Palifermin Compared to Supersaturated Calcium Phosphate Rinse in Prevention of Severe Oral Mucositis after Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy-Based Myeloablative Conditioning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Conditioning Regimens
2.3. Study Drugs
2.4. Study Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy
3.2. Prediction of Severe Grades of OM
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OM | Oral mucositis |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| TBI | Total body irradiation |
| SCPR | Supersaturated calcium phosphate rinse |
| FBT | Fludarabine, busulfan, and total body irradiation |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| FCT | Fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation |
| CT | Cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation |
| VT | Etoposide and total body irradiation |
References
- Keefe, D.M.; Schubert, M.M.; Elting, L.S.; Sonis, S.T.; Epstein, J.B.; Raber-Durlacher, J.E.; Migliorati, C.A.; McGuire, D.B.; Hutchins, R.D.; Peterson, D.E.; et al. Updated clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of mucositis. Cancer 2007, 109, 820–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tooley, K.L.; Howarth, G.S.; Butler, R.N. Mucositis and non-invasive markers of small intestinal function. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niscola, P. Mucositis in malignant hematology. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2010, 3, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vokurka, S.; Steinerova, K.; Karas, M.; Koza, V. Characteristics and risk factors of oral mucositis after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with FLU/MEL conditioning regimen in context with BU/CY2. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 44, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, B.S.; Thall, P.F.; Madden, T.; Couriel, D.; Wang, X.; Tran, H.T.; Anderlini, P.; De Lima, M.; Gajewski, J.; Champlin, R.E. Busulfan systemic exposure relative to regimen-related toxicity and acute graft-versus-host disease: Defining a therapeutic window for i.v. BuCy2 in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2002, 8, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, H.M.; Bruce, A.J.; Wolf, R.C.; Litzow, M.R.; Hogan, W.J.; Patnaik, M.S.; Kremers, W.K.; Phillips, G.L.; Hashmi, S.K. The Incidence and Severity of Oral Mucositis among Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients: A Systematic Review. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielberger, R.; Stiff, P.; Bensinger, W.; Gentile, T.; Weisdorf, D.; Kewalramani, T.; Shea, T.; Yanovich, S.; Hansen, K.; Noga, S.; et al. Palifermin for Oral Mucositis after Intensive Therapy for Hematologic Cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2590–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.; Friebe, A.; Foulstone, P.; Grigg, A.; Hempton, J.; Bajel, A. Impact of palifermin on mucosal toxicity in autologous stem cell transplants using busulfan–melphalan conditioning chemotherapy for Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 1415–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Stokman, M.; Spijkervet, F.K.L.; Burlage, F.R.; Dijkstra, P.U.; Manson, W.L.; de Vries, E.; Roodenburg, J.L.N. Oral mucositis and selective elimination of oral flora in head and neck cancer patients receiving radiotherapy: A double-blind randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytlik, R.; Beneš, P.; Patorkova, M.; Chocenska, E.; Gregora, E.; Procházka, B.; Kozák, T. Standardized parenteral alanyl-glutamine dipeptide supplementation is not beneficial in autologous transplant patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled study. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2002, 30, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Sayed, S.; Nabid, A.; Shelley, W.; Hay, J.; Balogh, J.; Gelinas, M.; MacKenzie, R.; Read, N.; Berthelet, E.; Lau, H.; et al. Prophylaxis of radiation-associated mucositis in conventionally treated patients with head and neck cancer: A double-blind, phase III, randomized, controlled trial evaluating the clinical efficacy of an antimicrobial lozenge using a validated mucositis scoring system. