- Article
Novel TiO2 Nanotube-Based Electrocatalysts for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Medium
- Bogdan-Ovidiu Taranu,
- Radu Banica and
- Florina Stefania Rus
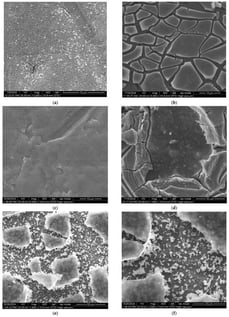
The increasing global energy demand and its negative environmental impact created the need for substantial changes in the energy infrastructure. A hydrogen-based infrastructure appears to be the most promising way to secure a clean and safe energy future. Water electrolysis is a method that can be used to generate green hydrogen, but suitable electrocatalysts are required for large-scale applications. This work investigates the electrocatalytic activity of electrodes modified with novel TiO2 nanotube-based electrocatalysts for water electrolysis. The focus was on the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and the electrodes that displayed the highest activity were the ones obtained with the procedure consisting of the growth of TiO2 nanotubes on a Ti plate by anodization, the subsequent deposition of MoO2 and Ni(OH)2, and a thermal treatment performed under different conditions. The results of the HER experiments performed in a strong alkaline environment showed that the electrode obtained via vacuum heat treatment exhibited the lowest overpotential value, of 238 mV at i = −10 mA/cm2. Furthermore, the electrode was electrochemically stable, and inter-electrode reproducibility tests revealed only a small variation of the HER overpotential.
12 January 2026