The Direct and Indirect Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on the Cardiovascular System in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathogenetic Overview of TKIs-Induced Cardiovascular Events
2.1. Atherogenesis and Occlusive Events
2.2. Hypertension
2.3. Arrhythmias
2.4. Pulmonary Hypertension
2.5. Metabolic Effects
2.6. Renal Impairment
2.7. Platelet Dysfunction
3. Cardiovascular Toxicity Risk Assessment and Stratification
3.1. Modifiable Risk Factors
3.1.1. Hypertension
3.1.2. Dyslipidemia
3.1.3. Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes
3.1.4. Smoking
3.1.5. Obesity
3.1.6. Renal Function Impairment
3.2. Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
3.2.1. Age and Frailty
3.2.2. Gender
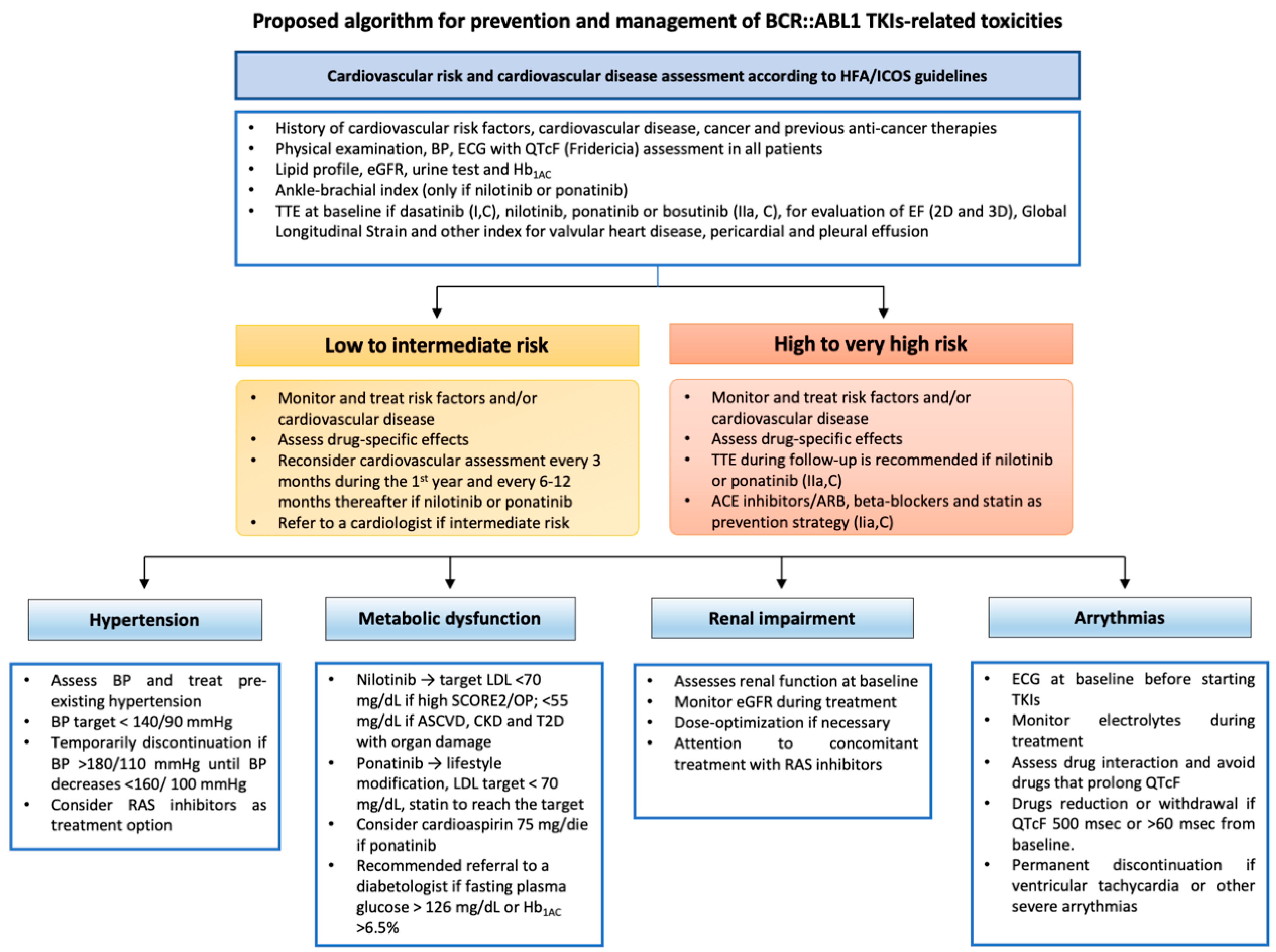
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Gutiérrez, V.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Available for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Efficacy and Safety. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, H.; Björkholm, M.; Dickman, P.W.; Höglund, M.; Lambert, P.C.; Andersson, T.M.-L. Life Expectancy of Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Approaches the Life Expectancy of the General Population. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2851–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, J.H.; Chuah, C.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Rosti, G.; Simpson, D.; Assouline, S.; Etienne, G.; Nicolini, F.E.; le Coutre, P.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Ponatinib versus Imatinib for Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia: An International, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorer, D.J.; Knickerbocker, R.K.; Baccarani, M.; Cortes, J.E.; Hochhaus, A.; Talpaz, M.; Haluska, F.G. Impact of Dose Intensity of Ponatinib on Selected Adverse Events: Multivariate Analyses from a Pooled Population of Clinical Trial Patients. Leuk. Res. 2016, 48, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, F.J.; Rea, D.; Rosti, G.; Cross, N.C.P.; Steegmann, J.L.; Griskevicius, L.; le Coutre, P.; Coriu, D.; Petrov, L.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; et al. Impact of Age on Efficacy and Toxicity of Nilotinib in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase: ENEST1st Subanalysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1585–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Nie, X.; Shi, L. Cardiovascular Adverse Events in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Nilotinib or Imatinib: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Integrative Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 966182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Mauro, M.; Steegmann, J.L.; Saglio, G.; Malhotra, R.; Ukropec, J.A.; Wallis, N.T. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Adverse Events in Patients Treated with BCR-ABL Inhibitors: Data from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, E66–E72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Kantarjian, H.; Jabbour, E.; Gonzalez, G.N.; Borthakur, G.; Pemmaraju, N.; Daver, N.; Gachimova, E.; Ferrajoli, A.; Kornblau, S.; et al. Ponatinib as First-Line Treatment for Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia in Chronic Phase: A Phase 2 Study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e376–e383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.P.; Wallis, N.; Farber, H.W.; Mauro, M.J.; Wolf, R.A.; Mattei, D.; Guha, M.; Rea, D.; Peacock, A. Clinical Features of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients Receiving Dasatinib. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D.; Mauro, M.J.; Hochhaus, A.; Boquimpani, C.; Lomaia, E.; Voloshin, S.; Turkina, A.G.; Kim, D.-W.; Apperley, J.; Cortes, J.E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety Results from ASCEMBL, a Phase 3 Study of Asciminib versus Bosutinib (BOS) in Patients (Pts) with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase (CML-CP) after ≥2 Prior Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs): Week 96 Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Saikia, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Alvarado, Y.; Nicolini, F.E.; Rathnam, K.; Khattry, N.; Apperley, J.F.; Deininger, M.W.; de Lavallade, H.; et al. An Update of Safety and Efficacy Results from Phase 1 Dose-Escalation and Expansion Study of Vodobatinib, a Novel Oral BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI), in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (Ph+ ALL) Failing Prior TKI Therapies. Blood 2021, 138, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Saikia, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Alvarado, Y.; Nicolini, F.E.; Rathnam, K.; Khattry, N.; Punatar, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Charbonnier, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Vodobatinib