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3956–3963. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodd, M.J.; Miaskowski, C.; Greenspan, D.; MacPhail, L.; Shih, A.-S.; Shiba, G.; Facione, N.; Paul, S.M. Radiation-Induced Mucositis: A Randomized Clinical Trial of Micronized Sucralfate Versus Salt & Soda Mouthwashes. Cancer Investig. 2003, 21, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Elad, S.; Rn, K.K.F.C.; Lalla, R.V.; Yarom, N.; Hong, C.; Logan, R.M.; Bowen, J.; Gibson, R.; Dds, D.P.S.; Zadik, Y.; et al. MASCC/ISOO clinical practice guidelines for the management of mucositis secondary to cancer therapy. Cancer 2020, 126, 4423–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla, R.V.; Bowen, J.; Barasch, A.; Elting, L.; Epstein, J.; Keefe, D.M.; McGuire, D.B.; Migliorati, C.; Nicolatou-Galitis, O.; Peterson, D.E.; et al. MASCC/ISOO clinical practice guidelines for the management of mucositis secondary to cancer therapy. Cancer 2014, 120, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsley, P.; Bauer, J.D.; Mazkowiack, R.; Gardner, R.; Bashford, J. Palifermin improves severe mucositis, swallowing problems, nutrition impact symptoms, and length of stay in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Support. Care Cancer 2007, 15, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raber-Durlacher, J.E.; For The Mucositis Study Group of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer/International Society of Oral Oncology (MASCC/ISOO); Von Bültzingslöwen, I.; Logan, R.M.; Bowen, J.; Al-Azri, A.R.; Everaus, H.; Gerber, E.; Gomez, J.G.; Pettersson, B.G.; et al. Systematic review of cytokines and growth factors for the management of oral mucositis in cancer patients. Support. Care Cancer 2013, 21, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papas, A.S.; Clark, R.E.; Martuscelli, G.; O’loughlin, K.T.; Johansen, E.; Miller, K.B. A prospective, randomized trial for the prevention of mucositis in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2003, 31, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, M.; Dzierzak-Mietla, M.; Frankiewicz, A.; Zielinska, P.; Koclega, A.; Kruszelnicka, M.; Kyrcz-Krzemien, S. Treating oral mucositis with a supersaturated calcium phosphate rinse: Comparison with control in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilla, E.; Atilla, P.A.; Demirer, T. A Review of Myeloablative vs. Reduced Intensity/Non-Myeloablative Regimens in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantations. Balk. Med. J. 2017, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MPR, Caphosol Rx. Available online: https://www.empr.com/drug/caphosol/ (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Miller, A.B.; Hoogstraten, B.; Staquet, M.; Winkler, A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 1981, 47, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahav, D.; Gafter-Gvili, A.; Muchtar, E.; Skalsky, K.; Kariv, G.; Yeshurun, M.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Antiviral prophylaxis in haematological patients: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaven, A.W.; Shea, T. Palifermin: A keratinocyte growth factor that reduces oral mucositis after stem cell transplant for haematological malignancies. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2006, 7, 2287–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blijlevens, N.; Sonis, S. Palifermin (recombinant keratinocyte growth factor-1): A pleiotropic growth factor with multiple biological activities in preventing chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-induced mucositis. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 18, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonis, S.T. Oral mucositis. Anticancer Drugs 2011, 22, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, J.D.; Zheng, J.; Castro-Malaspina, H.; A Jakubowski, A.; Heller, G.; Brink, M.R.M.V.D.; Perales, M.