The Opportunities of Cellulose for Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Critical Review
Abstract
1. The Properties of Cellulose Materials
2. The Triboelectric Effect of Cellulose Materials
3. The Application of Cellulose Materials in TENGs
4. Paper TENGs
- Types of electrodes on paper triboelectric material;
- Application of paper-based TENGs;
- Types of paper product used in TENGs.
4.1. Types of Electrodes on Paper Triboelectric Material
4.2. Application of Paper-Based TENGs
- Energy Harvesting:
- Self-Powered Sensing:
- Extend the Lifecycle of Paper Products:
5. Nanocellulose-Based TENGs
- Altering surface properties, such as hydrophobicity [44];
- Enhancing charge generation;
- Modifying permittivity.
6. Regenerated Cellulose-Based TENGs
7. The Opportunities of Cellulose Materials for TENGs
- Functional Group Influence on Triboelectric Effect:
- Crystal Structure Influence on Triboelectric Effect:
- Impact of Fiber Size on Triboelectric Effect:
- Innovative Applications:
- Towards Green Triboelectric Nanogenerators:
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, L.-H.; Liu, B.; Meng, L.-Y.; Ma, M.-G. Comparative Study of Cellulose/Ag Nanocomposites Using Four Cellulose Types. Mater. Lett. 2016, 171, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zugenmaier, P. Conformation and Packing of Various Crystalline Cellulose Fibers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 1341–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulluri, C.; Balasubramaniam, R.; Velankar, H. Generation of highly amenable cellulose-Iβ via selective delignifcation of rice straw using a reusable cyclic ether-assisted deep eutectic solvent system. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trache, D.; Tarchoun, A.F.; Derradji, M.; Hamidon, T.S.; Masruchin, N.; Brosse, N.; Hussin, M.H. Nanocellulose: From Fundamentals to Advanced Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.E. Experiments on Tribo-Electricity. I.—The Tribo-Electric Series. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character 1917, 94, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Kar-Narayan, S. Nylon-11 Nanowires for Triboelectric Energy Harvesting. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Olin, H. Material Choices for Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Critical Review. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mo, J.; Fu, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Enhancement of Triboelectric Charge Density by Chemical Functionalization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dahlström, C.; Zou, H.; Jonzon, J.; Hummelgård, M.; Örtegren, J.; Blomquist, N.; Yang, Y.; Andersson, H.; Olsen, M.; et al. Cellulose-Based Fully Green Triboelectric Nanogenerators with Output Power Density of 300 W m−2. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Guo, H.; Yan, P.; Hu, C. Recent Progresses on Paper-based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Portable self-powered Sensing Systems. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, C.; Wang, F.; Li, Z. Cellulose-Based Nanomaterials for Energy Applications. Small 2017, 13, 1702240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Du, H.; Liu, K.; Nie, S.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Si, C. Fabrication and Applications of Cellulose-Based Nanogenerators. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Cheng, W.; Cao, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.; Han, J.; Long, Y.; Han, G. Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 87, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Du, C.; Zhang, D.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, J. Cellulose for Sustainable Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2022, 3, 2100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Bai, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrathin, Rollable, Paper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Acoustic Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sound Recording. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4236–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Triboelectric Generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-S.; Su, M.; Brugger, J.; Kim, B. Penciling a Triboelectric Nanogenerator on Paper for Autonomous Power MEMS Applications. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Yoo, J.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, S.-Y. All-Inkjet-Printed, Solid-State Flexible Supercapacitors on Paper. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2812–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kima, T.W.; Sung, S.; Park, J.H.; Li, F. Ultrasoft and Cuttable Paper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankanahalli Shankaregowda, S.; Sagade Muktar Ahmed, R.F.; Nanjegowda, C.B.; Wang, J.; Guan, S.; Puttaswamy, M.; Amini, A.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, D.; Sannathammegowda, K.; et al. Single-Electrode Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Economical Graphite Coated Paper for Harvesting Waste Environmental Energy. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Du, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z. Sliding-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Paper and as a Self-Powered Velocity and Force Sensor. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 13, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Park, J.H.; Sung, S.; Koo, B.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, T.W. Integrable Card-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerators Assembled by Using Less Problematic, Readily Available Materials. Nano Energy 2018, 51, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, L.; Tao, X.; Li, L. Ultra-Flexible and Large-Area Textile-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators with a Sandpaper-Induced Surface Microstructure. Materials 2018, 11, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Lin, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Paper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators Made of Stretchable Interlocking Kirigami Patterns. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4652–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, T.; Yao, C. The Recent Progress in Cellulose Paper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chao, M.; Liang, E. A Paper Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Electronic Systems. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 14499–14505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hummelgård, M.; Örtegren, J.; Andersson, H.; Olsen, M.; Chen, W.; Wang, P.; Dahlström, C.; Eivazi, A.; Norgren, M. Energy Harvesting Using Wastepaper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2300107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Deng, M.; Tang, Q.; He, W.; Hu, C.; Xi, Y.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.L. A Nonencapsulative Pendulum-Like Paper–Based Hybrid Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Double-Folding Paper-Based Generator for Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Front. Optoelectron. 2017, 10, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.-K.; Lin, Z.-H.; Pradel, K.C.; Lin, L.; Li, X.; Wen, X.; He, J.-H.; Wang, Z.L. Paper-Based Origami Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Pressure Sensors. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Luo, J.; Dong, S. A Novel Rhombic-Shaped Paper-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Energy from Environmental Vibration. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 302, 111806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatankhah, E.; Tadayon, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Boosted Output Performance of Nanocellulose-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators via Device Engineering and Surface Functionalization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, H. Processing Nanocellulose to Bulk Materials: A Review. Cellulose 2019, 26, 7585–7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufresne, A. Nanocellulose: A New Ageless Bionanomaterial. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Fu, Q.; Lin, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S. Enhanced Performance of a Cellulose Nanofibrils-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Tuning the Surface Polarizability and Hydrophobicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Yin, X.; Yu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Wang, X. Chemically Functionalized Natural Cellulose Materials for Effective Triboelectric Nanogenerator Development. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, H.; Wu, M.; Sun, Z.; Gao, M.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Cellulose-Reinforced MXene Composite Film. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2102124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Yan, N.; Li, Y.; Teng, M. Magnetic Recoverable MnFe2O4/Cellulose Nanocrystal Composites as an Efficient Catalyst for Decomposition of Methylene Blue. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriphan, S.; Charoonsuk, T.; Maluangnont, T.; Pakawanit, P.; Rojviriya, C.; Vittayakorn, N. Multifunctional Nanomaterials Modification of Cellulose Paper for Efficient Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Yu, D.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Song, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, H. Fabrication of Polyethyleneimine-Paper Composites with Improved Tribopositivity for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2022, 93, 106859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K.; He, M.; Xue, Y.; Yang, G. Preparation of Salt-Induced Ultra-Stretchable Nanocellulose Composite Hydrogel for Self-Powered Sensors. Nanomaterials 2022, 13, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Fang, L.; Cao, B.; Tu, X.; Zhang, R.; Dong, K.; Lai, Y.-C.; Wang, P. Biodegradable, Conductive, Moisture-Proof, and Dielectric Enhanced Cellulose-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Human-Machine Interface Sensing. Nano Energy 2023, 107, 108151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhao, H.; Huang, H.; Ma, X.; Cao, S. PEO/Cellulose Composite Paper Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Its Application in Human-Health Detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, E.