in Patients (Pts) with Chronic Phase Philadelphia Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (Ph+ CML): A Sub Group Analysis by Lines of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) Therapy. Blood 2022, 140, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Meng, L.; et al. Updated Results of Pivotal Phase 2 Trials of Olverembatinib (HQP1351) in Patients (Pts) with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI)-Resistant Chronic- and Accelerated-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML-CP and CML-AP) with T315I Mutation. Blood 2022, 140, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, A.R.; López-Fernández, T.; Couch, L.S.; Asteggiano, R.; Aznar, M.C.; Bergler-Klein, J.; Boriani, G.; Cardinale, D.; Cordoba, R.; Cosyns, B.; et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on Cardio-Oncology Developed in Collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 4229–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baseline Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Cancer Patients Scheduled to Receive Cardiotoxic Cancer Therapies: A Position Statement and New Risk Assessment Tools from the Cardio-Oncology Study Group of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology in Collaboration with the International Cardio-Oncology Society—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32463967/ (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Cohen, P. The Role of Protein Phosphorylation in Human Health and Disease: Delivered on June 30th 2001 at the FEBS Meeting in Lisbon. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5001–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D. Management of Adverse Events Associated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslehi, J.J.; Deininger, M. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor–Associated Cardiovascular Toxicity in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4210–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, T.; Kolaja, K.L. Cardiotoxicity of Kinase Inhibitors: The Prediction and Translation of Preclinical Models to Clinical Outcomes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rix, U.; Hantschel, O.; Dürnberger, G.; Remsing Rix, L.L.; Planyavsky, M.; Fernbach, N.V.; Kaupe, I.; Bennett, K.L.; Valent, P.; Colinge, J.; et al. Chemical Proteomic Profiles of the BCR-ABL Inhibitors Imatinib, Nilotinib, and Dasatinib Reveal Novel Kinase and Nonkinase Targets. Blood 2007, 110, 4055–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Du, B.; Liu, K.; Yu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, P. Nilotinib Related Acute Myocardial Infarction with Nonobstructive Coronary Arteries: A Case Report and Literature Review. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2022, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadi, A.; Grigg, A.P.; Dobie, G.; Burbury, K.L.; Schwarer, A.P.; Kwa, F.A.; Jackson, D.E. Ponatinib Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Induces a Thromboinflammatory Response. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emir, H.; Albrecht-Schgoer, K.; Huber, K.; Grebien, F.; Eisenwort, G.; Schgoer, W.; Kaun, C.; Herndlhofer, S.; Theurl, M.; Cerny-Reiterer, S.; et al. Nilotinib Exerts Direct Pro-Atherogenic and Anti-Angiogenic Effects on Vascular Endothelial Cells: A Potential Explanation For Drug-Induced Vasculopathy In CML. Blood 2013, 122, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhawiti, N.; Burbury, K.L.; Kwa, F.A.; O’Malley, C.J.; Shuttleworth, P.; Alzard, M.; Hamadi, A.; Grigg, A.P.; Jackson, D.E. The Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Nilotinib Potentiates a Prothrombotic State. Thromb. Res. 2016, 145, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmaier, A.H.; Merkulova, A.A.; Mitchell, S.; Stavrou, E.X. Ponatinib and Cardiovascular Complications. Blood 2016, 128, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzijusufovic, E.; Albrecht-Schgoer, K.; Huber, K.; Hoermann, G.; Grebien, F.; Eisenwort, G.; Schgoer, W.; Herndlhofer, S.; Kaun, C.; Theurl, M.; et al. Nilotinib-Induced Vasculopathy: Identification of Vascular Endothelial Cells as a Primary Target Site. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Sukegawa, M.; Fukatsu, M.; Sano, T.; Takahashi, H.; Harada, K.; Kimura, S.; Ohkawara, H.; Nakamura, K.; Mita, M.; et al. The Link between Interleukin-1β and Acute Myocardial Infarction in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Nilotinib: Cross-Sectional Study. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Interleukin-1 Beta as a Target for Atherosclerosis Therapy: Biological Basis of CANTOS and Beyond. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Libby, P. Clonal Haematopoiesis: Connecting Ageing and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonna, R.; Pieragostino, D.; Cufaro, M.C.; Doria, V.; Del Boccio, P.; Deidda, M.; Pierdomenico, S.D.; Dessalvi, C.C.; De Caterina, R.; Mercuro, G. Ponatinib Induces Vascular Toxicity through the Notch-1 Signaling Pathway. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousif, S.; Singh, A.P.; Umbarkar, P.; Galindo, C.; Wheeler, N.; Toro Cora, A.; Zhang, Q.; Prabhu, S.D.; Lal, H. Ponatinib Drives Cardiotoxicity by S100A8/A9-NLRP3-IL-1β Mediated Inflammation. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 267–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarda, N.; Travers, R.; Yang, V.K.; London, C.; Jaffe, I.Z. VEGF Receptor Inhibitor-Induced Hypertension: Emerging Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caocci, G.; Deidda, M.; Noto, A.; Greco, M.; Simula, M.P.; Mulas, O.; Cocco, D.; Fattuoni, C.; Mercuro, G.; La Nasa, G.; et al. Metabolomic Analysis of Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Cardiovascular Adverse Events after Treatment with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, J. Vascular Toxic Effects of Cancer Therapies. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, A.J.; Li, X.; Hall, M.E.; Hall, J.E. Obesity, Hypertension, and Cardiac Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Yang, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Dong, M. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors-Induced Arrhythmias: From Molecular Mechanisms, Pharmacokinetics to Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 758010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Sun, J.; Li, C.; Qiu, S.; Shi, C.; Ma, J.; Xu, Y. Downregulation of HERG Channel Expression by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Nilotinib and Vandetanib Predominantly Contributes to Arrhythmogenesis. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 365, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension: Developed by the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) and the European Reference Network on Rare Respiratory Diseases (ERN-LUNG). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgür Yurttaş, N.; Eşkazan, A.E. Dasatinib-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guignabert, C.; Phan, C.; Seferian, A.; Huertas, A.; Tu, L.; Thuillet, R.; Sattler, C.; Le Hiress, M.; Tamura, Y.; Jutant, E.-M.; et al. Dasatinib Induces Lung Vascular Toxicity and Predisposes to Pulmonary Hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3207–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Alimena, G. The Metabolic Consequences of Imatinib Mesylate: Changes on Glucose, Lypidic and Bone Metabolism. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, S.; Anderson, N.; Hainz, C.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Serkova, N.J. Imatinib (STI571)-Mediated Changes in Glucose Metabolism in Human Leukemia BCR-ABL-Positive Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6661–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovits, N.; Kurnik, D.; Friedrich, C.; Gueta, I.; Halkin, H.; David, S.; Lomnicky, Y.; Topol, Y.; Tirosh, A.; Loebstein, R. Effects of Imatinib on Glycemic and Lipid Profiles: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Singh, P.; Gupta, S.K.; Ali, V.; Jyotirmayee; Verma, M. Alterations in Cellular Metabolisms after Imatinib Therapy: A Review. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitter, S.; Vandyke, K.; Gronthos, S.; Zannettino, A.C.W. Suppression of PDGF-Induced PI3 Kinase Activity by Imatinib Promotes Adipogenesis and Adiponectin Secretion. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 48, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Muscaritoli, M.; Cannella, L.; Stefanizzi, C.; Frustaci, A.; Alimena, G. Fasting Glucose Improvement under Dasatinib Treatment in an Accelerated Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patient Unresponsive to Imatinib and Nilotinib. Leuk. Res. 2008, 32, 1626–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K.; Niwa, H.; Kato, T.; Takeda, J. Dasatinib Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Affects Lipid Metabolism in a Patient with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2015214284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Suzushima, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Kikukawa, Y.; Shimomura, T.; Furukawa, N.; Kawaguchi, T.; Araki, E. Rapid Amelioration of Hyperglycemia Facilitated by Dasatinib in a Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Intern. Med. 2012, 51, 2763–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostino, N.M.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Lynch, C.J.; Koszyk-Szewczyk, A.; Gingrich, R.; Sivik, J.; Drabick, J.J. Effect of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (Sunitinib, Sorafenib, Dasatinib, and Imatinib) on Blood Glucose Levels in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Patients in General Clinical Practice. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2011, 17, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaami, O.; Kuo, C.