-A. Palifermin is efficacious in recipients of TBI-based but not chemotherapy-based allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blijlevens, N.; De Château, M.; Krivan, G.; Rabitsch, W.; Szomor, A.; Pytlik, R.; Lissmats, A.; Johnsen, H.E.; De Witte, T.; Einsele, H.; et al. In a high-dose melphalan setting, palifermin compared with placebo had no effect on oral mucositis or related patient’s burden. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 48, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, E.B.; Peterson, D.E.; Schubert, M.; Keefe, D.; McGuire, D.; Epstein, J.; Elting, L.S.; Fox, P.C.; Cooksley, C.; Sonis, S.T.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of cancer therapy-induced oral and gastrointestinal mucositis. Cancer 2004, 100, 2026–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonis, S.T.; Lindquist, L.; Van Vugt, A.; A Stewart, A.; Stam, K.; Qu, G.Y.; Iwata, K.K.; Haley, J.D. Prevention of chemotherapy-induced ulcerative mucositis by transforming growth factor beta 3. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Sonis, S.T. Defining mechanisms of action of interleukin-11 on the progression of radiation-induced oral mucositis in hamsters. Oral Oncol. 2000, 36, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodd, M.J. The Pathogenesis and Characterization of Oral Mucositis Associated with Cancer Therapy. Oncol. Nurs. Forum 2004, 31, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiff, P. Mucositis associated with stem cell transplantation: Current status and innovative approaches to management. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001, 27 (Suppl. 2), S3–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisa, Y.; Mori, T.; Kudo, M.; Yashima, T.; Kondo, S.; Yokoyama, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Okamoto, S. Oral cryotherapy for the prevention of high-dose melphalan-induced stomatitis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Support Care Cancer 2005, 13, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartarone, A.; Matera, R.; Romano, G.; Vigliotti, M.L.; Di Renzo, N. Prevention of high-dose melphalan-induced mucositis by cryotherapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2005, 46, 633–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonis, S.T. Mucositis: The impact, biology and therapeutic opportunities of oral mucositis. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, T.; Zhelnova, E.; Sucheston, L.; Demidova, I.; Savchenko, V.; Battiwalla, M.; Smiley, S.L.; Ambrosone, C.B.; McCarthy, P.L. A deletion polymorphism in glutathione-S-transferase mu (GSTM1) and/or theta (GSTT1) is associated with an increased risk of toxicity after autologous blood and marrow transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, October 2019 ASP Pricing File (Updated 09/30/19). Available online: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Medicare-Fee-for-Service-Part-B-Drugs/McrPartBDrugAvgSalesPrice/2019ASPFiles.htmlAccessed (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- GoodPx, Neutrasal. Available online: https://www.goodrx.com/neutrasal?form=carton&dosage=120-packets&quantity=1&days_supply=&label_override=Neutrasal (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Elting, L.S.; Shih, Y.-C.T.; Stiff, P.J.; Bensinger, W.; Cantor, S.B.; Cooksley, C.; Spielberger, R.; Emmanoulides, C. Economic Impact of Palifermin on the Costs of Hospitalization for Autologous Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplant: Analysis of Phase 3 Trial Results. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007, 13, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, A.; Tenore, G.; Rocchetti, F.; Del Vecchio, A.; Ricci, R.; Barberi, W.; Cartoni, C.; Iori, A.P.; Pippi, R.; Polimeni, A.; et al. Photo-Biomodulation as a Prevention Modality of Oral Mucositis in Patients Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadik, Y.; On behalf of The Mucositis Study Group of the Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer/International Society of Oral Oncology (MASCC/ISOO); Arany, P.R.; Fregnani, E.R.; Bossi, P.; Antunes, H.S.; Bensadoun, R.