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.D.; Karvelis, P.; Giannakeas, N.; Vrachatis, A.; Glavas, E.; Tzallas, A.T. How Natural Language Processing Derived Techniques Are Used on Biological Data: A Systematic Review. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inform. Bioinform. 2024, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šebela, M. Biomolecular Profiling by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry in Food and Beverage Analyses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Machine Learning-Assisted Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry toward Rapid Classification of Milk Products. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 7609–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, P.; Freire, D.; Licon, C.C. A Comprehensive Review of Machine Learning and Its Application to Dairy Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 1878–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Calabuig, A.M.; Pradana-López, S.; Lopez-Ortega, S.; Beleño Sáenz, K.d.J.; Cancilla, J.C.; Torrecilla, J.S. Application of Residual Neural Networks to Detect and Quantify Milk Adulterations. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 122, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritikou, A.S.; Aalizadeh, R.; Damalas, D.E.; Barla, I.V.; Baessmann, C.; Thomaidis, N.S. MALDI-TOF-MS Integrated Workflow for Food Authenticity Investigations: An Untargeted Protein-Based Approach for Rapid Detection of PDO Feta Cheese Adulteration. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, S.; Tsangaris, G.T.; Tzora, A.; Skoufos, I.; Banos, G.; Argiriou, A.; Arsenos, G. Analysis of Genome-Wide DNA Arrays Reveals the Genomic Population Structure and Diversity in Autochthonous Greek Goat Breeds. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, G.C.; Saratsis, P.; Tzora, A.; Linde, K. Naturally Occurring Subclinical Ovine Mastitis Associated with Listeria Monocytogenes. Small Rumin. Res. 1998, 31, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.; Dyk, M.; Wenninger, O.; Hiller, E. MALDI-TOF-Mass Spectrometry: Sample Preparation Protocols for Meat and Milk Products. In Mass Spectrometry for Food Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- de Amorim, L.B.V.; Cavalcanti, G.D.C.; Cruz, R.M.O. The Choice of Scaling Technique Matters for Classification Performance. Appl. Soft. Comput. 2023, 133, 109924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrar, D. Cross-Validation. Encycl. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. ABC Bioinform. 2019, 1–3, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; López, A.; Peña-Méndez, E.M.; Vaňhara, P.; Hampl, A.; Havel, J. Artificial Neural Networks in Medical Diagnosis. J. Appl. Biomed. 2013, 11, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulec, N.; Plavljanić, D.; Špoljarić, J.; Radeljević, B.; Havranek, J.; Antunac, N. Proving the Adulteration of Ewe and Goat Cheeses with Cow Milk Using the Reference Method of Isoelectric Focusing of γ-Casein. Mljekarstvo 2013, 63, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, H.K.; Lenz, K.; Halbauer, E.M. “A2 Milk” Authentication Using Isoelectric Focusing and Different PCR Techniques. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behkami, S.; Zain, S.M.; Gholami, M.; Khir, M.F.A. Classification of Cow Milk Using Artificial Neural Network Developed from the Spectral Data of Single-and Three-Detector Spectrophotometers. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Chen, R.; Sun, Y.; Pan, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Multi-Omics Analysis of Five Species of Milk and Specific Composition Links within Each Species. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Bu, S.; Liu, J.; Niu, C.; Wang, L.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L.; Song, Y. Label-Free-Based Proteomics Analysis Reveals Differential Proteins of Sheep, Goat, and Cow Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 8908–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, A.; Bennato, F.; Ianni, A.; Grotta, L.; Henry, M.; Meleady, P.; Martino, G. Comparative Label-Free Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Milk Proteomic Profiles Highlight Putative Differences between the Autochthon Teramana and Saanen Goat Breeds. Animals 2023, 13, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, M.; Di Giuseppe, M.; Wicochea Rodríguez, J.D.; Cammà, C. Validation of a Fast Real-Time PCR Method to Detect Fraud and Mislabeling in Milk and Dairy Products. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, A.; Jha, A.; Sharma, R.; Singh, H.B.; Rai, A.K.; Sharma, N. Detection of Adulteration in Milk: A Review. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2017, 70, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysova, L.; Cejnar, P.; Hanus, O.; Legarova, V.; Havlik, J.; Nejeschlebova, H.; Nemeckova, I.; Jedelska, R.; Bozik, M. Use of MALDI-TOF MS Technology to Evaluate Adulteration of Small Ruminant Milk with Raw Bovine Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 4882–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, C.V.; Jutzeler, C.R.; Borgwardt, K. Machine Learning for Microbial Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing on MALDI-TOF Mass Spectra: A Systematic Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, L.; Di Girolamo, F.; Mennini, M.; Masotti, A.; Salvatori, G.; Rigon, G.; Signore, F.; Pietrantoni, E.; Scapaticci, M.; Lante, I. A MALDI-TOF MS Approach for Mammalian, Human, and Formula Milks’ Profiling. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, A.D.; Cîrîc, A.I.; Begea, M. A Review of Milk Frauds and Adulterations from a Technological Perspective. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, A.; Vouraki, S.; Morin, E.; Koutouzidou, G.; Arsenos, G. Efficiency Analysis and Identification of Best Practices and Innovations in Dairy Sheep Farming. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, C.K.; Lianou, D.T.; Vasileiou, N.G.C.; Mavrogianni, V.S.; Petinaki, E.; Fthenakis, G.C. Longitudinal Study of Subclinical Mastitis in Sheep in Greece: An Investigation into Incidence Risk, Associations with Milk Quality and Risk Factors of the Infection. Animals 2023, 13, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M. Proteomics and Food Analysis: Principles, Techniques, and Applications. Foods 2021, 10, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkons, I.; Varunjikar, M.S.; Rasinger, J.D. Unveiling the Potential of Proteomics in Addressing Food and Feed Safety Challenges. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e211013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-G.; Zhang, X.; Ni, L.-J.; Xue, Z.-B.; Gu, X.; Huang, S.-X. Rapid Identification of Adulterated Cow Milk by Non-Linear Pattern Recognition Methods Based on near Infrared Spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Folds | 0 (Bovine_Milk) | 1 (Goat_Milk) | 2 (Sheep_Milk) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.275814276 | 0.95086429 | 0.662724759 |
| 2 | 2.273923279 | 0.950781702 | 0.662925431 |
| 3 | 2.279447491 | 0.95102951 | 0.662337138 |
| 4 | 2.272978959 | 0.950341475 | 0.663219969 |
| 5 | 2.285793833 | 0.949407343 | 0.662591046 |
| 6 | 2.275183594 | 0.9495446 | 0.663420941 |
| 7 | 2.270621586 | 0.951690961 | 0.662764884 |
| 8 | 2.281687858 | 0.949636612 | 0.662825119 |
| 9 | 2.278363628 | 0.950406128 | 0.662731486 |
| 10 | 2.28629444 | 0.950131158 | 0.66219695 |
| Average | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|
| Train Loss | 0.43 | 0.005 |
| Test Loss | 0.53 | 0.015 |
| Train Categorical Accuracy | 0.76 | 0.003 |
| Test Categorical Accuracy | 0.75 | 0.007 |
| Train Precision | 0.77 | 0.003 |
| Test Precision | 0.76 | 0.007 |
| Train Recall | 0.75 | 0.004 |
| Test Recall | 0.74 | 0.009 |
| Train AUC | 0.90 | 0.023 |
| Test AUC | 0.90 | 0.018 |
| Sample | Bovine | Goat | Sheep | Error |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | ±0.1 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.57 | 0.43 | ±0.07 |
| 3 | 0 | 0.55 | 0.45 | ±0.05 |
| 4 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | ±0.1 |
| 5 | 0 | 0.48 | 0.51 | ±0.03 |
| Average | ±0.07 |
| Predicted Class | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bovine (Class 0) | Goat (Class 1) | Sheep (Class 2) | ||
| True Class | Bovine (Class 0) | 14,846 | 240 | 932 |
| Goat (Class 1) | 855 | 29,563 | 7976 | |
| Sheep (Class 2) | 4531 | 13,021 | 37,503 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karamoutsios, A.; Oikonomou, E.D.; Voidarou, C.; Hatzizisis, L.; Fotou, K.; Nikolaou, K.; Gouva, E.; Gkiza, E.; Giannakeas, N.; Skoufos, I.; et al. Innovations in Proteomic Technologies and Artificial Neural Networks: Unlocking Milk Origin Identification. BioTech 2025, 14, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020033
Karamoutsios A, Oikonomou ED, Voidarou C, Hatzizisis L, Fotou K, Nikolaou K, Gouva E, Gkiza E, Giannakeas N, Skoufos I, et al. Innovations in Proteomic Technologies and Artificial Neural Networks: Unlocking Milk Origin Identification. BioTech. 2025; 14(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaramoutsios, Achilleas, Emmanouil D. Oikonomou, Chrysoula (Chrysa) Voidarou, Lampros Hatzizisis, Konstantina Fotou, Konstantina Nikolaou, Evangelia Gouva, Evangelia Gkiza, Nikolaos Giannakeas, Ioannis Skoufos, and et al. 2025. "Innovations in Proteomic Technologies and Artificial Neural Networks: Unlocking Milk Origin Identification" BioTech 14, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020033
APA StyleKaramoutsios, A., Oikonomou, E. D., Voidarou, C., Hatzizisis, L., Fotou, K., Nikolaou, K., Gouva, E., Gkiza, E., Giannakeas, N., Skoufos, I., & Tzora, A. (2025). Innovations in Proteomic Technologies and Artificial Neural Networks: Unlocking Milk Origin Identification. BioTech, 14(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biotech14020033