-L.; Drake, M.T.; Kuchel, G.A.; Kirkland, J.L.; Pignolo, R.J. Antidiabetic Effects of the Senolytic Agent Dasatinib. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2021, 96, 3021–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.K.; Xu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Weivoda, M.M.; Hachfeld, C.M.; Prata, L.G.; van Dijk, T.H.; Verkade, E.; Casaclang-Verzosa, G.; et al. Targeting Senescent Cells Alleviates Obesity-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Inagaki, N.; Kondoh, H. Cellular Senescence in Diabetes Mellitus: Distinct Senotherapeutic Strategies for Adipose Tissue and Pancreatic β Cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 869414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Jiang, Q. Adverse Effects of Dasatinib on Glucose-Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia in the Chronic Phase. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iurlo, A.; Orsi, E.; Cattaneo, D.; Resi, V.; Bucelli, C.; Orofino, N.; Sciumè, M.; Elena, C.; Grancini, V.; Consonni, D.; et al. Effects of First- and Second-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients: A Real Clinical Problem? Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33944–33951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racil, Z.; Koritakova, E.; Sacha, T.; Klamova, H.; Belohlavkova, P.; Faber, E.; Rea, D.; Malaskova, L.; Prochazkova, J.; Zackova, D.; et al. Insulin Resistance Is an Underlying Mechanism of Impaired Glucose Metabolism during Nilotinib Therapy. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, E342–E345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racil, Z.; Razga, F.; Drapalova, J.; Buresova, L.; Zackova, D.; Palackova, M.; Semerad, L.; Malaskova, L.; Haluzik, M.; Mayer, J. Mechanism of Impaired Glucose Metabolism during Nilotinib Therapy in Patients with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Haematologica 2013, 98, e124–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Kostara, C.E.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Salamou, E.; Guzman, E. Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 03000605231164548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicuranza, A.; Ferrigno, I.; Abruzzese, E.; Iurlo, A.; Galimberti, S.; Gozzini, A.; Luciano, L.; Stagno, F.; Russo Rossi, A.; Sgherza, N.; et al. Pro-Inflammatory and Pro-Oxidative Changes During Nilotinib Treatment in CML Patients: Results of a Prospective Multicenter Front-Line TKIs Study (KIARO Study). Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 835563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wages, P.A.; Kim, H.-Y.H.; Korade, Z.; Porter, N.A. Identification and Characterization of Prescription Drugs That Change Levels of 7-Dehydrocholesterol and Desmosterol. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1916–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; McDonald, J.G.; Aryal, B.; Canfrán-Duque, A.; Goldberg, E.L.; Araldi, E.; Ding, W.; Fan, Y.; Thompson, B.M.; Singh, A.K.; et al. Desmosterol Suppresses Macrophage Inflammasome Activation and Protects against Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2107682118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spann, N.J.; Garmire, L.X.; McDonald, J.G.; Myers, D.S.; Milne, S.B.; Shibata, N.; Reichart, D.; Fox, J.N.; Shaked, I.; Heudobler, D.; et al. Regulated Accumulation of Desmosterol Integrates Macrophage Lipid Metabolism and Inflammatory Responses. Cell 2012, 151, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodgrass, R.G.; Benatzy, Y.; Schmid, T.; Namgaladze, D.; Mainka, M.; Schebb, N.H.; Lütjohann, D.; Brüne, B. Efferocytosis Potentiates the Expression of Arachidonate 15-Lipoxygenase (ALOX15) in Alternatively Activated Human Macrophages through LXR Activation. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1301–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Lin, X.; Lai, Y.; Han, C.; Fan, X.; Tang, J.; Mo, S.; Su, J.; Liang, S.; Shang, J.; et al. Ponatinib Modulates the Metabolic Profile of Obese Mice by Inhibiting Adipose Tissue Macrophage Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1040999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.K.; Hussain, S.; Ahmed, R.; Agrawal, N.; Bhurani, D.; Klugar, M.; Sharma, M. Impact of Imatinib Treatment on Renal Function in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Patients. Nephrology 2022, 27, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Kim, D.-W.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Lipton, J.H.; Lahoti, A.; Talpaz, M.; Matczak, E.; Barry, E.; Leip, E.; et al. Effects of Bosutinib Treatment on Renal Function in Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Leukemias. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 684–695.