-J.; Gueiros, L.A.; Majorana, A.; Nair, R.G.; et al. Systematic review of photobiomodulation for the management of oral mucositis in cancer patients and clinical practice guidelines. Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 3969–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Variable. | SCPR a Group N = 26 (%) | Palifermin Group N = 122 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age-years | ||
| Mean ± SD b | 51 ± 13.9 | 50 ± 12.6 |
| Range | (23–68) | (20–74) |
| Female-n (%) | 11 (42) | 55 (45) |
| Diagnosis—n (%) | ||
| Lymphoid disorder | 18 (69) | 63 (52) |
| Non-lymphoid disorder | 8 (31) | 59 (48) |
| Myeloid disorder | 7 | 55 |
| Plasma cell disorder | 0 | 2 |
| Others | 1 | 2 |
| Conditioning Regimen—n (%) | ||
| FBT c | 26 (100) | 116 (95) |
| Others | 0 (0) | 6 (5) |
| FCT d | 0 | 3 |
| CT e | 0 | 2 |
| VT f | 0 | 1 |
| Donor—n (%) | ||
| Autologous | 8 (31) | 42 (34) |
| Allogeneic | 18 (69) | 72 (59) |
| Umbilical cord | 0 (0) | 8 (7) |
| Disease Status—n (%) | ||
| In complete remission | 12 (46) | 51 (42) |
| Not in complete remission | 14 (54) | 71 (58) |
| Variable | Palifermin Group N = 122 | SCPR a Group N = 26 | Adjusted OR b | p–Value | 95% CI c for OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
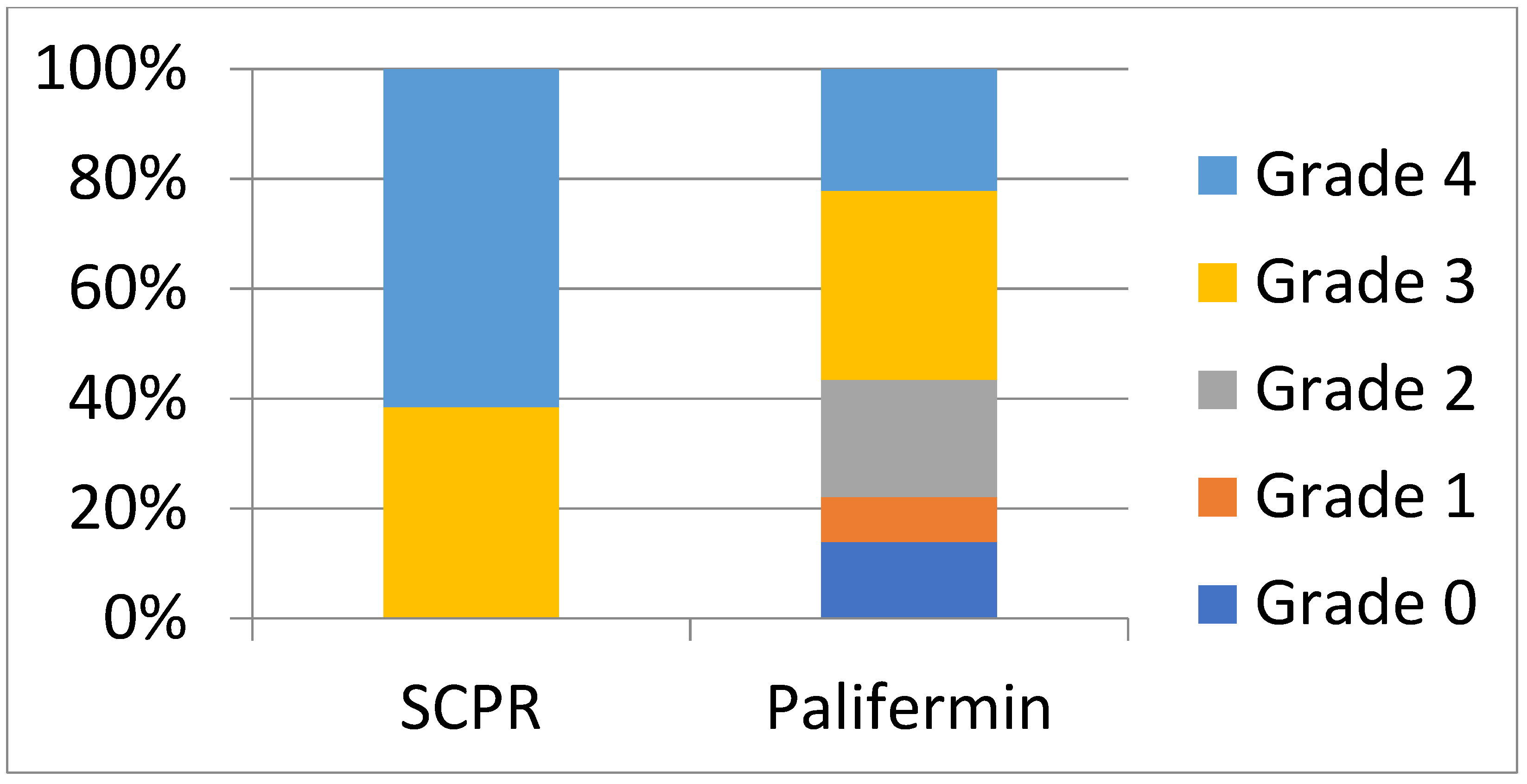
| Overall OM prevalence—n (%) | 105 (86) | 26 (100) | 0.136 | 0.15 | 0.009 to 2.08 d |
| Prevalence of WHO e grade ¾ f—n (%) | 69 (57) | 26 (100) | 0.026 | 0.01 | 0.002 to 0.41 d |
| Prevalence of WHO grade 4 f—n (%) | 27 (22) | 16 (62) | 0.191 | 0.0006 | 0.07 to 0.49 |
| Variable | OR a | p-Value | 95% CI b for OR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agent used (palifermin vs. SCPR c) | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.002–0.413 |
| Age (year) | 0.97 | 0.1 | 0.943–1.005 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 0.85 | 0.67 | 0.39–1.83 |
| Diagnosis (lymphoid vs. non-lymphoid disorders) | 1.19 | 0.69 | 0.5–2.85 |
| Conditioning Regimen (FBT d vs. other) | 7.25 | 0.69 | 0.79–66.7 |
| Donor allogeneic vs. autologous UC e vs. autologous | 0.87 4.19 | 0.78 0.2 | 0.33–2.27 0.47–37.16 |
| Disease Status (in CR f vs. not in CR) | 1.28 | 0.54 | 0.58–2.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hadid, T.; Al-Katib, A.; Binongo, J.; Berteotti, G.M.; Fazal, S.; Rossetti, J.M.; Lister, J. Palifermin Compared to Supersaturated Calcium Phosphate Rinse in Prevention of Severe Oral Mucositis after Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy-Based Myeloablative Conditioning. Hemato 2023, 4, 58-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4010006
Hadid T, Al-Katib A, Binongo J, Berteotti GM, Fazal S, Rossetti JM, Lister J. Palifermin Compared to Supersaturated Calcium Phosphate Rinse in Prevention of Severe Oral Mucositis after Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy-Based Myeloablative Conditioning. Hemato. 2023; 4(1):58-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleHadid, Tarik, Ayad Al-Katib, Jose Binongo, Gina M. Berteotti, Salman Fazal, James M. Rossetti, and John Lister. 2023. "Palifermin Compared to Supersaturated Calcium Phosphate Rinse in Prevention of Severe Oral Mucositis after Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy-Based Myeloablative Conditioning" Hemato 4, no. 1: 58-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4010006
APA StyleHadid, T., Al-Katib, A., Binongo, J., Berteotti, G. M., Fazal, S., Rossetti, J. M., & Lister, J. (2023). Palifermin Compared to Supersaturated Calcium Phosphate Rinse in Prevention of Severe Oral Mucositis after Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients Receiving Radiotherapy-Based Myeloablative Conditioning. Hemato, 4(1), 58-67. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4010006