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Pan, C.; Liu, X. Multifunctional and Superhydrophobic Cellulose Composite Paper for Electromagnetic Shielding, Hydraulic Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Joule Heating Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, B.; Han, E.; Lim, G.; Kim, S.; Lim, B. Highly Conductive Ferroelectric Cellulose Composite Papers for Efficient Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1904066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecunia, V.; Silva, S.R.P.; Phillips, J.D.; Artegiani, E.; Romeo, A.; Shim, H.; Park, J.; Kim, J.H.; Yun, J.S.; Welch, G.C.; et al. Roadmap on Energy Harvesting Materials. J. Phys. Mater. 2023, 6, 042501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the Triboelectric Series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, J.; Chi, M.; Meng, X.; Du, G.; Cai, C.; Wang, S.; et al. Cellulosic Gel-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Emerging Applications. Nano Energy 2023, 106, 108079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, X.; Sun, B.; Wu, Z.; He, J.; Jiang, P. Cellulose/BaTiO3 Aerogel Paper Based Flexible Piezoelectric Nanogenerators and the Electric Coupling with Triboelectricity. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, S.; Kaur, H.; Arora, B.; Aswal, D.K.; Mahajan, A. Self-Powered Monitoring of Ammonia Using an MXene/TiO2/Cellulose Nanofiber Heterojunction-Based Sensor Driven by an Electrospun Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, J.; Song, Y.; Yang, Q.; Shi, Z.; Xiong, C. Flexible and Environment-Friendly Regenerated Cellulose/MoS2 Nanosheet Nanogenerators with High Piezoelectricity and Output Performance. Cellulose 2021, 28, 6513–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Shi, Z.; Hu, G.-H.; Xiong, C.; Isogai, A.; Yang, Q. Recent Advances in Cellulose-Based Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 1910–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
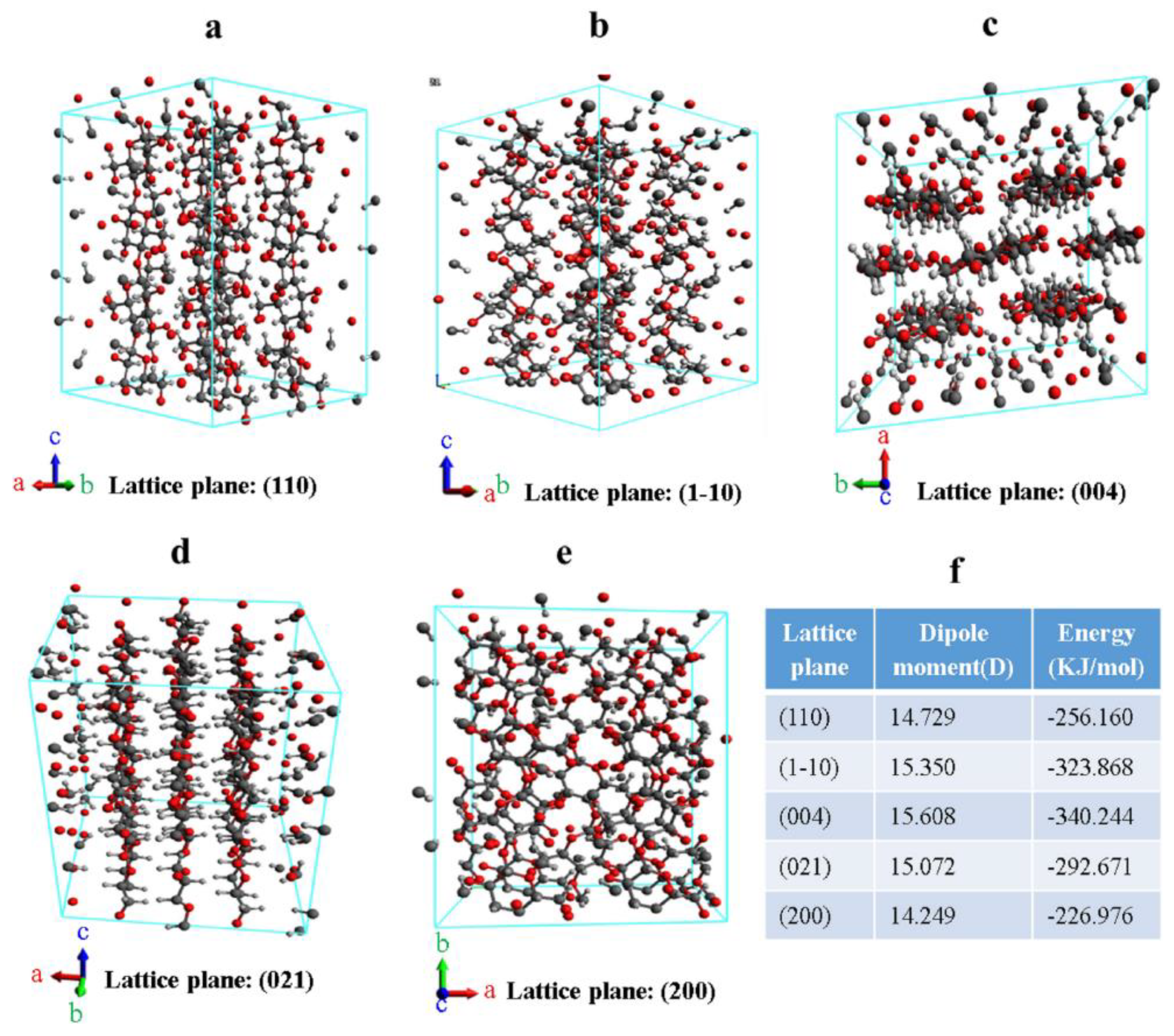
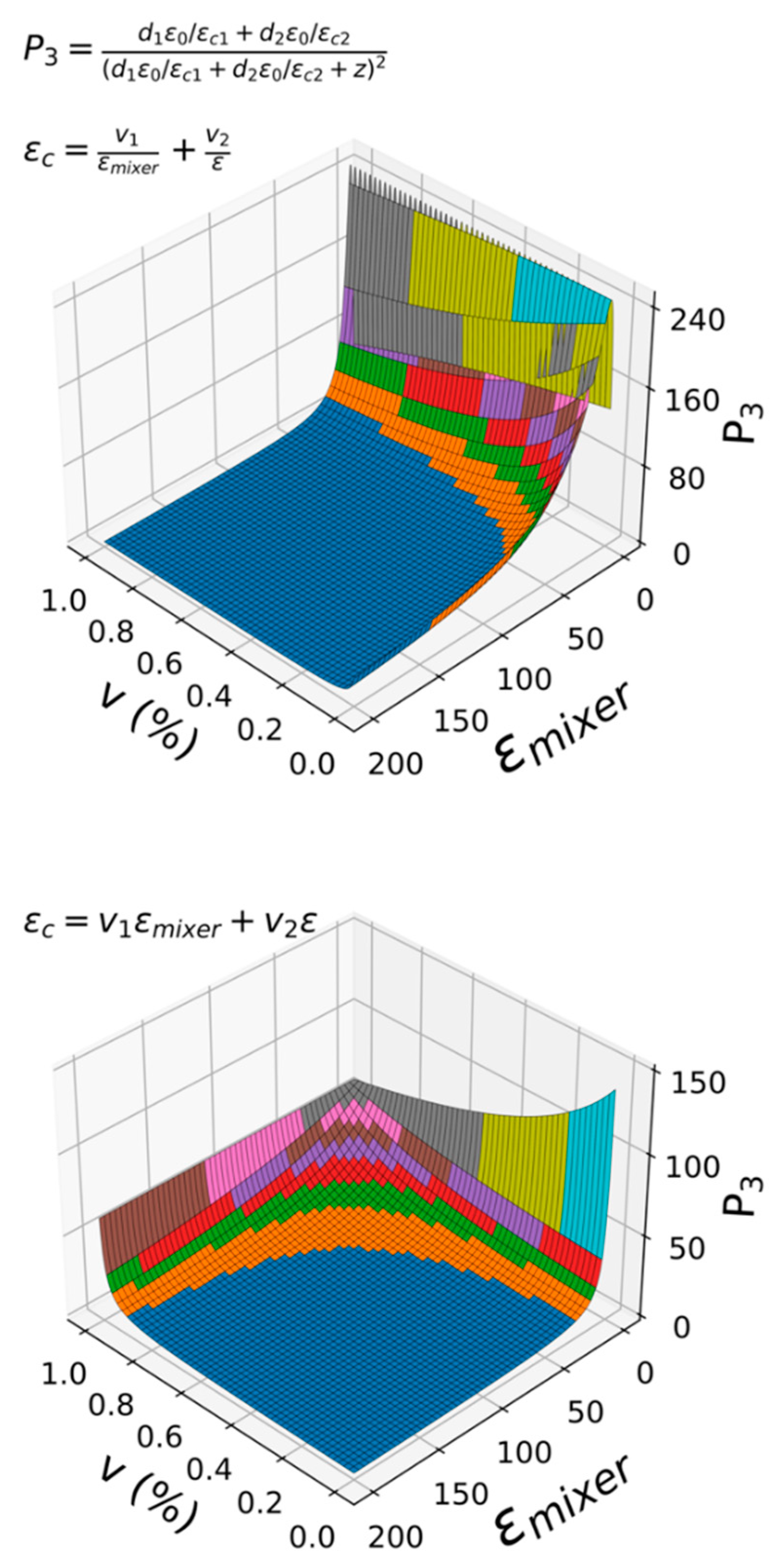
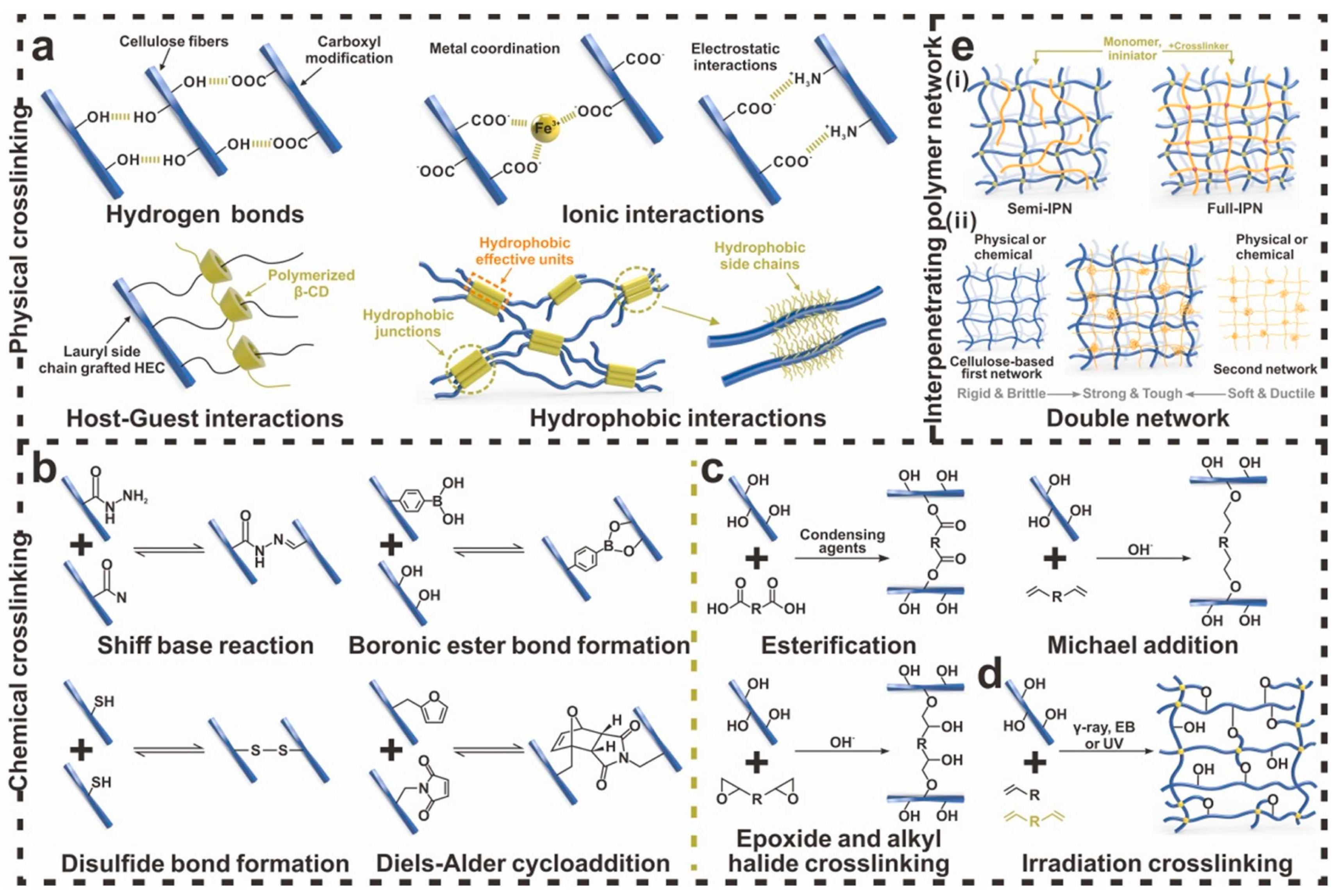

| Cellulosic Substrate | Nanocellulose | Preparation Method | Diameter (nm) and Structural Morphology | Average Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Apparent Crystallinity (%) | Maximum Degradation Temperature (°C) | Average Tensile Strength (MPa) | Zeta Potential (mV) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comcob residue | CNC | H2SO4 hydrolysis | 5.5 ± 1.9, short rod-shaped | - | 55.9 | 313 | - | −33.8 ± 1.7 | Liu et al., 2016 |
| CNC | Fomic acid hydrolysis | 6.5 ± 2.0, long rod-shaped | - | 63.8 | 360 | - | −14.3 ± 0.4 | ||
| CNF | TEMPO-mediated oxidation | 2.1 ± 1.1, twisted structure | - | 49.9 | 305 | - | −23.1 ± 2.3 | ||
| CNF | PFI refining | 43.1 ± 25.3, twisted | - | 52.1 | 336 | - | −40.3 ± 1.5 | ||
| Staliks of wheat straw (Triticum paleas) | CNF | H2SO4 hydrolysis and ultrasound treatment | 10–40, a mesh-like multilayer structure | 11.45 | 72.5 | ca. 400 | 42.3 | - | Barbash et al., 2017 |
