Solvent Relaxation NMR as a Tool to Study Particle Dispersions in Non-Aqueous Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Theory
3. Results and Discussions
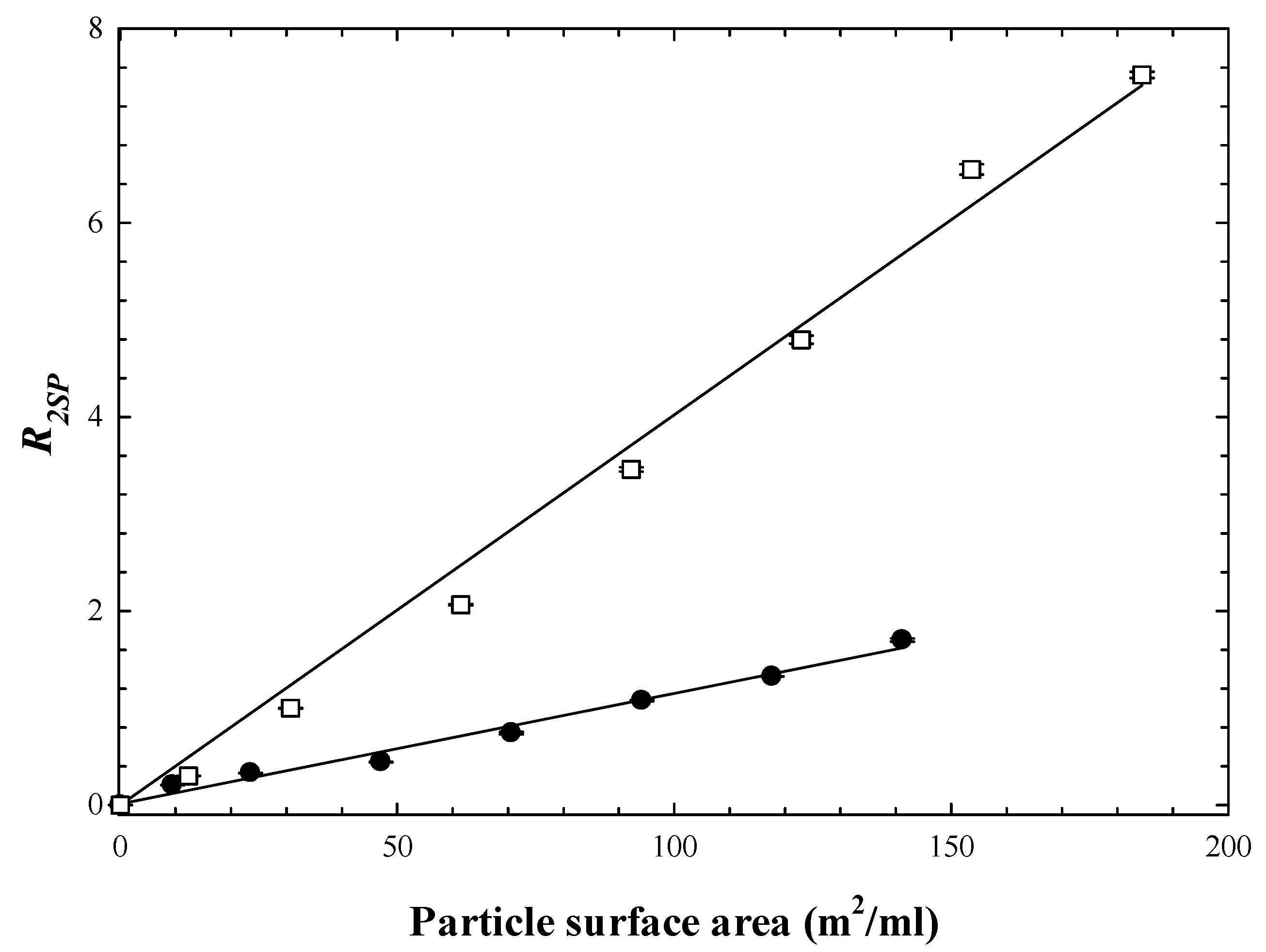
3.1. Comparison of Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Single Solvent Particle Dispersions
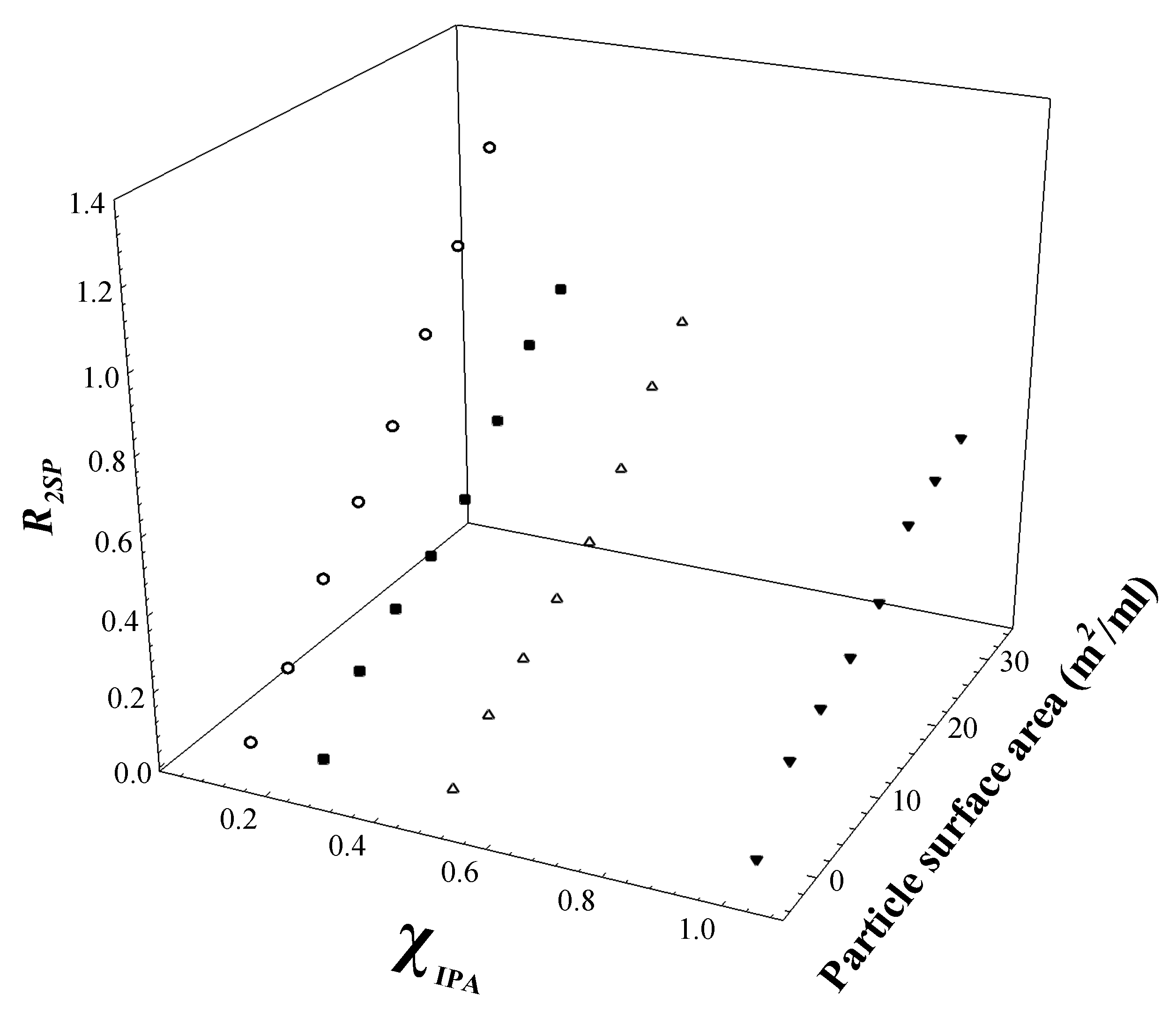
3.2. Characterisation of Aqueous–Alcohol Solvents
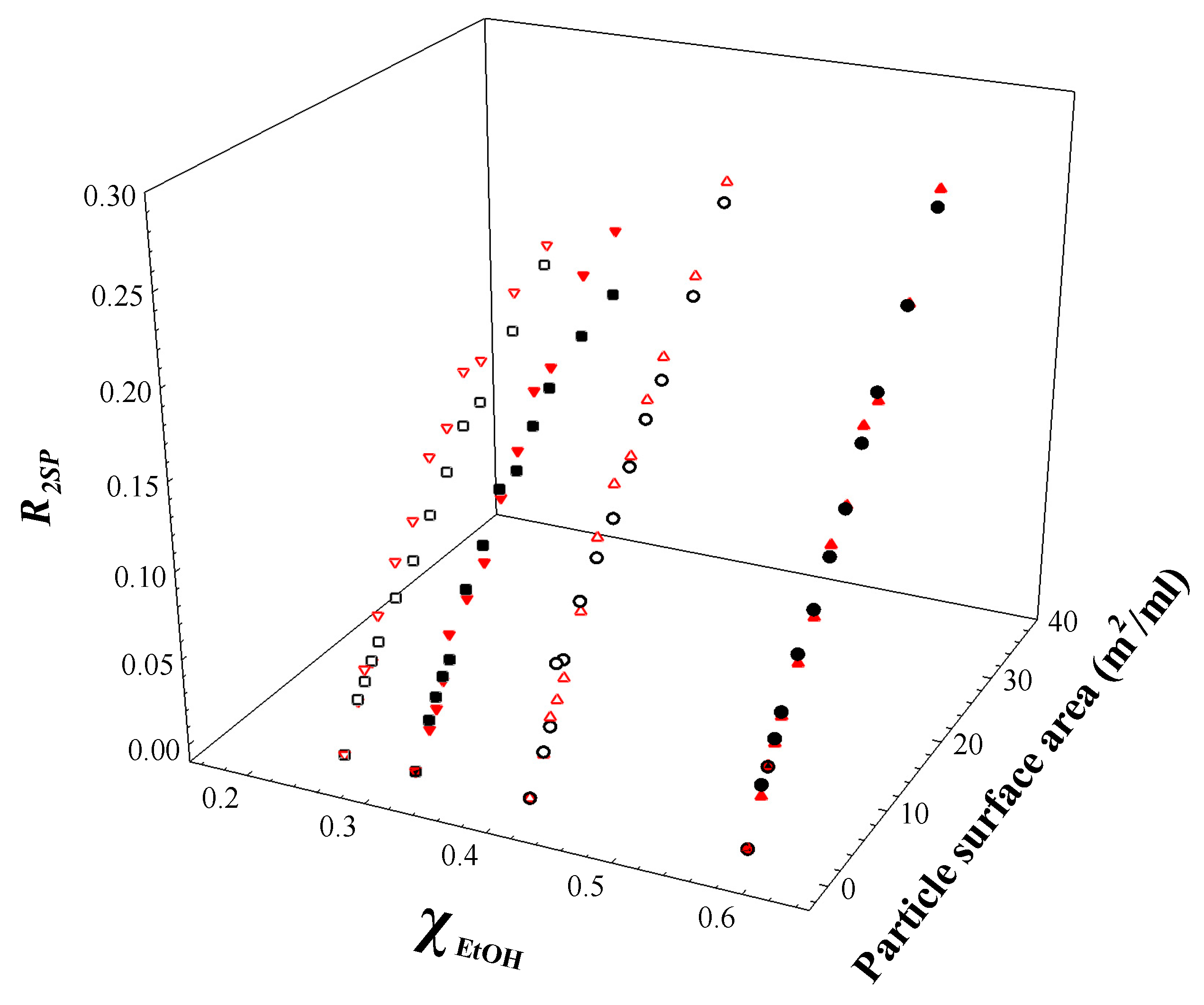
3.3. Characterisation of Non-Aqueous/Alcohol-Mixed Solvents
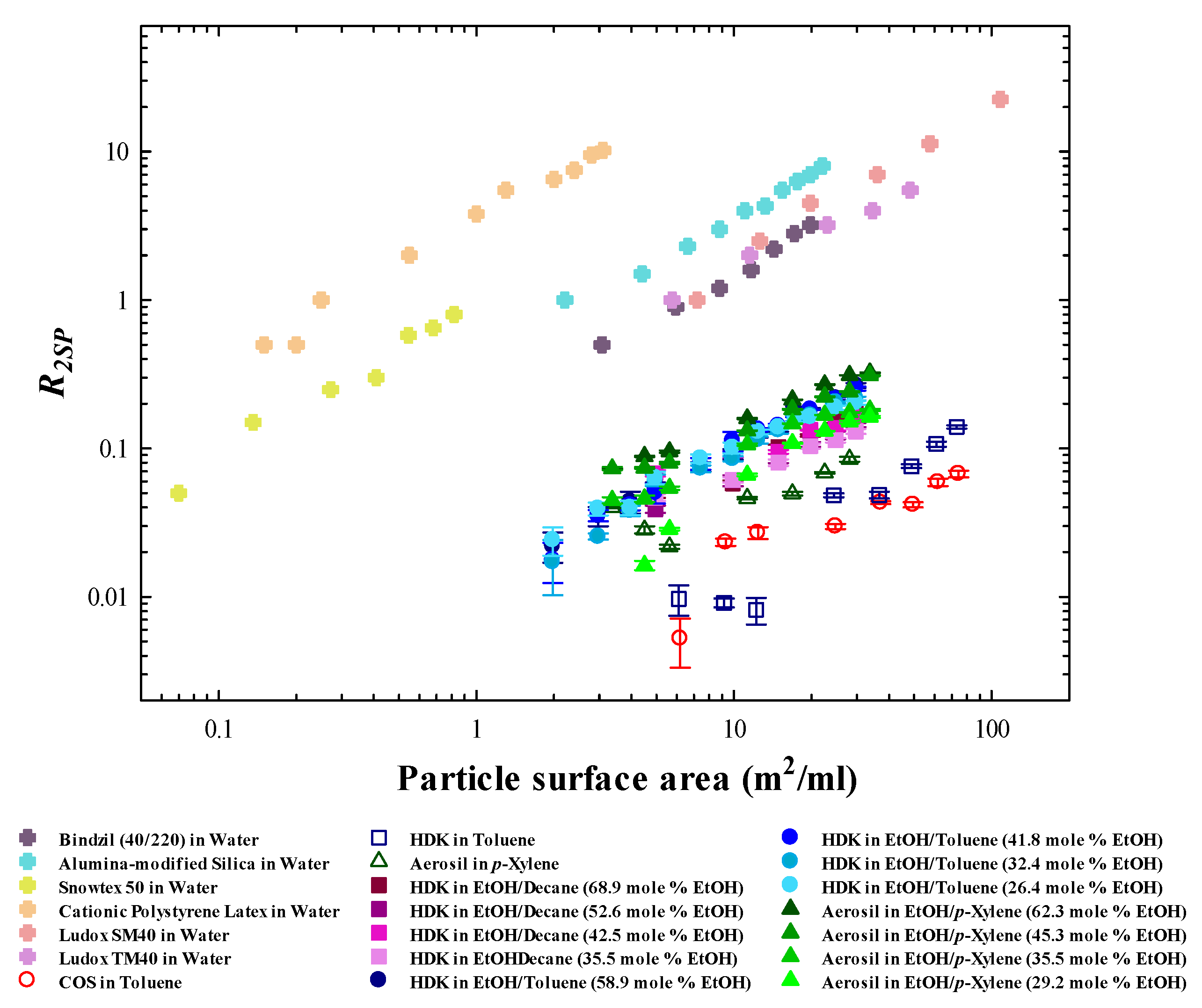
3.4. Characterisation of Aqueous Binary Mixtures—Particle Dispersions in the Aqueous System
3.5. Characterisation of Non-Aqueous Binary Mixtures—Particle Dispersions in Non-Aqueous System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daniel, F. Natl. Paint, Varn. Lacq. Assoc. Sci. Sect. Circ. 1950, 774, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, G.D. The role of the surface in the dispersion of powders in liquids. Pure Appl. Chem. 1981, 53, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.D. Dispersing Powders in Liquids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, C.L.; Cosgrove, T.; van Duijneveldt, J.S.; Murray, M.; Prescott, S.W. The use of solvent relaxation NMR to study colloidal suspensions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 7211–7228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shantz, D.F. PFG NMR studies of lysine–silica solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 383, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, L.; Hoffmann, H.; Linders, J.; Mayer, C. PFG-NMR self-diffusion measurements in the single phase channels of a microemulsion system with an anionic–nonionic surfactant mixture. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6731–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, C.; Cosgrove, T.; Espidel, Y.; Welfare, E.; Howell, I.; Revell, P. Fourier-Transform Carr−Purcell−Meiboom−Gill NMR experiments on polymers in colloidal dispersions: How many polymer molecules per particle? Langmuir 2008, 24, 7875–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Graaf, A.J.; Boere, K.W.M.; Kemmink, J.; Fokkink, R.G.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Rijkers, D.T.S.; van der Gucht, J.; Wienk, H.; Baldus, M.; Mastrobattista, E.; et al. Looped structure of flowerlike micelles revealed by 1H NMR relaxometry and light scattering. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9843–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.P. Applications of high-resolution 1H solid-state NMR. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2012, 41, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, J.V.; Smith, M.E. Recent technique developments and applications of solid state NMR in characterising inorganic materials. Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson. 2010, 38, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Beek, G.P.; Stuart, M.A.C.; Cosgrove, T. Polymer adsorption and desorption studies via proton NMR relaxation of the solvent. Langmuir 1991, 7, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, S.J.; Cosgrove, T.; Thompson, L.; Howell, I. Solvent relaxation NMR measurements on polymer, particle, surfactant systems. Langmuir 1998, 14, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.; Jack, K.S.; Cosgrove, T.; Kozak, D. NMR solvent relaxation in studies of multicomponent polymer adsorption. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2750–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.R.; Wray, D.; Paul, A.; Griffiths, P.C. Probing the surfaces of core-shell and hollow nanoparticles by solvent relaxation NMR. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2018, 56, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, T.; Obey, T.M.; Taylor, M. Solvent relaxation NMR: Bound fraction determination for sodium poly(styrene sulphonate) at the solid/solution interface. Colloids Surf. 1992, 64, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, T.; Griffiths, P.C.; Lloyd, P.M. Polymer adsorption. The effect of the relative sizes of polymer and particle. Langmuir 1995, 11, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, T.; Turner, M.J.; Thomas, D.R. The adsorption of polydimethylsiloxane onto silica from the melt. Polymer 1997, 38, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.L.; Cosgrove, T.; van Duijneveldt, J.S.; Murray, M.; Prescott, S.W. Colloidal particles in competition for stabilizer: A solvent relaxation NMR study of polymer adsorption and desorption. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16588–16595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, H.Y.; Purcell, E.M. Effects of diffusion on free precession in nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. Phys. Rev. 1954, 94, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiboom, S.; Gill, D. Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1958, 29, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woessner, D.E.; Zimmerman, J.R. Nuclear transfer and anisotropic motional spin phenomena: Relaxation time temperature dependence studies of water adsorbed on silica gel IV. J. Phys. Chem. 1963, 67, 1590–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, W.O. Cationc-Polymer-Induced Aggregation of Single and Binary Anionic Particulate Dispersions; University of Greenwich: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fairhurst, D.; Sharma, R.; Takeda, S.-I.; Cosgrove, T.; Prescott, S.W. Fast NMR relaxation, powder wettability and Hansen Solubility Parameter analyses applied to particle dispersibility. Powder Technol. 2021, 377, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, K.; Kitajo, A.; Yamaguchi, T. 17O NMR relaxation study of dynamics of water molecules in aqueous mixtures of methanol, ethanol, and 1-propanol over a temperature range of 283–403 K. J. Mol. Liq. 2006, 125, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | State | Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| Aerosil R104 (particle size 10–30 nm, surface area 140 m2·g−1) | Powder | Evonik Degussa, Essen, Germany |
| HDK H18 pyrogenic silica (particle size 15–50 nm, surface area 124 m2·g−1) | Powder | Wacker Chemie AG, Munich, Germany |
| Cab-O-Sil TS-720 (particle size 15–45 nm, surface area 122 m2·g−1) | Powder | Inoxia Ltd., Cranleigh, UK |
| Ludox SM30 (particle size 8 nm) | 30 wt% suspension in water | Sigma Aldrich, Dorset, UK |
| IPA-ST (particle size 10–15 nm) | 38 wt% dispersed in isopropanol (IPA) | Nissan Chemical Corporation, Tokyo, Japan |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alaei, Z.; Cattoz, B.; Dowding, P.J.; Griffiths, P.C. Solvent Relaxation NMR as a Tool to Study Particle Dispersions in Non-Aqueous Systems. Physchem 2022, 2, 224-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem2030016
Alaei Z, Cattoz B, Dowding PJ, Griffiths PC. Solvent Relaxation NMR as a Tool to Study Particle Dispersions in Non-Aqueous Systems. Physchem. 2022; 2(3):224-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem2030016
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlaei, Zahra, Beatrice Cattoz, Peter John Dowding, and Peter Charles Griffiths. 2022. "Solvent Relaxation NMR as a Tool to Study Particle Dispersions in Non-Aqueous Systems" Physchem 2, no. 3: 224-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem2030016
APA StyleAlaei, Z., Cattoz, B., Dowding, P. J., & Griffiths, P. C. (2022). Solvent Relaxation NMR as a Tool to Study Particle Dispersions in Non-Aqueous Systems. Physchem, 2(3), 224-234. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem2030016