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Qin, Y.; Huang, X.; Zuo, L.; Jiang, Q. Assessment of Chronic Renal Injury in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the Chronic Phase Receiving Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kali, A.; Farooq, S.; Tfayli, A. Tumor Lysis Syndrome after Starting Treatment with Gleevec in a Patient with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2009, 34, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Hirata, A.; Tokunaga, S.; Masuda, T.; Haji, S.; Kimura, D.; Nojiri, C.; Nakashima, Y.; Shiratsuchi, M.; Kato, K.; et al. Rapid Decrease in EGFR with Concomitant Use of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Renin–Aldosterone–Angiotensin System Inhibitors in Patients with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2022, 116, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Petiot, E.; Rea, D.; Serrano, F.; Stehlé, T.; Gardin, C.; Rousselot, P.; Peraldi, M.-N.; Flamant, M. Imatinib Increases Serum Creatinine by Inhibiting Its Tubular Secretion in a Reversible Fashion in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016, 16, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumiya, M.; Takahashi, N.; Takahashi, S.; Yoshioka, T.; Kameoka, Y.; Miura, M. Effects of SLC22A2 808G>T Polymorphism and Bosutinib Concentrations on Serum Creatinine in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Receiving Bosutinib Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkurt, S.; Temiz, G.; Acikalin, M.F.; Soydan, M. Acute Renal Failure under Dasatinib Therapy. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, S.; Sato, Y.; Minakawa, A.; Fukuda, A.; Fujimoto, S. Dasatinib-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome in a Patient with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: A Case Report. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Cardama, A.; Han, X.; Kantarjian, H.; Cortes, J. Dasatinib-Induced Platelet Dysfunction. Blood 2007, 110, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, Y.; Okay, M.; Aydin, S.; Buyukasik, Y.; Akbiyik, F.; Dikmen, Z.G. TKI-Related Platelet Dysfunction Does Not Correlate with Bleeding in Patients with Chronic Phase-Chronic Myeloid Leukemia with Complete Hematological Response. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 25, 1076029619858409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, L.C.; Cummins, K.D.; Costello, B.; Yeung, D.; Cleary, R.; Forsyth, C.; Tatarczuch, M.; Burbury, K.; Motorna, O.; Shortt, J.; et al. The Incidence and Natural History of Dasatinib Complications in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.-T.; Corrà, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2315–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caocci, G.; Mulas, O.; Abruzzese, E.; Luciano, L.; Iurlo, A.; Attolico, I.; Castagnetti, F.; Galimberti, S.; Sgherza, N.; Bonifacio, M.; et al. Arterial Occlusive Events in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Ponatinib in the Real-Life Practice Are Predicted by the Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) Chart. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caocci, G.; Mulas, O.; Capodanno, I.; Bonifacio, M.; Annunziata, M.; Galimberti, S.; Luciano, L.; Tiribelli, M.; Martino, B.; Castagnetti, F.; et al. Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Levels and Risk of Arterial Occlusive Events in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Nilotinib. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipayo-Gonzales, D.; Ramakrishna, H.; Nuñez-Gil, I.J. Score2: A New Updated Algorithm to Predict Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Europe. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2022, 36, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lisi, D.; Madaudo, C.; Alagna, G.; Santoro, M.; Rossetto, L.; Siragusa, S.; Novo, G. The New HFA/ICOS Risk Assessment Tool to Identify Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia at High Risk of Cardiotoxicity. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Bentham, J.; Di Cesare, M.; Bixby, H.; Danaei, G.; Cowan, M.J.; Paciorek, C.J.; Singh, G.; Hajifathalian, K.; Bennett, J.E.; et al. Worldwide Trends in Blood Pressure from 1975 to 2015: A Pooled Analysis of 1479 Population-Based Measurement Studies with 19·1 Million Participants. Lancet 2017, 389, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Townsend, R.R. Chemotherapy Agents and Hypertension: A Focus on Angiogenesis Blockade. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2007, 9, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulas, O.; Caocci, G.; Mola, B.; La Nasa, G. Arterial Hypertension and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 674748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Hughes, T.P.; Larson, R.A.; Kim, D.-W.; Issaragrisil, S.; le Coutre, P.; Etienne, G.; Boquimpani, C.; Pasquini, R.; Clark, R.E.