| Comhusk | CNC | H2SO4 hydrolysis | 26.9 ± 3.35, short rod-shaped | - | 83.5 | 351 | - | −34.6 ± 2.3 | Yang et al., 2017 |
| CNF | TEMPO-mediated oxidation | 10.48 ± 1.83, slender interconnected webs | - | 72.3 | 279 | - | −69.4 ± 1.7 | ||
| CNF | High-intensity ultrasonication | 20.14 ± 4.32, slender interconnected webs | - | 53.4 | 348 | - | −24.3 ± 2.5 | ||
| Banane pseudostem | CNF | High-pressure homogenization | 30–50, entangled network of polydisperse bundles | - | 67.0 | 337 | - | - | Velásquez-Cock et al., 2016 |
| Cotton | CNC | H2PO4 hydrolysis | 31 ± 14, rod-like shape | - | 81.0 | 325 | - | - | Camarero Espinosa et al., 2013 |
| Ushar (Calotropis procera) seed fiber | CNC | H2SO4 hydrolysis | 14–24, needle shape | - | 70.0 | ca. 330 | - | - | Oun and Rhim, 2016 |
| CNF | TEMPO-oxidation | 10–20, web-like shape | - | 59.0 | 316 | - | - | ||
| Bacterial strain Komagataeibacter xylinus (BCC529) | BNC | Static culture for 96 h at 30 °C | 29.13 ± 6.53, denser network structure | 0.72 | 47.4 | 335 | 0.235 | −44.1 ± 0.9 | Gao et al., 2020 |
| BNC | Agitated culture: 300 rpm at 30 °C | 29.51 ± 8.03, loose and porous network | - | 22.1 | 310 | - | −46.5 ± 1.5 | ||
| Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) fiber | CNC | H2SO4 hydrolysis and ultrasonic treatment | 10–28, morphology not defined | - | 80.0 | ca. 420 | 61.4 | - | Barbash and Yashchenko, 2020 |
| J. Wilcke (1579) | M. Faraday (1840) | P. Shaw (1917) |
|---|---|---|
| + Glass Wool Quills Wood Paper Ground glass Pb Sulfur Metals - | + Cat’s Fur Wool Quills Flint glass Cotton Linen Silk Hand Wood Fe, Cu, Ag, Pb Sulfur - | + Glass Wool Cat’s fur Pb Silk Paper Cotton Wood, Fe Ground glass Resin Cu, Ag Sulfur - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R. The Opportunities of Cellulose for Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Critical Review. Nanoenergy Adv. 2024, 4, 209-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4030013
Zhang R. The Opportunities of Cellulose for Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Critical Review. Nanoenergy Advances. 2024; 4(3):209-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4030013
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Renyun. 2024. "The Opportunities of Cellulose for Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Critical Review" Nanoenergy Advances 4, no. 3: 209-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4030013
APA StyleZhang, R. (2024). The Opportunities of Cellulose for Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Critical Review. Nanoenergy Advances, 4(3), 209-220. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv4030013






