- Article
Functional Analysis of the NinaB-like Gene in Body Color Regulation of Neocaridina denticulata sinensis
- Haifan Li,
- Lili Zhang and
- Tanjun Zhao
- + 1 author
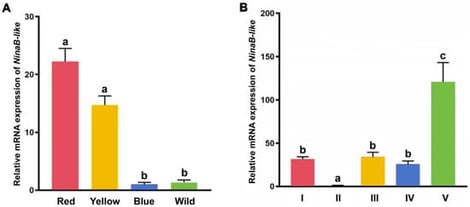
Carotenoid-based pigmentation is crucial for the ornamental and commercial value of the cherry shrimp (Neocaridina denticulata sinensis). While several genes are known to influence carotenoid metabolism, the genetic basis for specific color strains remains largely unexplored. Here, we functionally characterized NinaB-like, a homolog of a carotenoid oxygenase, in cherry shrimp pigmentation. We employed qPCR to gain gene expression profiles, utilized RNAi technology to analysize the relation between its expression level and carotenoid accumulation, and performed GT-seq to identify genotypes of different color strains. Significant differential expression of NinaB-like was observed not only across distinct color strains but also during embryonic development of cherry shrimp (p < 0.05), peaking at the red strain and post-larval stage of cherry shrimp. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of NinaB-like resulted in a marked increase in red pigment deposition at the metanauplius and pre-zoea stages, confirming its role as a negative regulator of carotenoid accumulation. Importantly, we identified two tightly linked, non-synonymous SNPs (927C > A and 935A > C) within the NinaB-like coding region that exhibited a strong association with body color. Our study provides the first functional evidence that NinaB-like is a negative regulator of carotenoid degradation and a major genetic determinant for body color in cherry shrimp, providing new insights for genetic breeding and biological research.
5 February 2026