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes with Frontline Nilotinib versus Imatinib in Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Chronic Phase: ENESTnd 10-Year Analysis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Corpo, O.; Harnois, M.; Busque, L.; Assouline, S. Real-Life Use of Nilotinib for Chronic Phase CML Demonstrates Similar Efficacy and Rate of Cardiovascular Events as Enestnd. Blood 2021, 138, 4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kim, D.-W.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; le Coutre, P.D.; Paquette, R.; Chuah, C.; Nicolini, F.E.; Apperley, J.F.; Khoury, H.J.; Talpaz, M.; et al. Ponatinib Efficacy and Safety in Philadelphia Chromosome–Positive Leukemia: Final 5-Year Results of the Phase 2 PACE Trial. Blood 2018, 132, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Apperley, J.; Lomaia, E.; Moiraghi, B.; Undurraga Sutton, M.; Pavlovsky, C.; Chuah, C.; Sacha, T.; Lipton, J.H.; Schiffer, C.A.; et al. Ponatinib Dose-Ranging Study in Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Randomized, Open-Label Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Blood 2021, 138, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Lomaia, E.; Moiraghi, B.; Sutton, M.U.; Pavlovsky, C.; Chuah, C.; Sacha, T.; Lipton, J.H.; McCloskey, J.; et al. Three-Year Update from the Optic Trial: A Dose-Optimization Study of 3 Starting Doses of Ponatinib. Blood 2022, 140, 1495–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Luciano, L.; Annunziata, M.; Attolico, I.; Malato, A.; Abruzzese, E.; Bonifacio, M.; Scortechini, A.R.; Cascavilla, N.; Di Renzo, N.; et al. Multicenter, Prospective and Retrospective Observational Cohort Study of Ponatinib in Patients with CML in Italy: Primary Analysis of the Oiti Trial. Blood 2021, 138, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.P.; Mauro, M.J.; Cortes, J.E.; Minami, H.; Rea, D.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Breccia, M.; Goh, Y.-T.; Talpaz, M.; Hochhaus, A.; et al. Asciminib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after ABL Kinase Inhibitor Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Réa, D.; Boquimpani, C.; Minami, Y.; Cortes, J.E.; Hughes, T.P.; Apperley, J.F.; Lomaia, E.; Voloshin, S.; Turkina, A.; et al. Asciminib vs Bosutinib in Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Previously Treated with at Least Two Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Longer-Term Follow-up of ASCEMBL. Leukemia 2023, 37, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancia, G.; Rosei, E.A.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; Kahan, T.; Mahfoud, F.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Kardiol. Pol. 2019, 77, 71–159. [Google Scholar]
- Sayitoglu, M.; Haznedaroğlu, I.; Hatirnaz, O.; Erbilgin, Y.; Aksu, S.; Koca, E.; Adiguzel, C.; Bayik, M.; Akalin, I.; Gülbas, Z.; et al. Effects of Imatinib Mesylate on Renin–Angiotensin System (RAS) Activity during the Clinical Course of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulas, O.; Caocci, G.; Stagno, F.; Bonifacio, M.; Annunziata, M.; Luciano, L.; Orlandi, E.M.; Abruzzese, E.; Sgherza, N.; Martino, B.; et al. Renin Angiotensin System Inhibitors Reduce the Incidence of Arterial Thrombotic Events in Patients with Hypertension and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Second- or Third-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-Density Lipoproteins Cause Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. 1. Evidence from Genetic, Epidemiologic, and Clinical Studies. A Consensus Statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D.; Mirault, T.; Cluzeau, T.; Gautier, J.-F.; Guilhot, F.; Dombret, H.; Messas, E. Early Onset Hypercholesterolemia Induced by the 2nd-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Nilotinib in Patients with Chronic Phase-Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, T.; Havelange, V.; Theunissen, K.; Meers, S.; Benghiat, F.S.; Gadisseur, A.; Vanstraelen, G.; Vellemans, H.; Bailly, B.; Granacher, N.; et al. P699: Real-life outcomes of ponatinib treatment in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (cml) or philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ph+all): 5-year-data from a belgian registry. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mela Osorio, M.J.; Osycka, M.V.; Moiraghi, B.; Pavlovsky, M.A.; Varela, A.I.; Fernandez, I.; Sackmann Massa, F.; Ferrari, L.; Giere, I.; Sighel, C.; et al. P715: Multicenter observational study of ponatinib in cml patients in Argentina. Real-world experience. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 610–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, E.D.; Jabbour, E.; Jammal, N.; Chew, S.; Bryan, J.; Issa, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Sasaki, K.; DiPippo, A.; Kantarjian, H. Real-Life Incidence of Thrombotic Events in Leukemia Patients Treated with Ponatinib. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, E350–E352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caocci, G.; Mulas, O.; Capodanno, I.; Abruzzese, E.; Iurlo, A.; Luciano, L.; Albano, F.; Annunziata, M.; Tiribelli, M.; Bonifacio, M.; et al. Low Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), Cholesterol and Triglycerides Plasma Levels Are Associated with Reduced Risk of Arterial Occlusive Events in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Ponatinib in the Real-Life. A Campus CML Study. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Bäck, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.-M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Pregno, P.; Spallarossa, P.; Arboscello, E.; Ciceri, F.; Giorgi, M.; Grossi, A.; Mallardo, M.; Nodari, S.; Ottolini, S.; et al. Identification, Prevention and Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Patients Candidate to Ponatinib: An Expert Opinion. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.J.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V.; Federici, M.; Filippatos, G.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hansen, T.B.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines on Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases Developed in Collaboration with the EASD: The Task Force for Diabetes, Pre-Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ôunpuu, S.; Dans, T.; Avezum, A.; Lanas, F.; McQueen, M.; Budaj, A.; Pais, P.; Varigos, J.; et al. Effect of Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors Associated with Myocardial Infarction in 52 Countries (the INTERHEART Study): Case-Control Study. Lancet 2004, 364, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, K.K.; Rafiq, T. Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Prevention: A Perspective from Developing Countries. Can. J. Cardiol. 2021, 37, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, J.R.B.; Blair, C.K.; Cerhan, J.R.; Nguyen, P.; Hirsch, B.; Ross, J.A. Risk of Adult Acute and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia with Cigarette Smoking and Cessation. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabat, G.C.; Wu, J.W.; Moore, S.C.; Morton, L.M.; Park, Y.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Rohan, T.E. Lifestyle and Dietary Factors in Relation to Risk of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauseker, M.; Hasford, J.; Saussele, S.; Kremers, S.; Kraemer, D.; Lindemann, W. Smokers with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Are at a Higher Risk of Disease Progression and Premature Death. Cancer 2017, 123, 2467–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, B.; Bernhard, D. Smoking and Cardiovascular Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiuri, S.P.B.; Pierce, G.N.; Ravandi, A.; Aukema, H.M. The Plasma Oxylipidome Links Smoking Status to Peripheral Artery Disease. Metabolites 2022, 12, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, S.S.; Yamamura, Y.; Kantarijian, H.M.; Cortes-Franco, J.E. Obesity, Weight Gain, and Risk of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Overweight and Obesity and Incidence of Leukemia: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1418–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breccia, M.; Loglisci, G.; Salaroli, A.; Serrao, A.; Mancini, M.; Diverio, D.; Latagliata, R.; Alimena, G. Delayed Cytogenetic and Major Molecular Responses Associated to Increased BMI at Baseline in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated with Imatinib. Cancer Lett. 2013, 333, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, M.; Canichella, M.; Colafigli, G.; Latagliata, R.; Diverio, D.; Alimena, G.; Foà, R.; Breccia, M. Body Mass Index Does Not Impact on Molecular Response Rate of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Patients Treated Frontline with Second Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 182, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, D.; Shikora, S.A.; Aarts, E.; Aminian, A.; Angrisani, L.; Cohen, R.V.; Luca, M.D.; Faria, S.L.; Goodpaster, K.P.S.; Haddad, A.; et al. 2022 American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) and International Federation for the Surgery of Obesity and Metabolic Disorders (IFSO): Indications for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2022, 18, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, F.G.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Bidikian, A.; Jabbour, E.J.; Short, N.J.; Ning, J.; Xiao, L.; Pemmaraju, N.; DiNardo, C.D.; Kadia, T.M.; et al. Association between Bariatric Surgery and Outcomes in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer 2023, 129, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 1: Definition and Classification of CKD. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 19–62. [CrossRef]
