- Article
Comparative Study on the Microwave-Assisted and Conventional Dyeing of Polyamide Fabric with Acid Dyes
- Raşit Dağlı,
- Murat Teker and
- Ayşe Usluoğlu
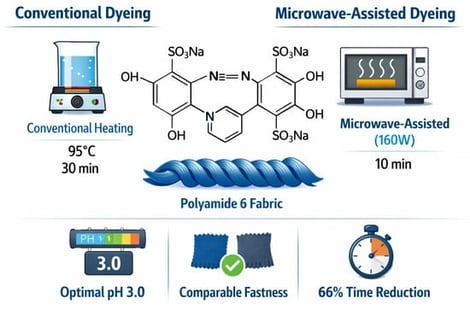
This study investigates the acid dyeing of Polyamide 6 (PA6) fabric by comparing conventional heating and microwave-assisted techniques. The influence of critical process parameters—namely pH, temperature, dyeing time, and dye concentration—on color strength (K/S) was systematically evaluated using C.I. Acid Blue 324. Results indicated an inverse correlation between pH and K/S for both methods, with the maximum color yield achieved at pH 3.0. While dye uptake improved with increasing temperature, time, and concentration in both systems, the microwave-assisted approach (160 W) significantly accelerated the process. Optimal conditions for conventional dyeing were established at pH 3, 95 °C, and a 30 min reaction time with 1.5% dye concentration. In contrast, the microwave-assisted process reached equivalent exhaustion levels in only 10 min under otherwise identical conditions. The findings confirm that microwave-assisted dyeing is a rapid, energy-efficient, and sustainable alternative for PA6 processing, offering substantial reductions in production time.
5 February 2026



![Clinker thermal energy intensity in EU27 and at global level (MJ/ton clinker) [19] along with key indicators in the RTS (Reference Technology Scenario) and the roadmap vision (2DS).](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/physchem/physchem-06-00010/article_deploy/html/images/physchem-06-00010-ag-550.jpg)