- Marcolino, M.S.; Boersma, E.; Clementino, N.C.D.; Macedo, A.V.; Marx-Neto, A.D.; Silva, M.H.C.R.; van Gelder, T.; Akkerhuis, K.M.; Ribeiro, A.L. Imatinib Treatment Duration Is Related to Decreased Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, M.; Scalzulli, E.; Colafigli, G.; Fegatelli, D.A.; Massaro, F.; Latagliata, R.; Foà, R.; Breccia, M. Changes in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Treated Front Line with Available TKIs and Correlation with Cardiovascular Events. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, A.; Yoshida, H.; Tada, Y.; Koike, M.; Minami, R.; Masaie, H.; Ishikawa, J. Changes from Imatinib Mesylate to Second Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Improve Renal Impairment with Imatinib Mesylate in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 104, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.L.; Jones, J.; Bolleddu, S.I.; Vanthenapalli, S.; Rodgers, L.E.; Shah, K.; Karia, K.; Panguluri, S.K. Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Gender and Aging. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, V.S.; Baccarani, M.; Hasford, J.; Lindoerfer, D.; Burgstaller, S.; Sertic, D.; Costeas, P.; Mayer, J.; Indrak, K.; Everaus, H.; et al. The EUTOS Population-Based Registry: Incidence and Clinical Characteristics of 2904 CML Patients in 20 European Countries. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iurlo, A.; Ubertis, A.; Artuso, S.; Bucelli, C.; Radice, T.; Zappa, M.; Cattaneo, D.; Mari, D.; Cortelezzi, A. Comorbidities and Polypharmacy Impact on Complete Cytogenetic Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Elderly Patients. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2014, 25, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breccia, M.; Palandri, F.; Luciano, L.; Benevolo, G.; Bonifacio, M.; Caocci, G.; Castagnetti, F.; Palumbo, G.A.; Iurlo, A.; Landi, F. Identification and Assessment of Frailty in Older Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Myelofibrosis, and Indications for Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallis, R.M.; Wang, R.; Bewersdorf, J.P.; Zeidan, A.M.; Davidoff, A.J.; Huntington, S.F.; Podoltsev, N.A.; Ma, X. Contemporary Practice Patterns of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Use among Older Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the United States. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2021, 12, 20406207211043404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luskin, M.R.; DeAngelo, D.J. How to Treat Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) in Older Adults. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2018, 9, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, G.; Maldonado, J.M.; Raha, S.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Khatun, R.; Atisso, C.; Shurzinske, L.; Gerstein, H.C.; Rydén, L.; Bethel, M.A. Gender Differences in Cardiovascular Risk, Treatment, and Outcomes: A Post Hoc Analysis from the REWIND Trial. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2023, 57, 2166101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirmi, S.; El Abd, A.; Letinier, L.; Navarra, M.; Salvo, F. Cardiovascular Toxicity of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Used in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: An Analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database (FAERS). Cancers 2020, 12, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantanos, T.; Jain, T.; Moliterno, A.R.; Jones, R.J.; DeZern, A.E. Sex-Related Differences in Chronic Myeloid Neoplasms: From the Clinical Observation to the Underlying Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, A.; Pittorru, R.; Caocci, G.; Migliore, F.; Tona, F.; Mulas, O.; La Nasa, G. The Direct and Indirect Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on the Cardiovascular System in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Hemato 2023, 4, 207-226. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030017
Costa A, Pittorru R, Caocci G, Migliore F, Tona F, Mulas O, La Nasa G. The Direct and Indirect Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on the Cardiovascular System in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Hemato. 2023; 4(3):207-226. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030017
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Alessandro, Raimondo Pittorru, Giovanni Caocci, Federico Migliore, Francesco Tona, Olga Mulas, and Giorgio La Nasa. 2023. "The Direct and Indirect Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on the Cardiovascular System in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia" Hemato 4, no. 3: 207-226. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030017
APA StyleCosta, A., Pittorru, R., Caocci, G., Migliore, F., Tona, F., Mulas, O., & La Nasa, G. (2023). The Direct and Indirect Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on the Cardiovascular System in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Hemato, 4(3), 207-226. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato4030017





